- Reports
- Plants
- Cotton
Cotton was known many centuries ago. In many countries, it is still called white gold. For the first time it was used for the production of yarn in India, then cotton began to be grown in other states.
In the common Slavic language, the word "cotton" was formed from the word "clap", which meant "klok". Cotton is a fine fiber of plant origin. It is considered not only the cheapest, but also the most important plant fiber. It is distinguished by its strength and practicality. Cotton fibers have been used to make clothing for many centuries. It was extracted from cotton, an amazing plant a little over a meter high.
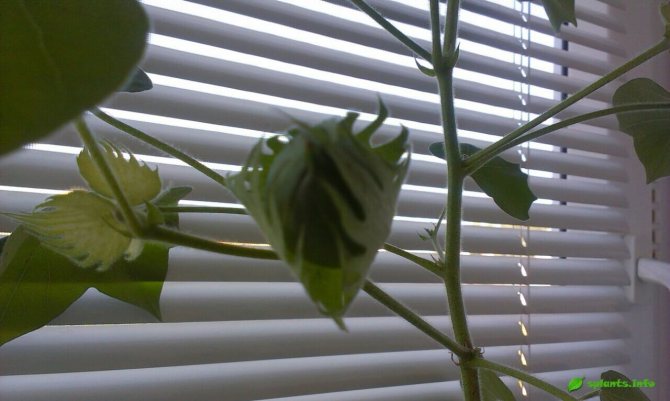
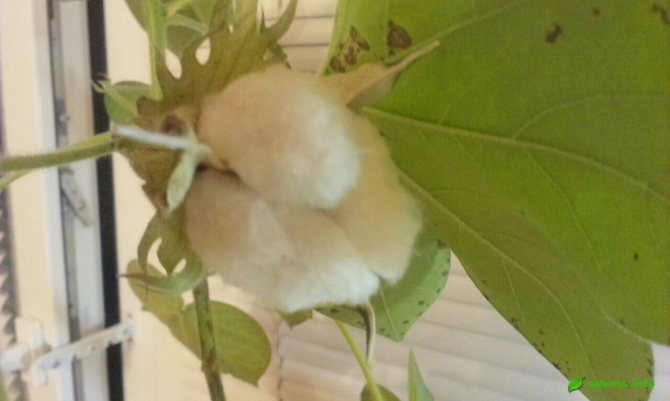
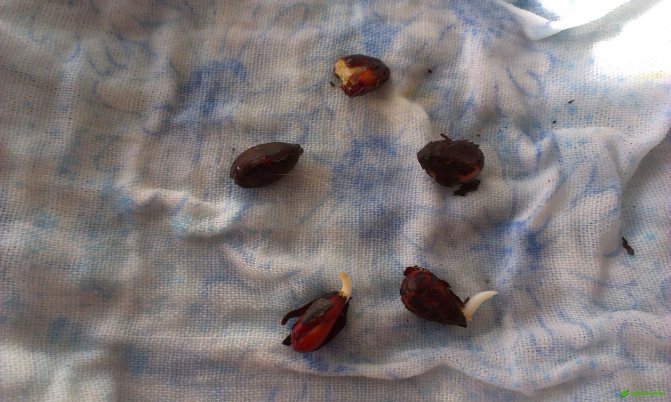
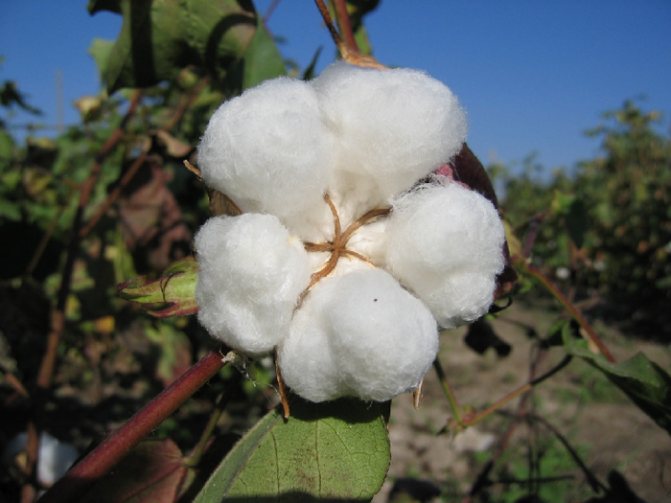
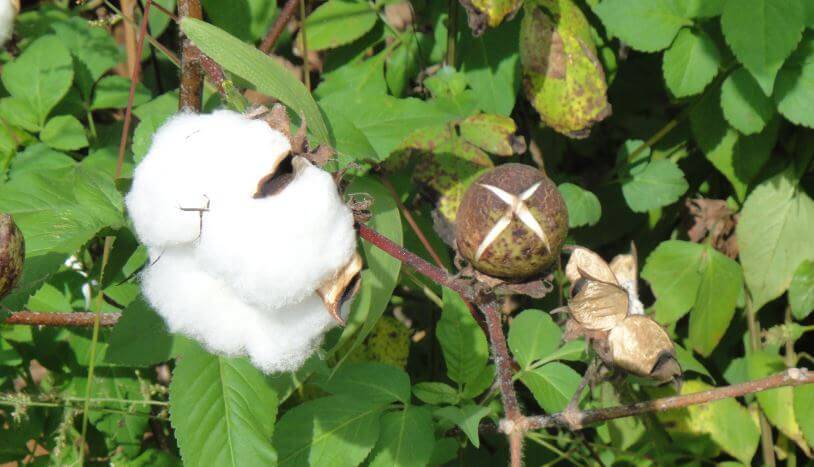
Cotton fabric is born gradually. After large creamy or yellowish flowers turn into a box with egg-shaped seeds, up to 15 thousand thin hairs appear on them. The strength of each hair depends on the maturation of the seeds, on which cellulose is deposited over time. The thickness of the hairs increases, they become like a ribbon twisted in a spiral. The highest quality fiber is considered to be the one that contains up to 96% cellulose. This is how high-quality raw cotton is obtained, which is cleared of various impurities, primarily from seeds. Later it is sent for processing.
The received raw material, depending on the purpose, undergoes special purification. It includes bleaching, coloring and degreasing. Cotton fabric is used most often in the textile industry. More than 65% of the world's cotton is used for bedding, underwear and clothing. The rest is used for medical products, tents, cosmetics.
Cotton has excellent properties: it is not only durable and washable, but also breathable easily. If you add insulation to the cotton, it can be used in cold weather. The fabric is ideal for allergy sufferers. Cotton bleaches and dyes well. Of course, this material has its drawbacks: the fabric wrinkles easily, fades and sheds. But if you just add artificial fiber to the cotton, the quality of the fabric improves.
In order for the cotton fabric to retain its appearance and quality, it is necessary to take care of it systematically. First of all, it is necessary to select the right detergent for washing, adhere to the required water temperature. Dry your cotton fabric in the shade and naturally.
general information
The cotton plant belongs to the bombax family. It is an annual plant with a height of about 80-100 cm. It has a well-developed taproot and 7-15 lateral branches. The stem is lignified in the lower part, and it has buds in the axils of the leaves. Branches appear in buds 3-5 leaves, while the rest of the buds are dormant. And the branches of this plant are growth and fruit. Growth or monopodial branches appear at the bottom of the stem and grow at an acute angle. Fruit or sympodial branches grow above the growth branches on the stem. Branches from the stem branch off at an obtuse angle, and because of this, they hang down a little. Flowers grow on them, and then the fruit-boxes are formed.In early ripening varieties of cotton, fruit branches grow from the axils of 3-4 leaves. In late maturing - 5-7 leaves from the axils. Fruit branches have a different number of internodes and different length of internodes. There are varieties with only 1 internode. This is because fruits and buds grow on all buds and on it, and from this the growth of the branch stops. And branches containing a large number of internodes are subdivided into types that differ in the length of internodes. A bush with branches of the first unsaturated type has internodes of 2-5 cm. It is pyramidal in shape with a narrow base. A bush with branches of the second type has internodes 5-15 cm and is also pyramidal in shape with a middle base. The third type has internodes of 15-25 cm. It is pyramidal in shape with an extended base. In cotton, the first 2-3 leaves of the main stem are whole-edged and cordate. And all the subsequent ones are already growing lobed.
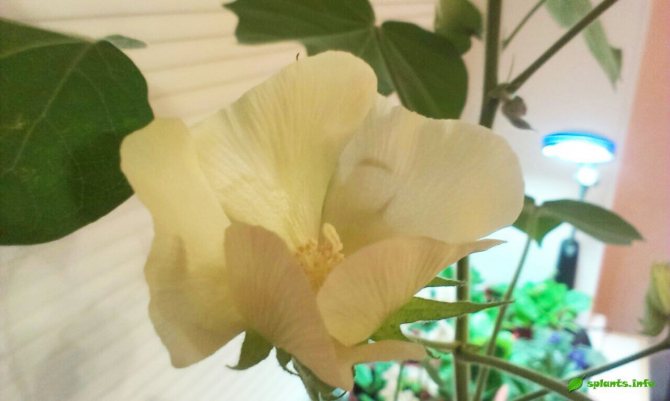
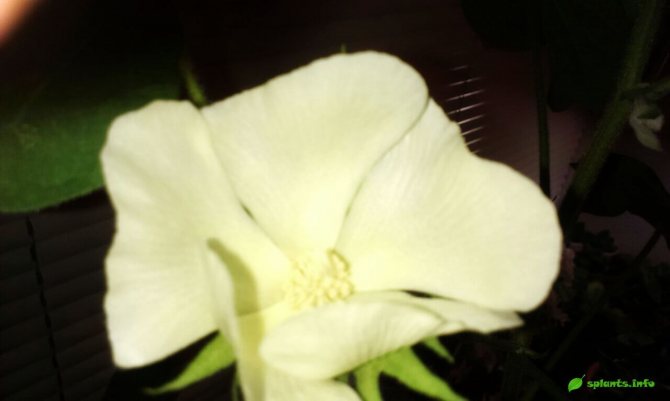
The flowers of this plant are quite large. They have an underdeveloped calyx and a yellow five-petal corolla. These flowers bloom early in the morning. In the afternoon, they turn red and close, and by the evening the flower bogs down. The next day, it becomes purple in color, and soon begins to dry and fall off. The fruits of this plant are a capsule that cracks and breaks when the seeds ripen. As a result, 5-11 seeds are obtained, which are covered with long and short hairs. Cotton fiber has a length of 20-50 mm. In one box, from 2 to 10 grams can be formed. raw. About 200 mature bolls can grow on a bush. The seeds are oval-ovoid. They can be covered with down, or completely naked. The cushions can be white or dyed.

Cotton is a plant that loves warmth and light. The most suitable temperature for the growth of cotton is 25-30 C. At lower temperatures, the plant develops more slowly. Seeds germinate at a soil temperature of 12-16 C, but germinate faster even at 20-25 C. For the swelling of seeds, water is needed in a percentage of 60% of their weight. After the shoots have appeared, after 8-10 days the first leaf is formed, and after a month the buds begin to develop. There are early ripening, mid-ripening, mid-late-ripe and late-ripening varieties of cotton. The growing season in early ripening days is 100-110 days, in mid-ripening days 115-120, in mid-ripe ones 130-135, and in late-ripening 150-170 days.
The powerful root system of cotton is fed with moisture from the deep layers of the soil. Therefore, it is quite resistant to drought, but with good watering, the yield of this plant increases significantly. He loves soils that are rich in nutrients and are highly permeable.
Description
A plant with a long taproot, the length of which can be up to two meters. The inflorescence is collected in a corolla, growing together into a tube. The fruit is formed in the form of a capsule, which cracks as it ripens. Inside there are brown seeds with soft hairs. Given the variety and growing conditions, the hairs are fluffy and long. One bush can have up to 200 boxes of cotton. After ripening, up to 10 seeds with fibers are poured out of the box.
The most popular type used by agronomists in various regions. It is a plant with white inflorescences. Medium quality fibers.
This grade has the highest fiber quality. Thanks to the efforts of breeders, it has become an annual plant. It was especially widespread on the coast of the United States, on the territory of Egypt.
It is tall, the shoots reach a length of 6 m, the plant belongs to tree-like perennials. The eye is delighted with red flowers, from which yellow cotton is formed. Cultivated in the tropics.
This annual is very common in the Transcaucasus and Asia. The smallest and most resistant variety. Grows very well in the north. The cotton is rough and short. The flowers are yellow with a red center.Small round capsules with small triangular seeds.


This is the general name for a biological genus that unites more than 50 plant species. Their spread began simultaneously from two centers - India and America. All representatives of this culture are herbaceous one- or two-year-olds. They can reach a height of 2 m.The core rhizome is well developed, extending to a depth of more than 30 cm.
When ripe, the box cracks and crumbles, 5–10 oval seeds fall out of it, covered with fibers 5–45 mm long. From one box remove from 2 to 10 g of raw.
In agricultural turnover, the most important are four types of cotton:
- ordinary (aka Mexican);
- Peruvian;
- tree-like;
- grassy.
The choice of the variety depends on the conditions of the area where the particular type of cotton is grown. In the European part, Transcaucasia and Central Asia, an ordinary line with a high stem and short fibers is traditionally cultivated. The rest of the species for our latitudes are considered "exotic".
Cotton is a herbaceous plant with a height of 1-2 meters. They have very branched stems with 3-5 lobed leaves, yellow flowers and fruits covered with hairs - cotton.
It should be noted that only some of the cultivated types of cotton have this kind. However, the diversity of representatives of this genus is quite large, so there is nothing surprising in the fact that there are also species with completely different properties. For example, there are even woody types of cotton, which are also very valuable, but not so common.
The height of the branched stem can reach 2 m, the root system is powerful, extending deep into the soil. The leaves of the plant have 3 - 5 lobes, grow on a stem on long petioles. Cotton flowers are similar to peony flowers and are white, cream or yellow in color. The plant blooms from July to September.
The fruit of the plant is a box, inside of which seeds ripen, covered with soft hairs or down, this is cotton.


