10.12.2016
Despite all the advances in the field of medicine, a huge number of diseases remain in the world. A special group is occupied by diseases of a parasitic nature. One of their varieties is head lice. It is simply necessary to know what lice is and how it occurs. After all, the prevention of the disease and timely response to its first signs are the guarantee of our health.
- What is head lice
- Types of head lice
- Causes of head lice
- Causes of head lice in children
- Causes of head lice in adults
- The first signs of head lice

Features of head lice
Pediculosis - what is it? This is a disease in which parasites start. A person has not only head lice, but also body lice, pubic lice. Often there is head lice. What it is? These are head lice that inhabit and reproduce on the hair. Most of all, they live on the temples, crown and back of the head. There, eggs are laid, which are called nits. Their size is 0.8 mm.


Nits stick to the hair with the help of a secretion produced by the female during laying. An individual develops within 9 days. The female's life lasts about a month, and during this period she lays 140 eggs. She eats small portions of blood up to 12 times a day. The female is sensitive to temperature extremes: when it decreases, the insect develops more slowly. For example, at 20 degrees, the laying of eggs and the existence of larvae cease. It is known that with fever, head lice remain in sick people.
Lice habitat: from head to toe
There are four types of head lice (by the type of lice on the human body):
- Wardrobe
- Head
- Pubic (phthiriasis)
- Mixed, in which two or three types of parasites can live on the carrier at once.
Clothes (body) louse


(Pediculus Humanus Corporis) is a translucent hematophage (a parasite that feeds on blood) up to 5 mm in size (females are one and a half to two times larger than males), which lives and lays eggs (nits) on clothes, temporarily passing to human skin for food.
Outside of humans, body lice remain viable for 2-3 days. The "mouth" of the parasite consists of stabbing needles enclosed in a soft proboscis-tube, the edges of which are tightly pressed against the victim's skin, and the saliva contains an enzyme that prevents blood clotting.
The average lifespan of an individual is 35-45 days, during which the female manages to lay up to 400 eggs!
Body lice affect areas of the skin in contact with the folds of the linen (lower back, shoulders, neck, upper back, abdomen, groin, armpits). Infection occurs through household contact, the use of contaminated clothing and bedding.
Signs of infection: focal rash with scratching on the skin, vascular cyanotic spots at the bite sites, severe itching, the development of pyoderma (purulent skin lesions) and hyperpigmentation.
The hero of Lev Kassil's autobiographical story "Conduit and Schwambrania" said:
“With good cleanliness, there are no lice. Typhus spreads lice. Point, and sha! "
Speech in this awkward quatrain is primarily about body lice, because they are carriers of typhus and relapsing fever and Volyn (trench) fever, which were a real scourge of society a century ago, but even today, alas, are not completely eliminated.
Their pathogens are localized in the gastrointestinal tract of lice, multiply and are excreted in excrement, maintaining their viability and pathogenicity for more than three months! A person becomes infected when these secretions hit the mucous membrane and wounds or when an insect is crushed.
Head louse


(Pedjculus humanus capitis) is a parasite that lives in the scalp, including the eyebrows, mustache, beard. Differs in a grayer color and a shorter body (male 2-3 mm, female 4 mm). The legs of a head louse are only suitable for living on the hair of the head, another species lives on the hairy parts of the body (we will talk about it later).
A female head louse lives for about a month and lays five nits every day, which are fixed at the base of the hair and mature for 7-10 days. When a young individual emerges from the egg, it remains hanging on the hair. A young louse needs 6-10 days to be able to reproduce.
The head louse feels comfortable at 28 degrees of heat (the norm for the scalp). When the temperature drops to 22 degrees and rises to 35, its vital activity slows down. Temperatures from 44 degrees and above are destructive for insects.
A head louse is less dangerous to humans than a body louse, since it is not a carrier of a dangerous sick person (typhus and others). However, itching caused by insect saliva getting into wounds leads to irritation and increases the likelihood of infections passing through damaged skin.
The statistics of infestation with head lice is 200-300 cases per 100 thousand people. Of these, 35% of the infected are young people 15-24 years old, 27% are children under 14 years old and 16% are adults 35-50 years old, the rest are elderly people.
Pubic louse, or ploshchit


(Phthirus pubis) an insect from the suborder of lice, living on humans mainly in the pubic area, on the genitals, around the anus, less often in the armpits, on the chest and in the abdominal area.
The pubic louse never lives on the scalp, which is due to the fact that its limbs are adapted to hold and move only through the hair with a triangular section that grows on the body, in contrast to scalp hair, which has a round section.
The size of the pubic louse reaches 1-3 mm (females are 1.5 times larger). It feeds exclusively on the blood of the host, without food it dies within 24 hours. According to some reports, the increase in the percentage of people removing pubic hair has put the population of this species in a number of countries on the brink of extinction.
You can get infected with any head lice in three ways:
- With close contact with a person suffering from lice.
- When transmitted through personal hygiene items (combs, hairpins, elastic bands, towels, washcloths), underwear, hats, scarves, pillows, mattresses.
