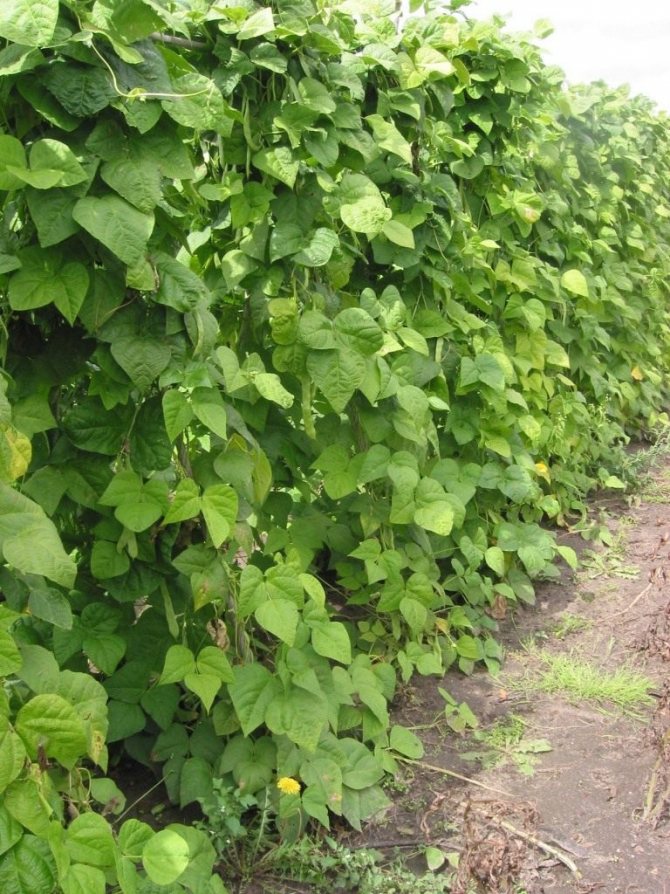
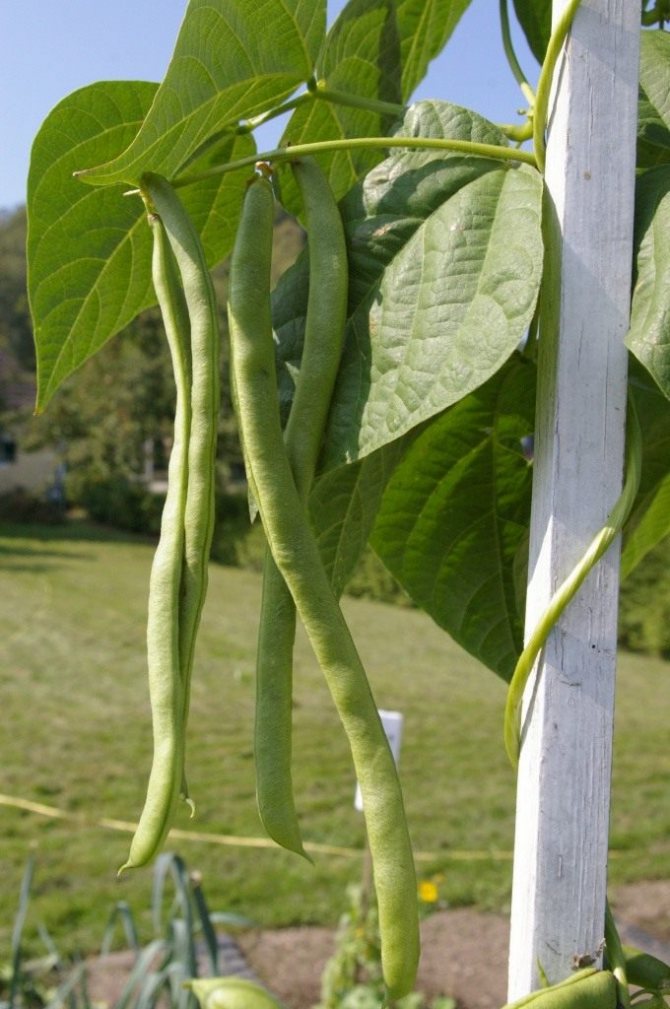
Green beans are not yet very common, you will not find it on every table, but those who tried it were able to appreciate it. Previously, it did not attract owners of household plots, and it was possible to find beans in pods only in supermarkets at a rather high price. Now planting vegetables in the garden is approaching the popularity of crops such as carrots, radishes, and even the obligatory guest of any summer cottage - tomato.
The seeds of green beans are offered for free sale, which means that now everyone has a chance to get an irreplaceable set of vitamins, micro and macroelements in combination with a great taste of new dishes for themselves.
Characteristics and yield
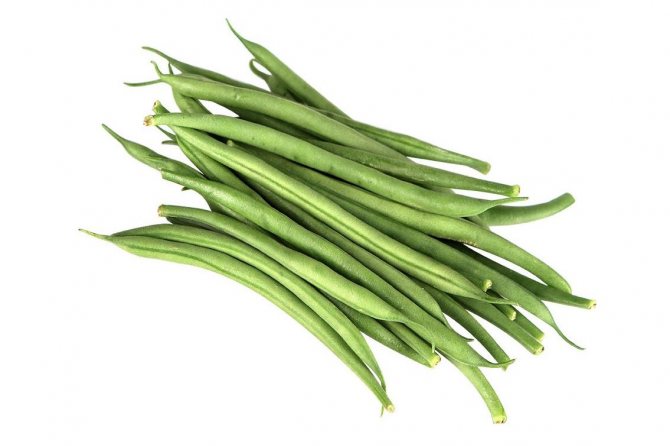
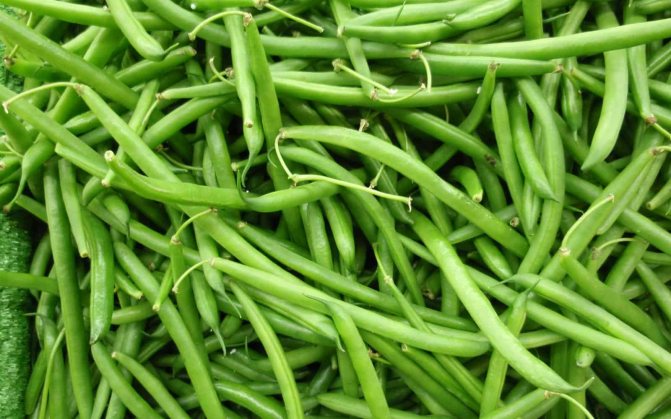
Green beans - a product that is widely used in cooking as a vegetable ingredient in salads, side dishes, first and second courses.
Asparagus beans are a type of green beans. They are long green beans, have softer shells and taste like asparagus.
Green beans are incredibly rich in nutrients and health benefits. This makes beans such a popular product all over the world. It contains vitamins such as: A, C, B1, B2, E.
In addition, green beans contain macro- and microelements:
- calcium; maintains the health and density of bones, joints, nails, hair;
- potassium; contributes to the normalization of the heart rate, and is also recommended for atherosclerosis;
- phosphorus and zinc; necessary for the body to metabolize fats and normalize hormonal levels;
- lecithin, which helps cleanse the walls of blood vessels;
- iron; has a beneficial effect on the supply of nutrients to the brain;
- folic acid; contained in pods and supports reproductive function in women, and during pregnancy it promotes fetal development. Plus, folic acid helps fight depression.
And even in addition to all of the above nutrients, green beans contain a large amount of simple protein and fiber, which improve digestion and cleanse the intestines.
The timing of harvesting green beans begins from the moment the fruits first appear. Green pods can be harvested several times per season. As a rule, the frequency of collection is 1-2 times a week. The number of pods harvested depends on many factors: the variety of beans, weather conditions, fertilizer and soil.
But in any case, by planting several germinated seeds of green beans of any kind, with proper care, even a novice gardener will reap a good harvest, which will be enough not only for the summer, but also for winter harvesting.
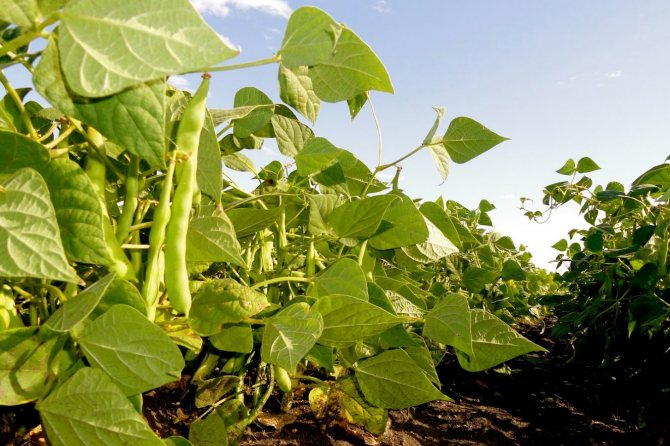
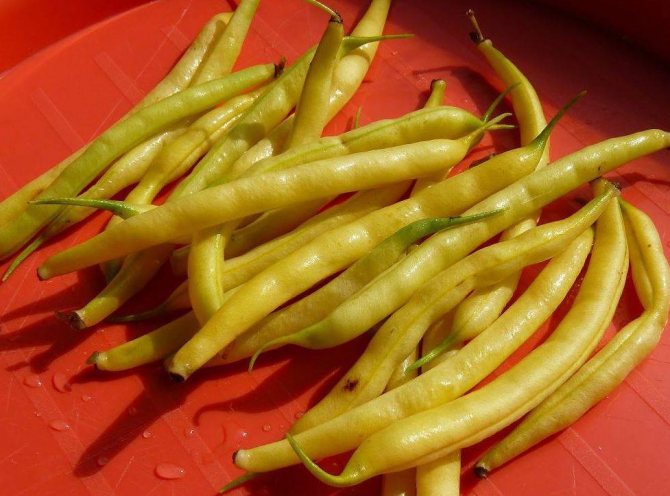
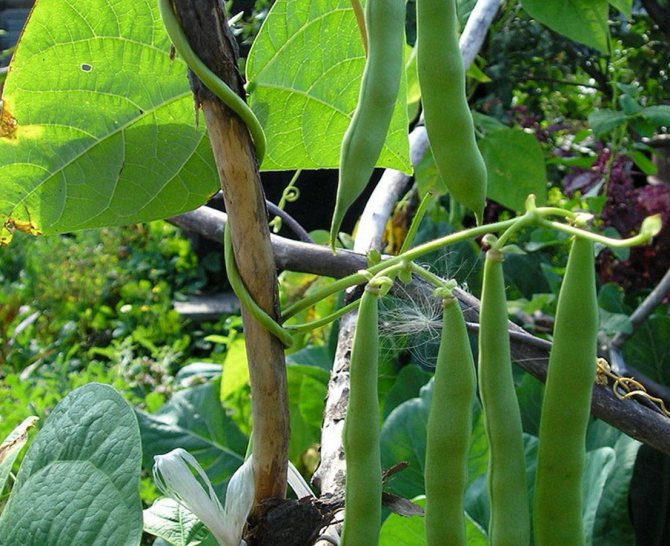
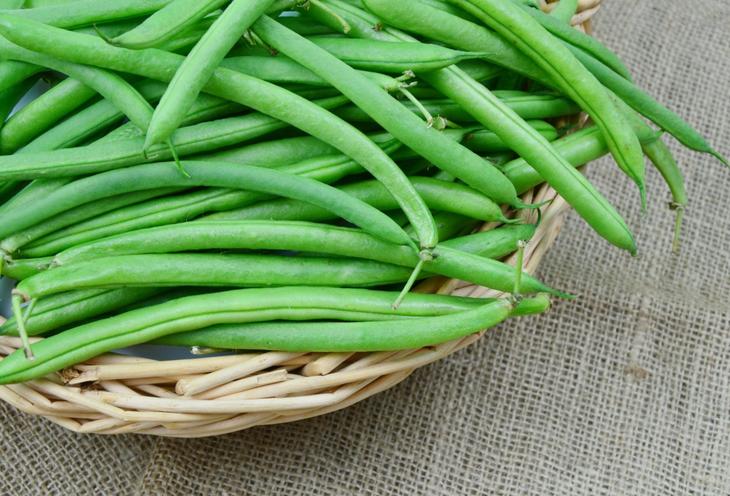
There are many varieties of green beans that vary in size, shape, color, and flavor. On average, the length of the pod ranges from 7 to 15 cm, up to 9 beans ripen in each pod.
In the photo of green beans, you can see what the beans look like in the pods and what different colors can be found depending on the variety. The seeds, respectively, of beans can also have a variety of colors.
Why plant and eat green beans
For 5000 years, mankind has known the value of beans. In America, Egypt, Rome and China, they not only ate it, but also actively used it in cosmetology.Even Cleopatra maintained her beauty by putting on masks made from this protein product. And in Europe, for a long time, beans were grown as a garden decor. And only 2 centuries ago they began to eat it here as well.
Today, scientists have explained to everyone the benefits of beans. It is rich in protein, which is important for building muscle. But there are very few calories in it: only 30 Kcal per 100 g. That is, the product is the most suitable for a healthy diet.

