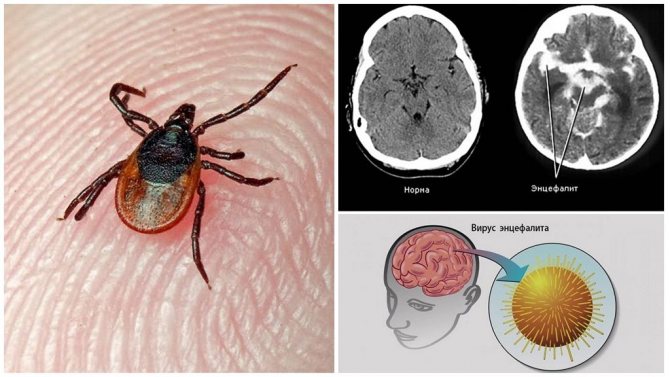
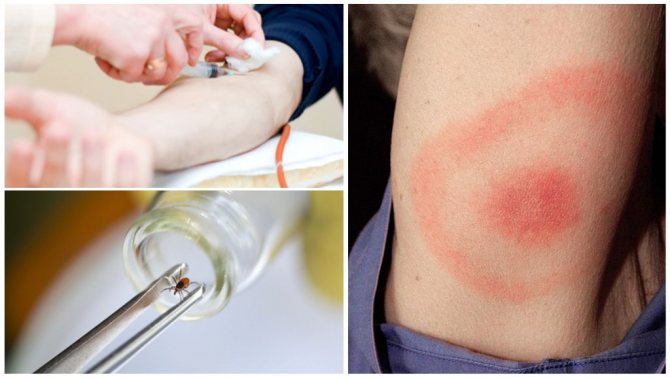
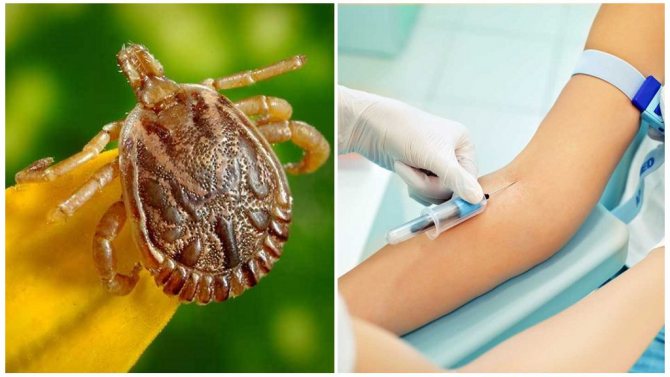
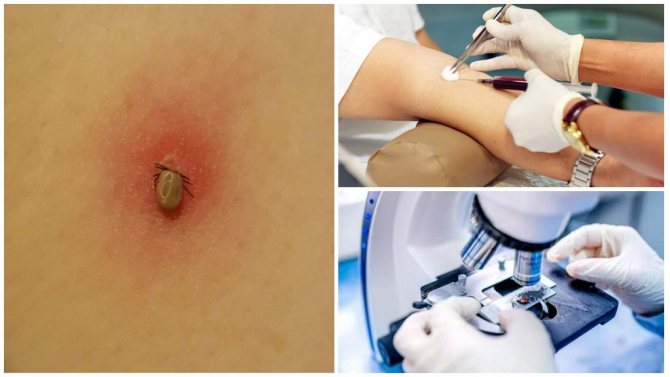
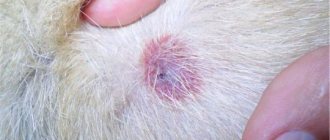
Tick bites are not at all harmless to humans. The fact is that these arachnids are carriers of many dangerous infectious diseases. Among them are tick-borne encephalitis, borreliosis and many others. etc. Therefore, after a tick attack, it is imperative to understand whether the parasite is infected with any virus? How do you know about this? An excellent option is to take a blood test. It will not be superfluous to take the tick itself for examination to specialists. This is the only way to determine whether infection occurred after contact with a bloodsucker.

What are the dangers of a tick bite?
Small arthropod parasites carry about 15 diseases, half of which pose a real threat to humans. The course of infections is usually very difficult, the rehabilitation period is up to 12 months, and some complications even lead to disability.