- Sexually.
In any case, the source of infection is people (both adults and children), which are parasitized by lice, and regardless of the degree of lice.
The habitat of body lice
Head lice can also appear from body lice. What it is? These are large individuals that live on clothes and bedding. The nits are attached to the villi of the material. Eggs remain on the human body - on the vellus hair. But usually they appear there for feeding.
Females lay up to 300 eggs. They consume blood - up to 2 mg at a time. Body lice are badly affected by high temperatures. They leave the sick with fever, passing on to those around them. When searching for an object, parasites crawl up to 30 mm per minute.
Myths about head lice
Lice are a disease of the poor. Rather, it refers to body lice, which are more common in poor countries. Head lice is often observed under quite favorable socio-economic conditions.
Lice are carriers of hepatitis B and HIV. False, since these viruses are quickly destroyed by the enzyme system of insects.
Lice love a certain blood type... In fact, hematophages do not care about the group, they digest absolutely any human blood.
Lice don't like people with dyed hair... Lice are not interested in hair, they need skin and blood. However, with existing head lice, the process of dyeing hair with ammonia dyes can partially kill parasites.
Lice can be transmitted from animals. Animals also have lice, but of a different species that does not pass to humans.
The louse jumps or flies from one person to another. Although these parasites belong to the subclass of Diptera insects, their anatomy allows them only to crawl slowly (about 23 cm per minute).
Lice only love long hair. To cling to the head or body of a person, you need hair only 3-4 mm long.
Lice penetrate human skin. The statement probably arose from the confusion of lice with mites, in contrast to which they do not penetrate the skin!
Lice can be completely combed out with a dense comb... Mechanical removal of parasites and nits gives an efficiency of no more than 40%, while chemical methods up to 98%.
Lice don't survive without a person... Lice are able to live in the environment without food for a couple of days to a week, and during this time they find a new victim.
Lice only love dirty hair... In fact, it is easier for lice to penetrate clean skin without a thick layer of sebum. h
Alcohol in the blood is the best prevention against parasites. Statistics show that alcoholics and drug addicts suffer from head lice more often due to an asocial lifestyle and neglect of the rules of personal hygiene.
Lice love dandruff and feed on the flakes of the epidermis... The hematophage is a blood-sucking parasite and does not feed on the secretions of the human body.
Head lice can be picked up in water... Despite the fact that lice can live in water (not lower than 17 degrees) for up to two days, it is extremely unlikely to become infected with them in a pool, river or other body of water.
Pubic lice
Compared to body lice, pubic lice are almost immobile. They are always in this state, having immersed the proboscis in the host's skin. Oviposition occurs on hairs growing on the pubis, eyebrows and eyelashes. Pubic louse lays no more than 50 eggs. You can get infected through sexual intercourse, but often it happens with the use of towels, washcloths and bed linen.


Lice as carriers of dangerous diseases
Diseases spread by human lice are caused by rickettsia, a bacteria from a special family, some of which are extremely pathogenic. Among these diseases:
- typhus
- relapsing fever
- quintan
... and some other related infections.
Do lice carry AIDS and hepatitis?
Body lice are similar to head lice but have different habits. While head lice live in your hair and feed on your scalp, body lice usually live in your clothes and bedding. They travel to the skin several times a day to feed on blood.
The seams of your clothes are the most common places for body lice to lay their eggs. You can get lice in your body if you come into close contact with a person who has body lice, or with clothing or bedding that is contaminated with body lice.
All types of typhoid are characterized by the severity of the course, the possibility of death and a weak immune response of the body: even after transferring the same relapsing fever, immunity is established for a short time. Volyn fever is not a fatal disease, but it is also very unpleasant.
People who are at higher risk of head lice tend to live in crowded, unclean conditions. Refugee War Homeless victims of natural disasters. ... Dogs, cats, and other pets do not spread lice.Organ lice diseases usually cause minimal problems. However, infestation of lice cells sometimes leads to complications such as.
When body lice scratch and dig to feed on your blood, they can irritate your skin. Scratching to relieve itching can also irritate your skin. If your skin gets soggy from these irritations, other infections can develop. If you become infected with body lice for a long time, you may experience skin changes such as thickening and discoloration, especially around your waist, groin, or upper thighs. The spread of the disease. Body lice can carry and spread some bacterial diseases such as typhoid, recurrent fever, or fever.
- Secondary infections.
- Skin changes.
To prevent infestation of lice, avoid close physical contact or sharing of bedding or clothing with anyone who has an infestation.
It is interesting
According to the doctors' calculations, during the Russian-Turkish wars, more soldiers died from typhus than in the actual hostilities. The conditions in which the soldiers lived and were were ideally suited for the development of diseases that are transmitted by human head and body lice.
In most cases, it is body lice that carry dangerous infections. The likelihood of contracting typhus from head lice is lower than from body lice, but due to the greater prevalence around the world, head lice cause various diseases in general, not much less often than body lice.
