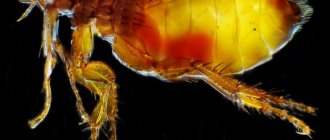
Lice are small parasitic insects that are part of the order of chewing lice, which feed on derivatives of the skin of living beings, in particular, wool, feathers, etc.
Many people believe that hair is what lice eat, but this is not the case. This opinion is due to the fact that head lice is accompanied by increased hair loss, but it is not caused by the fact that lice eat them, the cause is inflammation on the scalp and metabolic disorders.
Lice are parasites, so their lifestyle is directly related to their host. On it they live, feed and reproduce.
Lice are ...
The louse is a parasitic insect that lives on the body of a person or animal. This type of insect is very dangerous, because they not only cause annoying inconvenience to their owner, but can also lead to serious diseases. Lice infestation is called head lice. In order to get rid of the disease, you should find out what kind of life the lice have, how they reproduce and develop, as well as how many lice and their nits live outside the head of a person.
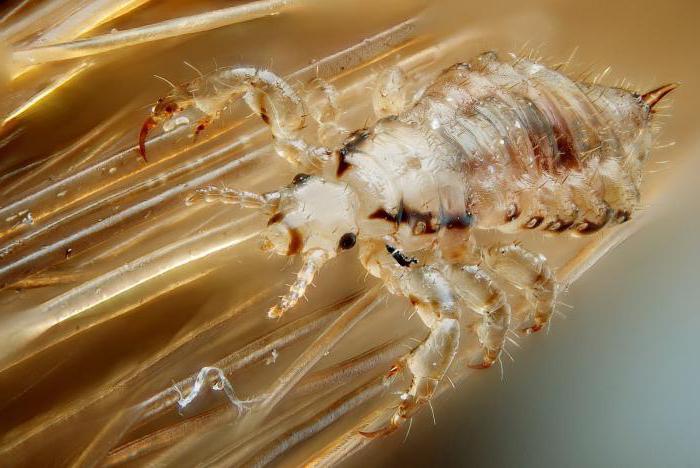

Lice living outside the head
Lice survive only at the expense of their host, on which they parasitize. Can and how long do lice live outside of a person? Each insect species can only live on a specific mammal.
The human head louse will never parasitize on horses. Just like those insects that live on animals will never pass to humans.
Blood-sucking insects often feed on small portions, and females bite more often than males, but how many lice can live without a person?
A head louse deprived of nutrition in the environment can exist without a person for about 2 days, more precisely, about 55 hours - that's the whole period how long lice live without a person.
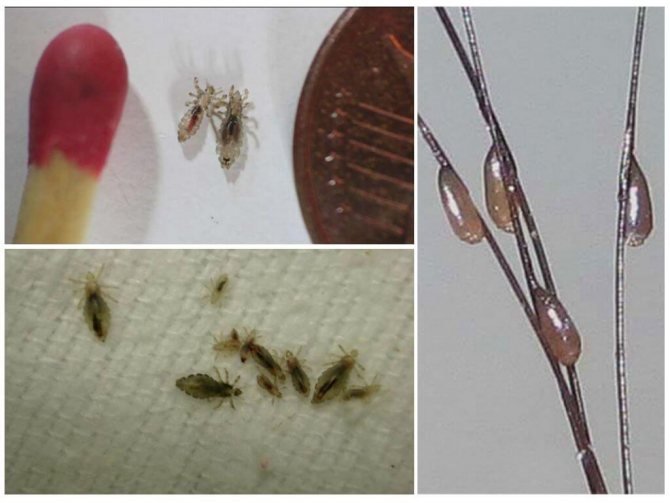


Louse without food
Therefore, head lice live without food outside the human body at a favorable temperature for no more than 55 hours. They are able to stay on pillows, clothing, personal hygiene items, etc. So they wait for the new owner to get blood.
The peculiarity of parasites is that they are not able to jump or fly high. But they can quickly crawl from one place to another in search of food. Insects are able to travel 50 cm in a minute.
When the temperature drops to 10 ° C, adults slow down and hibernate. Their existence on any hard surface lasts a week or a little longer. Lice live without a person in fresh water for up to 4 days in warm weather, but during a cold snap they can wait 15 days.
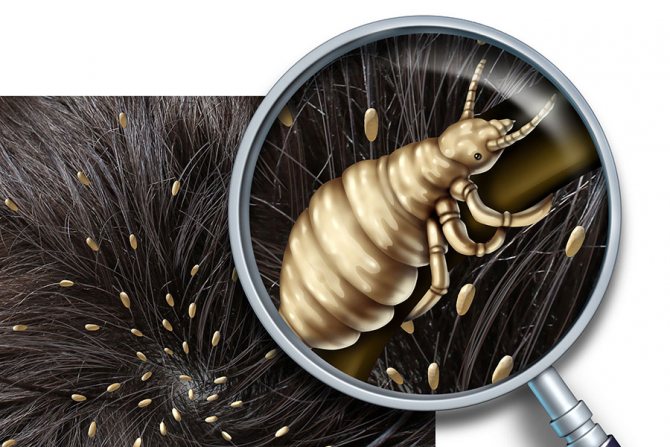