Appearance
How the soil is cultivated
Winter plowing is usually carried out in August-September to a depth of 40 cm with two-tier plows. Before the fall of the plow, the soil is peeled 5-6 cm after the alfalfa. This event prevents its regrowth. Also, at the same time, the rhizomes of weeds are combed out, herbicides and fire burning are used. If the soils are saline, they are washed after autumn plowing and loosened with plows and cultivators. In the spring, the soil is armored in two tracks. By introducing manure in the spring, the plow is plowed. Then the soil is washed with watering and chisel-growing is carried out.
The history of cotton cultivation
All four main types of cultivated cotton are believed to be cultivated independently in four different regions of the planet.
Probably the first to start cultivating cotton were the inhabitants of the Indus Valley about 7 thousand years ago. Gradually, cotton has spread to the adjacent regions, today belonging to India and Pakistan. Interestingly, some of the cotton processing methods invented at that time were applied right up to the modern industrialization of India.
For a long time, the cotton plant remained unknown neither in China, nor in the Middle East, and even more so in Europe. The first mentions of it in Western chronicles date back to the era of Alexander the Great, when Europeans first saw "wool growing on trees" in India.
At the turn of our era, cotton began to be grown in southern China. Around the same time, the Persians were trying to master this culture. Exactly when the cotton plantations in Iran became really large is unknown, but in the Middle Ages, cotton was already one of the most important articles of the Persian economy.
In parallel with India, cotton cultivation began in the territory of modern Mexico. The oldest finds of cotton fabrics discovered here date back to the beginning of the 6th millennium BC. e.Another, completely independent center of cotton cultivation was in Peru.
By the end of the Middle Ages, cotton was already an important import commodity in northern Europe, but where this miracle fiber comes from, the Europeans only dimly understood, knowing only that fiber of plant origin. Many in all seriousness believed that such trees grow in the East, on which, instead of flowers, small sheep appear, from which they get cotton, so similar to sheep's wool. These misconceptions have even left their mark on modern European languages. For example, literally translated from German "cotton" means "wood wool".
By the end of the 16th century, cotton was grown everywhere in those regions of Asia and America, where there were suitable climatic conditions. Subsequently, it was cotton that became the locomotive of the industrial revolution in England, which changed the attitude of the state to the economy, and the people to entrepreneurship. Raw materials were imported from tropical colonies, processed in England, and then supplied to the British colonies, China and the countries of continental Europe. Cotton, on the other hand, became one of the causes of the American Civil War, but that's a completely different story.
Historically, cotton has never been grown on the territory of Russia, since the climate was not suitable for cotton, but it was simply ideal for flax. By and large, cotton and flax quite successfully replaced each other, so in our country, before the arrival of the Bolsheviks, no one seriously thought about growing cotton. For the first time, we began to seriously cultivate cotton in the 1930s in the North Caucasus. However, after the war, it was decided that it would be more rational to concentrate Soviet cotton growing in the Central Asian republics. The idea of growing cotton on the territory of the Russian Federation was returned only a few years ago.
How is irrigation done
To increase the moisture in the arable layer and remove harmful salts from the soil, pre-sowing backup and flush irrigations are carried out. If the land is highly susceptible to salinity, leaching irrigation is carried out annually in October-December. At this time, groundwater is at its deepest. Vegetation irrigation promotes plant growth and development. Lack or excess of moisture adversely affects the harvest, so the main thing is to comply with the norms and timing of watering. It is very effective to irrigate cotton crops with flexible pipeline irrigation hoses and sprinkler irrigation. The pipelines on the sites are replacing the outlet furrows and temporary sprinklers. For the development of the root and aerial part of the plant, 1-2 watering is carried out. This is done before flowering - 1 time, when there are 3-5 true leaves, and the second - in the budding phase, somewhere in 20-25 days after the first watering. During flowering and fruit formation, the plant's need for water increases. When cotton is ripe, the irrigation rate should not exceed 600-700 cubic meters per hectare. Such irrigation provides normal soil moisture before defoliation. Watering is carried out no later than 5-7 days before defoliation.
Types and varieties of cotton
For a long time, botanists could not draw up an accurate classification of plants of the genus Cotton, for which there were several reasons. Firstly, there are indeed many types of cotton - more than 50. Secondly, most of these species are subject to high variability under the influence of various conditions and circumstances, such as weather and soil composition. Thirdly, cotton plants are easily amenable to cross-pollination between plants of different species, as a result of which more and more new hybrids are formed.
The founder of modern biological taxonomy, Karl Linnaeus, believed that there are from 3 to 6 types of cotton. Many other botanists also believed that there are few types of cultivated cotton - about a dozen.But there were also more radical views: one assured that there are only two types of cotton - American and Asian, while others, on the contrary, numbered about fifty species or even more.
Currently, only the following types of cotton are used in the agriculture of the planet:
- Herbaceous cotton plant. This annual species is most widespread in Central and Southeast Asia, as well as in the Caucasus. It is the shortest, but at the same time the most persistent species. Of all types of cotton, this one can grow the farthest in the north. The cotton obtained from it is the shortest and coarsest, which is why it is sometimes called woolly.
- Indo-Chinese cotton plant. The tallest type of cultivated cotton, capable of growing up to 6 m. Treelike perennial. The cotton flower of this species has red, not yellow petals, from which high-quality yellow cotton then ripens. Cultivated in tropical regions.
- Peruvian cotton. The kind with the longest and highest quality fiber. It was originally a perennial, but through the efforts of American breeders, about a century ago, it became an annual. It is not widely spread, it is grown in small quantities along the southeastern coast of the United States, as well as in Egypt.
- Common cotton. The most common type. It is grown ubiquitous in regions with a suitable climate. Annual with white flowers. Medium quality fiber.
Since mainly ordinary cotton was grown on the territory of the former USSR, it is necessary to talk about varieties only in relation to this species. In the countries of Central Asia, the most widespread varieties were Eloten-7, Dashoguz-114, Serdar, Regar-34, Tashkent-6, Bukhoro-6, Omad, Andijon-35 and others. But for the southern regions of the Russian Federation and Ukraine, the Bulgarian varieties Garant, Balkan and Ogosta, which have time to ripen in our latitudes, are better suited. Also worth mentioning are purely Russian varieties of cotton: Yugtex, POSS, Pioner, Mikhailovsky and others.
How crops are fertilized
Cotton is fertilized fractionally, applying a large amount of fertilizer. To get 1t. raw cotton, you need 45-50 kg of nitrogen, 40-50 kg of potassium and 12-17 kg of phosphorus. Organ-mineral mixtures promote better utilization of mineral fertilizers. With depleted and scarce soils, manure or compost, as well as phosphorus and potash fertilizers, are applied under the plow. Pre-sowing superphosphate is also very effective. In the phase of true leaves, budding and flowering, nitrogen fertilization is carried out. Potash fertilizers are used in the budding phase, and phosphorus - during flowering and fruit formation.
In cosmetology
In addition, the oil is used in dermatology, it is perfectly absorbed by the skin. On its basis, emulsions, lotions, soaps, gels, shampoos are made.
The substances contained in cotton tighten, improve the condition of the skin, and are a natural barrier to the negative impact of the environment. As a result of regular use of a product based on it, blood circulation and complexion improve. The structure of the skin is regenerated, elasticity increases. It is ideal for aging skin. Also, the oil allows cells to retain water, restoring the lipid film in the nuclei.
This is a great massage tool. Shampoos based on it can improve the structure of colored hair.
Following simple tips, you can grow cotton in your summer cottage and use it with benefits for beauty and health.
How is sowing carried out
First of all, the seeds are prepared before sowing. They are removed from them mechanically or chemically. Then they are subjected to air-thermal heating, soaked in water and boric acid solution and disinfected. The earlier the sowing is carried out, the better in the qualitative and quantitative sense the harvest. Cotton is sown at a soil temperature of 12C.Sow in a square-nested method and a rectangular-nest method. 80-120 thousand plants are located on 1 hectare of land. The comb method of sowing seeds helps to increase the yield of raw cotton. When caring for this plant, the crust is destroyed, 3-4 inter-row cultivations are carried out in two directions, they break through in the nests and watered as needed. Herbicides and mulching help kill weeds. Removing the tops of the growth branches and the top of the main stem can increase the yield of raw cotton and reduce the dropping of buds and ovaries.
Preparatory work
Before sowing, it is worth learning more about where, on what kind of soil, cotton grows best.
The ideal option would be land without salt plugs. Groundwater should lie deeper - waterlogging is undesirable. The soil will have to be brought to the required condition in the fall, in several stages.
Soil preparation
Many farmers use winter watering to compact the soil. After such moistening in the spring (even before harrowing), chisel-making must be done. This is a technique of non-moldboard plowing to a depth of 8-15 cm, followed by a harrow.
Seed preparation
High-quality, conditioned seed material collected for frost is used. Only zoned varieties give a stable harvest - "exotics" take root with difficulty.
The workpieces are pre-treated mechanically or chemically. The first is to remove the underpinnings (partial or complete). "Chemistry" is reduced to etching with vapors of hydrochloric or sulfuric acids.
Air heating is also important:
- The seeds are kept in the air for 20-30 days.
- For disinfection, take copper trichlorophenolate or 65% fentiuram (no more than 12 kg / 1 ton).
- Before sowing, they are soaked in water for 9-10 hours. This technique is often replaced by moisturizing (3 treatments with an interval of 8-12 hours). At the same time, 500-600 liters of water are consumed per ton of material.
When the preparations are over, you need to wait for the heat and start sowing.
Cotton harvesting
Since the ripening in cotton is uneven, and the capsules open gradually over 1-1.5 months, they are removed in several stages. Defoliation is also very common in cotton growing. This is the removal of leaves before harvesting, as they carry pathogenic bacteria and fungi, and also interfere with the work of cotton pickers. When most plants open 1-2 or 2-3 bolls (having 11-15 fruit branches), they are treated with defoliants. If this is done too early, you can lose part of the harvest, and if it is too late, the efficiency is not high. This is usually done early in the morning or in the evening using tractor sprayers or pollinating from airplanes. Defoliation accelerates the maturation of the bolls. When the opening of the bolls reaches 50-60%, the cotton is harvested using special machines.
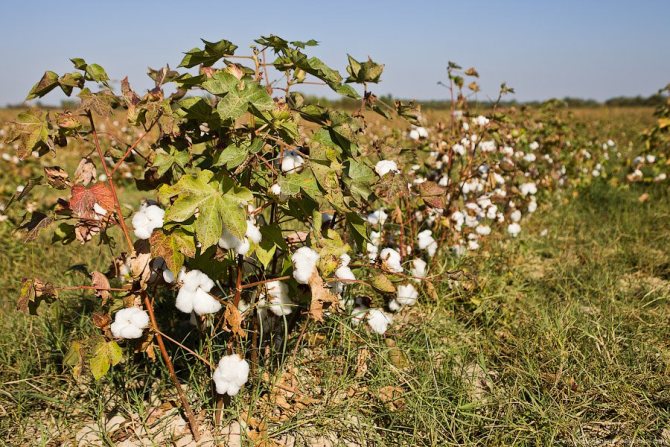
Cotton is an annual plant, it is grown on an industrial scale on all continents of the planet, in warm and hot regions. The fruit of the cotton plant is an amazing and useful "box", when ripe, the shell opens, releasing delicate fluffy fibers. Each fiber is one plant cell and has the shape of a tube. This tube is extremely strong and resistant to bending. This led to the use of cotton in the production of fabrics. Cotton fabric is the main application of cotton fiber.
Cotton, depending on the region of growth and processing conditions, has different color shades: from white, pale cream, yellow and blue. By crossing cotton varieties, breeders also achieve unusual colors: purple, brown and green.
Cotton fabric
To obtain a cotton thread from soft and delicate fibers, cotton goes through successive stages: it is peeled from the seed capsule, sorted according to the length of the fibers. With the help of a special treatment, wax is removed, which protects these fibers. Then the fibers are twisted and compressed.In this form, he gets to factories. The next stage is the production of threads and yarns.
Various cotton fabrics are made from cotton threads. Dense and durable: denim, - trousers and jeans, outerwear are sewn from it. Light and pleasant fabrics: satin, poplin and chintz, translucent - marquise and batiste. Velvety - velveteen and velor - these fabrics are also beautiful and loved by everyone. Lace and knitted cotton yarn are popular and trendy. You can buy cotton fabric in specialized online stores that sell both fabrics and cotton laces. It is convenient and reliable. In addition, there is more assortment of goods in such stores than in the bazaar.
The so-called organic cotton, which is grown without the use of harmful chemical fertilizers, is highly valued. In the manufacture and dyeing of organic cotton fabrics, natural dyes are used. The price for such cotton is slightly higher than usual.
Cotton application
Cotton fabric ranks first among natural materials in terms of polarity and low cost. When sewing special and home clothes, healthy and environmentally friendly bed and table linen. In the manufacture of fabrics, cotton is mixed with synthetic components. As a result of this combined application, the fabric acquires properties that are not typical of 100% fabrics. They wrinkle less, keep their shape well, do not fade in the sun and during washing.
The use of cotton is not limited to this. Cotton fiber products are used in medicine as a dressing material. And in different industries. Valuable cottonseed oil is squeezed out of its seeds, which is used for food. Glycerin, soap, lubricants for various types of machines and devices are made from it. Waste is used for the manufacture of compound feed for animal husbandry.
Sakura is most often associated with Japan and its culture. Picnics under the shade of flowering trees have long become an integral part of the welcome of spring in the Land of the Rising Sun. The financial and academic year begins here on April 1, when the magnificent cherry blossoms are in full bloom. Therefore, many significant moments in the life of the Japanese pass under the sign of their flowering. But sakura grows well in cooler regions - certain species can be successfully grown even in Siberia.
We have prepared a hearty, incredibly appetizing and simply elementary dish for you today. This gravy is one hundred percent universal, as it goes with every side dish: vegetables, pasta, or whatever. Gravy with chicken and mushrooms will save you in moments when there is no time or you don't want to think too much about what to cook. Grab your favorite side dish (you can do this ahead of time to keep everything hot), add the gravy and lunch is ready! A real lifesaver.
Agriculture refers to such types of human activity, the successful outcome of which is not always directly proportional to the efforts made. Unfortunately, nature does not necessarily act as our ally in growing plants, but often even, on the contrary, throws up new challenges. Increased reproduction of pests, abnormal heat, late return frosts, hurricane wind, drought ... And one of the springs presented us with another surprise - a flood.
With the advent of the summer cottage season, the question arises of growing strong and healthy seedlings of our favorite vegetables: cabbage, tomatoes, sweet peppers, eggplant and many other crops. Along with this, the question arises - how to grow decent seedlings and in the future to get healthy plants and a decent harvest from them? For example, I have been growing seedlings for a single season and protecting my garden from diseases with the help of biological preparations Alirin-B, Gamair, Glyokladin, Trichocin.
I will allow myself to confess my love today. In love for ... lavender.One of the best unpretentious, evergreen and flowering shrubs that can be successfully grown in your garden. And if someone thinks that lavender is Mediterranean, or at least southern, then you are wrong. Lavender grows well in more northern regions, even in the suburbs. But in order to grow it, you need to know some rules and features. They will be discussed in this article.
Having once tasted such a priceless product as pumpkin, it is already difficult to stop looking for new recipes for serving it to the table. Korean style pumpkin, despite its pungency and spice, has a fresh and delicate taste. After cooking, you will need to cover the salad and let it brew for at least 15 minutes. My butternut squash is very juicy and sweet, so there is no need to crush it. If the pumpkin is of a different variety, then you can knead it with your hands so that it slightly sips the juice.
Salad, as the earliest and unpretentious green culture, has always been held in high esteem by gardeners. Most summer residents usually start spring planting by sowing lettuce, parsley and radish. Recently, the desire for a healthy diet and a large selection of greens in supermarkets make gardeners wonder which of these plants can be grown in their beds? In this article, we will tell you about nine of the most interesting, in our opinion, types of salad.
Another "bonus" is always "attached" to the flowering of indoor roses - capriciousness. When they say that it is easy to grow roses in rooms, they are cunning. For indoor roses to bloom, it is necessary to create literally ideal conditions. And vigilant care, attention and response to any plant signals is the main guarantee of success. True, no matter how capricious roses are, you can grow them in a pot format quite successfully. And attentive flower growers should not be afraid of this.
Pollock is best cooked in a casserole, separating the fillets from the skin and bones. Pieces of fish are mixed with a variegated vegetable set, poured with a sauce of cheese, sour cream and eggs. This fish casserole has a presentable look, and its taste is a whimsical mixture of subtle nuances. Vegetables and fillets are soaked in sour cream, the cheese will harden with a golden brown crust, eggs will tie all the ingredients together. Pieces of fish are abundantly sprinkled with Italian herbs, and pollock acquires an unusual piquancy.
Despite the fact that the calendar spring begins in March, you can truly feel the awakening of nature only with the appearance of flowering plants in the garden. Nothing testifies to the arrival of spring as eloquently as the clearing of flowering primroses. Their appearance is always a small holiday, because winter has receded, and a new gardening season awaits us. But, in addition to spring primroses, there is still something to see and admire in the garden in the month of April.
Growing rapidly and turning into wild thickets, hogweed disrupts the existing ecosystem and suppresses all other plants. The essential oils contained in the fruits and leaves of hogweed cause severe dermatitis. At the same time, it is much more difficult to deal with it than with other common weeds. Fortunately, today a tool has appeared on the free market that can rid your site of most weeds, including hogweed, in a short time.
Carrots come in various colors: orange, white, yellow, purple. Beta-carotene and lycopene predominate in orange carrots, the yellow color is due to the presence of xanthophylls (lutein); white carrots are high in fiber, while purple carrots contain anthocyanin, beta and alpha carotenes. But, as a rule, gardeners choose carrot varieties for sowing not by the color of the fruit, but by the timing of their ripening. We will talk about the best early, middle and late varieties in this article.
We recommend a fairly easy pie recipe with an appetizing chicken and potato filling.Open pie with chicken and potatoes is a great hearty dish that is perfect for a hearty snack, it is very convenient to take a couple of these baked goods on the road. The cake is baked in the oven for one hour at 180 degrees. After that, we lay it out on a wooden surface, having previously released it from the mold. It is enough to slightly cool the baked goods and you can start tasting.
The long-awaited spring for many indoor plants is the start of an active growing season, and for most, the return of their decorative effect. Admiring young leaves and emerging shoots, one should not forget that spring is also a great stress for all indoor plants. Sensitive and versatile, all indoor crops are exposed to much brighter lighting, changes in humidity and temperature conditions.
You can easily cook homemade Easter cake with cottage cheese and candied fruits, even without having any pastry experience behind you. You can bake Easter cake not only in a special form or in a paper mold. For the first culinary experiences (and not only), I advise you to take a small cast-iron pan. The cake in a frying pan will not turn out as high as in a narrow form, but it never burns and always bakes well inside! Yeast curd dough turns out to be airy and aromatic.
A cotton flower is a corolla of three to five wide and accrete petals and a toothed calyx. The calyx is surrounded by a three-bladed wrapper, and a large number of stamens grow together into a tube. Cotton flowers are usually white, yellow, or cream in color.
Cotton plant is an annual or biennial herb
reaching a height of seventy centimeters to two meters. The large number of branches on the stem makes it look like a bush.
The height of the plant determined its predominantly outdoor cultivation.
Cotton flowers are pleasing to the eye from July to September, and later the cotton flower is replaced by a box filled with a large number of seeds. On each seed, from five to fifteen thousand fibers with a length of three to five millimeters can develop.
It is these fibers that make cotton such a valuable plant, although other parts of it are also used in various industries, although not so widely.
What is cotton made?
Cotton seeds are used for:
- planting new cotton;
- oil production;
- production of feed for livestock.
Down (lint) and underpads (delint) are used:
- as a basis for the production of synthetic thread;
- paper (cotton is 95% cellulose);
- plastics;
- explosives.
Cotton fibers are used for the production of:
- elite, thin fabrics - only long-staple cotton is used for them;
- cheaper fabrics, such as calico, chintz, etc. - use medium staple cotton;
- knitwear - short-staple cotton can also be used in the manufacture (this sometimes explains its lower durability), for strength they add synthetic components;
- medical cotton wool;
- batting;
- cotton filler for pillows, blankets and mattresses - modern methods of careful processing of cotton fiber allow you to obtain a material that perfectly holds its shape, does not cake and is environmentally friendly.


