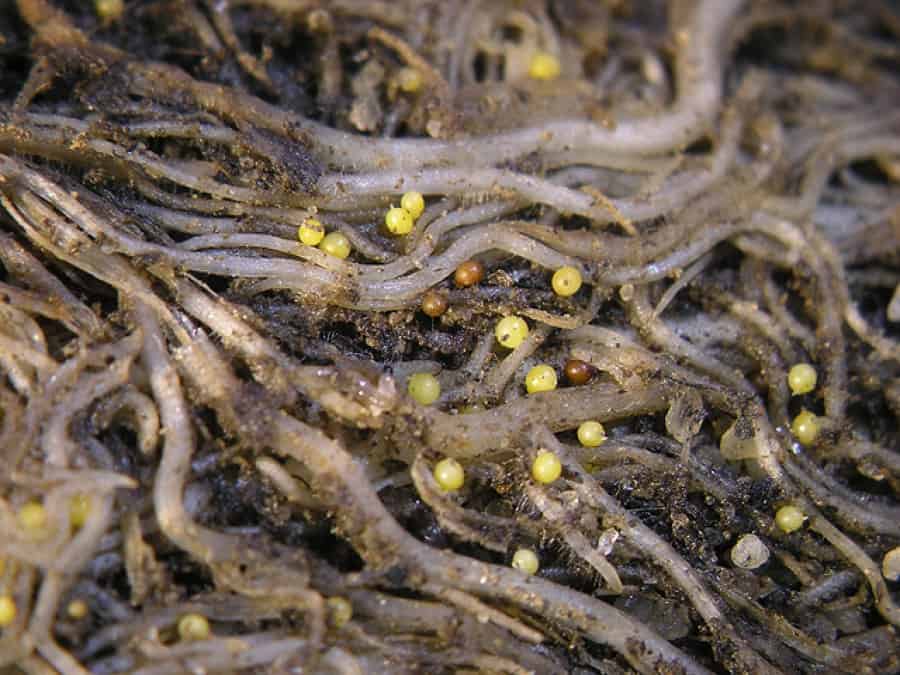
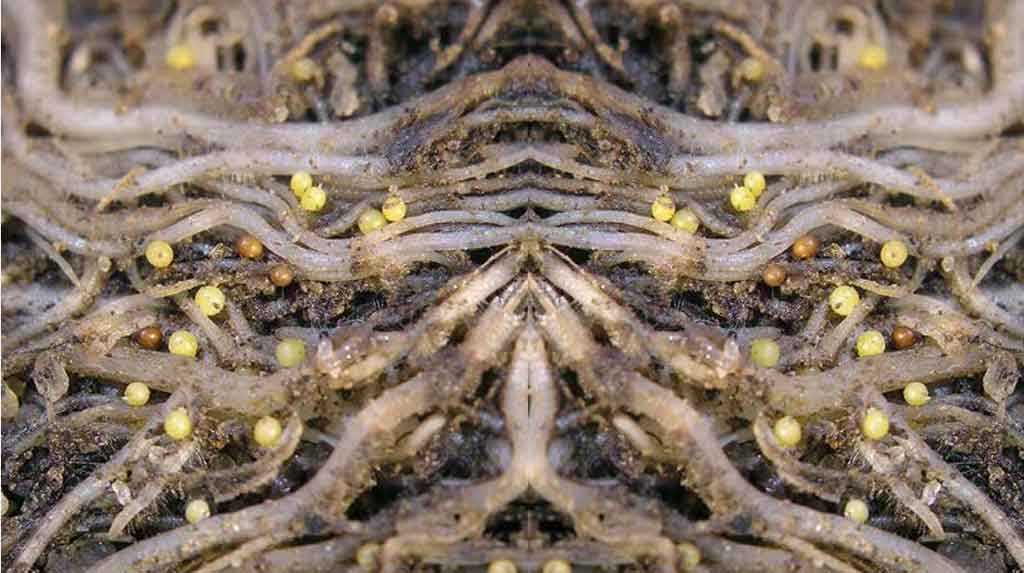
Gall nematode (root) / Meloidogyne
Gall nematode (root)... This pest is quite rare, but it causes very serious harm when a plant is infected. Nematoda are tiny worms that are colorless and grow to one and a half millimeters. In 3-4 weeks, the nematode gets out of the egg and begins to feed. The pest invades the roots and releases a digestive enzyme into them, which leads to the appearance of galls (sizes can range from the size of a seed to the size of a walnut), consisting of loose tissue, the destruction of which leads to rotting of the roots and the ingress of fungi, viruses and bacteria.
Leaf Nematode / Aphelenchoides
Leaf nematode... The worms are smaller than stem and root nematodes (up to 1 millimeter), colorless. They settle in the leaves of plants. Places of leaves where nematodes feed lose color and spots are visible when viewed under light. The leaf becomes thinner, dry spots of dead tissue appear, after which the leaf turns brown, dries and rots. A plant can become infected through water or soil from another plant. Larvae can live in soil for up to several months, even at very low temperatures.
Stem Nematode / Ditylenchus
Stem nematode... The worms reach up to 1.7 millimeters in length. Often, nematodes infect only one plant and do not migrate to other species. The stems, leaves and flowers of tulips, begonias, phloxes, carnations and others are affected. The nematode through the roots gets from the soil into the leaves and stems. Thickening appears on the affected parts of the plant - stems and leaves are formed and develop incorrectly, swellings appear. Over time, the color of the leaves and stems turns pale, then turns brown, and the leaves and stems themselves die off.
Types of nematodes
Different types of nematodes specialize in damaging roots, stems, leaves, buds and flowers. On the basis of this, a species classification of phytoparasitic nematodes was constructed.
Leaf nematodes
Movable colorless worms up to 1 mm long. Distributed everywhere. But in the open field, they harm more in wet years in the Central lane, in the north-western region and in the south of Russia. They parasitize on the aboveground part of plants: outside or inside leaves, buds or buds. The soil for them is a temporary habitat. They move along a thin water film on the surface of the plant, penetrate inside through small lesions and stomata.
