Onset of symptoms
On our site there is a similar article: What scabies looks like in the photo.
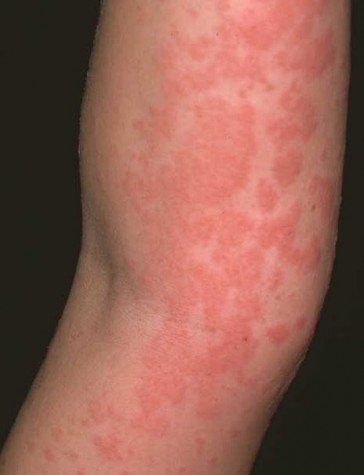
Leading the list of signs and symptoms of scabies is intense itching, which begins within a few days after the tick enters the body. The incubation period, the time between the tick enters the body and the first symptoms appear, may be absent altogether if you have had an infection before.
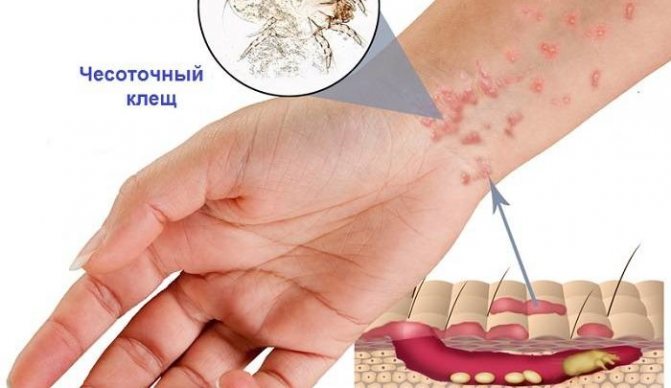
Itching most commonly occurs in the armpit, elbows, wrist, finger, chest, buttocks, or genitals and usually does not affect the face. Itching is usually present all the time, but worse at night.
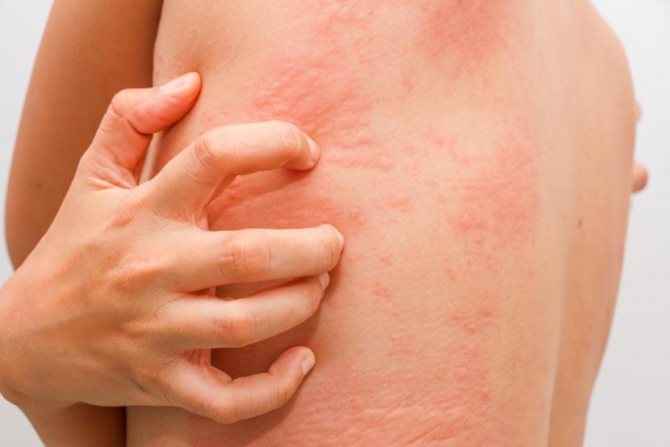
Itchy scabies can be accompanied by a visible rash that can show up as small red or scaly scars.
Symptoms and itching are worse if you have an allergic reaction to a tick.
In children under 2 years of age, mite rashes tend to appear on the head, neck, palms, and soles of the feet. In older children, the rash usually occurs in one of the following areas:
- Hands
- Between the toes
- Wrist
- Navel
- Groin area
- Chest area
- Armpits
- The reasons
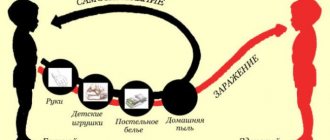
Scabies is caused by a mite invading the skin, which occurs when there is direct contact with an infected person. Whether it's sex or other close and prolonged skin contact, a quick hug or handshake usually doesn't put you at risk.
A tick does not live longer than a day or two outside of a living organism, so it is rare to catch scabies by touching things that have come into contact with someone who has had scabies.
The parasitic mite is tiny, too small to be seen with the naked eye. The female tick burrows under the skin and lays 10 to 25 eggs before dying. The eggs hatch after three days and the larvae move to the surface of the skin.
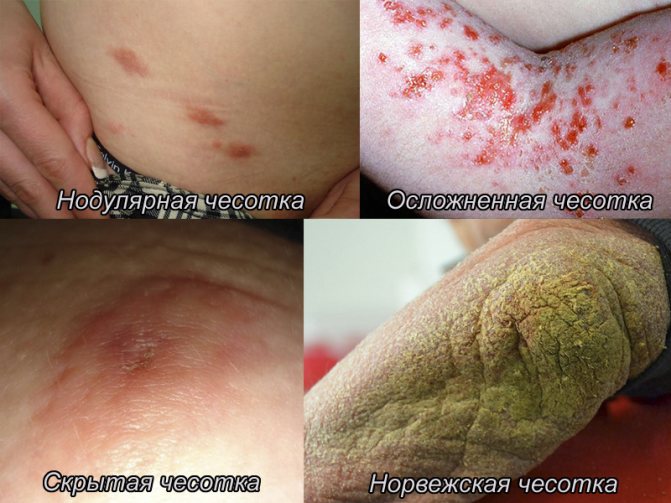
Norwegian scabies
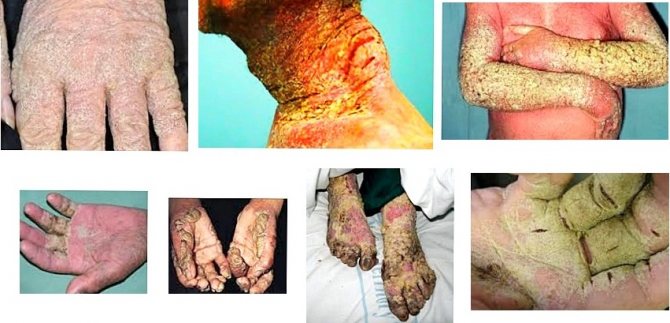