Buy cotton bed linen
Is the cotton flower edible or not
Cotton - nonfood culture
and its flowers themselves are not eaten. Accordingly, it is not edible by itself. However, plant parts such as long fibers, seeds, roots and root bark are often used in medicine.
So cotton broth is used for stomach cancer or during the rehabilitation process after surgery, and the bark of the plant has hemostatic properties.
Vitamin E deficiency, viral diseases, atherosclerosis, herpes, high blood pressure, infertility, menstrual irregularities - in the fight against these diseases
cotton also plays an important role.
Oil prepared from cotton seeds is suitable not only for external use (plasters and ointments), but is also widely used in the food industry along with sunflower, flax or sesame seed oils. Cottonseed oil is edible and often used in margarine and mayonnaise making.
In addition, delicious and healthy honey and flour are made from cotton in the food industry.
Useful properties and use of cotton as raw material
Since picking cotton by hand under the scorching sun is a very time consuming process, cotton pickers are used. They clean the untreated mass of debris, leaves, branches and seeds. Leaves are used for making citric and malic acid... Cotton fiber is a raw material for the production of gunpowder. In the regions of Asia, dry stems are used as fuel.
Among other things, the plant is a melliferous plant - honey of a light shade, after crystallization it becomes white. It has a peculiar taste and pleasant smell.
This plant is used almost everywhere: for the production of paper due to its high cellulose content, and for the production of plastics, and even for the production of explosives. The seeds are also not disposed of - flaxseed oil is squeezed out of them. Oil is used for a variety of purposes: added to food, made cosmetics, medicines, made soap, candles, technically oils, and more.
Cotton is also valuable for what it contains many useful substances:
- essential oils;
- resinous substances;
- vitamins; minerals;
- organically acid.
The plant is used in the treatment of diseases of the reproductive system, as well as for toxicosis in pregnant women. Cotton plant also used for herpes, lichen, some viral diseases and a lack of vitamin E due to the high content of this vitamin in the composition. Cotton bark is considered a natural hemostatic agent.
How it grows: cultured or wild
Consider is it a cultivated plant or not
... Cotton plant appeared about a hundred million years ago in tropical forests. Here it grew in the form of spreading cotton trees, and in semi-desert zones it evolved into shrubs resistant to dry periods.
Later, the plant significantly expanded its habitat, "adjusting" to the climate of the area. In fact, it is both cultured and wild. It grows in the following places:
Cultivated cotton is grown all over the world, but it is an extremely capricious plant. It requires a lot of heat and moisture, and the seeds do not germinate at temperatures below fifteen degrees.
The best conditions for the growth of cotton are considered to be thirty-degree heat and abundant watering, especially during flowering.
Also be sure to fertilize the soil before planting
, and to increase the yield in summer, it is necessary to cut off the tops of the central stem and side branches. After the box bursts, cleaning begins.
Since maturation does not occur simultaneously, the entire harvesting process takes place in several stages.
One-year-old cotton can also be grown at home. The main conditions for good flower growth are an abundance of sunlight, warmth and reliable protection from drafts. Also for him timely watering is important
and feeding.
Today, there are thirty-two wild and five cultivated varieties of cotton on the planet.
Interesting facts about cotton
Cotton is an ideal fabric, hygienic, environmentally friendly, "breathable" and biologically compatible with the human body. Today TextileControl has interesting facts about cotton.
• In the Middle Ages, people knew that cotton was picked from a plant, but few saw this plant.Many believed that animals like lambs appeared on this plant, from which cotton was cut.
• Cotton - a fiber of plant origin, obtained from the bolls of cotton - plants of the genus Gossypium, which in Latin means "a tree that gives cotton"
• The English "cotton" comes from the Arabic "kattan", which means cotton, and the Russian "cotton" comes from the word "flakes".
• The cotton plant originated about a hundred million years ago in the Malvaceae family. Now there are thirty-two wild and five cultivated types of cotton on the planet, united in six sections and two subgenera according to their habitat, peculiarities of life and appearance. Cultivated species fall into nineteen more subspecies, each of which contains hundreds (!) Of annual and perennial, tree, shrub and herbaceous varieties.
• The first people who began to cultivate cotton are ancient tribes living near the Indus River in the territory of modern Pakistan, India and China 6000 years ago
• The first recorded cotton harvest in the United States took place in 1556 in Florida
• More cotton is used in the world than any other fabric
• The first machine-woven cotton garment was made in England in 1730
• The quality of cotton is assessed by three parameters - color, clarity and fiber strength
• Egyptian cotton is considered to be softer and more durable, therefore more expensive than American
• Oil, flour and husks are obtained from cotton seeds
• Cotton is one or perennial grasses (less often trees reaching heights of up to 7 meters) with large leaves, white, yellow or pink flowers. When ripe, cotton fruits open into 2-5 segments and are seeds enveloped in the finest fibers from 15 to 55 mm long, usually white. The longer and thinner the fibers, the more valuable they are.
• After harvesting, the cotton is placed in the sun to dry - this is necessary to separate the fibers from the seeds. The cotton picking stage is labor intensive; however, in the most developed countries, the collection takes place using special mechanical devices. In cotton processing plants (as a rule, they are quite far from the plantations), the raw materials are broken up and combed out until a thin ribbon appears, in which all the fibers are located in parallel.


The importance of cotton can hardly be overestimated, this plant in the literal sense of the word dresses almost half of the world, despite the fact that synthetic fabrics are gaining popularity from year to year. In addition, cotton is used for the production of other things, sometimes completely irreplaceable. It was once assembled by hand, and it was very hard work, but since then the development of science has made it possible to create machines that greatly facilitate this task.
Cotton facts
- In addition to yarn, threads, cotton wool and even explosives used in the mining industry are made from it.
- Even 150-170 years ago in Russia, cotton was called "cotton paper".
- About 95% of the cotton composition is cellulose.
- It absorbs moisture perfectly. If there is enough of it, cotton can absorb so much that it will increase in volume by 40%.
- Most fabrics, when wet, lose some of their strength, but cotton fabrics, being saturated with water, on the contrary, become stronger.
- Fabrics made of cotton are sensitive to sunlight. Studies have shown that 940 hours of exposure to light is enough to halve their safety margin.
- The strength of cotton is comparable to that of silk, and surpasses that of wool.
- In the 20th century in the GDR, housings for some Trabant cars were made from pressed cotton waste. As a result, several cases were recorded when in rural areas goats tried to chew car body parts, and not without success (interesting facts about goats).
- Archaeologists have established that humans first began cultivating cotton about 7,000 years ago.
- In Uzbekistan, ill-considered cultivation of this plant and excessive water intake for irrigation of cotton fields have led to the desertification of large areas and the virtual disappearance of the Aral Sea.
- Breeders have bred cotton varieties of different colors, which makes it possible not to dye it in the future.
- India ranks first in the world in cotton production.
- The first machine-woven cotton garment was made in Great Britain in 1730.
- To this day, cotton is the most popular and widespread fabric in the world.
- Cotton seeds are used to make oil and flour.
- Some types of cotton are trees that grow up to 5-7 meters in height (interesting facts about trees).
- Modern machines pick up to 700-800 kg of cotton each day. Manual labor is about 10 times less efficient, not to mention being extremely hard.
- One ton of cotton is enough to produce about 600-700 pairs of jeans or trousers.
- In ancient China, cotton, due to its rarity, was valued higher than silk, which was in abundance there.
- The legionnaires of ancient Rome wore clothing woven from cotton.
Cotton - denim flower
People often call cotton a denim plant, since it is from it that everyone's favorite denim is made.
The advantages of such fabric are considered strength, durability, comfort
and the ability to "breathe". The quality of denim directly depends on the cotton from which it is made.
For example, Mexican cotton with fibers of twenty-four millimeters in length makes it possible to produce high quality denim, which has practically no scars. Fabrics made from Barbados cotton are very soft and strong.
However, it is quite difficult to process and assemble it, so the number of jeans made from such fabric on the modern market is small - about seven percent.
Zimbabwean cotton fabrics
are of high quality at an inexpensive cost. The most popular is the fabric made from Asian and Indian cotton with short staple fibers.
This kind of jeans takes up to half of the modern clothing market.
Thus, jeans fabrics are quite diverse both in composition and in the method of manufacture and appearance. It is this variety of choices that have made denim clothing so popular over the years.
Denim also has its own varieties, where cotton is a priority.
It is unlikely that in the world you can find things more comfortable and practical than denim.
Why is cotton good?
Everyone knows that textiles made from 100% cotton (for example, cotton towels, bed linen, bathrobes) create special comfort. How can this be explained? Why is cotton so good?
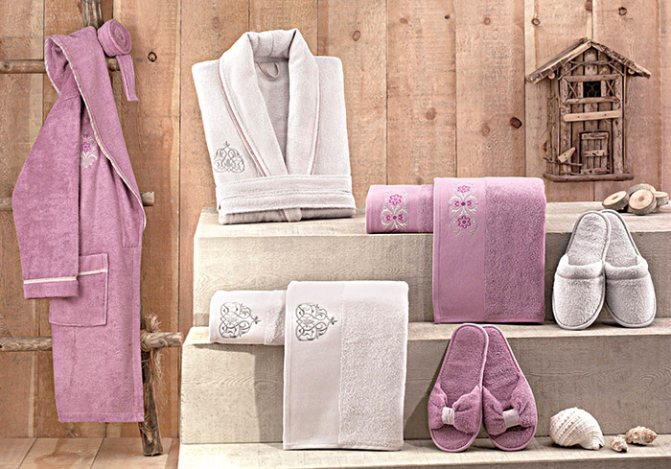


Cotton has the following properties:
- good hygroscopicity and breathability;
- good tensile strength;
- resistant to high temperatures (up to 150 C);
- resistant to organic solvents (alcohol, acetic acid, formic acid);
- softness;
- good coloring;
- relative cheapness.
Cotton and hand-made
Handmade cotton flowers are widely popular in handicrafts such as scrapbooking and cardmaking
... They fit perfectly into flower arrangements, decorative wreaths.
Also in work in country styles, eco, etc. Such flowers can be made quite simply and economically.
Required materials and tools
For manufacturing you will need the following materials
:
- cardboard egg tray;
- brown paint;
- brown threads;
- sewing needle;
- brush;
- scissors;
- cotton wool or synthetic winterizer;
- hot melt glue.
In general, one flower takes no more than ten minutes, excluding the time required for the paint to dry.
How to make cotton flowers with your own hands
It is nowhere easier to make a cotton flower with your own hands: a cardboard tray will become an excellent sepal for a flower, and a synthetic winterizer or cotton wool will become a realistic bud. To manufacture
flower follows
in several stages
:
- The tray is divided into cells, then blanks of a four-lobed sepal are cut out from each.
- These blanks must be painted with brown paint. For a more natural color, it is better to mix several shades of paint.
- During staining, the cardboard will become slightly soggy and more pliable, which will help to easily wrap the petals towards the center.
- After the paint has dried
for more realism, you can cut thinner, short strips along the edges of the petals. - From a small piece of padding polyester or cotton wool, you need to roll a ball, which is stitched with thread in 4-5 places to divide the flower into sections.
- Next, the ball is attached to the cup with glue, after which you need to form petals for a naturalistic look.
Even artificial, cotton is a good decoration
Such a flower by sight
practically
no different from the present
, so it is not necessary to waste time looking for cotton - it is much easier and faster to make it with your own hands.
So, the cotton flower is one of the most widespread plants in the world. It owes such popularity to a variety of applications.
In addition to the above industries, he is also involved in the production of cellulose, paper, gunpowder, soap, varnishes, etc.
Total in the world produced
about
twelve hundred cotton products
, thanks to which only about four percent of the raw material remains unused. The fragrance of the flower used in perfumery is compared to purity and tenderness, and the plant itself is called the "child of the sun".
Cotton is grown primarily in tropical and subtropical climates. But if you want to decorate your garden with bright flowers and snow-white cotton bolls, our article will help you realize your plan.
We will tell you everything about growing cotton and caring for adult plants. You will also learn about the main varieties of crops and the peculiarities of harvesting.
Harvest
After harvesting, the cotton is sent for cleaning from seeds, dust and other impurities. Then the longest fibers are selected from the finished raw materials, which are used to obtain yarn. Cotton fabrics of various types are made from threads of the appropriate thickness. In the process of spinning, the fiber undergoes special processing: sizing, bleaching, cleaning, dyeing.
Our company owns production facilities with the latest equipment, which produces at least four tons of carded and combed yarns daily. We produce from it a wide range of cotton knitted fabrics, such as satin stitch, footer, interlock, pique. We also have our own yarn and fabric dyeing lines.
Thus, using high-quality Uzbek cotton, we make good-quality functional promotional clothing. At affordable prices and in any quantity.
Having found out how and with what measures valuable cotton is grown, let's move on to the final stage.
It looks simple, but in fact it is a very painstaking work that requires expensive devices.


