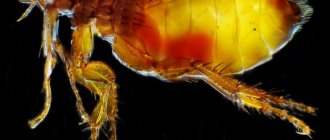
Consequences and complications of tick-borne diseases
Owners should inspect their pet's head, neck, chest, ears and groin after each walk for bloodsuckers. If single individuals are found, they must be urgently removed and burned. To avoid contracting diseases dangerous to humans, do this with protective gloves. Avoid crushing the tick and getting it into the mouth or mucous membranes. For multiple bites, see your veterinarian.
If you are far from medical care, give your dog 100-150 ml of water every hour. If you vomit, give an enema or injection subcutaneously. You can subcutaneously inject 20 ml of glucose solution and vitamins B6 and B12 in an ampoule three times a day. In case of pronounced symptoms and lack of help, an injection of 7% Veriben or Azidine solution is given at the rate of 1 ml per 20 kg of the dog's weight.
How to take a dog's blood for analysis on your own: treat the ear with alcohol, cut the vessel close to the edge, collect the blood on a glass plate, dry it a little and take it to the clinic.
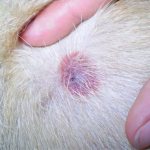
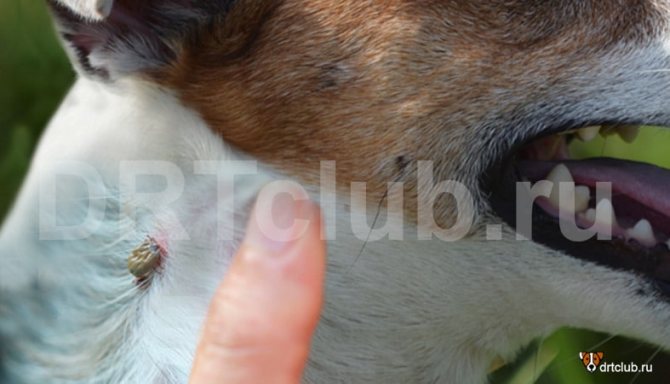
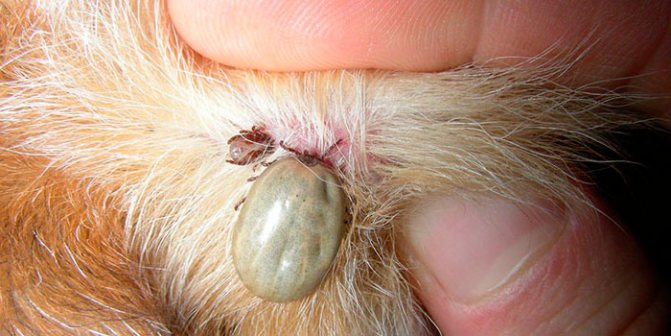
What symptoms will appear if a dog is bitten by a tick? Often, the animal is worried about this: it itches, shakes its head if a tick has climbed into the ear. What does the bite site look like? Most often, at the site of the bite, two to three hours after the removal of the parasite, there is a pronounced local redness, which gradually goes away on its own.
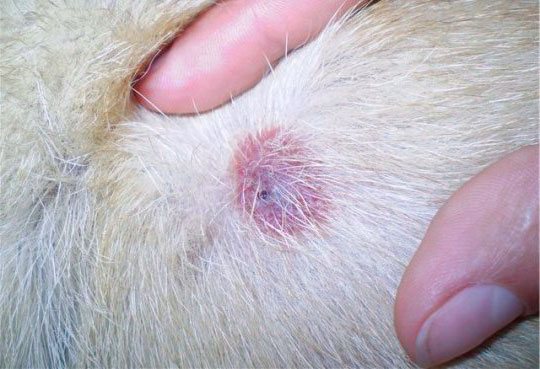
In the photo - a mark from a tick bite in a dog
Clinical signs are swelling, increasing radially from the center, increased skin temperature in this area, redness, itching and pain. The animal licks and combs the bite site. In some cases, granulomatous dermatitis begins on the second day after the tick is removed. If a bump appears at the site of the bite, this may be the result of an allergy to the parasite's saliva or infection of the wound.
In place of the bump, hair may fall out, the dog reacts painfully to touching it. Purulent inflammation at the site of the bite appears due to the introduction of pyogenic microbes into the open wound. Careful antibacterial treatment is required and, if necessary, the introduction of antihistamines. Another reason for the bump is the tick head remaining in the wound.
It is most likely that the symptoms of the disease will appear 6-10 days after the tick attack, but it matters how the disease progresses. With the lightning-fast development of the disease, you may simply not have time to take action. Fortunately, this option is not common.
Pay attention to the rapid rise in body temperature to 41-42 ° C. This is the response of the dog's body to the introduction of the parasite, and after a couple of days the temperature will return to normal, and later will decrease. After removing the tick, measure the temperature in the anus of the animal daily. Normal temperature in dogs is 38.5 ° C.
Usually, the difficulty in making a diagnosis is that the symptoms of a tick bite can vary. But almost all animals refuse to eat, show drowsiness and apathy. Some of the following symptoms may appear: trembling, thirst, shortness of breath, pallor of the mucous membranes, abdominal pain, fetid odor from the mouth, blood in the urine, vaginal bleeding (in bitches), impaired motor reflexes:


As you can see, the consequences and complications of diseases carried by the tick are almost always fatal. Even in the case of the transition of the disease into a chronic form, sooner or later, it will lead to depletion of the body and relapse in full.
A tick found on a dog's body must be removed. Further, the pet is recommended to be delivered to the veterinary clinic for the necessary tests.
The most dangerous disease transmitted by ticks is piroplasmosis. A blood parasitic disease destroys blood cells, provoking serious disturbances in the functioning of the body.
If a tick bite in a dog occurred in nature, and there is no way to quickly deliver a pet to a veterinary clinic, you need to act at home. A pet that refuses to eat and drink can suffer from dehydration.
It is necessary to infuse a small amount of water directly into the mouth every half hour. When nausea and eruption of gastric contents appear, a subcutaneous injection with glucose can be given, thereby restoring the lost amount of fluid by the body.
After removing the tick from the body of the animal, it is important to provide the pet with daily injections subcutaneously with a solution of glucose and B vitamins (biotin and cyanocobalamin). This will make it possible to increase the strength of the body in the fight against infection.
Show the animal to a veterinarian as soon as possible. The doctor will prescribe laboratory tests to determine the type of infection obtained by the bite of an ixodid tick. As a rule, the doctor prescribes complex treatment that can prevent the development of serious complications.
Symptoms after a tick bite in a dog depend on the infection the parasite has transmitted to the animal. After finding and removing a tick from his pet, the owner's task is not to relax, but to carefully observe the changes in the pet's condition. Depending on the type of infection, symptoms may appear on day 3 or after a month.
If a dog is bitten by a tick, which is a carrier of bartonellosis, then there will be increased drowsiness, a sharp loss of body weight, inflammation in the joints, weakness of the pelvic limbs. In some cases, a symptom of bartonellosis is hemorrhage in the eyeballs or nosebleeds.
With hepatozoonosis, the characteristic clinical picture is absent for a long time, while the body's immune forces are able to fight the infection. As soon as a provoking factor arises - a stressful condition, birth process, hypothermia or a respiratory infection, hepatozoonosis comes into an active stage. Discharge from the eyes, fever, severe weakness and muscle pain in the pet occur.
Symptoms of a tick bite in a dog with ehrlichiosis are characterized by decreased activity of the pet, refusal to play and inhibited reaction. Severe fever occurs. Ehrlichiosis is dangerous not only for pets, but also for humans.
Borreliosis is also dangerous to humans. Signs of borreliosis in a dog are inflammatory processes in the joints, the development of arthritis. The animal suddenly begins to limp, neurological disorders are observed. With borreliosis, the pet refuses food, there is increased apathy and weakness.
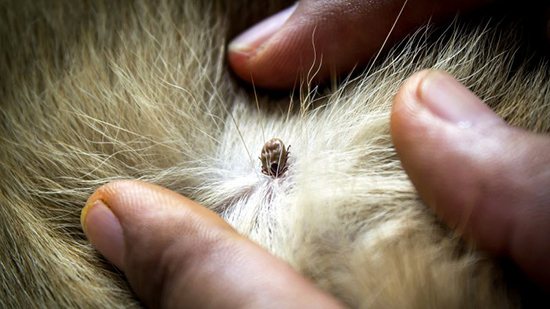

One of the most common tick bite infections in domestic dogs is piroplasmosis. Treatment at home does not give positive results, since with piroplasmosis, it is necessary to introduce specific drugs that destroy blood parasitic infections. Signs of piroplasmosis in a dog is refusal to eat, while the animal suffers from polydipsia (thirst).
Also find out what a tick looks like under the skin of a dog {amp} gt; {amp} gt; {amp} gt;
Unfortunately, rarely when a tick lesion passes without a trace.In the best case, the dog will develop inflammation of the skin, which will need to be removed with medication.
But the practice of veterinary medicine suggests that the result is a disease of dogs from ticks. They are quite difficult and can end in disastrous if you do not provide the pet with proper assistance in a timely manner. Each disease has its own specific symptomatology.
Pyroplasmosis
A very common ailment.
- In the first days after the defeat, the animal is lethargic and constantly needs liquid.
- The second stage is gastrointestinal upset.
- The temperature rises and shortness of breath appears.
- The urine becomes reddish and dark.
This disease is dangerous not only for the dog, but also for humans. In the animal, joint inflammation begins, first near the bite, and then the condition spreads throughout the body.
Veterinarians can diagnose developing arthritis. The animal begins to limp, neurological disorders occur. The dog experiences weakness, apathy, does not want to play and walk, practically does not eat anything and drinks a lot.
Bartonellosis
- Weakness.
- Drowsiness.
- Can drag its hind legs.
- During the week, there is a sharp loss of weight.
- The eyelids become inflamed.
- Problems with the heart and blood vessels are aggravated.
- Some joints become inflamed.
- If you look at the eyeballs, you can see numerous hemorrhages.
- When the stage is advanced, the animal begins to bleed from the nose.
Hepatozoonosis
This state is insidious in that it does not manifest itself in any way until a certain period. If the animal has good immunity, it will be able to cope with the disease on its own.
If the dog has suffered an illness, childbirth, moving, surgery, parasites find fertile ground for existence.
The dog begins:
- purulent discharge from the eyes;
- weakness;
- muscle pains appear;
- fever.
Ehrlichiosis
In this case, ticks in dogs cause:
- inhibited reaction;
- fever;
- decreased activity;
- anxiety.
What is piroplasmosis
And now in more detail about what kind of byaka is, causing so many problems, how the process of infection occurs, and which animals get sick more often.
Who is the causative agent
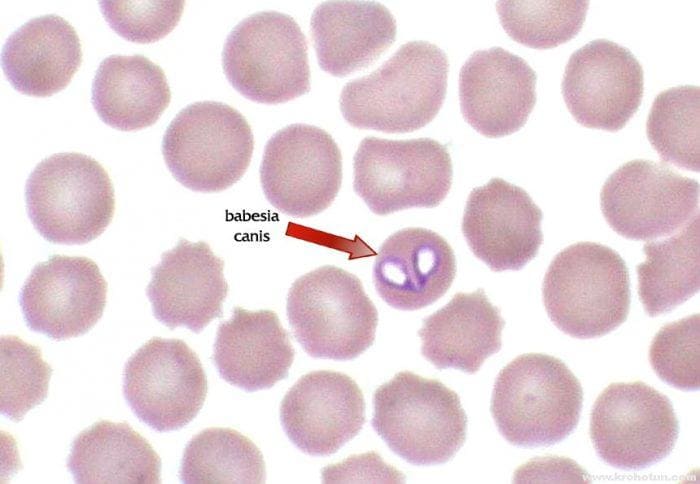
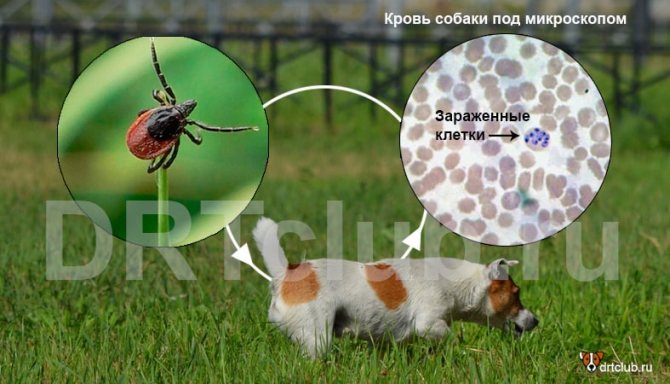
Piroplasmosis in dogs is a disease caused by a tick bite. But it is not the tick itself that causes the disease, but the microscopic protozoan parasites - babesia from the order of pyroplasmids, which are carried by ixodid ticks.
Babesias live and reproduce in the body of an insect. Moreover, the tick itself does not suffer from this microscopic parasite. Moreover, he transfers parasites to his offspring. Studies have shown the presence of babesia in the stomach, ovaries, and most importantly in the saliva of the ixodid tick.
This disease affects tetrapods all over the world. Its symptoms and consequences are the same. The only difference is that in different countries the causative agent of the disease is different subspecies of babesia.
The main transitional link in the body of which this parasite reproduces is: dogs, foxes, wolves, jackals, that is, representatives of the canine family.
As a rule, without proper and timely treatment, the dog dies within 5-6 days after the first clinical signs of infection appear.


