Home »Garden and vegetable garden» Vegetable garden »Vegetables
Vegetables
Olga Polyakova
1 comment

Zucchini
Zucchini is a type of common pumpkin. It is a vegetable with elongated fruits of the most varied colors. Zucchini fruits can be eaten in a variety of ways - from raw to preservation. Planting and caring for zucchini is a very rewarding experience, since the harvests obtained more than pay off the costs of buying seeds and growing them. Several kilograms of fruit can be obtained from one plant.
- Description of the plant
- Outdoor cultivation
- Pick-up location
- Seedless cultivation
- Growing with seedlings
- Outdoor care
- Diseases and pests
- Diseases
- Pests
- Growing in a greenhouse
- Growing conditions
- Plant care
- Conclusion
See also: Growing seedlings at home: tomatoes, cucumbers, peppers, eggplants, cabbage, strawberries and even petunias. All the subtleties of this issue
When to sow zucchini outdoors


Zucchini can be easily grown from seed by sowing directly into the open field. It is important to take into account the weather conditions of the region.
- For seed germination, a temperature of + 12-15 degrees is required. In the southern regions, the heat comes already in April.
- In central Russia, such weather sets in by the end of the first week of May. If the spring is cold, sowing is carried out 1-2 weeks later.
- In the Leningrad Region, the weather is cunning and unpredictable, there may be unexpected frosts, so it is better not to rush to plant zucchini with seeds in open ground. Postpone this procedure until the end of May.
- Around the same days, you can sow zucchini in the Urals, or do it a little later - in early June.
- In Siberia, sowing is carried out not earlier than the second decade of June. After all, here even in the first month of summer it sometimes snows.
Frost can kill tender, freshly hatched sprouts. To protect crops, residents of cold regions are advised to use temporary shelters.
Variety selection
It is very important to choose the right seeds. An inexperienced gardener can get confused by the variety of varieties of zucchini. The varieties differ in shape, color, taste, skin thickness.
According to the ripening rate, all varieties are divided:
- early ripening;
- mid-season;
- late ripening.
On the territory of cultivation for cultivation:
- in outskirts of Moscow;
- in the Urals;
- in Siberia.
There are many varieties, so before choosing seeds, you need to decide on some criteria. The selected variety must correspond to the region where it will be grown, the climatic zone. If you pay attention to this, then this culture will delight you with a bountiful harvest. It is difficult for a beginner to navigate, so it is worth listening to the opinion of professionals.
List of varieties for open ground
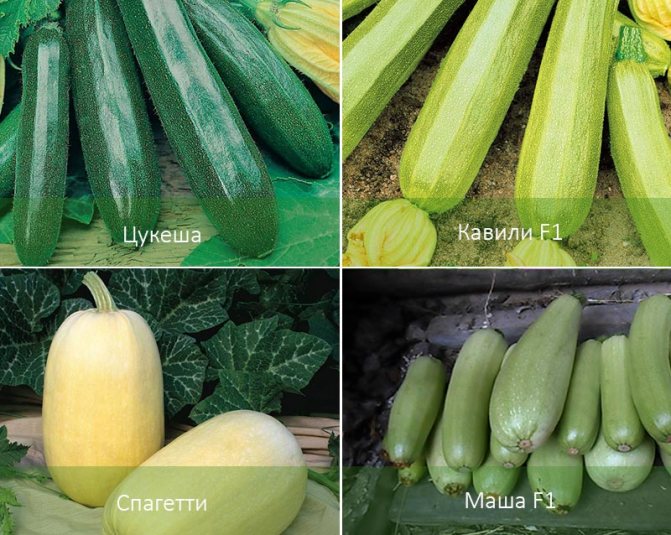
Cavili F1 - hybrid, belongs to the Dutch selection. Suitable for outdoor cultivation. This is an early variety, its fruits are in the form of a cylinder, light green in color. It is recommended to plant in May, early June. Ripens in forty days. It is resistant to diseases, does not outgrow. Not more than 22 cm long. Weight is about 350 grams.