A complication of scabies, Norwegian scabies, is characterized by areas of the crust that contain a large number of mites.
Varieties of scabies
Scabies can develop differently in different individuals.
- Typical scabies, the most common. It is characterized by the presence of all of the above symptoms (itching, itching, etc.)
- Scabies without moves... Its difference from typical scabies is that there are no scabies on the skin, but there are bubbles up to 2-3 mm in diameter. Scabies without strokes develops in people who have been in contact with a patient with scabies, but they were infected not by adults, but by larvae, which take time to develop.
- Scabies "clean" similar to typical scabies, but develops in people who wash frequently and remove most of the mites from their bodies. Thus, their scabies is not as pronounced as typical.
- Norwegian scabies develops in people with weakened immunity (for example, with AIDS, tuberculosis), drug addicts, people with Down syndrome. Norwegian scabies is very severe, affects the entire body, including the head, and is highly contagious.
- Pseudo scab (pseudosarcoptic mange) develops in people infected from animals. The scabies mite of animals is not able to cause scabies typical for humans and is manifested only by severe itching. The cure occurs on its own after the termination of contact with a sick animal.
- Complicated scabies develops with untreated typical scabies and is a consequence of the addition of an infection. The lesions become red, sore, damp, and smell unpleasant.
Diagnosis
Rash
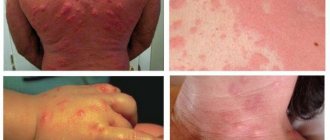
The rash that scabies causes can often look similar to other rashes. Again, the scabies rash usually occurs on the wrists, between the fingers, in the armpits, around the waist, and in the genital area. While a rash in these areas does not directly support scabies, it certainly enhances its outlook.
The rash causes red papules with small lines. Since the tick does not usually spread far from the infected area when it is under the skin, burrows may not be visible. The rash can also cause intense inflammation of the skin with blistering, redness, and itching.
Diagnostic tests
There are no good tests that can diagnose scabies, but a doctor may consider scraping off a small portion of the rash and examining it under a microscope for mites or mite eggs. However, mites and eggs are often not visible under a microscope.
Clinical picture
Infection with itch pruritus can manifest itself in different ways, it all depends on the stage of the disease and the state of the person's immune system. The main symptoms of scabies are:
- itching of the skin, the intensity of which increases at night (this is due to the life rhythm of the pathogen),
- the presence of gray lines on the skin 5-7 mm long and papules,
- the presence of traces of scratching on the skin, they can appear as lines or dots,
- the formation of bloody and purulent crusts.
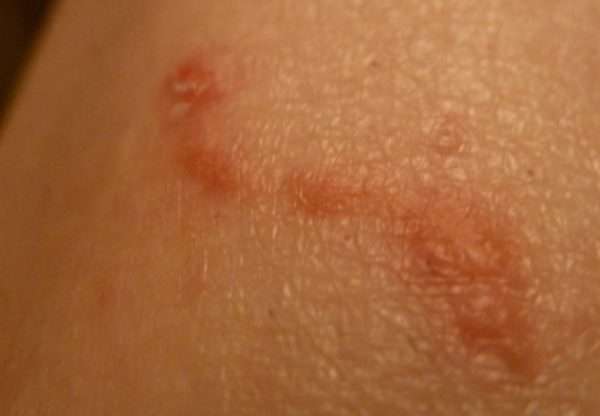

Scabies is characterized by a specific location of the rash, they are localized:
- on the buttocks,
- in the interdigital spaces,
- on the stomach
- in the area of the mammary glands.
The prevalence of certain symptoms also depends on the form of the disease. For example, nodular scabies results in the formation of reddish-brown nodules on the skin; cork scabies are indicated by crusty sores.
To establish an accurate diagnosis, you must consult a doctor and undergo laboratory examinations.
Treatment
The following treatment options can help get rid of the scabies rash.


