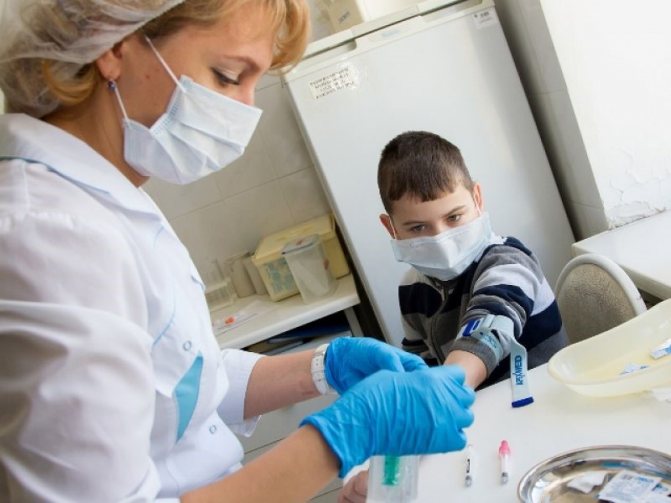
Every day a person contacts with many small, practically invisible creatures. Some of them are friendly, while others are dangerous to human life.
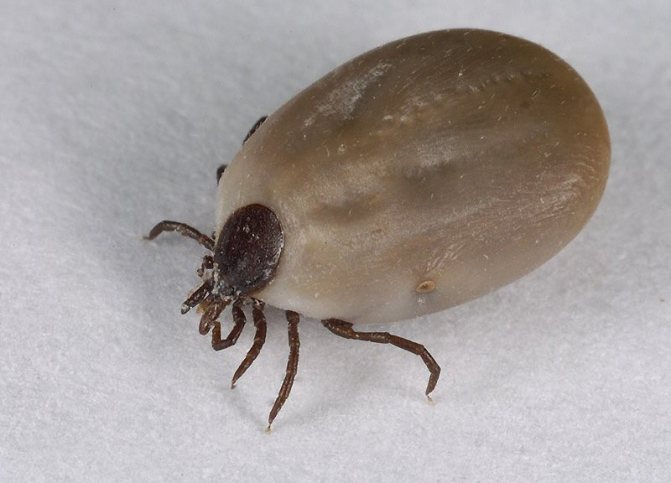
Ticks are small parasites that carry dangerous diseases by infecting their host through a bite.
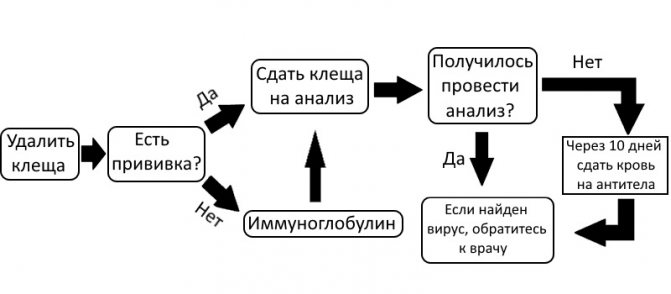
After a tick bite, it is important to carefully examine the damaged skin, carefully monitor your condition, so that with the development of diseases carried by the parasite, their manifestations can be detected in time and as soon as possible to seek qualified help.
Arthropods come in many varieties, some of which are not dangerous to humans. Nevertheless, everyone should know what to do after a tick bite, because attacking parasites can be found almost everywhere.
How a tick bites
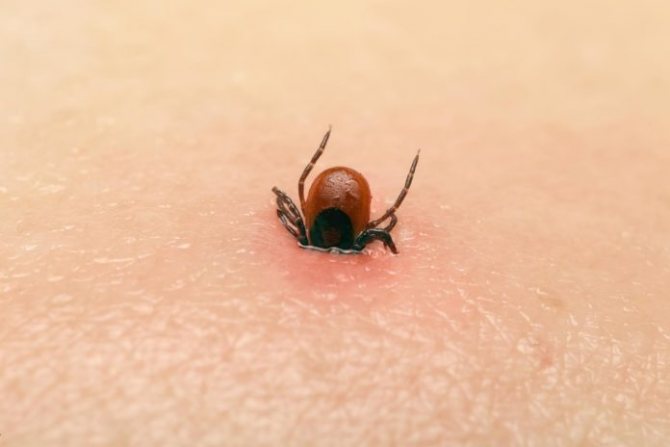
The tick bites much more difficult than similar blood-sucking insects. His oral apparatus is represented by two parts at once: chelicerae and proboscis. In fact, the head of the tick is the entire oral apparatus of the parasite. He has no eyes, and the function of touch is performed by pedipalps located in the same place. They are two antennae that can bend back when feeding, and also allow you to find a prey.
The tick does not immediately dig into the body of its host. It takes about 20-30 minutes to get to the blood vessels and start absorbing blood. The exact time of immersion in the epidermis differs from species to species. After the victim has been identified, the parasite looks for a suitable place for a bite for some time. The most common insect bite sites are described below. It is most convenient for a tick to get food where the epidermis is thinned or easy to penetrate. He prefers to stop at areas where the capillaries run close to the surface of the skin.
With the help of chelicerae, two chitinous processes, which are usually protected by covers, the arthropod cuts through the victim's skin. Chelicerae are located on the sides of the proboscis. They are oblong processes with chitinous setae. At the base, they are the largest, and the closer to the tip, the smaller. The bristles are bent back. This allows the parasite to firmly anchor in the victim's body, which protects it from accidental slipping off due to wind or movement of the host.

