Basil is a perennial herb with a decorative appearance and graceful flowering.
The homeland of this plant is the southern part of Africa, the highlands of America, the Northern Hemisphere with a temperate climate. The basil was spread in our country due to its decorative qualities, high resistance to frost, as well as useful properties.
general description

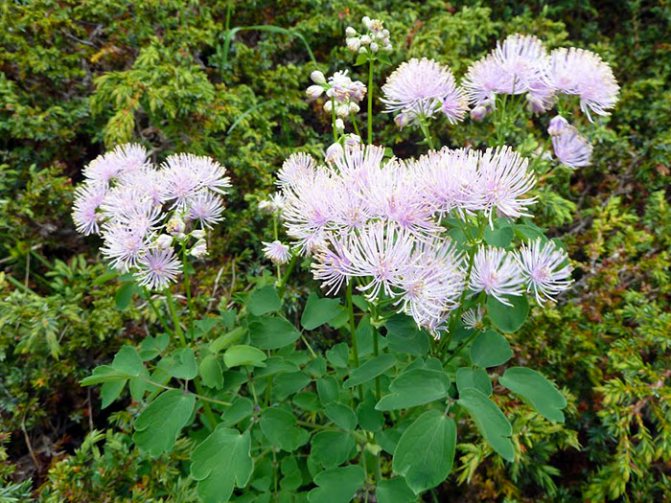
The plant belongs to the buttercup family. As you can see from the photo, the basil is distinguished by an erect stem, completely devoid of foliage or with a very scarce presence of such. The root system of this flower is creeping, it spreads over the site, but slowly. There are basal leaves, very cute - openwork, triangular in shape. The bush grows to more than two meters, it depends on the variety of the basil. The photo cannot display all the beauty of the flowering bush! Inflorescences can be paniculate, racemose and brush-like, and the colors are pink, white, cream, greenish, lilac and yellow.
Yellow cornflower
temperate zone of Eurasia
river banks, floodplain and swampy meadows, bushes
seedlings bloom in the 2nd year
from late June - early July
without perianth, composed of numerous yellow erect stamens 5-7 mm long
flowers on short, 2-3 (5) mm pedicels, clustered several at the ends of the inflorescence branches and form a rather dense, often almost corymbose panicle, 6-15 cm long and 2.5-7 cm wide
leaves deviated from the stem, lower ones with petioles 2-6 cm long, upper sessile and gradually decreasing upward, their plates are triangular in outline, 10-20 cm long and 7-15 cm wide; leaflets are rather large, 2-4 cm long and 1-3 cm wide, obovate, rounded-wedge-shaped at the base, 3-lobed or 3-toothed in front, dull green above, lighter below
ovate, sessile, obtusely ribbed achenes with a straight spout up to 1 mm long
upright grooved plant
Thalictrum flavum ssp. glaucum - has bluish foliage with a waxy bloom
Basil is a plant that is increasingly famous for its medicinal and decorative properties among domestic gardeners. This is due to a large number of advantageous features: perennial, blooms beautifully, excellent frost resistance, and is also easy to grow and care for. And the article will tell you everything about the basil: varieties, planting and care features.
Popular varieties and types of basil
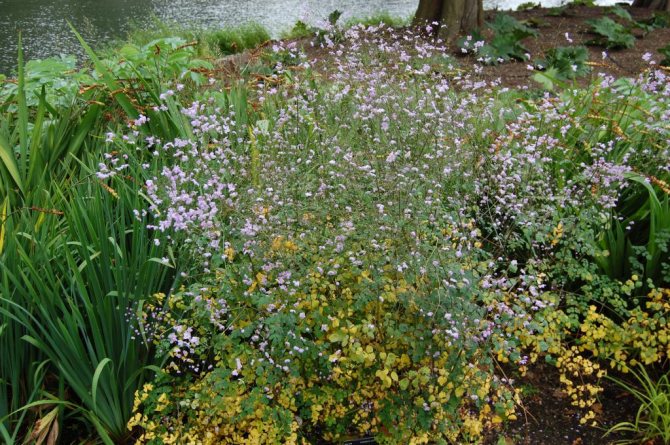