How does an animal become infected?
The ixodid tick is a fairly common species. It feeds on blood and biological material. But, as mentioned earlier, in addition to this, they are also carriers of various diseases.
So how does the infection take place:
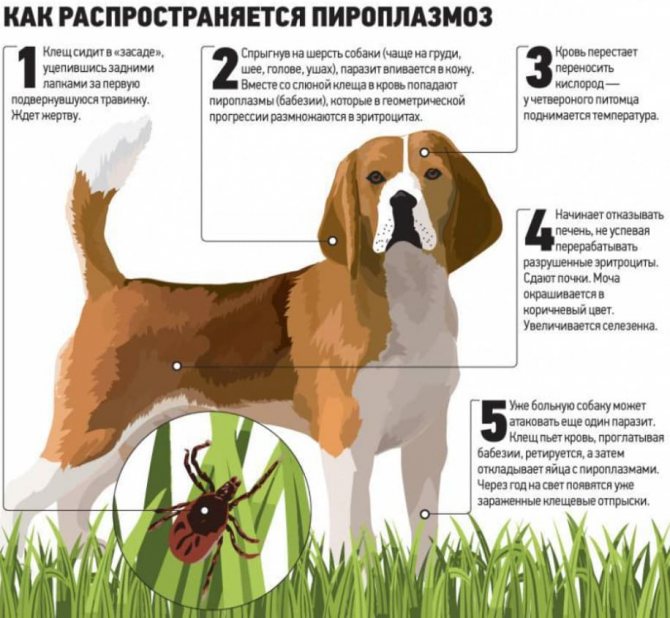
- Once on the victim's body, in anticipation of a "delicious lunch", with its sharp-toothed proboscis, the tick cuts through the victim's skin to get to the blood vessel.
- The mouth apparatus of the tick is designed so that it contains two canals.Through the first channel, the tick injects saliva into the victim's body, containing anesthetic substances, thanks to which the "owner" absolutely does not feel the moment of the bite. Through the second channel, the victim's blood goes into the tick's digestive system. So, with the very first portion of the insect's saliva, babesia also enter the victim's blood.
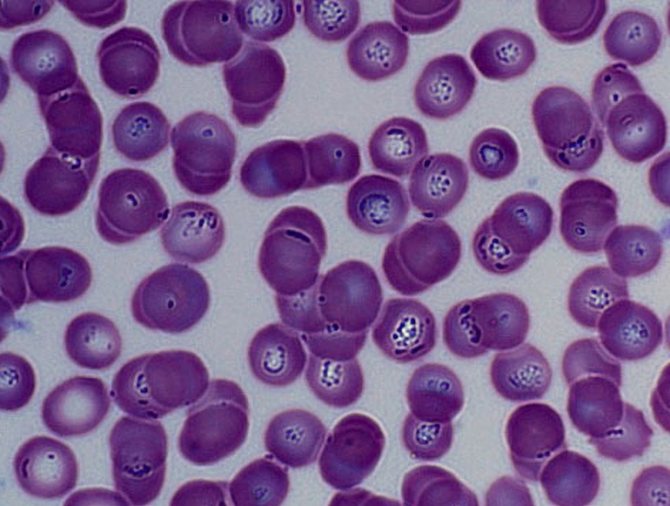
- Babesias "settle" in erythrocytes and eat their contents - hemoglobin. There they share. When the erythrocyte is completely devastated, and numerous Babesias are already cramped in it and have nothing to feed on, they destroy its shell, and each new parasite seeks and penetrates into a new healthy erythrocyte ... And so on endlessly.
At the very beginning of infection, the number of babesia in the blood is low, therefore, no characteristic symptoms of piroplasmosis are observed in dogs.
The first signs begin to appear when the number of parasites reaches a certain level. Depletion of the cells of the animal's body occurs: intoxication, oxygen starvation due to disruption of the activity of erythrocytes. In addition, the waste products of babesia are very toxic to the four-legged organism.

Duration of the incubation period
The incubation period can last from 2 days to 2 weeks, and this depends on many factors:
- The number of parasites that bit the dog.
- The number of babesia in the blood.
- The state of the animal's immunity.
- Age.
- Carrying out preventive measures.
What animals get sick more often
Barbosiks of all breeds and ages can get sick. Puppies and young tetrapods are especially susceptible to infection. In dogs over 4 years old, the disease is much easier.
Pyroplasmosis in pregnant dogs
The disease is milder in pregnant dogs. However, unfortunately, there are frequent cases of miscarriage. Bitches recover more easily from the effects of babesiosis. This is due to the fact that the unborn offspring takes the whole blow, for which in most cases everything ends very sadly.
Is the disease transmitted from dog to dog
Normal contact from dog to dog does not transmit the disease. Infection is possible only if the blood of a sick animal is transfused to a healthy pet.
Can a person get infected from a dog?
No, he can not. Firstly, babesias, dangerous for dogs, do not pose a threat to humans. And secondly, again, infection can occur only through blood transfusion.
Therefore, you can safely contact a pet sick with piroplasmosis. Moreover, during periods of such serious illnesses, he needs your support and attention more than ever.
Is re-infection possible
Unfortunately yes. After suffering an illness, the caudate remains weak immunity, which lasts about 4-6 months. Well, then the risk of infection arises again.
Moreover, in recovered animals, as a rule, the disease proceeds in a chronic form and the symptoms do not appear too soon. But this does not make the disease less dangerous. Therefore, it is imperative to pay attention to changes in the condition of the pet. But more on that later.
The most dangerous seasons for infection
There are two most active waves of the disease: spring and autumn.
The first attacks of ticks are recorded with the melting of snow and the onset of warm weather. The peak in the number of dogs with pyroplasmosis is observed from April to the last day of June. During this time, ticks are most active, hungry and aggressive.
The next powerful wave of reptile activity occurs in late August and early October.
However, cases of the disease are recorded throughout the summer period. The activity of ticks directly depends on the weather conditions. Warm summers and prolonged autumn significantly extend this period.
Favorite habitats of blood-sucking parasites are shady places and high dense grass along paths in forests, squares or parks. The small size does not allow the tick to rise high from the ground.And because of the rapid dehydration, the parasite is forced to constantly descend to the soil in order to replenish its moisture reserves. But, being near the ground, it is very difficult to get hold of a potential victim. Therefore, the ticks are forced to crawl onto the blades of grass and wait.