After the tick cuts through the keratinized layers of the skin with chelicerae, sharp as a razor blade, it plunges its proboscis into the resulting wound. First, with the help of the proboscis, the parasite injects salivary secretions into the body. They soften the skin, facilitating further advancement to the source of nutrition, stop blood clotting, and also eliminate the victim's pain. The wearer may not notice for more than a day that he was bitten, since the natural anesthetic lasts for a long time.
The tick begins to feed only when it completely immerses its mouth apparatus (and therefore the entire head) into the skin. The bristles of the chelicerae firmly fix it, and with an incorrect attempt to pull the arthropod, its body splits into two parts. The head stays in place and can cause inflammation.
Helpful information
Ticks belong to the group of arthropods, some of them feed on human blood. Distinguished by an exceptional sense of smell, they easily find a victim for themselves.Once on the skin, insects pierce it to suck blood. They usually choose moist and warm areas on the body with a superficial arrangement of blood vessels, for example, armpits, legs, arms, neck, area behind the ears, groin, buttocks.
If the tick has bitten, saliva is injected, which contains a large amount of analgesic substances. It is not surprising that a person practically does not feel any discomfort when bitten. A sucked insect can parasitize on the skin for several days, increasing in size, after which it disappears on its own.
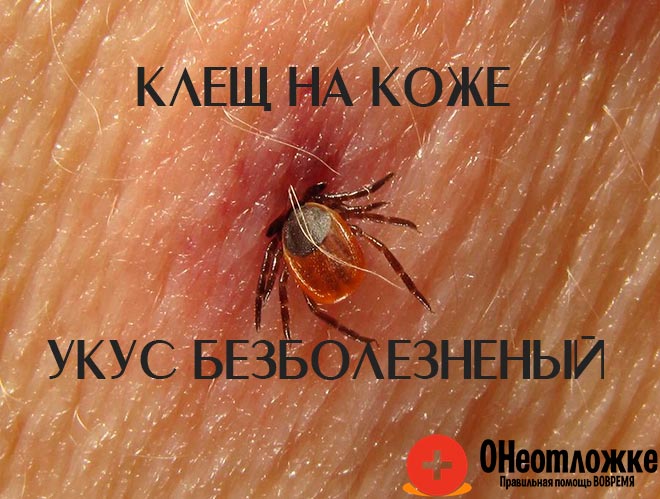