In the photo in the article, you can see several varieties, and all of them are not very much, but still differ from each other. In total, there are more than one and a half hundred varieties of this plant, but the most popular are the following:
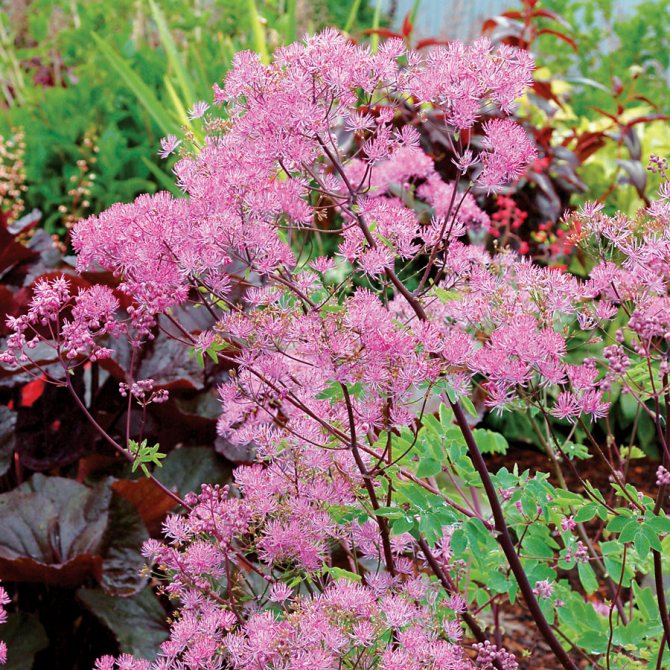
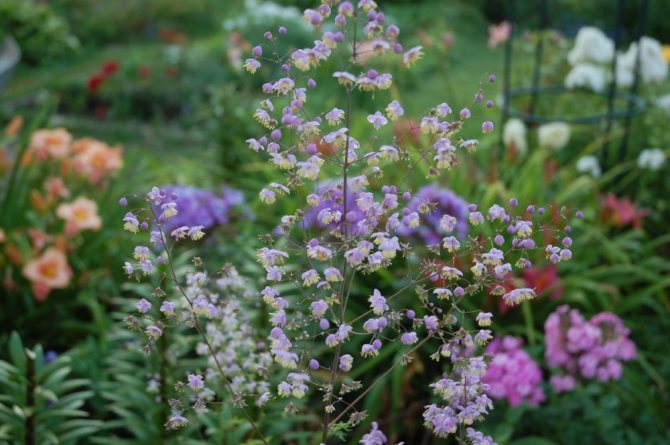
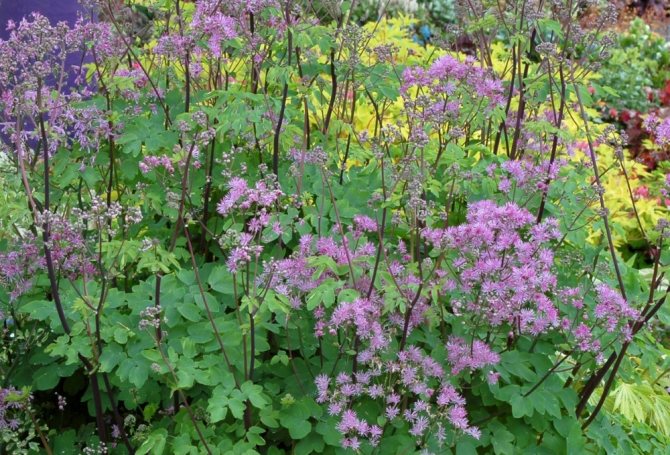
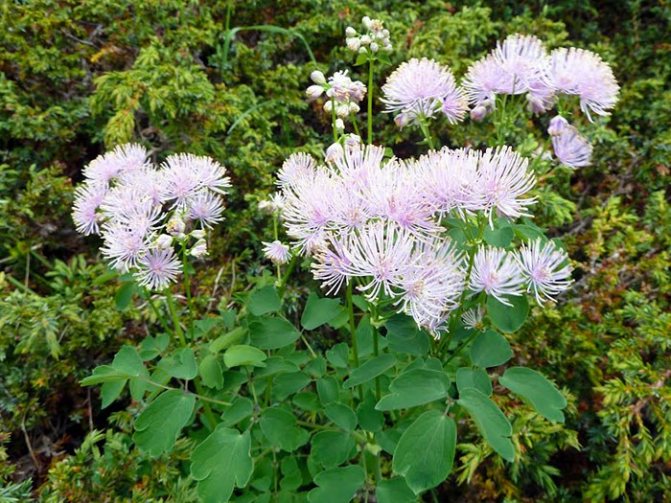
- Watershed basil. It is a compact, perennial plant. The size of the bush reaches a height of no more than 1.2 meters. The leaves are gray, openwork. This variety blooms with small, fragrant flowers, which can be white or lavender, paniculate inflorescences. There are hybrids of the water-collecting basil, and the color of the flowers can already be red, lilac-pink and dark purple.
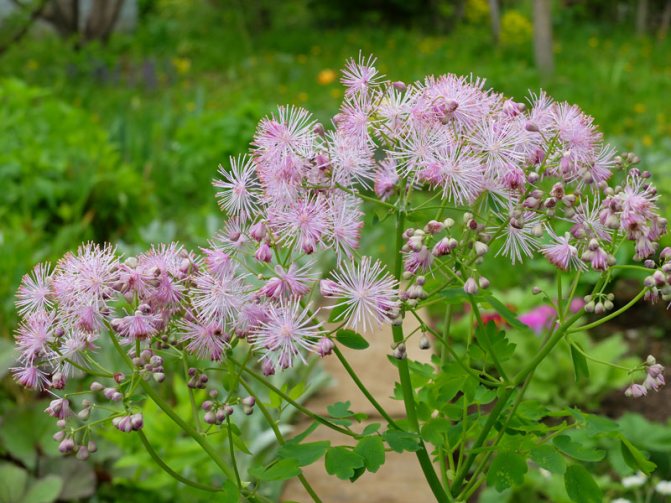
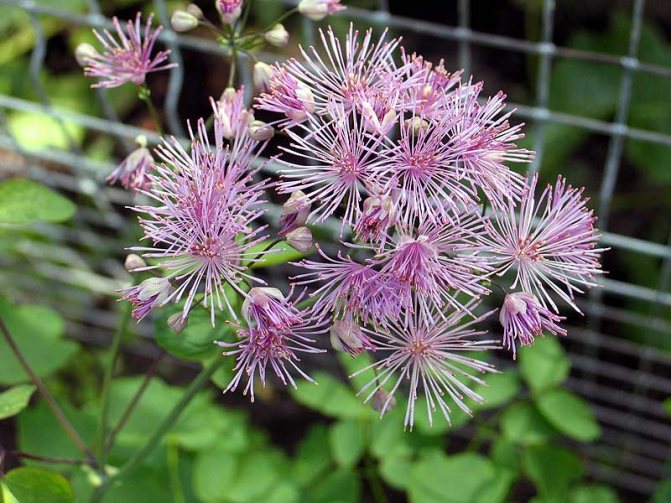
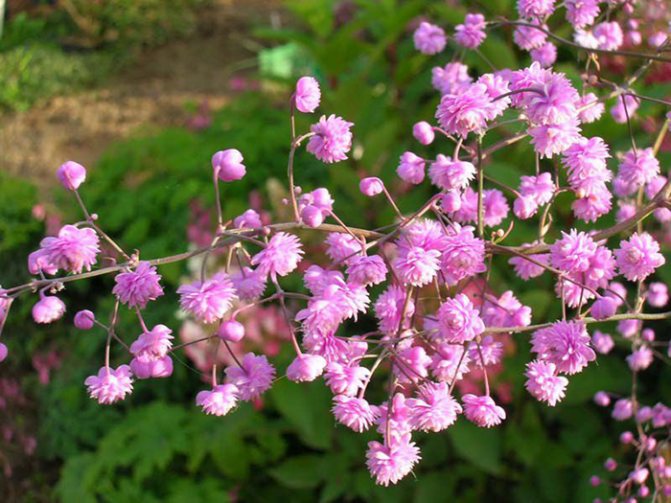
- Delaway.This is also a herbaceous plant, but higher than the previous one, it can reach a length of one and a half meters. A distinctive feature is the inflorescences that look like pompons. The color of double flowers can be pink, lilac-lilac. This plant begins to bloom in August. When flowering, oblong, large leaflet fruits appear.
- The smelly basil has got its name deservedly, as it emits an unpleasant aroma during flowering. A distinctive feature of the flowers - purple sepals with a yellow tint, stamens with bright yellow anthers. Basil is short, grows at least 15 cm, maximum - 65 cm. The foliage is beautiful, feathery, has no stipules.
- Hybrid basil. This plant is a giant of its kind, it can reach a height of 2.5 meters. Stems are straight, completely devoid of foliage or with weak foliage of gray-green or brown-brown shades. Inflorescences are paniculate, they can grow up to 15 cm. The flowers are light yellow or lavender, there are also two-colored.
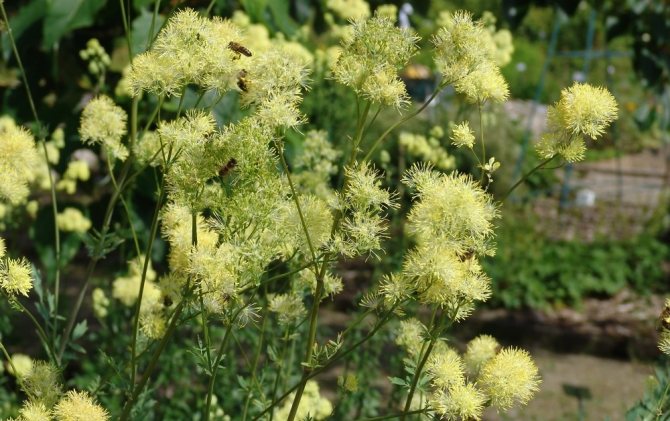
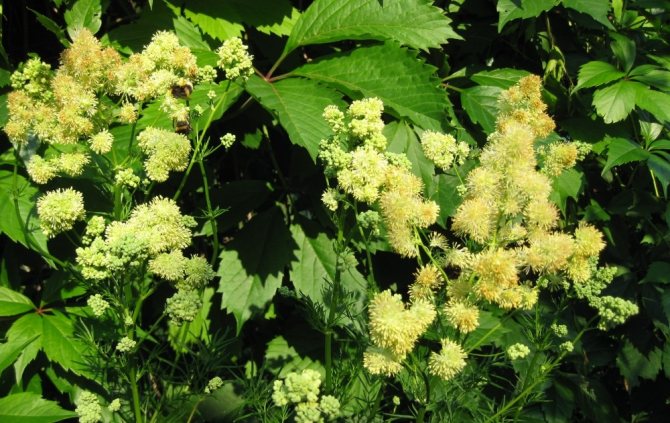
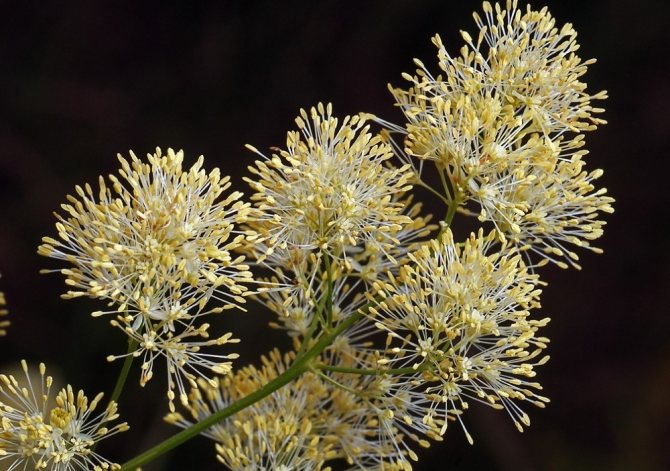
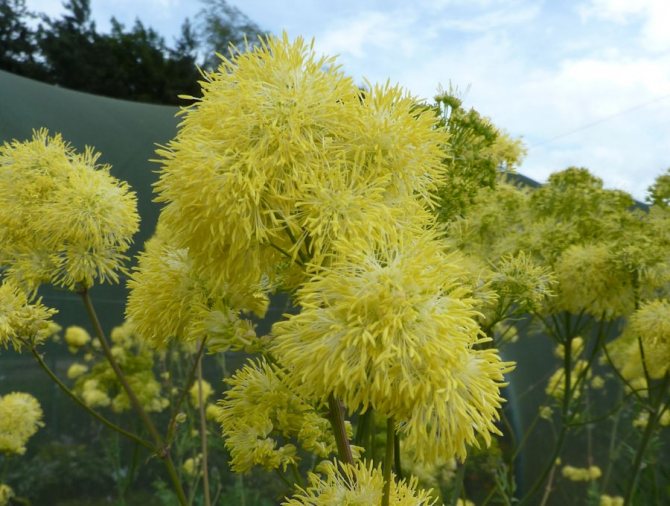
- Yellow. This is a kind of basil, growing from 60 cm to more than a meter. The stem is straight, dull, sharp-toothed leaves are evenly planted on it. The flowers are yellow, small, drooping, collected in brush-like inflorescences. The aroma is pleasant, blooming in June and July.
- Small basil. This plant is up to a meter in height, the stems can be either straight or curved. Foliage on stems of various shapes - trifoliate and multi-pinnate petiole. Inflorescences are panicle, spreading, loose or drooping, consisting of small flowers, decorated with a green corolla. The color of the petals is often white and cream.
In the article you see images of some varieties of basil. Photos of this marvelous plant attract the eye with their brightness, pretty look. But at the same time, it seems that this is a very simple flower that resembles meadow plants. At the end of the post, you will learn how to use these flowers to decorate your site. In the meantime, we suggest that you familiarize yourself with the rules of the basilist agrotechnics, planting and care. Photos of the plant are presented in the article.
Features and description of the basilist
Basil is a perennial herb that is characterized by its decorative appearance and flowering. Almost 150 representatives of this plant belong to the Buttercup family. The natural habitat of this plant species is the temperate territory in the Northern Hemisphere, the highlands of America and southern Africa. These seemingly simple flowers can be found throughout Europe and Asia; many different types of basil grow in Russia. In the wild, these herbaceous plants prefer to grow at the edges of forests, where there is a lot of sunshine, along the banks and in meadows.
The basil plant was previously very popular in Europe. It could be found in the gardens of noble people and in parks; the peculiarities of its cultivation were written in old gardening books. Loved these flowers and people who lived in the Victorian era. However, then there was a lull and this plant was practically forgotten. Just recently, interest in the basil rose again, as now natural landscape designs using fairly simple plants with a cute and delicate appearance have come into vogue.
The name itself is of ancient Greek origin. It comes from the words "thalos", which means "green branch" in translation, and "icter", which means "pleading" in translation. Literally translated as a branch asking for help. In appearance, the basil branches are very similar to the branches of an olive, which is a sign of a request for protection. Many people associate the origin of the name with the name of the mythical creature Basilisk. The meaning of the name of the basilist is also associated with the name of the drug, which in the days of Ancient Rus treated warriors.Her name was Vasilisa, but over time there was a confusion of letters in the word and the basil plant turned out. This origin is connected with the fact that the basil is a medicinal plant that is widely used in folk medicine.