A small parasite can become a source of dangerous infection
Video: what you need to know about the consequences of a tick bite - recommendations of Dr. Komarovsky
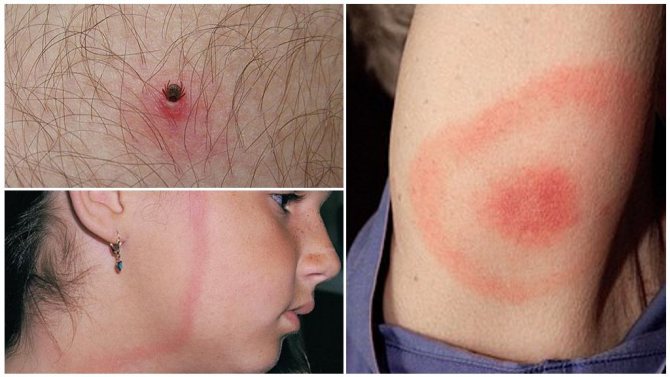
What does a tick bite look like?
A tick bite looks like a dotted speck with redness around it, which occurs as a result of an allergic reaction to the tick's saliva, which it secretes to anesthesia and prevent blood clotting.
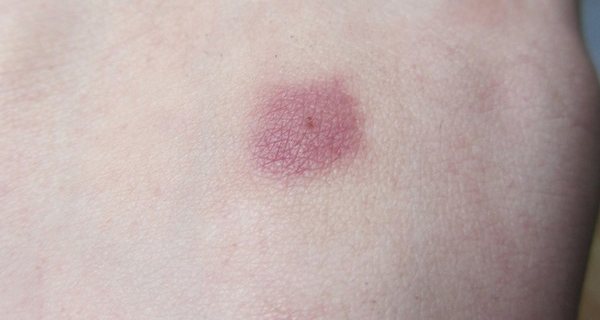

A red spot around the puncture site is the result of an allergic reaction to the tick's saliva.
Sometimes a small black dot can be observed at the site of the bite. This suggests that as a result of some unsuccessful manipulations, the tick's head fell off and remained on the skin. In this case, the first thing to do is to remove the foreign body. After the affected area of the skin has been treated with alcohol, we clean the wound with a disinfected needle and lubricate it with iodine or alcohol.
Prophylaxis
- Vaccination is effective against viral encephalitis. There is no vaccine against borreliosis.
- When hiking in the forest, in areas with tall grass, clothing should cover the body.
- It is advisable to use protection against ticks. They are applied to skin and clothing. Repellents scare them away, acaricidal drugs kill. There are also drugs of combined action.
- It is necessary to carefully examine the body and clothing for ticks during and after hiking in nature.
Compliance with simple rules will allow you to protect yourself and children from infections transmitted through ticks.
Additional information on the topic of the article can be obtained from the video:
Two options for the consequences of contact with a bloodsucker
After a parasite bite, there are two options for the development of events. First: successful. If the tick was sterile, that is, uninfected, redness and possible itching in the area of the bite will disappear without a trace. It is important to remember that the affected area of the skin with a sterile mite does not cause (!) Pain. And the second scenario of the development of events: unsuccessful, that is, the parasite was infected.
Tick bite symptoms
Since a tick bite can go unnoticed, even after it has sucked blood and fell off, you should deal with the more obvious symptoms of contact with the parasite. These include:
- temperature;
- chills;
- muscle pain;
- aches (which, by the way, is perceived by many as a sign of a cold after a vacation in nature);
- increased sleepiness;
- discomfort on contact with light.
The listed symptoms may appear within 2-4 hours after the bite. On average, they appear 1-3 weeks after infection.