Now cotton care is no secret for our readers. We hope the sowing process will not be difficult either. Good harvests!
Growing and picking cotton
Cotton is a one- or biennial herb up to two meters high with branched stems. It has a tap root system, where the root penetrates into the ground up to three meters, but the main branches are located at a depth of 30 cm.
The flowers are solitary, numerous with different colors, consisting of a corolla with three to five wide petals and a double five-toothed green calyx, which is surrounded by a three-lobed envelope. Numerous stamens grow together into a tube.
Figure 1. Photo of the culture at different stages of cultivation
The fruit is an oval or round capsule with several compartments, which cracks along the valves, with dark brown seeds, which are covered with soft hairs on the surface - cotton (Figure 1).
Hair is divided into two types. They are long and fluffy, as well as short and fuzzy (down). Depending on the growing conditions and the variety, there can be both long and short hairs, or only long ones. Wild varieties have no long hairs. The seeds of the culture are covered with a thick skin and contain the embryo, which consists of a root and two seed lobes.
What types of cotton are there?
There are several types:
- herbaceous cotton;
- tree cotton;
- ordinary cotton;
- Peruvian cotton.
The quality of the material depends on the type. The thinnest and longest fiber is obtained from Peruvian cotton. This variety is valued more than anyone else, because more than sixteen kilometers of material are obtained from one ton of such cotton. And, for example, from ordinary cotton, only about nine.
Cotton is divided according to the length of the fiber:
- short-fiber (from 27 mm);
- medium-fiber (from 30 to 35 mm);
- long-fiber (from 35 to 50 mm).
Growing cotton at home
Cotton is grown in a well-lit, sunny place protected from strong winds. Feels good in summer heat, but does not tolerate frost. In early spring, flowering plants are fed with fertilizer every two weeks. Water as the earth dries up.
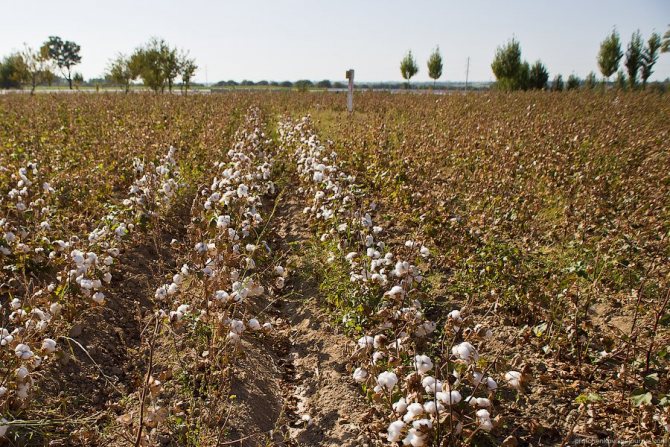
Figure 2. Map of regions suitable for cotton growing
Figure 2 shows a map of the regions whose climate is best suited for growing this crop.
Crop rotation
Alfalfa is considered the best precursor for cotton (Figure 3). To increase the fertility of the soil and the productivity of the plant, green manures (mustard, vetch, peas or rye) are used. In order for these plants to grow well, careful pre-sowing watering must be carried out. Long autumn or warm winter also has a positive effect. The use of green manure allows maintaining high soil fertility during cotton-alfalfa crop rotations.
Figure 3. Table of alfalfa use for cotton crop rotation
Growing alfalfa lowers the water table and removes excess salt from the soil, resulting in a high yield of cotton.
Soil preparation
In August and September, autumn plowing is carried out, changing the depth of soil cultivation annually. After growing alfalfa, in order to prevent re-germination of the culture, the soil is husked by 5-6 cm. Winter plowing is carried out with two-tier plows to a depth of half a meter.
After autumn plowing, salty soils are washed, then loosening is carried out. In the spring, they are harrowed in two tracks, after the introduction of manure and plowed. The fields are cleared of weeds by combining fire burning, combing out weed rhizomes and applying herbicides.
Reproduction
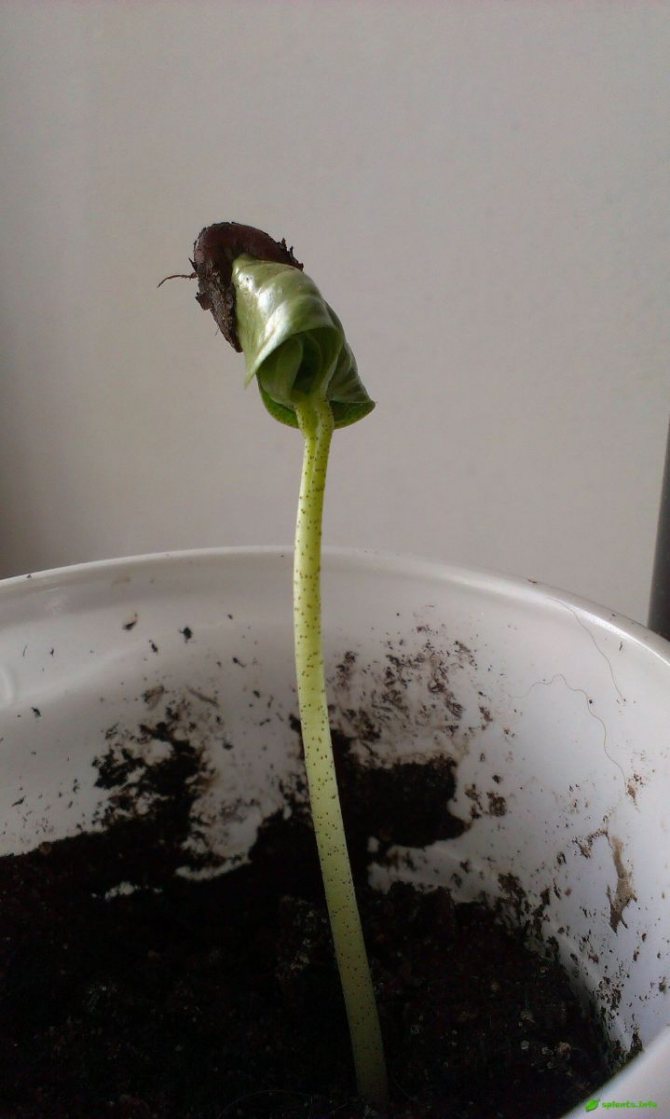
Propagate the culture by seeds (Figure 4). They are sown in January or February in greenhouses, deepening 1 cm into the soil. Germinate at temperatures up to +24 degrees in a bright place.
After a few days, the first shoots appear, which need to be provided with a sufficient amount of moisture. So that the plants are not crowded, they are dived into separate containers, and then planted in pots, where they will remain until autumn.
Figure 4. Seeds, flowers and fruits of cotton
The plant blooms for 8 weeks after the appearance of the first shoots.
Place in the crop rotation
The key to a good harvest is the use of alfalfa in crop rotation. This culture improves the composition of the soil, helps to accumulate humus. After planting, the soil acquires good drainage, air circulation in the upper layer is normalized.


A similar "multifield" looks like this: 6-7 fields for cotton "prepare" 2-3 alfalfa massifs. If alfalfa is not planted, it's okay: any cereals and legumes are considered good predecessors on the site.This also applies to sugar beets with corn.
Cotton care
When processing cotton, pre-sowing and vegetative irrigation is used.
Note:
Pre-sowing backup irrigation is needed to increase moisture in the arable layer, and pre-sowing flush irrigation is needed to remove harmful salts from the soil.
In the process of plant growth and development, vegetative irrigation is provided, which improves the quality of the fiber. Watering should be moderate and regular (Figure 5).
At the moment, sprinkler irrigation and hoses are considered the most effective irrigation methods. The pipelines are replaced with temporary sprinklers. Irrigation in deep furrows is especially convenient and effective.
Note:
To enhance the development of the root system, 1-2 waterings are carried out: the first in the presence of 3-5 first leaves, the second in the budding phase. In this phase, the culture needs more water.
Figure 5. Watering and fertilizing crops
To maintain normal soil moisture before the leaves fall, the irrigation rates should be high enough (about 700 liters per 1 ha) to create conditions for normal boll ripening.
To get a good harvest, you need to regularly fertilize the crop, taking into account the soil, climatic and biological characteristics:
- It is recommended to apply small doses of superphosphate before sowing;
- During the formation of true leaves, buds and flowers, they are fed with potash and phosphorus fertilizers (during the period of budding and flowering, respectively);
- During the first feeding, fertilizers are introduced at a distance of 15-20 cm from the row, during budding - at a distance of 22-25 cm.
Particular attention is paid to the destruction of the crust, which includes 3-4 inter-row cultivations, plant breakthrough and watering. Plants burrow in nests with 1-2 leaves.
Note:
When the first shoots appear, the first cultivation is carried out to a depth of 8-10 cm, the second - on the eve of vegetative irrigation.
Weed control is carried out using mulching and herbicides, which accelerate the growth and maturation of plants. Also increases the yield and reduces the shedding of the ovary of raw cotton by removing the top of the main stem. Treatment with chemicals reduces the growth of shoots, since the leaves and bolls are not damaged during treatment.
Benefit
- Cotton fiber is produced from this wonderful plant. It is light and natural. Things made from it are pleasant to the touch.
- Seeds are a source of useful oil that can be eaten and also used for industrial needs.
- The cake is quite suitable for cattle as a feed, in which there is a large amount of protein.
- The fibers inside the box are actively used to make pillows.
- Cellulose is used to make plastic, paper, felt.
ethnoscience
Given the composition of cotton, it is used in folk medicine as an antiviral, antiseptic and hemostatic agent. It contains components that fight hypertension, atherosclerosis and diseases of the nervous system.
- Oil and various tinctures have found their application in cosmetology. They have anti-inflammatory properties;
- However, there is a component in plants that can lead to dysfunctions of the reproductive system;
- Plants are used by Ayurvedic specialists. The seeds of the plant contain protein, vitamins, trace elements, fatty oils, starch. The leaves contain organic acids, which are the raw material for the production of malic or citric acid. The bark contains tannins, vitamins;
- Flowers contain antioxidant flavonols and anthocyanins;
- Cottonseed oil is an excellent dietary product, indispensable during the growth and formation of a child's body. It allows vitamins A and D to accumulate in the body.
ethnoscience
Harvesting and processing
Harvesting takes place in the fall. The boxes are collected by hand or using a special technique.Cotton mixed with seeds is called raw cotton (Figure 6).
Figure 6. Harvesting for processing
Fibers are cleaned of seeds at special ginneries, then cleaned of dust, packed in bales and sent to spinning mills, where they make yarn.
The seeds are used to make cottonseed oil, from which margarine and canned food are made. The remains of the cake are fed to pets.
From the video you will learn how you can grow cotton on your own backyard.
How is cotton grown?
Before the plant produces soft fiber, it goes through several stages:
- The formation of a bud from which a flower will grow over time.
- The flower and its pollination. After pollination, the flower turns from yellow to violet-pink, which falls off after a few days, leaving the fruit (seed capsule) in its place. The flower self-pollinates, which does not tie the cotton production process to the presence of pollinating insects.
- The growth of the seed box and the formation of cotton fibers from it. The fibers begin to grow only after pollination. The capsule expands, bursts, releasing cotton fibers.


Care
There are various species, including annuals and perennials. In indoor conditions, annuals are most often grown. This plant should be grown in a bright, sunny and draft-free place. It can also be kept in an open-air garden, but in this case it will be necessary to use a shelter from the rain.


The cotton plant tolerates the summer heat well, but it dies during the first frost. Water the plant as the earthen clod dries out in the pot. In early spring, it needs to be fed every two weeks with fertilizer for flowering plants.
Preparing the soil for sowing
The cotton field has been prepared since autumn. Winter plowing to a depth of 30 cm is performed in late summer - early autumn. If before that alfalfa was growing in the field, then before plowing it is necessary to carry out preliminary peeling of the soil by 5-6 cm, thereby preventing the regrowth of perennials.
In irrigated agriculture (and cotton is one of those crops that need irrigation), autumn plowing is recommended to be carried out with two-tier plows. If necessary, procedures for combing out the rhizomes of weeds and the introduction of herbicides are also carried out.
In the spring the field is harrowed in 2 tracks. If manure is introduced during this period, it is recommended to repeat plowing. Before sowing cotton, the field is usually watered, after which it is required to chisel at a shallow depth (up to 15 cm) with repeated harrowing. A field that has not been watered in winter needs to be cultivated.
Main advantages and disadvantages
Products are easily cleaned of dirt, therefore they are preferred when buying clothes for a child. Like other natural fibers, cotton does not dissolve in formic acid, alcohol and vinegar.
Cotton clothes are distinguished by good hygienic properties and breathability, therefore they are often used in the summer. Another plus of the products is practicality and versatility.
Despite the huge number of advantages, cotton products have disadvantages. The main ones are considered to be a high percentage of abrasion, wrinkle and deformation. Despite the fact that these facts are confirmed, they do not make the products less popular and in demand.


Cotton plant
How to grow cotton
How to prepare the ground. How to properly water, fertilize, feed. How to sow seeds. How to harvest (10+)
Cotton
‘);
Table of Contents :: Search
Cotton
has been the most important spinning crop for a long time. It was grown even 3000 years BC. It is widely applicable in our country as well as around the world. Long fiber and valuable seed puffs are obtained from it. Approximately 30-45 kg. fiber comes out of 1 c. raw cotton. From the same amount of seeds, 52-65 kg are obtained. 20 m of linen is made from 1 kg of cotton fiber.So it is the main raw material in the textile industry. And cottonseed oil has nutritional and technical properties. Cotton is also a valuable honey plant.