Black Eyed Peas
In addition, the composition of green beans includes vitamins A, C, E and the entire group B. There is fiber, folic acid, carotene, zinc, iron, magnesium, calcium, potassium, chromium. Doctors recommend that beans be included in the diet after 40 years. You need to eat it at least 2 times a week.
Advice. For those who do not know how to cook green beans, you can turn to the recipes for the cuisine of Eastern countries: Armenia, Georgia, Azerbaijan, Turkey and even Japan. It can be fried in batter, served with meat and sauce, cooked soup and even make preparations for the winter.
For those who listen to doctors and eat beans, it will help to improve digestion and heart function. This product facilitates the fight against rheumatism, bronchitis, diabetes, skin diseases and tartar. Beans can even be a sedative for those who get a lot of anxiety and irritation quickly.
The best varieties of green beans
Consider the most popular types of green beans.
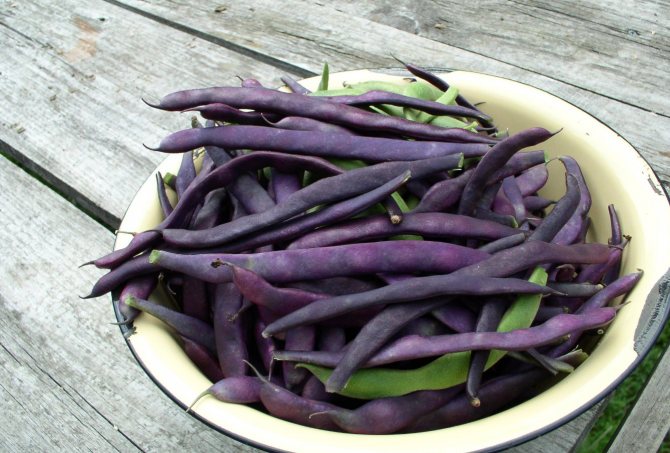
Purple queen
A bushy variety of green beans that combines fruit and ornamental functions. Produces dark purple pods that grow up to 16 cm in length. This bean variety is resistant to many diseases and pests, as well as to adverse weather conditions. Gives a large harvest.
Crane
The variety is small in size, not exceeding 60 cm in height. It is unpretentious and brings a good harvest. Suitable for preparing a wide variety of dishes, as well as for freezing and preserving.
Sachs 615
A bushy early-ripening bean variety that produces large green pods (about 13 cm long). Differs in saturation with a variety of vitamins and nutrients.
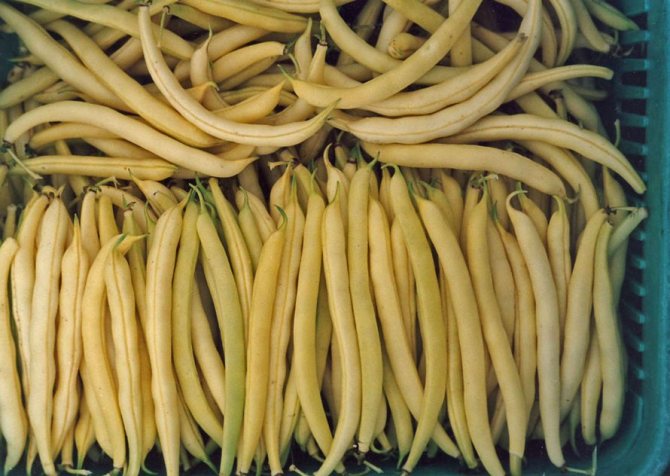
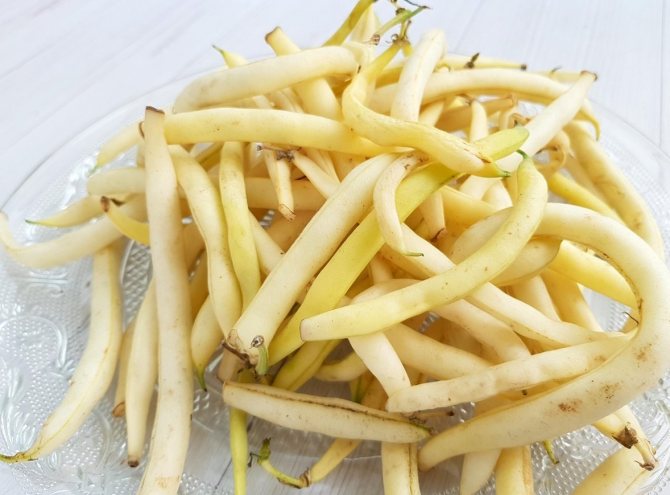
Oil king
An unusual bean variety that bears fruit in yellow pods with a very specific flavor. The growth and development of this variety of beans occurs within two months.
Choosing the right varieties of asparagus beans
Asparagus vegetable beans are divided into 2 groups: American and Asian (vigna).
Representatives of the first group are more common and differ in flat fruits (beans) and pods up to 0.4 m long.
The second group is characterized by cylindrical beans and pods up to 1 m long.
According to the shape of the ground part, the plants are bushy and climbing.
The most popular and demanded varieties of bush asparagus beans are:
1 out of 5


Sachs beans without fiber 615. An old variety of early ripening terms (45-50 days before technical ripeness). The bush is up to 0.35-0.4 m high, pale green curved pods up to 9-12 cm long. Excellent taste, high sugar content.


Asparagus Beans Butter King. High-yielding, early maturing (45-50 days). A neat bush about 0.4 m high. The pods are fibrous, golden yellow, tubular, pot-bellied, up to 20-25 cm long, with a high protein and trace element content.


Vegetable beans Zhuravushka. An early sugar high-protein variety with good yields. A small compact bush grows no higher than 0.5 m. Delicious delicate rounded fruits up to 12-13 cm in size. The ripening period is 40-45 days, there is no parchment layer.


Asparagus beans Allure. Early maturing (55-65 days), disease-resistant variety. A low (0.3-0.4 m) bushy plant with numerous narrow and long (about 12-13 cm) dark green pods. Non-crumbling leaves without parchment layer. High content of vitamins and proteins.


Beans Caramel asparagus. A short bush (45-60 cm), erect with long green tender sugar-sweet shoulder blades. Ripening period from 55 days.
The curly form, in addition to eating, is also used for landscaping and decorating areas.
The most common varieties of curly asparagus beans include the following:
- Harmony. Unpretentious liana up to 3-4 m long, late ripening (65-80 days). Long golden pods (up to 20 cm).
- Green giant. Liana-like plant up to 3 m long with delicate sugar green pods about 22 cm in size, which do not contain fibers and are not covered with parchment. The ripening period does not exceed 55 days.
1 of 3


Purple Queen (Purple Lady). Low liana that does not require support (up to 1.5 m). Fruit ripening period is average (55-60 days). Dark purple parchmentless beans up to 15-17 cm long.


Beans asparagus Tenderness (Sissy). Erect, curly, medium-late ripening (56-58 days) variety 1.3-1.5 m high. Golden wide fruits (blades) are devoid of fibers and parchment layer.