A characteristic spot is formed at the site of the tick bite. The skin noticeably swells and reddens, thus reacting to contact with an insect. If complications do not join, the symptoms will go away on their own after the successful elimination of the parasite. This process is accelerated by appropriate medications prescribed by the doctor.
What does a tick bite look like?
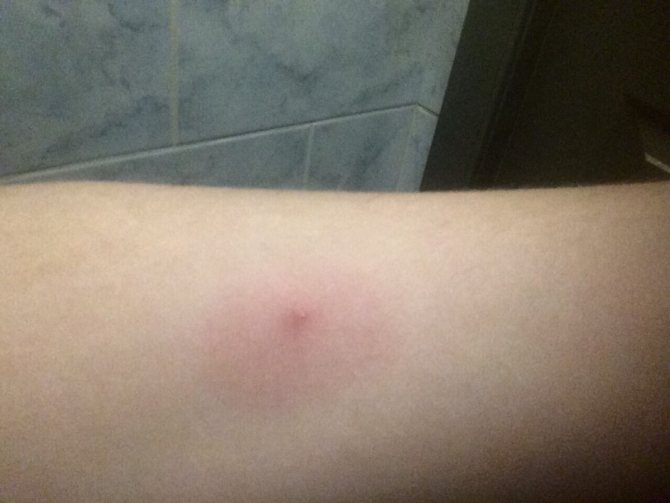
Recognizing an insect bite is fairly easy. If the parasite finished feeding on its own and pulled out the mouthpiece, then a small reddish mark with a diameter of about 1 cm will remain at the site of introduction. There may be a trace of dried blood in the middle. If the victim of a tick attack has sensitive skin, then a slight swelling may also develop in the middle of the mark.
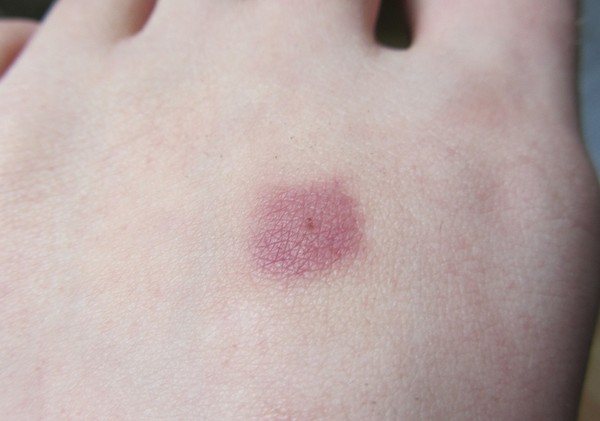

If some time has passed after the bite, and the host of the parasite did not notice the tick and did not treat the wound, inflammation may begin. Typical symptoms will appear:
- weak heat at the site of the lesion;
- severe redness;
- the appearance of pus.
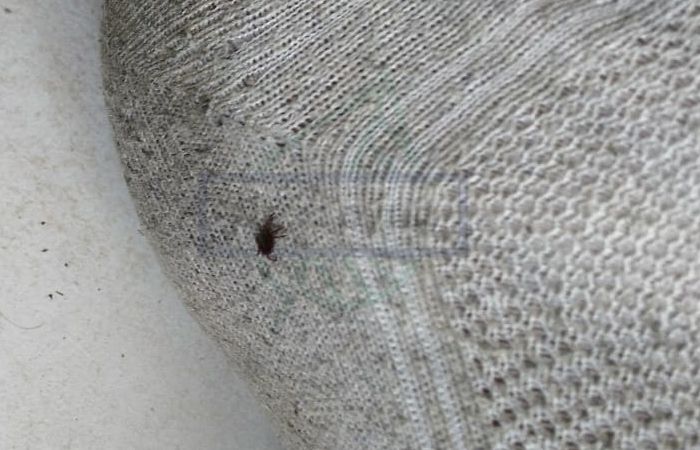
The worst case is when the tick's head remains in the skin. The mouth apparatus of a tick may contain traces of various microorganisms, toxins, viral diseases. If the chelicerae and proboscis are not removed, this can lead to the development of various diseases. If the head of the parasite remains in the body, outwardly it will look like a small dark lump in the middle of the reddish mark.
Medicinal prevention of tick-borne encephalitis
In order to avoid the development of tick-borne encephalitis after the initial medical care measures and while waiting for the test results, it is recommended to use the drug Yodantipirin, which suppresses the virus that could enter the human body.
It is necessary to take Yodantipirin according to the following scheme:
- 3 tablets 3 times a day for the first 2 days after the bite;
- 2 tablets 3 times a day for the next 2 days;
- 1 tablet 3 times a day for the next 5 days.
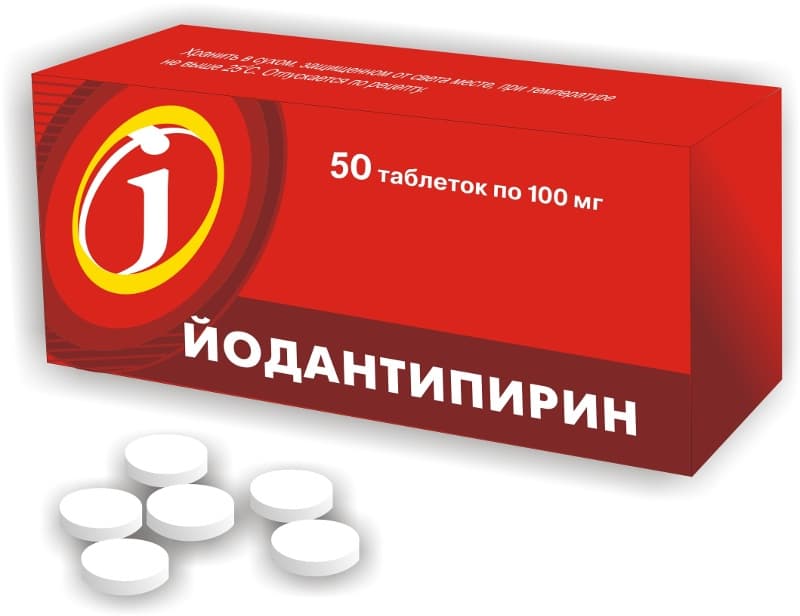