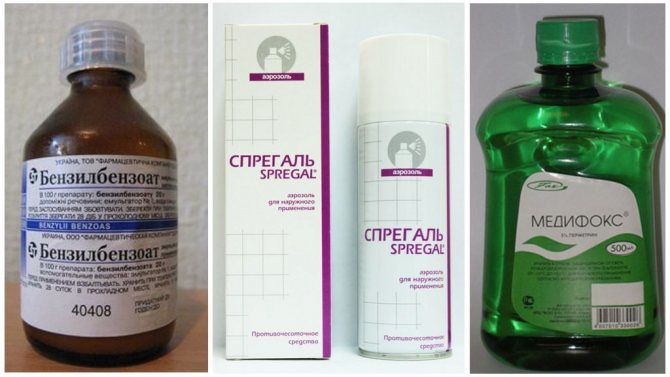
- Permethrin 5% cream: Apply liberally from the top of the neck to the soles of the feet before going to bed and wash off in the morning. Permethrin is the safest treatment for pregnant women.
- Ivermectin: An alternative therapy, but not recommended for children under 15 kg. This is an oral medication, the dose used is calculated based on your weight.
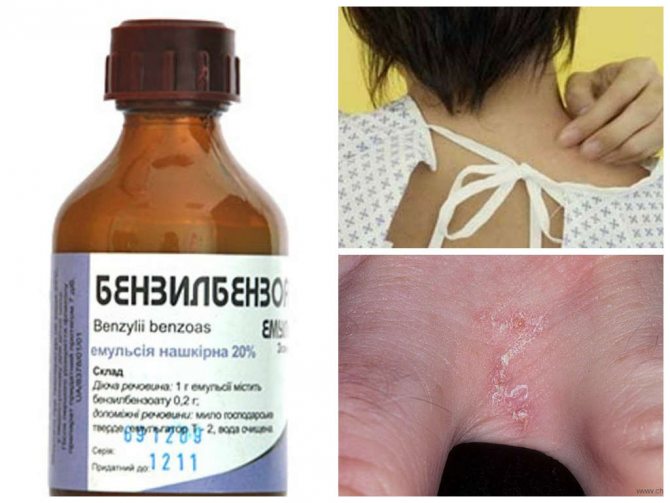
- Benzyl benzoate: drug against scabies and other ectoparasitosis. Benzyl benzoate is included in the list of essential and essential medicines and can be obtained free of charge.
The medications kill the mites, but they remain in the skin until the body destroys and expels them. This process can take about four weeks.
Differential diagnosis
To make the correct diagnosis and prescribe an adequate treatment regimen, it is necessary to carry out a comparative diagnosis.
Difficulties in making the correct diagnosis may arise due to the fact that the elements of the rash are hidden under an infection of a secondary nature, the appearance of which provokes scratching. It is difficult to determine the presence of the disease in children under one year old, because its course at this age is atypical.
The main method for confirming the diagnosis of scabies is the detection of itch or larvae.
Differential diagnosis of scabies is carried out with the following diseases:
- rash of newborns
- atopic dermatitis,
- eczema of bacterial genesis,
- hives,
- chickenpox,
- allergy,
- nodular pruritus,
- infection of a bacterial or fungal origin.