Regular bathing and changing to clean clothes at least once a week can also help prevent and control the spread of lice. As a parent who dutifully combed the nits out of my children's hair, the promise of a comb-free treatment for head lice sounds very appealing.
Why lice are dangerous: a complication of head lice in children
This decision was based on two trials that included a total of 765 adults and children over six months of age. Both were randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trials. This means that people with head lice or their caregivers have been given a 4-ounce coded tube for use. Neither the doctor nor the recipient knew if the vial contained ivermectin or a placebo.
The reasons
Pediculosis can occur in children and adults. The reasons for this phenomenon are varied. The main one is the contact of a sick person with a healthy person. Parasites are transmitted through household items - combs, towels, clothing. Often, infection occurs in transport or in places where a large number of people congregate.


And how does pediculosis appear in children? Often the disease occurs in girls with long hair, because the parasites cling to them better. Many children use only combs and hairpins, but these things are the main carriers of lice. It also happens when trying on someone else's clothes. Lice do not jump, as many believe, they crawl, and they do it very quickly. Children often get sick in camps because the beds are close. Head lice occurs at school, as children are constantly in the same room.
How does the infestation of head lice occur?
In order to prevent the appearance of lice, it is necessary to know the main routes of infection. The transmission of insects from an infected person to a healthy person occurs in 70% of cases with a large crowd of people, for example, in public transport.
It is important to remember that clean hair attracts parasites more than greasy hair, as it can take hold and begin to multiply. Colored and damaged hair is also a kind of protection against head lice. Also, places of increased risk are:
- swimming pools;
- baths;
- Metro;
- hospitals;
- schools (kindergartens).
Emerging local epidemics, poor nutrition, and insufficient hygiene contribute to the spread of lice. The duration of the latent period of the development of the disease is from 30 to 45 days. Later, characteristic symptoms appear.
Diagnostics
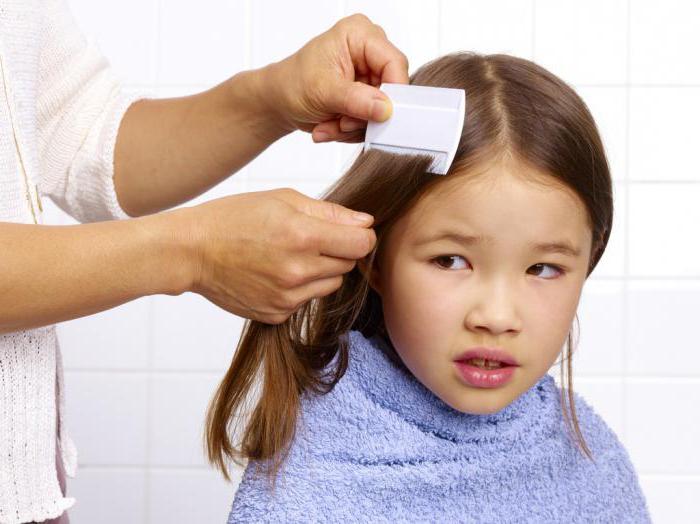
It will be possible to detect the disease only by examining the scalp using a lamp. A magnifying glass and a fine-toothed comb are also required. During crushing, a click appears, which is a sign of these particular parasites. Even if there is one individual, we can talk about head lice.
Often, doctors find inactive infection. This diagnosis will be when there are only nits on the hair that look like dandruff. The difference is that the dandruff can be combed out easily and the eggs are securely attached to the hair shaft. Children's scalp should be examined regularly, especially if they go to school and kindergarten.
If there is a suspicion of a disease, then you can consult a doctor. The specialist will tell you what is best to use for treatment and prevention.
Pediculosis is the main consequence of lice infestation
The most common symptoms of head lice are:
Although relatively rare, children who scratch their heads can get secondary infections. They can range from fairly mild to quite heavy. You certainly don't want to put your child at risk of more discomfort and the need for further treatment.
All lice go through the same stages - the Nitsa or egg stage, the three nymphal stages, and the adult stage. But the three types of lice that are found in humans are different whiskeys that cannot live or lay eggs anywhere other than hair, body lice lay eggs only on clothing or bedding, and pubic lice can only survive on the pubis or Body hair.
- itching on the head, which becomes permanent at some stage
- the appearance of bluish-gray spots on the skin
- persistent scratching of the scalp
- excess keratinization of the scalp and dandruff
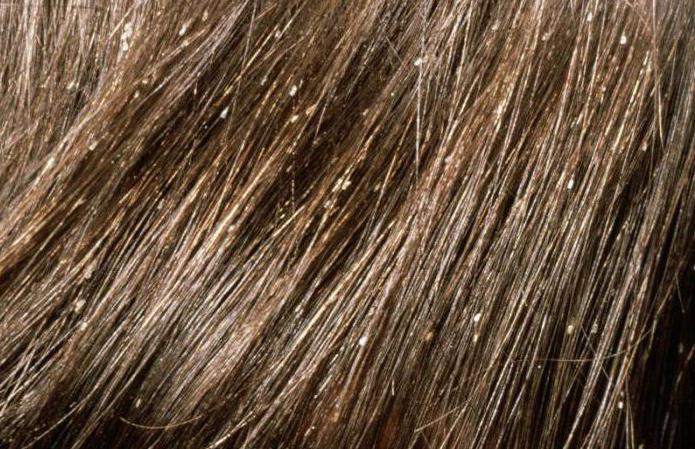
- as well as the presence on the head of the lice themselves and the presence of nits (lice eggs) attached to the hair at different distances from the surface of the head.