Symptoms may appear several days after the bite
Symptoms in Sensitive People
This category includes children and pregnant women. The manifestations of the consequences of a tick bite in them can be expressed as follows:
- severe migraine;
- unhealthy blush;
- nausea, diarrhea;
- temperature rise up to 39 degrees;
- redness of the eyes;
- hoarse breathing;
- hallucinations.
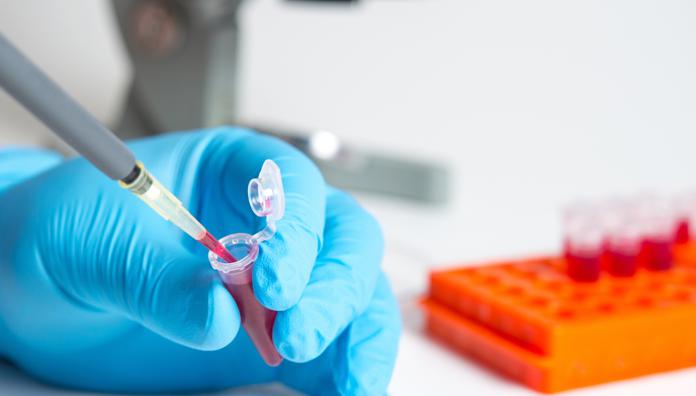
Blood test for tick-borne encephalitis and borreliosis in invitro
The disease proceeds in several stages:
- the incubation period (the period from the moment of infection to the appearance of the first symptoms) - lasts from 3 to 32 days;
- Stage I - coincides in time with the reproduction of borrelia at the site of penetration and in the lymph nodes;
- Stage II - corresponds to the phase of spread of the pathogen with blood throughout the body;
- Stage III - chronic. During this period, one system of the body is mainly affected (for example, the nervous or musculoskeletal system).
Stages I and II are called the early period of infection, and stage III is called late. There is no clear transition between stages, the division is somewhat arbitrary.
The incubation period for borreliosis usually lasts from 2 to 50 days, but in rare cases it can last for several months or even years. After this, clinical
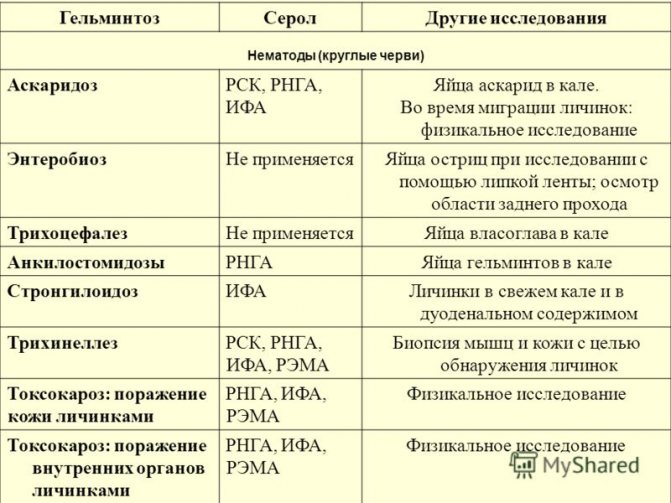

infections. Borreliosis has a staged course, therefore, depending on the type of prevailing pathological changes and symptoms, three stages of the disease are distinguished, each of which is characterized by a strictly defined clinical picture.
The early period of borreliosis includes stages 1 and 2, which, in fact, are an acute process. Stage 3 is referred to the late period of Lyme disease, which does not always develop and is chronic borreliosis that lasts for years. Let's consider the clinical manifestations of all three stages of borreliosis separately, since they differ significantly.
Sad statistics say that every third of those infected with tick-borne encephalitis dies if there was no treatment or it was carried out late. Therefore, timely diagnosis and initiation of treatment are extremely important. The leading role in the diagnosis of tick-borne encephalitis is taken by the analysis for encephalitis.
What is the average cost of blood tests for tick-borne infections? About 400-600 rubles in commercial organizations. At the same time, for this amount, you will be analyzed for the presence of one type of pathogens of the virus - for example, for encephalitis or borreliosis. Accordingly, the cost of a comprehensive study can cost 1000–2000 rubles. In government agencies, tariffs are usually lower by about 30-40%.
We offer you to familiarize yourself with: Subcutaneous mite on the face - photo, symptoms, treatment
Ticks are also dangerous for pets. Especially for dogs, in which these parasites usually bite while walking in the forest or park. Therefore, if your pet does not feel well or you find a tick on its body, then immediately contact the veterinary clinic and take a blood test for piroplasmosis. Indeed, without timely treatment, mortality among dogs from this disease reaches 98%.
There are several research methods. The most specific is the enzyme immunoassay for encephalitis and borreliosis. Other tests are done when a false negative is suspected.
Is it possible to identify a sterile or encephalitis tick by its appearance?
The answer to this question will be unequivocal - no. There is a misconception that encephalitis mites are larger than sterile ones. However, the size of the parasite is determined by its age, species, and not the carrier of the infection.The only chance, before laboratory tests, to tell whether a parasite that has bitten is infected is to determine its species: it is believed that the most likely carriers of encephalitis are taiga and forest (dog) ticks.
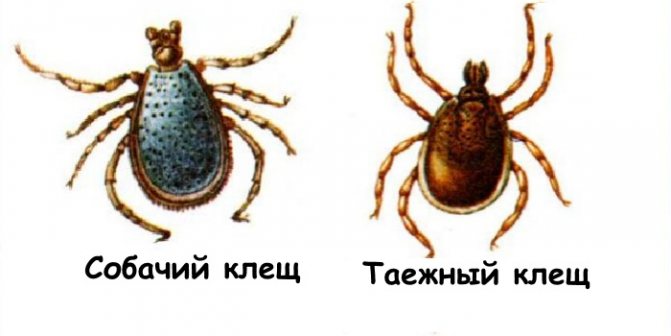