Some people believe that lice live outside the human head on animals. There are several nuances that support and refute this theory:
- The lice present on cats and dogs have a different focus. They feed on the top layer of skin and hair, and reproduce only on wool. Transmission of parasites to humans is impossible. Head lice that live on humans do not breed on the wool of cats and dogs, therefore their habitation on these animals outside the human body is excluded.
- In a laboratory environment, lice live without a person on selected species of monkeys with a similar hair structure. Scientists specially plant insects for them for further study. In some laboratories, parasites are fed with rat blood.
In accordance with the temperature regime and the usual period of development, nits live without a person. They can leave their heads only with lost hair or when combing them out. The duration of their life outside the head in the absence of blood does not change - 5 days in the warm and 12 days in the cold. Destruction of eggs is possible with the use of physical force and under the action of some aggressive substances.
Head lice (lice): causes, symptoms (itching, scratching), stages
What does a louse look like?
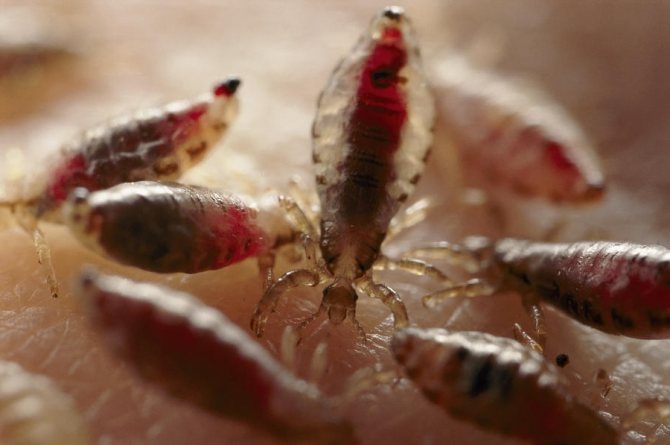
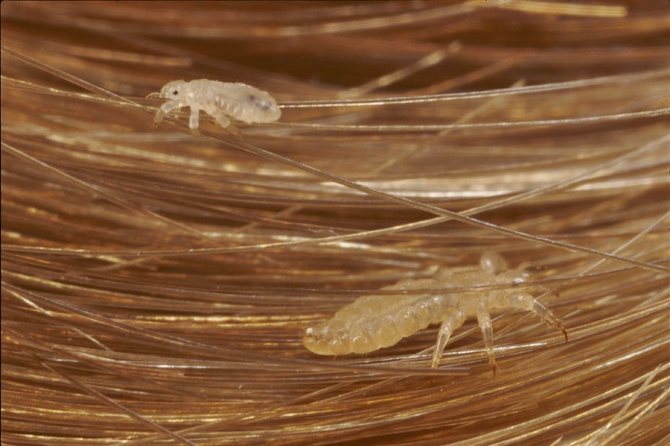
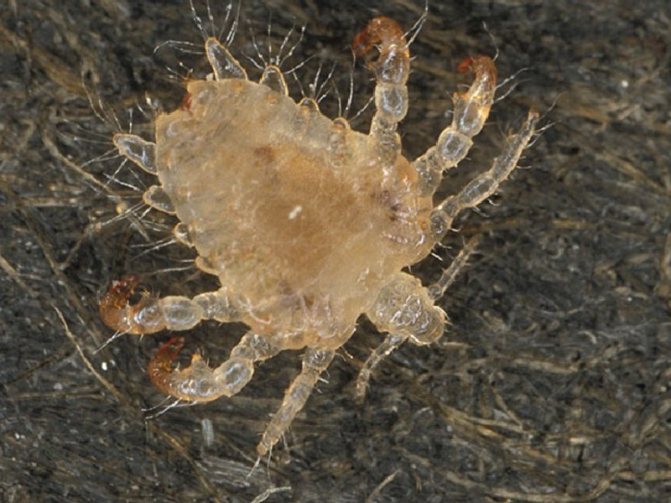
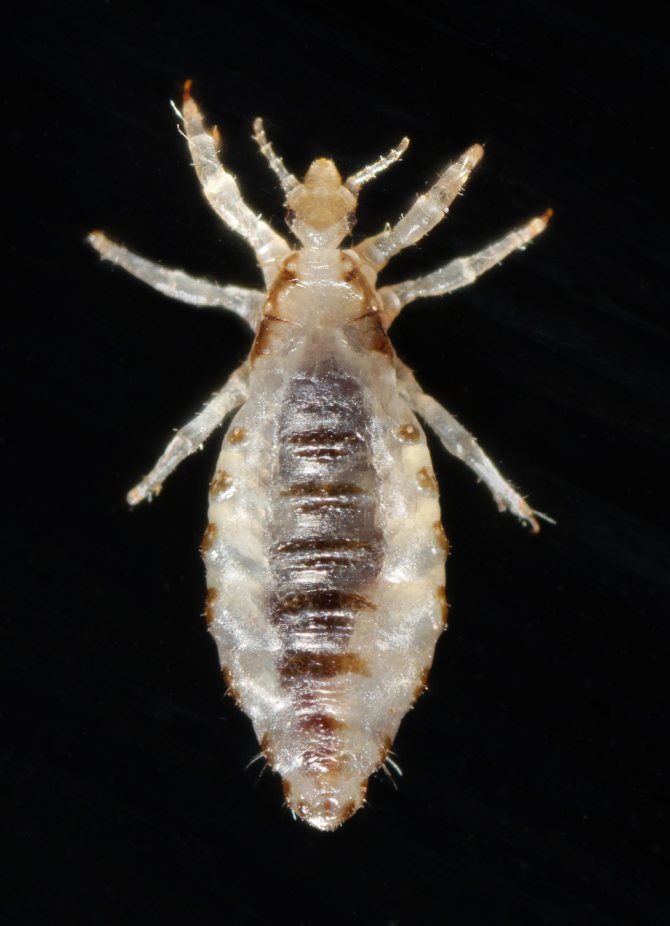
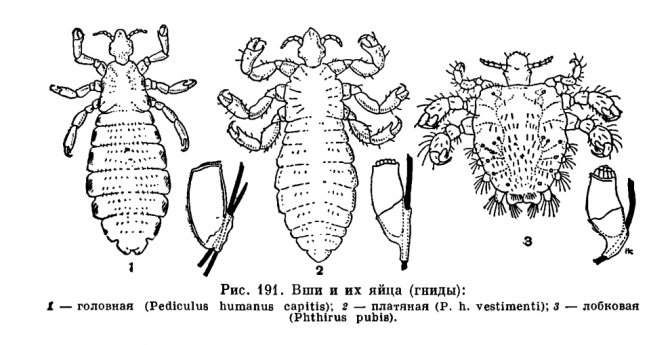
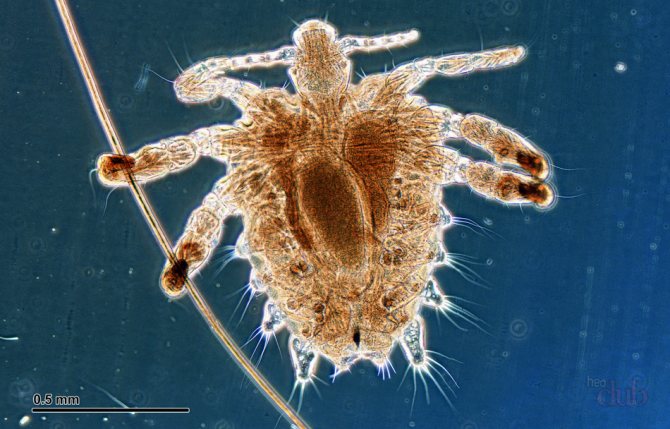
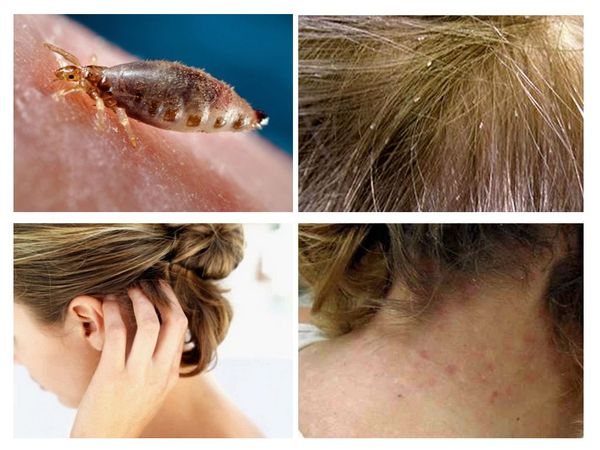
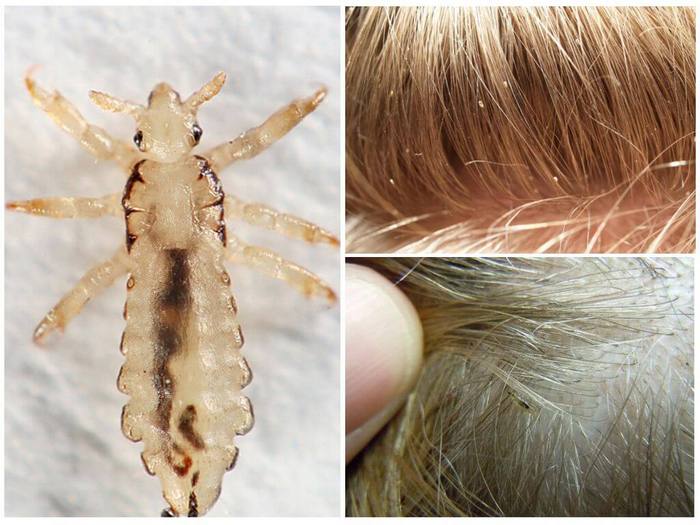