This drug can also be used as a preventive measure. To do this, it is enough to take 2 tablets 1 time a day during the entire period of being in an endemic area. Or start the appointment 2 days before outdoor recreation. In this case, the dosage regimen changes: you need to take 2 tablets 3 times a day for 2 days before visiting the endemic area.
It is worth remembering that in the case of a tick sucking against the background of preventive regimens for taking the drug Yodantipirin, you should switch to an emergency prevention scheme (prevention after a tick bite) - this will enhance the protective effect and will not give the virus any chance to develop.
Tick bite symptoms
The initial symptoms of a bite are the same as for any other wound with an inflammatory process. The patient may experience the following ailments:
- headaches;
- weakness;
- pain in the area of the bite (develop no earlier than 24 hours after the tick attack);
- itching and redness of the skin;
- increased skin temperature in the area of the bite;
- slight swelling of the epidermis.
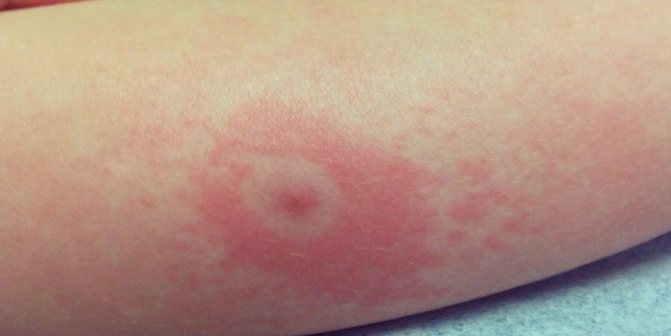