Iskander F1 - also a hybrid representative of the Dutch selection. It is resistant to low temperatures and can be sown in the ground as early as April.They grow up to 20 cm long and weigh up to 600 grams. The color is light green, the skin is thin, the pulp is juicy. Aging period 40-45 days.


Ardendo 174 F1 - a variety of Dutch origin, clavate and light green with dots in color. Average weight 600 grams. Ripens within 45 days. Can be planted in May. Resistant to temperature extremes, but requires abundant watering, loosening the soil and top dressing.


Aral F1 - also a hybrid, gives an early harvest. It is recommended to sow in May, it is not afraid of frost. Fruits are light green in color and weigh up to 800 grams. Formation period - 45 days. Abundant watering is required.


Tsukesha - early maturing and high-yielding variety. Dark green with small specks of color, grows up to 30 cm and weighs 1 kg. Sow in open ground in May. Ripens in 45 days. It has tender and juicy flesh.


Belogor - a hybrid of high productivity. The term of formation is 45 days. It is resistant to cold, seeds can be sown in April. It has a greenish white color and weighs up to 1 kg.


According to professionals, these varieties are most suitable for mid-latitudes, are distinguished by high yields and quick ripening.
How to properly grow zucchini from seeds in the open field
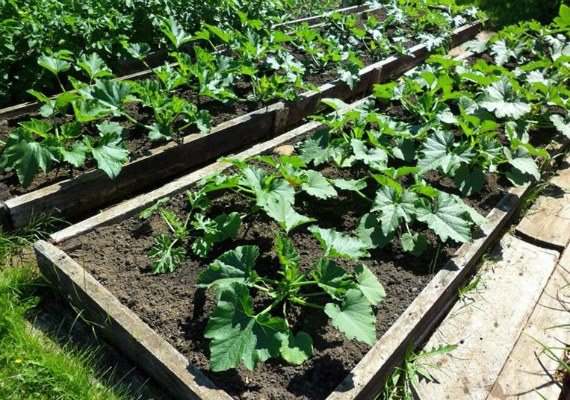


Zucchini do not have such a long growing season, which allows them to be grown using seed sowing in open ground, even in short summer conditions. But this does not mean that you can cancel the preparatory activities.
Seat selection
Zucchini love warmth and sun, in such conditions they ripen faster. Choose the most lighted area for them, sheltered from the wind. It will be good if the garden bed is illuminated by the sun from the south, and tall plants, for example, sunflowers, corn, protect it from the north.
Zucchini grow best on clay, sandy loam and chernozem soil with a neutral acidity index. Clay, peat soil and places with a high groundwater table are not suitable for them.
For this culture, warm beds are often used. This option is especially recommended for those summer residents who have damp and heavy soil on the site. You can also see the planting of pumpkin crops on a compost heap, decomposing organic matter warms the roots of the squash, and they grow well.
On a note! Do not even try to plant zucchini in partial shade in the middle lane or northern regions. Plants will set few fruits, the bushes will be very elongated. This sad experience has already been gained by many gardeners who have decided on a similar experiment.
Garden bed preparation
The garden for planting zucchini begins to be prepared in the fall. The soil is dug onto the bayonet of a shovel, cleaned of the remnants of rhizomes, fertilized with compost or humus, and a balanced mineral fertilizer is applied. You can sow siderates in the garden in early autumn, then mow them and dig them up along with the ground. This technique will not only increase the fertility of the soil, but also improve its structure.
If for some reason it was not possible to prepare the land in the fall, do it in the spring:
- loam will need to be fertilized with compost and superphosphate;
- sandy soil will need to be weighted with a mixture of compost and humus, as well as add ash and dolomite flour;
- chernozem is fertile in itself; as a fertilizer when sowing, a little ash and humus is put in the hole.
If there is a need for a warm bed, it is better to make it raised. To begin with, a box is built of boards or slate, then it is filled with layers of various organic materials. It can be sawdust, tops, weeds, food waste. You can add some manure or poultry droppings. Each layer is watered with water, raw organic matter quickly rotted. The soil is poured on top. Such a bed is prepared in the fall, after harvesting.
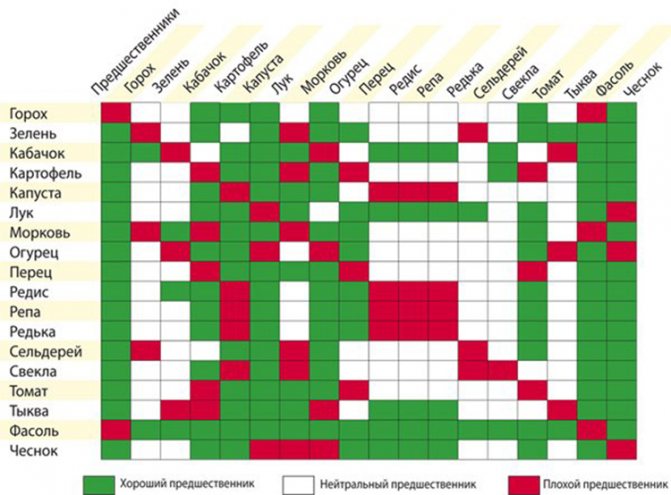
Crop rotation