Blood hunters
Ticks are carriers of pathogenic microorganisms and bacteria that infect domestic animals and their owners. Their attacks are effective because the body, touch, smell of the insect is aimed at finding the victim.
The first pair of legs is equipped with Haller's organs, which are complex in their structure, recognizing thousands of odors, including sweat, pheromones (products of external secretion) of a dog, or carbon dioxide exhaled by it. Ticks respond to vibration, pet shade, and heat. As a good hunter, they sense their prey at a distance of 20 m, remaining unnoticeable for them at 0.2-0.4 mm in size.
A common place for mites to accumulate is in the woods or the border between a bush and a meadow. There, clinging to the underside of the leaves, parasites sit, waiting for a person or an animal. In such corners, shade and moisture are common, and the mite is very sensitive to dry air and hides from it. That is why it is active in the morning and from 15 to 24 hours, when the heat subsides.
Dogs often catch ticks near roadside bushes.
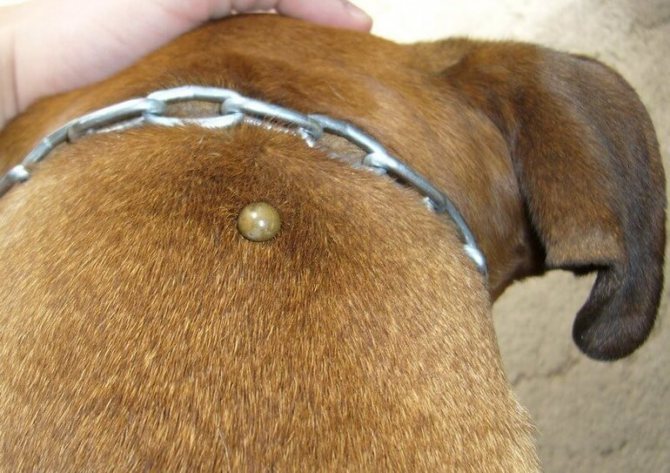
After the attack, the tick moves along the dog's body in search of warm, damp and poorly protected places, closer to the blood vessels. Most of them are located on the neck under the muzzle, in the armpits, groin.
Therefore, the tick bite is imperceptible, and it can feed on the blood of its prey for several hours or days.
The biggest threat to humans and pets comes from two types of parasites:
- canine (Ixodes ricinus) - a carrier of Lyme disease, babesiosis, encephalitis, Marseilles fever and tularemia;
- meadow (Dermacentor reticulatus) - a conductor of tick-borne typhus of North Asia, Omsk hemorrhagic fever, tick-borne encephalitis, causative agents of plague, tularemia, brucellosis.
Types and description of ticks
Ticks on the dog are fixed very quickly, because the skin under the hairline of the animal is very delicate, and is easily affected by the insect. But do not rush to remove the parasite. Each species is unique and there are nuances in the fight against it.
In total, scientists have counted about 40,000 dangerous species of ticks. In the conditions of the Russian climate, only a few take root.
Let's consider the most common varieties.
Ixodid ticks
Adult insects have hard chitinous plates that protect the body from external factors. The tick looks frightening, because its size is on average 2.5 cm, and when parasitizing on an animal, it increases several times.
This tick lives in central Russia. Most often it hides in foliage and shrubs. It can be dangerous for humans as well. Able to lay up to 17,000 eggs, from which larvae emerge. They multiply rapidly. The adult has a brown color, a young yellow tint.
Argasovye
Can be found in outbuildings, old houses, bird nests. Most often they parasitize pets and cattle. Rarely, but can strike a person. The bite of this insect brings painful sensations, itching and burning immediately occur.
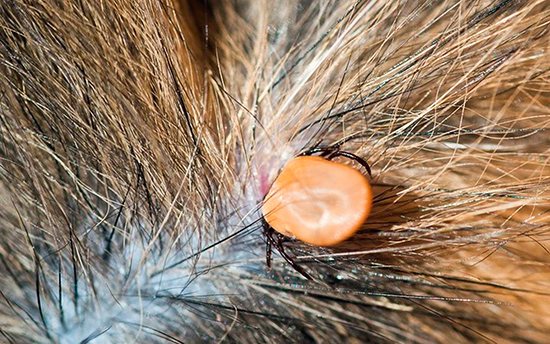

The parasite has a light color, its body is practically unprotected, so the animal can brush off the tick, while its trunk will remain, which can cause skin diseases.
Carapace tick
Its habitat is the topsoil. Less commonly found in trees. It feeds on mushrooms, plants, lichens. Dangerous for poultry and animals. Transfers helminths.
Subcutaneous (sarcoptic)
It parasitizes both humans and animals. It feeds on dead skin. It causes itching and burning.

