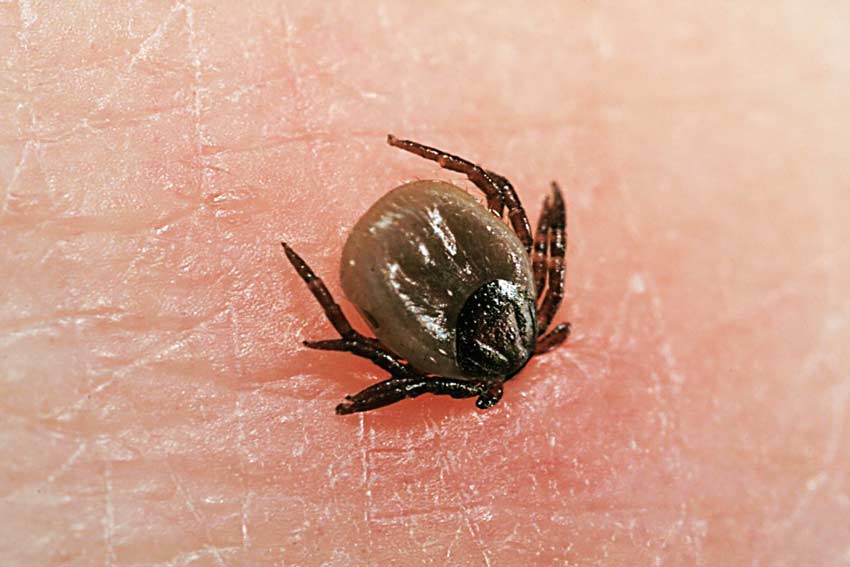
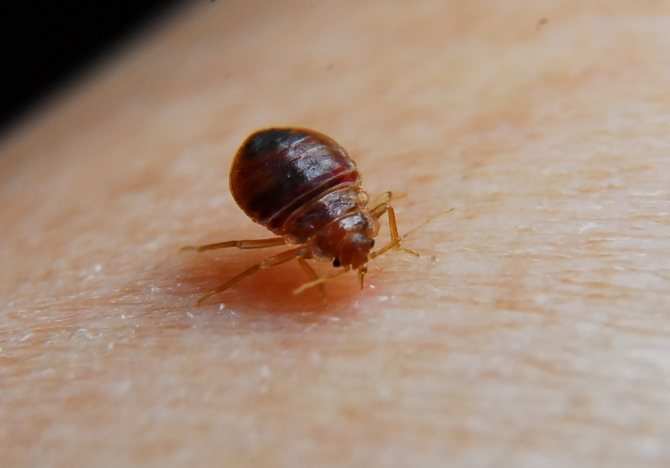
There is no fundamental difference in the choice of means of how to treat a tick bite if it was detected immediately, because in this case the main danger is the insect itself, which lets poisonous saliva into the human body at the site of the bite, allowing it to inflict a wound imperceptibly.
A strong allergic reaction can occur to the released substance, and dangerous diseases develop from pathogens of infectious diseases carried by the tick. You can disinfect the wound surface only after removing the insect.
How to treat a tick bite in humans with a normal reaction
After the extraction of the parasite, there is swelling, redness, inflammation, and slight itching. To improve the condition of the epidermis, to speed up the recovery process, it is necessary to disinfect the wound, then apply a remedy with a soothing, anti-inflammatory effect.
Any antiseptic agent is used for disinfection:
- medical alcohol;
- ammonia;
- iodine;
- hydrogen peroxide;
- alcohol tincture - motherwort, valerian, hawthorn, calendula, etc.
To speed up the restoration of the epidermis, apply an ointment or cream:
- Menovazine;
- Calendula;
- Balm Asterisk;
- Bepanten;
- Boro Plus;
- Rescuer.
If nothing is at hand, folk remedies are used at home or in nature.
- Shaving foam - apply for 5 minutes.
- Toothpaste with menthol - rinse off after 5 minutes.
- Baking soda paste - diluted with water to a gruel state, applied until dry.
- Vinegar solution - 1 glass 1 teaspoon of the product. Lubricate the wound after the bite or apply a compress for 20 minutes.
- A slice of lemon - anoint the tick bite, repeat the procedure twice more a day.
- Vodka - you need to lubricate the wound or apply a compress for 5 minutes.