If a tick has introduced a virus or infection into the body, additional ailments may be added to this list.For example, with a simple bacterial process, subfebrile body temperature develops, redness increases, signs of general intoxication of the body may appear (nausea, vomiting, weakness, bone aches).
First aid for a tick bite
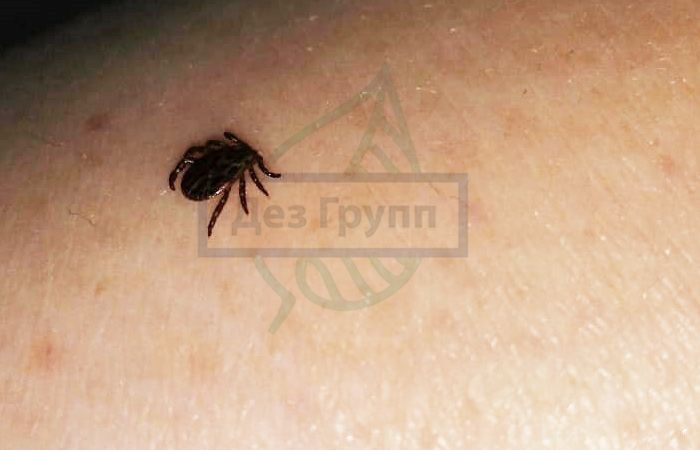
If a bite is found, it is necessary to check if there is a tick head under the skin. The parasite can remain entirely in the body. A well-fed parasite takes the form of a ball with a diameter of up to 1 cm of black or olive light. If it has not yet sucked, then it reaches a size of only 1-2 mm and is barely noticeable on the skin.
You need to act according to the situation:
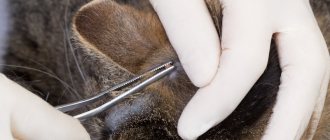
- If the tick has not yet seized. It is necessary to remove it from the skin as soon as possible using tweezers. The insect is placed in a closed box or under a glass, and it is best to immediately kill it and burn it (provided that there was definitely no bite).
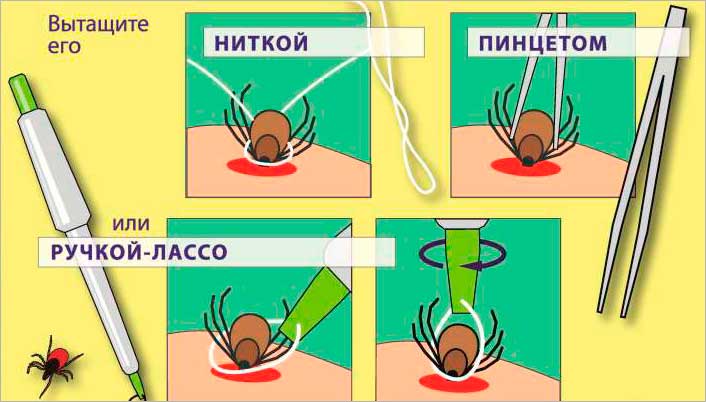
- If the parasite has already dug, but has not yet had time to puff up strongly. This suggests that he sucked just half an hour ago. This does not eliminate the likelihood of transmission of encephalitis, but it already makes the risk lower. The tick must be carefully removed using tweezers or thread. Tie a thread or fasten tweezers with forceps as close to the skin as possible. You cannot press on the torso: this will lead to the injection of poison. Read more about insect removal below. After pulling out, you need to treat the wound with disinfectants and consult a doctor, taking a tick with you.
- If the tick is completely inflated... You can wait a while. Perhaps he will pull out the oral apparatus himself, and then the risk of accidental rupture of the body and head will disappear. If the parasite does not come out on its own, it is removed in the same way as in the second paragraph. The wound is being processed.


Peroxide or chlorhexidine should be used to treat the bite site. Then iodine is applied along the edges. It is advisable to cover the bite site to protect against infection or dirt. If itching, burning, inflammation occurs, you should immediately consult a doctor (if the patient did not do this immediately after the bite).
Protective drugs
Throughout the walk or rest, clothes should be treated with special preparations several times. All means of protection against ticks for humans are divided into three groups:
- Repellents - their main active ingredient is diethyltoluamide. They are available in the form of lotions and aerosols. The drug is applied to exposed skin and clothing, or only to clothing. These include: "Biban", "Medilis", "Off", "Ultrathon", etc.
- Acaricides - here the active ingredient is usually alphamethrin or cypermethrin and its derivatives. These substances have a nerve effect on ticks. Upon contact with the treated areas, the parasite loses its ability to move and simply falls off the clothing. Release form, in most cases, aerosol. Among acaricides, the most popular are such products as "Picnic - Antiklesh", "Gardex", "Fumitoks", "Tornado - Antiklesh", etc.
Important! Only clothing is allowed to be treated with acaricides. It is forbidden to apply them on the skin! In this case, clothes are sprayed not on a person, but spread out, for example, on the floor. Put it on only after the preparation is completely dry!
- Combined preparations are insecticidal and repellent. They are called combined because they combine the main functions of repellents and acaricides. They are based, as a rule, on alphametrin and diethyltoluamide, and therefore show activity not only against ticks, but also against mosquitoes. These products include: "Moskitol spray", Klesh-Kaput "," Gardex Extreme ", etc.
Recommendations for use
How to protect yourself from ticks with these drugs?
- If we consider the above groups of funds and make a choice, then preference should be given to acaricides or combined drugs.
- Before proceeding with the direct use of a particular tool, you must carefully read the instructions.
- Tick protectors are applied in circular stripes, paying particular attention to the cuffs, collar, waist, ankles, knees and hips.
- Do not forget that the preparation layer must be renewed from time to time. You will find the validity period in the same instructions.
- Hot weather, increased sweating, rainfall and strong winds are factors that can significantly shorten the duration of the drug's action.
How to remove a tick
The tick is pulled out with tweezers or a thread. In pharmacies, special forceps are sold to remove them. It is advisable to purchase them before the start of the summer season.
Several rules for deletion:
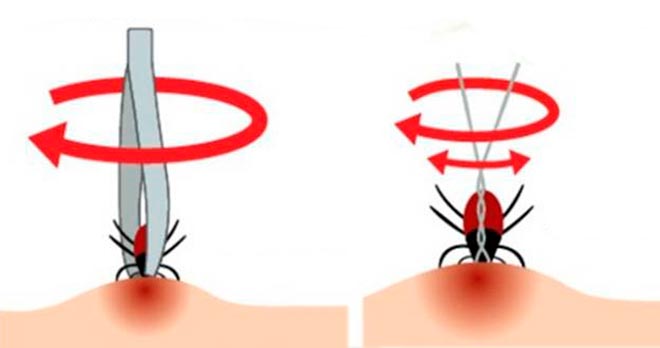
- You cannot pull on the torso. The tweezers are placed on the head.
- Pull out in a circular motion clockwise.
- Do not jerk sharply. It is necessary to smoothly twist the insect.
- It is important to try not to squeeze the parasite too much. This will lead to a protective reaction and the splash of hazardous substances into the human blood.
In no case should you use alcohol, oil, glue and other compounds to choke the tick.