A subcutaneous mite is very difficult to recognize.It has a white tint and small size, so it is well masked. The lifespan is up to 3 months. During this time, he manages to lay more than 100 eggs. Internal mites are especially dangerous in dogs.
Scabby
It becomes the reason for the occurrence of an unpleasant disease - scabies. Parasitizes on humans, animals. It feeds on a secret that is secreted from the skin. Easily distinguishable, as it has a gray tint and impressive size. In places after a tick bite, the dog has redness and itching. Lives up to one and a half months.
Read Symptoms of Bordetella in Dogs: 3 Steps of Treatment


How to properly remove a tick from a dog?
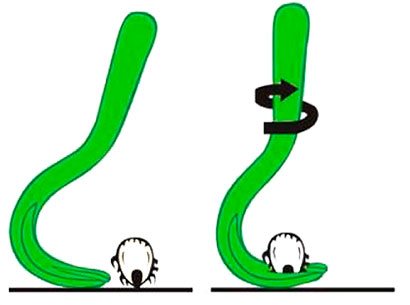
Remove the tick with tweezers, trying to grab its body closer to the skin. Pull the parasite slowly, holding the skin of the animal with your free hand. Twisting can cause the head of the parasite to come off, so be careful. Zoo shops sell special tweezers for removing ticks.
Then you should abundantly treat the wound with iodine. Now it remains only to observe the dog every day for the next 2-3 months, as well as to measure the temperature. If you develop clinical symptoms: lethargy, decreased activity, poor appetite, diarrhea, changes in concentration, color and odor of urine and others mentioned above, urgently contact your veterinarian.
Symptoms of piroplasmosis after a tick bite
Most often, pets become infected from ticks with piroplasmosis. The virus develops within a day or two. How long the infection takes place depends on the age of the pet and the date of vaccination. The first stage of piroplasmosis is manifested by fatigue, apathy and loss of appetite. If the disease was detected in the early stages of development, then the disease can be cured in a few days.
When the stage is advanced, there is a high temperature of up to 42 degrees, urine with blood, an unpleasant odor from the pet's mouth. Shortness of breath, vomiting, yellowness of the eyeballs may be observed. If the pet is in serious condition, then the symptoms of the first and second stages are combined together. Convulsive seizures, loss of coordination are noticed, paws may even fail.
In a severe stage, it is rarely possible to save a pet. The duration of treatment is up to three weeks. Convulsions can lead to swelling of the brain, then the dog will die.
Consequences and complications of tick-borne diseases
Single-celled protozoa piroplasma (Piroplasma canis) destroy erythrocytes. A blood test shows a sharp decrease in the number of red blood cells. The body accumulates poisonous decomposition products of hemoglobin, which disrupts the functioning of internal organs. How many days does a dog get sick after being bitten? The answer to this question depends on the initial state of the animal, but usually the incubation period is 4-15 days.
The condition of the dog can deteriorate dramatically. With an ultra-fast course, the animal dies without pronounced signs of the disease.
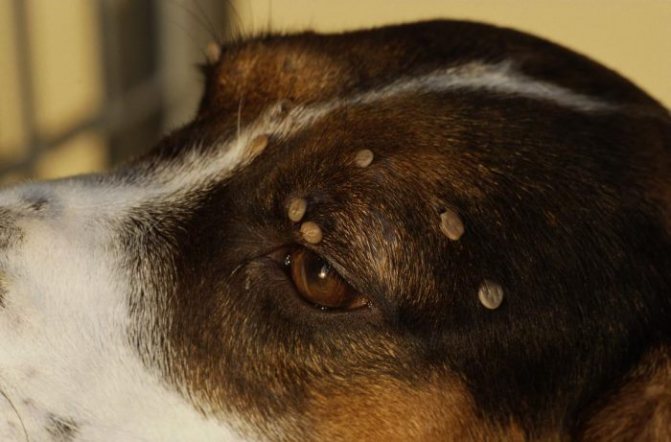

In an acute form, the following symptoms appear: change in behavior, weakness, lethargy, loss of interest in what is happening, fever up to 42 ° C, refusal to walk, dark urine, pale or yellow mucous membranes, shortness of breath, paralysis of the limbs occurs. Death - 3 - 7 days from the moment of infection. With timely treatment, the chances of a dog's survival are quite high.
In chronic piroplasmosis, all symptoms are blurred, only fatigue and weakness are expressed. In the latent form, symptoms do not appear.
The earlier the treatment of piroplasmosis is started, the higher the animal's chance of survival. Recovery will last 4 to 5 weeks at best.
For proper treatment, it is important to exclude similar ailments: liver damage, poisoning, leptospirosis, glomerulonephritis, plague.
Blood and urine tests are urgently needed. A blood test will help to quickly identify babesiosis by the many destroyed erythrocytes and pyroplasmas in them. Hemoglobin in the urine of a sick dog confirms the diagnosis.
Step-by-step treatment:
- Antiparasitic drugs: Veriben, Berenil, Azidine (diminazine) - less toxic. Stronger: Imidocarb, Imisol, Piro-stop.
- Alkalization of urine for normal kidney function. Sodium bicarbonate is injected intravenously, preventing blockage of the renal tubules with hemoglobin crystals. The animal is also watered with a solution of 2 g of soda per 10 kg of body weight until the hemoglobin is completely removed from the urine. Instead of soda, you can give the drug blemaren - 1 tablet per 10 kg of body weight per day.
- Vitamins, diuretics, glucose, tonic, hemostatic.
- Purification of blood by transfusion or filtration.
- A recovered dog should be restricted in movement for 10-15 days. Special care and diet will be required.
After the disease, unstable immunity remains for 4-6 months. After that there is a risk of contracting piroplasmosis again.
Of course, in the first place, encephalitis is dangerous for humans, but if the immune system is weakened, the dog can also get sick. From a bite of an encephalitis tick, severe symptoms occur. The incubation period is about 2-3 weeks. Usually there is an increase in temperature, convulsions, impaired motor functions, paralysis.
A characteristic symptom is hypersensitivity of the head and neck, severe pain. Mood changes may occur - apathy or aggression, later - paralysis of the facial and eye muscles. Brain damage is evident, and since there is no specific treatment for encephalitis for dogs, the prognosis is unfavorable: almost one hundred percent death.


