Ticks are harmful blood-sucking parasites that are dangerous to humans and four-legged pets. If the cat loves to walk outside, the chances of picking up a tick are quite high. Animals that do not leave the apartment are also at risk - the parasite can enter the house by catching on the owner's outer clothing or shoes. Subcutaneous and ear ectoparasites are no less dangerous.
If a cat is bitten by an encephalitis ectoparasitis - why is it scary and what are the consequences? To avoid complications, you must act immediately. What harm can a cat bite from an arthropod bloodsucker? How to help an animal suffering from subcutaneous or ear mites?
Who is a tick, how can its bite be dangerous for a cat?
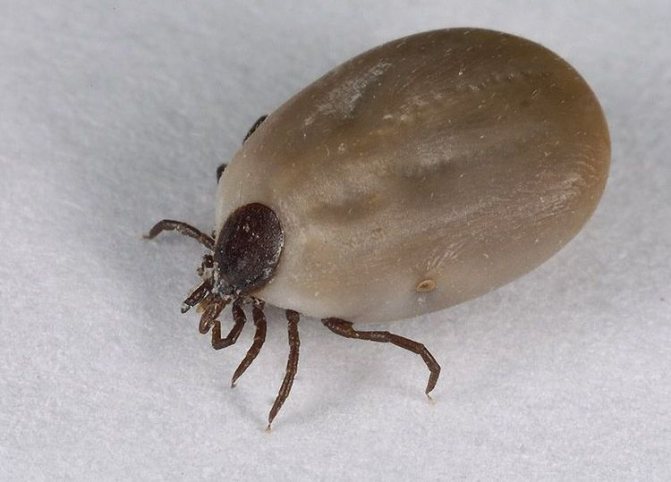
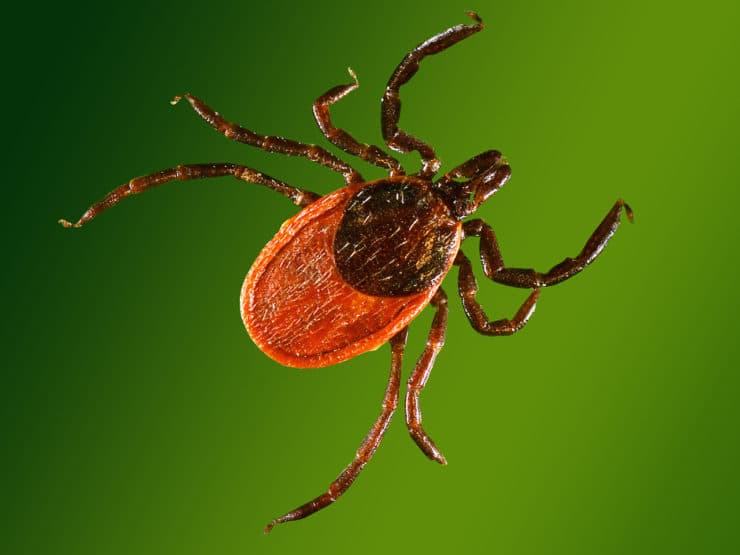
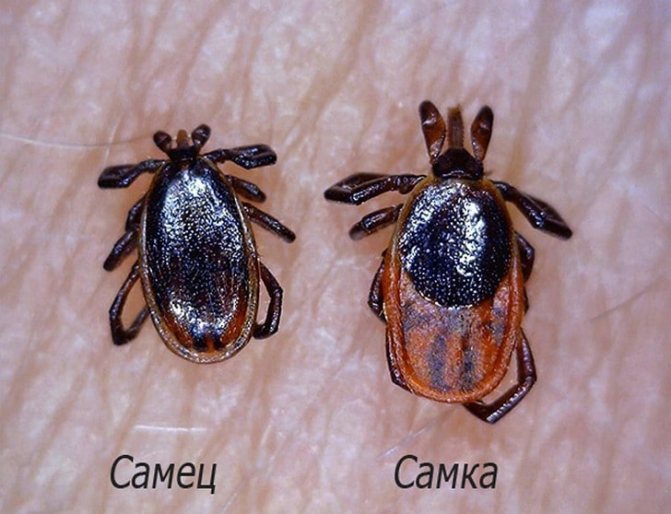
The parasite belongs to the class of arachnids, the oval body is protected by a chitinous shell, a small head and four pairs of legs are attached to it. When saturated, the tick increases in size by 2.5 times. The volume of a hungry insect depends on gender: in the male - 2.5 mm, in the female - 3.5 mm.