What to do if the head remains under the skin
It is almost impossible to remove the tick head separately from the body. If the patient is not afraid of pain, a needle can be used.
Algorithm of actions:
- Treat stainless steel needle with alcohol or heat.
- Treat the wound with alcohol or peroxide.
- Pick up the proboscis or head with a needle.
This option is unpleasant and does not always work. If you cannot reach the head with a needle, it is enough just to smear the wound with iodine and consult a doctor. You shouldn't hesitate. It is especially important to get professional help if suppuration has begun.
Some patients, from their own experience, advise applying Vishnevsky ointment to the wound. The head will come out in a day with pus. But it is best to go to a specialist so that he slightly dissects the skin and removes the foreign body.
Insect elimination methods
Tweezers are a proven tool often used to retrieve the parasite. It is desirable that its ends are rounded or blunt. The algorithm of actions is simple:
- The insect is gently captured as close to the skin as possible.
- It is not necessary to make sharp jerks, it is necessary to manipulate with light pulling or twisting movements directed upwards.
Gentle movements will prevent the tick from fragmentation. If parts of the proboscis remain in the wound, they will gradually come out on their own. The main thing is to properly process the skin and prevent infection. Some healers advise removing the remaining fragment with a needle on the principle of a splinter. Such trauma to the bite site is unacceptable.
First aid for a tick bite, or rather, its extraction, can be carried out without tweezers, you will need an ordinary thread. A loop is created from it, which is carefully thrown over the body of the parasite. The loop is tightened at the very proboscis, after which the body is slowly pulled up with light swinging movements to the left and right. It is important to correctly calculate the forces and not to damage the insect, to keep its abdomen intact.

Methods for self-removal of a tick
Parasites can be removed from the surface of the skin with your fingers. In this case, you should worry about protecting your hands, use gloves, a thick cloth available. After the procedure, hands must be washed with soap and treated with an antiseptic.
What not to do
The tick can carry dangerous diseases. For this reason, it must be handled as carefully as possible, especially if it is still in the patient's body. However, many victims violate this requirement, which is why they face unpleasant consequences.