Beans Barlotto asparagus. Strong liana up to 3-3.5 m high, reddish color. First, bright green pods 12-14 cm long and up to 1.5-2 cm wide with large beans, eventually acquire a marbled dark red pattern. The growing season is medium late (up to 55-60 days).
Chinese asparagus beans - vigna - are gradually gaining popularity among vegetable growers.
The most commonly cultivated varieties are:
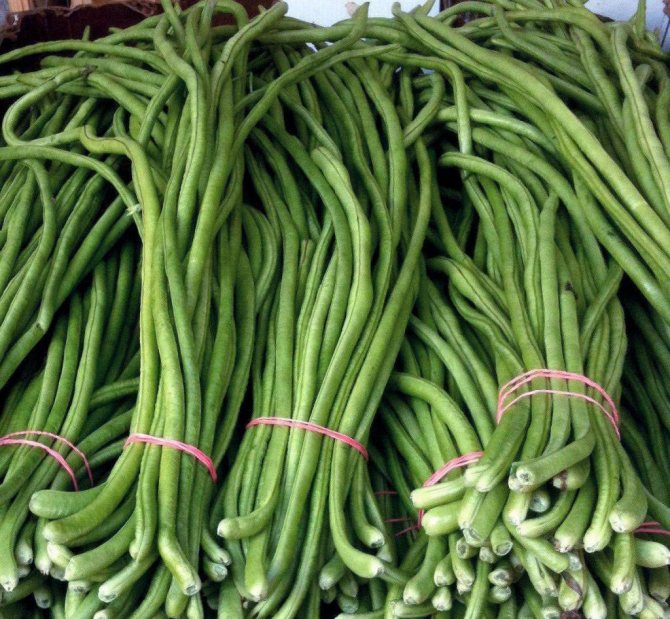


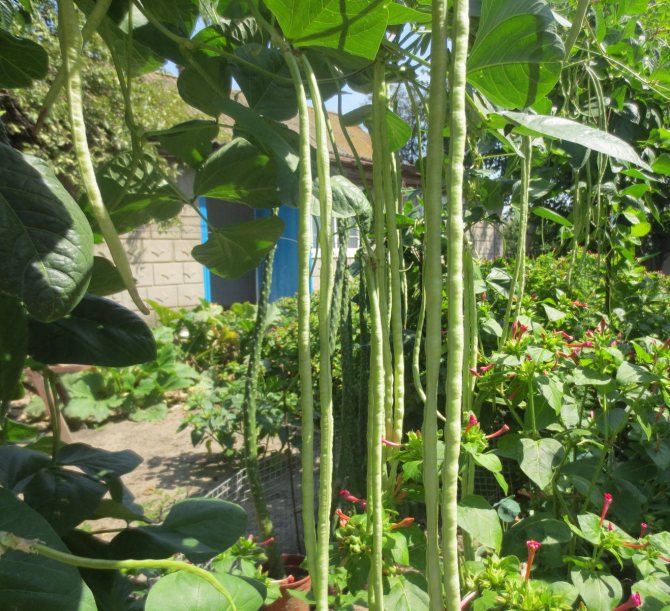
- Beans of vigna Fakir. A bushy vine up to 3 m high with green pods up to 35-50 cm long and a valve up to 1 cm wide. Delicate taste
- Spaghetti beans. A mid-ripening climbing variety with a ripening period of 60 days. Green straight cylindrical pods can be up to 55 cm long and no more than 1 cm wide.
- Macaretti. A powerful, fast-growing climbing shrub that requires support. Dense crunchy fruits up to 35 cm long ripen in 60-65 days. The pods come in green, red, and various shades of purple.
- Serengeti asparagus beans. High-yielding early maturing (55 days) bush hybrid of Dutch selection. The bush is upright, 45-50 cm in height. Dark green round pod 0.6-0.8 cm in diameter, up to 15-17 cm long, has no fibers and parchment layer.
- Vigna Countess. A tall climbing plant up to 5 m long. A large number of green pods, growing up to 1 m in length, with a valve width of no more than 1.5 cm.
How to grow green beans
How to grow green beans in the garden? This question is asked by all novice summer residents. In fact, the algorithm for planting and caring for a plant is extremely simple and does not require much effort. Growing beans begins with preparing the soil for planting a plant.
How to prepare a garden bed
First of all, you need to choose the right place for the location of the garden. The plant requires a well-lit area, but not prone to drafts. The chosen place is thoroughly dug up. It is advisable to do this already in the fall.
In addition to the usual digging into the soil, it is worth adding a number of fertilizers:
- Humus (5 kg per 1 sq. M).
- Superphosphate (30-40 g per 1 sq. M).
- Potassium chloride (about 20 g per 1 sq. M).
In the spring, you can also add a little complex fertilizers (with potassium content): 30 g per 1 sq. m. After that, you need to loosen the earth, which will contribute to a good planting, and subsequently help the roots of plants to receive nitrogen.
Important! Do not plant green beans in too stony or clayey soil! This can interfere with seed germination.
Sowing seeds
After preparing the soil, we are preparing the seeds for planting. Planting green beans is similar to planting any other legume.
The algorithm for soaking seeds for their favorable germination will help you:
- The seeds are poured into a tissue bag and immersed in a warm (about + 40 ° C) solution of water and potassium permanganate for a short period of time.
- Then the seeds are washed with water and wrapped in any damp cloth for 5-6 days. Be sure to make sure that the fabric does not lose moisture, moisten it as needed.
- Maintain a temperature of + 25-30 ° C to create a favorable climate for the seeds.
Approximately in May (or that week of the season in which the earth warms up to + 15-17 ° С), the sprouting seeds are planted in the soil.
Important! At first, the seeds are sensitive to temperature changes. It is worth excluding the onset of frost or protecting the planting site with a greenhouse or greenhouse.
A few minutes before laying the beans, it is necessary to soak for about 4 minutes in an aqueous solution of boric acid (0.2 g / l) for increased immunity to diseases.
It is better to plant the seeds at a distance of at least 10 cm from each other (if it is a variety of curly beans) or at a distance of 20 cm (if it is a bush bean). This method of planting will simplify the growth and development of plants, as well as make it convenient to care for the garden and harvest.
For any variety, germinated seeds are laid to a depth of about 3 cm, 2-3 pieces in each hole. After that, sprinkle the bed with humus. According to statistics, the first shoots appear 10 days after planting.
Care and feeding
Green beans, like asparagus, require regular watering. but regularly doesn't mean a lot... Green beans do not like too much moisture; there should be no standing water in the garden bed. If you follow the watering rate (2-3 times a week, depending on the climate), you will get fleshy juicy pods and a good harvest.
Watering is increased during the flowering period (a month after the emergence of sprouts). To increase the yield, add a variety of fertilizers to the water (even the simplest nutritious infusion is suitable: soak the weeds in a barrel of water for 7 days and add the resulting fertilizer to a bucket of water, 1 liter each for watering the garden).
The main rule is to avoid dry crust on the ground. This will damage the growth and development of the plant (for example, freshly sprouted seedlings can break on hard, dry soil).
Important procedures are soil loosening and weeding. This should be done regularly: loosen after each watering, weed as weeds grow. Loosening will allow the roots to be oxygenated, while weeding will keep the nutrients inside the plant.
Since beans are in most cases a tall plant (depending on the variety), they require tying for normal development. If you are making a vertical garter, you need to install a support for the bush (this can be a peg, a stick) and tie a branch or stem that falls under the weight to it with a piece of rope. This will make it easier for the plant to grow and develop.
Planting beans
All varieties are planted in the same way, so a specific planting algorithm should be followed.
Landing dates
For a regular harvest, you need to plant several varieties at the same time, however, with a different growing season. Three types of beans are planted on one ridge: early ripening, medium and late.
From a bush of a culture of an early ripening period, the fruits can be plucked already 2 months after the formation of the beans, late varieties bring a crop only after 3.5 months.
Landing is carried out only when the air temperature reaches +16 degrees Celsius, and there will be no night frosts. In almost all regions, this period falls on the end of April-beginning of May. Planting later will result in less harvest.
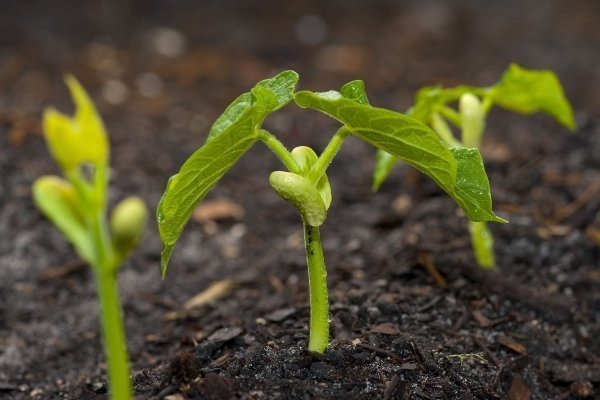