Umbilical lice do not carry any diseases, but they can cause severe itching and sometimes allergic reactions. They can also cause secondary infections and can be very uncomfortable and uncomfortable. They are much more common in adults and are transmitted intimate, usually sexual, contact, but can affect anyone who is puberty enough to have some pubic hair. Umbilical lice are considered a type of sexually transmitted disease by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Occasionally, umbilical lice may appear on the legs, armpits, mustaches, beards, eyebrows, or eyelashes. Pubic lice treatments contain chemicals that act as insecticides. The body of a louse is a different animal than head lice or pubic lice. Body lice live on bedding and clothing and lay their eggs there. They come to the skin to feed several times a day. Body lice, unlike head lice, can spread diseases such as typhus, trench fever, and rising fever.
Such symptoms usually appear after a month and a half after the infection itself. During this time, those who fell on time to give the first offspring and significantly increase their number on the head of a person.
Typhus epidemics are no longer common, but outbreaks occur in prisons and in areas affected by war, unrest, chronic poverty or disaster, where people restrict access to showers, baths and laundry. Body lice are transmitted by people living in the immediate vicinity, but access to showers and baths, as well as laundry facilities, is usually all that is required to treat lice.
The body of the lice is tiny insects, about the size of sesame seeds.Body lice live in your clothes and bedding and travel across your skin several times a day to feed on blood. The most common bite sites are around the neck, shoulders, underarms, waist, and groin, where the seams of clothing most often touch the skin.
As a result of scratching the scalp, if untreated, pustular inflammations can develop in those places where an accidental infection enters the bloodstream. Such lesions are already painful and require medical attention to develop a treatment plan.
Pediculosis is not a life-threatening disease. But besides him, lice carry pathogens, which at one time led to huge massive and devastating epidemics.
Lice body is most common in crowded and unhygienic living conditions such as refugee camps and homeless shelters. Body lice bites can spread certain types of disease and can even cause epidemics. Clothes and bedding that have been infested with lice should be washed in hot, soapy water and machine dried in a hot cycle.
Lice bites in the body can cause severe itching, and you may notice small patches of blood and bark on your skin at the site of the bite marks. See your doctor if improved hygiene does not clear up an infection, or if you develop a skin infection from bite scratches.
Signs of infection
How to identify the symptoms of head lice? The main symptom is considered to be severe itching, which appears due to the salivary secretion of lice. Because of this, scratching and bloody crusts appear on the skin. The patient develops irritability, insomnia.
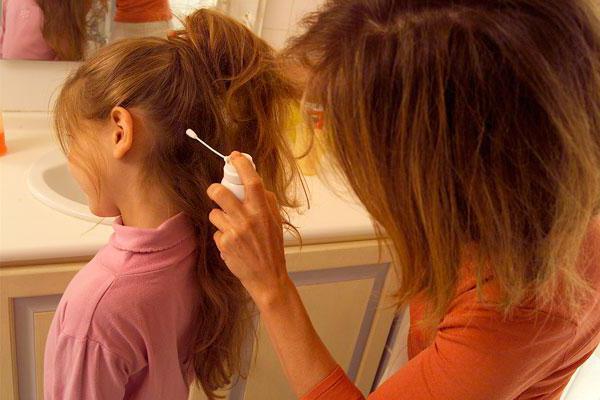
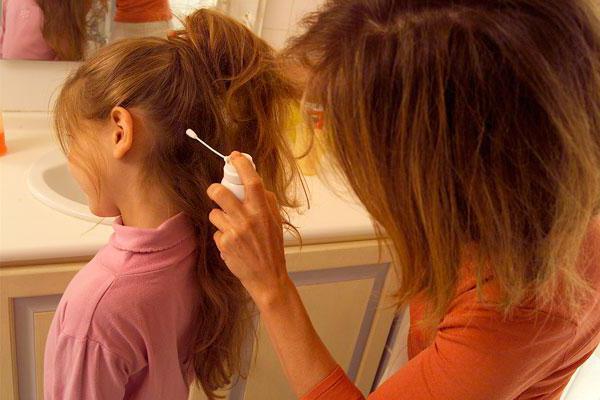
Lice and nits similar to dandruff appear in the hair. Up close, you can see that these are white sacs filled with liquid. Papular urticaria appears on the bite sites - it is full in the form of small nodules. If the disease is not treated, then dermatitis, cutaneous eczematization and pustular inflammation appear. With the spread of pyoderma, enlarged lymph nodes appear.
Mayonnaise and kerosene against lice
In ancient times, table vinegar, herbal decoctions, essential oils (lavender, tea tree and others) and even kerosene were used to combat lice. Ancient folk remedies have not lost their relevance and popularity today.