In order not to earn yourself a complication, you need to avoid the following mistakes:
- Touching the parasite with bare hands. From the body of a blood-sucking person, juices dangerous to humans can be released, containing the microorganism borrelia, encephalitis virus, Lyme, as well as other diseases. At the same time, up to 6 infections can sleep in the body of an insect. If you remove the parasite yourself, then only with tweezers, with gloves or using an impervious plastic bag.
- Simple pulling out of a tick. It seems that it is very easy to remove the parasite: just grab its torso and stretch it out. In fact, the arthropod is firmly anchored in the patient's epidermis due to its oral apparatus. When trying to roughly remove the insect's head remains under the skin. It is not only capable of causing inflammation, but also leads to infection with dangerous viruses (the longer the contact, the higher the likelihood).
- Pulling out the tick counterclockwise. The tick enters the proboscis counterclockwise. The pull-out principle is the same as the screw pull-out. It is necessary to spin the parasite in the opposite direction, that is, strictly clockwise.
- Discarding the tick after pulling it out. It is advisable to send the parasite to the laboratory. There he will be tested for bacteria and viruses, which can save the life and health of the patient. In addition, the body of the parasite can cause further spread of the disease if it is eaten by a bird or pet. If it is too far to the laboratory (more than 2 days, after this time it will no longer be possible to carry out the analysis), it is necessary to burn the bloodsucking one.
- Lubrication of the parasite with oil, alcohol, glue. It is believed that if you make it difficult for a tick to breathe, it will relax the mouth apparatus and come out on its own. In fact, the arthropod will react aggressively. It will splash into the blood an additional portion of the poison, and with it dangerous microorganisms, pathogens of viruses. The likelihood of infection will increase significantly.
- Ignoring the need for a doctor's examination. A visit to the clinic after a bite is mandatory. If the patient becomes infected and does not go to professionals, there is a high probability of death.


What measures to take
When a tick bites, first aid is to extract it. Then the wound is treated with antiseptic agents. It is not recommended to crush an insect that has stuck to the skin. Viruses are present in his body, and they can enter the blood through microcracks and wounds.
If possible, the victim must be taken to the nearest hospital, where the doctor will help get rid of the uninvited guest, and will process the damaged skin. The insect must be sent to the laboratory for analysis, refutation or confirmation of the presence of infection.


What is the first aid sequence for tick bites?
That's what really mattersif you plan to act without medical assistance:
- Timely detect an insect on the skin. The bite is completely painless, so the person does not feel it. Examine yourself and your children when you return from the forest.
- Extraction must be done with extreme caution so that no part of the parasite remains in the skin.
- If the proboscis of the tick still remains in the wound, do not get it out with improvised items - needles, scissors. So you can only injure the skin and provoke inflammation.
- Before carrying out the manipulation, the person providing assistance must disinfect his hands with alcohol or any alcohol-containing liquid.
- For your own safety, it is recommended to use gloves.
Many actions that are popular among the population are unacceptable from the point of view of medicine and common sense. So, a tick bit - what not to do:
- It is unacceptable to cauterize the insect with hot objects, its abrupt tearing away from the skin.
- Traditional methods indicate the use of alcohol or oil, hot wax. All this is applied to the tick in order to block breathing.
These actions are dangerous. This can cause the parasite to penetrate the skin or die, leading to complications.
What tick carries diseases
A tick bite can cause up to 6-7 infections at the same time, a significant part of them are fatal. List of transmitted viruses and bacterial diseases:
- Encephalitis. Causes fever, muscle aches and atrophy, brain damage, vomiting, and ultimately death.
- Lyme disease / borreliosis. A viral disease that leads to brain damage.
- Spotted fever. It affects the internal organs from the kidneys to the heart, lethal outcome in up to 14% of cases.
- Tularemia. Not the most dangerous disease, but infectious complications are possible.
- Ehrlichiosis. It manifests itself as a fever with signs of poisoning and muscle spasm.
- Relapsing fever. Illness with an incubation period of 14 days, characterized by fever.
- Babesiosis. Dangerous only for persons with weak immunity.


Where and when are you most likely to get a tick bite?
Like any other insect, ticks follow certain biorhythms. There are clear seasons when they are most dangerous, since they are actively looking for a victim:
- April;
- May;
- June;
- August;
- September.


Tick season conventionally begins in April. Insects are activated with the onset of heat. They remain active until severe cold weather, right up to November.
The greatest danger to humans remains in the period from mid-May to mid-June. If in April arthropods just begin their activity, slowly reviving as the air and soil warms up, then from mid-May they constantly hunt. The main purpose of bloodsucking is to obtain blood, which is necessary for the reproduction process. Around mid-June, ticks complete their short life cycle and die after laying eggs.
A small additional peak may occur in August and September. Residents of not only villages and towns, but also cities should be careful during the warm season. The parasite can catch on clothes when visiting a park, forest park, even from grass in its own area.
Most likely to meet him in the forest. The parasite prefers tall thickets of grass from which it is easy to reach the victim, dry foliage and shrubs about 0.5 m high. It most often attacks dogs. Cats are the second most popular, so care should be taken to protect pets. They can not only suffer themselves, but also transfer the tick to the owner.