One generation develops within 10–11 days, and 20 or more generations may appear in a year. The pest hibernates only in the ground parts, most often in young shoots. It multiplies in leaf axils, buds and mesophyll microorganisms on the surface of plants.
Leaf nematodes infect strawberries, ornamental plants: chrysanthemums, asters, begonias, dahlias, phloxes, primrose, iris, gerberas, pelargonium, peonies, violets, lilies, cyclamen and others.
Stem nematodes
Transparent filamentous worms up to 1.7 mm in length. In our country, this species is found everywhere on heavy soils, is actively manifested in regions with a temperate climate. The life cycle of one generation lasts 3-5 weeks, the favorable temperature for the development of the pest is 5-34 ° C. During one season, 4–6 generations appear. Females of this nematode are fertile, laying from 200 to 400 eggs.The pest overwinters in rhizomes, roots and stem bases.
Stem nematodes live on 500 species of vegetable, berry and flower-ornamental crops. They damage aerial parts: stems, leaves, flowers, as well as seeds, rhizomes and bulbs. Almost no damage to the roots. They penetrate only into living tissues through the stomata, where they live and reproduce.
Stem nematodes prefer to parasitize on one host plant, without switching to other species. Vegetable crops often suffer from stem nematodes: onions, potatoes, tomatoes, peppers, eggplant, carrots, pumpkin (cucumber, watermelon, pumpkin), ornamental plants: tulips, phloxes, begonias, hyacinths, carnations.
Root nematodes
Round colorless worms 1.3–1.5 mm long, living in the soil near the roots of plants. This type of nematode is divided into 3 groups:
Gall nematodes
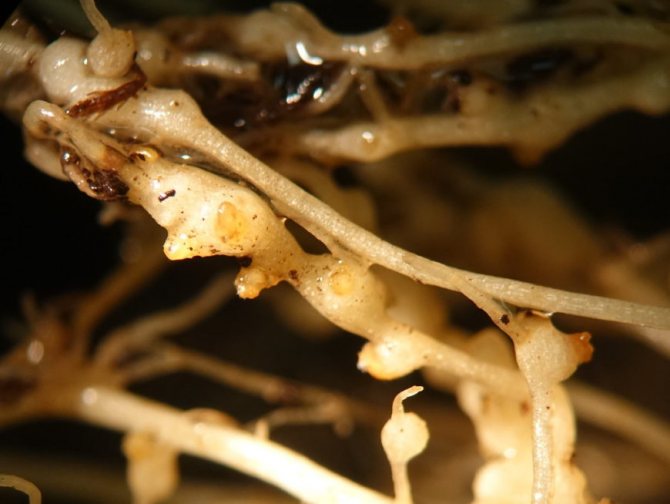
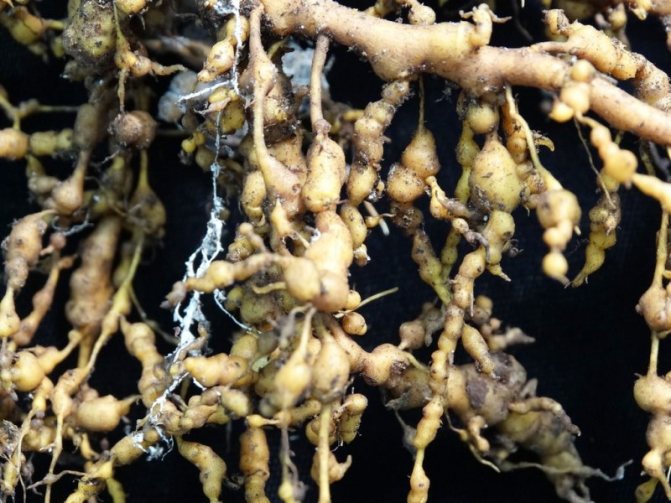
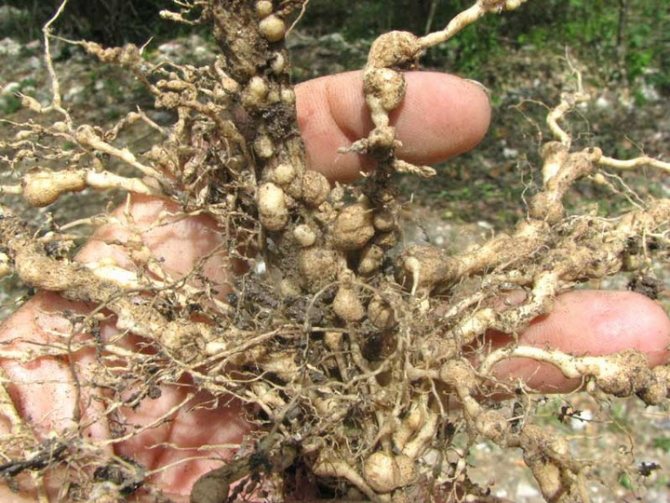
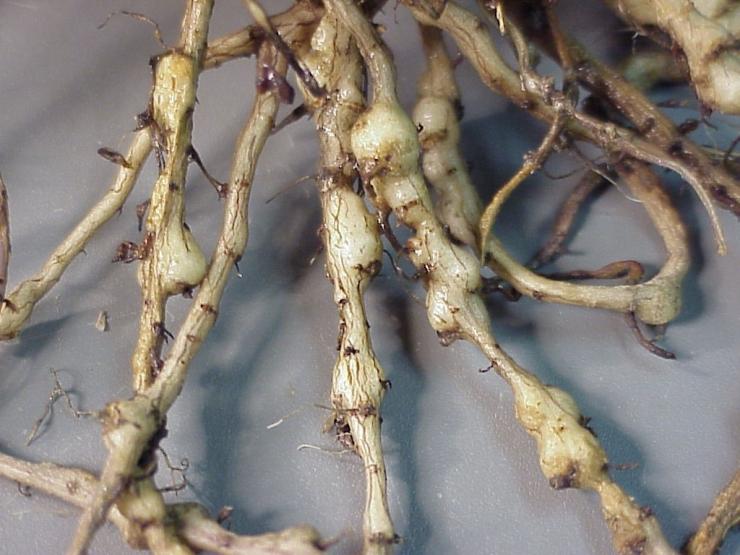
The saliva secreted by the pest causes the formation of round or elongated thickenings on the roots - galls 3-5 mm in size. Inside the galls, nematodes feed on plant sap and multiply from 1 to 13 times annually. Females lay up to 2000 eggs in special egg sacs within 2–3 months. Males do not always take part in breeding. The emerging larvae migrate, find the roots of a new host plant and begin to feed. They reach sexual maturity in 3-4 weeks.