In order to be sure that a person has head lice, you need to know what a louse looks like. This is a small insect, the body length of which is up to 3 mm. The louse, as a rule, is gray or brown in color, has all the body parts necessary for the insect: legs (6 pieces), abdomen, antennae and cephalothorax. Moreover, the parasite has no wings at any stage of development. If you look at a louse without enlargers, then it resembles an ordinary grayish insect. And the insect known as the body louse is white in color. The pubic parasite of a dark color is closer to brown, and the body resembles a crab.
Nits Supplement
Each type of lice nits have their own characteristics:
- Head lice nits are up to 0.8 mm in size, elongated and have a light shade of cover, due to which in the early stages they can be confused with dandruff. As they mature, the eggs darken and grow;
- clothes lice eggs have an oblong shape up to 0.5 mm long. Females lay them in the most inaccessible places of clothing, and therefore it is very difficult to detect egg-laying;
- Pubic lice nits are dark in color and have a pointed shape that resembles a tiny droplet.
Very often people find it difficult to understand what they have found on their hair: nits or dandruff. There are several differences between nits and dandruff:
- It is very easy to remove dandruff from hair: just shake a curl or comb it. When manipulating hair, nits do not leave their place, since they are well glued.
- Nits are oval in shape, their color varies from whitish to brown, the size is the same. Dandruff is always white and may vary in size.
- The eggs are located closer to the skin, where there is more warmth, the places of the greatest accumulations of egg-laying are the back of the head, the area behind the ears. Dandruff can be found anywhere on the head.
- Pediculosis causes unbearable itching, from which skin lesions appear. Itching from dandruff is also present, but less noticeable, so it does not leave visible damage.
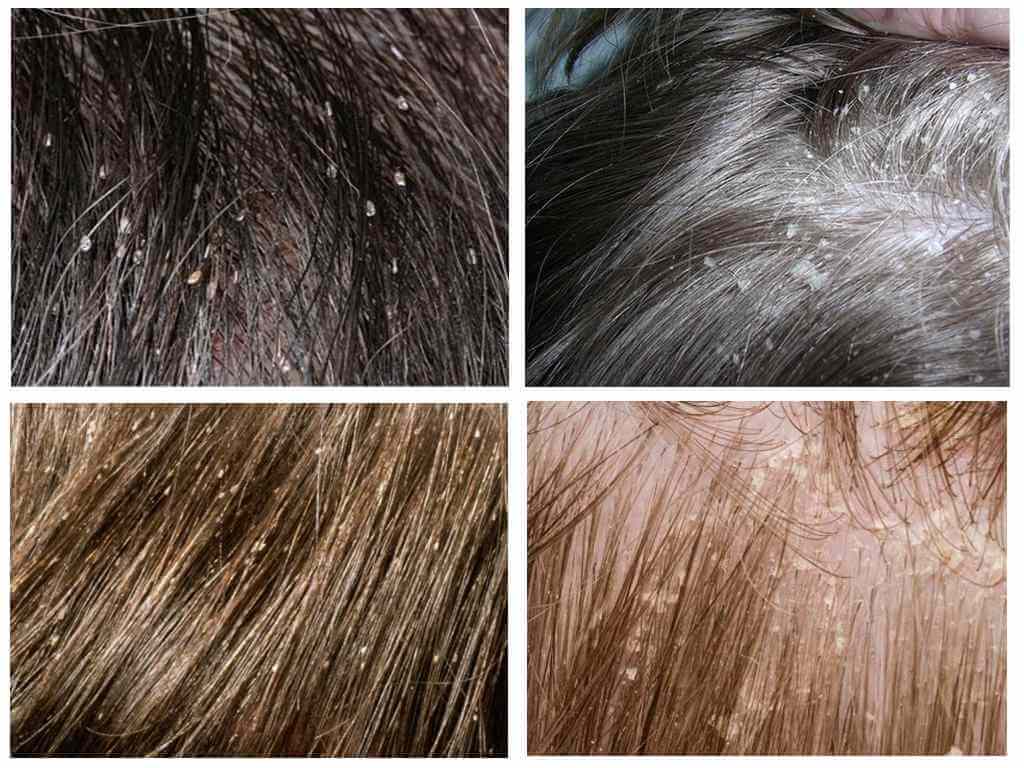