Experts recommend planting all crops on the site in compliance with the rules of crop rotation.This allows you to maintain soil fertility, avoid disease outbreaks and reduce the number of pests on the site. Crops planted after each other should not belong to the same family.
It is best to grow zucchini after eggplant or tomato. Potatoes are also considered a good predecessor, but after that you need to apply increased doses of fertilizers with phosphorus and potassium.
You can place zucchini in the garden bed after legumes, cabbage, carrots and corn. Beets and various greens are considered neutral precursors to squash.
It is not recommended to plant this crop after related plants (squash, melons, pumpkins) and the squash themselves. Failure to follow this rule increases the risk of disease manifold. Zucchini can be returned to its original planting site only in the 5th year.
Seed preparation before sowing


Zucchini seeds are large, if necessary, they can be easily sorted by hand by removing small and flat seeds. Seed material emerges without problems, the process can be accelerated by preliminary germination. If you are using seeds of unknown origin, pickle them in a weak solution of potassium permanganate, holding for 20-30 minutes. Purchased planting material does not need such a procedure.
For growing zucchini in a cold climatic zone, the seeds can be hardened by wrapping them in a damp cloth and placing them in the refrigerator for a day. Germinate seeds on a platter between two wet wipes, which need to be sprayed with water from time to time, preventing them from drying out. From above, you can cover the saucer with foil. As soon as the tails of the sprouts appear several millimeters long, you can start planting. Do not wait for the sprouts to grow long, they are easily damaged.
Sowing
Wells for sowing zucchini are made at a distance of 40-50 cm. Each of them is preliminarily spilled with water, after which 1-2 seeds are placed. A gap of 70 cm is left between the rows.
There is also a slightly different landing method: 4-5 seeds are planted in a circle in a depression at a distance of 30-40 cm from each other. The holes are made with an interval of 1m.
This method of growing zucchini is especially popular in regions with hot climates, as overgrown bushes cover the ground with a solid carpet, which prevents moisture from evaporating. The seeding depth is 3-4 cm. Each seed must be placed with an edge. When planting 2 seeds in one hole, the strongest plant is left in the future.
Site selection and soil preparation
We choose a place for zucchini sunny, on the south or south-west side, sheltered from the wind, with a low occurrence of groundwater, with a neutral or slightly alkaline soil reaction.
We prepare the soil on the site in the fall: we dig a shovel to the depth of the bayonet, adding 1 sq. meter of 10-15 kg of compost, 50-60 g of superphosphate and a handful of wood ash.
Forerunners: good and bad
Good predecessors for zucchini are: peas, tomatoes, parsley, lettuce, cabbage, onions, garlic, radishes, carrots, potatoes, green manure.
In areas where pumpkin plants grew (all types of squash, cucumbers, squash, pumpkin), squash should not be grown for at least three years, otherwise the risk of disease typical for pumpkin plants will be too high.
What can be planted next to zucchini - a favorable neighborhood