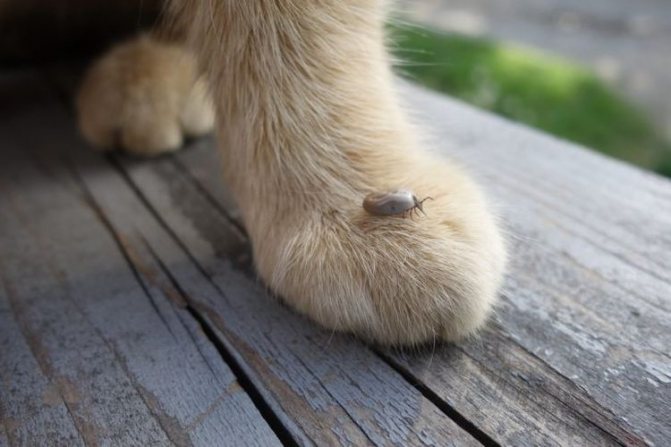
A tick bite is accompanied by the release of saliva with an analgesic effect - with its help, it firmly adheres to the animal. On a cat, the parasite is from several days to a month. The color of the insect depends on the degree of satiety:
- hungry - brown, black, dark brown;
- well-fed - pinkish, grayish, red, brownish.
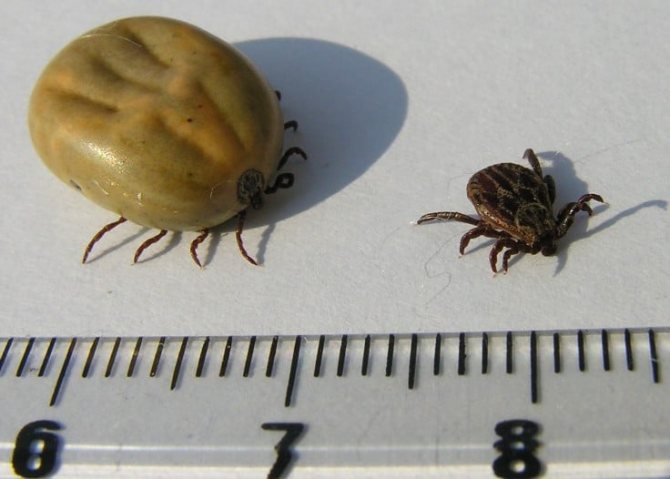


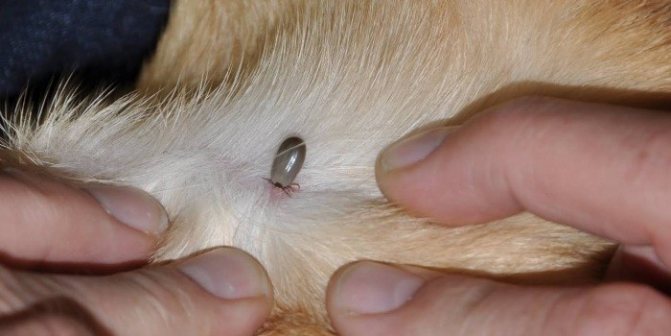
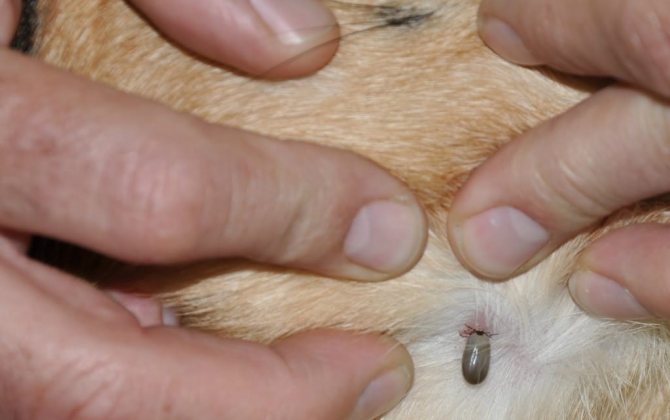
Hungry and well-fed tick
A full female tick lays eggs and dies. The male continues to parasitize on the cat or disappears to digest blood.
The danger of a tick is the transfer of infectious diseases to animals and humans. Pathogenic microflora multiplies in the body of the parasite, accumulates in its salivary glands. When bitten, some of them fall into an open wound, the rest are passed on to new generations of insects when laying eggs.