Nits resemble dandruff
Signs of infestation with head lice
To diagnose the disease "head lice", it is necessary to identify a number of symptoms. As a rule, these are:
- Lowered immunity.
- Increased sleepiness.
- Chronic fatigue.
- Depression.
- Frequent headaches and spasmodic pains of internal organs.
Also, the main sign that a person has lice is the detection of bite and scratching sites. The fact is that parasites feed on blood throughout the entire period of development and existence. This raises a logical question: how many lice live without a person outside the head?


Head lice symptoms
It is almost impossible to determine the moment of infection, because clear signs of the presence of lice appear after a few weeks. Common symptoms for all types of human disease are as follows:
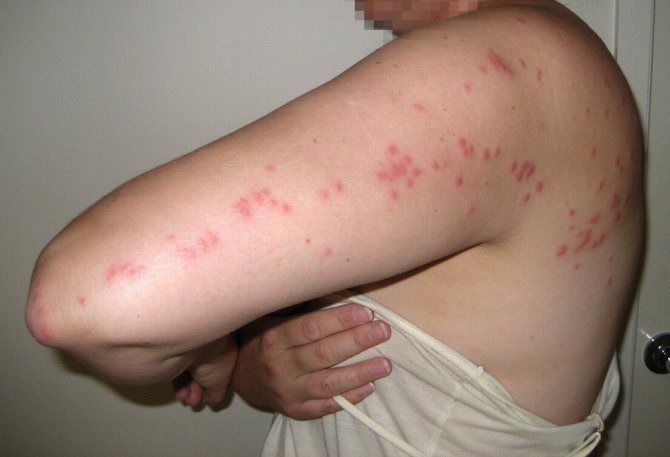
- Itching from insect bites and movement. They move with the help of clawed paws that irritate the skin, and painful bites are accompanied by the release of a protein foreign to humans, which causes an additional allergic reaction.
- The appearance of age spots. Due to the breakdown of hemoglobin in the vinegar sites, the skin turns brown.
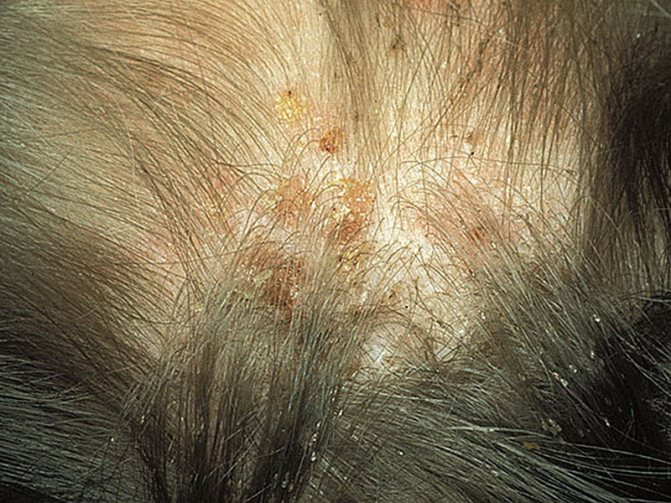

Brownish spots appear on the skin where lice bites - Rash. Insect bites damage the skin, causing pinpoint rashes and swelling.
- The presence of nits. Unlike mobile adults, which cannot always be detected visually, lice eggs are visible with the naked eye.
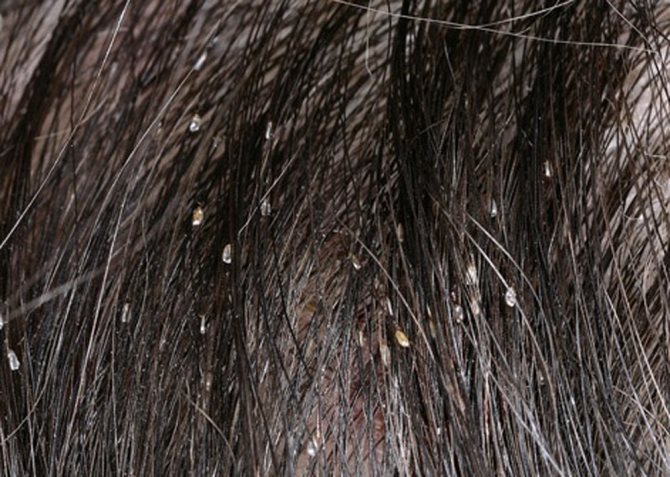