Here are some folk recipes


- Boil coniferous branches for a couple of hours. Wash your hair with soap and rinse with the resulting broth.
- For three days in a row, water the head with the following solution: 2 tbsp. tablespoons of vinegar (9%) diluted with 1 glass of water.
- Rinsing your hair with pomegranate or cranberry juice of the acids they contain is not tolerated by lice.
- Dilute kerosene with sunflower oil in a ratio of 1:10, spray on hair, wrap it up and leave it overnight. In the morning, wash your hair with baby soap and comb thoroughly.
- Wash your hair with laundry soap, and then apply warmed 5% vinegar on it, hold for a few minutes and rinse with water.
- 2 tbsp. spoonful of mint pour a glass of pomegranate juice and boil for 10 minutes. Rub the resulting solution into the hair and scalp.
- Mix crushed black cumin seeds with apple cider vinegar. Strain, rub into the roots and strands of hair. After the procedure, you need to stand in direct sunlight for about 20 minutes and do not wash off the composition from the head for 5 hours. Such manipulation should be carried out daily for a week.
- Pour boiling water over the stems of burdock or elecampane together with the leaves, leave for half an hour, strain and rinse the hair and their roots with this broth.
- Mayonnaise mask brings benefits. When applied to hair and skin, this product contributes to breaking | respiration of insects, which leads to their death. But then barely blowing, be sure to clean out all the nits from the hair.
- A vodka compress is also effective. You need to spray it with a spray bottle and rub it into the hair roots. Rinse the head covered with polyethylene and wrapped in a towel after half an hour.
- Apply hellebore water generously to wet hair and scalp (you can prepare it yourself or use a ready-made one from the pharmacy), paying special attention to the treatment of the occipital region and behind the ears. Tie the head with a scarf and leave for 20-30 minutes. Then comb out dead lice with a fine comb and wash and dry hair thoroughly. Repeat if necessary after 24 hours. Carry out the procedure with gloves!
- To dye your hair there is an opinion that hydrogen peroxide, which is part of hair dyes, helps to cope with the problem of head lice.
- Lather hair with tar or dusty soap, soak for about half an hour, then rinse thoroughly and rinse with water and apple cider vinegar.
- Both adult lice and nits die under the influence of high temperatures, so a hair straightener (iron) can contribute to the fight against them. You just need to scrupulously iron them every, even the thinnest strand. Then it remains only to comb out the remains of nits well from the hair.
And yet, in terms of effectiveness, folk remedies are significantly inferior to pharmacy ones. So, for example, it is important to know that vinegar does not kill adult lice, but only destroys the substance with which the female sticks nits to her hair.
Not very effective and hellebore water only half of the lice die from it, and all the nits remain viable.
And as for kerosene, despite the fact that although it destroys lice quite effectively, it negatively affects the skin and the hair itself, so its use even in a diluted form with water can be hazardous to health.
Treatment
It is important to consider that pediculosis cannot go away on its own. The reasons, prevention must be known to a person to protect against this ailment. The disease cannot go away on its own, so it must be treated. Because of what head lice appears, it is necessary to take measures to protect a person from a relapse of the disease.
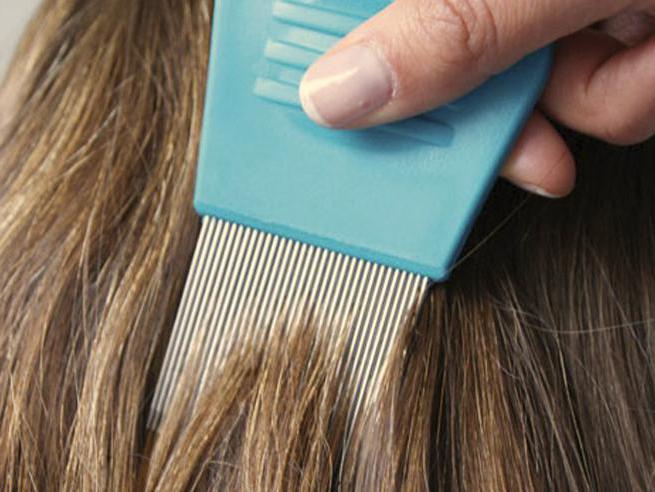


Pediculosis, a photo of which shows the type of disease, is eliminated by chemical means. These are pediculocides that allow you to get rid of parasites forever. These include ointments, shampoos and sprays consisting of antiparasitic substances. They are used depending on the course of the disease. Sometimes multi-stage therapy is required. Mechanical means are also used, in which lice and larvae are eliminated with a comb.
Danger to an adult
Adults are less likely to encounter lice, but this does not mean that head lice disappears completely without a trace. The insect causes severe itching on the head and leads to scratching. The wounds themselves are not dangerous, but through them the infection easily enters the human body.
The insect nit also does not carry any particular danger. She only spoils the hair on her head and tangles it. Sometimes you have to completely cut your hair to get rid of the lice eggs.