Vigna develops rapidly and takes root at an air temperature of +22 degrees Celsius.
If planting is carried out directly into open ground without preliminary germination, then the occurrence of seeds should not be more than 4 cm.Planting too deep will slow down the growth of the seedlings.
Step-by-step landing scheme
Algorithm for planting cowpea using the germinated sprouts method:
- Inspect the planting material carefully. Do not plant beans that are stained, darkened, or rotten.
- Plant sprouted shoots in containers with soil mixture. In 1 pot, place a couple of beans 3 cm deep. Pay attention to the sprouts, they should be facing up.
- Sprinkle the sprouts gently with soil.
- Water the seedlings from a spray bottle so that the seeds do not start to rot, but the earth does not dry out either.
- After the appearance of 2 leaves, transplant the seedlings into open soil.
- Feed the soil a week before planting. Perfectly saturates the soil with horse manure and compost.
- Leave distances between plants based on the variety of beans. For example, a plant between a bush or a tall crop may be small.
- Plant the seedlings in rows. Leave a distance of 0.4-0.5 m between them.
- If you are planting the beans directly in the soil, then deepen them 4 cm.
Prevention of diseases and pests
Watch out for pests or plant pathogens to avoid losing your crop.
The most common diseases of beans:
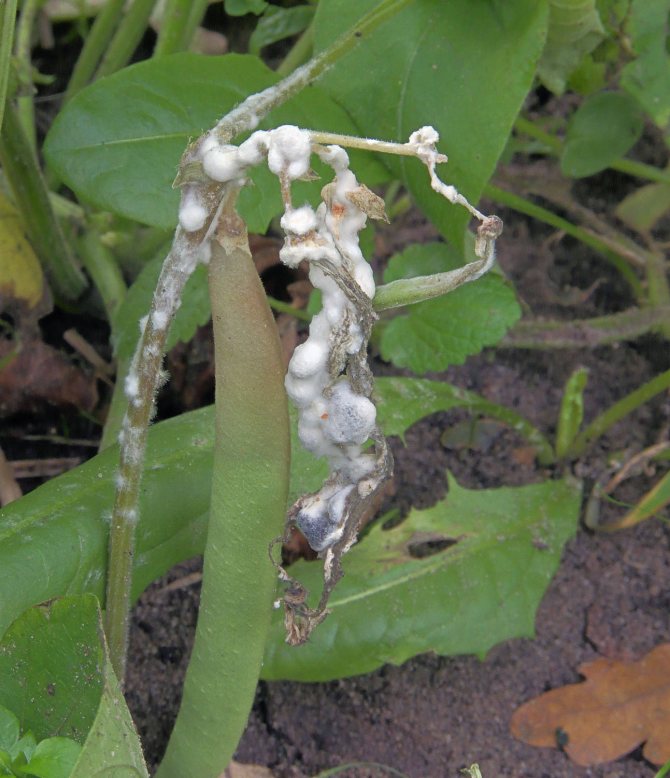
- Powdery mildew... A fungal disease that affects the leaves of a plant with a white bloom. Diseased leaves may fall off over time, but do not wait. Tear them off as soon as you see the onset of the disease to avoid transfer of the fungus to healthy leaves. Spray the bushes with a 1 to 9 solution of milk powder and water twice a week. You can also add 1 part vinegar or baking soda to improve the effect.
- Anthracnose... The disease leads to fruit rotting and manifests itself as a brown rash on the leaves of the plant. As a treatment, spraying with Bordeaux liquid is suitable. Copper oxychloride treatment is also recommended.
- Whiterot... The disease leads to softening of stems and leaves or the appearance of white spots on them. For treatment, it is necessary to remove the diseased parts of the plant or sprinkle them with charcoal or chalk.
- Root rot... With such a disease, the main root of the plant suffers, as a result of which the plant withers. Plaque may form on infected areas. To fight the disease, soil disinfection is needed.
- Mosaic... The color of the leaves gradually becomes bright, multi-colored, like a mosaic. Leaf tissue may wrinkle and swells in some places. The growth and development of the plant is severely disturbed. Use aphid repellent as a preventive measure.
There is also the possibility of damage to green beans by some pests, including:
- Slugsthat live on weeds. They can simply move from them to the bed of beans, so it is necessary to carry out weeding on time.
- Whitefly... Absorbs all the juice from the leaves. As a preventive measure, it is recommended to rinse the leaves.
- Sprout fly... It gnaws at the base of young shoots and can completely destroy the crop. Sprout flies are initially found in the ground in the form of larvae, which must be mechanically removed.
- Melon aphid... Transfers various diseases. It is recommended to pollinate with ground sulfur or soapy water (add 1/4 piece of grated laundry soap to 1 liter of water, you can add 1 tablespoon of baking soda).
Useful and medicinal properties of green beans
- Thanks to the fiber in beans, as well as folate, magnesium and potassium, green beans can help reduce the risk of heart attack.
- Green beans are useful for people suffering from diseases of the digestive system, they will help get rid of intestinal infections.
- Eating green beans is very beneficial for the body as a whole. Thanks to the trace elements and minerals it contains, as well as the high level of vitamin C, it increases the body's resistance to infections from the outside, strengthens the immune system. It has been proven by doctors that with the help of green beans you can get rid of the flu virus.
- It will also be useful for anemia, low hemoglobin, since copper well activates the production of hemoglobin, having a positive effect on the function of red blood cells.
- Consuming green beans consistently leads to improved liver function.
- Green beans are a real medicine for diabetics as they lower blood sugar levels. This is due to arginine, an insulin-like element that is able to normalize the amount of glucose in the blood.
- The microelements contained in it strengthen blood vessels, have a positive effect on the work of the heart, and are suitable for the prevention of hypertension, atherosclerosis, arrhythmia, poliomyelitis and many other diseases.
- Some experts claim that green beans have a beneficial effect on male sexual function. This is due to the action of zinc, which is found in large quantities in beans. In addition, this culture is useful for the prevention of prostatitis, cholecystitis and calculous pyelonephritis.
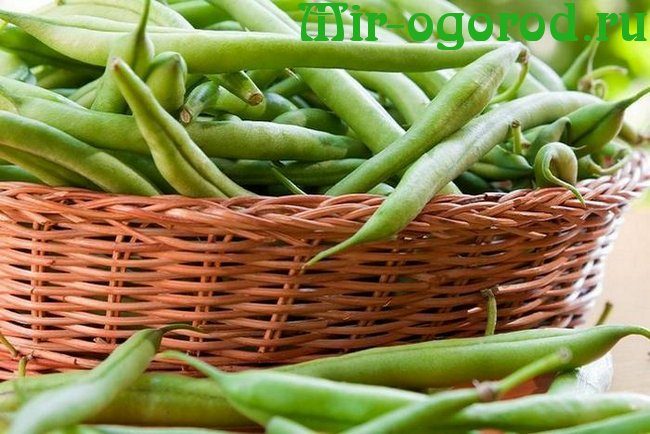


Nutritional value


Green beans are a tasty product and a valuable source of protein, successfully replacing meat dishes in the vegetarian menu.
Green beans have excellent taste and are very beneficial for the body. Delicate green pods contain:
- proteins (easily digestible, structurally similar to meat);
- cellulose;
- vitamins B1 and B2, folic and ascorbic acid, provitamin A;
- minerals (phosphorus, iron and calcium, chromium, magnesium).
Eating a vegetable culture helps to eliminate toxins and toxins from the body, to normalize the functions of the kidneys, stomach, and liver. The culture is recommended for men to use for the prevention of prostate adenoma.
The plant's delicate pods are widely used in cooking. The fleshy fruits of bush crops are canned, thin weaving pods are added to soups, stews and other vegetable dishes. The wax (aka oily) variety is ideal for salads.
Description of popular varieties and existing varieties
The asparagus bean is an annual agro-plant with feather-shaped leaf blades. It belongs to the category of weaving and bush crops. The flowers of the culture are formed in the axils, the fruits are presented in the form of bivalve beans, inside which are large beans with a spongy septum. Legumes are characterized by a high concentration of protein and nutrients.
This culture is able to grow and develop even in low light conditions, it can be planted in semi-dark glades. In addition, agriculture does not need additional pollination, which makes it possible to grow several varieties of beans in the garden. The classification is carried out according to the following parameters:
- Ripening terms: early maturing (2 months), mid-early (2.5 months), medium (2.5-3 months), mid-maturing (up to 100 days), late (from 100 days).
- Type of land plant: climbing, bush.
- Taste qualities and areas of application: shelling (grain), sugar, universal (semi-sugar).
Hulled beans stand out with a very dense shell, only grains are used for food. It grows best in areas with a warm climate, if planted in the middle lane, then the fruits will not have time to ripen, and all the work will be in vain.
Among the popular varieties of grain beans are noted:
- Ballad, which belongs to crops with a medium early ripening and has a high degree of drought tolerance. The color of the pods is green, and the grains are light yellow with purple splashes.
- Ruby, it is known as a variety with high productivity and delicious beans. The mid-ripening culture is distinguished by the burgundy color of the fruits.
- Shokoladnitsa, the owner of long yellow pods. A medium late plant can grow up to 1 m in height.
Asparagus beans, or sugar beans, are actively used in cooking, their fruits are consumed whole.This is due to the lack of a special permanent layer in the pods. In addition to excellent taste, sugar beans are able to remove excess fluid from the body.
Such varieties are especially in demand:
- The oil king. The plant is distinguished by its ultra-early ripening period, high productivity, delicate flavor of the pods.
- Hell Rem. It is a climbing plant, the fruits have a light pink color and an exquisite mushroom flavor.
- Crane. The plant attracts the attention of gardeners with its compact size, fiberless pods and pleasant taste.
Varietal features
Green beans are sometimes called asparagus beans. In fact, asparagus beans are the unripe green fruit of the green beans. And do not confuse asparagus beans with the culture of the same name: asparagus is a completely different plant.
Sugar and semi-sugar fruits are suitable for consumption. The pods of different plant species differ: they are not only green, but also white, yellow, and even pink or purple. Beans differ not only in the shape, size and type of pods, but also in the nature of the growth of the stem. Today, various varieties of green beans have been bred: curly, semi-climbing, bush.
The advantages of bush varieties are compactness and beautiful flowering, the ability to grow well in a temperate climatic zone, and no need for support. While curly types of green beans are distinguished by excellent decorative qualities, they give a much larger yield.
Post-plant care and plant cultivation in the garden
After the asparagus beans have sprung up, caring for it consists in watering, loosening and weeding, fertilizing and pest control.
If after planting there is a threat of night frosts, then the sowing should be covered with a film or special material. A month after the emergence of seedlings, you need to carry out the first feeding with nitrogen fertilizers. This procedure is especially important in dry weather. With an insufficient organic content in the soil, complex fertilizers can also be applied.
During the period of pod ovary, feeding with potassium-phosphorus fertilizers will be appropriate. For climbing beans, it is advisable to build supports. If the variety you have chosen also has a beautiful flowering, then you can use it as a decorative one.
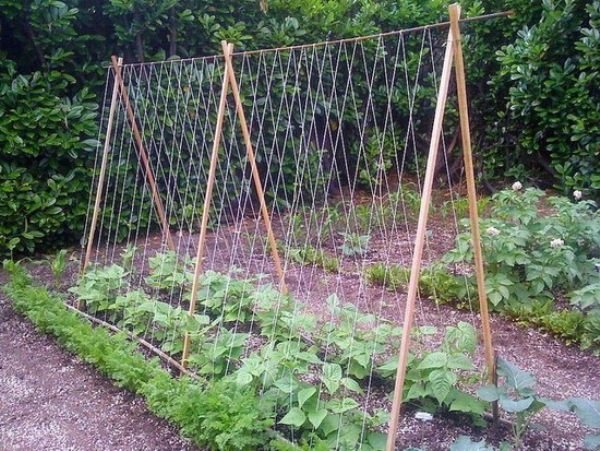


Rope Trellis for Curly Asparagus Beans
When weeding the beds, the grass can not be thrown away, but used as mulch. Later, it can serve as a good fertilizer, since beans respond well to organics.
Growing and care
The cultivation of green beans does not require special care. The main thing is timely weeding, loosening and maintaining soil moisture. And of course, in order for the beans to grow well, you need warmth.
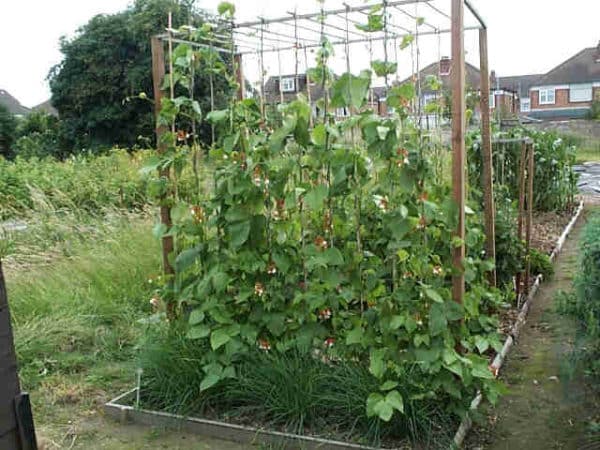