Lice are not always easy to see on hair, but nits are. - The presence of lice. It is easier to identify them when combing with a frequent comb over a light surface - cloth, paper.
- Psychological discomfort. Lice cause disgust and irritation in a person. Constant itching leads to sleep disturbances, which contribute to fatigue and depression.
Features of the symptoms of different types of disease
For successful treatment, it is important to correctly determine the type of parasite. This can be done according to the characteristic features inherent in different types of pediculosis:
- Head. Caused by head lice, the main symptoms are concentrated in the back of the head, temples and behind the ears. In case of infection, the largest number of nits and lice bites is located there.
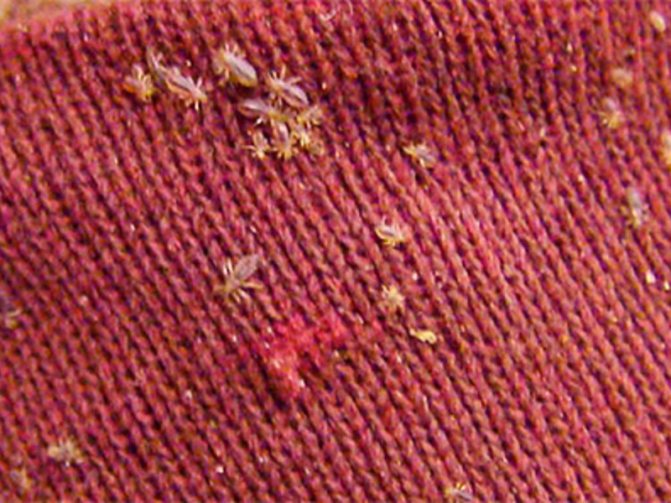
- Wardrobe. Symptoms such as itching and other effects of insect bites are seen in the upper shoulders and back, in the neck and buttocks. Nits are found in the folds and seams of clothing, as well as in places where matter is tightly attached to the human body.
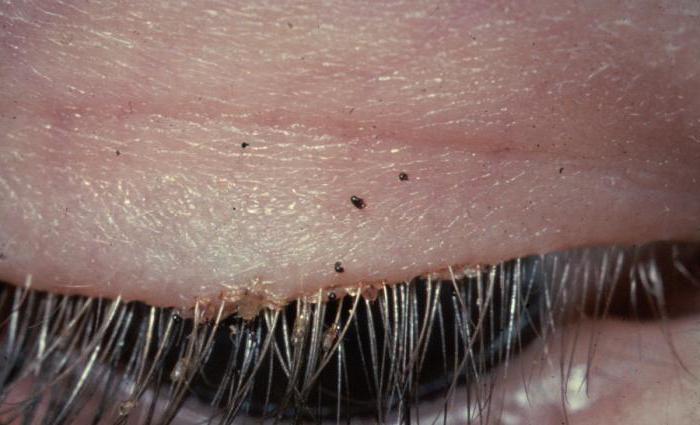
- Pubic. Common symptoms shift to the groin and anus and, in rare cases, extend to the eyelids, eyebrows, and armpits.
Can a louse live without a person and for how long?
Almost every person is at risk of contracting head lice, regardless of their financial or social status, age or gender. Infection can occur in any government office, school, hospital, elevator or vehicle. Once on the human body, the parasite begins its reproduction very quickly. Infection can occur through contact with clothing, bedding, personal hygiene items (combs), or on objects around people. But in the latter case, how long the lice live outside the head depends on the rate of colonization of the parasite per person. Also, personal hygiene does not give 100% protection against lice, one contact with a sick person can lead to the transfer of the disease.
In the first days after contact, it is possible and not to reveal the ailment, provided that the insect does not appear on the eyes. The fact is that a single parasite does not cause any inconvenience to a person. But you should not expect that a louse that has fallen on a person will leave on its own. The insect will not just let go of its new victim. The parasite clings tightly to the hair, while actively multiplying. For a period of thirty days, one female lays up to one hundred and fifty eggs - nits. This raises a logical question: how long does a louse live outside the head? The answer is simple: an insect can live no more than two days without food. But if the ambient temperature drops to 10 degrees Celsius, then the louse is able to survive a period of hunger for up to 10 days.
And the louse is not adapted to life without a person!
The full life cycle of an insect lasts no more than a month. In comfortable conditions, it can live up to 46 days. The head and pubic louse feeds exclusively on blood.
Given the incredible ability of this species to survive, it is logical to wonder how long lice live outside of humans. Left without a food source, they will die on day 3. If the ambient temperature is at 10 ° C, the insect will fall into a state of suspended animation and remain viable for up to 10-12 days.
Lice cannot be washed off or destroyed with water. These parasites are not afraid of liquids and can live in the aquatic environment for up to 2 days. The most common places where you can get lice infestation are natural bodies of water and swimming pools. Water lice live in stagnant water, but you can not be afraid of them - this species is harmless to humans.
The insect will live no more than 3 days without food.In the nits stage, the parasite can remain viable until larval time within 7 days. If, after this period, no food source appears, the insect will die.
Each biological species has “its own” types of parasites. Lice parasitizing on humans are not able to live on animals. In humans, thinner skin and blood vessels are located closer to the surface. The insect does not have a long proboscis for deep penetration and cannot bite through the dense skin of the animal.
The types of blood-sucking inherent only to its species reproduce on animals. Even in cats and dogs, they are different, so interspecies infection is impossible. In the same way, lice are not able to pass from an animal to a person. Therefore, a person cannot get infected from an animal, just like an animal from a person.
The life cycle of an insect is approximately 40 days. It includes stages:
- an egg, or a nit;
- larva passing three molts;
- an adult.
The first two stages take up to 15 days. At the larval stage, the parasite already feeds on blood, but can reproduce only when the third stage is reached. The female lays up to 4 eggs per day, so that the population grows very quickly.
There are three types of lice in humans:
- head louse - lives only on the scalp;
- body louse - it also feeds on human blood, but prefers to live in bedding and accessories, mattresses, towels, clothes - it is in textiles that the most favorable conditions are for hiding and laying eggs;
- pubic louse - lives on the hairy part of the genitals, around the anus, in the armpits.
We suggest that you familiarize yourself with Analysis for ureaplasma in women and men: norms in a smear
The difference between a pubic louse and a head louse is in the structure of the legs. In the head, they are adapted to move along the hairs with a round section, and in the pubic, with a triangular section. Accordingly, pubic lice do not reside on the head, and head lice do not reside on the genitals.
Body lice, despite their lifestyle, must have quick access to the human body. They do not go far from him. They need to eat often - up to 6 times a day, so parasites cannot go far.
Yes, lice can live outside the human body. However, this is a forced state of theirs, and not an ordinary one. Insects can move on any surface and even withstand slight pressure. For example, if they are covered with sand or pebbles on the beach, they will still survive and get to the surface. The louse can easily crawl a distance of up to 50 cm, or even more.
They do not know how to fly, but they crawl fast enough. This explains the high risk of catching lice even without close contact with an infected person and without using his things. It is enough to spend some time at a distance of half a meter from a sick head lice or from his personal belongings for the parasite to reach a new victim.
But being outside the head or genitals of a person is a temporary period. The insect will strive to get to the food source, it should receive food 4 - 5 times a day. Without food, it can live in the most ideal conditions for up to 4 days, but more often 2 days is a critical time outside the human body.
The ideal temperature for lice to live is 30 - 36 degrees, which is why the parasite prefers the human body. These insects also tolerate temperatures above 23 degrees. When the temperature drops below 10 degrees, the parasite will live no more than 24 hours. In case of frost, it will not last even a couple of hours. If the air temperature exceeds 39 degrees, the insect will also die.
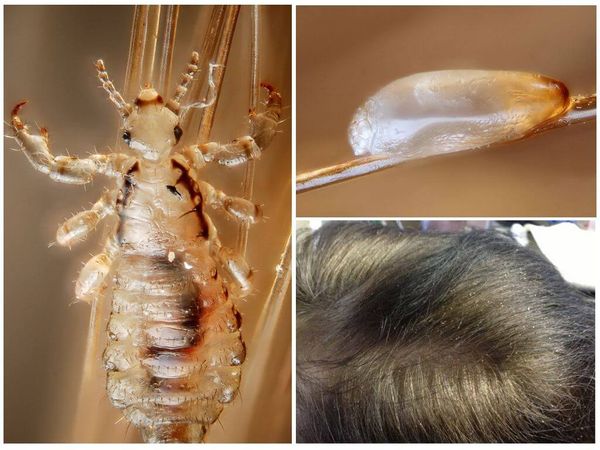
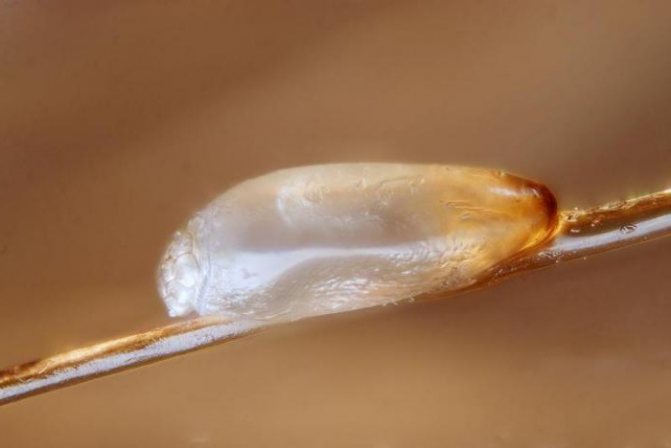
Lice eggs are called nits. During her life, the female lays up to 120 eggs. They are small, round, white in color, attached to the base of the hair with an adhesive. The larva ripens in them within a week. The nits have a fairly strong shell that protects the larva from mechanical and partly from chemical damage.
When unfavorable conditions occur, nits, or rather, the larvae in them, are able to fall into a state of suspended animation. This is a conditional deep sleep with "freezing" of all body functions. The larva stops its development, but remains alive. In a state of suspended animation, some nits spend up to two weeks. If after that they fall into normal conditions, they will continue their development and turn into adults, and then into adult lice.
Lice infestations are not uncommon in swimming pools, spas, saunas and on beaches. Parasites survive even in water, in which they can spend up to two days. Being in the water does not affect their development in any way. After hitting the victim, they retain the ability to feed and reproduce.
The body structure and lifestyle of lice indicate that during their evolution they managed to fully adapt to life on humans. Their paws have been modified so that they can do almost nothing but hook onto their hair. The mouth apparatus of lice is adapted only for sucking blood.