Tick bite remedies
The condition of the skin is normalized within 3 days, the traces of a tick bite completely disappear in a week.
How to treat a wound after a tick bite for allergies
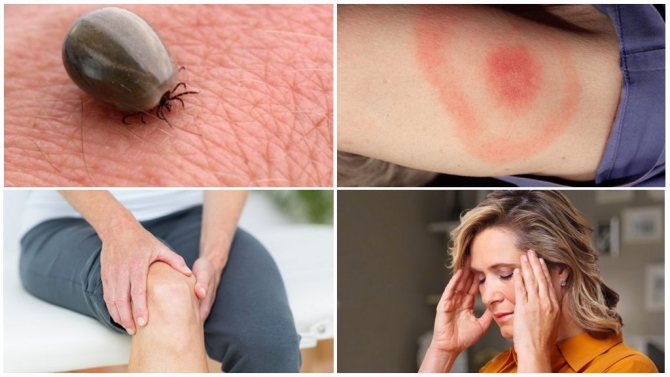
You can determine the presence of an allergic reaction by severe itching, large-scale redness, additional rash, inflammation. If the tick is pulled out, you should immediately disinfect the wound with an antiseptic. After that, smear the affected area with an antihistamine, antiallergic effect.
It is necessary to smear the wound twice a day with a thin layer. Only the inflamed area of the epidermis is treated. Antihistamines have anti-inflammatory, antipruritic, sedative, regenerating effects. Unpleasant symptoms disappear almost immediately, the skin after regular treatment of the wound is restored in 3 days.
- Fenistil-Gel;
- Psilo-Balm;
- Advantan;
- Elokom;
- Betamethasone;
- Hydrocortisone ointment.
The cost of the drug is from 200 rubles. up to 800 rubles You can buy it at pharmacies. Available without a prescription.
If the bite site after tick removal becomes inflamed, itchy, cannot be treated at home, after 3 days you should immediately seek help from specialists. It is required to take antihistamines by mouth. The dosage is selected depending on the age, body weight of the victim.
Popular questions and answers
Such a safety net is pointless and dangerous.Firstly, not every tick is infected, and secondly, not every sick tick will transmit this or that ailment to you, and thirdly, antibiotics are not accidentally issued by prescription, without proper knowledge you will not find the optimal drug and dosage.
Worst of all, procrastination due to antibiotics can lead to serious problems.
What are the consequences after a tick bite?
If a tick was not a carrier of any infection, this does not mean that its bite is harmless.
- If you do not seek medical help in time, you can face various consequences of such a bite. First, suppuration may occur at the site of the tick bite. Secondly, allergies of various kinds, edema (Quincke's edema) are possible. The consequences can be very serious, including paralysis, respiratory arrest, cessation of brain activity and death, - explains therapist Olga Fedorenko.
It is a different matter when a tick transmits a particular virus to a person. There are a lot of diseases that they endure, but let's dwell on the main ones:
Tick-borne encephalitis... It is an infectious viral disease that usually affects the central nervous system.
The incubation (latent) period of encephalitis lasts up to two weeks, but it can stretch for two months. The disease always begins acutely. The first symptoms of encephalitis: chills, headache, a sharp rise in temperature up to 39 degrees, nausea, vomiting, muscle pain.
Possible consequences of this ailment include neurological and psychiatric complications, paralysis and even death.
Borreliosis, or Lyme disease. Another infectious disease that affects the nervous system, heart and joints. The incubation period is usually 1–2 weeks, but can be shorter or longer. The first symptoms of the disease, like encephalitis, resemble the flu: headache, muscle pain, fever. Lyme disease is characterized by stiff neck muscles. Further - worse, sleep and memory disorders, meningitis, paralysis of the facial nerve, arthritis may begin.
If you do not treat borreliosis, you can become disabled, or even die altogether. And if you start to treat on time, then the prognosis is very favorable.
Ehrlichiosis - a bacterial infection that causes kidney and respiratory failure.
Symptoms of infection are noticeable 1-3 weeks after the tick bite. Ehrlichiosis is characterized by headache, fever and chills, abdominal pain. If left untreated, the abdominal organs and nervous system will suffer. In severe cases, death is possible.