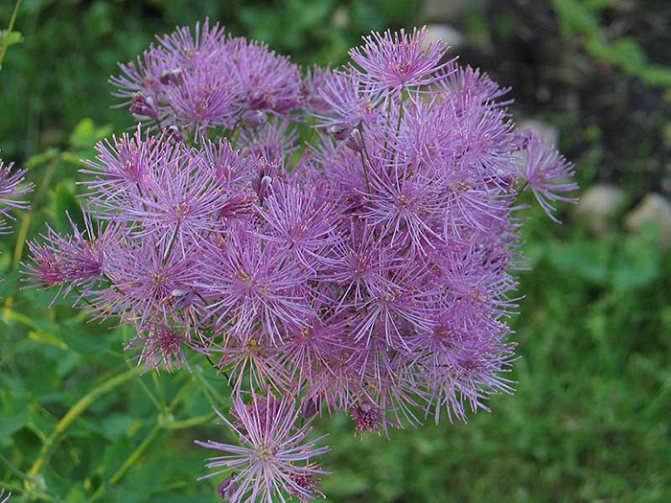
Basilist description:
- Basil is a herb for open ground, which belongs to the group of perennials and is distinguished by decorative flowering.
- The root system of the plant is very large and branched. It is also called creeping, since the roots are able to grow rapidly and penetrate long distances underground.
- Basil stems are erect and very tall. On average, the height of one plant can reach 50-200 cm.
- The stem is most often leafless, less often varieties with a small number of leaves that grow on the stems are found.
- Basil leaves are collected in a basil rosette, they represent a pinnately-divided shape, very beautiful and delicate.
- The leaf plate is shiny on the upper side, and on the lower side it has a slight pubescence or bloom.
- The flowering of this herbaceous perennial begins around June-July, it all depends on the specific species and variety of basil. Flowering lasts about 3-4 weeks.
- Flowers, which have a rather unusual structure, give a special decorative effect to the basil. At first glance, it seems that the flower consists of simple petals and a large number of stamens. But in fact, the basil flowers do not have petals at all, these are ordinary stipules, which can be painted in pink or yellowish shades. After the buds have completely bloomed, the sepals fall off and only stamens remain, which make the flower look like a lush ball.
- The flowers themselves are not very attractive, but they create beautiful inflorescences of various shapes: paniculate, corymbose or racemose.
- The color of the flowers is also different. There are varieties with white, red, yellow, pink, purple flowers.
- When the basil blooms, it seems that the entire plant is wrapped in a soft and fluffy pink, purple, burgundy or white cloud of flowers.
- The flowers of the plant have a pleasant, fragrant aroma that attracts bees and other insects.
- After the flowering of the inflorescences on the plant, the fruit begins to ripen, represented by a multi-root. The fruit can be sessile or is mounted on a stem, inside it are seeds.
- Basil seeds are rather large and oblong.
- Basil is popular in landscaping and is also used for cutting. Flowers of this plant can be dried and then used to decorate bouquets.


Pick-up location
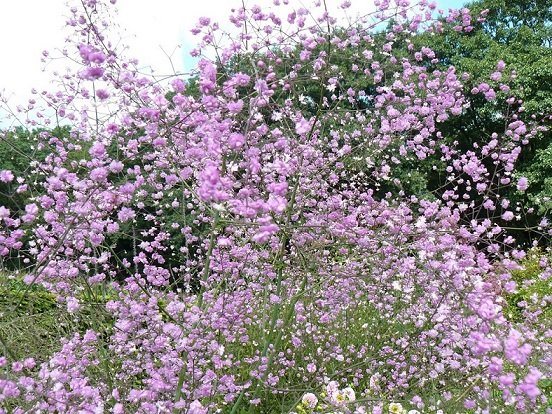


In the wild, basil grows in humid places. These can be river valleys, damp forests, mountainous areas. Therefore, you can safely plant a plant along the edges of reservoirs, under tall trees, near massive bushes. You can also plant a basil in an open area, where the sun is constantly shining, but in this case, you will have to water the plantings twice as intensively. In heavily shaded areas, the plant will begin to stretch, the flowers will be small, not so bright. Therefore, the best option is the area where the sun enters, but the light from it is scattered, or it does not stay in this area all day.
In any case, you need to choose a place where the basil will grow for many years. You can see a photo of the approximate site in the article. This plant does not like transplants, it does not tolerate them well, then it gets sick, it may even die. The basilist does not like the neighborhood of other cultures. If the site is already occupied by him, then the neighbors will have to be located no closer than half a meter!
Basil diseases and pests, how to deal with them
Like many other plants, basil can be affected by various diseases and pests.
Golden Bronze can deal serious damage to Basil.
Golden bronze. This is a pest that eats inflorescences. Insecticides will help fight these beetles. It is only worth remembering that only those individuals who are on the flower at the time of spraying this agent will die. And other insects, for example, bees, can also be poisoned. Therefore, you can choose another method of pest control - cultivating the land under the bushes with such means as "Medvetoks" or "Diazin".
To protect your site from bronze, it is worth removing all rotten stumps in which these parasites multiply.
Powdery mildew. If the leaves began to turn yellow on the shrub, or white spots appeared on them, then you should use a drug such as "Topaz", etc.
Aphid. This pest most often appears in drought. To get rid of it, insecticides are also used.
Landing features
Basil grows on absolutely any soil, it is not a picky plant. But without fertilizers before planting, the flower is unlikely to grow quickly and delight with abundant flowering. In order for the plant to take root well, to be healthy, you need to put in the prepared holes:
- some compost;
- about 50 grams of any mineral fertilizer (buy a simple complex for flowering plants);
- a little leafy ground.
In order for the plant to take root quickly, it is recommended to soak the roots in Kornevin, Epin, Humat or similar products for 4-6 hours before planting.
Plant the plants, compact the soil. Next, dilute the rooting solution in a double portion of water, in which the bushes were kept, and water the plantings abundantly with this composition. The soil will sink, so you will have to fill up the soil so that the root neck of the basil is flush with the ground.
As you already understood, the plant loves moisture very much, and in order for it to linger longer after watering, cover the planting area with mulch.
Necessary plant care
Everyone knows that the basil belongs to the unpretentious inhabitants of the garden.
But be that as it may, some care for him will need to be carried out:
- Watering. If your plant is still young or growing in the sun, then it needs regular watering. In other cases, you need to water the basil only for long periods without rain.
- Fertilizers. Having fertilized the soil during planting, it will be possible to forget about it for the first three years. Subsequently, a special set of mineral fertilizers and organic matter will need to be applied every autumn.
- Loosening the soil. In order for the basil to develop well, regular loosening of the soil is required.
- Weed removal.
- Mulching. Using peat or humus as mulch will avoid rapid evaporation of moisture in the roots of the shrub, and will also protect against overgrowth of weeds.
Pruning
Not all types of basil are pruned, especially undersized ones. The shrub is pruned in order to avoid self-seeding, and also after flowering.
Watering
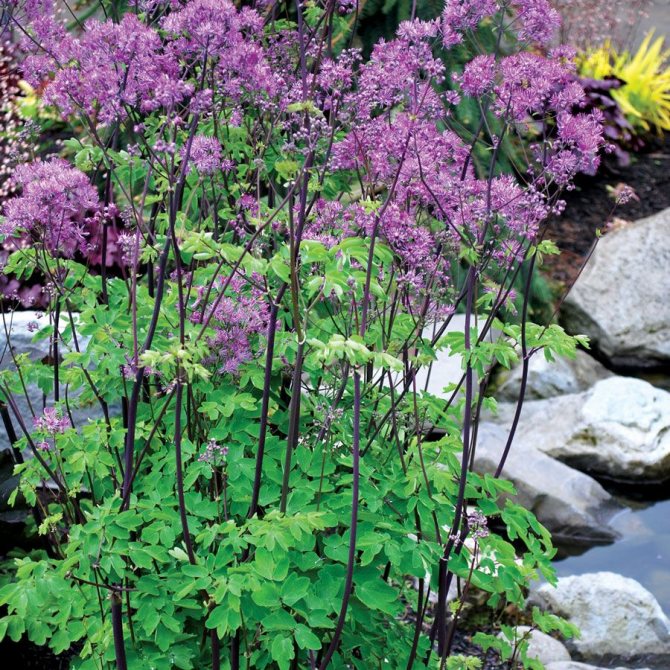


Once you have planted a basil flower, you will have to pay maximum attention to watering. Young plants (up to 2-3 years old) need good, abundant moisture. If you have a summer cottage, where you come only for the weekend, and there is no opportunity to irrigate more often, then just plant the plants in a group in a shaded place, under trees or along a high fence.
Adult plants do not require frequent watering, they need to be produced twice a week on hot days and once a week on cool days with little sun. That is why many summer residents choose a basilist for decorating plots, because even with a rare visit, the local area will be beautiful and well-groomed!
Preparation before planting a basil
By all its characteristics, the basil is considered an unpretentious plant with a lot of positive qualities. Almost without requiring additional work on growing, the basil will delight you with a beautiful and unusual flowering.The main thing is to properly prepare for planting this plant in compliance with all requirements. It is important to purchase high-quality planting material and find the most suitable place for planting on your site, after that you will only have to plant a seedling and observe its full development and rapid growth.
Stage 1. Selection of a variety and seedling of a basil
- First of all, you need to worry about choosing a suitable variety of basil. Today there are a large number of them. Above are just a few of them. It is necessary to buy only zoned varieties that have been successfully adapted to the climate in your region.
- The basil variety is also selected based on its decorative qualities, as well as its height. First, you need to decide on the future garden composition, and then go buy the basil varieties of the height you need.
- You can purchase seedlings, seedlings or basil seeds from specialized garden centers, nurseries or agricultural firms. Choose the form of the planting material according to your personal preferences. Seeds require more time and effort, it is best to buy mature seedlings.
- It is important to carefully check the planting material before purchasing. It must have a healthy appearance, strong shoots and firm roots. There should be no signs of disease or pests.
- You should not buy basil saplings from roads or spontaneous markets, since you will not receive any guarantee as to what you are paying for.
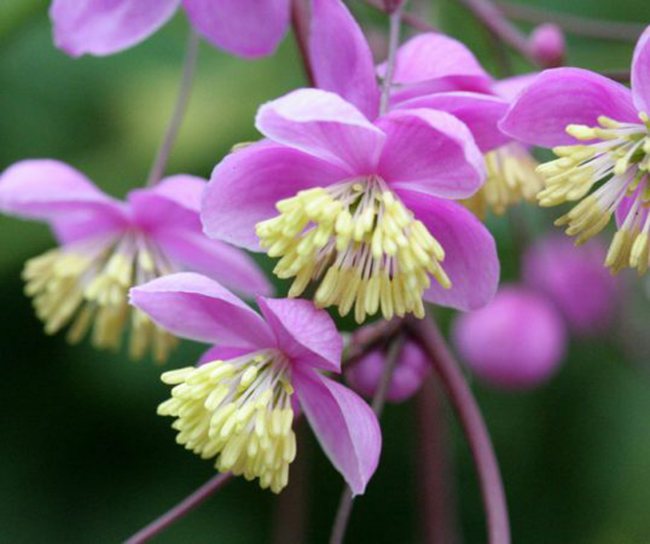