For protection from the wind, you can plant corn next to the zucchini, and it will be appropriate to plant greens, various types of salad, and early cabbage directly on the same garden bed. When these crops are harvested, the squash will continue to develop and grow freely. This vegetable can also be combined with legumes, onions, beets.
It is recommended to plant nasturtium, calendula, marigolds in the aisles. These flowers are repellent, repelling pests with the scent of essential oils.
On a note! Do not plant squash, pumpkins, cucumbers, melons at close range - these plants can get dusty with zucchini and then the crop will be spoiled.
Crop rotation and compatibility with other crops
Accelerated growth and large fruit production is facilitated by the selection of suitable precursors. It is better to plant bush squash after cabbage, legumes, tomatoes, onions and potatoes. It is not recommended to grow zucchini after pumpkin and any kind of cucumber.
The rules of agricultural technology for growing zucchini also imply the provision of crop rotation. It is forbidden to grow zucchini on the same land for two seasons in a row. Simultaneously with zucchini, pumpkin culture should not be placed in the garden.
It is allowed to grow zucchini in different parts of the garden, using small unoccupied areas. It is important that such areas are located in a lighted and warm place.

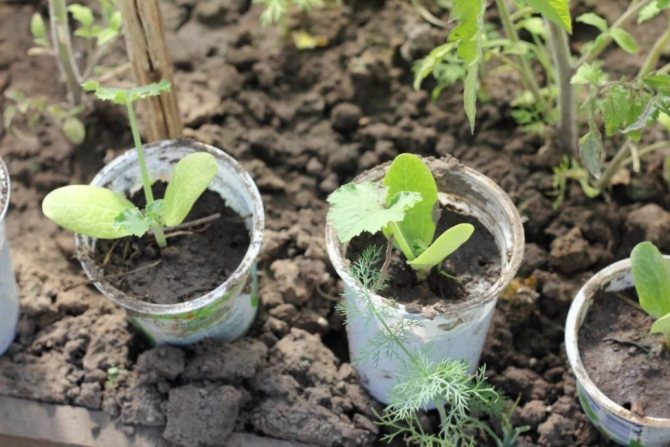
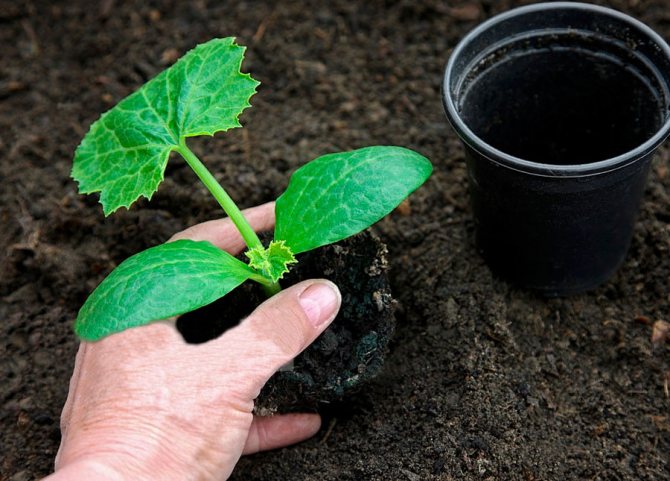
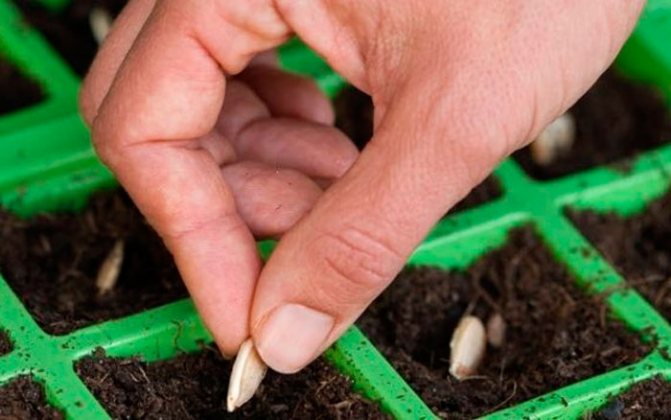
Growing zucchini through seedlings