Lice infestation prevents a person from leading an active life and communicating with other people. Pediculosis is easily transmitted, so the patient has to become a recluse until he recovers.
On a note!
A louse settles even on a washed head, and you can catch head lice in public transport, a bathhouse, or a swimming pool.
Drugs used
Medicines for the treatment of head lice are reliable, odorless and fast acting. They can be purchased at any pharmacy. If head lice appears, home treatment can be performed with Russian and foreign means. These include Pedikulen R Ultra, Medilis-bio, Paranit Lotion, Para-Plus and Full Marks.
During treatment, you must follow the instructions, as well as take into account age restrictions. If, due to skin diseases or allergies, it is impossible to use chemicals, doctors advise choosing the mechanical elimination of parasites. This procedure involves combing or cutting your hair. You should not use kerosene, as it negatively affects the condition of the curls.Chemicals should not be used for severe scratching and inflammation of the scalp, as well as during pregnancy and lactation.
Head lice symptoms
Lice usually "attack" the area around the back of the head and behind the ears, but can also be found on the eyebrows, eyelashes and beard. A typical symptom head lice is:
- itching, due to an irritant-allergic reaction to enzymes contained in the saliva of the lice;
- scalp inflammation;
- the head continues to itch after shampooing;
- the appearance of a rash (a sign of an allergic reaction to bites);
- desire to scratch (due to itching that does not pass for a long time).
It is important to emphasize that itching takes days or even weeks to appear, which means that if itching occurs, the infection may be at an advanced stage and may have already infected other people.
First symptom head lice, which becomes noticeable on the skin - itchy acute dermatitis, then small ones appear education - bright red papules and vesicles. If you do not take measures to localize the process, do not use means to combat dermatitis, then the symptom will develop into an independent disease - chronic dermatitis, which will be accompanied by suppuration of papules.
The next problem that develops against the background of dermatitis is associated with the formation of secondary infections, often against their background anemia develops.
In the case of head lice formation on the head, a coma of matted hair is a characteristic symptom. They stick together and smell unpleasant, as nits produce a special substance that allows them to stick to the hair. In addition to the head, the place of localization of parasites can be the pubic zone, the body (if body lice appear). You can determine the presence of head lice by the bite sites:
- occipital part;
- whiskey;
- the area behind the ears.
Superficial damage caused by scratching can cause impetigo of the head and inflammation of the lymph glands located behind the ears and in the back of the head (regional lymphadenopathies). Sometimes an infection may not have any special symptoms, making it even more difficult to detect.
Processing rules
An important step is the treatment of head lice with a drug. Only first you need to wash your hair with shampoo, and then dry it. Then, with a cotton swab, you need to apply the product in an amount of 20-50 ml, it all depends on the length of the curls. Then you need to process the scalp. If you buy a spray, the procedure is easier.


The head should be wrapped in foil for 40 minutes, and then rinse the hair with warm water and shampoo. Dermatologists believe that modern remedies do not provide a guarantee of complete elimination of lice. This defeat cannot be cured in 1 procedure. Secondary processing is performed after 7-10 days.
Do lice carry AIDS and hepatitis?
There is a widespread belief that blood-sucking insects can carry viruses that cause AIDS and hepatitis. Accordingly, lice are sometimes suspected of carrying these terrible diseases.
Lice do not tolerate AIDS or hepatitis. Both of these diseases are caused by viruses that infect the cells of the internal systems of human organs. The AIDS virus invades the cells of the immune system, while the hepatitis virus invades the cells of the liver. And these viruses are indeed present in the blood of a sick person.
The contents of the tube were applied to dry hair and scalp, left for 10 minutes, then rinsed with water. No one had to use a comb to remove the nits attached to their hair. The clinician checked the person's head after two days, then again after one and two weeks.
On the second day, 95% of those using the ivermectin lotion were lice free, compared with 31% of those using the placebo lotion. On day 15, the score was ivermectin 74%, placebo 18%.Some people in the study experienced side effects that included eye irritation, burning sensation in the skin, and skin redness. They were somewhat less common among those using ivermectin.
However, these viruses cannot infect lice and use them as intermediate hosts. Getting along with human blood into the digestive tract of insects, virions - virus particles - are quickly broken down by insect enzymes and cease to exist.
While these results look impressive, here are a few things to keep in mind. The trials compared ivermectin to a placebo rather than another head lice treatment known to be an effective treatment for head lice and nits. It makes sense that any treatment with an active ingredient would be better than a lotion without any medication.
Treatment of head lice traditionally requires the use of an over-the-counter product containing permethrin or pyrethrins as the first salvo against head lice. Shampoos and rinses made with these substances generally work well. Most head lice treatments need to be used twice, for seven to ten days, and comb through wet hair with a fine-toothed nits comb. Some lice are resistant to pyrethrins and permethrin. That's when it makes sense to turn to stronger prescription drugs like ivermectin and spinosad.
On a note
To date, no cases of transmission of AIDS and hepatitis viruses by lice are known in medical practice.
All speculation about this route of transmission is considered imaginary hazards and has not been supported by any research.