But the adaptability of the lice reproductive organs to the human body is most noticeable: the female lays an egg in an abundant sticky shell, and she does this only by moving along the hair. As a result, the egg remains attached to the hair. After leaving the egg, the larva immediately falls on the scalp and can feed.
Of course, lice do not live on pillows and bedding. If only because here they have nothing to cling to and nowhere to lay nits.
In some cases, head lice can fall on the pillows from the hair of an infected person and stay there for several hours, waiting for the opportunity to crawl onto the person's head again. Body lice can even settle in the folds of blankets and sheets, but these insects do not form permanent populations here.
But lice can be transmitted through towels, combs and hair bands. To prevent infection, you should first of all check the hygiene products and the person with whom you are communicating.
Lice are species-specific insects. This means that different types of lice are parasitic in humans and animals. Therefore, if an animal is infected with head lice, it does not pose any danger to humans. This rule also works in the opposite direction, the sick owner will not be able to transmit the disease to his pets.
Important! If lice are found
The child has
or an adult does not need to treat the cat with special products or
dog
living in the house.
There are several mechanisms for the transmission of lice from a sick person to a healthy one.
- Contact is the most common method of infection. Lice crawl during close contact, during games, hugs, joint photos.
- Household - the transmission of parasites occurs through items of clothing, bedding, a shared towel, and a comb.
- Sexual is a special case of a contact mechanism. It is characteristic only for pubic lice, which pass to the partner during sexual intercourse.
We suggest that you familiarize yourself with thrush in men
Lice can stay in water for about two days at temperatures no lower than 17 degrees above zero. However, the likelihood of infection in a pool or other body of water is extremely small.
At the hairdresser
It is very easy to get new hair and pick up lice. This happens if the employees of beauty salons do not process tools, especially combs, in a special solution after each client.
On the train
Human lice can survive without a host for two to three days. Unfortunately, they can also be contracted on the train. Especially if a person with head lice has traveled to a specific place before.
Through the clothes


Most often, a body louse is transmitted through clothes, which lives in the folds of clothes, and passes to a person only in order to eat. In this regard, doctors do not recommend trying on or wearing other people's wardrobe items.
Through the hat
A hat, like any clothing, can serve as a source of infection. Head lice can be transmitted by wearing a headgear of a person infected with lice.
Through the bed
A pubic louse is not able to live a day without a person, but a clothes louse can live for a week. Lice eggs - nits can stay in the environment for up to two weeks, after which lice hatch from them. Therefore, you cannot sleep in the same bed with a person who has been diagnosed with head lice. All bedding must be washed during and after treatment to prevent re-infection.
Through the pillow
The situation with the pillow is similar to the contamination through bedding. Lice do not live in the pillows themselves. Despite the fact that the parasite dies without a person in two days, it is better to wait this time or just wash before using someone else's pillow.
Full symptoms of the disease can appear only 3 weeks after contact with a sick person. During this period, they manage to multiply and spread over their new host. However, the first bites are possible already 2-3 hours after infection. This is due to the fact that the louse is not able to survive for a long time without food.


The appearance of lice against a background of stress is a myth. Nervous experiences have nothing to do with head lice, especially if there was no contact with an infected person. Under the influence of stressful situations, itching may appear, which is one of the symptoms of head lice. But for this disease, the presence of other manifestations is necessary.
Can nits live separately from humans?
A nit is a lice larva. For its full and correct development, one condition is required - the human body and its warmth. Under other conditions, the larva may die. But under favorable temperature conditions, the nit successfully passes all stages of development, and the louse is born. But if for a short period of time the newly appeared parasite does not have access to food, that is, blood, then the insect will die. This means how long lice live outside the head directly depends on access to human blood.