Anaplasmosis - blood disease. It develops 3-21 days after the tick bite. The disease is characterized by an acute onset - severe fever, weakness, headache and muscle pain. In addition, blood pressure drops and heart rate drops.
Typhus - a disease that provokes a rash on the skin and affects the lymph nodes.
Tularemia - a bacterial disease that affects the internal organs.


Why is a tick bite dangerous?
By itself, a tick bite in humans does not pose a serious danger, the main risk is infections that the arachnid can reward its victim with. Most of these infections respond well to treatment, but only in the early stages. Therefore, it is so important to diagnose them as soon as possible. It's good if you still have the same tick, because if it is infected, the doctor can take preventive measures. It will be possible to find out if you are infected only two weeks after the bite, only then antibodies to viruses will appear in the blood, namely they serve as a marker of the disease.
- Ticks are examined by PCR for six infectious diseases. If an infection is found in it, emergency prophylaxis is carried out. From encephalitis - the introduction of immunoglobulin, from borreliosis - a course of antibiotics, - explains physician Olga Fedorenko... - You also need to donate blood for tests: for encephalitis and borreliosis - no earlier than 10 days after the bite.
If you seize the disease at an early stage, there is every chance of a safe cure, but if you miss the moment, you can wait for serious complications, the worst of which is death.
Bite infection after tick removal
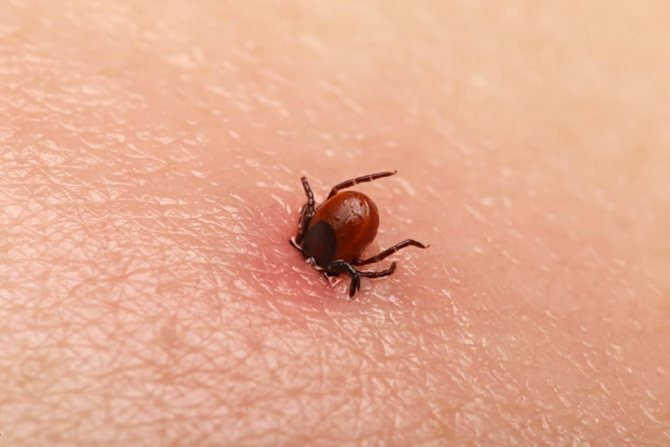
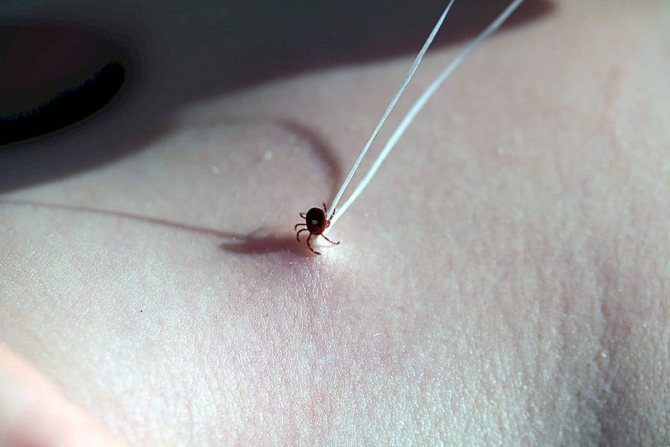
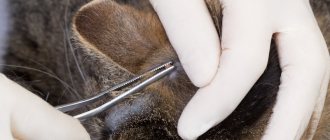
In most cases, the parasites are extracted on their own at home. You can pull out a tick using a thread, tweezers, special devices, and a syringe. Sharp movements are not allowed, since the head comes off, remains under the skin. If the tick is removed incorrectly, a part of its body remains under the skin, which can lead to inflammation and decay of the wound.

Tick removal methods
After removing the tick, the bite site must be disinfected. All tools used must be pre-treated with an antiseptic. If these rules are not followed, an infection enters the wound, swelling, inflammation, itching, mucus, pus appears. Symptoms develop several days after tick removal.
The affected area should be smeared with antibacterial drugs. Local antibiotics are available in the form of an ointment, cream, and lotion. Meta bite treatment begins with flushing the wound with hydrogen peroxide. Remove accumulations of pus, mucus, dirt.
You can treat a tick bite with one of the following medicines:
- Vishnevsky ointment;
- Tetracycline ointment;
- Levomekol;
- Elokom S;
- Salicylic ointment.