It is possible to grow a curly variety of green beans even on a small plot of land.
Soil and plot
The best for the plant are light and medium clay soils (loam), as well as soil with a predominance of sand and an insignificant part of clay (sandy loam). The ground should be moderately moist.
On heavy and cold soils with high groundwater levels, green beans do not grow well.
It is better to plant the plant in a well-warmed, protected from strong gusts of wind and illuminated place, but you can also plant in an area with a slight shadow. Before planting, the land must be cleared of weeds.
Temperature and humidity
Seeds germinate best and plant shoots develop at temperatures from 20 to 25 ° C. Beans love moisture - with sufficient watering they bear fruit well, gives fleshy, juicy pods. Watering should be moderate, but systematic.
Fertilizers
String beans respond well to the application of mineral fertilizers: potash (1 part), phosphorus (2 parts), nitrogen (1 part). The introduction of top dressing in the soil before planting helps to increase the protein content in the fruits, increase yields.
During growth (in the middle of the season), the plant is fed with complex fertilizers, scattering them at a distance of about 20 cm from each bush. It is important that substances do not fall on the leaves.
Features of growing climbing varieties
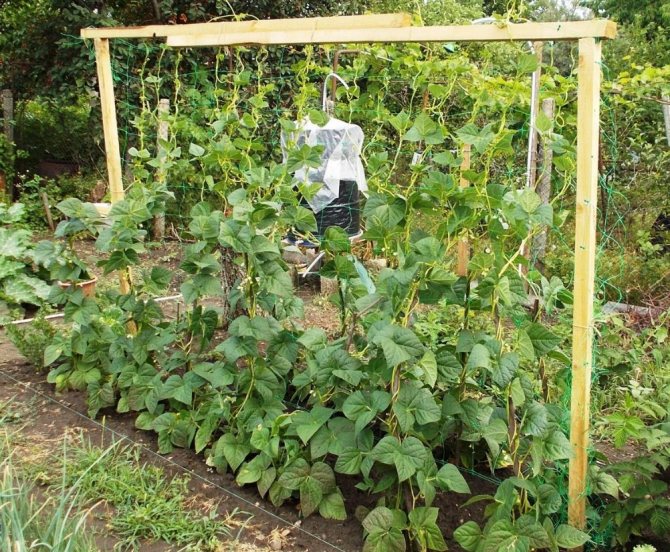
For climbing varieties, you need to build strong supports that can support the weight of the tied plants. More often, high wooden stakes are used as a support, which are driven into the ground to a depth of 40-50 cm. You can plant climbing species near high trellises and fences, pillars.
As they grow, the climbing stems need help finding support - winding the vines around a support system. It is better to limit their growth - pinch the top when it reaches two meters in length, otherwise the harvest will not be possible.
Bean varieties with photos and descriptions
Green beans are a low-calorie food packed with many vitamins, amino acids, organic acids, flavonoids and minerals. It is widely used in cooking as a vegetable ingredient in salads, side dishes, first and second courses. The asparagus variety got its name from its characteristic taste, reminiscent of asparagus.
- The purple queen. An interesting bush variety that combines fruit and decorative functions. Produces dark purple pods up to 15 cm long. The variety is not afraid of many diseases and is suitable for planting in different regions.
- Crane. A compact plant reaching half a meter in height. A non-capricious variety with enviable productivity. The delicate taste of the fiberless pods is excellently preserved in canning and freezing.
- Sachs 615 (without fiber). Shrub early ripe hybrid with a height of up to 45 cm and green pods up to 12 cm. Very popular due to its high-vitamin composition.
- The oil king. A bush variety with a growing season of 55 days. By the end of summer it produces yellow pods with a distinctive taste.
- A common, fast-ripening curly variety, the pods of which grow up to 13 cm in length. Up to 10 pods are harvested from one plant per season.
- Winner. Curly flat-pod variety that decorates the garden with fiery red flowers during flowering. Brings flattened fruit pods up to 30 cm long.
- Caramel. Early ripening fiberless beans, called by many summer residents the best among the species. Produces short pods with large seeds inside. The plant is popular for its high immunity to common viruses.
- Fatima. A variety of curly beans with a medium ripening period. Growth can be 3 meters, but the foliage is always average. The pods are straight in shape - they can be 21 cm each. They have a good taste and a delicate, fibrous structure.
- Panther. Another bushy variety with yellow, fibrous fruits. Differs in high resistance to fungal diseases and a special spicy taste.
- Hell Rem. Curly variety with light pods and rare lilac-pink grains. Differs in characteristic mushroom aroma and high resistance to pests and diseases.
- Neringa. A bush bean variety that ripens in 7-9 weeks. Gives green long (14-16 cm) pods with juicy leaves without a parchment layer. The plant bears excellent fruit in different conditions, is versatile in processing.
- Deer king. A bushy variety of green beans with extremely tasty fruits. The bright yellow ripe pods have dense white grains inside. In warm regions, it is possible to harvest twice a season.
- Bona. A plant with a compact bush up to 40 cm in height. It produces rounded pods 13-16 cm long without a parchment layer with 5-6 white seeds. It is appreciated by gardeners for its immunity to diseases, good productivity and versatility of use. Ripens in 50-75 days after sowing.
- Blue Lake. A tall variety that needs solid support.The green pods grow up to 16 cm in length and reach maturity 50-56 days after the sowing date of the beans. Small white seeds form inside. It is a fruitful hybrid with decent resistance to infection and disease.
- Sweet courage. A shrub plant with fast maturation. Differs in cylindrical yellow pods, growing up to 16 cm in length.
- Gina. A bushy early ripe variety with slightly curved pods up to 17 cm long. It has excellent qualities that are preserved during canning. Highly prized for its productivity and disease resistance.
- Paloma. Dutch beans for early sowing. Bears abundantly in 11-12 cm dark green pods. Versatile in culinary use.
- Bergold. A high-yielding bush variety with soft, parchment-free pods. Slightly curved fruits grow up to 14 cm in length and keep well in ice cream or canned.
- Nagano. Asparagus beans from a Dutch manufacturer. Suitable for sowing from early to medium terms. High resistance, good yield with 13 cm pods. Good in freezing and preservation.
- Mascott. Western low-growing variety with ripening in 50-55 days after breaking through the seedlings. For dense, fiberless pods with a pleasant crunch, Mascott is very fond of the French. Can be grown at home on a windowsill.
- Pensioned Under Black Wax. Low-rise Italian beans with bushes up to 40 cm in height. Differs in good yield, excellent commercial qualities of fruits, high immunity. The pods grow up to 15 cm and are well preserved in conservation and freezing.
- Kentucky Blue Pole. Favorite by many American farmers, beans have a 65-day growing season. A climbing plant with a total length of up to 2.5 meters. It is very similar in growth and fruit characteristics to the Blue Lake variety.
- Gold Mine. Bush beans, called by some summer residents super-sweet. Strong, upright bushes yield up to 800 grams of juicy pods.
- Serengeti asparagus beans. Planting of this early maturing variety is possible in all climatic zones. This variety is distinguished by resistance to many diseases, as well as pleasant taste characteristics and high yields.
We suggest you familiarize yourself with: Fir planting and care in the open
On a note!
For middle and northern latitudes, you should choose among early maturing or mid-ripening hybrids that ripen in 50-80 days. Late-ripening varieties of beans are suitable for cultivation in the south, as they reach ripeness no less than 100 days after sowing.
Green beans planting and care
The first thing to think about before planting beans is the ideal garden plot. To allocate a place for this plant at the last moment, where it works out, is incorrect, since it is rather capricious in relation to the illumination and the nature of the soil:
- In the initial stages of development, beans require intense, but not unnecessarily long exposure to sunlight. They should get on plants no longer than 12 hours a day.
- Curly bean varieties should be planted next to a support for lifting branches, and if there is none, make a trellis yourself. Planting of three plants with a support in the form of a high tripod is practiced.
- Beans grow well and bear fruit when planted after potatoes, onions, cucumbers, carrots, cabbage, and other root plants.
- Poor precursors for green beans are sunflowers, legumes and legumes, and perennial herbs like clover.
- Bush varieties of green beans grow well in the aisles of potatoes and cabbage, they do not need supports for weaving.
In most cases, sowing seeds of green beans is carried out in the middle of May - early June. The main indicator is the degree of heating of the earth at the depth to which they are embedded (5-6 cm). The temperature here must be at least 10˚C.Basically, in the Russian regions, frosts should be over by this time. If, according to the weather forecast, a repeated decrease in temperature is promised, the crops will need to be covered with polyethylene or non-woven garden cloth.
Green beans should be planted to a depth of 60 mm on very loose soils. The tougher the soil, the closer the seeds should be placed to the surface so that the soil structure does not interfere with germination. Landing scheme:
- for bush varieties: 15-20 cm between holes and 35-40 cm between rows, the optimal number of rows for cross self-pollination is 4;
- for climbing varieties: 20-30 cm between holes with the obligatory presence of a strong non-plastic support (branches can grow very heavy).
We suggest you familiarize yourself with: Cauliflower in the oven with cheese
In both cases, it is recommended to throw 2-3 beans into the holes in order to have a guarantee of germination. At least one of them will definitely break through. And if several come up, then you just need to choose the strongest among them, and pull out the rest.
After sowing, you need to water the garden bed and slightly press down the soil with a rake. When punching seedlings, it is necessary to huddle them in a timely manner to impart greater stability and accelerate development.
It is good if the site chosen for planting will consist of nutritious soil and, more importantly, well-drained soil. The lush soil will allow the beans to self-feed on nitrogen from the root nodules. It is not worth risking planting in clay soils or areas with a close passage of groundwater - the seeds may simply not sprout.
To increase the yield, the soil must be enriched with humus or heated compost before deep digging. Ammonium nitrate with the addition of calcium chloride and superphosphate is also a useful additive. Nitrogen is not needed - if you constantly make the soil loose, it will be extracted in excess by the plants themselves.
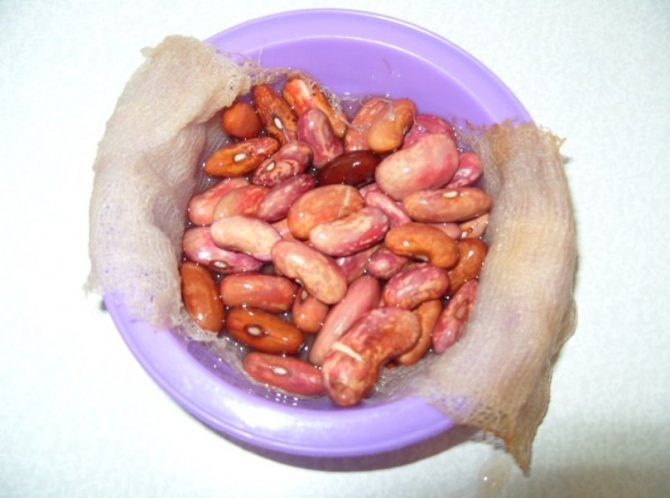
Presowing treatment of beans:
- Sort out the grains, discarding the damaged ones.
- Soak in thawed water at room temperature for no longer than 12 hours.
- Before sowing for 3-5 minutes, lower the beans in a solution of 2 g of boric acid and 10 liters of water.
Asparagus beans planting and care
To germinate seeds before sowing, you can use the following method:
- Pour them into a linen bag (or tie them with a cloth) and immerse them in a light solution of potassium permanganate heated to 35-40˚C.
- Rinse the grains with clean running water and wrap them in a damp cloth for 5-6 days. It is necessary to maintain its moisture content during this period.
- At temperatures in the range of 20-30˚C and being in a humid environment, the seeds germinate quickly.


