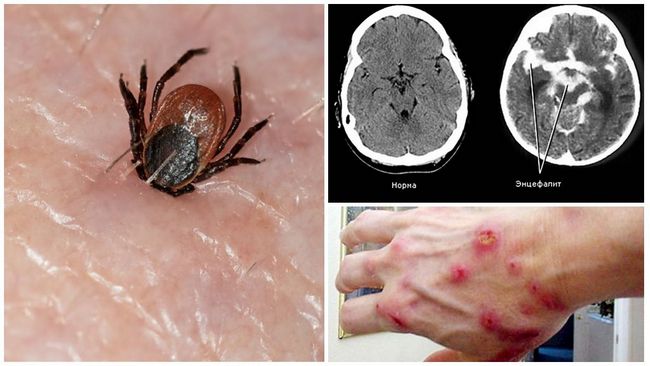
The development of encephalitis is defined as a pathological course in the brain, which is the result of infection, virus activity, or changes in the autoimmune course. Since ticks often act as carriers of this disease, it passes to humans through the bite of the parasite. Therefore, knowledge of the signs will make it possible to promptly start treatment and prevent the consequences of an encephalitis tick bite in humans.

encephalitis tick bite
What is a tick


It is an insect parasite that carries a viral disease called encephalitis (inflammation of the brain). The increase in its activity depends on the seasonality (spring-summer period) and a certain habitat (Russia, Ukraine, Europe). It is visually impossible to distinguish an encephalitis tick from an ordinary one. The virus is often carried by European and taiga ticks.
The insect feeds exclusively on the blood of its "owner" (animal, human). If the male quickly drank blood leaves the body of the donor, then the female continues to suck blood for about two weeks, gradually increasing in size. A short bite is enough for the PNA-containing virus to enter the bloodstream with saliva and cause illness.
How does the bite happen
The parasite lives in tall grass, bushes and waits for its prey. When a person approaches, he attaches himself to his clothes or any part of the body. These insects do not fall from trees and bushes, do not jump or fly, but crawl from foliage to a person. They bite in the soft and warm parts of the human body (neck, armpits, abdomen, groin). The insect bites with an organ called the hypost, which is a proboscis with teeth. The hypostasis is screwed into the human body, fixed with teeth and held there for a long time.
A person absolutely does not feel the penetration of a tick, because when biting into the skin, it releases an anesthetic substance.
The place where it has invaded the skin is the site of the bite. If a tick is found, it must be immediately removed from the human body.
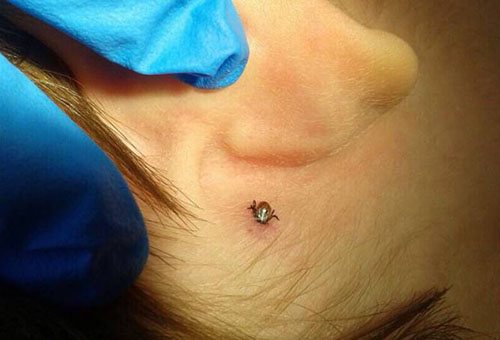

If a tick is found, it must be removed from the body immediately.
Preventive measures and parasite removal
As they say, it is better to prevent the problem than to look for ways to get rid of it later. What should be remembered in this case?
- If you want to walk in the woods or tall grass, you need to wear protective clothing. It is imperative to cover the entire body with it.
- Various special sprays and ointments for parasites can be applied to the skin.
- You should regularly check your clothes and skin for mites.
- Well, if the risk of a bite is increased, you can first be vaccinated.
If a tick is found on the body, it must be pulled out as soon as possible. If this is done during the first days after the bite, the risk of encephalitis decreases significantly. Pulling out the parasite is easy. This can be done with tweezers, thread. But do not pull out the insect, so its head may come off. It is necessary to twist the tick in the opposite direction from the clockwise movement. It is worth remembering that all manipulations must be carried out with gloves so as not to get infected (for example, through microcracks in the skin).
What should I do if bitten by a tick
The main thing is not to panic.If bitten by an encephalitis tick, encephalitis does not necessarily occur. Until the tick has drunk blood and swelled, it is quite difficult to detect it on the body. Visually, the bite site appears as a small black dot, which may not bother you in any way. This place is more pronounced when the arachnid gets drunk on blood and increases in size. If a bitten area is found on the body, it is advisable to immediately contact the nearest clinic (infectious diseases department), the center for epidemiology and prevention (former sanitary and epidemiological stations) or an emergency room, where experienced specialists will carefully remove the tick, treat the wound with an antiseptic.
How to remove a tick yourself
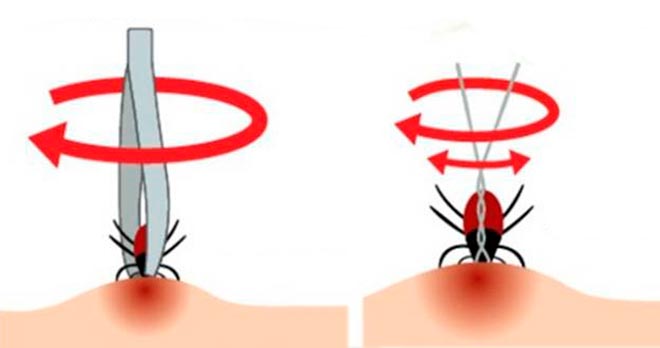