You can buy medicines at the pharmacy. Cost from 50 rubles. up to RUB 500 There are contraindications, age restrictions.
If a tick has bitten, an infection has got into the wound, the use of antiallergic agents is not allowed. But the use of combined drugs is allowed, which include a glucocorticosteroid, an antibiotic.
Severe consequences
Ixodid ticks spread dangerous diseases - Lyme disease, tick-borne encephalitis. The incubation period lasts an average of 14 days. With borreliosis, eczema appears at the place where the tick has stuck. Its size reaches 60 cm in diameter. In this case, self-treatment is not allowed, you must immediately seek help from specialists. How to treat the skin, the doctor will tell you. For the treatment of borreliosis, a course of antibiotics is prescribed.
At the sight of a stuck tick on your skin, you want to pull it out right away. But this cannot be done. The tick is not a harmless insect; it can carry serious infections. Incorrect extraction of an insect, errors in wound treatment can cause negative consequences.
There are a number of simple rules on how to treat a tick bite. They should not be neglected.
Treatment of local reactions
Local reactions are expressed in the form of inflammatory and allergic manifestations.
If there are signs of allergy, then the patient is prescribed an antihistamine - initially in the form of a local drug (Fenistil gel, Panthenol). Rescuer ointment will not only relieve the reaction, but will also help wound healing. With a more extensive manifestation of allergies, Suprastin, Tavegil, Diazolin are used orally. In addition, it is recommended to consume as much liquid as possible and stay in bed.
To reduce fever, antipyretic drugs are used: Nurofen, Paracetamol, Ibuprofen.


To prevent infection from a tick bite, take Ergoferon
For the prevention of infectious diseases, in particular borreliosis, a course of an immunomodulatory drug is prescribed. It can be Anaferon, Polyoxidonium, Ergoferon and others.
With high degrees of risk of contracting borreliosis, encephalitis, etc. a course of immunoglobulin is prescribed.
To treat the consequences of tick bites, the drug Prednisolone is used.
With the manifestation of symptoms of encephalitis, Polyglukin, Ribonuclease, Reopolyglucin are used. For the treatment of borreliosis, various antibiotics are used, most often it is Yodantipyrine, as well as various bacteriostatics.
In cases of inflammatory reactions - seals at the site of the bite, lymph nodes, various ointments and creams can be applied. In particular, Menovazin is recommended, which relieves pain and eliminates the inflammatory process.
How to treat a wound correctly