It is advisable to sow seedling beans in April. Moreover, it is necessary to place crops in a greenhouse or under a film, since at first they are extremely sensitive to temperature conditions.
It is better to plant according to the 6 × 6 cm scheme - it will be convenient for the plants themselves to grow, but also for the gardener to take care of them. Seeds for seedlings should be laid at a depth of about 2 cm.
Care features:
- for germination and good development of sprouts, you need to constantly water the soil, but at the same time maintain its looseness;
- after the initial weeding, you can start feeding the plantings with a mullein (1: 6 with water) or ammonium nitrate (20 g per 1 m2);
- you should not just flood the seedlings - the soil is needed moist, but without standing water - so the seeds can ferment;
- during the summer, it is necessary to carry out such a make-up several more times, but about 40 g of superphosphate should be added to 10 liters of the mixture;
- to protect against low temperatures in the cold season, it is necessary to cover the seedlings with straw compost or melted manure in autumn.
- Due to the short season, the earliest varieties should be chosen.
- Beans are thermophilic, so you have to wait for favorable weather. Sowing is usually carried out not earlier than the end of May. In cold spring, it is better to think about seedling planting.
- Seeds are best planted dry, without soaking.
- Beans must be hilled after the sprouts are higher than 10 cm, so that they do not die from the wind or their own weight.
- It is imperative to tie up climbing plants, since there is a lot of precipitation and leaves and pods on the ground can rot.
- During a cold snap, it is better to cover the beans with a film material.
Soil composition
- Compost or humus (4 kg), 2 tablespoons of superphosphate and dolomite flour, 1 tablespoon of ammonium nitrate.
- About 2 kg of humus or compost, 30 g of superphosphate, 20 g of wood ash.
Garden bed preparation
- Planting of planting material should occur after the end of the frost. It should also be warmed up to a temperature of 10 degrees. The optimal landing periods are mid-June.
- Since the seedlings of green beans react very badly to negative temperatures, they immediately die. To protect the plants, cover them with a film.
- It is necessary to sow the plant on the ground where crops such as cucumbers, tomatoes, potatoes, carrots used to grow.
- Green beans require the introduction of various organic and mineral fertilizers. It is worth bringing them in in the fall. In the spring, the soil should be fertilized with wood ash. It is equally important to fertilize with mineral components. They have a positive impact on the growth and development of culture. It is also worth introducing fertilizer in the summer.
- 1. Watering.
Landing
When choosing a variety of beans for ripening periods, it is important to take into account climatic features. In the Urals and in other northern regions, it is better to plant varieties that ripen early, and in the southern regions any varieties can be grown.
You can sow green beans in the country as soon as the spring frosts pass. The optimal time is the end of May or the beginning of June, when constant warm weather sets in, and the soil is already well warmed up. Additionally, you can warm up the soil using the greenhouse method - cover the ground with a transparent film 10-15 days before sowing.
Before sowing, the seeds are soaked in water to swell for at least a few hours, but it is better to wait until the moment of germination. Seeds are sown at a distance of 7–10 cm from each other and with a row spacing of 20–40 cm. The optimum sowing depth is 2–3.5 cm. At least two seeds are placed in each hole. For white seeds of green beans, the optimum temperature for germination is about 20-25 ° C, for dark-colored beans - 2-3 ° C lower.
In order for the seeds to germinate well, abundant watering is necessary.
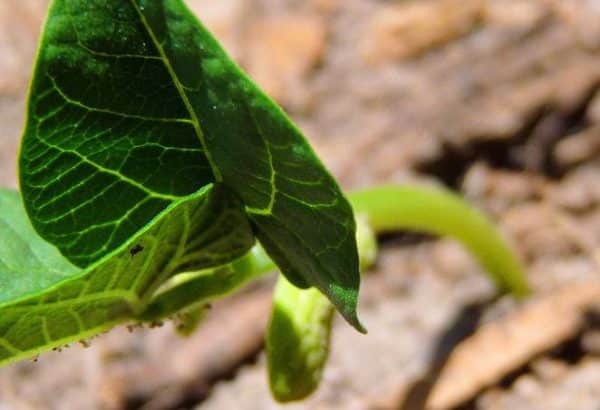


Sprouted seeds take root better in the open field and germinate faster.
Planting and growing rules in the open field
A legume crop is characterized by the simplest agrotechnics - preparation of the plot and seeds, sowing and maintenance procedures.
Seed preparation
In order to achieve a good yield of legumes, you should prepare the grain material in advance. The work is carried out in several stages:
- Selection. You will need to sort through the beans and pick out whole, unspoiled beans.
- Disinfection. The seeds are immersed in a solution of potassium permanganate for 30 minutes.
- Flushing. After disinfection, the grains are washed and again left to swell in heated, but not hot water for 2 hours. This time is sufficient for swelling.
- Additional processing. Before sowing, it is recommended to treat the material with boric acid dissolved in water. The proportions are on the label of the product.
Consistent preparation will minimize the risks of damage to the crop by insects and various ailments, and achieve good yields.


Preparing the soil and choosing a place for sowing
For planting green beans, an illuminated plantation is selected, windless, without drafts. The culture takes root on limestone soil, but may not germinate in moist, acidic and heavy soil. The optimum acidity level for a legume plant is considered to be pH 6.5-7.Therefore, asparagus beans can be grown on loams or sandy loams with deep underground waters. The preparatory stage includes:
- cleaning and weed control;
- loosening the soil, digging for one shovel bayonet;
- application of mineral and organic fertilizers;
For 1 m2, add 4 kg of compost or humus, 2 tbsp. l. dolomite flour, 2 tbsp. l. superphosphate and 1 tbsp. l. ammonium nitrate.


It is better to sow beans in the area where carrots, potatoes, tomatoes, peppers, eggplant, cucumber previously grew.
Planting scheme and depth, planting beans through seedlings
Delicious bush green beans are sown according to a certain pattern:
- the optimal hole depth is from 5 to 6 cm;
- the distance from one hole in the row to another is 25 cm;
- 40 cm recede between the in-line segments.
Curly varieties are planted as follows:
- the seeds are placed in the soil 6 cm;
- adhere to an inter-row spacing of 50 cm;
- the interval between the holes is 30 cm.


5-6 legume seeds are laid in each hole. When shoots form on the bush, 3 sprouts are left in each hole, the rest are pinched.
Diseases of vegetable crops
Green beans are attacked by the same pests and diseases as other legumes. It:
- bacteriosis;
- powdery mildew;
- rust;
- white rot.
Diluted milk powder (1 part powder to 9 parts water), weak solutions of baking soda or apple cider vinegar are used to fight diseases. Processing is carried out twice a week. Removing all diseased plants will help prevent the spread of the disease.
The main source of contamination is unhealthy seeds, so careful selection of clean, non-contaminated seeds for sowing is key in disease prevention. The destruction of post-harvest residues and deep digging of the site in the fall will also help reduce the risk of infection.
Testimonials
Growing green beans is easy. Therefore, such a culture can be grown even by novice gardeners. Ornamental climbing varieties show high yields. In addition, they become an excellent decoration for a summer cottage and improve the structure of the soil.
Tags: growing, planting, pod, care, beans
About
«Previous post
Harvesting
The timing of the first harvest differs depending on the type of crop. A grown bush of an early bean variety will bear its first fruits 45-60 days after germination. Medium varieties bear fruit in 65–100 days, late varieties - after 100–130 days.
Multiple harvesting lasts on average from July to September. Usually, green beans are harvested at least 5 times per season. The collection is carried out when the pod leaves are still juicy, and the fruits are unripe. If the fruit is not removed in a timely manner, new pods will cease to appear. Therefore, you need to inspect the shrub and remove the fruits at least once a week. The last crop can be left for seeds by harvesting the already fully ripe pods.


The optimal harvest time is early morning, when the pods have not yet warmed up in the sun and have retained their moisture and juiciness.
The more often you harvest, the more new fruits will form. And when planting beans annually in the same place, from time to time the crop yield will increase. A large harvest of beans can be stored in the freezer - the frozen pod does not lose its taste and useful composition.
Knowing how to grow green beans in the country, you can get a tasty and healthy culture. Many gardeners and summer residents have already appreciated the advantages of green beans - not troublesome care, high productivity, excellent decorative qualities of climbing plant varieties. A fast-growing liana enlivens any vertical surface and decorates the suburban area. In addition, like all legumes, beans improve soil quality and are the best precursor for almost all garden crops.
The cultivation of green beans in summer cottages is becoming widespread. Not so long ago, only large farms grew this useful product. You can buy green pods without any problems - fresh, in the vegetable departments of supermarkets, or frozen, in the refrigerators of all stores, mostly imported products. Meanwhile, growing this "green miracle" in the country is not difficult. The most important thing in growing green beans, unlike other legumes, is to harvest on time. Do not overdo the pods in the garden, making them tough and tasteless.


Green beans: growing and care
Contents of step-by-step instructions:
Storing beans
Fresh beans will not last very long; after the harvesting process, they should be consumed almost immediately. For the winter, you can prepare a freeze by picking unripe fruits in advance and placing them in the refrigerator. Asparagus can be preserved in whole pods, various salads can be prepared. Once ripe, the beans are removed from the pod and stored in a dry place. Green beans are not picky crops, do not require special care, are grown in different latitudes, and are resistant to diseases and parasites. It gained its popularity due to its rich vitamin composition and excellent taste. For these reasons, most gardeners prefer the cultivation of legumes.
The oldest representative of legumes
Beans are reasonably considered by biologists to be the oldest cultivated plant on the planet. There are officially three botanical types of beans.
- The shelling, from which the beans are obtained, is characterized by a dense parchment shell.
- Semi-sugar - this species has a parchment shell of medium hardness.
- Sugar, aka asparagus, in which there is no parchment shell at all, but green, juicy and soft is present.
In the garden culture, it is customary to call the latter type of green beans, which are eaten together with the pods. In contrast to peeling varieties, the pods of which are not suitable for food.