On a note
Another misconception is the myth that lice can be used to treat hepatitis. This is also nonsense - the louse does not in any way affect the course of this disease, especially since hepatitis can occur for a variety of reasons.
This is not the case for any other treatment for head lice, including ivermectin. She also recommends checking the head of everyone in the family, including adults, and laundering in sheets of hot water, pillowcases, clothing and anything else that might come in contact with the victims' leaders. Lice have 3 stages - egg, nymph and adult.
How do you know you have head lice?
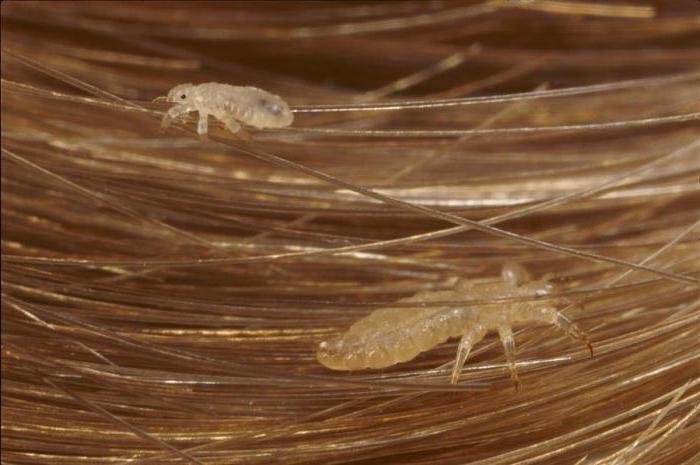
Adult lice can live up to 30 days on a person's head, but they die within 3 days from the head.
- Nite is a whitish-gray, brown or yellow oval, about the size of a grain of sand.
- They stick to the hair near the scalp and can look like dandruff.
- They are similar to adult lice, but smaller.
- Adult lice are about the size of sesame seeds and are difficult to see.
One of the first signs of head lice is an itchy scalp. But it is possible to have head lice without any symptoms.
Using folk remedies
In addition to medications, folk methods can be used at home. They are recognized as effective, as they have been used for many years to treat head lice. One of these is alcohol, from which you need to make a hair mask. The finished product is applied to all curls for 30 minutes. Alcohol allows you to eliminate lice and nits in 1 procedure. But it should be borne in mind that due to alcohol, burns of the head and respiratory tract can occur. Therefore, before performing such treatment, you need to consider whether such a method should be used.
Traditional medicine uses table vinegar, which is considered less hazardous. In water (1 glass), you need to dilute vinegar (2 tablespoons). This means you need to wash your hair. Then the lice and nits are combed out.
The people also use a garlic and onion mask. The vegetable must be grated and then applied to the hair. This remedy will not help completely eliminate lice, it has only a small effect. Therefore, it must be used in combination. Any folk remedy should not be used on its own.It is necessary to consult a doctor who will suggest effective treatments.
Head lice treatment
Products sold for treatment head lice, contain one or more parasiticides and are available in various formulations. Based on the experience of the last few years, it seems that no active ingredient is an ideal choice in terms of effectiveness and lack of toxicity, and in no case can any of them be used as a preventive measure. The most widely used:
- malathion;
- pyrethrins;
- permethrin.
Malathion - This is a phosphoric ester, which is quite effective in the treatment of head lice. Its action causes an irreversible block of acetylcholinesterase, which leads to the accumulation of acetylcholine at the receptor level and, therefore, paralyzes the airways of the lice.
However, the same effects in rare cases can be toxic to humans when ingested in large quantities, causing cholinergic symptoms (nausea, vomiting, increased secretion, bradycardia, bradypnea, coma, cardiovascular arrest). Symptoms appear in 30-60 minutes. In addition, the safety level of malathion in children under the age of six has not yet been determined, and there have been recent cases of treatment resistance.
Pyrethrins (pyrethrum extract) and permethrin (an artificial derivative of pyrethrum) mainly acts by blocking the peripheral nervous system of lice, causing paralysis and death. These substances have low toxicity to humans, if not taken in large doses, in which case they can cause nausea, abdominal pain, contact dermatitis, rhinitis, asthma. However, in the past few years, their effectiveness against head lice has declined dramatically due to the huge increase in resistance in recent generations of lice.
Resistance problem
It is generally accepted that development of resistance is the main reason for the growing spread of head lice since the 90s. Lice infections in schools and communities occur every year and are increasingly difficult to eradicate. Overuse of parasiticides leads to a kind of "tolerance" for lice, making them gradually resistant and therefore able to spread even more.
This situation, in addition to the risk of toxicity to humans, raises the need for alternative strategies that can combine efficacy, lack of resistance and harm to humans. In addition, it is important to implement preventive measures to avoid infections and transmission in schools and communities, not only through accurate periodic examinations of the hair and scalp, but also through the use of products that can be applied locally and on a daily basis. as a preventive measure.