Description of the parasite and its variety
Ticks (Acari - lat.) Belong to small arthropods of the subclass of arachnids. Their main diet: decaying organic matter, vegetable juices and small brethren. Habitat: grass, leaves of shrubs and trees, buds, skin of animals and birds, where they find food in the form of blood, lymph and epithelial particles.
Interesting!
Not all pet owners know that cats have ticks not only those that can cling to wool in the forest or outdoors, but also subcutaneous ticks that live in the upper layers of the epidermis or in the ear canal. Therefore, it is necessary to talk about all the diversity of the species, of which there are more than 1000 in the world.
The most common types of ticks in cats and cats are:
- ixodid or forest, which can be carriers of infectious diseases that are dangerous to both humans and animals;
- subcutaneous or scabies, causing various diseases of the epidermis;
- ear, settling in the ear canal of a cat or cat.
Tick bite symptoms
Signs of a parasite attack appear after 2-3 weeks. After removing it, the owner must monitor the condition of the pet. The symptoms of tick infestation are manifested by:
- an increase in body temperature;
- loss of appetite, refusal of food, a sharp decrease in body weight;
- indifference, apathy, lethargy;
- vomiting, diarrhea, dehydration;
- cough with shortness of breath - signs of unstable heart function;
- anemia - pallor of the mucous membranes;
- pinkish tinge of urine, yellowing of the skin.


The bite of the parasite causes allergies in animals prone to the disease. It manifests itself as irritation, suppuration and abscess.
First aid