Dangerous for more than 400 species of plants - vegetables and ornamental crops. They are sensitive to low temperatures and are more common indoors. They severely damage celery, lettuce, carrots, tomatoes, eggplant, peppers, strawberries, melons and legumes. Ornamental plants include roses, clematis, ficuses, begonias.
Free living nematodes
Distributed on large-porous and sandy soils. Thanks to good aeration, the pest actively moves in the ground. Salad, celery, carrots are often affected by this pest.
Free cyst nematodes
The spread of the pest occurs with the help of cysts formed on the roots - dark brown capsules the size of a poppy seed. Dead females with viable eggs and larvae turn into cysts. Each cyst contains up to 700 eggs and larvae.
The larvae do not die in winter and leave their shelter with the arrival of heat, but they can remain in such a conserved state for up to 10 years. Representatives of this group include the golden potato nematode on nightshade crops, and the beet nematode that damages cruciferous plants and beets.
Pests deplete plants and contribute to the spread of fungal, viral and bacterial diseases, the pathogens of which penetrate through damaged roots. With a strong infection of the roots, losses among vegetable crops in 3-4 months reach 25-80%.
Description and photo
Microscopic worms are called nematodes. Parasites live and develop in a humid environment, harm the development of plants, and can lead to the death of both garden and indoor crops.
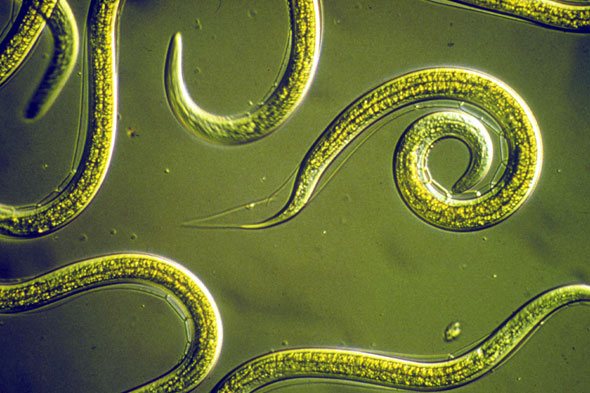
Parasites under the microscope
In total, there are about 30 types of pests. They feed on plant sap. The size of the worms is up to 2 mm. There are three types of nematodes, according to the places of life of the parasites:
- Leafy ones are beige in color, up to 1 mm long, filiform.
- Stem, also filiform, up to 1 mm.
- Root or gall, about 2 mm long, damage the roots, on which thickenings (galls) are formed.
How to get rid of nematodes on potatoes?
Often it is not possible to completely defeat the nematode on the site, however, it is in your power to significantly reduce the number of this pest and reduce the number of nematodes on the site to a minimum.
Chemical control agents
For effective control of a nematode, it is appropriate to use insecticides from the group of nematicides.
1. It is quite possible to use drugs from the contact group, such as
- Karbofos,
- Lindane,
- Phosphamide.
2.It is permissible to use fumigants that, in the form of a gas, penetrate the pest's body and kill it, these are preparations:
- Chloropicrin,
- Nemagon,
- Carbation.
Biologicals
It is quite permissible to use biological preparations to combat the nematode, however, their effectiveness is not very high and with strong infection of the soil and plants with a nematode, they can be said to be ineffective.
These are biologics:
- Metarizine,
- Basamil.
Popular means of struggle
It is not effective to use various infusions and decoctions to combat the nematode, you just waste your time and energy, there will be no sense from them, or it will be, but extremely small. In this case, biological drugs will be much more effective than folk remedies based on decoctions and infusions, and there will be no harm to the environment from biological drugs as well as from infusions and decoctions.
Watering with boiling water
Of the popular control measures, perhaps the most effective will be the use of boiling water to scald the soil with it.
- For this, the steepest boiling water is used.
- The soil must be loosened and generously watered with boiling water.
- It is advisable to repeat the procedure several times in order to disinfect the soil as much as possible and to the greatest possible depth.
It is clear that cultivation of the soil by spilling it with boiling water is appropriate to carry out in small areas. But in large areas, from 10 acres and more, it is appropriate to use chemicals.
Marigold
There is also an opinion that the smell of marigolds scares off the potato nematode, whether it is difficult to say or not, but there is nothing easier to sow marigolds around the perimeter of the site with potatoes - beautiful, and there is a chance that the nematode will not appear or leave your site.
How to prevent serious infection
As you know, it is almost impossible to completely destroy the rootworm nematode. For this reason, greenhouse farms are usually faced with the question of how to reduce the number of parasites to a safe limit and prevent large crop losses. Proper prevention will help here, which is based on:
- timely destruction of weeds;
- increased spillage of the substrate in the greenhouse, which should alternate with drying;
- laying manure in the soil;
- spilling the substrate twice with infusion from the plant that is currently being processed, and alternating it with drying the soil;
- cultivation of peas and beans, which are trapping plants for root root nematode, as well as watercress, which can dramatically reduce the number of harmful individuals.
Nematode control measures
There are several types of fight against this pest, starting with folk methods and ending with agrotechnical techniques. There are also chemical and biological drugs that can be used to kill the parasite. Let's consider all effective methods in more detail.