ethnoscience
Since scabies on the hand refers to ailments that were well known to representatives of ancient peoples, many folk recipes have come down to our times that allow you to effectively cope with this ailment. The treatment of parasitic disease with improvised means is successfully implemented through the use of tar or sulfuric ointment, as well as all kinds of decoctions of herbs and essential oils.
Folk recipes not only decrease scabies mites, but also contribute to the rapid regeneration of the skin, a significant improvement in their condition, and the elimination of other dermatological problems.
Folk recipes for scabies on the hand
The most popular folk remedies include:
- lubrication of the affected areas of the body with an ointment based on celandine (for preparation, you should take 4 parts of celandine and 1 part of petroleum jelly) until the manifestations of the disease completely disappear;
- applying a birch tar product to the skin (5 g of birch tar, 10 g of soap, 10 g of animal fat, 10 g of sulfur) for a week with a daily change of linen and taking a shower;
- processing the skin with a decoction of onion and garlic, prepared by boiling the components for 30 minutes over moderate heat;
- washing the skin with soap made from onions and garlic for a period of time necessary for the complete extinction of pathological symptoms.
Treatment scheme for animals at home and prevention of re-infection
For the treatment of sarcoptic mange in cats, Frontline, Advocate, Stronghold drugs are most often used in the form of drops that are applied to the withers. The tool is usually used every two weeks for 3 months. But such drugs as Fosmet, Amitraz and sulphurous lime are applied to the affected areas with a tick during three procedures carried out with an interval of 2 weeks. In some cases, the insecticidal drug Ivermectin is administered, however, it has many contraindications.
For the treatment of dogs from scabies, external preparations containing selamectin and doramectin, sulfur-containing ointments, etc. are prescribed. Every 7 days for 6 weeks, the animal will need to be bathed using special antiparasitic shampoos based on birch tar and chlorhexidine with a keratolytic effect. Among them:
- DermaPet;
- Antiparasitic and Antiseborrheic Shampoo from Synergy Labs;
- Doctor, etc.
Also, the pet is treated with Advantage or Stronghold preparations in the form of drops once. In the case of advanced scabies, it is possible to administer injections of Vormil, Ivermectin, Ivermek.


Bathing dogs with healing shampoo is the key to successful scabies treatment
Before using insecticidal ointment:
- If your pet's coat is very thick and long, you may need to trim it to apply the product.
- It is advisable to bathe the animal or at least wet it with warm water so that the crusts soften on the combed places. The softened scab must be carefully removed from the skin with tweezers. Keratolytic (removing dead cells) and anti-seborrheic shampoos can be used to remove the crust on the affected skin and wash off the crawled hair.
After applying medications to the animal, you need to put on a special collar that does not allow licking the wool in order to prevent poisoning of the four-legged friend.
To prevent re-infection:
- the animal should be kept clean, it is advisable to wash it after every walk on the street;
- pet litter should be regularly wiped out and washed;
- it is preferable to castrate the animal so that it does not feel an ardent desire to meet its love on the street;
- a fluffy pet must be protected from communication with stray brethren;
- The diet of a cat or dog should be balanced so that the animal's immunity allows it to resist infection with itchy itchy.
Photo gallery: drugs for the treatment of scabies in animals
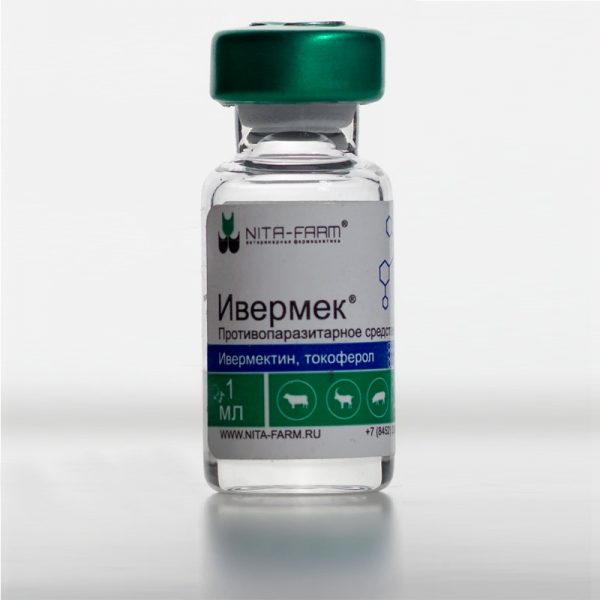

Ivermek is an antiparasitic complex agent of systemic action


DermaPet specialized shampoos are suitable for frequent use and adapted to the pH of animal skin
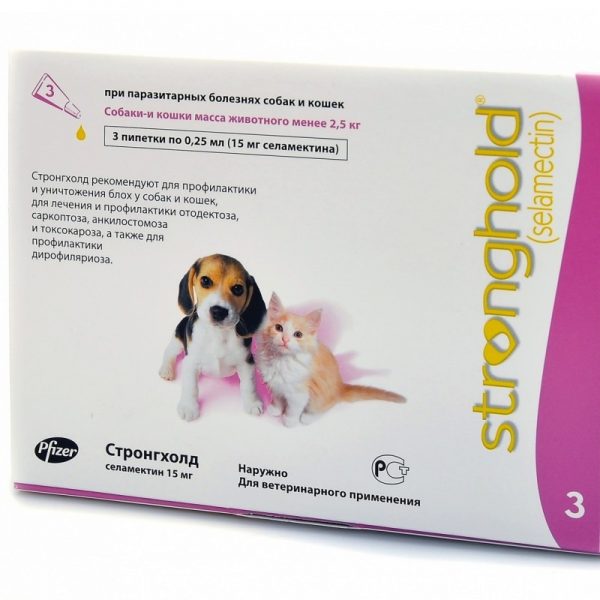