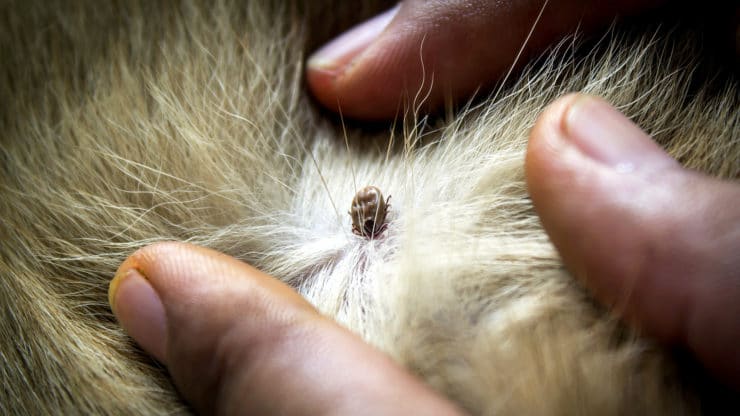
Most often, the tick bites where the thinnest skin is on the animal's body. Usually a bloodsucker can be found in the armpits, on the chest, around the neck, on the abdomen.
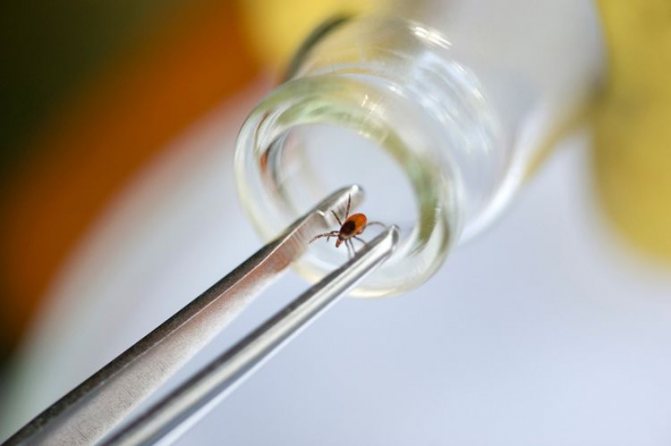
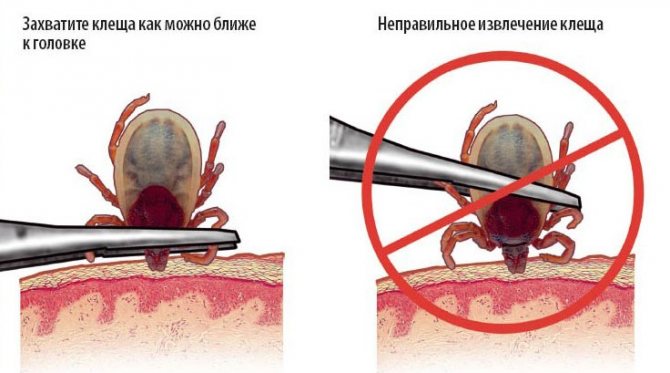
If your cat has been bitten by a bloodsucker that has not yet fallen off, you need to remove it yourself. To do this, fix your pet and gently, hourly hand, twist the parasite, taking it by the abdomen. Try not to tear off the head. After the tick is removed, place it in a matchbox to be taken for examination. Some diseases that are carried by the bloodsucker have a very long latency period. The sooner you can start treatment, the faster your pet will recover.
Lubricate the bite site with an antiseptic and carefully observe the cat's behavior.
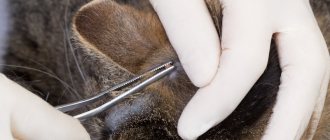
First aid for finding a tick or bite mark on a cat's body
Before removing the insect, put on gloves, prepare an antiseptic solution and a removal device. Regardless of the method chosen, it is important to be careful: excessive pressure on the tick will cause saliva to be released into the wound and increase the risk of infection of the cat.
Accidental division of the parasite into fragments will leave its head under the skin - a foreign body will provoke an inflammatory process. If this happens, you need to do periodic treatment of the affected area with hydrogen peroxide - the body will reject it itself.
Removal is carried out with tweezers or a special device, with gentle movements. After extraction, the bite point is lubricated with an antiseptic solution. If you wish, you can test the tick for infection at the local veterinary clinic or sanitary epidemiological station.
After the procedure, the cat needs constant monitoring - symptoms of an infectious lesion may appear within 3 weeks. Self-medication will not give the expected result and will lead to complications of the developing ailment. The cat must be shown to the veterinarian, it is important to undergo a diagnostic examination and a course of treatment.
Subcutaneous bloodsuckers
The habitat of subcutaneous (demodex) or scabies mites in cats is the upper layers of the skin and hair follicles, zones of weak pubescence: head, paws, places around the eyes. Cat mites can live on an animal for many years, feeding on dead cells of the epidermis without harming the pet.
The manifestations of the disease become noticeable with a decrease in the pet's immunity. Symptoms indicate that the cat is sick:
- the animal begins to itch constantly, becomes irritated;
- hair falls out on the affected areas up to baldness;
- combs appear until blood, crusts, blisters with pus appear.
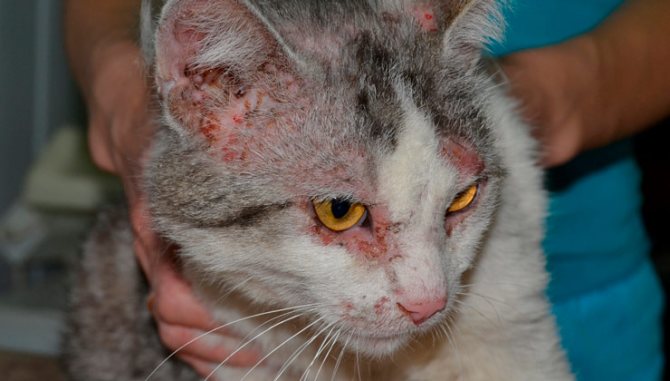

The increased activity of the demodex mite causes the skin disease demodecosis in the animal
Subcutaneous mites can infect humans as well as dogs, but cats are more susceptible to this danger. Parasites cause the following diseases in felines:
- Demodecosis - affects the top layer of the skin with constant itching and allergic reactions.
- Feline scabies, or notoedrosis - first on the head, and then ulcers form throughout the body, causing severe itching and baldness. The disease can be transmitted to humans and other animals.
- Heiletiellosis is a type of profuse dandruff with a mass of microscopic mites. It manifests itself as scaly nodules on the skin of the back, hair loss. A person can be infected with this disease.
- Sarcoptic mange - the formation of scabs and crusts. At the beginning of the disease - on the face, then the whole body is affected, unbearable itching occurs.
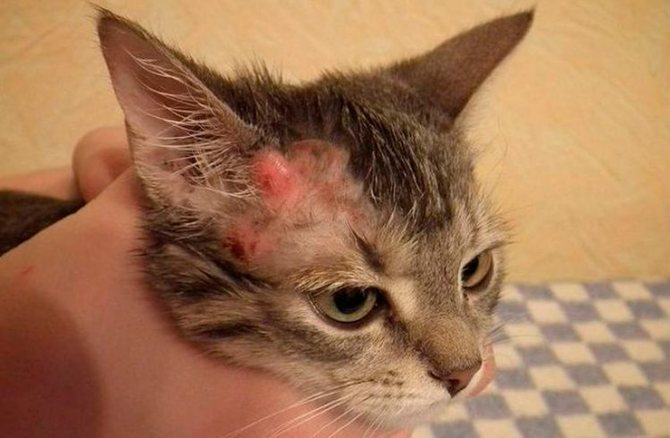