Agrotechnical
To combat the nematode, agronomists use several proven methods:
- crop rotation - regular change of culture on the site;
- applying organic fertilizers for potatoes - this will strengthen the plant and make it resistant to pests;
- weed control - the main crop will be healthier and more resilient.
If the vegetable is grown for seeds, then the false sowing method can be applied - dig up the first seedlings and burn them 15-20 days after germination. The larvae have already entered the root system, but have not yet begun reproduction, and this will save up to 85% of the harvest from infection.
Chemical
Synthetic substances are actively used by farmers, but the fight with chemicals is possible only with the appropriate equipment and observing safety measures. Two types of poisons are used:
- Fumigators are poisonous gases that are inhaled and killed by microorganisms. Among them:
- carbation;
- chloropicrin;
- nonmagon;
- methyl bromide.
- Contact poisons - they are absorbed through the skin from the soil and kill pests. Most often used:
- methylmercaptophos;
- karbofos;
- phosphamide;
- lindane.
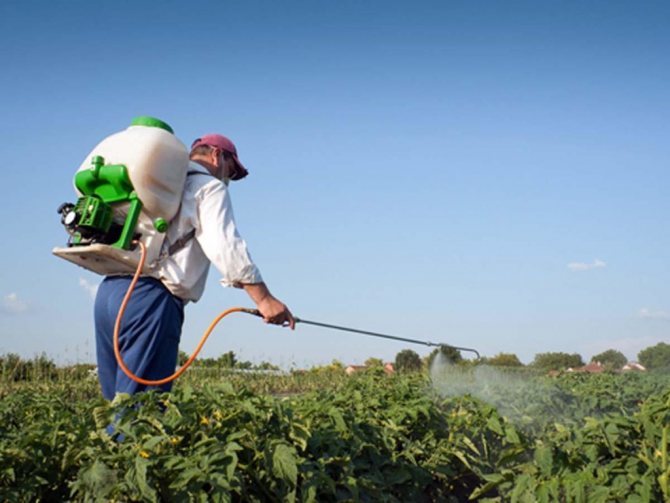


The chemical method of control is chosen by farmers and enterprises that grow vegetables for export, since the drugs help to establish a high level of control over the crop and reduce the chances of its damage.
Biological
Preparations that were created on the basis of natural substances are also used in the fight against pests of potatoes. They are effective in small areas of infection and do not harm the plant itself, being considered environmentally friendly. There are three groups of such nematicide preparations, which are based on:
- Predatory fungi that devour larvae and cysts.
- Waste products of microorganisms.
- Herbal extracts (based on garlic, marigolds)
Popular drugs for fighting are Nematofagin BT, Aversectin C, Metarizin, Pecilomycin, Narcissus, Basamil, Phytochit. They are environmentally friendly, but have a narrow range of activities, so you should first read the instructions.
Folk
Folk recipes are chosen by summer residents and gardeners who grow potatoes for themselves and strive to get the cleanest ecological product possible. Plants are treated with improvised means. For this:
- Urea is added to the site and everything is well watered with infusion from the sprouts. The larvae hatch ahead of time and die from cold and hunger.
- The site is abundantly fertilized with ash and rotted manure - the mixture kills all parasites.
- Water the soil immediately after planting potatoes with diluted chicken droppings in water (ratio 1:20). For 1 sq. m requires 1-5 liters of solution.


But the best way to destroy the nematode is to plant marigolds, rye or corn after the potatoes in the area. The root secretions of these crops cleanse the contaminated soil and kill pathogens.
Nematode control methods
In general, you can endlessly describe various kinds of nematodes on various plants, better let's move on to the story about the methods of combating this infection.
Folk remedies
The main and, perhaps, the only effective folk remedy for fighting the nematode "cheerfully and cheaply" is spilling the soil with boiling water on the eve of planting.
High temperatures are fatal for tiny nematodes, and at the end of such a procedure, their number on the site really drops noticeably. You just need to remember that for a real effect, the earth must be filled with hot water with a temperature of at least 50–55 ° С to a depth of at least 15–20 centimeters. After that, you can also cover it with polyethylene to cool it more slowly.
Alas, the measure is not fully effective. Although a significant number of nematodes live in the outer layers of the substrate and, as a rule, die during such thermal disinfection, some of the parasites can migrate into deeper layers of the soil and escape.
In addition to the soil, the affected plants themselves should be treated with hot water - as a rule, this applies to the roots and bulbs affected by the rootworm nematode. They are washed off the ground and then soaked in warm (45-50 ° C) water for 10-30 minutes. As a useful additive, formalin can be added to this water at a concentration of 0.06%.
Chemicals
Alas, the chemical method of getting rid of parasites is the most effective. A serious effect can be achieved only by using nematicides, chemicals that destroy nematodes parasitizing plants. Some poison parasites through the respiratory system. These are carbation, chloropicrin, methyl bromide and nemagon. Others penetrate the skin, such as methyl mercaptophos, karbofos, phosphamide, lindane.
Certain chemicals have a complex effect, in particular, chloropicrin. They lead to complete sterilization of the soil. Planting after processing can be done only after a few weeks, and after using some in general only for the next season.
The chemical method of control consists in spraying horticultural crops with chemicals to exterminate leaf and stem nematodes. To exterminate the root, you need to spill the soil with a solution of the drug. Sprinkling and spilling should be done in dry, sunny, calm weather, preferably before noon or after 17:00 pm. The procedure must be performed several times, since the poisons act exclusively on mature worms.
Chemicals must be used in strict accordance with the practical guidelines, with the use of protective equipment.
Preventive methods
Both preventive measures and nematode control measures without the use of chemicals are conditionally effective. It:
- Compliance with crop rotation.
- Selection of hybrids and varieties that are relatively stable to nematode damage (in particular, for tomatoes - Nagano F1, Eupator F1, Malika F1; for garden strawberries - Festivalnaya, Pearl, Dessertnaya, Saxon, Raketa; for potatoes - Scarlet, Freska, Picasso, Diamant ).
- Scrupulous selection of healthy seed.