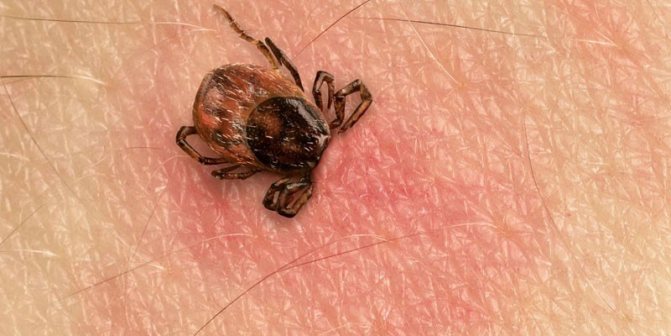
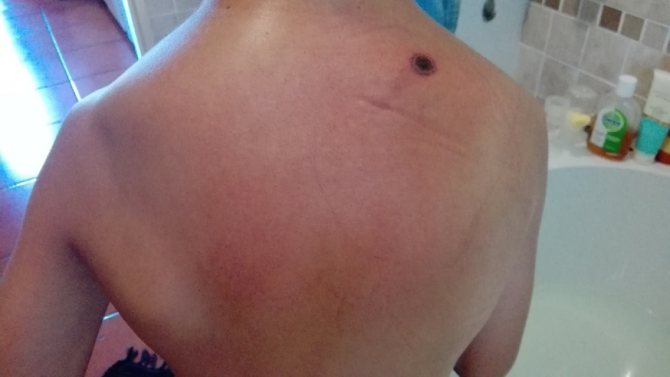
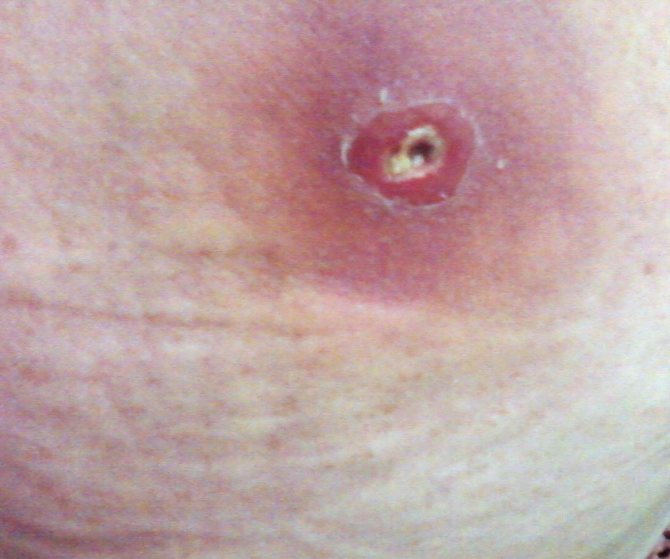
After carefully removing the tick with tweezers, the loops should be carefully examined. The photo shows a tick bite wound, which is a reddish round spot with a hole in the middle. The size, intensity of redness, swelling depend on the individual properties of a person, stronger manifestations are noted in allergy sufferers, people with weak immunity.
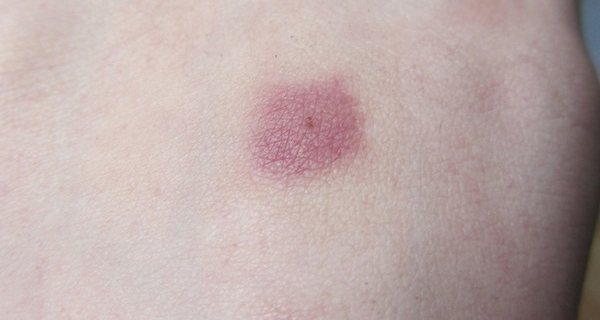

Possible consequences
Taking the wrong action when a tick is found can have serious consequences. It is often advised to lubricate the sucked insect with oil. In this case, the insect will not be able to breathe, but before suffocating, it will vomit the entire contents of the stomach, including possible viruses, microbes, into the wound.
If you crush a tick, removing it from the wound, the likelihood of infection and inflammation also increases significantly. Therefore, you need to remove the tick very carefully. If you are unsure, it is best to see a healthcare professional. After removal, the insect should remain intact, it must be submitted for research in order to find out exactly whether it was infected.


Proper treatment of the wound after a tick bite will ensure rapid tightening, healing of the bite site. If the wound is left untreated, it can become inflamed due to dirt and tick secretions, even if it has not been infected with encephalitis or other serious illness.


Tick bites are common during the warmer months when the number of outdoor trips increases. Everyone knows about the danger that this small insect carries, but not everyone knows how to handle a wound.
First aid
An attack by a blood-sucking parasite is not only unpleasant, but also very dangerous. After all, ticks belong to those parasites that are carriers of dangerous diseases and, when bitten, can transmit an infection to a person. From spring to autumn, bloodsucking can attack humans.
The most frequent visits to medical institutions are associated with suspicions of infection with encephalitis, borreliosis, as well as inflammatory processes that developed after the attack.
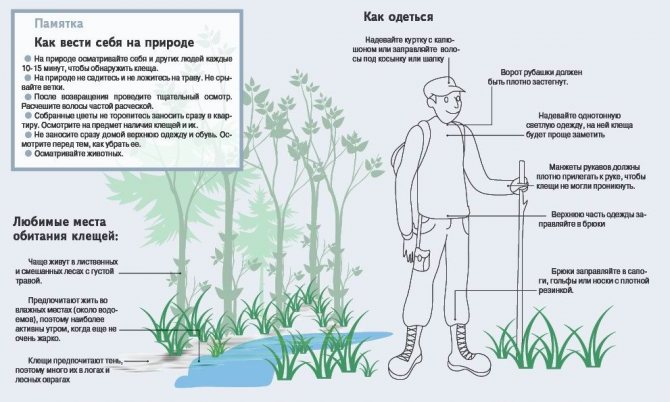
The most dangerous parasites are in regions where the largest number of outbreaks of encephalitis. Not every tick is dangerous, but only one that is infected itself, but the risk of infection is quite high. In many ways, it is human actions that can minimize the risk of infection. In cases where a bite has occurred, the further situation, possible complications and the development of the disease depend on the actions.