Subcutaneous mites can cause a variety of skin conditions in both animals and humans.
Treatment is carried out only after a correct diagnosis, depending on the type of parasite, tests and scrapings from the affected areas.
Sometimes the disease takes on a neglected look, and then the treatment will take a lot of time and perseverance to perform various procedures:
- baths with keratological shampoos;
- hair cutting on damaged areas with the application of Fungin, Safroderm, Amitrazin ointments on them;
- a course of antibiotics prescribed by a doctor;


Give antibiotics to your pet only after consulting your veterinarian. - the use of vitamins and supplements to boost immunity and accelerate wound healing;
- processing of animals in contact with the sick;
- disinfection and disinsection of the premises and care items with Delta Zone acaricidal solution, etc.
The result of treatment depends on the neglect of the disease. With a mild form, self-healing often occurs, and proper nutrition and careful care will further strengthen the pet's immunity.
Tick-borne encephalitis, piroplasmosis and their symptoms
Both diseases occur when an infection from an infected tick enters the bloodstream. Tick-borne encephalitis develops in three directions:
- acute pathology with a rapid course - pumped in by irreversible consequences and death;
- the classic form - with an incubation period, main phase and remission, which takes place in 8-14 days;
- asymptomatic disease with the transition to chronic meningitis.

The acute course of the disease is observed in cats with immune dysfunction 2-3 hours after the bite. A day later, pronounced clinical manifestations of pathology appear:
- febrile syndrome, weakness;
- refusal of food and water;
- diarrhea, profuse salivation;
- blanching of the mucous membranes;
- painful sensations in the muscles.


The last stage ends with convulsions, paralysis, coma. With sufficient functioning of the immune system, the disease lasts about 2 weeks:
- the incubation period is characterized by weakness, a slight increase in body temperature - by 2-3 degrees;
- discharge from the nasal passages, refusal to eat are observed.
The penetration of the virus into the bloodstream leads to inflammation of the meninges. After 14 days, the work of the central nervous system is disrupted, the cat develops paralysis, convulsive syndrome, loss of consciousness or lethargy.


Piroplasmosis is triggered by babesias that enter the cat's body during a bite. The simplest organisms spread in the blood by capturing red blood cells. Active reproduction leads to the destruction of red blood cells. Signs of piroplasmosis:
- lethargy, lethargy, loss of appetite;
- reddish or brownish tinge of urine;
- yellowing of the mucous membranes;
- increased body temperature;
- vomiting with large volumes of bile.
When the primary symptoms of pathology appear, the cat needs hospitalization. The disease is characterized by rapid development, a large number of complications.
Theileriosis
Theileriosis is caused by the unicellular protozoa of the genus Cytauxzoon. Like all other protozoa transmitted by the bloodsucker, these parasites live in the blood. However, in addition to blood cells, they actively colonize the liver, lungs, spleen, and even lymph nodes. For cats, this is a very serious illness that begins with nonspecific symptoms - sudden lethargy, anemia, heavy breathing, loss of appetite, fever and jaundice. Most often, theileriosis is confused with piroplasmosis and the animal dies during improper treatment.
The diagnosis can be made on the basis of laboratory tests, as well as using PCR. Unfortunately, the treatment of theileriosis is now too difficult a task. Most animals do not survive after the introduction of maintenance therapy, even with the use of special drugs.Therefore, to prevent this disease, veterinarians recommend vaccinating their animals before tick activity begins.