- Heating tubers and corms before planting for 15 minutes at approximately 45-50 ° C, or 3-5 minutes at 55-60 ° C.
- Before planting soil disinfection with hot water, removal of the top layer, digging and indispensable mulching.
- Systematic planting care - thinning and weeding.
- Careful watering - drops of water should not remain on the leaves and stems for a long time, because this favors the development of nematodes.
- Planting phytoncidal plants in the aisles that help repel pests, for example, marigolds or calendula.
- If an infection is detected during the growing season, the affected and oppressed plants are cleaned on time.
- At the end of the harvest, harvesting all grass residues from the site, removing (burning) all the rest of the infected plant material together with the surrounding soil.
- To increase fertility and partial extermination of the nematode, the site vacated at the end of harvesting in August - early September must be sown with grain (preferably winter) crops. First, the site is cleaned of weed plants and plant fragments, the soil is loosened and only then it is sown with grain “randomly” to a depth of 2-3 centimeters.
- With the arrival of stable frosts, the earth is dug up together with winter crops, making a full rotation of the layer. Thus, it is enriched with organic matter and gets rid of the most dangerous pest - the nematode, which, in such unfavorable circumstances for it, simply freezes.
Types of nematodes
There are a huge number of nematodes that harm human plantings. The most significant of these are three. They differ from each other in that they affect different parts of the plant.
Root
Roundworms up to 2 mm in length. This species is also called gallic, because in the places where the root is expressed, galls are formed on it - seals and tubercles. They are yellow at first, but turn brownish brown over time.
Galls disrupt the movement of nutrients in the root system, so it begins to malfunction.
Favorable conditions for the life of root nematodes are:
- temperature from 18 ° C to 24 ° C;
- soil moisture 40–60%.
In such conditions, the pest actively feeds and multiplies rapidly. The full life cycle of a root nematode takes about a month. Its duration depends on the surrounding conditions: if they are suitable, then up to 6 generations appear per year.
Root nematodes spread primarily through the soil. You can also bring the pest into the ground with planting material, pots, garden tools.
Leafy
Leaf nematodes are very small: the length of their body is 1 cm. They are characterized by a high speed of movement and parasitism in the leaf plates of plants.The most vulnerable to infection with this species are strawberries and chrysanthemums. The danger of leaf nematodes lies not only in feeding on the vital sap of the plant, but also in the fact that they carry viral diseases. The leaf nematode often harms strawberries and chrysanthemums.
They spend almost their entire life in a sheet, where they penetrate through mechanical damage to its surface. Only occasionally do these pests descend to the ground, which serves as a temporary shelter in case of emergency. In winter, worms usually survive in dry leaves.
Stem
The length of stem nematodes also does not exceed 1 mm. Most often, they parasitize in the stem of the plant, but can move into leaves and flowers. Infection occurs through the root system, into which the larvae of the worm penetrate. This species usually affects vegetable crops: tomatoes and cucumbers, as well as onions and garlic.
Gallic root
Parasitizes on plant roots vegetable crops... Interestingly, the females of these nematodes are immobile, while the males are larger and have an activity to move.
The root nematode is a parasite. The body length of these parasites does not exceed 2 mm, in the early stages of development they have a whitish color, which fades with age and becomes transparent... That is why the fight against rootworm nematode is considered one of the most difficult: independently, without the help of a microscope, nematodes are difficult to distinguish from other root cells.
Gall root nematode - photo:
The big danger is the way the parasite enters: gall nematode does not need open wounds on the plant, it pierces the cells with a sharp needle located in the mouth opening, after which it penetrates into the tissues and settles in them. The plant is exposed destructive toxins parasite.
Plant shoots experience lack of water, and therefore begin to lag behind in growth and perish.
When examining the root system, it is not necessary to immediately destroy the plant at the sight of blisters. Sometimes galls can appear from completely harmless symbiotic organisms, for example, nodule bacteria... It is best to give a part of the root for examination.
The root knot nematode is the first to spread with soil, soil and sand, direct infection is also possible through contact of root systems during transplantation.
Most plants are killed by this parasite, but cabbage, garlic and cereals nematode resistant... Gall nematode is capable of causing meloidoginosis, accompanied by yellowing and wilting of leaves, slow growth of the plant.
There are some safe control methods with a nematode, in addition, due to the narrow specialization of parasitism, the root nematode does not penetrate above the roots, and therefore the probability of entering the human body is minimal.
You will learn how to recognize a root nematode by watching this video:
As you can see, even the smallest pest is capable of inflicting more damage to the plantthan ordinary birds and rodents, attacking the plant imperceptibly and slowly bringing it closer to death. Fight him very difficulthowever, based on the symptoms and characteristics above, one can try to limit its spread to other healthy plants.
Gall nematodes are a dangerous pest that affects both different types of vegetable crops grown in greenhouses (for example, tomatoes) and some types of ornamental crops (for example, begonia, rose, carnation, chrysanthemum), although it is extremely rare.
This pest resembles a worm and feeds on the roots of crops by eating them from the inside. Gall nematodes also emit toxic substances, and therefore galls are formed - growths, neoplasms and swellings (nodules) on the roots of plants where newborn larvae grow.This pest inhibits plant growth and reduces yields, since the vegetative part of the plant cannot receive sufficient water and nutrients for normal functioning. The ability of the root to absorb substances decreases and over time the plant dies. Externally, the weakened plant looks dehydrated, and the color of the leaves turns yellow.
Females of root gall nematodes multiply rapidly, since they can lay 2-2,5 thousand larvae at a time, and hundreds of galls can form on the roots of one plant. Although there are crops that are not susceptible to infection by this parasite (such as garlic and cabbage). But unfortunately, there are still a lot of cultures that are adversely affected by root-knot nematodes. How to deal with this enemy?
A plant susceptible to infection can no longer be saved and you will have to get rid of it, as well as remove the infected layer of earth. It will also require cultivation of the land with such means as carbation, tiazon, dazomet, vidat, ipam, onetion. You can, of course, process it with steam, but this will take more time (about three hours of processing). In addition, there are varieties of vegetable crops that are resistant to infection by root gall nematodes.