Only a specialist can distinguish these two types of ticks, especially in areas where their habitats overlap.
What to do after bite detection
The incubation period for the development of tick-borne infections is on average 2 weeks. During this period, in the absence of the described symptoms, it is useless to take any tests: the results will not be objective. In this case, it is very important to determine as soon as possible whether the infection has entered the human body. To do this, you need to take the bitten parasite to the laboratory. The results of the study will be known in a few days (on average, in 3 days), but the analysis service is paid. On average, its cost ranges from 900 rubles.
How to find a laboratory
The analysis procedure is carried out in:
- a clinic or hospital with the necessary equipment;
- SES;
- private laboratories researching viruses;
- Rospotrebnadzor Center.
You can find out the address of a specific organization that accepts ticks for research at the registry of the local clinic.


To find out the address of the nearest laboratory examining ticks for the carriage of infections, you need to contact the nearest clinic
How to save material for analysis
Since the necessary DNA remains in the body of the tick for about 72 hours to detect the carriage of infections, it is advisable to deliver a live individual to the laboratory. If the parasite is still alive, then it must be properly preserved until the moment of diagnosis.
Instructions:
- We moisten the cotton wool with water.
- We put it on the bottom of a container with a tight-fitting lid.
- We place the tick in the vessel.
- We store in the refrigerator at temperatures up to +5 degrees for no more than one and a half days.
The brought bloodsucker must be examined not only for encephalitis, but also for borreliosis, since after analysis the parasite is not returned, which means that there is no way to take it to another laboratory.
For PCR research, it is possible to use parts of a tick. But this type of analysis is rarely used.
What tests need to be passed to a person
If the tick tests showed a positive result, or if the bite tick could not be saved, the victim should visit an infectious disease doctor, who, after examining the bite site, will prescribe tests. The material for the study is the patient's blood serum.
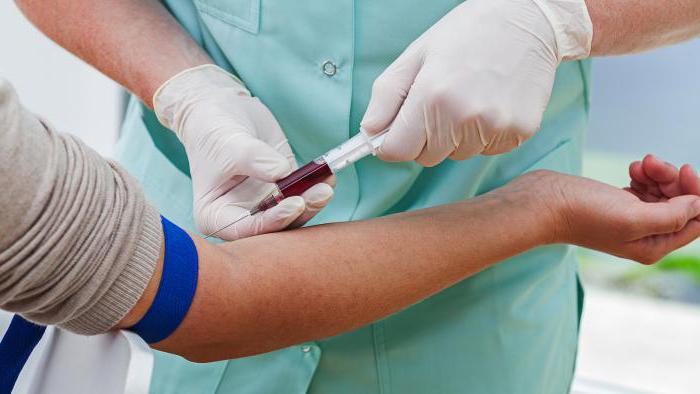

For analyzes, the blood of a victim of a tick bite is examined
Table: types of tests that are prescribed for a tick bite
| Study | Features of the |
| Immunofluorescence (MFA) | It is done everywhere, the simplest and cheapest method of analysis. Infectious agents in a fluorescent microscope will glow like fireflies. |
| Immunoassay diagnostics (ELISA) | Gives the most accurate result, detects infection at an early stage. |
| Western blot | Reliably shows infection with borreliosis and encephalitis. Appointed to confirm the results of other studies. |
| PCR (polymerase chain reaction method) | Often shows a false result for infection with encephalitis. For reliable diagnosis, several PCR systems should be used (blood tests, skin cells, urine, cerebrospinal and articular fluid). |
Immediately after the bite, you do not need to rush to donate blood: the study will not show an objective picture of the consequences of contact with the parasite. An analysis for the presence of antibodies to encephalitis is given 2 weeks after a tick bite, to Borrelia - after 3 weeks, and PCR is performed 10 days after contact with the parasite.
If the first cycle of analyzes gave negative results, but for their final confirmation, you can repeat the diagnostic procedures after a month.
If the tick did not have time to bite, you do not need to be tested.
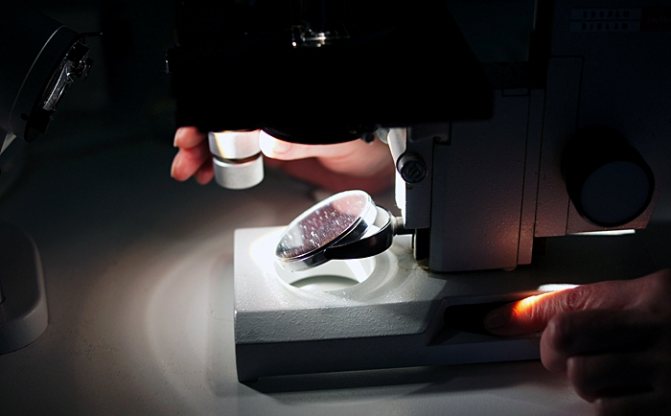