Growing zucchini through seedlings allows you to harvest vegetables 2-3 weeks earlier than usual. Sowing should be done in separate containers, zucchini do not tolerate picking well. The cups should have a volume of 0.5 liters if you want to grow seedlings at home for 25-30 days.
In principle, you can transplant seedlings into the ground even at the age of 2 weeks. In this case, the seedling containers may be smaller. The ideal solution would be to use peat pots, they will do without damaging the root system of plants.
The seeding procedure is as follows:
- Pre-germinated seeds are planted in cups one at a time.
- It is better to plant dry seeds in the amount of 2-3 pieces for each container, in the future they leave one strong plant.
- Immediately after sowing, the soil is watered abundantly and the seedlings are placed in a warm, bright place.
Zucchini shoots appear quickly, after just a few days. As soon as the sprouts appear above the surface of the soil, it is advisable to reduce the temperature in the room to 18ºC, otherwise the seedlings will be strongly stretched. The sowing time must be commensurate with the possibility of planting in the ground. Please note that you can keep zucchini seedlings at home for no more than a month.
The seedlings do not require special care. Zucchini grows well, quickly turning into powerful plants. Seedlings need to be watered regularly and fed from time to time.
For irrigation, use warm, settled water. An approximate soil moistening schedule is once every 3-5 days.
For a month, seedlings will need 2 feeding.
- The first time they are fed a week after germination.
- Secondly - after the same period of time.
Any complex mineral fertilizer is suitable for this purpose.
Seedlings are relocated to the beds in accordance with the climatic characteristics of the region. Usually squash and tomatoes are planted in the ground at the same time. By this time, warm weather with temperatures above 10 ºC should be established outside. If a cold snap has come, and the seedlings have already reached the age of one month, they are still planted in the ground, protecting them from the cold with a temporary shelter.
Tips from skilled gardeners:
- planting seedlings in the right place (open area, suitable soil);
- ensuring regular watering (water consumption per square meter is not less than 30 liters of water);
- regular feeding (3 times at a certain time) contributes to a good fruit set, an increase in their number.
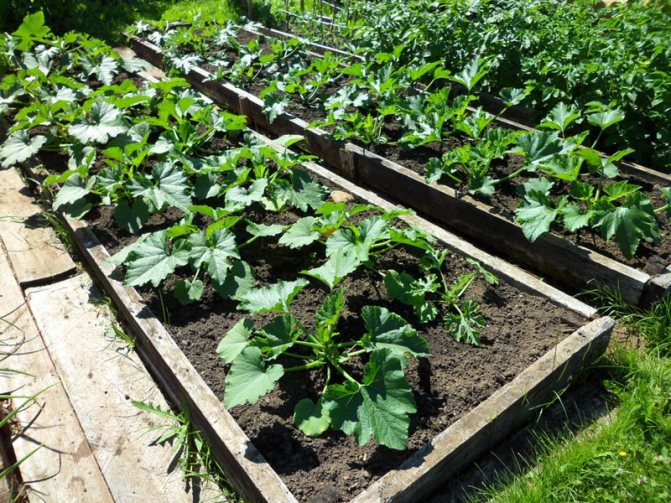
Growing zucchini in the open field requires the implementation of simple recommendations for planting, care, collection of ripe fruits. If you follow all the tips, you can grow a decent harvest in your home garden.
Previous
Zucchini diseases and pests of zucchini: description and methods of treatment
Next
Squash trimming: when and how to remove it
Outdoor zucchini care
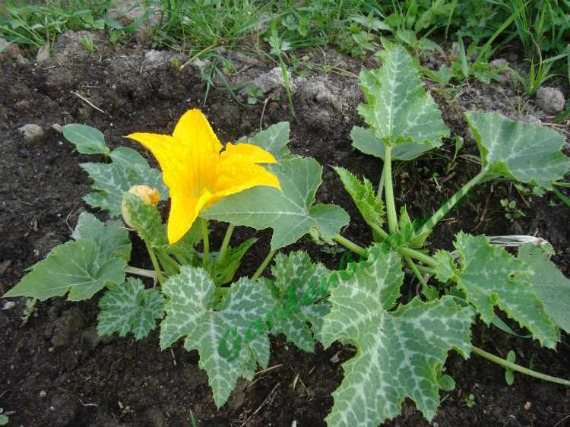