For ornamental plants, you can use a water bath from 45 to 50 ° C, in which the roots, washed from the sand, are immersed for 15-30 minutes, depending on the type of plant. A 0.02-0.03% solution of an organochlorine or organophosphorus insecticide can increase the effectiveness of such a bath. Regarding the pots in which the plant was located, then they need to be sterilized - the easiest way is to do this with boiling water.
Also, do not forget about the prevention of infection with root knot nematodes. It is important to properly prepare the soil, through sterilization, or holding for 6 to 8 months. Also, you should not immediately place new plants next to others. It is better to put it in a two-month quarantine, followed by checking the roots for infections, which will help to avoid further costly actions in the form of soil cultivation, sterilization, as well as crop loss.
What are the signs to determine the nematode
The main signs of a nematode are oppressed, squat plants, lagging behind in growth. Leaves, peduncles, petioles, deformed mustaches,
- The leaves wrinkle, curl, may shrink, become leathery (rough and similar to corrugated paper), in appearance as if pulled to the central vein. The central vein of the leaf has bulges, it seems that the leaf is broken in several places.
- The petioles are shortened, thick, twisted, acquire an atypical reddish color, the pubescence disappears.
- Stems thicken and branch strongly
- Buds, flowers and ovaries take on an ugly shape, sometimes forming a kind of green cauliflower head in miniature.
- Pale green growths are formed on the mustache, the mustache is thickened, shortened.
- Berries become small and ugly
- The tissues of leaves, petioles, peduncles and whiskers become loose.
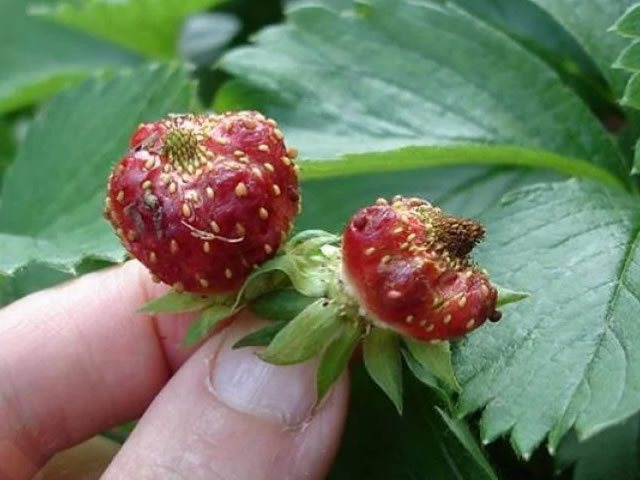


Signs of plant damage
Signs of a leaf (strawberry) nematode infection are as follows:
- Brown spots appear on the leaves and buds, they curl, lose their natural color.
- The petioles swell, the growth of the plant stops.
- Spots appear on the bottom of the leaves, which subsequently become red, the leaf becomes thinner, the yield decreases, and the plants eventually die. Strawberries, carnations, asters, chrysanthemums are more susceptible to leaf nematode disease.
Infection with a stem nematode leads to cessation of growth, thickening of the stems, loss of color in stems and buds, and ultimately death of the plant.
At risk are onions, garlic, cucumbers, parsley, tomatoes, radishes.
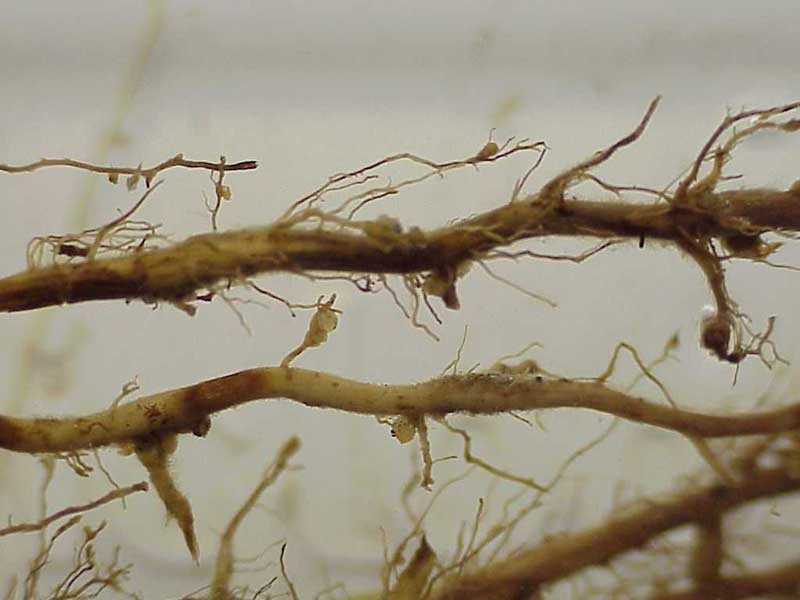
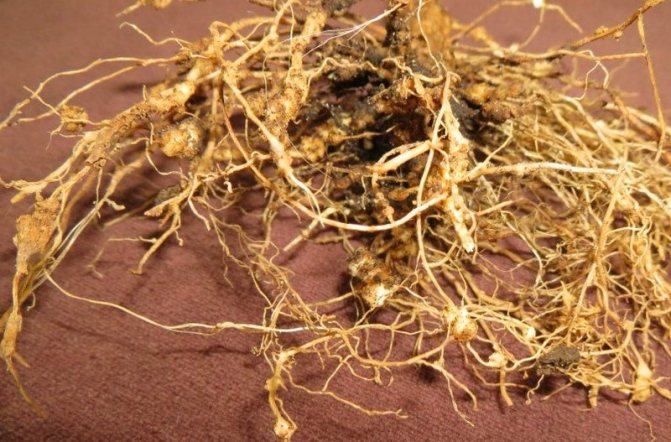
Crops affected by the root nematode weaken and wither. The roots below the thickenings die off. Thin roots and root beard appear.