Stage 2. Choosing a place for planting a basil
- Choosing the right place for planting a basil will be the key to getting a beautiful and luxuriantly flowering plant.
- It is important to thoroughly tackle the selection of a site, since the basil has been growing in one place for almost 10 years and does not really like transplants.
- It is necessary to take into account the natural preferences of this plant, all in the wild it grows on sunny edges and on the banks of rivers. Therefore, on your site, select a bright place, but not in the sun itself, since in this case the basil stems will stretch out strongly and require frequent watering.
- It is better to choose a place with a little shading, for example, under trees or on the banks of an artificial reservoir or pond.
- Also, do not choose a place near other plants for planting a basil, since this culture does not tolerate any neighborhood.
Stage 3. Selection and preparation of soil for planting basil
- Basil is a completely unpretentious plant regarding the choice of soil, it can grow almost anywhere.
- But if you want a lush and beautifully flowering plant in the end, it is better to choose well-hydrated and fertilized soils with plenty of nutrients. Moderately moist sandy loam or loamy soils are suitable.
- Also, the soil should be pH neutral.
- Before planting, it is important to remove all weeds and thoroughly dig up the area. After that, the place needs to be loosened and leveled.
Top dressing
Another advantage of the plant that will appeal to busy gardeners who are not too eager to dig in their area. Basil, planted according to the rules described above (with the introduction of fertilizers into the holes), does not need any additional feeding in the first three years of growth! From the fourth year in the spring, apply nitrogen-containing mineral fertilizers. They do not feed in summer. Further, it will be necessary only in autumn, when the plant has faded, to add organic matter to the soil - 40-60 grams for each plant.
Yes, fertilizing is still needed, but everyone will agree that these are not the chores with weekly fertilization that most flowering plants require.
Basil: planting and care
It doesn't take much time and money to grow and plant this plant. For active growth and lush flowering, it is important to choose the right place for planting, as well as the time.Basil feels more comfortable in partial shade conditions, therefore, it is better to plant it in a slightly shaded place. Under the influence of direct sunlight, the flowers turn pale and fade.
The optimal time frame for planting a plant in open soil is late autumn or early spring. Plants that are propagated by dividing the bush must be planted exclusively in the spring.
Read also Pots for ampelous plants
Can grow successfully on any kind of soil
This flower can grow successfully on any kind of soil, but, of course, it is better to give preference to fertile and moist. It is important that the soil is free of weeds. There are no special requirements for the chemical composition of the soil.
Shortly before planting, you need to prepare the holes, between them you should maintain a distance of at least 40 cm. Next, the planting material is lowered into the holes, sprinkled with earth and carefully tamped. After that, another plentiful watering is needed.
Note! When propagating by cuttings or dividing a bush, you need to drive a peg into the middle of the hole to support the cutting.
Plant care
The basilist is unpretentious in leaving, he does not need careful care. A perennial plant without transplanting can grow in one place for more than 10 years.
As for watering, the flower is drought-resistant, therefore, it is not afraid of short-term heat. Excess moisture does not have a detrimental effect on the plant. But with a deficit, there will be lush flowering, but, unfortunately, not long.
The culture does not need frequent feeding; it is enough to introduce mineral complexes with an interval of 3 years in the spring. But in preparation for the upcoming wintering, the basil's near-stem circle must be mulched using rotted humus or peat.
The culture does not need frequent feeding
The flower also needs pruning. Soon after flowering, the stem is cut at the root. But undersized varieties do not need this. To prevent self-seeding, you need to cut the inflorescences shortly after flowering.
All varieties of basil are cold-resistant plants, therefore they do not need careful preparation for wintering. Most varieties are able to withstand air temperature drops down to -30 ° C.
With regard to diseases and pests, the plant is rarely subjected to such attacks. Perhaps the most common problem, especially in dry weather, that a florist will encounter is aphids. To prevent the formation of colonies on the plant, you need to regularly carry out preventive irrigation using insecticidal preparations. The most common are biotlin, karbofos, tanrek.
Other care
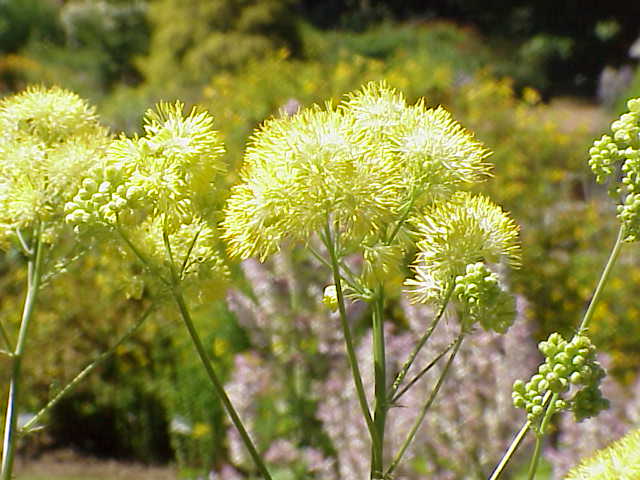


Throughout the season, it is necessary to loosen the soil under the plants so that oxygen and moisture can better penetrate into it. Only you need to loosen it very carefully so as not to harm the roots.
Do not forget that although the plant is dense in itself, it needs to be cleaned of weeds, withered foliage, because all this takes a lot of energy, a large amount of useful substances.
Tall plants require pruning, which is done in autumn, in spring as needed, in summer broken stems are removed.
Basil is a frost-resistant plant, so it does not require shelter for the winter.
Reproduction methods
The plant reproduces in three ways:
Propagation by cuttings
Perhaps this is the easiest way to breed a basil. The only favorable time for breeding is spring. Rhizomes or small sections of the shoot are used as a cutting. Before planting, the cut area must be treated with a disinfectant and growth stimulant.
It is necessary to plant a common basil in open light soil in partial shade.
Cover the plants with agrofibre or a plastic bottle.To prevent the development of fungal diseases or root decay, the basil must be ventilated daily. It is also worth protecting the cuttings from direct sunlight.
Seed propagation
This breeding method is considered the most time consuming. Planting should be carried out shortly after collecting seeds in mid-September or shortly before the onset of the first frost. Seed material that ripens in August can simply crumble. To prevent this, you will need to tie the inflorescences with gauze in July. Before planting, the planting material must be thoroughly dried.
Important! With the seed method of reproduction, the varietal characteristics of the plant are lost.
Basil flowers bloom in the second year after planting.
Dividing the bush
Shortly after the onset of spring, before the start of the active growth phase, the bushes must be carefully dug up and divided into the required number of parts. Each constituent should have 1 to 3 buds of renewal. You need to plant the planting material in a semi-shaded place. The ground is preliminarily watered abundantly, after which it is mulched. Taking care of the plant is simple, just water it regularly and loosen the soil. If organic and mineral fertilizers were introduced into the soil before planting, then there is no need to fertilize the crop for the next 3 years.
Note! Basil has found wide application in folk medicine, due to its unique chemical composition. The plant has pronounced anti-inflammatory and disinfectant properties.
Basil is an ornamental flowering culture that has become widespread due to its medicinal and decorative properties. It will decorate any personal plot, and even a novice florist can grow it.
In Russia, the medicinal herb basil was successfully used in folk medicine, and its healing properties were directly reflected in the names. More often in ancient legends, people associated this plant with the name of the legendary healer Vasilisa, who healed courageous warriors who were wounded in battles with the enemies of the Motherland. There is another old, but now less common name Veredovets, which emphasized the ability of a flower to effectively treat various unpleasant "veredy" - boils, abscesses, pimples.
Read also How to propagate a money tree at home


It should be noted that, in addition to medicinal properties, the basil has other useful qualities - unpretentiousness in cultivation, frost resistance, decorative appearance, and a long flowering period. The plant has openwork foliage and is decorated with wonderful fluffy inflorescences of various shapes and colors for almost the entire warm season. Not surprisingly, many species of this culture have become widespread in landscape design and horticulture.
This perennial belongs to the Buttercup family. The genus of basilists is diverse and has about 150 species. The height of the Veredovets ranges from 5-20 cm to 2.5 m. In a herbaceous plant, the roots are often fibrous, only some varieties have shortened tuber-shaped rhizomes. Stems are erect, foliage is concentrated mainly near the base. Leaf blades of a complex openwork shape, trifoliate or multiply pinnate.
Basil inflorescences have small petals, but the filaments are very long, multi-colored and give the flower a decorative look. The perianth consists of 4-5 sepals, which crumble relatively quickly. The shape of the inflorescences is paniculate, racemose, corymbose. The color of the numerous stamens differs from species to species. They are found among basil plants of varieties with inflorescences of white, purple, green, yellow or mauve. By autumn, many roots with large ribbed seeds are formed on the peduncles.
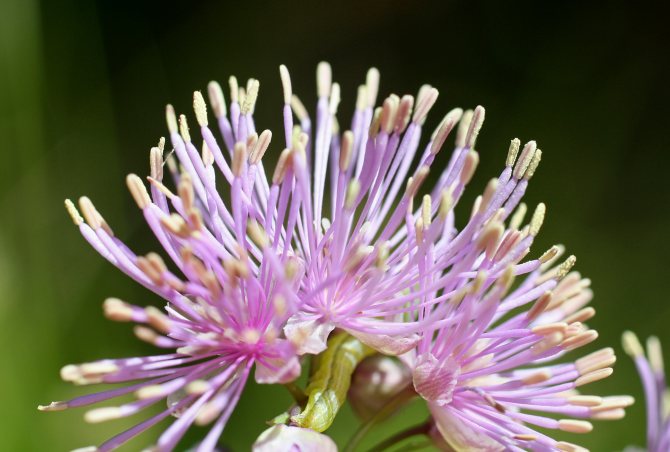