Cotton
Ripening, the box dries up, its walls crack, and it opens.
The degree of disclosure of mature bolls is a hereditary trait of very important economic importance. The types and varieties of cotton on this trait are very different. Of particular value are varieties in which the bolls open well, but at the same time, raw cotton is firmly held between the valves and does not fall out of the bolls. Such varieties are called storm-resistant. In this case, raw cotton is easier to harvest by machines.
The ripening and opening of the bolls on the plant proceeds in the same sequence in which the buds were formed and the flowers opened. A sequence of short and long lines in the maturation of individual bolls leads to the formation of ripening cones within each bush. On a cotton plant, significantly more fruit organs are formed than they are fully ripe. Many buds and bolls fall off during the growing season. Most modern forms of medium staple cotton fall off 60-70%, and fine staple - 30-40%. Under the conditions of Central Asia, with high agricultural technology and normal planting density, an average of 8-10 bolls with raw cotton are formed on one plant.
Seed.
In cultivated cotton, the seeds are large, ovoid or irregularly pear-shaped, and dark brown in color. The length of the seed is 12-14 mm, the diameter in the wide part is 6-8 mm. The weight of 1000 seeds is 90-110 g. Wild species have much smaller seeds.
Sow or buy
With the collapse of the USSR, Russia lost its own cotton, and textile enterprises were forced to buy imported raw materials, says Andrei Oleinikov, Deputy Minister of Agriculture of the Stavropol Territory. In recent years, imports have stabilized at about 250-300 thousand tons. The main suppliers of uncombed cotton fiber are the CIS countries - Tajikistan (34%), Kazakhstan (29%), Kyrgyzstan (24%) and Uzbekistan (11%).
According to Anna Orozova, executive secretary of the cotton committee of Soyuzlegprom, Uzbekistan has already reduced the export of cotton in the form of raw materials, since the country's leadership has set the task of increasing processing at local textile factories and exporting finished products. However, this did not have a noticeable effect on the raw material supply of Russian cotton spinning factories, since their needs are now met mainly through supplies from Tajikistan, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, and in the last year from Azerbaijan, whose export potential has grown sharply.
However, in other countries of Central Asia, an active construction of processing facilities is underway, Golfand is known. In a few years, it will be extremely difficult to export minimally processed cotton from these regions, she said. Now about 73% of Russian imports are cotton fiber, cotton threads and yarn, the rest is fabrics, about (ICSI) Nadezhda Kanygina.
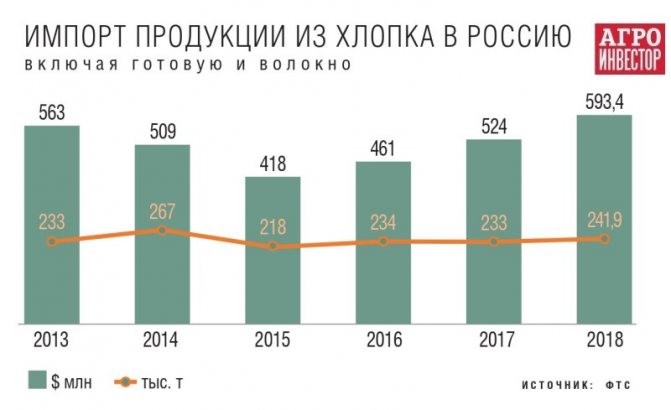

According to the Federal Customs Service, imports of cotton products, after a slight decline in 2019, have been increasing over the past three years. However, if we talk about the import of fiber, then its deliveries to Russia in value terms really decreased - from 2015 by about 1.4 times, and from 2013 - by 2.1 times. At the same time, the import of yarn containing more than 85% of cotton fibers has grown - since 2019, too, by 1.4 times. Nevertheless, at the moment there is no shortage of fiber in Russia, Orozova says. “Traders say that it is not always possible to sell the entire volume on the domestic market,” she says.
According to Dmitry Potapenko, managing partner of the Agroinvestservice consulting group, the Russian textile industry in terms of cotton fabrics is irrevocably reoriented to imported raw materials.There is no systematic and significant incentive for investment in domestic production of raw cotton from Russian producers of fiber and fabrics and will not be. And the demand for imported raw materials will remain as long as the appropriate equipment for its processing at domestic enterprises remains in working order.
In Russia, in 2019, according to Rosstat, about 80 tons of cotton were harvested - this is nothing at all, Potapenko notes. But the expert does not see any problem in this. “We don't even make sugar beet seeds ourselves, as well as the genetics of poultry and animals. What can we say about cotton! He exclaims. “For many years now it has been a global exchange commodity with a very specific financial and economic model of production and turnover, which cannot be localized in Russia.” According to Potapenko, in many countries cotton and cotton products are part of the historical national economic structure (for example, in China and India, the traditions and skills of growing agriculture and its processing have existed for more than 2 thousand years), and Russia's enthusiasm alone is not enough to effectively and meaningfully compete with such manufacturers.
Associate Professor at the Department of Horticulture, Breeding and Seed Production, Cand. s.-kh. On the other hand, Igor Podkovyrov of the Volgograd State Agrarian University (VolGAU) believes that now is the time to think about the development of cotton growing in Russia. “There is a huge global demand, so in the future it will be possible to supply domestic products abroad,” he is optimistic. “We can become exporters and dictate our conditions on the world market, influence pricing, which is why the government should pay more attention to the development of the industry.”
For state money, you can even grow pineapples in Murmansk, Potapenko sneers. “But seriously speaking, Russia simply does not have the ability to support cotton growing at the expense of the budget on a scale that is significant for the domestic textile industry,” he thinks. "And in most cases state support is a temporary factor." It is worth considering that cotton does not imply a reverse crop rotation. It cannot be cultivated for a year or two and abandoned, since its industrial production involves investment in a systemic train of complex and expensive elements of agricultural technology and precision agricultural chemistry specialized specifically in raw cotton. That is why it is pointless to engage in this agricultural culture in Russia, Potapenko insists. The volume of world production is quite enough to cover the needs of our country. “In the context of globalization, the main thing is the presence of an objectively and naturally formed civilizational expertise regarding the use of competitive natural and climatic potential,” he emphasizes. “We do not have this in relation to the production of raw cotton”.


For the development of cotton growing in Russia, a combination of several factors is necessary, says Alexander Borisenko, general director of the Volgograd spinning and weaving factory "Kamyshinsky Textile". Among them are economic feasibility, availability of accessible information on cotton cultivation, seed material, sowing and harvesting equipment, receiving and processing points (raw material processing plants) and government support. If one of the links is lost, success cannot be guaranteed. That is why today the prospects for the development of the cotton industry are not entirely clear, says the head of the Center for Applied Genetics, Breeding and Seed Growing of Cotton at VolGAU, Professor Oybek Kimsanbayev. “Processing enterprises, in particular textile ones, are in great need of their own raw material base.But many farmers are not happy with the fact that tomorrow cotton may be included in the list of the main agricultural crops cultivated in the country along with wheat, corn, sunflower, vegetables and others, because it needs special support, he says. “There are too many questions about technologies, although sooner or later the industry in Russia should begin to develop.”
In the meantime, cotton growing in Russia is at an early stage of development. In 2019, the area of cotton did not reach even 80 hectares. And only two regions were engaged in the cultivation of agriculture - the Volgograd and Astrakhan regions. At the same time, for our country, cotton is not a new, but a forgotten agricultural culture, assures Podkovyrov. They tried to grow it even before the Great Patriotic War in the southern regions of the country, but since the republics of Central Asia gave the best results, production was moved there.


Fiber imports in money terms decreased 1.4 times Photo: Shutterstock
Cotton in the world Cotton is cultivated in 97 countries of the world, located in tropical and subtropical zones, reaching 36 South latitude and 48 North, according to Igor Podkovyrov from VolGAU. According to the US Department of Agriculture, in the 2018/19 season, the world harvest of raw cotton will amount to more than 27.3 million tons. 177 countries import cotton products and 169 export them. “Cotton is considered to be an agricultural crop that ensures the rapid economic growth of states. The largest economies in the world, such as the USA, China, India, have achieved their development largely due to the production and processing of cotton fiber. It is these countries that lead the seven leaders of raw cotton producers, ”says Podkovyrov. They provide half of the world's fiber production. These same countries, with the exception of the United States, process most of the raw cotton grown on their territory. Moreover, the volume of consumption exceeds production by 13-36%. The largest importers of fiber are China, Bangladesh, Vietnam. The USA is the leader in export, which sells more than 3 million tons of fiber annually.
"White gold" or how cotton is harvested
Protchenkov pictures
Before my trip to Uzbekistan, I had never seen cotton grow. It turns out that "white gold" grows in the fields on small bushes about waist-high:


In simple terms, these are just pieces of cotton wool on the branches:


Before harvesting, water is no longer supplied to the fields. Therefore, the cotton dries up. The "cotton wool" itself matures in the so-called box. In this photo, the box has cracked and opened (possibly in the reverse order).
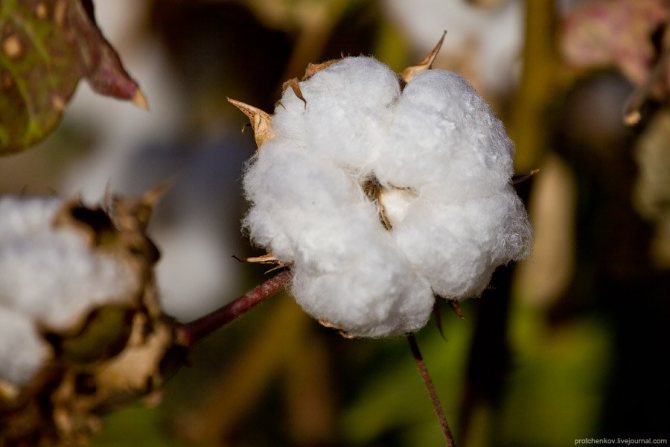


But I picked this box personally. It was green and completely closed:
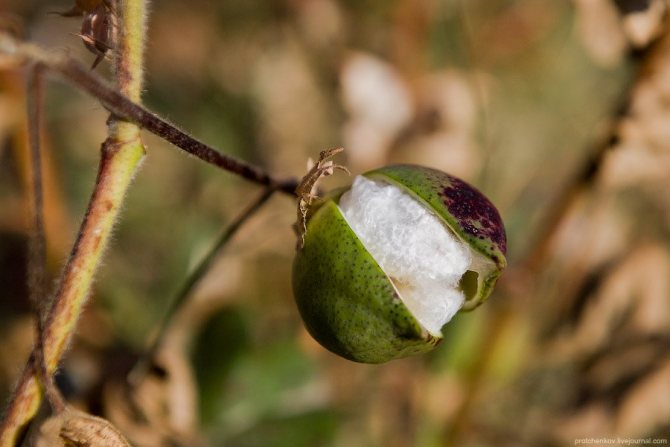


There were some adventures that day. I left Tashkent and about 10 km from the city stopped near a large cotton field, where just a bunch of people worked. I went to the field and only had time to ask a couple of questions to the guys who worked there, and to take a few shots, a man came up to me and said that it is strictly forbidden to take pictures of the cotton harvest. I asked who I was and what I was doing here. I said everything as it is - they say a tourist, I photograph.
A minute later, another man came up and introduced himself as the owner of the field, said that it was private property, it was forbidden to take pictures and he called the police. I called on my mobile, two more arrived - one in civilian clothes, the other in uniform. The one in uniform showed his ID and identified himself as a precinct. They started asking if I had permission, why I was taking pictures, and so on. They even said that now they would take me to the prosecutor's office
As a result, they asked me to remove the four frames that I had taken, and said that they could not allow me to take pictures without official permission. Why is it forbidden to take pictures of the cotton harvest, he allegedly did not know.
All this lasted no more than half an hour, and ended with the fact that one of them gave me a lift to the taxi rank so that I could leave for Tashkent. But I did not go to Tashkent, but to the next field, where no one forbade filming.
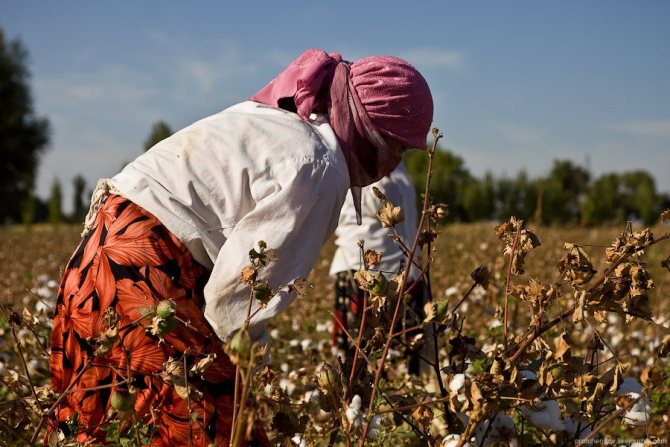


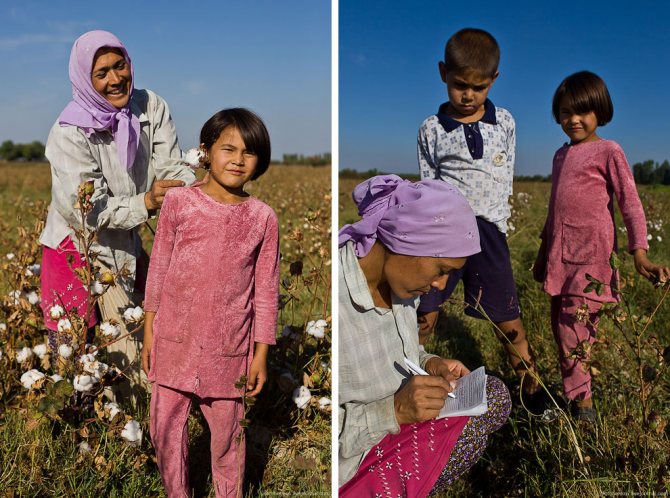
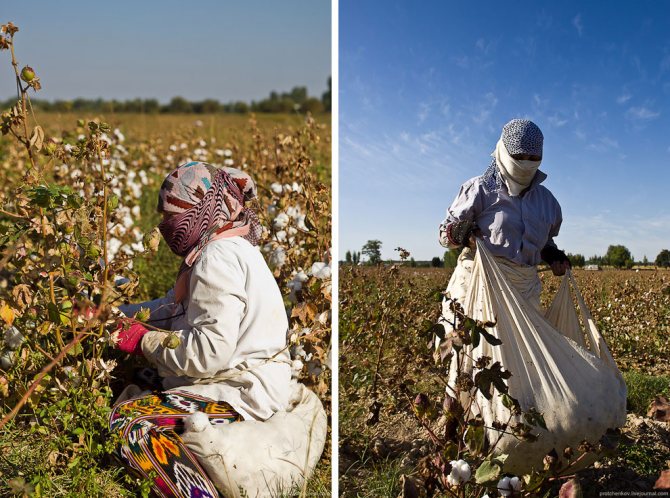
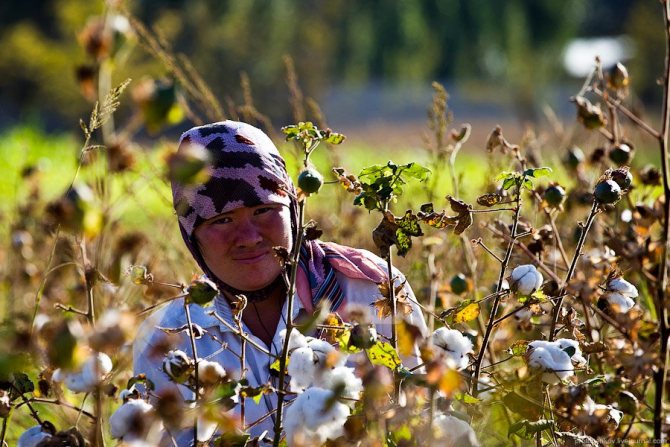
Child labour.Schoolchildren in Uzbekistan begin their holidays in mid-September, when the heat subsides. They last for about two months; but many schoolchildren do not rest during this period. They must "serve their country" - pick cotton.
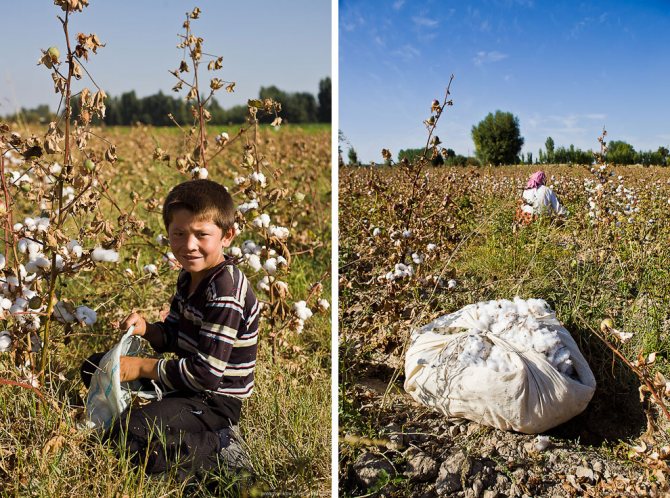


Uzbek officials have to constantly reassure the West that no child labor is used in the country. However, every year in late spring and autumn hundreds of thousands of Uzbek children and adolescents are taken out of school, loaded onto buses and taken to cotton fields, where they work for months almost free of charge for the good of their homeland. Therefore, the organizers of the cotton harvest are not very fond of people with cameras.