It is not always possible to notice the parasite stuck to the body, and this greatly complicates the situation. The fact is that these parasites, when bitten, release an anesthetic enzyme and the person does not feel any discomfort at all. After drinking blood, he falls off the body on his own and it is possible to understand that an attack has occurred only by the appearance of symptoms.
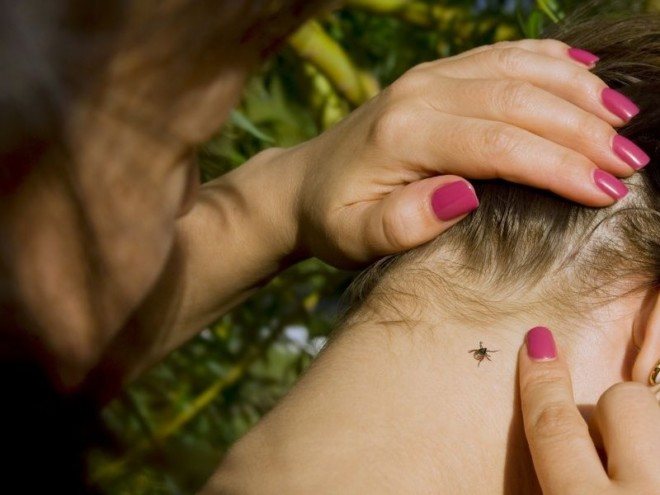


Another danger is that if a person does not know about the attack and after a while he develops symptoms, he does not associate them with the tick, but thinks that it is a cold or flu. Without using the correct treatment, the infection develops in the body, causing severe consequences.
Therefore, it is very important to take a shower and carefully examine the body after every walk in nature, in the park area. The parasite takes a long time to satisfy hunger, which makes it possible to detect it.
If we talk about symptoms, then they include an increase in body temperature, weakness and drowsiness, aching joints appear, a person loses his appetite. If a person has hypersensitivity, dermatitis develops on the skin.There may also be swelling where there is a dot in the center. It is very easy to notice a parasite that is saturated with blood.
How to treat the place of a tick bite
Choosing the right product and treating the tick bite are important activities that should not be neglected. Otherwise, the likelihood of infection increases, which can lead to numerous problems in later life.
Antiseptics
The only way to help after removing the tick is to clean the area around the wound. To do this, you can use the following tools:
- iodine;
- chlorhexidine;
- tincture of calendula;
- hydrogen peroxide;
- brilliant green solution (brilliant green).
Method of using antiseptics:
- Take a clean cotton swab.
- Moisten it with the agent of choice.
- Lubricate the area around the wound.
Note! Before the procedure, you need to wash your hands with soap and water.
It is not recommended to fill the injury site with the indicated means; it is only necessary to treat the surface around the wound. The exception is green stuff, but the bite site is covered with it only after disinfection. It is not recommended to bandage the wound: it must remain free. If the redness increases and the state of health worsens, then you should immediately seek medical help.
It is important! It is not recommended to try to cauterize a wound with an unremoved parasite: when dying, the insect will intensively splash out a large amount of saliva, namely, it contains infectious agents that the tick carries.
Antiseptics for treating the bite site - photo gallery
Products after disinfection: ointments, gels and other forms - table
| Drug name | Impact | Mode of application |
| Polymyxin (powder for solution preparation) | Antibacterial | Apply to the affected area 1-2 times a day |
| Ointment Bacitracin | Broad spectrum antibacterial effect | Apply 2-3 times a day, can be applied under a bandage |
| Zinc ointment | Drying and antiseptic | Apply in a thin layer 2 times a day |
| Vishnevsky ointment | Drying and antiseptic | Apply with a tampon 2 times a day |
| Ointment Yam | Destroys skin parasites and fights fungal infection, which prevents the development of inflammation in the wound | The tool is used 2 times a day in the following way: |
- Rub in with light and smooth movements into the affected area.
- Leave for 10-15 minutes.