Useful properties of green beans
Beans can be divided into two more types according to the growth method.
When growing all types of beans, the basic agrotechnical standards are observed, which include the following points.
- Beans do not tolerate sandy, acidic and too heavy soils.
- Loves light, humidity, warmth, drought with difficulty. If the dry season falls on flowering time, the ovary may fall off and there will be no harvest.
- Beans don't like drafts and winds. The plant must be grown quietly.
- Sowing is carried out not earlier than the soil warms up to + 13 ° C (May - June).
- Sowing is preceded by a procedure for warming up and soaking the seeds.
- The seeds of the plant are buried no more than seven centimeters.
- Seedlings of all varieties must be loosened and preferably mulched.
- When the stem grows back by 15 centimeters, the plants need to be spud.
- For climbing varieties, you need to provide support immediately upon planting.


Varieties of green beans
By the way! Not all varieties have classic green pods. In some, the fruits are whitish, yellowish and even bright yellow, purple. Therefore, it is better to be guided when collecting not by the color of the fruit, but by the period of the expected milk ripeness, which is indicated on the package with the seeds.
Asparagus beans: growing from seeds at home
Asparagus beans can be grown quite successfully in indoor conditions, for example, on a glazed loggia or a well-lit windowsill. Better, of course, to choose bush varieties that do not rise above 50 centimeters in height. Curly varieties can be planted on the balcony, not about this you need to be prepared that they will entwine it from the inside, turning it into an indoor jungle.
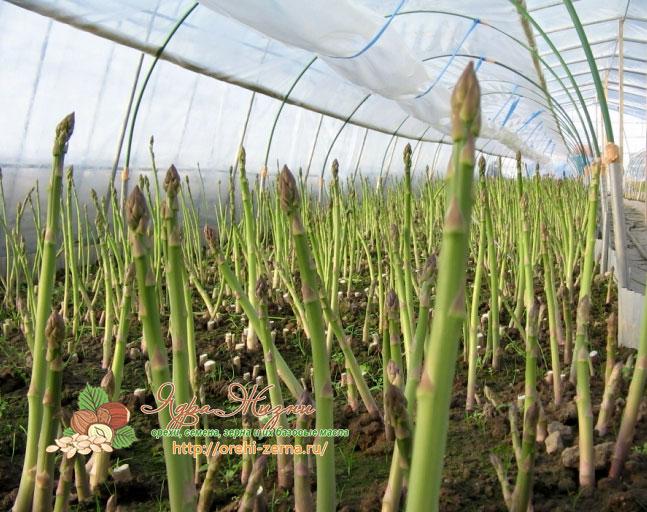


Asparagus beans - greenhouse cultivation
Planting can be carried out either by direct sowing into a growing container or by seedling through peat pots.Planting time depends on individual conditions, you can even organize year-round cultivation. For such a crop cultivation, the varieties Mask, Fatima, Violetta, Zelenopodrukovy 517 and Zolotaya neyka are well suited.
Growing at home often requires additional lighting equipment, but plants do not need a long daylight hours. The soil for planting should consist of two-thirds of garden soil and one-of humus. You need to constantly keep it loose. Top dressing is desirable - it is enough to use complexes with potassium and phosphorus a couple of times a month. Overexposing the harvest on the branches is only when collecting seed.
Growing
Green beans are thermophilic, but not too warm. This is not an exotic representative of the African flora, which must be carefully grown in seedlings and planted only when the very last of possible frost threats has passed. Beans, along with other garden crops, can be safely sown in the spring directly on the ridges, having subjected the beans to preliminary presowing treatment.
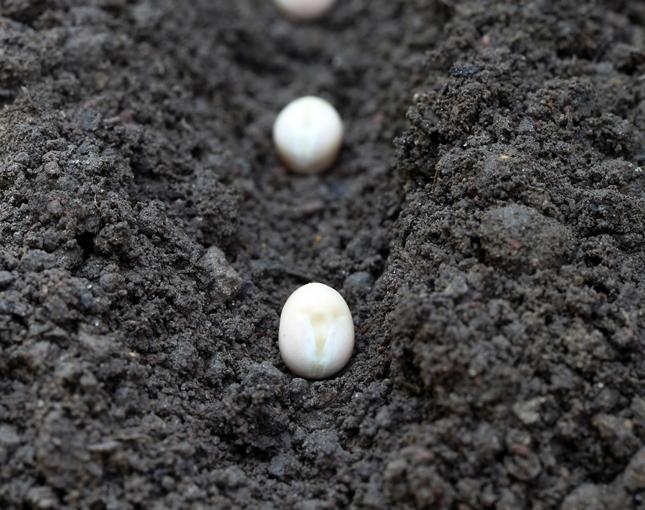

Sowing beans on ridges
How to process beans before sowing
Bean seeds need to be warmed up. And it's best to do it naturally, not on a battery, but in the sun. In industrial agricultural technology, they are heated in special dryers, where the temperature is maintained at + 30 ° C ... 35 ° C. The process takes two days. An acceptable option for summer residents is warming up by the sun. To do this, the seeds must be placed on the southern windowsill and kept there for at least a week. After that, the beans must be soaked. A day spent by seeds in warm clean water (change the water four times) will be enough.
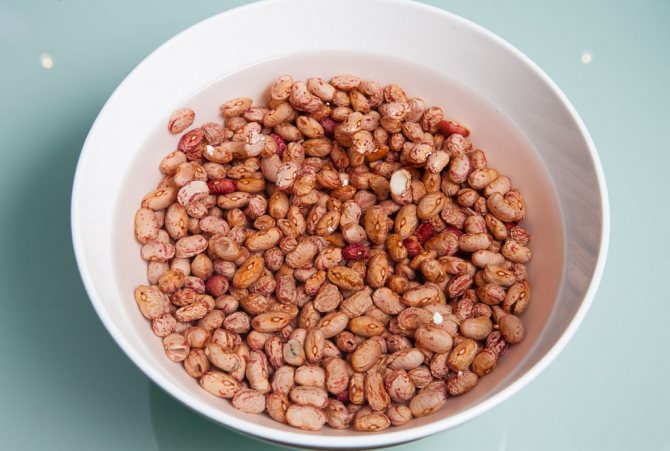


Soaking beans before sowing
How to cook a bed for beans
The soil needs a normal alkaline reaction, in any case, not acidic. Wood ash or dolomite flour will help remove acidity. If you are not sure about the acidity parameters of the soil on the site, add ash to the hole anyway, it will help the plant develop better.
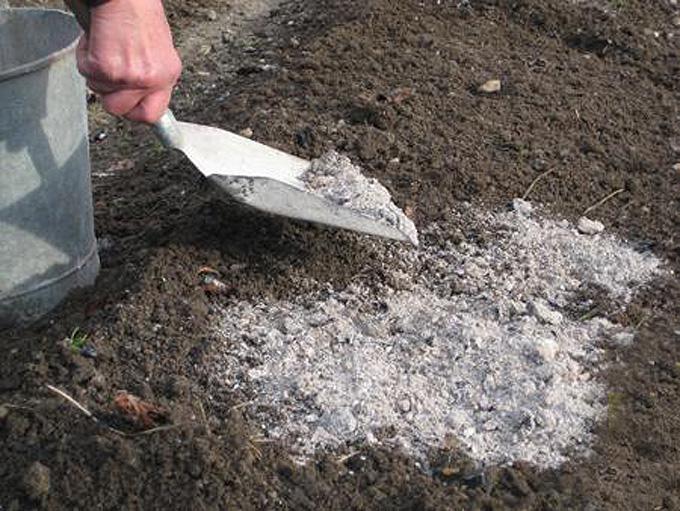


Removing the acidity of the earth with wood ash
Sandstones and heavy clay soils will not work. It is best if the soil is light, fertile, moderately drained.
An important parameter for green beans, especially curly varieties, is the absence of wind. The site should be selected not only warmed up, but also protected from the winds. It is better to place the plants in partial shade than in a draft.
Before sowing the beans, be sure to rid the garden bed and the surrounding paths of weeds. Tomatoes, potatoes and different types of cabbage will be excellent precursors for the crop.
Do I need to remind you that the plot intended for growing beans needs to be dug up and filled with fertilizers in the fall. Be sure to organic - traditional 6 kg per square meter, superphosphate - 35 g, potassium chloride - 20 g.
In the spring, it is also necessary to add a complex that has a high potassium content - this element of green beans is needed more than all other garden plants.
Choosing a landing site
Asparagus beans are very selective about where they grow. The speed of development of the plant, as well as the amount of fruit that it will give, depends on the correct choice of place.
These beans love warmth and sunshine, so care must be taken to ensure that the plant does not obscure anything during all stages of its growth. It is also desirable that there is less wind on the site. Do not worry that the culture will burn out in the open sun - its leaves will independently create shade where they need it.


These beans will feel better on fertile and water-permeable soil. It is good if the groundwater is deep. An acidic, clayey, excessively moist soil is considered an unfavorable soil for this plant.
If the site is in a northern area, it is best to choose a sandy soil for the beans.This type of land warms up faster than others, which will benefit the heat-loving plant.
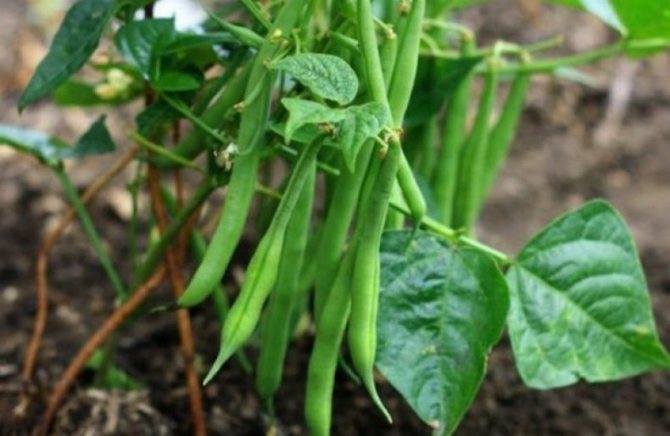


Predecessors
Best of all, beans take root and bear fruit in places where crucifers or nightshades grew. These include:
- potatoes;
- cabbage;
- eggplant;
- tomato and others.
Sowing seeds
The seeds have been prepared, the ridge is waiting for new "tenants". When starting sowing, you need to decide on what scheme to carry out it.
By the way! The sowing depth of beans depends on the density of the soil. If the mechanical composition is light, it can be buried. If heavy, sow as much as possible to the surface. But in all cases, the range of beans sowing depth is 2-7 cm.
Bush varieties are sown in rows (two, three) or staggered. Holes of a given depth are made. Two beans are placed in each hole. Try to maintain a distance of about 25 cm between the holes, and between the rows: two - 45 cm, three - 35 cm.
Planting seeds
Despite the fact that green beans are not particularly critical to frost, it is still worth waiting for not only the prevalence of a constant positive temperature, but also the warming up of the topsoil to at least 15-18 degrees Celsius. Accordingly, planting is carried out at the end of May, but sometimes the weather allows you to plant beans in the second decade of this month. Early maturing varieties can be planted in early June.
As a rule, germination of seeds is not required - it is enough to soak them, and this can be done together with other legumes. Some gardeners, before planting beans, keep them in a pink solution of potassium permanganate for 20 minutes, after which they are watered abundantly with warm running water. Landing is carried out in open ground, but if the climatic conditions are not warm enough, then after planting the ground can be covered with a film. The seed is placed at a depth of 3-4 cm, but if your seeds have sprouted, then planting is no longer allowed to such a depth, and then the seed is placed in a hole up to 20mm deep. Then, when planting germinated seeds (the lower part of the stalk), they are slightly covered as the plant grows. The seeds should not be allowed to wash out of the ground, therefore, at first, a film shelter or the construction of another shed may be needed for the period until the plant reaches a height of 40mm. It is by this time that it takes root well and does not die during intense rainfall. Some gardeners sprinkle the seeds with humus immediately after planting, but this is not required with proper autumn soil preparation.