Symptoms of subcutaneous lice or scabies
Subcutaneous lice in humans appear upon contact with infected objects, the skin of a sick person. The incubation period lasts about 2 weeks. But from the very first days, you can notice the symptoms of subcutaneous lice.
- Scabies begins with skin lesions between the fingers. Intolerable itching appears, which intensifies in the evening, progresses at night. At this time, the scabies mite is especially active.
- Liquid-filled bubbles appear on the affected area. After scratching, wounds remain, moves are visible.
- As the disease progresses, the extent of the damage to the body spreads. The pathological process involves the arms, legs, neck, abdomen, back, genitals, face. Lice do not live under the scalp.
- The body becomes covered with a small rash, large red blisters appear in some places. Manifestations on the buttocks are clearly visible.
- The skin is thickened in the affected areas, there is swelling of the hands.
The lack of measures leads to the addition of a secondary infection, complicating the situation.
Lice life cycle
The reproduction and development of the parasitic louse takes place in a fairly short time. Under suitable conditions, the period for an adult louse to form from an egg lasts an average of 15 days. But in the case of unfavorable conditions, this period can increase to one month.
There are several stages of lice development:
- An adult female lays from two to five eggs at a time, which are fixed with particular strength by the parasite on a hair, at a short distance from the surface of the scalp.This method of attachment is provided by a sticky substance in the outer shell of the egg, which is the nit. When trying to remove from hair, difficulties arise due to strong fixation. The stage in which the nits develop before the lice appear lasts five to eight days.
- A larva is a small louse that emerges from an egg (nit). As a rule, the larva of ordinary insects do not resemble the adult, but this parasite is an exception. The larva is similar to an adult louse, but small in size, with an underdeveloped reproductive system. As soon as the larva takes food for the first time, it begins to molt, and it becomes a nymph. The period of initial development of a nymph lasts up to five days.
- Molting occurs three times, which means that the nymph is in three stages of development. The parasite needs molting in order to throw off the chitinous shell. It cannot grow with the individual, and it is necessary to replace it.
- After all three stages of chitin change, the louse turns into an adult. This stage is called the imago. The female begins to mate immediately and after one day, and in some cases several hours, lays nits. For the entire life period, the louse is able to lay up to one hundred and forty eggs. As a rule, a month and a half is the period how long lice live. Outside the head, they cannot exist for a long time, up to a maximum of two days.
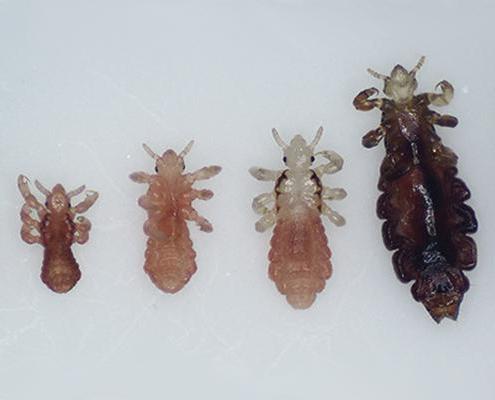


So, we can say that the life span of a louse from the moment the egg is born and until the death of an individual is up to two months, provided that it exists on the human body.
Getting rid of lice is a long and difficult process
Indeed, it used to be a difficult process, especially for girls. After all, everything was used: from cutting beautiful long hair under a hedgehog, to folk remedies.
Now, for the treatment of head lice, it takes only a few minutes, modern drugs take care of the scalp and allow you to keep the hair intact. Especially if you have chosen a quality and proven product.
Currently, one of the best drugs for the treatment of head lice is Couple Plus.
Couple Plus Is a product that contains three effective active ingredients (malathion, permethrin and piperonyl butoxide). They penetrate well through the chitinous cover of both adult lice and nits, which allows you to completely get rid of head lice after the first use of the product. The three active ingredients in the preparation potentiate the action of each other, which makes them effective in the fight against insects that are resistant to other remedies for head lice. In addition, this combination can reduce the application time to just 10 minutes!
Couple Plus is produced in the form of an aerosol, which makes it easier to use for any hair length, and can be used in children from 2.5 years old.
You just need to apply it to dry hair along the entire length, timed for 10 minutes and rinse off with regular shampoo. After that, it remains only to comb out the dead lice and nits well.
If the child's hair is long and thick, there is a chance that some parts of the head and hair will be missing during treatment. Therefore, in such cases, it is advisable to repeat the procedure after 5-7 days.
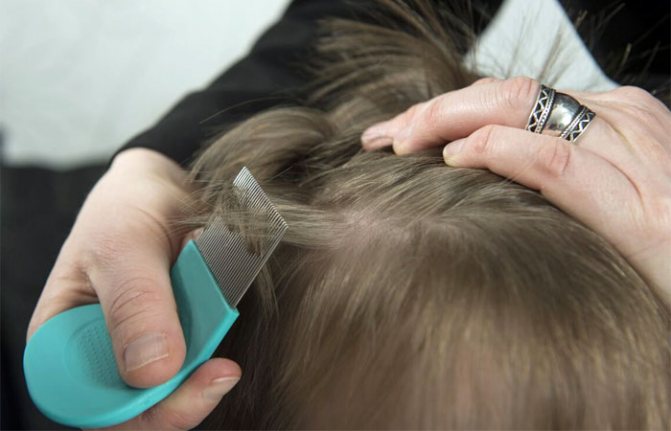


Lice habitat on humans
The louse is a parasite that is not adapted to exist without a person and his blood. Insects that parasitize the human body are unable to exist on other mammalian species. That is, a human louse lives only on a person and cannot survive on another animal. The only type of food for individuals is blood. Lice do not feed on hair, as some misguided people believe. This opinion could arise due to the fact that the louse clings tightly to the hair in order not to fall off the person when he is carrying out hygiene procedures or simply scratching his head.
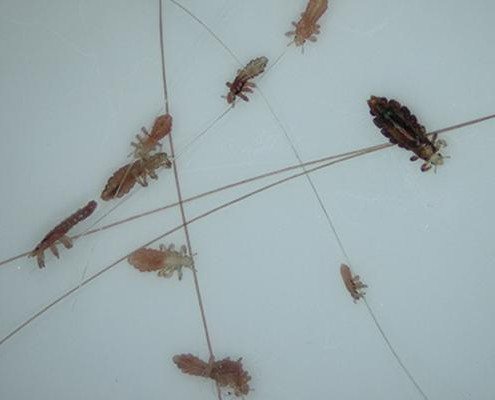


There are three types of human lice in nature:
- head;
- pubic;
- linen.
Head individuals parasitize on the human head, in preference - long hair.Insect transmission is possible from one host to a new host with minimal contact. And how long do lice live outside the head and body of a person without access to food? In the process of moving from one person to another, the maximum life span is up to forty-eight hours. The parasite must be fed or die. The lice feed on for 24 hours, and numerous bites are inflicted by the parasites.
The pubic parasite infects areas with coarse hair. This can be a mustache, eyebrow or eyelash, as well as the axillary region and vegetation on the genitals of a person. The route of transmission of such lice is sexual or contact.