Caring for zucchini consists of simple activities that even a beginner can handle. However, you will still have to pay attention to an unpretentious culture.
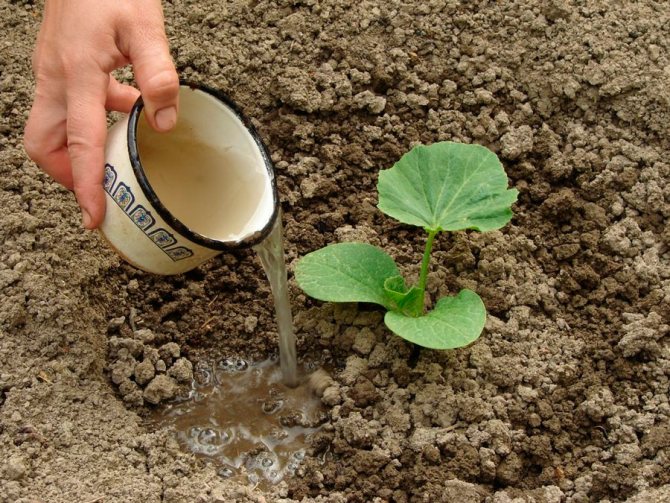
Watering
At first, the plants are watered gently, in small doses, until they get stronger. It is advisable to pour water for irrigation into a barrel in advance for settling and heating. Lack of moisture can be easily noticed by the leaves of the zucchini, which become lethargic and drooping. The earth must be shed to the full depth of root growth (30-40 cm). Due to poor watering, the zucchini will form small fruits. After the irrigation procedure, the soil must be loosened and weeded.
Top dressing
For feeding zucchini, mineral and organic fertilizers are used, alternating between them.
You need to feed the plants three times:
- at the stage of budding;
- during fruit setting;
- during active fruiting.
Before flowering, nitrogen fertilizers are used (for example, urea in the amount of 1 tablespoon per bucket of water). 1 liter of nutrient solution is added under each bush. For the next feeding, you can use mullein solution or nettle infusion. The next time a complex mineral fertilizer is used.
Pollination
Since zucchini are grown outdoors, there should be no problem with pollination. You can additionally attract bees and other insects with foliar feeding. For spraying zucchini, use a solution prepared from 1 tsp. honey in a glass of water. The sweet smell coming from the leaves will act as bait.
This technique will significantly increase the amount of ovary on plants. To make it easier for insects to access flowers, it is advisable to break off especially large leaves that thicken the bush.
Growing in bags
Many gardeners do not want to engage in the farming of vegetable marrows, because this culture grows, taking up a lot of space on the site. Breeding in bags can be a way out of this situation.
This clever method not only saves space, but also allows you to grow beautiful, attractive fruits.
Technology:
- Take a regular flour or sugar bag and punch a few small holes in the bottom of it.
- Place any organic waste on the bottom of the future "bed": fallen leaves, straw, thin branches, etc.
- A layer of soil and sawdust should be poured on top of the organic content. Moisten the soil in the bag if necessary.
To create a greenhouse effect, the bags can be covered with plastic on top. In this case, it is necessary to regularly ventilate the seedlings until they gain enough strength to grow on their own.
Care involves regular moistening of the soil, and the zucchini themselves need to be treated with remedies for diseases and pests.
During the ripening period, the zucchini do not lie on the ground, but are located near the bag, so there are few defective fruits.
Prevention of diseases and pests