How to deal with the disease
If a nematode appears, it will be quite difficult to get rid of. Removal from the site can take longer than 3 months.
For this, the following methods can be used:
- Agronomic (these include deep digging of the earth, soil optimization and changing the planting site);
- Mechanical (treatment of the root system of plants with hot water);
- Chemical (treatment with nematicides);
- Biological (planting next to a bed of plants, the neighborhood with which the nematode does not tolerate).
You can learn more about the fight against nematode in the video below:
Severely affected bushes must be destroyed immediately. This will prevent contamination of healthy plants. The best effect is obtained by a combination of these measures.
Reference!
It is impossible to completely get rid of the nematode on the site. But you can reduce its amount to an acceptable amount.
Method of treatment with folk remedies
Proven folk remedies include hot water treatment.
The method is effective at the initial stage of root infection. Thus, it is possible to "cure" the seedlings if female nematodes are found in the root coma of the earth. For this:
Dig up an adult bush
When it comes to seedlings, they are carefully removed from the pots; Thoroughly rinse the soil from the roots along with the nematodes. This water should not be watered on other plants or used for compost; Plant roots are immersed in a container of water
A water temperature of 45 - 50 C will ensure the death of not only adult worms, but also eggs. You cannot use hotter water, so as not to damage the bush. Keep for 5 to 20 minutes.
You can learn more about biological control of nematodes in the video below:
After that, the bush is carefully transplanted to a new place and watered abundantly. A good effect is also given by spraying with decoctions of plants poisonous to the nematode.
It can be:
- Marigolds (1 kilogram of inflorescences per 10 liters of water, spray the bushes with a filtered solution;
- Calendula (1 spoonful of flowers per 1 liter of water);
- Large nasturtium (300 grams of plants per 1 liter of water);
- Batun onion (30 grams of dry plant per 5 liters of water).
Unlike chemical nematodocytes, plant spraying can be done during flowering and ovary formation.
How to handle with chemicals
The most popular nematicides include:


The solution is prepared and used according to the instructions accompanying the preparation. Processing is usually carried out before flowering.
Caution! Nematocides are highly toxic. Work must be carried out using personal protective equipment
These include a respirator, gloves, and heavy clothing.
Nematode resistant strawberry varieties
If the site already has such a problem, it is worth paying special attention to prevention. One of the most effective measures is the use of pest resistant varieties. The most popular ones are:
One of the most effective measures is use of pest-resistant varieties.
The most popular ones are:
- Festivalnaya;
- Saxon;
- Granddaughter;
- Pearl oyster;
- Rocket.
At the same time, they have strong immunity to viral and fungal infections.
Features!
The use of resistant varieties is the prevention of the most dangerous fungal diseases of garden strawberries.
Roundworm biology
They reproduce in two ways:
- The female is on the surface of the root and lays eggs in a sac, from which the larvae first enter the soil, and then make their way into the root system of the host plant, after which it becomes infected.
- The female is completely in the root tissues and lays eggs inside it. The hatched larvae move along the root tissues and settle in it for nutrition and development. They are no longer affected by biological methods of protection.
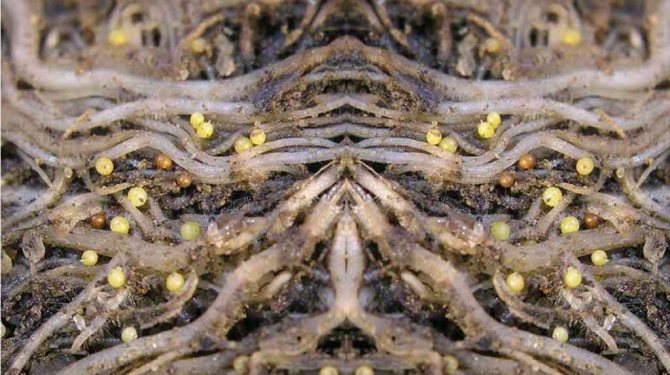

It should be noted that the larvae from the roots, under favorable conditions, are able to move through all organs of the plant.
Prophylaxis
To prevent infection of the site with a nematode, the following rules must be adhered to:
- After harvesting, carefully remove all plant residues, leaves and grass from the garden.
- Weed and loosen crops in a timely manner.
- When yellow leaves appear and the color of the stems changes, remove them from the site as soon as possible.
- Use proven planting material.
- Carry out deep digging of soil in autumn and early spring.
- Avoid waterlogging of the soil.
The use of nematode resistant varieties is also an important preventive measure. Among the tomatoes are Nagano F1, Eupator F1, Malika F1, potatoes - Diamant, Picasso, strawberries - Dessert, Saxonica
The nematoda is one of the most common sucking pests. About 200 species of plant nematodes are known that affect shoots, roots and fruits of various plants. Therefore, familiarity with the parasite and knowledge of measures to combat it will allow amateur gardeners to feel more confident.
Nematodes (Nematoda, Nematodes), or Roundworms, are small, colorless, sucking worms armed with a proboscis. They parasitize plants, animals and humans, being dangerous harmful quarantine microorganisms for them.
In the article, we will focus on the parasites of plants that cause nematosis in the backyard, and also consider the main types of plant nematodes and give advice on how to combat them.
Preventive actions
It is very difficult to find and get rid of nematodes, so it is best to take care of preventive measures and prevent the appearance of these parasites. This requires:
- carefully carry out autumn soil treatment;
- kill weeds in time;
- do not bring closed-root plants from botanical gardens, greenhouses and shops into greenhouses;
- cleaning fallen leaves;
- observe crop rotation;
- loosen the soil regularly;
- fertilize the soil with organic matter;
- carry out periodically abundant irrigation of the land, followed by drying;
- try not to overmoisten the soil.


One of the modern ways to protect greenhouses from pests is the use of sulfur bombs.
Harm caused by nematodes
Nematodes are very dangerous for plants, because these worms feed on their sap. As a result, plantings begin to grow more slowly and literally wither before our eyes, which ultimately negatively affects the harvest. With mass infection, the plants completely stop developing and eventually die.