Tick removal methods
You can pull the insect out on your own by grabbing its body with tweezers closer to the head and proboscis, and pull it up, rotating it in either direction. Do not pull in any way. After two or three turns, the whole parasite is removed. There is a thread pulling method. To do this, you need to pull a strong thread closer to the proboscis and tie a knot and twist the thread in one direction. If the insect has got, but the proboscis remains in the skin, it is necessary to remove it with a sterile needle. If the tick is removed on its own, then it must be placed in a container with air access and delivered to the laboratory of the infectious diseases hospital within 12 hours. Treat the bite site with an antiseptic (iodine, brilliant green, alcohol).
Important! The tick cannot be pulled out, but must be carefully twisted entirely. A large amount of the virus can be obtained by improper extraction (especially when a tick is crushed). You can not grease the bite with oil, as the tick will begin to suffocate and even more saliva with the virus. To diagnose an infected insect, it must be brought to the laboratory alive.
The faster the parasite is removed from the skin, the less likely it is to contract the virus.
After removing the insect, it must be examined in a medical institution (laboratory of the infectious diseases department) for the presence of encephalitis virus in it. This service is paid. In the clinic, the patient is injected with an anti-mite specific immunoglobulin or interferon. If it is introduced within 3 days from the moment of bite, then the development of encephalitis and the consequences of an encephalitis tick bite can be prevented. In addition, the patient is prescribed antihistamines (suprastin, citrine) and a course of antibacterial agents (doxocycline and ceftriaxone).
The main therapeutic measures and the admissibility of using folk remedies
At the first manifestations of the disease, urgent hospitalization of the victim in the infectious diseases department is necessary. The patient is shown strict bed rest, dietary meals and intensive therapeutic measures.
Do not hope that you will be able to cope with the disease on your own, using only folk remedies. They are ineffective for encephalitis. The sooner drug treatment is started, the more likely you are to minimize negative effects.
In the first days of the disease, injections of anti-tick globulin or serum of a person who has already had tick-borne encephalitis, as well as specific antiviral drugs, are prescribed. The therapy involves the use of:
- antipyretics (at high body temperature);
- analgesics;
- antibacterial and hormonal drugs (if necessary);
- nootropics that improve brain function.
Detoxification therapy is used by intravenous administration of solutions containing electrolytes. If there are signs of cerebral edema, diuretics are indicated. In addition, doctors prescribe vitamin complexes of group B. An important role during the treatment period belongs to ascorbic acid, which is administered in large doses to stabilize the work of the adrenal glands and liver.
In the therapy of encephalitis, procedures are provided aimed at saturating the body with oxygen - sessions of hyperbaric oxygenation (in a pressure chamber) or the introduction of humidified oxygen through catheters.
Rehabilitation period
Therapy is selected depending on the severity of the disease and consists of massage, physiotherapy exercises.
Sometimes classes are needed to restore vision, speech, hearing. In this case, you will need the help of related specialists: an ophthalmologist, an otorhinolaryngologist, a speech therapist.
In case of depressive conditions, the rehabilitation program is associated with the help of a psychologist.
After stabilization of the condition and discharge from the hospital, the ill person is under the supervision of a neurologist for another 3 years.
Clinical manifestations of an encephalitis tick bite
Marks on the body from a tick bite are easy to notice
The likelihood of infection with tick-borne encephalitis depends on the time the parasite is in the skin and the amount of virus that has entered the bloodstream. It is not possible to determine whether the tick was infected by the skin symptoms of the bite or not. Tick-borne encephalitis virus affects the central and peripheral nervous systems.
Symptoms of an encephalitis tick bite after it is sucked to the skin are manifested:
- Slight itching in the area of the bite.
- Redness (erythema).
If the insect was healthy, then after a few days these symptoms will disappear.
Signs of tick-borne encephalitis occur over a period of a couple of days to 3 weeks (incubation period). Most often, they appear after one to two weeks. At the site of the bite of the skin, the virus begins to multiply actively and quickly enters the blood and lymph. The onset of the disease and the severity depends on the state of the body's immune system, the amount of saliva injected into the skin, and the proximity of the bite to the brain.
Symptoms of viral encephalitis:
- General weakness and weakness.
- Increase in body temperature to 38-40 C. Fever can last up to 10 days.
- Changes at the site of the bite (secondary redness of the skin, the appearance of a blister).
- Chills.
- Disorder of the gastrointestinal tract.
- Rash on the skin.
- Decreased appetite.
Forms of encephalitis
- Feverish form (mild) - manifested by chills, an increase in body temperature to 39-40 C. It occurs when the virus cannot pass through the blood-brain barrier. The disease is relatively easy, and after timely treatment, its symptoms disappear after 10 days.
- Meningeal form - occurs when the virus penetrates through the blood-brain barrier and enters the brain (meningitis is an inflammation of the lining of the brain). The more severe form is manifested by severe head pain, photophobia, neck muscle stiffness (limited movement of the head to the chest). The most common form.
- The meningoencephalic form is characterized by damage to brain cells (encephalitis, an inflammation of the gray matter of the brain, joins meningitis). This is a severe form, which is expressed by mental disorders, seizures, memory loss, hallucinations, mental disorders, paralysis of the upper body, seizures of epilepsy, impaired consciousness.
- The poliomyelitis form is manifested by damage to the cells of the spinal cord of the cervical spine and, as a result, paralysis of the muscles of the limbs. Symptoms: frequent feeling of goosebumps, pain and sensory disturbances in the limbs. This form has a high risk of complications and disability.
- Polyradiculoneurite form. It is characterized by damage to the peripheral nervous system. The patient complains of soreness and lethargy of the extremities, the development of flaccid paralysis of the lower extremities, a violation of their sensitivity, a feeling of goose bumps.
On a note! The disease can be completely asymptomatic. This manifestation of the disease is explained by the production of antibodies to the virus by the body.Only a laboratory blood test can indicate the presence of an infection.
It is dangerous when a person did not notice the bite of the parasite, and took the initial symptoms of the disease for a cold.