Due to improper care, zucchini can be sick with bacterial and fungal diseases. Most often they are affected by powdery mildew, bacteriosis of fruits, root rot.
To reduce the risk of diseases, it is necessary to pickle the seeds before sowing, plant zucchini according to the recommended scheme, process the bushes at the initial stages of growth with a 1% Bordeaux mixture, and fight pests in a timely manner.
To scare off whiteflies, spider mites and aphids, squash is sprayed with a solution of laundry soap with the addition of copper sulfate. It is undesirable to use chemical insecticides at the fruiting stage, during this period biological preparations are used (Fitoverm, Bitoxibacillin, Trichodermin, Alirin B).
How to determine the maturity of zucchini, when to remove it from the garden


First of all, pay attention to the ripening time of the vegetable, due to the variety. This information can be found on the seed package. Typically, the grower characterizes the ripe fruit.
In addition, the fact that the zucchini is ripe can be determined visually. Its peduncle becomes very stiff, partly stiff. If you are going to remove the fruits for long-term storage, wait until their crust becomes hard. Taking a ripe zucchini in hand, and knocking on it, you can hear a dull sound.
No one will prevent you from picking young zucchini 15-20 cm long for eating in the middle of summer.If you are going to keep the fruits until winter or use them to prepare canned vegetables, you need to plant late varieties and harvest in 100-120 days from the moment the shoots appear ...
Description of zucchini and an overview of varieties
Zucchini forms a powerful bush up to 70 cm high, sometimes more, on which oblong yellow, dark green or white fruits grow. Only 7-14-day-old young fruits are eaten. Older fruits are much larger, but they become tough and practically unsuitable for food. They are used to feed livestock, but their feed value is low, because the fruits of squash of any age are low in calories. But this quality makes them simply irreplaceable in the diet of a person for losing excess weight.
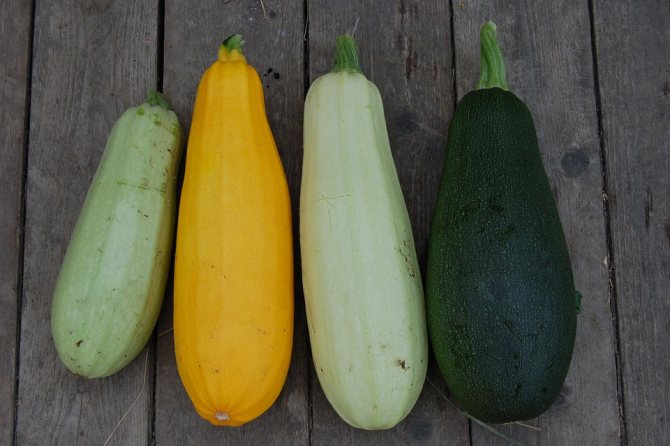


Four different varieties of zucchini
100 g of zucchini gives only 27 kilocalories. Of the nutrients, it contains the most potassium - 240 mg. There is iron, organic acids and a set of vitamins of groups C, PP, B and carotene.
Self-pollinated zucchini varieties
Used for growing indoors, in the absence of pollinating insects:
- Cavili.
- Parthenon.
- Jellyfish.
Early varieties
- The ball.
- Tsukesha.
- Aeronaut.
Late varieties
- Calabaza.
- Spaghetti.
Old varieties
- Gribovskys.
- Odessa.
- Kuldzhinskie.
- Greek.
How to properly collect and prepare your zucchini seeds