Treatment with folk remedies
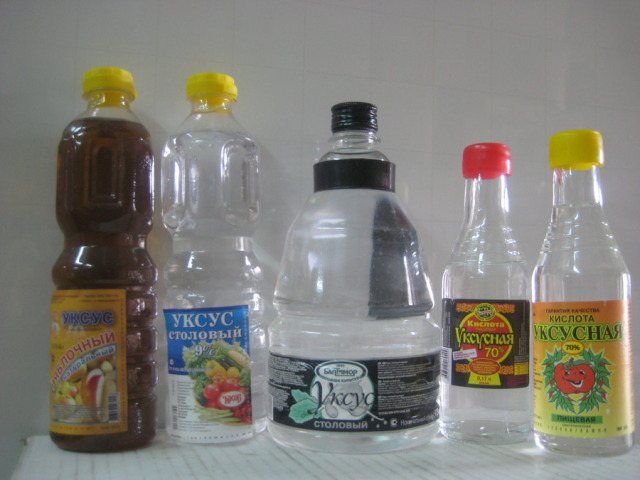


Vinegar - a substance common in folk medicine. In order to get rid of lice, it is recommended to wet the hair with it along the entire length, then wrap your head with a thick cloth or towel. Soak for 2 hours, and then rinse hair thoroughly with warm water and shampoo or soap. You can use not only table vinegar, but also apple cider, wine.
Works no less efficiently turpentine. Before use, the composition must be diluted using vegetable oil in a ratio of 1: 8. After that, you will need to apply the mixture on the head, cover it with a film and stand for 60 minutes. Then rinse the curls thoroughly and comb them.
It is used in the fight against insects and gruel prepared from fresh garlic. It should be rubbed into the scalp 2-3 times a day, and then comb out the nits.
An effective oriental recipe will quickly get rid of lice and not damage the hair structure. To prepare it you will need:
- Apple vinegar;
- Roman coriander.
The ingredients are mixed in equal amounts, and then applied to the head and hair along the entire length. It is recommended to warm up the head a little and soak the composition on the hair for 20 minutes.
Folk remedies for the treatment of head lice have not undergone any clinical studies and they cannot guarantee getting rid of the disease. It is recommended to consult a dermatologist and begin treatment with drugs.
Complications
Pediculosis does not threaten human health, but it causes unpleasant itching and psychological discomfort. Complications are determined by the form of the disease. The appearance of lice that are not removed can cause serious diseases, for example, dermatitis, boils. If the form of the disease is clothing, then there is a risk of contracting typhus. Scratching areas can lead to secondary infection.

Chronic head lice
The disease can take on a chronic form and poison a person's life for a long time. The skin with chronic head lice becomes rough, takes on a brown tint and begins to peel off. Insect bites on the head merge into one spot that extends beyond the hairline.
On a note!
Typhus
The disease is provoked by rickettsia. Carriers can be a louse living on the head and clothes. The bacterium enters the human body through an open wound along with insect feces.
Typhoid fever is manifested by the following symptoms:
- heat;
- damage to the nervous system;
- fever;
- disruption of the heart and blood vessels;
- rash.
In civilized countries, disease outbreaks do not occur. But rickettsia is able to live for a long time in the human body. When living conditions deteriorate, it manifests itself. Prevention of head lice reduces the risk of typhus.
Relapsing fever
The disease is caused by borrelia. The bacterium enters an open wound after being bitten by a blood-sucking insect. A pest living on the head does not tolerate the disease. A person becomes infected due to body lice.
On a note!
There is a vaccine against typhoid that protects the human body for several years. It is recommended for those who are going to go to India or Africa.
The symptoms of relapsing fever are as follows:
- fever;
- headache;
- severe joint pain;
- vomiting and nausea.
Borrelia releases endotoxin, which damages the liver, nervous and circulatory systems. Bacterial antibodies are the cause of microinfarctions.
Quintan
The body louse carries the Volyn fever. The disease does not end with the death of a person, but this does not mean that it is not dangerous.
The symptoms of the disease are as follows:
- fever that subsides and returns;
- chills;
- joint pain;
- Pain in the eyes.
Volyn fever lasts six weeks and then goes away.
Prophylaxis
When treating head lice in the family and in the team, anti-epidemic measures must be taken. For this, the disinfection of hats, clothes, bed linen is carried out. You also need to often clean up the room where the sick are. You should not be in the same room with those who are infected. You need to use only your own things. Only then can one be protected from disease.
Measures for the prevention of head lice involve hygiene: hair care, change of linen, using only your own clothes. Regular check-ups can help reduce the risk of infection. If you pay close attention to your health, then this will avoid the disease.
Disease prevention
Not a single person, especially a child, is immune from head lice. Even casual contact in crowded public transport can lead to infection. Nevertheless, doctors recommend keeping in mind the basic rules of prevention:
- observe personal hygiene;
- wash clothes and clothes at the maximum temperature possible for a thing;
- steam things and iron them;
- have your own comb and hair tools;
- do not wear other people's hats.
You should be especially careful with children, conducting regular self-checks. Children often pick up parasites at school or summer camp. Parents should ensure that camp authorities are taking the necessary steps to identify infected children in a timely manner.