The cause of monocytic ehrlichiosis (MES) is the gram-negative bacteria ehrlichia. Their main carrier is the same dog tick that feeds on the blood of an infected animal.
A tick bite with dangerous contents at any time can cause infection of a healthy animal.
Splenomegaly - liver enlargement - a poor diagnostic sign
There are no statistics of infection and gradation of dogs by age, sex and breed, but it has been noticed that MES affects German shepherds more often than other breeds.
The clinical symptoms of ehrlichiosis are nonspecific. One of the main ones is a violation of blood clotting, but at first there are:
- depression, lethargy;
- loss of appetite and weight;
- heat;
- hemorrhagic spots on the skin and mucous membranes;
- bleeding from the nose (considered a rare symptom);
- vomiting (rare);
- purulent catarrhal rhinitis (rare);
- lameness, imbalance due to damage to the cerebellum (ataxia).
Later, splenomegaly (enlarged spleen), swelling of the lymph nodes and mucopurulent nasal discharge are possible. As a result of inflammation of the blood vessels of the eyes, discoloration and visual impairment with possible blindness can occur.
A dog's blood test shows a decrease in white blood cell count, thrombocytopenia, low hematocrit (red blood cell volume), monocytosis, increased blood protein. Therapy is based on antimicrobial agents (such as Doxycycline) given over three weeks. Glucocorticoids are connected to the main course.

After an acute manifestation of MES, the dog can recover, but if the body cannot get rid of the pathogen, the form of the pathology will change to subclinical. In this case, the pet will remain a source of danger to other animals. The development of a chronic form of this disease is possible. The progressive pathology of the MES with massive blood loss is fatal.
It is not always possible to notice the parasite in the thick hair of the animal with the naked eye. Therefore, you need to be able to pay attention to signs that directly indicate the presence of a bite.
Ticks themselves are not dangerous in dogs. The bite causes a slight itching and burning sensation that goes away quickly. However, this insect can become a carrier of various diseases and infections.Depending on the parasites that the tick has awarded your dog, there are several types of symptoms.
Any breed is susceptible to parasite attacks:
- spitz;
- Labrador;
- shepherd;
- chihuahua;
- yorkies;
- etc.
It manifests itself as tick-borne paralysis. The deterioration of the condition occurs in stages.
- The hind limbs are taken away.
- The pelvic region ceases to function.
- The front limbs are taken away.
- Loss of voice. It is called dysphonia at the level of the working ligaments.
- Violation of the vessels in the cranial region.
- The swallowing reflex ceases to function.
- Suffocation.
Local reactions
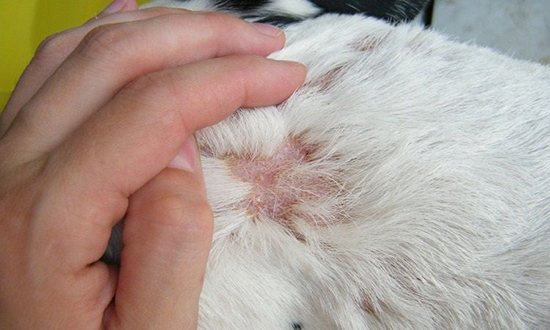
Already after a couple of hours from the moment the animal was bitten by the parasite, skin changes can be seen with the naked eye.
This is an allergic reaction to a similar condition. Various factors can affect the appearance of the skin:
- parasite;
- animal immunity;
- the duration of the tick's stay on the skin;
- weather.
The affected area should be examined carefully. If the parasite remains, then the skin begins to swell and the redness increases. Itching appears, pain on contact.
At the same time, you need to monitor how the animal behaves. If it is anxious, trying to scratch, bite, lick the place, then the pain intensifies.
After a few hours, a purulent reaction and a tick-borne infection may begin. Thus, the body tries to cleanse itself of harmful substances.
Pyroplasmosis
Treatment methods
After the diagnosis and assessment of the pet's condition, the question of the place of its treatment is decided. A request for home therapy will be granted only in mild to moderate cases. A seriously ill animal must be in a hospital.


If you decide to treat the dog yourself, then leave the selection of drugs and dosage to the veterinarian. Experimenting with this can cost the dog his life. The doctor selects the therapy and develops the scheme, giving all the necessary instructions, and the owner's task is to do everything exactly.
Usually, several steps are needed to cure:
- Antiparasitic drugs that will kill the entire population of Babesia. These drugs are toxic, so a specialist in the clinic should select the dosage and inject. The rest of the manipulations can be carried out at home.
- Adjunctive therapy to maintain the body, it includes a vitamin complex and preparations for the heart and kidneys.
- To maintain water-salt balance and to cleanse the body of intoxication products, the animal is given a little warm water mixed with soda, and special droppers containing nutrients, vitamins and sodium nucleinate are placed.
After Babesias are destroyed and removed from the body, and the intoxication is removed, a long recovery process begins. Depending on the severity of the course of the disease, this period can last from a month to six months. At this time, the dog needs additional care and special nutrition.
It is forbidden to use folk methods and methods for piroplasmosis, as they can adversely affect the condition of the animal. There is no way to kill the pathogen, except with a special drug, and without this it is impossible to be cured. The use of home recipes, for example, herbal preparations, simultaneously with drugs is possible only after the permission of a doctor, as they can seriously harm.
Why are ticks dangerous for dogs?
By itself, the bloodsucker is practically not dangerous, but it carries blood parasites that cause piroplasmosis (babesiosis) and other vector-borne diseases by destroying blood cells, completely disrupting metabolic processes in the body and causing strong neurointoxication. Their reproduction occurs very quickly, therefore, without treatment, with a 98% probability, the animal dies.
It is not always worth panicking if a dog is bitten by a tick. By itself, the bite of a blood-sucking parasite does not pose a particular threat to the pet's body. Receiving small portions of blood, he is not able to exsanguinate the animal.
The main danger posed by the ixodid tick is the ability to carry serious infections, infecting a large number of animals. The consequences of a tick bite for a dog can result in serious damage to internal organs with piroplasmosis, bartonellosis, ehrlichiosis, up to the death of the animal.
You should not panic, because the carriers of blood parasitic infections that destroy red blood cells in the body are not all ixodid ticks, but only a tenth of the entire population.
In order to prevent infection, it is necessary to treat the dog from ticks in a timely manner, especially at the peak of parasite activity and in those regions where there are more deciduous shrubs and trees. If, after the owner has discovered the tick, it must be removed correctly.
It is impossible to pull the parasite out of the skin, as the mite burrows deep enough into the skin. With a sharp separation, the mouth apparatus of the ixodid tick can remain under the skin and cause the development of an inflammatory process.
It is also important to observe the condition of the animal for the first 3-4 days after the detected and removed tick. With the defeat of blood parasitic infections, the condition of the animal is aggravated, there is an intoxication of the body. The development of febrile states, lethargy and severe weakness in the dog is possible. The pet refuses to eat and may refuse water.
In addition to the obvious discomfort associated with parasite bites and the threat of skin inflammation, ticks are carriers of dangerous diseases.
The only measure of pet protection is timely, regular prophylaxis of blood-sucking parasites. If your dog has been bitten by a tick, there is no need to immediately run to the vet.
Preventive measures
To protect your pet, you need to follow simple rules:
- Examine the dog after every walk, even if it was not in a park or forest. Ticks have moved close to human homes and can attack anywhere. Pay special attention to areas where the parasite loves to eat - ears, neck, abdomen, armpits.
- Timely application of acaricidal drugs and repellents will reduce the likelihood of an attack by blood-sucking parasites. The effect of drugs decreases over time, and with frequent bathing, it happens faster.
- If a tick is found in the pet's fur, it is necessary to remove it correctly. Over the next week, carefully observe the condition and behavior of the dog. Any manifestation of symptoms of the disease is a reason for contacting a veterinarian.
The most caring and responsible dog owners will not be able to prevent a tick bite while walking. The main thing is to competently respond to the incident and do everything to avoid tragic consequences.
Insidious Lyme disease
Borreliosis (Lyme disease) is a polysystemic disease of infectious etiology caused by the spirochete Borrelia burgdofer.
The disease is dangerous for both humans and animals. Tick-borne infection leads to chronic destructive changes in the joints of dogs. Sometimes the kidneys or heart are affected.
Lameness is one of the hallmarks of Lyme disease in dogs
At an early stage of the disease (2 - 3 days after infection), the symptoms are as follows:
- the appearance of erythema migrans at the site of the bite (inflammation on the skin in the form of a red expanding ring);
- fever;
- lethargy;
- lack of appetite;
- lameness;
- touch sensitivity.
As the disease progresses, the joints swell, and other visual and neurological disorders are added: severe depression, anemia, dark urine.
Diagnosis of Borrelia infections is based on a blood antibody test. IgM cells indicate recent infection. They appear after 3 - 4 weeks, disappear after 3 - 4 months. IgG antibodies appear in about a month.