To collect seeds, you should select healthy and strong plants in advance. This is done 2 months after the appearance of the ovaries. On such bushes, no more than two fruits are left, each of which must fully comply with the characteristics of the variety, have a healthy and beautiful appearance.
Plants are cared for as usual, with the exception of top dressing. For these specimens, the dose of nitrogen fertilizers is reduced by 1.5-2 times.
The seeds can be harvested after the crust has completely hardened, this stage can be easily determined by running your fingernail over the zucchini. There should be no trace left on the skin of the fruit. The color of a fully ripe vegetable marrow becomes bright. The fruit is removed and allowed to lie down for 2-3 weeks in a dry ventilated room.
If you use seeds from not fully ripe zucchini for planting, they will have poor germination. After waiting for the allotted time, the fruit is cut into pieces and the seeds are taken out by hand. You cannot rinse them. Drying seeds is best done outdoors, but not in direct sunlight.
Experienced summer residents recommend removing seeds from fruits in winter, and then drying them at home at room temperature.
On a note! Seeds should not be overheated, as well as left damp, so that they do not lose germination.
Growing on a compost heap


Growing on a compost heap will yield a rich harvest
A compost heap is a garden bed, which is based on all types of organic fertilizers that can decompose under the influence of certain microorganisms. Use dry mowed grass, fallen leaves, overripe straw, etc.
A rich harvest is obtained on a properly formed compost heap.
You need to take care of zucchini in the same way as for their congeners, which grow in open space.
The soil in the compost pit is always a few degrees higher than in normal soil, so it is excellent for thermophilic crops, in particular for squash.
Zucchini storage methods
It's great if you have a cool basement for storing zucchini. If necessary, they can be stored in winter and indoors.
For long-term preservation of fruits, humidity up to 85% and low temperature (5-10ºC) are needed. It is better if the zucchini lie in the dark, without touching each other.
Please note that freezing will spoil the fruit. Only pumpkins can be stored in the store next door. Joint storage with other vegetables negatively affects the quality of zucchini. The fruits can be laid out on a plank scaffold in one row with some interval, stored in a suspended state or placed vertically (the stalks should be facing up).
For better preservation, you can wrap each fruit in newspaper or cloth. At home, you can store zucchini on a glazed and insulated balcony, putting them in wooden boxes or cardboard boxes. If the balcony is open, place the zucchini on the floor near the balcony door, where it is cool enough.
Read more in the article: Zucchini caviar for the winter - the best recipes
Read more in the article: Zucchini casserole in the oven - recipes with photos
Growing in winter


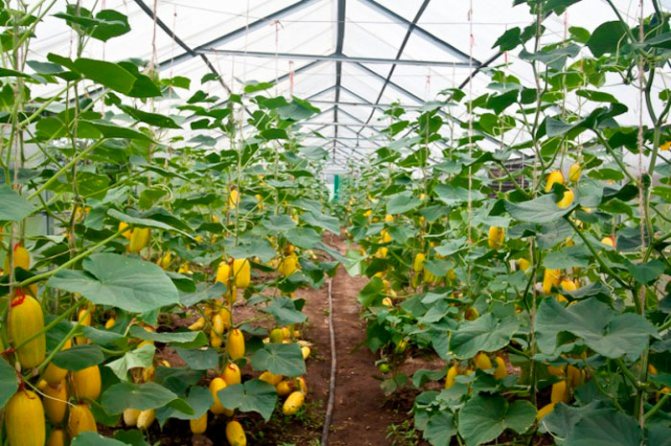
Zucchini can be grown in a greenhouse in winter
It is possible to plant seedlings in a greenhouse already in winter, and then at the beginning of spring there will already be a full harvest (a polycarbonate greenhouse is perfect).
The yield of the crop will depend on the quality of the soil.
It is better to plant from already strengthened seedlings - so the plants will sooner take root, and begin their active development.
Recommendations
- Greenhouse zucchini do not require the introduction of nutrients into the soil; those that were used before planting will be enough. Otherwise, this will lead to too active growth of the ground part of the plant, and, as a result, a small number of ovaries and fruits.
- In order for the zucchini to give the maximum number of ovaries, they need pollination. In greenhouse conditions, this is done by the gardener.
- It is better to pick greenhouse fruits at the earliest stage of ripeness. This way you can extend the fruiting period of plants and increase yields.