Plant diseases caused by this worm are called nematode diseases. Herbaceous species, shrubs and trees are also susceptible to them. Both wild and cultivated species are affected by pests, so it is very difficult to escape from the parasite.
Another aspect of the harmfulness of nematodes is associated with damage to the integrity of the plant by these worms. The holes and passages made by them are an excellent way for the penetration of pathogenic microorganisms, which also provoke the appearance of diseases. Thus, landings receive a double blow, the consequences of which are always negative. The degree of damage caused by nematodes depends on their number and environmental conditions: in a favorable environment, they harm much more than, for example, in a cold spring. But, unfortunately, the climate of the middle zone can be called ideal for the life of the pest.
What is dangerous and how to find a nematode in the garden
Nematodes are very dangerous pests, they quickly multiply on plants and lead to their death. Parasites, getting into plant tissues, feed on their sap and take away all the nutrients. In addition, in the process of vital activity, nematodes release toxic substances that poison crops, lead to excessive thickening of their stems and petioles. Plants affected by nematodes lose their color, look lethargic and exhausted, deformed, and their yield significantly decreases.
Nematodes are very difficult to spot because they are tiny.
Leaf and stem nematodes can only be seen by examining the leaves, buds and stems through a magnifying glass. Root parasites can be found by digging up the plant. They betray themselves by the formation of brown seals on the roots. In addition, when the plant is removed from the soil, small earthy clumps will fall off from the roots. If you take such a lump and sprinkle it with warm water, the worms will come out.
Important! Nematodes can cause irritation and allergic reactions to the skin, therefore, work with the plant must be carried out with gloves.
Methods of dealing with nematodes
Chemical control methods
If a nematode has appeared on a strawberry or any other plant in the garden, at home, you need to start fighting immediately. In particular, it is the various chemicals that most often help. You can safely buy chemicals for spraying, which include mercaptophos or phosphamide. For example, "BI-58", "Dimetoat", "ROGOR".
As for phosphamide, it is excellent for fighting nematodes and ticks, leaf rollers and worms. Getting on the plant, the drug under the influence of the rays of the sun and water quickly breaks down on the surface of the flower. But inside, the drug remains toxin for two dozen days. This chemical is highly toxic to warm-blooded parasites.
When using preparations based on the described substance in the fight against nematodes on strawberries or any other plants, you need to exercise the utmost care. If the treatment is carried out indoors, it is imperative to ventilate after treatment.
The described drugs, unfortunately, only affect adults. That is, the eggs that the parasite lays cannot be destroyed by the already indicated means.
What other drugs can be used (for indoor flowers):
- "Buck Eco-Gel". With the solution, you just need to water the soil before planting the seeds, after planting the seedlings. If a nematode has appeared on strawberries (see photo), then next year it will simply be necessary to carry out additional soil treatment with this preparation.
- "Nemaphos";
- "Nemago";
- "Vidat".
Many of these drugs are highly toxic. It is better not to process the plant with these agents in closed rooms and go out into the open air to carry out various manipulations.
Folk methods of struggle
When nematodes appeared: treatment by folk methods, oddly enough, is rather small in number. This is because it is extremely difficult to get rid of this small parasite and, most often, when a defeat is noticed, only chemistry will help.
If you remove the development of the parasite at an early stage, then you can try such a popular method of dealing with the nematode as heat treatment of the plant. It is especially relevant for root species. It will be necessary to remove the plant from the pot, remove the earth and rinse the roots under running water.
In places where there are lesions, the roots no longer function, that is, these parts of the root system can be safely removed
But here it is important to look so as not to remove most of the root system, because without it the flower simply will not survive
When the root system is washed and cleaned as much as possible, you need to bathe the whole plant in the shower. The water temperature should be around 55 degrees Celsius. This temperature is still safe for the plant, but for the nematode it is already destructive.
Regardless of the species, all nematodes are afraid of high temperatures. For life, they need warmth of 18-24 degrees, but no more. As soon as the temperature rises from 40 degrees or more, the parasite dies.
To completely get rid of the parasite and eggs, which he had time to lay on the plant, the heat treatment should last about a quarter of an hour. If the lesions are not severe, the exposure time can be shortened. After the procedure, transplant the plant into a new land. You can mix some anti-nematode poison into the ground.
These are the main ways to deal with a nematode at home. Of course, chemical action when a plant is damaged by these parasites will be more effective.
In order to prevent the development and reproduction of worms on their indoor flowers or garden crops, it is important to remember about prevention
Folk remedies for nematosis and prevention
If the plants are massively infected on the site, it is better to destroy them by culling and burning, so that the pests do not move to other crops.
There are few chemical methods of controlling parasites, therefore, the usual prevention in the form of observing crop rotation, planting defenders on the backyard helps to drive out the nematode or suppress it so that it will lose its ability to reproduce.
The most effective green manure (plant) means of fighting nematosis are marigolds, rye and marigolds.
- Rye... The roots of the cereal release substances into the ground that are deadly for the nematode. The most effective method of clearing the field from parasites is sowing winter rye before the September frosts, the efficiency reaches 80%. Before freezing, rye is cut down, and the green mass, along with the roots, is buried in the beds.
- Marigold... Against nematosis, undersized varieties are planted between the rows of other flower crops, as well as along the borders of strawberry and strawberry beds. On the area of the potato plot, marigolds are planted in islands.
The roots of the flower penetrate deeply into the soil and disinfect it. During harvesting, the tops and roots of marigold flowers are chopped up, crushed and embedded deep into the soil. The parasites do not tolerate the specific phytoncidal smell of this plant and die.
And also for the treatment of bulbs and tubers before planting, an aqueous solution of marigolds is used.
- During flowering, the whole plant is harvested and dried in the open air.
- Half a bucket of chopped marigolds are poured with ten liters of water and insisted for 2-3 days.
- Add 50 grams of laundry soap and filter. Soap is needed for better fixing of the liquid on the plant.
- For 8-12 hours, the bulbs and tubers are kept in the infusion.