The most common types of basil are:
- Basil is water-collecting.The height of perennial grass is up to 1.2 m. The leaves of the plant are openwork, gray-green in color. Inflorescences are paniculate, flowering is long and lasts from June to late summer. The color of the flowers can vary from rich dark red to pale pink.
- Basil of Delaway. An elegant perennial has terry inflorescences of lilac-lilac or pink color, reaching a height of one and a half meters. The flowering period is June-September.
- Rochebrune basil. The plant is graceful with bright green foliage, reaches a height of 1.5 m. It forms loose, but unusually pleasant lavender inflorescences for the eye.
- Small basil. The grass reaches 80-120 cm in height. It forms erect stems, the inflorescence looks like a wide-pyramidal panicle. In June-July, the perennial is decorated with inconspicuous yellow drooping flowers with 10-15 thin filamentous stamens.
- Smelly basil. Perennial stems grow 20-70 cm high, but it is relatively weakly leafy. Numerous tiny flowers are formed in the first half of summer, attached to pedicels up to 3 cm long. The sap of this flower is yellow with strong coloring properties. A distinctive feature of the species is that the leaves and stems are covered with short hairs that emit an unpleasant persistent odor.
- Basil yellow. Plant height 60-180 cm. The foliage of the grass above is dull green, petioles up to 6 cm long. Thyroid paniculate inflorescences are yellow in color, flowering occurs from early summer to late July.
- Basil is simple. The erect plant reaches a height of 120 cm, the double-pinnate leaves are evenly spaced and pressed against the stem. Perennial inflorescences of purple or green color, collected in pyramidal or oval panicles.
- Light basil. Herbaceous perennial reaches a height of 60-145 cm. The lower and basal foliage is four times pinnate, and the stem foliage in the middle and upper parts is three times pinnate. The pyramidal or thyroid panicle is pale yellow in color.
- Basil sprawling. The height of the shoots is 70-90 cm. The perennial forms loose inflorescences. This variety has the largest flowers of a delicate purple color, reaching a size of up to 2 cm


Like other plants of the buttercup family, the basil contains many toxic alkaloids. In aboveground organs, their number reaches 2%, in rhizomes - up to 0.4%. The chemical composition may differ slightly depending on the species, so you should clarify the name of the flower growing in your region, planning to use it in folk recipes. The list of active substances is as follows:
- magnoflorin;
- berberine;
- tannins;
- flavonoids;
- choline;
- organic acids (ascorbic, phenolcarboxylic);
- lithium;
- fixed oils;
- saponins.
About 36 species of this plant grow in Russia. More often it can be found on the edges, in sparse forests, in river valleys, along the edges of reservoirs and in steppe meadows. Less decorative, but the most common type is the common basil. Its range includes the Far East, the Caucasus, the European part of the country and Siberia. Common plants for most regions of Central Russia are also light and yellow basil. The homeland of the undersized alpine basil, popular among gardeners, is located in relatively harsh places. It grows on the banks of mountain streams, in rocky terrain, at the foot of glaciers, in the desert tundra.
Read also Saddle pad size for a horse


This flower is prized by gardeners for its many beneficial properties. Decorative deciduous species of basil rarely get sick, grow well in shaded places, have a long flowering period, and are suitable for cutting. You can get seedlings of your favorite plant by sowing seeds, dividing a bush, using propagation by cuttings.For the first three years, perennial fertilization is not required; regular watering, loosening the soil and weeding are enough for normal development.
This culture has been widely used in folk medicine for many years. An alcoholic tincture of this plant is used to treat hypertension. The aerial parts of the basil grass were included in Zdrenko's antitumor collection, which helped many patients to avoid surgical intervention. In homeopathy, there are many basil-based medicines that help with painful menstruation, in the postpartum period, as a general strengthening and wound healing agent.
Basil helps in the treatment of the following diseases:
- ascites;
- angina;
- edema, including cardiac;
- flux;
- diarrhea;
- tuberculosis;
- diphtheria;
- diseases of the digestive system;
- inflammation of the liver and gallbladder;
- nervous disorders;
- purulent wounds;
- hypertension;
- diabetes;
- dermatitis.
The presence of lithium and alkaloids in the chemical composition allows the use of preparations from this perennial for many diseases. Experts have found that basil can exhibit the following beneficial properties in the treatment of diseases:
- bactericidal;
- antineoplastic;
- laxative;
- choleretic;
- anti-inflammatory;
- fortifying;
- wound healing.
Due to the presence of alkaloids in the basil, it is imperative to follow the dosage and recommendations of experienced folk healers when preparing the medicine.
It is undesirable to take drugs based on this flower in the following cases:
- under reduced pressure;
- with atonic constipation;
- during pregnancy and lactation;
- with bradycardia;
- with heart failure;
- with individual intolerance.
The roots and aerial organs of a perennial plant are used as raw materials for medicines. The foliage and flowers of the basil must be collected during the flowering period, cutting off the leafy upper part of the shoots up to 35 cm long in June-July. It is advisable to remove old withered leaves. At home, the collected grass must first be tied into small bunches, then hung or spread out in a small layer in a place sheltered from direct sunlight. For these purposes, a well-ventilated attic, a wide canopy, and a dry utility room are suitable. The dried herb has a faint odor and a bitter taste. The roots are dug up for harvesting from September to early November and also dried. It is allowed to store raw materials in a dry room for up to three years.
- With diabetes mellitus and cardiac edema. Take a tablespoon of chopped basil roots, pour 2 glasses of water, bring to a boil and cook for about 10 minutes. Leave for 20 minutes and strain. Take the broth in equal portions for two days.
- Basil tincture for the treatment of hypertension and angina pectoris. Pour 10 g of rhizome powder with 100 ml of alcohol and leave for up to 7 days. After straining, take 25-30 drops.
- Water infusion for the treatment of diabetes. Pour the chopped roots in the amount of a teaspoon with a glass of boiling water and leave for one hour. After straining, take 2 tbsp. spoons 3-4 times a day.
- Treatment of skin diseases and diaper rash on the toes. Chop fresh leaves of a basil and apply to a sore spot.
- Infusion for the treatment of skin diseases. Pour 10 g of dry grass with 200 g of boiling water and leave for 30 minutes. Moisten a tampon with the resulting solution to wipe the pustules.
- Infusion for diarrhea. 10 g of herbs pour 200 g of boiling water and leave for an hour. Drink 1 tbsp. spoon up to 4 times a day.
- Water infusion. Pour 30 g of dry herb with 300 g of water, bring to a boil and cook for 7 minutes on low heat, leave for an hour, then strain. Take 1/3 cup three times a day for diarrhea, for sore throat, the remedy is suitable for rinsing the throat. This infusion can be used to wash wounds or use it for lotions with flux.
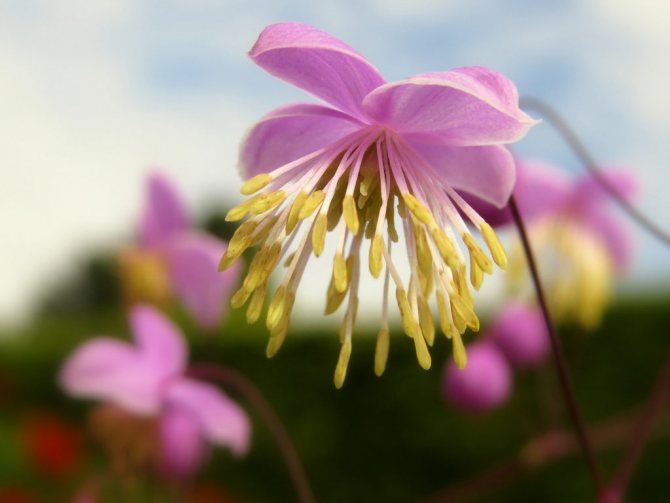


Growing an undemanding border plant with airy inflorescences in a flower bed, many do not realize that the basil has healing properties. A decorative flower with openwork foliage is a treasure trove of valuable substances, it is a part of folk remedies, helping to treat numerous diseases.
Seed reproduction
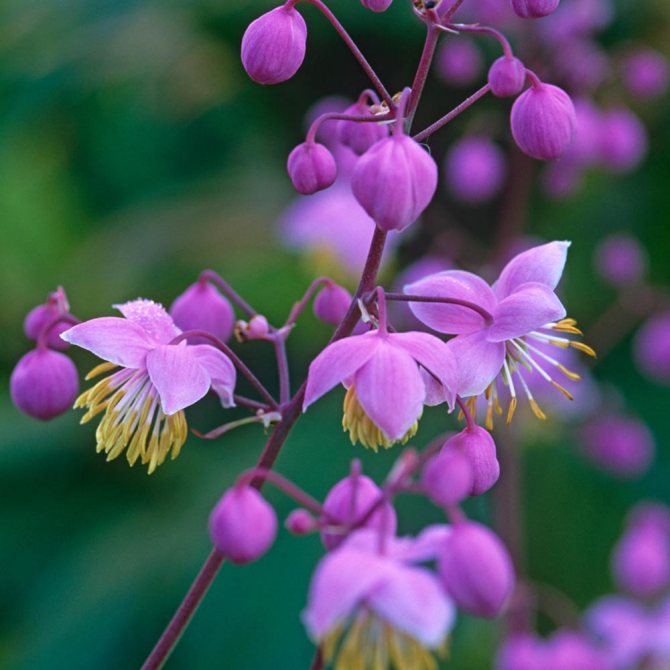


This is a laborious process, but many people use the method. After flowering, fruits appear, inside which there are seeds. You need to harvest at the end of autumn, but before that time, in July-August, they themselves can get enough sleep. To prevent loss of material, tie the fruits with gauze as soon as they appear.
Sow the seeds in the right spot in the spring. New plants will begin to bloom only from the second year.
Minus - with such reproduction varietal characteristics and qualities are not preserved.
How to propagate a basil
Basil breeding can be done in three ways:
- growing from seeds;
- dividing the bush;
- by cuttings.