Emergency prevention of tick-borne encephalitis
Q: I live in an endemic region for tick-borne encephalitis. Yesterday I was bitten by a tick, noticed it in the evening, immediately removed it and took it to the laboratory for analysis. Today they called from the laboratory, they said that the tick-borne encephalitis virus was found in the tick and that I needed to drink a course of iodantipyrine. What else can be done to prevent tick-borne encephalitis? Very worried.
immunoglobulin
V .: I was bitten by a tick, I threw it out, and now I'm worried - suddenly the tick was encephalitis. When can I donate blood for analysis?Q: I am pregnant (10 weeks). Bitten by a tick - what to do to prevent tick-borne encephalitis?
immunoglobulin
Q: A tick bit a one-year-old child. What can be done to prevent tick-borne encephalitis?Q: I was bitten by a tick, I am vaccinated against tick-borne encephalitis, what can I do to prevent it?
Vaccination
Q: A week ago I was given immunoglobulin for tick-borne encephalitis, and today I was bitten by a tick again. Should I be worried about tick-borne encephalitis?Q: I took iodantipyrine according to the prophylactic (before the tick bite) scheme. I was bitten by a tick, what should I do, how should I take iodantipyrine?Q: The tick was removed, most likely on the 4th day from the moment of suction. The tick has not survived, has not applied to anywhere, I feel good. What can I do to prevent tick-borne encephalitis?
iodantipyrine immunoglobulin
Q: I am going on a long hike, I will not have the opportunity to see a doctor in case of a tick bite. What do i do?
Prevention of tick bites
Q: I was bitten by a tick, I pulled it out. I am very worried, but there is no way to go to a doctor (I am far from civilization), there is no way to buy medicines. How to be?
What is the threat of a tick bite?
The consequences of an encephalitis tick bite are actually the consequences of encephalitis. The consequences of encephalitis depend on a number of factors: the form of the disease, the area and size of the affected brain. Persistent disorders of the nervous system may occur: paralysis, memory impairment, frequent headaches. In severe forms, improper and untimely treatment, there is a likelihood of loss of performance, disability and even death.
The consequences for children are especially dangerous, due to the insufficiently formed immune system and the central nervous system. Children are more likely than adults to have serious consequences and death.
Tick bite precautions

Vaccination is the best way to protect against encephalitis
When going to the forest, in nature, adhere to the rules for the prevention of insect bites:
- Get vaccinated.
- Wear suitable clothing and shoes that cover exposed areas of the body (headgear, socks, high shoes, etc.).
- Conduct immunotherapy with immunoglobulin.
- The use of acaricides (remedies for tick bites) or insectoacaricides (remedies for gadflies, mosquitoes, ticks) on exposed areas of the body and clothing.
- After walking in nature, carefully examine the body at home.
- Knock out the clothes.
Bites of blood-sucking insects are dangerous not only for infection with encephalitis, but also for other diseases, for example, Lyme disease (borreliosis). If you adhere to preventive measures against tick bites in nature, you can prevent the development of these diseases.
Is the person contagious during the incubation period?
It has been proven that encephalitis can be obtained in several ways. This could be:
- an infected tick bite;
- the use of dairy products that were obtained from infected livestock.
It is also reliably known that a person who is a carrier of encephalitis is not dangerous to the people around him. This infectious disease is not transmitted by airborne droplets or by contact. Pets also cannot spread the infection.