It is difficult to say from the outside whether the information about child labor is true. In this field, the children did not look tortured and oppressed:
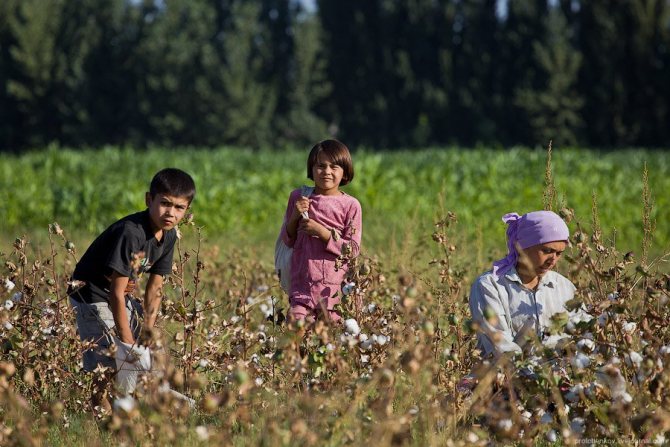


The size of this field is 2.5 hectares. I counted those who pick cotton, 30 of them are no more than 3 men, about 8 children, the rest are women:
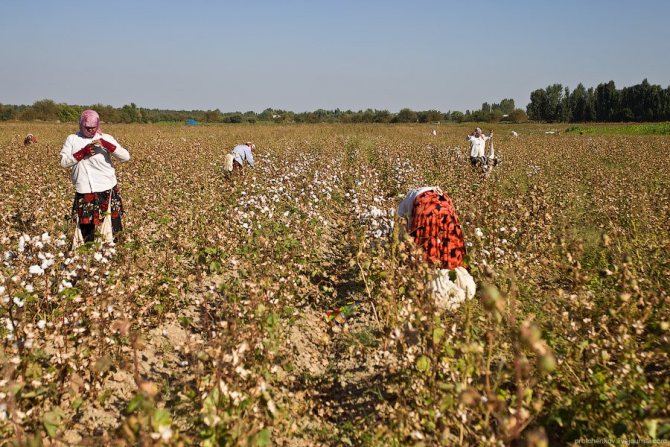


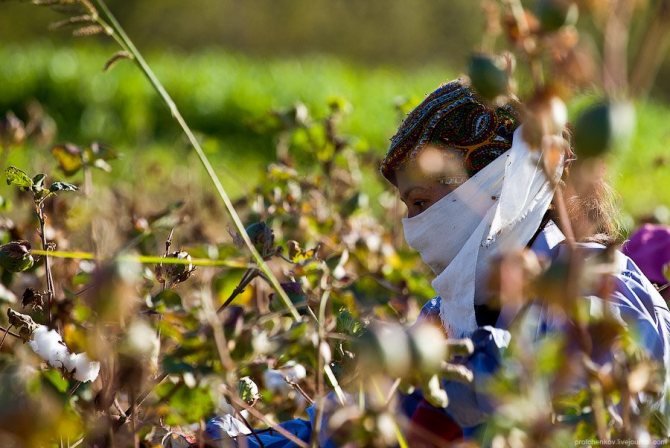
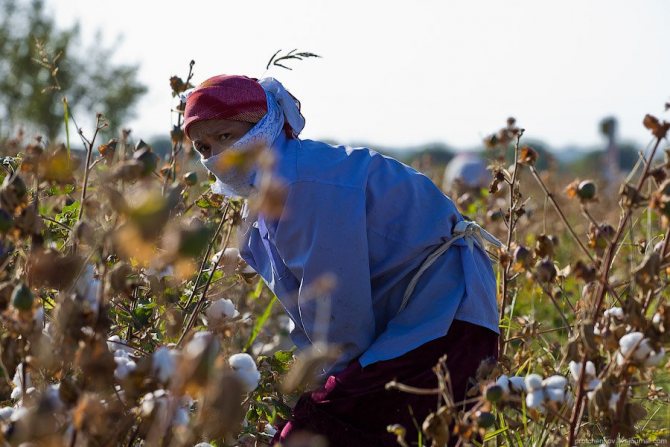
Women cover their faces with handkerchiefs. Firstly, protecting yourself from the sun, and secondly, to breathe less dust from dry land:


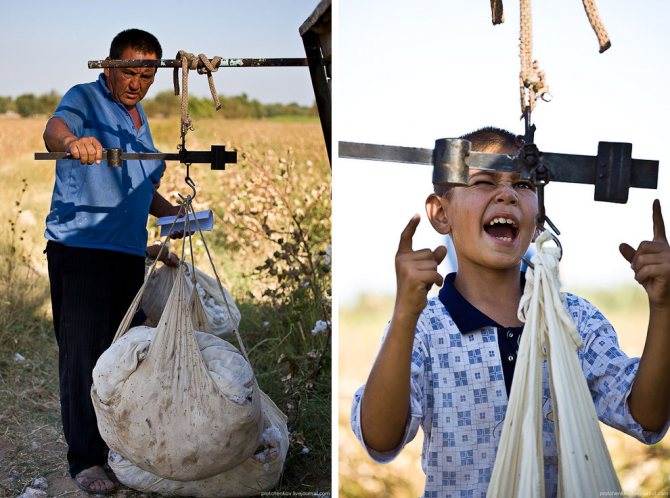
The collected cotton is folded into such a knot, which is tied to the belt:
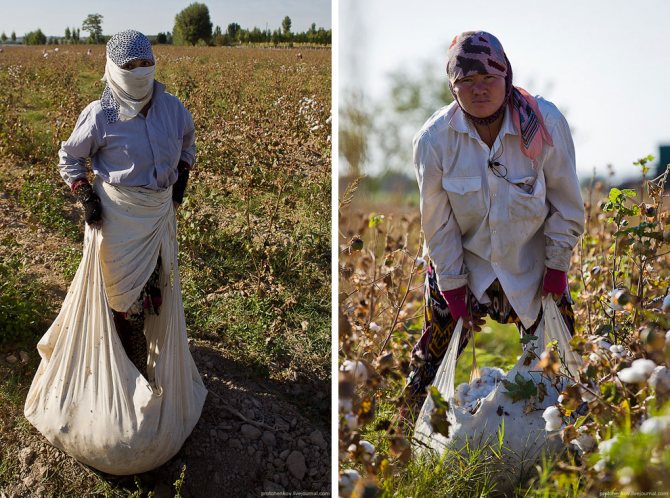


When it is full enough, it is comfortable to sit on. This woman on the right had picked 118 kilograms of cotton the previous day. Collectors are paid 130 sum for 1 kilogram. That is, last day the woman earned about 15 thousand soums, which is about 260 rubles at the current exchange rate.


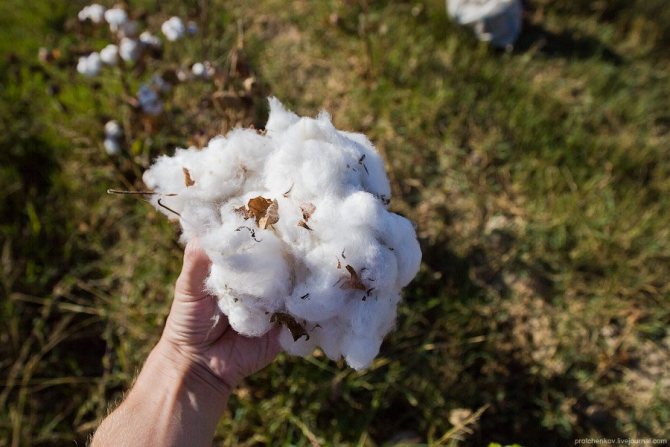
I picked one bush and got this many. The leaves and boll are dry and prickly, so you need to work with gloves:


Last year, about 120 tons of cotton were harvested from this field:


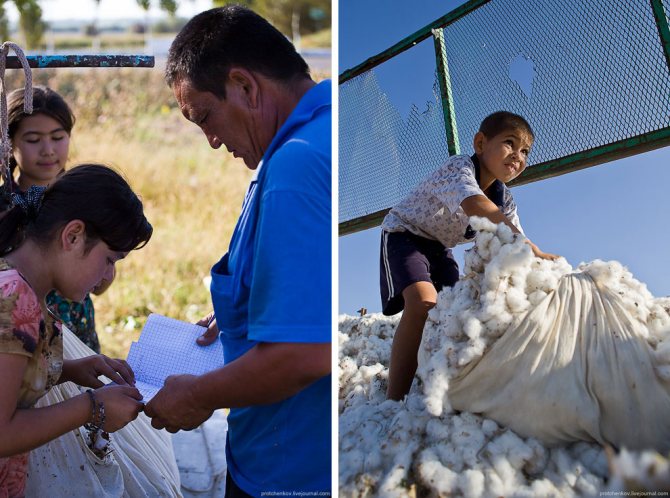
Mom with daughter and son. Write down the address where the photos are to be sent. I do this a lot - I print photos and then send them by regular mail. Sometimes this is the only way to persuade someone to take a photo:
The harvested cotton is carried to the trailer:
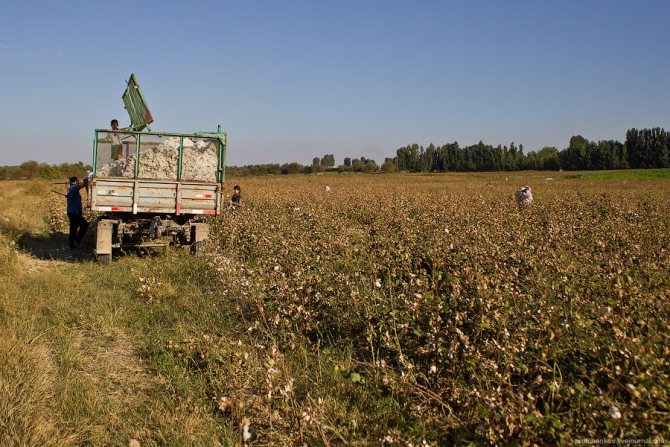


So much was collected in one day:
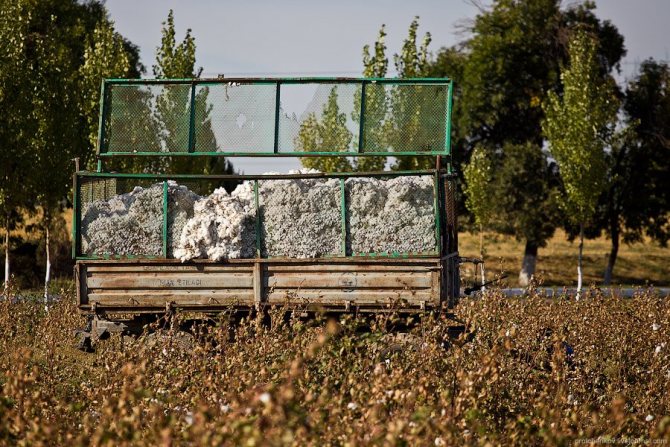


Weigh:
Picking cotton is not the safest activity. It is estimated that 300-500 thousand people are poisoned by pesticides on cotton plantations in the world every year, 20 thousand of them die.


From ancient times to the present, cotton has been and remains one of the most important industrial crops. From this plant, a valuable fiber is obtained - cotton, which is then used for the production of fabrics, knitwear, threads and cotton wool. Since cotton is a fairly thermophilic crop, only the southernmost regions of Russia are suitable for its cultivation, and even then on a very limited scale.
Differences between natural and organic cotton


Natural cotton
Natural cotton is practically no different from organic. According to the description, the difference lies in the safety of production and quality control. At the same time, the basis for the production of conventional cotton is making a profit, regardless of the possible negative consequences. At the same time, the collection of eco-cotton is done by hand, while ordinary cotton is picked using special equipment. When growing organic cotton for pest control, every meter is processed exclusively with natural products that do not have any harmful effects.


Organic cotton products
Genetic modifications [edit | edit code]
The purpose of genetic modification (GM) in cotton is herbicide tolerance
(HT): reducing the negative impact of herbicides that cause significant damage to crops, as well as providing more effective weed control. GM cotton requires 80% fewer pesticides than original plants.
The second direction of modifications is entomocidal, or insect-resistant crops
(IU), which are resistant to the negative effects of harmful insects. For 2006, such resistance is achieved in the only way - the introduction of the gene of soil bacteria
Bacillus thuringiensis
(Bt) [5].
Seed preparation and sowing
Before sowing, the seed is warmed up in the open air for 3-4 weeks, and then sequentially soaked in water and a solution of boric acid. After that, the seeds are disinfected with a suspension with copper trichlorophenolate.
Since cotton has a rather long growing season, sowing should be done as early as possible so that the capsule fruits have time to ripen before frost. But at the same time, crops should not be allowed to suffer from spring frosts. This is what creates difficulties for the cultivation of cotton in Russia. It is recommended to start sowing when the soil reaches a temperature of 12 ° C.
For cotton, a square-nest planting method is used with a step of 60 or 45 cm. About 80-120 thousand plants should fall on one hectare. However, many farmers note the economic feasibility of wide-row sowing, where the distance between plants is 90 cm. The average consumption of seeds per hectare is about 40-70 kg, depending on the sowing scheme and seed size.
Magic Garden
Today, cultivated cotton is ubiquitous; this fibrous plant is widely used to make high-quality fabrics and more. Cultivation of cotton is a major agricultural activity in many regions of the world, and in some it is the only one. As with many parts of Africa, cotton plays a fundamental role in the fierce battle against poverty for many segments of the population in Burkina Faso, South Africa, Uganda, Mozambique and many other countries south of the Sahara Desert. Thanks to the cultivation of this crop, more than 20 million people do not die of hunger, and cotton is the third most important agricultural export in Africa. Small farms in southern Africa are making incredible efforts to ensure a high environmental standard and excellent quality of African cotton, because their lives literally depend on it. Cotton is very capricious and needs constant care. He constantly needs sufficient moisture and a lot of sunlight. Quite often, cotton fields need to be artificially irrigated, for which special installations are purchased and canals are dug throughout the field. Of course, all the channels are broken by the poor peasants manually, without the use of any technique. All summer (and in our opinion - all winter) poor African peasants cultivate and care for the crop in order to harvest cotton in the fall. Sometimes there are not enough cotton pickers, they come to harvest them on their own. The boxes will be recycled, and high-quality fabric will be made from the received raw materials, which will be sent to the best fashion houses in Europe and America. Couturiers will sew exclusive outfits, and secular ladies will gladly wear dresses made of wonderful, light, delicate material. African cotton is valued all over the world as an expensive material. Fashion designers and fashion designers of leading fashion houses make a lot of money on it, and sophisticated ladies and gentlemen are happy to pay fabulous money for African cotton products. Almost every major fashion house owner owns a collection called African cotton. But many salons and boutiques, selling fashion items from the "Africa Cotton" series, donate a few cents of the cost to the fund of poor African peasants who cultivate this wonderful crop called African cotton.
Properties of cotton fabric