Having established the diagnosis, the veterinarian prescribes long-term antibiotic treatment. The most commonly used are Doxycycline and Amoxicillin.It is possible to decide on infusion therapy using anti-inflammatory agents and drugs that support the functioning of the liver and kidneys.
The disease is very insidious, it may not appear from 2 to 5 months, as if waiting for time for an attack. If left untreated, it will result in the death of the pet. A common complication of Lyme disease is glomerulonephritis - an immune-inflammatory pathology of the kidneys with a predominant lesion of the renal glomeruli.
In order to protect your pet from various infections carried by blood-sucking parasites, it is necessary to carry out preventive treatments with special means. Ticks can carry not only blood parasitic infections, but also all kinds of viruses, bacteria and helminths. Vaccinations against ticks for dogs will help protect your pet from parasites.
- Piroplasmosis is a seasonal disease provoked by protozoan parasites. The disease is also called babesiosis from the name of the cells of the pathogen. Babesias attack red blood cells, gradually causing them to break down. Symptoms of pathology differ depending on the type of pathological process - fulminant, acute or chronic. An accurate diagnosis of the presence of pyroplasmas in the body is made on the basis of laboratory studies in a veterinary clinic. Treatment of diagnosed piroplasmosis includes the use of specific medications, as well as drugs that eliminate symptoms. The animal is shown special dietary food, cardio and hepatoprotectors, as well as drugs to maintain the functioning of the renal structures.
- Bartonellosis is an infectious disease provoked by pathogenic bacterial microorganisms. In addition to lesions of red blood cells, Bartonellae infect blood macrophages and destroy the walls of blood vessels. After infection, the pathological process can proceed without pronounced symptoms and end with the sudden death of the pet. The chronic form of bartonellosis, in the absence of timely treatment, leads to a gradual damage to the cellular structures of the myocardium and brain.
- Lyme disease or borreliosis is an infectious process characterized by a chronic course. The disease is transmitted by the bite of an infected tick. Borreliosis can affect not only pets, but also humans. The insidiousness of the disease lies in a prolonged asymptomatic course for 1-3 months from the onset of infection. The characteristic signs of Lyme disease are febrile conditions, the occurrence of edema in the joints, pain and inflammation of the joints, as well as inflammatory processes in the regional lymph nodes. The pet may begin to limp, failure of the renal structures develops, and in advanced cases, inflammatory processes of the brain tissues are diagnosed. Treatment consists in prescribing a course of broad-spectrum antibiotics. The duration of treatment depends on the degree of neglect of the pathological process.
- Ehrlichiosis is an infection that affects blood cells (monocytes). The danger lies in the ability of pathogenic microorganisms to spread to all organs, affecting the spleen, hepatorenal and lymphatic systems. There are several stages of pathology. In an animal with ehrlichiosis, iron deficiency anemia develops, spontaneous hemorrhages are possible.
- Hepatozoonosis is a disease provoked by unicellular protozoa parasites that enter the bloodstream and affect white blood cells. When conducting a blood test, there is a sharp increase in leukocytes in the blood. Hepatozoonosis is treated with antimicrobial drugs. Symptomatic therapy is also prescribed, aimed at the speedy regeneration of the body. It is not possible to get rid of hepatozoonosis completely. Therefore, relapses are often observed.
Hepatozoonosis.They are caused by protozoa of the genus Hepatozoon, which infect leukocytes, spreading throughout the body of the animal. This is usually due to the ingestion of a parasite. Often, the disease does not make itself felt for several years while the immune system is normal. With a decrease in immunity, fever begins, pain in joints and muscles, weakness, eye discharge. Not hazardous to humans.
Ehrlichiosis. Provoke rickettsia - Ehrlichia. It settles in white blood cells: platelets, monocytes and granulocytes. There are rickettsias that are dangerous to humans. The disease came to Russia from Europe and the United States. The symptom of all ehrlichiosis is a debilitating, growing fever.
Monocytic ehrlichiosis: weight decreases, the animal urinates with blood, the number of platelets and leukocytes decreases, weakness, hemorrhages on the cornea, mucous membranes, skin, nosebleeds, anemia, and heavy breathing are observed.
Granulocytic ehrlichiosis: high fever, weakness, convulsions, inflammation of the eyelids, joint tenderness, enlarged liver and spleen, protein in the urine, low albumin and platelet counts. After 2-3 weeks, the activity of the animal decreases and lethargy appears. Sometimes it develops in a latent form and leads to severe damage to the eyes, bone marrow, joints, liver and other organs.
Bartonellosis - erythrocytes, macrophages and endothelial cells infect bacteria of the genus Bartonella. Some of the Bartonella is also dangerous to humans. Symptoms: from long-term carriage to sudden death without pronounced signs. Clinic: high fever, inflammation of the joints, drowsiness, weight loss, weakness of the hind legs, anemia, disturbances in the functioning of the heart and blood vessels, inflammation of the eyelids, nosebleeds, hemorrhages in the eyes, inflammation of the subcutaneous vessels, meningitis, pulmonary edema.
Borreliosis (Lyme disease) is a dangerous disease for dogs and humans, caused by bacteria of the genus Borrelia. It is transmitted in utero and often leads to the death or nonviability of the young. Causes arthritis and neurological disruptions. First, the joints near the bite site become inflamed. Sometimes the limp goes away on its own. The hosts become infected with borreliosis when a tick is crushed. The consequences of the disease are neurological disorders, chronic inflammation of the joints, blood vessels, internal organs, etc.
Babesiosis (piroplasmosis) is the most common disease in dogs. It is not dangerous for people. Cause different types of babesia. Symptoms: lethargy after a bite, jaundice, fever, shortness of breath, gastrointestinal disorders, disorders in the liver, heart, lungs, kidneys and other organs. Dark: Brownish or red urine indicates kidney failure. The animal refuses to eat, drinks a lot of water.
Diagnostics
If you suspect that something is wrong, you should contact your veterinary clinic as soon as possible. Diagnostics is carried out in a comprehensive manner.
To begin with, the doctor examines the four-legged, determines the presence of symptoms of the disease.
Despite the fact that 90% of pyroplasmosis is determined by the results of a blood test, it is recommended to supplement it with other laboratory tests.
Blood test
To determine the amount of babesia in the blood and to determine the level of red blood cells, the following blood tests must be taken:
- Clinical analysis shows the presence of leukocytes and the number of destroyed erythrocytes in the blood, the concentration of hemoglobin.
- With the help of biochemical analysis, it is possible to identify the functional state of the liver, the presence of inflammatory processes and much more.
- A blood test for babesia (a smear for piroplasmosis). This is a study of blood under a microscope, with the help of which the presence and number of protozoa in the blood is determined. Microscopic examination is very important, as it shows the number of pyroplasmas in the blood and allows an individual approach to treatment. Blood sampling for this analysis is done as follows. In the area of the animal's ear, the hair is shaved off and a small incision is made. A drop of blood is taken from the incision, placed on a glass and examined under a microscope.