Basil is most often grown from seeds.
Important! When multiplied by the first method, many varietal characteristics of basil may disappear.
The collection of seeds and their planting is carried out in the following way:
- In the middle of summer, basil inflorescences are tied with gauze. This measure will not allow the seeds to spill out when ripe.
- The collected planting material must be sown in the ground in the fall before the onset of frost.
- In the spring, seedlings are thinned out.
- After a year, young plants can be resettled for permanent residence.
The soil for the seedlings must be nutritious.
Reproduction by dividing the bush is done in early spring. The basil bush is dug up, divided into several parts, each of which is planted separately. This method is the most common and simplest.
Cutting is an easy way to grow a basil. To implement it, you need to cut off a young twig with still unopened leaves and put it in water. After the roots appear on the cuttings, the shoot can be planted in a prepared place where the shrub will live permanently.
Application in landscape design


You can use the basilisk flower in any way you like. We have posted a photo of an approximate application in the landscape in the publication. You can plant a plant along the edges of gazebos, near ponds, decorate borders with them, just place them in flower beds.
Basil does not tolerate the close proximity of other plants, but in one area it is perfectly combined with any flowering and non-flowering plants. Other flowers can be planted both in the foreground and in the background.
Basilist photo
Basil is a beautiful and simple plant that will certainly decorate and highlight your site, while not requiring much effort and cost from you to grow it. This is the whole plus of flowering plants understandable to everyone, which were undeservedly forgotten.
Briefly about culture
Basil is a herbaceous perennial plant from the Buttercup family. Various studies have found that there are from 120 to 200 varieties of it, but the exact number has not been determined. Even in Ancient Russia, some species were used for medicinal purposes. And today it is also used to create bouquets.


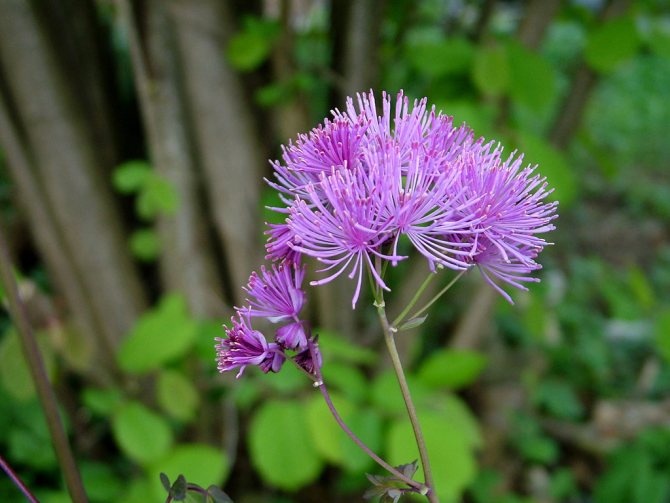
Delaway Basil
How to care?
Grooming is not difficult, but necessary. Young plants need regular and abundant watering, adult plants have enough rain - with the exception of those planted in sunny places.
Loosening and weeding will be required. Basil aquifer needs pruning.
If the soil is sufficiently nutritious, or has been prepared as described above, there is no need to feed the first three years. In the future, nitrogenous fertilizing is introduced in the spring (to stimulate growth), before winter, complex organic fertilizers are embedded in the soil around the plant.
Reproduction


After flowering, reproduction occurs by self-seeding, but this process can be taken under control by the florist. The seeds can be harvested to keep them from scattering around the garden. Dried and prepared for planting seeds are characterized by 100% germination. Seedlings bloom in the second year.
In addition to the fact that the plant can be propagated by seeds, dividing a bush or grafting will also not cause trouble. The bush should be divided in early spring or after flowering (in September). Attention must be paid to ensure that there are 2-3 kidneys on each separated part.
You can graft in the spring. To do this, the shoot is carefully cut off with a sharp knife and planted in a semi-shaded place with light soil. From above, you can cover the sprout with a piece of a plastic bottle.
Pharmacological properties
A number of therapeutic effects have been identified, among which the most obvious are:
- bactericidal;
- diuretic;
- choleretic;
- laxative;
- slowing down the development of tumors.
- strengthening the whole body.
One of the most important pharmacological properties of basil is its ability to produce lithium. This element helps to maintain the normal state of the human nervous system. Alkaloids can have different effects on the body.
For example, talmin relieves tension from smooth muscles, quickly reduces pressure, and depresses the nervous system.
Berberine inhibits cell proliferation and has a therapeutic effect in cases of malaria infection. Alcohol tincture made according to the rules helps to quickly expand blood vessels and reduce pressure.

Basil has the ability to calm the nervous system

Lowering blood pressure - one of the effects of the basil
Indications for use
When diagnosing the following diseases, official medicine recognizes the possibility of their treatment with drugs based on basil:
- The manifestation of purulent boils on the surface of the skin.
- The first signs of urination problems.
- Swelling of the extremities.
- Failure of the rhythm of the heart.
- High blood pressure.
- Infectious diseases: measles, smallpox, tuberculosis, malaria, syphilis, diphtheria.
- Purulent wounds, bruises, damage to the skin, diaper rash.
- Diarrhea.
- Neuroses.
With convulsions, drugs containing basil are also indicated.


Basil is part of many medications
Contraindications for use
All medicines and tinctures prepared on the basis of the culture in question are used with caution. This is due to the presence of toxic substances in it.
RECOMMENDATION! (click to find out)
It is not recommended to use basil in any form without consulting a doctor, exceed the prescribed dose or abuse it.
Doctors categorically prohibit the use of it in any form by pregnant women, persons under the age of 12 and in case of intolerance to chemical elements.


Basil is contraindicated in children
Cultivation, reproduction
Basil anemone prefers to grow in light partial shade of deciduous trees. Needs well-drained, sandy-humus or light loamy soils rich in organic matter. Medium-demanding on soil moisture, capable of tolerating slight drought, but it develops optimally and blooms well on constantly moist, acidic and slightly acidic soils (pH 4.6-6.0). In conditions of waterlogging, the rhizomes rot. Mulching with a small layer of compost helps to maintain moisture.
The plant propagates by seeds and vegetatively. Sowing in the winter provides the seeds to undergo cold stratification in winter.
The plant can be affected by powdery mildew, rust, damaged by slugs.
The plant is difficult to tolerate division, so it is not completely dug out, but the division is separated in the fall, digging up the plant.
Basil anemone is a delicate, slightly competitive plant that needs to be kept free of weeds.It is best planted in small clumps on the shady slopes of rocky gardens, in forest areas of natural-style gardens so that neighboring plants cover the place that has been vacant since the middle of summer after the dying off of the aboveground part.
Basil is a plant that we often meet, but do not know its name. Low bushes with bright caps of fluffy inflorescences, reminiscent of light clouds, growing in forest glades - this is the very basil. The forest handsome man is also found in a cultivated form, in personal plots. Its airy inflorescences and bright green foliage fit perfectly into any landscape, and the unpretentiousness of the spectacular representative of the kingdom of Flora attracts many gardeners.
The unusual name of the perennial came from Ancient Russia: according to legend, the healer Vasilisa treated warriors with a healing decoction, and the plant was named after her. Other names that sound similar are basilis, basilis grass, basilist. The Latin name - thalictrum (taliktrum) - comes from two words translated as "green branch" and "supplication". And the English, because of the similarity with the rue, call the plant meadow rue (meadow rue).
Some recipes using basil aquifer
In numerous publications on traditional medicine, you can find many recipes describing the correct use of basil. So, with uterine bleeding, an infusion is made according to the following scheme: 1 tsp. herbs for 200 ml. boiling water, use half a glass 2 times a day until the pain disappears. For joint pain, the recipe for the infusion is as follows: 1 table. a spoonful of crushed roots is poured in 200 ml. boiling water and infused, then the infusion is filtered and used in poultices and compresses.
With hypertension, the infusion is made in this way. 100 g chopped grass is poured with 1 liter of forty-degree alcohol, then tightly corked and stored for one week in a dark place, shaking occasionally, then filtered and used, in particular, at the initial stage of the disease in a dosage of 20-30 drops per half a glass of water 3-4 times day for 3-4 weeks. The medicine has a cumulative effect, which begins to manifest itself on the 4th day of treatment and persists for some time after the drug is discontinued.
First meeting
Basil (or, more correctly, basil) is a herbaceous perennial in the form of a compact low bush with a height of 50 to 100, less often 150 cm.It can be found both in Europe and in Asia - mainly in China, Japan and the countries of Asia Minor ... Among other shrubs - especially shrubs of its kind - it stands out as follows:
- short rhizome and leafy erect stem branched at the top.
- large compound leaves, consisting of numerous small leaves 2-5 cm long. Leaves are bicolor: the upper side is green, the lower side is bluish. Arranged evenly and alternately, the upper ones are almost sessile, the lower ones are on grooved petioles.
- the presence of stipules in the branches of the petiole.
- lavender, less often white small fragrant flowers in the form of a large loose, slightly flattened corymbose panicles up to 20 cm long.
- perianth, consisting of 4 greenish ovoid leaves, which fall off when the flowers bloom.
In appearance, the plant looks like an olive branch covered with fluff. In ancient Greece, this symbolized a plea for protection, so the basil has a specific name "Thalictrum aquilegifolium", which in a very rough loose translation means "pleading green branch". In addition to such an unusual appearance, which gave rise to such a name, the shrub is also notable for the fact that both sunny open places and shady ones are equally suitable for it. It is not surprising that it can be found on wet soils along the banks of reservoirs, and in mixed forests, in glades and forest edges.With its leaves, outlines similar to a wide triangle, it resembles the leaves of shrubs from the genus Vodosbor ("aquilegia") - hence the word "catchment" in the name.