Properties of cotton fabrics
Cotton fabrics are distinguished by tactile sensations, environmental friendliness and hypoallergenicity. In addition, cotton has properties:
- breathability;
- hygroscopicity;
- softness;
- ease;
- strength;
- keeping warm;
- thermoplasticity.
The high performance characteristics of cotton fabric, combined with low cost, explain the popularity of the material for sewing various products. Cotton is used for sewing men's, women's, children's clothing, as well as underwear, bedding, table linen, curtains and thin curtains.
Description of cotton
Cotton is a botanical genus that belongs to the Malvov family and has at least fifty species, among which there are both woody and herbaceous plants, both annuals and perennials.
The cultivated species used for the production of cotton are annual or biennial herbaceous plants that reach a height of 1–2 m, but at the same time have a very branched stem. Cultivated cotton plants have a taproot system, and the root is quite long - from 30 cm to three meters.
On cotton bushes, the leaves are attached with long petioles and are arranged alternately. The shape of the leaves is lobed (3-5 lobes), which is why they can resemble maple leaves.
Many single flowers appear on each plant. Most species and varieties have yellow flowers. The number of petals is from three to five.
After the flowering period has passed, a very peculiar fruit is formed - a round or oval box in which the seeds ripen. When the seeds are ready, the capsule cracks and opens, exposing the white fibrous mass, in which the cotton seeds are located. Fibrous mass is cotton, which consists of two types of hairs: long and fluffy, as well as short and fuzzy.
Fertilization
The cotton plant needs additional feeding and responds well if it is introduced correctly. Here are the basic steps for seasonal replenishment:
- Application of manure under the fall (at least 15 tons per hectare). It is often replaced with compost at the same dosage. Be sure to add phosphorus oxide (20 kg) and potassium (55-60 kg). Such treatment is especially effective on weak soils or with grain predecessors.
- The first vegetative top dressing occurs during the leaf growth phase. Nitrogen is placed 15–17 cm from the row and below 2–4 cm from the irrigation hole (35–50 kg / ha).
- During budding, potash compounds come into play (50-60 kg of potassium oxide will be enough). But they are already receding more - at least 22 cm from the row, deepening at least 4 cm from the "waterline".
- Flowering is a specialization of phosphorus, usually 25–27 kg are taken.
Cotton watering
When cultivating this culture, not only vegetative, but also pre-sowing irrigation is used. Moreover, the second type of irrigation is done not only to moisten the arable layer, but also to remove excess salts from it.
On fields prone to salinization, pre-sowing leaching irrigation is carried out in late autumn - early winter, when there is still no severe frost, but the groundwater has already receded to its maximum depth. The irrigation rate on slightly saline soil is 3 thousand cubic meters per hectare before plowing, on highly saline soils - 3-4 thousand cubic meters per hectare after plowing with one or two repetitions.
Vegetation irrigation is necessary in order to obtain the maximum fiber quality and increase the efficiency of all other agrotechnical measures. All terms and rates of watering are calculated so that the plants do not experience a lack of water throughout the growing season. The need of plants for water increases especially strongly during the periods of flowering and fruit formation.
First experiences
Real attempts to revive the cultivation of cotton in Russia began relatively recently. The main efforts are concentrated in areas with a temperate continental climate: in the Astrakhan, Volgograd regions, Stavropol Territory, Kalmykia and Dagestan. These are the most promising regions for growing cotton, Chapaev notes.
The Volgograd Region has been developing cotton growing for several years, says Sergei Chumakov, Deputy Chairman of the Volgograd Region Agriculture Committee.According to Kimsanbayev, the region is the northernmost point of the world cotton growing. “And only one of the regions of the region has one and a half million hectares of unoccupied areas! Of these, 150-200 thousand hectares are suitable for growing cotton, ”he says.
In the regional budget in 2019, 8 million rubles have been allocated to reimburse farmers 50% of the costs of purchasing machines for harvesting and primary processing of cotton. Compensation for direct costs of growing is also provided, Chumakov reports. Some farms of the region this year will take up the cultivation of cotton. So, 30 hectares of agricultural crops plans to occupy "APK Raigorod".
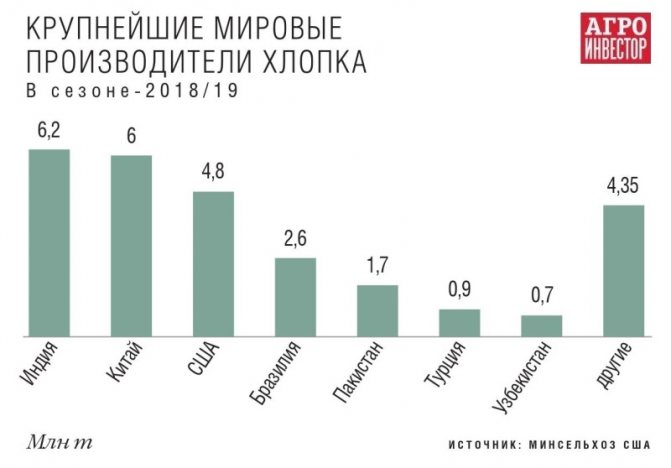

The presence in the region of a processing enterprise - "Kamyshinsky Textile" - creates the preconditions for the creation of a whole textile cluster in the Volgograd region, Chumakov believes. There are intentions and opportunities to occupy from 200 to 500 hectares with cotton. The main difficulty in achieving this result, according to the official, is that specialized equipment is needed to grow agricultural crops, which leads to additional high costs.
In 2019, the Center for Applied Genetics, Breeding and Seed Production of Cotton was created at VolGAU, where agrotechnical methods of its cultivation are also studied. The breeding work resulted in the development of a new ultra-early ripening cotton variety PGSSH 1, which manages to ripen from April to September: 105 days pass from sowing to harvest, says Kimsanbayev. The variety is already successfully grown in Uzbekistan on an area of 497 thousand hectares and in Kazakhstan on 18 thousand hectares, adds Podkovyrov. The yield of this variety on light chestnut soils of the Volgograd region is 20-22 c / ha. The resulting fiber is recyclable. "The specialists of the Kamyshinsky textile mill highly appreciated the raw materials produced in the Volgograd region," the scientist says. However, he draws attention to the fact that in the adjacent regions, where work is also underway on the selection and cultivation of cotton, it has not yet been possible to obtain marketable products, despite the significant sowing areas.
In the Volgograd region, the issue of placing a point for receiving and primary processing of cotton fiber in the region is also being considered. The mills accept exactly the fiber, it makes up 36% of the total harvest and requires additional drying, purification of impurities and seeds, packing in bales, Podkovyrov lists. “Even farmers can invest in the simplest cotton ginning machines, these are feasible expenses - 100-300 thousand / rub. per unit of technology, - he knows. “If we talk about a large workshop, which will be built in compliance with all fire safety measures, supplying powerful power lines, water and other infrastructure, it will cost about 0.5 billion rubles.”
The soil and climatic conditions of the Astrakhan region also make it possible to grow cotton, while the quality of the resulting fiber is not inferior to world standards, says Andrei Timofeev, First Deputy Minister of Agriculture and Fishing Industry of the Astrakhan Region. In past years, the area of agricultural crops in the region reached 500 hectares. However, then the industry fell into decay. Only a few hectares were planted with cotton last year for experimental purposes. Nevertheless, there is even a so-called "Astrakhan technology" for growing agricultural crops, based on the mechanization of all work, including harvesting, and also provides for drip or sprinkler irrigation, the official said. The region has already zoned productive and early ripening varieties of cotton, capable of producing 20-25 c / ha of raw cotton of IV-V type ("Limansky", "Mikhailovsky", PX 146, PX 150 and others). The lack of material and technical base hinders the development of the industry in the region.“The capital-intensive nature of cotton projects, including the reconstruction and construction of irrigated areas, the purchase of harvesting equipment, equipment for processing cotton, makes them impossible to implement using private capital or with the help of financing within the framework of economically significant regional programs,” Timofeev admits. "Real federal government support is needed."
It is planned to open a cotton processing plant on the territory of the production base in the Astrakhan region in 2020. The capacity of one section of the enterprise will be 1 ton / hour with the possibility of further expanding the production to six sections. Investments in the project are estimated at 100 million rubles. “Together with VolGAU and another cotton-producing farm - the peasant farm of Eduard Pak, which is one of the most advanced in the Volgograd region in terms of yield and fiber quality, this year we will sow more than 100 hectares of cotton in the Volgograd and Astrakhan regions, as well as Dagestan. The study of the theory and history of the cultivation of this agricultural crop in Russia, as well as practical experience have shown that this business is in great demand and it only needs to be scaled up, ”Chapaev is sure. Now all the raw cotton harvest received by the company is primarily processed at the facilities owned by VolGAU for fiber and seeds. The main consumers of the products are Kamyshinsky Textile and the Yaroslavl Industrial Fabrics Plant Krasny Perekop.
Perhaps the most ambitious plans are in the Stavropol Territory. The regional authorities are promoting the idea of building a primary cotton processing plant worth 12 billion rubles. The cotton will be briquetted and refined at the plant. It is also planned to build a fiber bleaching workshop for 0.44 billion rubles. Subsequently, a textile factory will be built in the Budyonnovsky district. According to Andrey Oleinikov, the Terskiy enterprise plans to create a whole reclamation network for the industrial cultivation of cotton, which will increase its sowing by more than 1 thousand hectares. Investments can reach up to 7.5 billion rubles, 2.24 billion rubles will be invested in the purchase of specialized equipment. “Economic indicators per hectare in case of taking measures of state support, according to our calculations, will be as follows: yield of raw cotton - 50 c / ha, fiber yield - 1.5 tons, revenue - 162 thousand rubles, profit - 86 thousand rubles, and the profitability - up to 46% ", - lists the official.
In Kalmykia, according to the local Ministry of Agriculture, cotton has been cultivated since the 1930s. Its yield then did not exceed 5-6 kg / ha when cultivated in dry conditions. But experiments on growing cotton, carried out by the Kalmyk Research Institute of Agriculture in the late 1990s in the eastern regions of the republic, proved the possibility of successful production of this crop. “So, in the state farms“ Krasinsky ”in the Lagansky District and“ Kormovoy ”in the Yashkulsky District, for two years, the cotton yield reached 15-20 c / ha. Good results were obtained at the Volodarsky state farm in the Priyutnensky district, ”says Deputy Minister of Agriculture of Kalmykia Sergey Antonov. The official is confident that the cultivation of early-maturing cotton varieties in compliance with modern technologies in the region can be highly profitable. But first, it is necessary to solve a number of problems. First of all, for the purchase of specialized machines and implements, as well as cotton harvesters. Means of chemicalization and protection of crops from pests and diseases are of no small importance. It is imperative to organize research work on the problems of cultivating this crop, ”says Antonov.
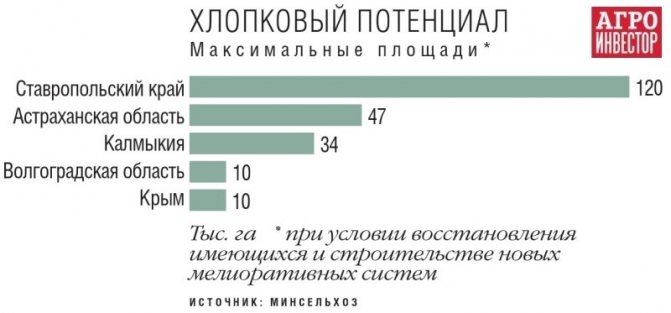

Experiments on growing cotton are also being carried out in the Crimea.Although so far, in conditions of an acute shortage of water resources in the republic, the organization of industrial production in the region is impossible, the First Deputy Minister of Agriculture of Crimea Vladimir Anyukhin told Agroinvestor. However, in the experimental plots of the Crimean Research Institute of Agriculture, cotton is grown for the purpose of ecological variety testing. Two experimental plots with drip irrigation (0.1 ha) and without irrigation (0.5 ha) appeared last year. And, as experiments have shown, an arid climate and areas without irrigation are not the best choice for agriculture: cotton reacted sharply to an increase in temperature, dropping some of the buds. The yield did not exceed 5-6 c / ha.
According to Aleksandr Kudeli, a member of the expert council of the Afanasy Nikitin Association, the implementation of projects for the cultivation of cotton will be hampered in the first place due to underdeveloped irrigation systems. Lands with irrigation can theoretically be made in the Astrakhan region and in the Stavropol region. For example, the crops of the Stavropol Territory could be supplied through the Tersko-Kumsky Canal (originates from the mountains of Kabardino-Balkaria) and the Kuban system. There is also an unfinished Stavropol Canal system. “Alas, the key word here is unfinished,” draws attention to Kudelya. - It would be possible to draw water from the Pravo-Yegorlyk Canal (originates from Nevinnomyssk, north of the Kuban), it was built in 1962, had a length of 450 km (the main channel, in total - 1150 km) and was considered the best water supply system in all of Europe ... But after the construction of the Stavropol SDPP, warm water was allowed through it, which led to the growth of long algae, and now the canal is inoperative. " Putting all this in order will require significant investments from the state.


The average price of a ton of "white gold" is 137 thousand rubles
General information about growing cotton
Cotton is a rather specific crop. To grow it successfully, it requires a long, frost-free warm period, with plenty of sun and moderate rainfall. In other words, the tropical and subtropical climates are best suited for cotton.
On the territory of our country, cotton can be grown more or less successfully only in the North Caucasus, and even then only using varieties specially bred for this climatic zone.
When growing cotton, it is recommended to alternate it with alfalfa in a crop rotation. The fact is that cotton bushes greatly increase the salinity of the soil, while alfalfa, on the contrary, reduces it. You can also alternate it with grains and other crops.
How is cotton harvested?
Elena Felgenhauer 811 4 years ago Candidate of Philosophy
Cotton picking was the main political, strategic, economic and financial task of our sunny republic of Uzbekistan.
As soon as the harvest season began, all newspapers, all television and radio broadcasts began with reports on the fulfillment of the cotton harvest plan.
And they collect it like this:
First, agricultural aircraft fly over the fields and water them with defoliants so that the leaves dry and fall off. It was a terrible thing, poisoning which could get sick with hepatitis, give birth to a child with disabilities, or even remain sterile. The defoliant got on watermelons and melons, which the collective farmers grew on melons located between fields, as well as in open reservoirs.
After the leaves had crumbled and the cotton bolls were made available, female cotton growers came out into the field. Around their necks hung a huge apron-bag, in which they picked cotton from the tops of the bushes - the best. After the women, cotton pickers came out into the field and picked the rest of the cotton. Students were released into the open fields. They were brought in from the cities, settled in barracks with two-story bunks, heated by stoves, and driven into the fields to collect "selection". Picking up - these are pieces of cotton wool caught on bushes, boxes near the ground, behind which the women did not bend and which the combine harvester did not catch.It was incredibly difficult to collect 100 kg of lightest cotton per day. It was impossible not to go - they could be expelled. Sometimes it was very cold at night. After all, the students were kept in the fields until the republic reports on the implementation of the plan.
When there was absolutely nothing to collect, he throws earth into the apron, guzapoy (cotton stalks), some stones, and sprinkles on top with cotton stolen from the khirman (the area where the contents of the aprons were dumped).
So we all took part in the postscript little by little!
Differences between cotton and other fabrics
You can distinguish the material from other natural fabrics by the following features:
- when burning, the material exudes white smoke and the smell of burnt paper;
- in addition to paper ash, nothing remains after combustion;
- when compressed, 100% cotton fabric feels soft and warm, the material wrinkles a lot.
When buying products, everyone should know how to distinguish cotton from synthetics. As practice shows, artificial materials are highly electrified, remain cold in contact with the skin, are distinguished by a strong shine and crease resistance. In addition to this product, which contains only natural cotton, it is problematic to stretch, but synthetic things will stretch a lot.
Diseases, pests and methods of protection
Pest and disease control measures:
- observance of agrotechnics and farming culture;
- destruction of weeds;
- correct crop rotation;
- cleaning plant residues after harvesting;
- deep autumn tillage - up to 30 cm;
- cultivation of varieties resistant to diseases.
The most dangerous pests of cotton:
- spider mite;
- aphid;
- tobacco thrips;
- winter scoop;
- cotton scoop.
Sucking pests. Aphid and tobacco thrips control involves several treatments. The first - in March-April, the subsequent ones - depending on the density of insects per 1 sq. m. Nitrafen 65% (40-75 kg / ha) is used against ticks. Against the winter moth - chlorophos 80% (1.5-1.8 kg / ha). Against cotton bollworm - thiodan (2-2.5 kg / ha). The amount of spraying and poisons are selected individually, taking into account the type of insects and their number.