The most reliable result can be obtained by passing several tests at once.
Timing of results
Health


When visiting places where ticks are suspected in spring or summer, protection from insect bites should be provided. If the attack of the parasite nevertheless occurred, it is necessary to contact the emergency department as soon as possible or get an initial consultation about further actions by calling 103, 112 or 625-78-31 (Sklifosovsky Research Institute).
If a parasite has stuck to the body, the actions to remove it should be carried out very quickly, since the likelihood of infection increases as the duration of the insect's contact with blood increases.
In addition to speed, the caution of the manipulations performed is of great importance to ensure the integrity of the arachnid with the aim of its subsequent transfer for analysis (the individual should be checked for tick-borne infections).
from the moment of suction, but it is not always possible to quickly seek qualified help. In this case, it is allowed to extract the parasite on its own or with the involvement of third-party assistants.
To minimize the risk of infection and save the specimen for laboratory analysis, the following rules must be followed:
- All manipulations should be performed with gloves (it is impossible to allow contact of the articulate with the open areas of the hands).
- You can use improvised means (thick thread, tweezers) to pull out the insect, but attempts to douse it with oil can lead to the death of the insect with the injection of its saliva, which will increase the likelihood of infection.
- The sucked parasite should be pulled out of the skin perpendicular to the surface of the body, keeping it as close to the head as possible without squeezing the body.
- Pulling movements should be directed strictly upward (in relation to the surface of the body), without twisting or loosening the parasite.
- Place the insect inside a clean glass container (to maintain the viability of the individual, put a damp piece of cloth in the container).
- Disinfect hands and bite sites.
- Within 24 hours after disconnecting the tick, it must be taken to the laboratory for analysis.
| Name | Address | Telephone |
| FGUZ "Center for Hygiene and Epidemiology in Moscow" | Grafsky lane, 4 | (495) 687-40-47 |
| Center for Sanitary and Epidemiological Examination and Certification | St. Pyatnitskaya, 45 | (495) 543-92-78 |
| FBUZ "Center for Hygiene and Epidemiology for Railway Transport" | St. Khodynskaya, 10a | (499) 253-01-31 |
| Hygienic Education Population Center | 1st Smolensky per., 9 | (495) 241-86-28 |
| Federal Center for Hygiene and Epidemiology | Varshavskoe highway, 19a | (495) 954-45-36 |
| Head Center for Hygiene and Epidemiology | 1st Infantry Lane, 6 | (499) 190-48-61 |
| Center for Hygiene and Epidemiology (by districts): | ||
| CAD | Krasnogvardeisky Boulevard, 17 | (499)256 07 71 |
| Zelenogradsky | Chestnut Alley, 6 | (495) 9445996 |
| Southeastern | Volgogradsky prospect, 113 | (495) 9193632 |
It is the responsibility of the affected person to ensure that the tick is checked for infectious agents.
Before taking an insect to a laboratory or medical center, it is necessary to check with the institution staff by telephone if they accept individuals for research.
When transferring a copy, medical personnel will need to provide information about the place, the approximate time of the bite, and present the following documents:
- medical insurance policy;
- passport;
- insurance contract - in the presence of insurance, all costs for the extraction, examination of the tick, as well as the responsibility for the delivery of the insect for analyzes are assigned to the insurance company.
The analysis for borreliosis is urgent. The sooner the treatment is carried out, the less complications for the patient. Therefore, the results are issued on the day of sampling of the biomaterial.
First aid for a tick bite
If a sucked tick is found, then it is necessary to contact the emergency room as soon as possible, where the specialist will correctly remove the parasite, preserving it as much as possible for subsequent diagnosis. If it is not possible to get to a medical institution, then you will have to remove the tick yourself. Please note: if a tick's head remains in the human body, then surgical intervention will be required to remove it.
Video: how to extract a tick in the field
Nuances of emergency preventive vaccination
Patients after a tick bite within 72 hours (later the effect decreases) can be given an intramuscular or intravenous injection of immunoglobulin - blood cells that support human immunity. There are several types of immunoglobulin, but doctors usually prescribe vaccination with antiencephalitis immunoglobulin, since this disease is considered the most dangerous. If you are infected with borelliasis or other tick-borne infections, there will be no effect of vaccination. The drug is made from the blood serum of people who have undergone tick-borne encephalitis, that is, having antibodies to it, and is administered to treat or prevent the development of the disease. The dose is calculated by the weight of a person, the average cost of a drug per 10 kg of body weight is 900 rubles. In the first 24 hours after contact with the parasite, 0.1 ml per kilogram of weight is injected, after 48 hours and 72 hours - 0.2 ml per kilogram.
It is interesting. Many victims are in no hurry to vaccinate, arguing that the percentage of infected ticks is very small. For example, in 2020 in Novosibirsk and the region, out of 10181 parasites submitted for analysis, only 198 were infected. And yet, even 2% is a risk.
Video: why ticks are dangerous and whether the vaccine saves from tick-borne encephalitis - expert opinions
Emergency vaccination conditions
Immunoglobulin injections after a tick bite are given if:
- there is no way to investigate the parasite for the carrier;
- the analysis of the tick showed a positive result for the presence of pathogens;
- a patient who has just begun a course of preventive vaccination has been attacked by a parasite;
- the person was vaccinated, but underwent multiple attack by ticks.
It is interesting. If the victim was vaccinated for prophylactic purposes, then the doctor must be told about this so that he can correctly calculate the dose of immunoglobulin.
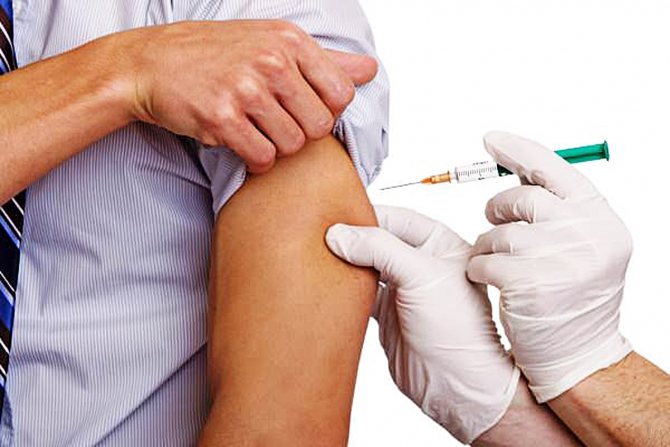