There are areas where bloodsucking is most active. In Moscow and the Moscow Region, as well as the Kaluga Region, the risk of being attacked by a tick is small. The incidence of encephalitis in these areas is 0 people per 100,000. The minimum, or zero, risk also falls on the entire Volga region up to Astrakhan. In Yakutsk, Magadan, Murmansk and adjacent territories, the risk is also zero.
Ticks are more active in Tver, St. Petersburg, the Urals, and Irkutsk. The incidence of encephalitis is also higher here. Its peak is in Barnaul and Krasnoyarsk (over 40 cases per 100,000).
Ixodid ticks: habitat, seasonality
The most common place where the blood-sucking tick lives is the woodland of the forest-steppe and forest zones. Locations of parasites are low bushes located along narrow paths, where they await prey. Often, the places of their concentration can become moist shaded areas of the forest with dense herbaceous thickets.


The chances of a bite are high in the season, which lasts from mid-April to the second part of July. The greatest activity of these parasitic forms is observed in the morning and evening hours of the day, the least probability of being bitten exists in hot and rainy weather.
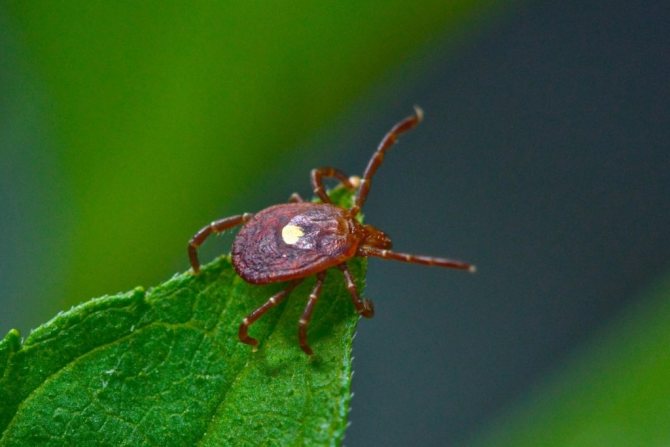
In appearance, the ixodid tick (Latin Ixodidae) resembles a bug with a red-brown color and sizes from 0.2 to 3 mm.Getting on the body, he tries to get to the most convenient places for a bite with a thin skin, including the groin area, lower back, abdomen, inner surfaces of the legs and elbows, areas behind the ears and on the neck.
Despite the fact that the number of individuals carrying the danger of potential infection does not exceed 20% of the total number of organisms, they are capable of carrying up to 60 different types of infections.
If you urgently need help and have no time to read, use the short instructions.
What parts of the body does the tick mainly bite on?
The parasite is selective. He almost never bites the skin where it is too thick or horny. The insect cannot dive too deep into the epidermis, which means it chooses more accessible areas. The exact point depends on where the parasite originally got to. For example, if he climbed onto the victim's chest, he is likely to bite around the neck. On contact with feet, it often bites in the groin.
Other most common points of defeat:
- popliteal fossa (most often);
- buttocks;
- shoulders;
- forearm;
- neck;
- chest;
- stomach.
In children, ticks most often bite on the head, although very few such cases have been reported in adults. Men and boys are more prone to groin bites. Less often, the parasite is interested in places such as elbows, hands, face (in adults), feet and legs. These results were carried out after a massive study in Germany. Doctors were interviewed who recorded cases of bites of more than 10 thousand patients. For this reason, the statistics can be considered quite highly accurate.


This does not mean that the patient can only protect the most vulnerable areas, and leave the rest open. If a person goes to the forest, dense field thickets, travels to an area with a high concentration of ticks, it is necessary to protect the whole body. You will need long pants, high-toed shoes, long sleeves and turtlenecks.
Signs of developing other diseases
Other diseases are no less dangerous, so it is important to know their symptoms:
- Lyme disease: fever, nausea and vomiting, erythema migrans rash.
- Tick-borne relapsing fever: papule of a dark burgundy hue, fever, acute headaches, jaundice is possible.
- Babesiosis: signs of poisoning, anemia.
- Ehrlichiosis: muscle spasm, chills, fever, gastrointestinal disorders, pain in the head.
- Tularemia: enlarged lymph nodes, possible development of necrosis against the background of bacterial lesions.
- Spotted fever: vascular and muscle damage, heart attack, stroke, renal failure.