- Wash off with water after the procedure
Possible complications
The consequences for the body can be very different. A tick bite causes many diseases. If you do not pay attention to the symptoms that appear in time, negative consequences may occur.
The following consequences are possible:
- Damage to the nervous system. It is expressed in the form of encephalitis, various types of epilepsy, headaches, paresis, paralysis, hyperkinesis, encephalomyelitis.
- Joint lesions. With bites near the joints, complications are possible in the form of arthritis, arthralgia.
- The cardiovascular system. She is most often affected. Manifestations include: sudden surges in pressure, arrhythmia (tachycardia).
- Respiratory system. Against the background of a weakening of the general immunity, the appearance of pneumonia (infectious type), pulmonary hemorrhage is possible.
- From the urinary system - glomerulonephritis, nephritis.
- Digestive system - indigestion, malfunctioning of the liver, pancreas, spleen.
- Endocrine system - inflammatory processes in the lymph nodes located near the bite.
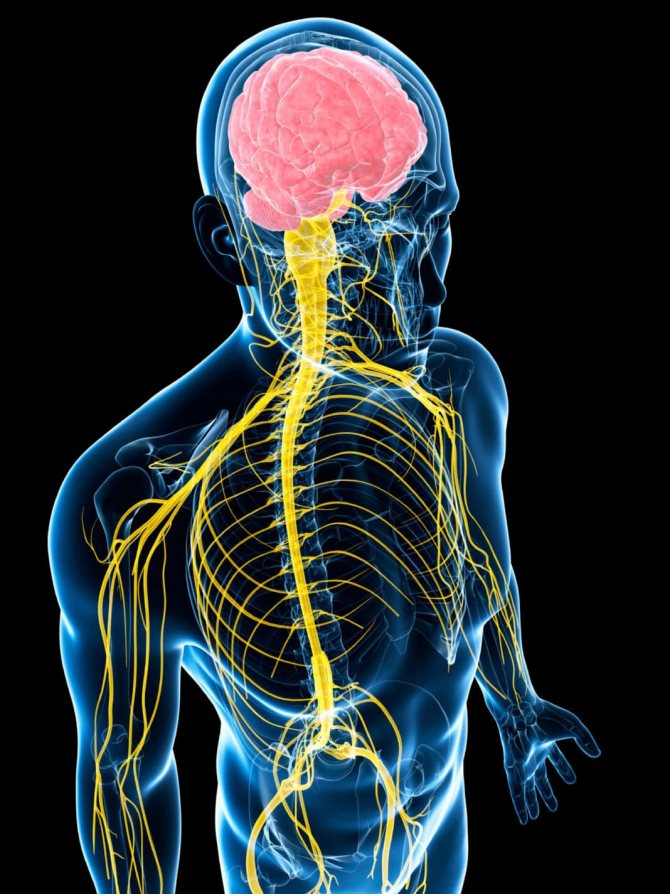

A possible consequence of a tick bite is damage to the nervous system.
In severe cases of these forms of complications, disability, disability (1, 2, 3 groups, depending on the complexity of the disease), as well as epileptic seizures, dementia are possible.
Also, about a quarter of all ticks are carriers of dangerous infectious diseases, which they transmit through a bite.
Borreliosis
Borreliosis, or Lyme disease, is an infectious vector-borne disease that is transmitted through the saliva of a blood-sucking insect. It has many clinical manifestations, according to which 2 main forms are distinguished - erythema (erythema develops on the skin near the bite) and non-erythema (when dermatological manifestations are not observed, but there is a fever, signs of intoxication).
There are also three stages of the disease:
- The first stage is characterized by an acute or subacute onset. The manifestations are quite nonspecific: fever, chills, fever. It is also characterized by stiff neck muscles. Some patients experience nausea, vomiting, sore throat, cough, sore throat.
- The second stage - intoxication occurs with the blood flow. But this stage does not occur in everyone, the period of its onset is 1-3 months after infection. Possible manifestations in the form of meningitis, cranial nerve paresis, photophobia, significant fatigue, chronic fatigue. The defeat also occurs in the cardiovascular system.
- The third stage occurs in 10% of patients with borreliosis. The period of manifestation is from 6 months to 2 years after the expiration of the acute form. The most common and studied is joint damage - chronic Lyme arthritis. As well as skin lesions and neurological syndromes resembling neurosyphilis.