The bush type of beans is sown in rows with an interval of 150-200mm, the row spacing is not less than 300mm. Moreover, sowing must be carried out in such a way that subsequently the bush will have to be piled up once or twice (and this is done even before flowering), because the frequency in two rows is quite enough to simplify care.
But the curly version is planted much more densely (70-80mm distance between plantings), but only in one row. Otherwise, the insolation of the plant will be insufficient and you will have to forget about a good harvest. As soon as the sprouts reach a height of 100 mm, they must be tied to the "supports" - the fence or the wall of the building. Further, the climbing plant will grow quietly and independently "find" the opportunity to catch on for further growth. But if the goal is not only the harvest, but also the decoration, then it is recommended to run the twine or twine in the direction of the desired growth. In this way, a natural green "wall" can be achieved, since dense foliage, when planted at intervals of no more than 80mm, will provide a continuous background. When the climbing plant reaches a height of 2000-2500mm, its tip is pinched to improve fruiting.


Seedlings and care
Beans sprout, despite the hard shell and the impressive size of the seed, not for long. A strong sprout emerges from the soil already on the sixth day after sowing. The main thing is the right temperature. For successful germination in the daytime, it should be about + 20 ° С.


Bean seed germination
Young sprouts are sensitive to the cold at night. That is why, at the slightest threat of a minus on the ground, it is necessary to cover them with spunbond overnight. And on the eighth - tenth day, all seedlings must be hilled.
Then, after the plants reach the fifteen-centimeter growth mark, they must be hilled again. And repeat the procedure several times throughout the season, as the soil subsides after watering.
Advice! As soon as the lashes of the curly varieties of beans grow to a length of two meters, their ends must be pinched. This will increase fruiting.
Mid-season green beans, with proper care, will begin to bloom massively on the fortieth day after germination. It will take another three weeks for the formation of full-fledged ovaries. And after that - attention! Harvesting of green bean pods begins ten days after ovary formation. If you miss this moment and overexpose the pods on lashes for at least a week, their taste will deteriorate significantly.


Bean Care Tips
Fertilizers
In addition to preliminary autumn and spring soil dressing, green beans will need additional feeding. At least twice more during the growing season, you will have to feed the crop - when it enters the budding phase, and at the beginning of the fruiting phase.
Fertilizer - superphosphate mixed with wood ash (15/50 g per square meter). If there is, you can add a complex with a high content of molybdenum, boron and manganese to the feeding. If there is no special fertilizer containing these three trace elements, ordinary potassium permanganate will help to get out of the situation. A medium pink solution is poured over the leaves and into the hole.
Watering
For green beans, moisture is important, especially climbing varieties suffer from a lack of watering. But it is necessary to water intensively and often the beans only during the period of forcing the whips and budding. As soon as the ovary begins to form, watering should be done less often, but more abundantly, and the soil around the bushes should be mulched.


Watering the green beans
Advice! For watering green beans, experienced gardeners use one secret - weeds are placed in a large barrel in the sun (any weeds after weeding the garden, you can slightly grind them beforehand) and fill them to the top with water. The infusion must stand for seven days. It needs to be stirred from time to time. After a week, a liter of the finished nutritious herbal infusion is diluted in ten liters of water and poured over the beans. It responds to this hydration with fleshy pods and healthy, powerful stems.
Care Tips
Asparagus beans are not as whimsical to care for as many other plants, however, in order to grow the desired crop, you still have to devote a little time to it.
Growing asparagus beans from seeds in the country, where the owner visits once a week, is not possible, since this plant needs constant watering and care.
After planting, the beans are watered every other day. After sprouting, continue watering as the soil dries out. It is best to water when the sun has already set. Watering is carried out at the root.
Some gardeners use a simple, useful solution for watering: fill 2/3 of the barrels with weeds, add water to the brim and leave for a week. For irrigation, a liter of solution is diluted in a bucket of rain or settled water.
Weeding and loosening
For better plant growth, it is necessary to regularly weed the weeds that appear next to the beans. Until the plant has grown to 10 cm, it is necessary to loosen the soil next to it after each watering or rain. The first loosening is performed when the sprouts have already gained a height of up to 7 cm.
Soil mulching
In order to facilitate the care of asparagus beans, the soil is mulched with straw. This will allow moisture to remain in the ground and also eliminate the possibility of weeds.
If the asparagus is a climbing bean, it must be secured to a firm vertical support.The height of such supports is usually about 1.5 m. A rope or wire is placed on top of them, along which the shoots of the plant will later be guided.
When the shoots release a curling arrow, you need to direct it to the support, and overnight it will itself twist around a stick or post.
Pinching escape
When the beans grow up to 10 cm, you need to huddle them. This is to strengthen the root system and improve the nutrition of the beans when the pods begin to set.
When the growth of the plant will already be more than 2 m, it is recommended to pinch the top so that it does not grow higher, and all the nutrients go to stimulate good fruiting.
For top dressing, cow dung is most often used. There are two ways to do this:
- combine with watering (dissolve 1 to 10 humus in water);
- spread the manure on the mulch so that it rotted.
Chemical fertilizing begins when the seedlings produce the first leaves.
At this point, the plant is fed with 40 g of superphosphate per square meter.
When the first buds appear, potassium salt is added to the soil - 10 g per square meter. When the fruits are already ripe, you can feed the soil with a solution of wood ash.


Nitrogen must not be fertilized at the flowering stage and further stages of development, as it can cause a strong development of the green part of the plant and leave the owner without fruit.
Important points of harvest
- In the early variety, the harvest begins on the 50th day after the first sprouts have hatched from the soil.
- In the mid-season - on the 70th day.
- In late maturing - on the 100th.
You need to pick the pods in a state of milk ripeness. It is characterized by the following features:
- pods are not hard, bend rather than break;
- pod length from 10 to 20 cm (depending on the variety);
- inside the pod is a green bean the size of a grain of wheat.


Bean pods in a state of milky ripeness
- Harvesting is carried out in stages, every two days.
- Leave the pods that you did not remove in time for seeds, and henceforth check the lashes more carefully.
- Removing the pods stimulates fruiting. This means that the more beans you harvest, the more they grow.
- Harvesting can continue until frost.
- Harvest per square meter of green beans - two kilograms.
Video - How to grow beans on the site
Care features
Green beans are an undemanding plant. But this does not mean that it is enough just to plant it. To get a good harvest, you should follow the simple rules of farming and caring for beans.
Germination rules
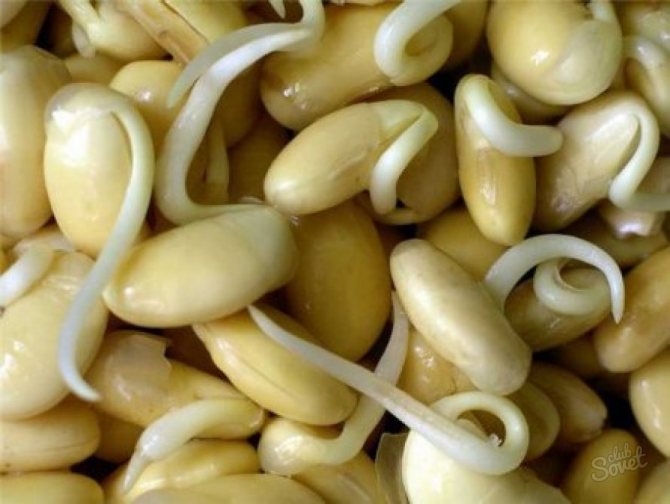


It takes about a week to sprout on time, provided that dry beans are used. If the air temperature is below the established criteria, then germination is observed later - after 10 days.
But you can accelerate the formation of seedlings. To do this, before sowing, the beans are treated with a growth stimulant. Beans also help germinate by hiding.
Many people use an interesting and original way of germination and further planting. Its essence lies in the fact that initially a ribbon with sprouted beans is prepared. To implement it, you need several trash bags, toilet paper, seeds and water.
Preparing the tape for planting is quite simple. First, the bag is spread, a dampened tape of paper or fabric is carefully laid on it.
Beans pre-soaked in warm water are carefully laid out on paper and rolled up. Gradually, the paper will turn into a roll with beans along one edge. The resulting twisted tape is placed in a narrow container with water and germinated.
Attention!
It is important not to miss the moment of transfer to the ground. This is done until the sprouts have turned into leaves.
After the sprouts with cotyledon leaves appear, hilling should be carried out. This will help strengthen the young shoots.
Watering
The culture is very fond of moisture, so they monitor compliance with watering.Do not allow the soil to dry out during the period of pod formation.
Watering is performed as the soil dries out and depending on the weather. There is no specific form for the volume of water, it is important that the earth remains moist. Rainwater is considered optimal watering. Experienced gardeners use settled water of at least 18 degrees.
Top dressing


To obtain a bountiful harvest, it is required to apply fertilizers at least 3 times during cultivation.
- The first time feeding is performed in 3-4 weeks. It is recommended to take complex formulations, in which phosphorus and nitrogen must be present. You can use superphosphate (30-40 grams per square).
- After 20-21 days, for the active formation of pods, a nutrient composition based on potassium salt should be added with a calculation of 10-15 grams. for each square.
- Once again, after 21 days, fertilizing is repeated using complex fertilizers.
A large amount of fertilizer can provoke overgrowth of the tops, so you need to be careful with the nutrient formulations.
