The waterwort blooms during May-June with fluffy ball-shaped flowers formed due to the abundance of long club-shaped stamens. At this time, a lot of insects - mainly bronze beetles - are always hovering around the bush, attracted by the aromas of flowers. Even when it fades, the airiness of the panicles remains until late autumn. Fruits in the form of small nuts, only about 7 mm long, of which the achenes, which are pear-shaped or obovate, with membranous wings along the ribs, hanging on the stalks, ripen in July-August.
Basil application
Due to its attractive appearance and its constituent chemical elements, basil is widely used in the creation of landscape designs, as well as in the manufacture of medicinal preparations.
In folk medicine
Leaves, stems and flowers of the culture are used as a basis for the preparation of decoctions, tinctures and ointments. The funds are used to treat and prevent cardiovascular diseases, relieve puffiness, headaches, gag reflex, disorders of the stomach, liver, gallbladder, bleeding, and also as a general tonic.
IMPORTANT! (click to find out)
Some varieties have a therapeutic effect on the body when infected with malaria, jaundice, tuberculosis.
In folk medicine, there are many recipes for basil preparations that women use for gynecological diseases. They are especially effective in opening uterine bleeding. Traditional medicine recommends using basil tincture to relieve symptoms of hypertension, normalize blood pressure, angina pectoris and restore circulatory function.

Basil is an excellent remedy for liver diseases
Funds from this culture are applied to the sites of bruises, burns, purulent wounds to speed up healing. A poultice of fresh leaves is used to relieve the symptoms of rheumatism, as well as arthrosis and arthritis.
When diaper rash occurs on the feet, crushed fresh leaves are applied to them.
The plant is popular in Tibetan medicine for neutralizing the effects of liver intoxication, treating dropsy, and accelerating the healing process of damaged tendons.
Fresh juice of the culture is used to treat skin lesions. A properly prepared paste helps in the fight against malignant and benign neoplasms. The root system is assigned when diagnosing ascites and the presence of edema.

Joint lesions - an indication for the use of basil
In gardening
The culture in question has decorative properties. Correctly formed bush has compact size and height up to 120 cm with large triangular leaves of gray-green color.
A large number of terry inflorescences in the form of tassels are painted in various colors: yellow, purple, lilac, white.
They are collected in bunches, and numerous stamens give the plant additional spectacularity. Each of them has a long thread, the size of which significantly exceeds the perianth leaf. Depending on climatic conditions, the flowering period can last up to 35 days. Due to its unpretentiousness and simple breeding methods, this culture is used as a decorative one.
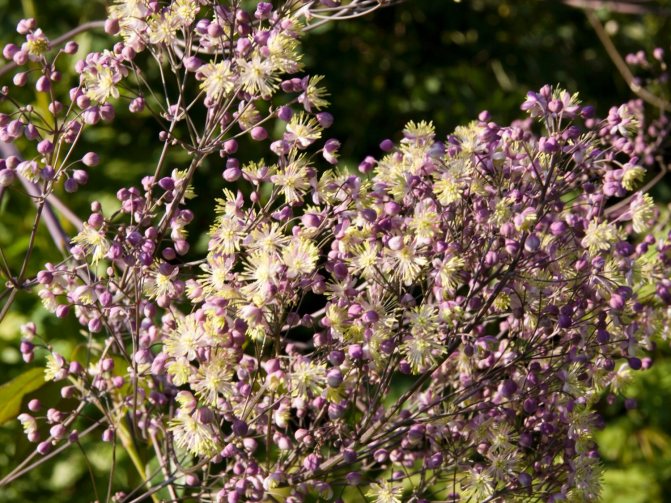


Basil - an ornamental plant
Basil - decoration of the site
It looks good both separately and as part of a flower arrangement in a garden area. It can become a real decoration if you correctly beat the contrast of the shades of each element of the composition.
Basil is often planted next to gazebos, arches or fences.
Popular questions from gardeners
A few basic questions that interest many gardeners:
| Question | Answer |
| Why, after two years of stable growth and development, black areas form on the stem and the leaves begin to turn yellow? What are the effective ways to combat and prevent. | The listed symptoms are clear signs that the plant is sick with powdery mildew. It is necessary to treat the leaves and stems with Topaz. Inspect the plant for insect pests. If found, treat the affected areas with a disinfectant. |
| How does botrytis manifest itself? How to deal with this disease? | The first sign of Botrytis is yellowed leaves. All new shoots begin to wither and dry out quickly. It is impossible to cure the plant, so it is dug up and burned, and the soil is treated with a disinfectant solution. |
| How does basil winters? | Bushes that winter outdoors for the first year must be protected with a covering material. In the future, the use of additional insulation means is not required. The snow will act as a natural insulation material, which will be sufficient for the wintering of the plant. |
Growing conditions
The plant is unpretentious and can tolerate small frosts without consequences. The optimal conditions for growing crops are shaded areas with moist soil. If you plant it in an area where the sun shines most of the day, the leaves will quickly turn yellow. If there are no other places for planting a bush, then it is necessary to shade it with the help of taller plants.
Planting a plant
Disembarkation rules may vary depending on the weather conditions in the region.
TIP! (click to find out)
In hot climates, it is recommended to plant in close proximity to tall trees and shrubs.
They will protect the bush from the negative effects of direct sunlight. You can use fences or buildings as a protective element and plant it in close proximity to them.
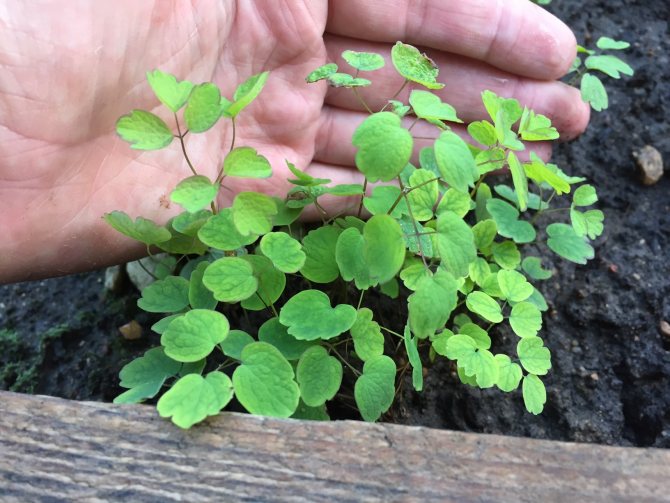


Basil seedling
To preserve life-giving moisture, it is recommended to constantly loosen the ground, especially in the first time after planting. The landing site is prepared in advance. For this, a shallow round hole is dug.
If there are not enough nutrients in the soil, then drainage is organized at the bottom of the prepared planting site.
It is made using the remains of broken stone, brick, gravel and other similar material. A full layer of fertile soil is poured over the prepared drainage. If the soil at the site of planting of the seedling is sufficiently fertile, then the depth of the pit should be slightly greater than the formed root system.
RECOMMENDATION! (click to find out)
If the soil is stony, then it is necessary to make a hole, the volume of which is an order of magnitude larger than the roots of the seedling. If in winter the soil freezes deep enough, then in spring a large amount of water will accumulate near the root.
As a result, the soil acquires the properties of a swamp, which negatively affect the development of the seedling. This can be avoided by making the planting hole wider and shallower. In this case, the roots of the plant will be closer to the surface and will warm up faster with the arrival of spring. Planting is carried out in the spring, so that during the summer period the seedlings can strengthen and prepare for winter.
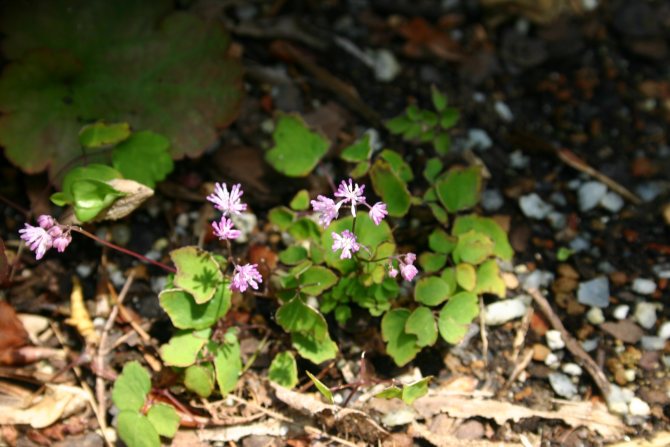


Young basilist
Reproduction and care
The plant is cultivated in various regions of the Russian Federation.
Reproduction of the basil is carried out in the following ways:
- Sowing seeds.
- Cuttings.
- Division of the root.
Prepared seedlings are planted in the ground in May. The roots are split after harvest at the end of September. The division of the bush in regions with a cold climate is carried out in the spring. At this time, the buds swell, and sap is formed, which indicates the readiness of the plant for the growth of the trunk and root system. If seedlings with leaves were planted, then they are watered abundantly.
IMPORTANT! (click to find out)
If you sow seeds that were obtained immediately after the completion of the flowering process, then the seedlings may have heterogeneous characteristics.
This situation can be avoided if the reproduction of the basil is carried out by dividing the mother plant. This method ensures the preservation of the external beauty and characteristics of each bush. The transplanting process has a negative impact on the bush.