Dangerous consequences of infection, untimely or poor-quality treatment
Lack of treatment, ignoring the symptoms of a developing disease provokes complications. Ixodid ticks carry pathogens of dangerous infectious pathologies that cause weakening of the animal's body, disruption of the internal organs and death.
Pyroplasmosis, theileriosis, without treatment, leads to the death of the cat. Hemobartonellosis, or infectious anemia, provokes chronic diseases of the kidneys, liver, digestive tract, heart. Tick-borne encephalitis is fatal in 50% of animals.

Preventive measures
It is absolutely impossible to protect your pet, who regularly walks on the street. Nevertheless, there are currently types of products, the use of which reduces the risk of contracting diseases from the tick. These include:
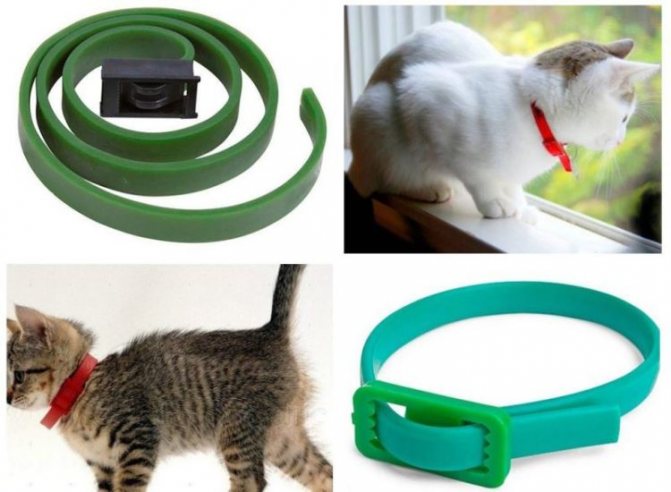
- Collar for cats that repels fleas and ticks - a leather or cloth strip impregnated with a special agent. Collars are highly toxic and should not be worn on kittens, pregnant or weakened animals. The devices are used for healthy cats and cats that spend a lot of time outdoors and sleep separately from people.


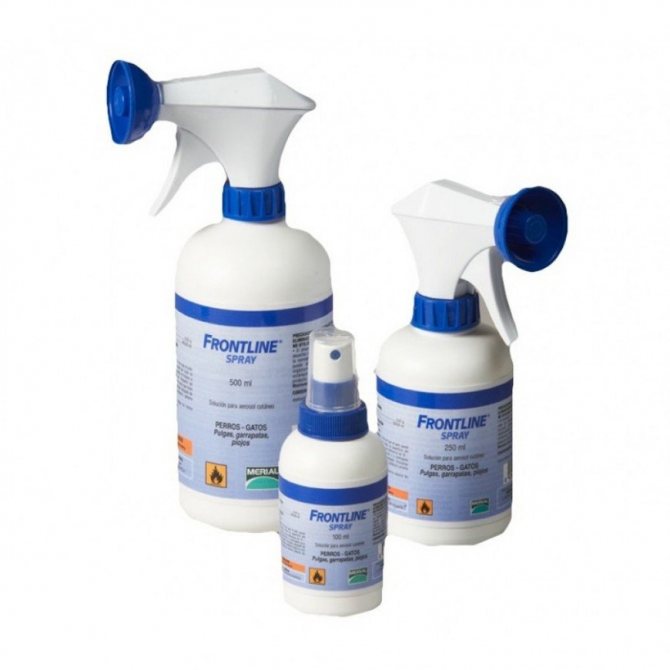
Tick collars for cats protect the animal for a long time from parasites - Sprays for cats and cats against ticks are effective, but not very convenient to use. The substance should be distributed, treating the entire surface of the body, and since the animal will lick itself, you will have to hold it for a while until the spray dries. The following types are used: Rolf Club, Hartz, Frontline.
- Drops from fleas and ticks. They should be applied to the skin at the withers. Being absorbed into the skin, the agent scares away or kills bloodsuckers. After application, the drug has an effect within 1-3 months. This is the most efficient and easy-to-use option. Quality drops Stronghold, Advantiks are used for pregnant cats and kittens.
Fighting ticks is necessary in various ways, but it is better to try to prevent the attack of parasites. The use of these funds on cats and cats will allow you to repel the attacks of bloodsuckers from the second half of spring to autumn, although it does not give a 100% guarantee.