Emergency vaccination is done as prescribed by a doctor or at the initiative of the patient, if there are no contraindications to this
Contraindications
There are a number of cases when the immunoglobulin is not put before the test results are obtained. These include:
- allergic reactions to components of donated blood;
- protein intolerance;
- pregnancy and lactation, since the effects of the drug on the fetus and the baby during this period are not fully understood (if the likelihood of infection is confirmed by a tick study, then vaccination is carried out, but the dose is calculated according to the gestational age or the age of the baby).
However, if the tick is infected or it is not possible to examine it, then the immunoglobulin is administered against the background of antihistamines or appropriate therapy.
For children, immunoglobulin is injected only (!) If the doctor, after examination, revealed clear suspicions of infection or the study of the tick that bit the baby, gave positive results.
Side effects with the introduction of immunoglobulin
Usually, in people who are not susceptible to allergic reactions, the administration of immunoglobulin does not cause any consequences. But patients with contraindications may experience:
- lethargy after a large dose;
- pain at the injection site;
- temperature rise to 37.5 degrees;
- anaphylactic shock.
Why get tested?
Ixodid ticks spread at least two socially significant pathologies.This is the well-known tick-borne encephalitis and Lyme disease (borreliosis). Diseases are by no means harmless, as it might seem at first glance. In some cases, infection of the body with borrelia causes very severe long-term consequences. Signs of damage to the heart, joints, nervous system develop. Only with a thorough investigation can they be associated with the once transferred Lyme disease. This is why it is recommended to have a blood test after a tick bite.


With late treatment started, the percentage of transition to a chronic course can reach 50%. Timely laboratory testing and appropriate therapy ensure a favorable outcome for these and other serious bacterial diseases transmitted by ticks.