It happens that at the very beginning of the incubation period it is not always possible to detect Babesia in the blood of a four-legged.
Important! If the research results do not confirm the presence of piroplasmosis, but all the symptoms indicate the opposite, and even more so if you removed the tick from the dog, it is recommended to do a second analysis in a day.
Analysis of urine
Many diseases in dogs have similar symptoms. It is for this that it is important to pass a urine test. If hemoglobin is found in it, piroplasmosis is considered confirmed.
Blood cell destroyer
Some of the consequences of tick bites previously for groups of animals did not stand out as independent, for example, anaplasmosis, from which people suffered most. This is reflected in its name - human granulocytic anaplasmosis. Dogs and other animals can also have this disease, but its manifestations are different from the effect on the human body.
The causative agent of the disease destroys platelets and leads to problems with blood clotting in the animal
The danger for dogs is that the causative agent of the disease - Anaplasma phagocytophilum - refers to intracellular parasites. Reaching a high concentration in the blood of an animal, it penetrates into platelets, which are responsible for blood clotting, and destroys them.
The symptoms are indeed very similar to the signs of the previously described pathologies - they are high fever, anorexia, soreness and swelling of the joints.
But along with neurological symptoms in dogs, an inflammatory process in the muscles begins, a weakening of their reflexes and atrophy, and paralysis of all limbs develops.
Failure of the immune system
Symptoms of these diseases in the early stages resemble those of a common cold. The absence of specific manifestations makes it difficult to quickly diagnose them.
They can live without oxygen, do not have a cell wall, therefore they are resistant to antibiotics. These bacterial parasites are transmitted by ticks, mosquitoes and other stinging insects. Infection can also occur through contact between an infected mother dog and a puppy.
Often the disease leads to the need to remove the spleen, which is a hematopoietic organ


Usually, the disease overcomes animals weakened by other pathologies. It is especially difficult in a dog with a splenectomy (removal of the spleen). This organ is a kind of filter that cleans the blood from red blood cells damaged by parasites. When it is removed, the immune system attacked by mycoplasma mistakenly recognizes its own red blood cells as foreign and destroys them.
You can determine the cause of the disease using a blood test. Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is also used - a high-precision method of molecular genetic diagnostics. Treat the infection for at least 3 weeks with antibiotics (tetracyclines), continuing symptomatic therapy.
Prophylaxis
Of course, any disease is better and cheaper to prevent than to cure. The prevention of piroplasmosis should never be questioned by dog owners - the infection is really very tough and insidious, it is better not to get sick with it!

The main methods of prevention include:
- regular treatment of dogs with drugs for ticks, which will scare them away from themselves or make animals "invisible" to the receptors of ticks (usually drops on the withers);
- obligatory examination of the animal's body after each walk (laziness can cost a pet's life!);
- vaccination against piroplasmosis;
- the introduction of specific drugs for prevention, without waiting for the manifestation of symptoms, as soon as the tick was found on the body.
List of some preventive measures for dogs


Vaccines:
- Piro-Dog;
- Nobivak Piro.
Tick sprays:
- Frontline;
- Bolfo;
- Beaphar;
- Leopard.
Tick collars:
- Foresto;
- Kiltix;
- Bolfo;
- Dana-ultra
Drops on the withers:
- Frontline Combo;
- Advantix;
- Binakar;
- Hartz Ultra Guard;
- Stronghold.