Stronghold is Safe for Dogs and Cats at Recommended Doses
Causes of the disease
The causative agent of scabies is called scabies mites. The female is predominantly active: her size is larger than the size of the male (can reach 0.4 mm), and she lays her eggs in the passages made between the granular and stratum corneum of the epidermis. After that, larvae appear from them, which quickly mature and also begin to be active. There is a certain set of factors that stimulate infection and the development of the disease:
- Failure to comply with the rules of hygiene - unclean people are affected by the itch mite with a greater frequency and transmit pathogenic microorganisms, too, with greater activity.
- Being in a crowded group - a large overcrowding (especially in the cold season) increases the chances of long-term contact between the tick carrier and a healthy person. If the presence among people is constant (boarding schools, military units, hostels, orphanages), the risk of a scabies epidemic increases even more.
- A decrease in the immune response to the pathogen - against the background of the genetic characteristics of the body, taking medications, the presence of HIV infection. If the immune system is weakened, tick reproduction occurs uncontrollably, but often asymptomatic. Such a person is a carrier, unaware of his own danger to others.
- Nervous strain, stressful situations are secondary factors that provoke a decrease in the body's defenses.

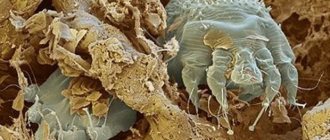
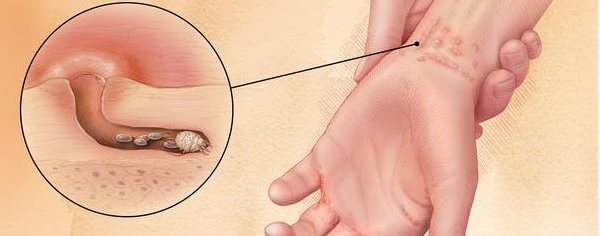
What does an itch mite look like?
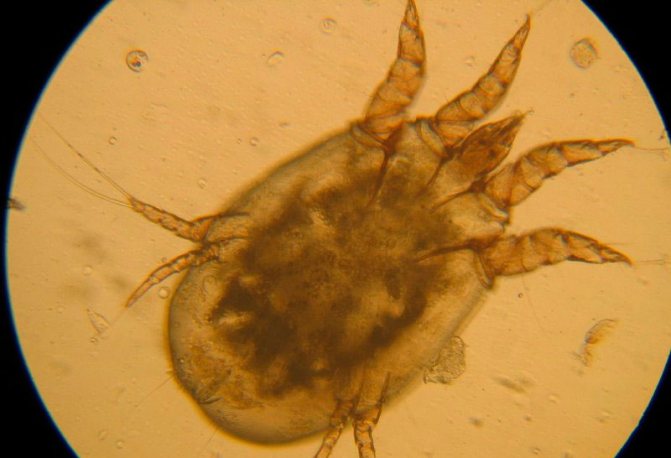
To understand who you have to fight with, it is important to know what scabies itch looks like, its structure and size. This microscopic human ectoparasite. It belongs to arthropods and settles mainly in the upper layers of the epidermis. Its shape is oval tortoiseshell. The forelimbs are pincer-shaped.
The tick has 2 pairs of legs with lateral suction cups and 2 pairs of bristles. Thanks to this, it moves freely along the scabby passages.
They have a pronounced sexual dimorphism. Females are cream, yellowish or gray. Their size reaches 0.5 mm. Males are darker and their size is 2 times smaller than that of females.
Scabies mite
The specificity of the course of pathology

The female scabies mite makes a move, leaving eggs.
Scabies mites multiply and lay eggs in places with weak vegetation and a large number of sweat glands - these are feet, palms, elbows, genitals (in men). Sweat fills the passages and creates favorable conditions for the life of the offspring. The period for individuals to grow up is 2 weeks. After this period, new mites repeat the development cycle.
Important to remember! Scratching the affected areas leads to the spread of the infection to healthy organs and parts of the body.
The scabies canals also store the waste products of parasites. These substances are foreign to the human body, their long-term presence in the integument of the skin causes inflammation, increased sensitivity, and allergies. The tick is nocturnal, therefore, the exacerbation of symptoms occurs precisely in the evening.