The dressing species of insects lives on a person's clothes, in dirty bedding, especially in its folds and seams. The parasite moves from tissue to person for blood saturation. In the process of evolution, parasites have adapted to the environment so much that it is not so easy to get rid of them by conventional means.
Lice are only found in people from socially disadvantaged strata of society
Indeed, everyone has heard a lot about vagrants and illegal migrants, who almost always have head lice. But the point here is not a person's belonging to any social class. Lice have no preferences and can parasitize on people of any income.
The main factor in the transmission of lice is crowding, which gives insects the ability to freely move from person to person.
At one time, noble ladies in the palaces of Versailles gave lice complete freedom to breed in their enchanting hairstyles. In developed European countries, lice are quite common in kindergartens and schools, because they strictly observe the personal boundaries of children, rarely check them for head lice and consider it incorrect to tell mothers that their child is the source of the disease.
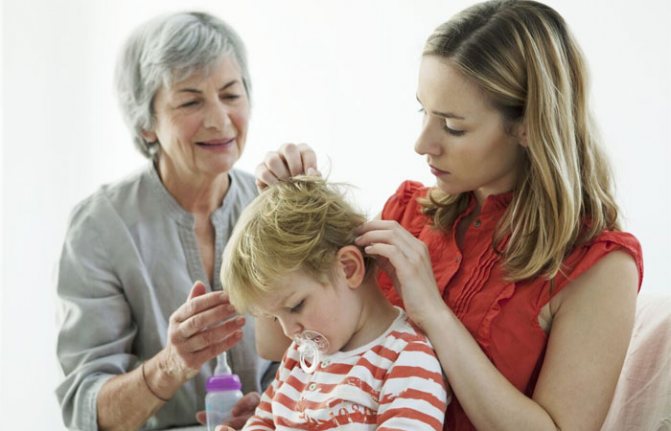


How to deal with lice and nits
There are several ways to combat parasites. These can be specialized drugs or folk methods. However, the most effective are special means - insecticides. Moreover, their use has a number of contraindications. These are pregnancy, childhood, allergies and asthma. In such cases, you can use softer means. Or resort to natural recipes. It should be remembered how long lice live outside a person's head - up to 48 hours.

Natural remedies for parasites include:
- cranberry juice;
- vegetable oil;
- decoction of tansy;
- juice or decoction of cheremitsa and wild rosemary;
- cosmetic hairspray.
When these products are applied to the hair, lice and nits die, after which they are usually combed out with a comb. If the louse was combed out, but it is still alive, then it should be remembered how long the lice live outside the head. It depends on how quickly the insect gets on the person again. Therefore, all combed out individuals should be destroyed immediately.
Why are pediculosis and phthiriasis dangerous?
In addition to unpleasant itching and disgust, diseases have a number of more serious health hazards:
- human lice carry relapsing fever and typhus, Volyn fever;
- the bite causes microscopic hemorrhage and the subsequent breakdown of hemoglobin, in its place a brown pigment spot remains;
- lice saliva contains substances that cause severe itching and an irresistible desire to scratch, and over time, such combs merge and form extensive areas of damage;
- scarring - due to damage caused by parasites, the skin is in a constant process of regeneration, if you do not get rid of the source of harm in time, the affected areas will become thickened and rough;
- severe skin diseases - with strong combs, boils and abscesses form on the damaged skin, which can only be eliminated with the help of antibacterial agents;
- bites and scratching sites are open gates for bacteria and other microorganisms, and in advanced cases, the pathogenic environment can cause infectious processes accompanied by severe inflammation.
How to avoid infestation with head lice
The process of getting rid of lice is quite unpleasant, so you should adhere to some rules to avoid becoming infected with parasites:
- do not use other people's personal hygiene products for the head and jewelry (towels, combs, combs, hairpins);
- observe hygiene;
- systematically check all family members for head lice infections;
- do not wear other people's hats.
By observing these simple precautions, you can save yourself and your loved ones from such an unpleasant ailment as head lice. After all, everyone now knows how long lice live outside the head and body of a person.
Where do parasites live?
Ectoparasites constantly arrive in hunger; for productive life and reproduction, they need to eat 4 times a day. Therefore, it is very difficult or even impossible for them to live outside the human head or body of an animal.
Lice feed exclusively on blood or skin. Their lifespan on the head lasts up to 42 days. Sometimes they move to a beard, eyelashes or eyebrows, but an adult is not comfortable living there, so this is extremely rare.
Parasites are completely dependent on body temperature. Their home is the head of a person or the body of an animal. And if they are deprived of this house, then within 2 days they die.
There are several types of lice in animals:
- Sucking louse - feeds exclusively on blood;
- Biting louse - feeds on skin particles.
Cats can be infested with lice. For many, this reality has become astounding. But it is so. Lice, or they are also called lice, living on animals in wool feed not on his blood, but on the skin. Therefore, one of the symptoms of infection will be bald patches or lack of hair on parts of the body.
Dogs are also susceptible to this disease. Parasites cling to hairs and attach to the skin. They feed on blood, sebaceous glands and skin of the victim. The pet suffers from itching and hair loss.
Head lice can cause more serious illnesses. Such as exhaustion or tapeworm. Therefore, animals need urgent treatment.
Can you get lice from contact with animals? Not! The lifestyle of these parasites is significantly different. They are adapted to a higher body temperature than humans.
Pests have a "narrow specialization". Their body structure is such that they cannot settle on another mammal and are not adapted to live on wool. Everyone is accustomed to believing that the parasite can live only on the human body, but few people think about where the lice live except for the head.
Lice types
The insect is divided into three types, depending on the place of life:
- Cootie. She is attracted by the human smell, she is not able to live on the body. The parasite lives in folds of clothes, bedding.
- Pubic louse. Can live where coarse hair grows - eyelashes, mustache, pubis, armpits.
- Head lice and nits. They live only on the head of a person.
Those who are faced with a disease such as head lice are beginning to wonder how long lice live without food. Each species is different in this regard from each other:
- The head dies after 2 days without human blood. The nit will go through its life cycle completely, but the hatched larva, not finding food, will be able to live only an hour.
- The pubic view won't last more than four hours. The egg will develop until it is time for the nymph to hatch, which will immediately die.
On the comb. The main means of preventing lice is to observe the rules of personal hygiene. You cannot use other people's combs, towels and try on the hats of his friends on the crumbs. Borrowing your own is also not worth it.
In the pillow.If the baby goes to the kindergarten, explain to him that he should sleep only on his own pillow - in another, evil biting insects can await him.
In toys. Tell the little one that it is better not to pick up soft toys of children from the sandbox or kindergarten. A louse, hiding on a charming teddy bear, is able to wait for a new owner for a day without food.