Transplanted basil
In case of separation of even one root, the whole system suffers. In order for the transplant process to be less painful, it is recommended that all operations be carried out as quickly as possible. For this, the root system is planted in pre-prepared pits. The seeds are placed in special containers after disinfection.
Fertile, well-moistened soil is poured into it.
Approximately 1 month after planting, seedlings with two leaves will appear, which must be dived.
By the time the soil has completely warmed up, and the seedlings are sufficiently strengthened, they are planted in open ground.
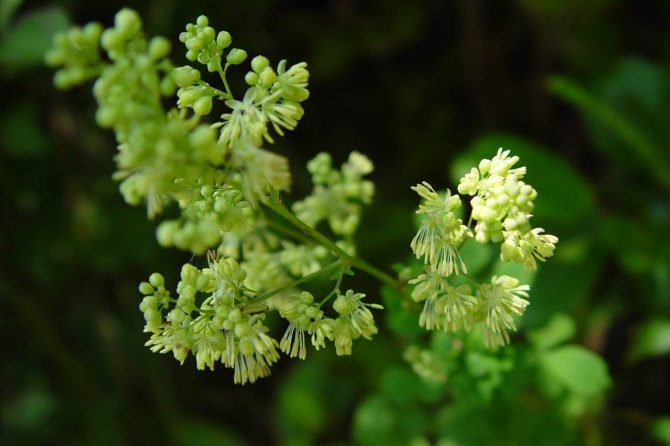


Blooming basil flowers
About planting a plant
In southern regions with sweltering sunshine, Basil is planted along with tall crops that shade the bush during the day. You can plant Basil by the fence or the wall of the building. Crushed residues of dry grass, rotted plant residues are used in the form of bedding, mulching material.
To preserve moisture, the root zone is cultivated (loosening) to a shallow depth and ennobled with organic fertilizers. The landing pit is prepared in advance - it has a round shape. In areas with depleted soil, drainage material is laid on the bottom from fragments of broken brick, gravel, and a layer of fertile soil is covered.
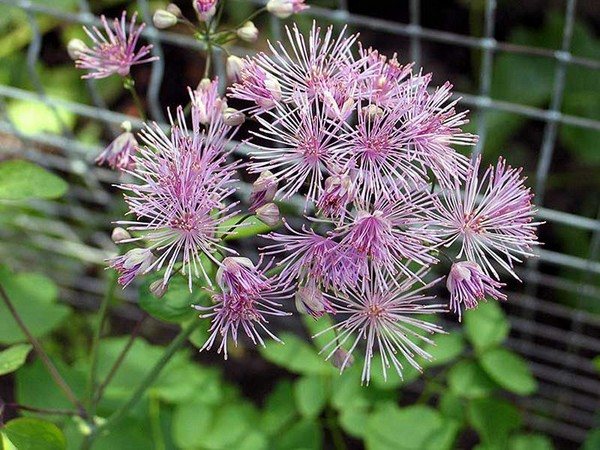


You can plant a Basil against a wall or fence - this can provide shade, besides, such plantings look very beautiful
Important! The culture from the container is placed in a hole and fertile soil is added. Watering is carried out with a solution with a rooting agent.
For fertile areas, the size of the pit should slightly exceed the volume of the root system (volume of the container). When landing in heavy soil, the pit is prepared 30 centimeters more than the volume of the container block. For rocky soils, a pit is prepared, significantly exceeding the size of the root system. It is also necessary to prepare a place for the placement of roots and development during the growing season, therefore they construct an "underground container" and fill it with a fertile mixture with organic elements. Thanks to this, the Basil will actively develop and bloom luxuriantly.
Basil
In the wild, it is found in light forests and meadows in Europe. The height is up to 150 cm. Its leaves are similar to the leaves of the catchment. Blooms in early summer. There are varieties and hybrids with large inflorescences and more varied colors, including apricot and yellow. However, the wild species also stands out for its grace and beauty, and therefore is quite attractive. It began to be grown in gardens in the first half of the 18th century. The leaves of this species of basil begin to grow when the night spring frosts stop, so they almost never freeze in the spring. Basil blooms in late June - July for 30-40 days. The flowers are fragrant, bees and bronze beetles are constantly rustling in them. The inflorescences, soaring up, do not stand very firmly on an elegant, but too long leg, so they should be tied up - otherwise they may fall under the influence of rain and wind, which are not uncommon during flowering.
There are other types of basilists that came from China, Japan, Siberia, the Mediterranean, North America, but they are extremely rare in gardens.
Look at the photo of the varieties of the basil flower, the description of which is given above:
General description and characteristics
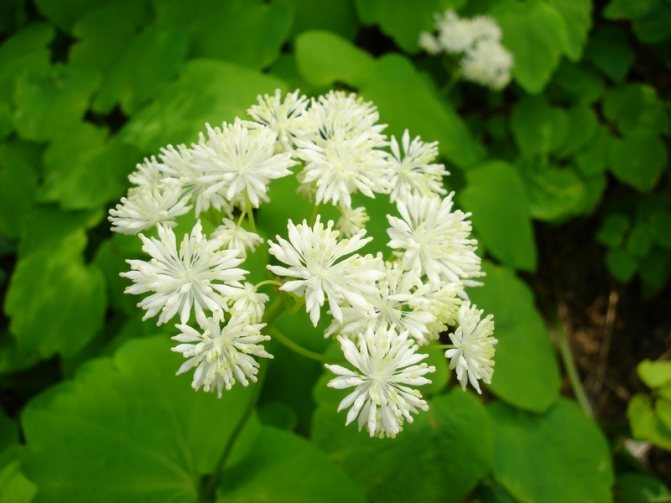
Basil filamentous is a species of the genus Basil of the buttercup family. Plots are decorated with it, it is the shortest of all types, its height is up to 0.15 - 0.25 m.It has a straight, smooth stem, a long tuberous rhizome. Leaves of 2 types: basal leaves are ovate, 6.5 - 9 cm long, cordate at the base, 3-lobed along the edge; stems are simple, ovate, oppositely located.
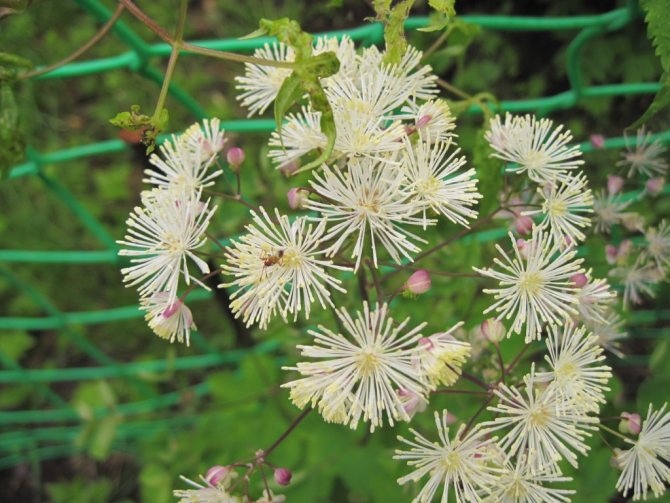


Basil of the "filamentous" species
The flowers are white, small. They are compactly concentrated in corymbose panicles 1.5 - 5.5 cm in diameter. After the buds open, the sepals of the flowers crumble, only long (5-8 mm) stamens remain.
The filamentous basil blooms from mid-May for almost a month. At this time, it smells quite strong, bees willingly fly to the aroma, therefore it is considered a good honey plant. After the end of flowering, the fruits of the basil are formed - achenes on thin petioles.
This plant is perennial, therefore it can grow without problems for 6-7 years on the spot. Some specimens differ in that they can grow longer - up to 25 years, but this is the maximum.
Basil in the culture of gardening
As an ornamental plant, the basil is known to gardeners since 1720. Unfortunately, history has not preserved the name of the first of them, who was able to discern a beautiful element in a wild poisonous plant, familiar only to medieval healers, that could serve as a decoration for any garden, but other breeders took up his initiative. To date, many artificially bred varieties of basil are known, among which the most popular are:
- Album. Tall variety up to 90 cm high with white flowers.
- Thundercloud. It has an average height of about 75 cm, flowers of deep purple color and purple stamens.
- Dwarf Purple. One of the smallest varieties, up to only 45 cm in height. The flowers are distinguished by a beautiful mauve color.
- "Black Stockings" is an amazing variety that has not only unusual lavender flowers, but also dark stems. It belongs to tall varieties of basil and has a height of 1.25 m.
- "Purpureum" from 60 to 90 cm high with purple flowers.
- Perfume Star. A bit like "Black Stockings" lavender flowers, though with a pinkish tint. Shrub height - up to 1 meter.
There are also varieties with dark red and white-purple flowers.
Folk medicinal use
Even if you are not a hereditary "medicine man of the globe", but only a person interested in folk medicine, you will surely be attracted by the healing properties of the basil, known since the times of the ancient Slavs. It is known that it contains many useful substances: alkaloids, vitamins, coumarins, flavonoids, phenol carboxylic acids, and in fruits - some fatty acids and fatty oil. Basil is used in folk medical practice as a means that:
- lowers fever.
- soothes pain.
- is a good laxative, diuretic and sedative.
- heals wounds and stops bleeding.
- possesses hypotensive, anti-inflammatory, antiseptic and antibacterial action.
Apply infusion and decoction of basil both externally and internally. Inside, it is used for the following diseases and disorders:
- jaundice.
- diarrhea.
- malaria.
- gastrointestinal diseases.
- liver disease.
- various female ailments (uterine bleeding, painful menstruation, some gynecological diseases).
- nervous diseases.
- epilepsy.
- dropsy.
- pulmonary tuberculosis.
- hypertension and rheumatism.
Almost all parts of the plant are used as external medicines.
- a decoction of leaves - for skin abscesses and diseases.
- root preparations - for edema and ascites, and an infusion of them - as poultices and compresses for joint pain.
- fresh crushed leaves - in the treatment of skin diseases, purulent wounds and diaper rash between the toes. Leaves, ground to the level of gruel, are applied to the affected areas.
However, you should always remember that basil is poisonous and toxic due to the presence of the cyanogenic compound linamarin in it, so it should be used very carefully, having previously consulted with your doctor. Self-medication without certain knowledge is never particularly productive, but in this case it is also fraught with death. In case of an overdose with drugs based on basil, the following symptoms of poisoning occur:
- nausea.
- stomach ache.
- vomiting.
- allergy.
- liver dysfunction.
In the event of such symptoms, it is necessary to flush the stomach, take activated charcoal in a dosage corresponding to the weight of the victim and call an ambulance.
The basil grass is harvested during its flowering, cutting off the tops of the stems 30-35 cm long with a sharp knife or scissors, then tied in bunches and hung or laid out in a thin layer under a canopy or in a ventilated room or dried in a dryer at a temperature of +40. After the grass is dry, it is put into cloth bags, tied tightly and stored. In this way, the basil can be stored for no more than 2-3 years.
The roots of the plant are harvested in the fall: they are carefully dug up, quickly washed in running water, finely chopped and dried in drying chambers. You can try to dry them in a natural way, but you need to make sure that they are not damp. After drying, they are packaged and stored in the same way as dried grass. The roots are stored for no more than two years.


