Types of weaves of cotton fabric


Plain weave
It is difficult to meet a person who does not know what cotton looks like, but not everyone has an idea of the types of weaving of threads. Currently, there are the following types of weave cotton threads:
- Plain weave is a type of weaving thread through thread. The result is a flat and smooth surface with high durability. The representatives are coarse calico, chintz, poplin, taffeta.
- Twill - the threads intersect 1 through 2 or 3, that is, through an asymmetric shift. The material is dense and abrasion resistant.
- Satin - characterized by the fact that weft threads predominate on the front side. The material is shiny, smooth and durable. Satin is a striking example of this weave.

Twill weave
Popular talks
- Report-message Life on earth 5, 9 grade in geography
The most frequently asked question in society is the question of the origin of life on Earth. Many scientists and specialists put forward a variety of, sometimes quite unpredictable and unproven theories. Yet the question remains relevant even - Report-message on the topic Sport grade 4
Most often, the choice of the sport for the child remains with the parents. At preschool age, children still do not understand anything about this, and completely rely on dad and mom. Where they led, it’s good there. When a child grows up, he does not always like that - Report on the city of Oryol
The city of Oryol was founded as a fortress during the reign of Ivan the Terrible in 1566. The fortress was located along the banks of the Oka River. She was defensive in nature. Later it became the center of the Oryol district.
Application
Cotton fiber is used in various spheres of human life.
Primarily, cotton is used in the textile industry.Fabrics of various characteristics and colors are made from it. For example, satin, flannel, chintz and many others. Cotton fiber is used in the manufacture of threads, yarn, cotton wool, paper, and even explosives.
Cotton seeds are also used in industry. Some of them are being prepared for further disembarkation. Oil is squeezed out of the rest of the seeds, which is used for food. Low quality oil is used for technical needs. The raw materials remaining after pressing the oil are rich in protein, therefore, animal feed is made from it.
Of the dozens of varieties of cotton, several are used for the manufacturing industry.
Information about how cotton grows and its industrial applications are interesting and important. This plant has played an important role in the history of mankind for many centuries.
Photo 1 of 3
Homeland cotton
- tropical regions of Asia, Africa, America. Therefore, people living in regions with a temperate climate do not know anything about it, except that chintz, flannel and other cotton fabrics are made from it. Cultivated cotton is a herbaceous plant with a height of 70 cm to 2 m. There are many branches on its stem and therefore it looks like a bush.
Cotton flowers are large, white, yellow or cream-colored. The best, fine-fibred varieties have a reddish spot at the base of the petals. The capsule fruit is divided into 3-5 nests. Each nest contains 5 to 11 seeds. Each seed develops from 5 to 15 thousand fibers 3-5 cm long. It is for these fibers that cotton is grown.
In Tajikistan, Uzbekistan, mainly Mexican cotton is grown, which has a medium length fiber. The thinnest and longest fiber in Peruvian cotton. Fine-fiber varieties are derived from it. This type of cotton is especially prized. 16 thousand meters of fabric are obtained from one ton of fine-staple cotton, and only 8.5 thousand meters from 1 ton of medium-staple cotton.
Cotton is a very capricious plant. He needs a lot of heat and a lot of moisture. Seeds germinate only at + 15 ° C. The plant grows and thrives best in thirty-degree heat and requires constant watering, especially during the flowering period, when it uses up the most water. Cotton plants hate shade. Before sowing, mineral organic fertilizers are applied to the soil. In order to ripen as many boxes as possible in the fall, in the summer the tops of the main stem and side branches are cut off from the plants. The boxes do not ripen at the same time, so cotton is harvested in 3-4 doses.
Cleaning begins when the box bursts and white, fluffy fiber appears from it. Collect the fiber with seeds and fluff. All this mass is called raw cotton. Picking cotton under the scorching sun is very difficult. The work of the pickers was made easier by the cotton pickers. Cotton ginners clean cotton from bolls, branches, leaves and other litter. Then the cotton fiber is separated from the seeds, from which the oil is squeezed out. It is used for food, industrial oils, soap, candles, and other products are made from it. Cotton is a relative of mallow, tall plants with large flowers that adorn gardens in Ukrainian villages.
Once, as an advertisement for a flower campaign, I sent a magazine with an offer to order seeds of a variety of sorts from them. At that moment, I was most impressed by the cotton plant, for some reason the idea of growing a spinning plant on my windowsill seemed extremely tempting. In general, I did not hesitate for a long time, I ordered myself a couple of bags of seeds.
The cotton plant (Gossypium) comes from the Malvaceae family, there are about a hundred species in nature, among which there are herbaceous and woody, perennial and annuals. The variety of cotton species is due to its variability, a change in the place of growth and the ability to cross-pollinate leads to the fact that more and more new varieties appear.
The habitat is extensive, it grows in the tropics and subtropics of Asia, Africa, America and even Australia.Plant height varies from 50 cm to 1 m.
The seeds are wrapped in a damp cloth moistened with epin for several days.
After a few days, when the sprouts hatch, they can be planted in a small container.


Don't forget about additional lighting and temperature conditions
The flower blooms for one day, emits a delicate pleasant aroma
Oval box ripens
After about 1.5 months, the capsule opens, the seeds are hidden in snow-white linters (cotton fluff)
Growing, in principle, is not difficult. But there are a few things to keep in mind:
The timing of sowing seeds. Sow as early as possible - no later than February. Delay can lead to the fact that the flowering and ripening of seeds will occur in late autumn.
Temperature.
Cotton plant prefers to grow at temperatures not lower than +20
C. Seeds at this temperature give the best similarity. As the seedlings grow, they can be gradually accustomed to lower temperatures.
Lighting.
Choose a well-lit spot on a windowsill for your cotton plant. It should also be well ventilated. If your place is dark, be sure to highlight it.
Humidity
should be moderate. Watering is plentiful, but make sure that the water does not stagnate.
Fertilizer.
Twice a week during vegetative and generative growth. Apply complex feeding.
Soil and replanting.
Prepare the substrate nutritious, rich in humus. Acidity about 6 Ph. Don't forget about drainage. The roots of the plant are long, so choose a deep pot. They are transplanted as they grow, the transfer method is preferable.
Cotton is susceptible to a wide variety of pests.
Almost half of the cotton growers' crops die every year on the plantations. To prevent our little things from adding to this sad statistics, carry out prevention, at the first suspicion of malaise, start fighting diseases and pests.
My, for example, cotton plant managed to pick up somewhere
septoria
So far, the fight has been unsuccessful, but I do not lose hope.
Most of the wardrobe items we use regularly are made from cotton. It is strong, durable, and most importantly, it allows our skin to breathe.
The thread from which this fabric is woven originated inside the fruit of a small heat-loving plant. The cotton plant looks like a small bush and grows in Asia, Africa or America. The flowers of the plant are white or light cream.
Diseases [edit | edit code]
During the summer, and especially shortly before the beginning of the ripening of cotton, various diseases usually appear. In these diseases, there are mainly two reasons: physiological, resulting from malnutrition of plants, or diseases caused by fungi and bacteria.
Pests [edit | edit code]
- Cotton weevil (Anthonomus grandis
) Is the most serious pest of cotton. In the late 19th and early 20th centuries, the enormous damage caused by the weevil was the cause of a number of economic downturns in the United States. - Cotton aphid (Aphis gossypii
). - Cotton scoop (Helicoverpa armigera
) and
Helicoverpa punctigera
- caterpillars that harm cotton shoots. - Green horsefly (Creontiades dilutus
) Is a sucking insect. - Spider mites: common (Tetranychus urticae
), as well as
Tetranychus ludeni
and
Tetranychus lambi
. - Thrips: Tobacco thrips (Thrips tabaci
) and
Frankliniella schultzei
Sowing seeds
The optimum soil temperature for successful sowing is at least + 12 ° C ... + 14 ° C. You should not rush - in unheated soil, the seeds will simply die.
The seeding pattern depends on the chosen method, but in any case, the row spacing is not less than 60 cm. Here are examples of such schemes:
- 60x25 (ideal for dotted pattern);
- 60x45 for rectangular-nested;
- 60x60 with a square-nesting technique;
- wide-row crops are also used at the rate of 90x15 (the "step" can be increased to 20 or 30 cm).
Place 2-3 achenes in the hole, the embedding depth for ordinary gray soils is 4-5 cm (on meadow or marsh soils they are taken smaller: 3-4 cm).
The consumption rate depends on the chosen method, but it is selected in such a way as to exclude thinning during the period of planting growth. This figure can range from 40 to 70 kg / ha.Bare seeds are required much less than pubescent ones - for example, 40–42 kg of "clean" hemicarps are needed per hectare, while "fluffy" seeds are needed for the same area at least 60 kg. Plant density - from 80 to 120 thousand / ha. Rows are immediately treated with 80% cotoran. In 100 liters of water (hectare norm) add 1.5-3.5 kg of this agent, and the resulting mixture is sprayed with a wide (30 cm) strip.
Origin
Many people do not even suspect that the cotton wool found in every home medicine cabinet grows in the field, and this is part of a plant called cotton. In countries with tropical and subtropical climates, huge plantations are occupied by this useful plant, and every year a crop of thousands of tons of cotton wool is taken from these fields. In factories, cotton is used to produce fabric - natural cotton. The world leaders in cotton production are India, Pakistan, USA, Brazil, China. Cotton is grown in Central Asia, on the territory of Uzbekistan and Tajikistan.
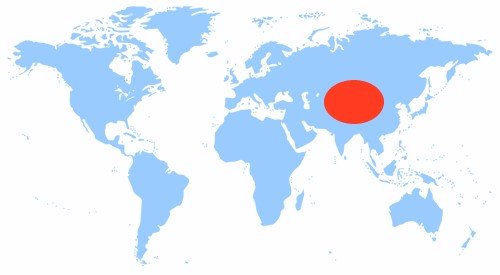

Homeland of the plant
Properties
Cotton fiber has a number of positive properties:
- perfectly absorbs moisture;
- does not cause allergies;
- warms, keeps warm;
- has high air permeability;
- does not need complex care;
- has a low cost;
- convenient for sewing various clothes.
Cotton also has several negative properties:
- without adding it is crumpled, stretched and thinned;
- quickly loses color when exposed to sunlight;
- loses its properties upon prolonged contact with water.
Description and interesting facts
The cotton plant is native to the tropics and subtropics. He is from the Malvaceae family. Its close relative is the well-known hibiscus. There are over 50 types of cotton. These are short trees, annual and perennial shrubs.
The cotton plant dates back to the third millennium BC. introduced into culture. It is grown for the sake of raw cotton, which is used in the production of cotton wool, cotton fabrics, threads. The fiber is mostly white in color, but it can also be greenish, creamy and brownish. Today, the cotton plant, from which cotton is obtained, is the main spinning plant. The seeds are rich in oil, which is used to make soap, glycerin, and margarine. Ethyl alcohol is made from the peel of seeds, and the most interesting is citric acid. The cake is used as an organic fertilizer.
Photo of a flowering cotton plant.
How to care for cotton clothes


The list of popular cotton fabrics is huge: in addition to what was mentioned above, several dozen more varieties can be distinguished. No matter how different they are, caring for each thing can be reduced to basic rules.
- We take out all the items from the pockets: it will be unpleasant to get out the soaked paper, and even more unpleasant if the ink from it remains on the white shirt.
- We clean clothes from stains, soak them in a special product if necessary.
- We check that all the fasteners are fastened, and that the clothes themselves are turned inside out. This will eliminate the risk of breaking buttons or lightning.
- We sort clothes by color: in no case should you wash white clothes with black or colored ones. The latter can shed, and your favorite thing will deteriorate.
- Cotton fabrics can be loaded into the washing machine. If the fabric is too thin or you value its color, it is best to wash it by hand.
- Temperature range: when washing, cotton clothes must be washed at 30-40 degrees. White trousers and shirts require several times hotter water.
- To know exactly how to handle a thing, always look at the icons indicated on the tags. You can get acquainted with the meaning of each here.
- Rinse in lukewarm water: avoid extreme temperature fluctuations when washing.
- We dry only in those places where direct sunlight is excluded.
- The main thing is not to overdry the cotton fabrics.If this unpleasant phenomenon cannot be avoided, then sprinkle lightly with water before ironing.
- When ironing, use the cotton or cotton setting on the iron.
- When storing, do not worry about moths - for her, cotton items are absolutely not edible.
Types of cotton fabrics by finishing method
Cotton fabrics are also distinguished by the complex of physical and chemical effects on the material, that is, by the method of finishing. Cotton trim can be:
- melange;
- harsh;
- bleached;
- multicolored;
- plain dyed;
- printed.
All of the above treatments are performed to improve the appearance of fabrics, as well as impart softness and strength.


Harsh fabric
History
In order to find out how cotton grows, it is useful to read a little historical background about it.
The cultivation of cotton has a long history. This is confirmed by excavations of ancient settlements. India is considered to be the country that started the development of cotton. It was there that the most ancient samples of material and tools for its processing were found. Further, cotton fiber became widespread in Greece and Arab countries. Excavations in China, Persia, Mexico, Peru also speak of the cultivation of cotton for several millennia BC.
From the countries that cultivate the culture, cotton products have spread to Asia and America. Self-cultivation of cotton by these countries began much later.
Before the beginning of cultivation in Europe, there were many legends about how cotton grows. Several variants of names in different cultures have survived to this day, as well as images according to people's ideas.

Harvesting cotton
The peculiarity of cotton is that on the bush of the plant there can be a flower, a green seed pod, and ready to harvest, with ripe cotton at the same time. Therefore, agronomists constantly monitor the state of the cotton field. As soon as 80% of the cotton bolls have opened, the plants are treated with a special preparation that promotes the fall of foliage from the bushes. Which facilitates further harvesting. When 90 - 95% of the cotton boxes have already opened, they start harvesting. Boxes with cotton fibers and seeds are called raw cotton.
Previously, cotton was picked by hand only. This backbreaking and monotonous labor was performed, mainly by women. The products were quite expensive. One person could collect no more than 80 kg of cotton bolls per day, and remove no more than 8 kg of seeds, husks and debris from the fibers.
With the advent of mechanization in cotton growing, labor productivity has increased significantly, and the cost of production has decreased. Machines not only pick cotton, but also clean it.



































