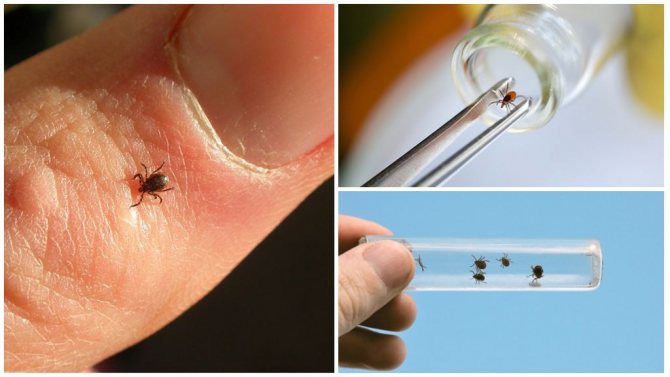
Every year from April to October in our country there is a peak in the activity of ixodid ticks, the bite of which is extremely dangerous for humans and animals. The fact is that many of these bloodsuckers are carriers of dangerous diseases. These include borreliosis and tick-borne encephalitis. At the same time, it is very difficult to protect yourself from these parasites. There is always a risk of meeting a tick - regardless of your region of residence.
Therefore, it is important to know where to go if, God forbid, you or your loved one has been bitten by a tick, to have an idea of which doctor can extract it and what emergency care the victim needs. This and many other things will be discussed further.
Which specialist you need to contact
If you find yourself with a tick bite, then you should not panic. First, try to gently remove the insect from the skin. After this, the tick must be sent to the laboratory, where it is carefully examined. Such a procedure is necessary, since ticks can carry such dangerous infectious diseases as tick-borne encephalitis and borreliosis.
If you have not been able to remove the tick from the surface of the skin, then you should not worry. In such a situation, you need contact an infectious disease specialist
, who, using a special tool, will extract the insect and send it to the laboratory. If there is no infectious disease specialist in your hospital, a surgeon can remove the tick.
Which doctor should I contact with a tick bite?
In the absence of an epidemic, a tick bite does not pose a danger to the body, health, and does not even affect the general well-being. After removing the parasite, redness, swelling, itching remains. Within a week, the skin is completely restored. This happens in most cases, so only urban residents begin to panic, who are less likely to encounter parasites than rural ones. There is a reason for panic. In the blood of villagers for many years of life in the wild, antibodies are produced, the disease does not develop.
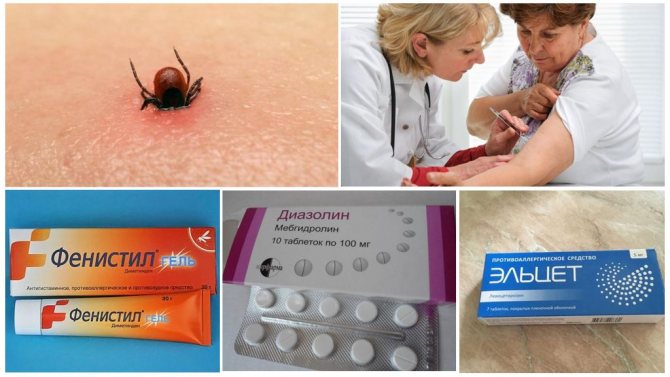
Actions for a tick bite
If an allergic reaction occurs after a bite, they seek help from a dermatologist, an allergist. Treatment is carried out with antihistamine tablets, local antiallergic ointments. With minor manifestations of an allergic reaction, the bite site is treated with an anti-inflammatory, antihistamine like Fenistil-gel. Inside from an allergy to a bite, they take the drug Diazolin, Elset, Eden to choose from.
If there is a threat of the development of the disease, in order to calm their nerves, they seek help from an infectious disease doctor. It is this specialist who provides treatment in case of subsequent infection with borreliosis, encephalitis or other tick-borne disease.
For yourself, you should find out where to go with a tick bite - go to an appointment with a private trader or a public hospital. In the first case, information about the location of the clinic, working hours is specified via the Internet, in the second - by phone to the registry. In Moscow, the addresses of polyclinics are available on the Internet.
The main signs of bites
After relaxing outside the city or a simple walk in the park in the spring and summer, you need to carefully examine your skin for the presence of various insect bites. Favorite locations for tick bites are:


ears and surrounding skin (including the scalp);- groin area;
- armpits, chest;
- neck;
- the area of the groin folds.
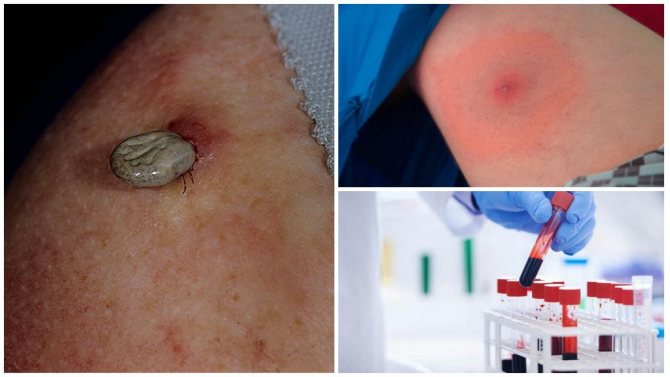
However, bites can also be found on any other part of the skin. As a result of skin damage, local tissue hyperemia, swelling and soreness develops. With borreliosis after a tick bite, a characteristic macular erythema
... Other symptoms of the disease may also appear:
- deterioration in general well-being, accompanied by weakness, increased drowsiness;
- chills;
- a feeling of soreness in the joints;
- increase in body temperature: usually the fever is kept within 37-38 0 С;
- increased heart rate;
- an increase in peripheral lymph nodes;
- an allergic reaction in the form of itching and rashes.
The severity of the main symptoms primarily depends on the number of sucked ticks and the general condition of the person. Regardless of the presence or absence of the above signs with a tick bite it is imperative to see a doctor
, since there is a risk of dangerous complications.
In some cases, the victim may develop a very severe reaction to the bite, accompanied by breathing disorders, repeated vomiting, convulsions, hallucinations. With such a pathological condition, you must immediately call an ambulance team.
What treatment can help


With a tick bite, a doctor's consultation is required
A doctor may prescribe emergency treatment after a tick bite in cases where there are no laboratory tests and it is not known whether the parasite was a carrier of any disease. In case the victim has been infected with encephalitis, emergency measures can help within 3-4 days after the moment of the insect bite. When it comes to barreliosis, drug treatment can help at any time, but success will depend on how quickly you seek help from a medical facility.
In addition to the introduction of immunoglobulin, the doctor will definitely prescribe the following drugs:
- Cycloferon
- Larifan
- Amiksin
- Panavir
- Ridostin et al.
Do not neglect the recommendations of doctors, because your health, and possibly life, may depend on it.
How does the diagnostic process take place?
After you send the tick to the laboratory for research, immediately consult with an infectious disease specialist. The doctor will begin the examination with a thorough collection of complaints and medical history. Since an important symptom of a bite is a change in the skin, the doctor first of all inspect the site of the tick bite
... If erythema macula is present, your doctor may suspect that Lyme disease is developing. It is also important for the doctor
determine the nature of the temperature reaction
patient (before visiting a doctor, try to remember when and to what numbers your temperature rose).
In cases where a person is bitten by an insect that is a carrier of serious infectious diseases, an important place for a doctor in diagnosis is occupied by laboratory research
... Experts determine the level of antibodies to various pathogens of viral or microbial infections. There is also a method for determining the genetic material of pathogenic microorganisms - PCR. All of these studies are available and carried out in any accredited laboratory.
If bitten by a tick, then you should not delay visiting a doctor. There are many health and life-threatening conditions that develop after a person is bitten by an infected tick. These include:

tick-borne encephalitis;- joint damage;
- pathologies of the cardiovascular system: heart rhythm disturbances, sudden changes in blood pressure;
- lesions of the urinary system.
In severe forms of the disease, disability is possible due to the development of persistent organic disorders of the nervous, musculoskeletal or other systems.
How to remove a tick
If bitten by a tick, what to do at home? The ideal option is of course to contact the emergency room. But this is not always possible. In this case, you will have to remove the tick yourself. Before proceeding with the extraction, you need to know what not to do. Do not try to pick it out, crush it. The body must not be separated from the head. In this case, all the poison will fall into the hole in the skin.
You can often find advice such as: pour oil, alcohol, wax and much more. So: this should not be done in any case. Thus, you ensure that the access to air is closed for the tick. He begins to panic and secretes more saliva containing poison. Without air, it is over after some time to fall off, but during these 10-15 minutes it will release the maximum possible dose of poison. So this method only works for non-infected ticks. And the presence of a pathogen can only be found out through the laboratory.
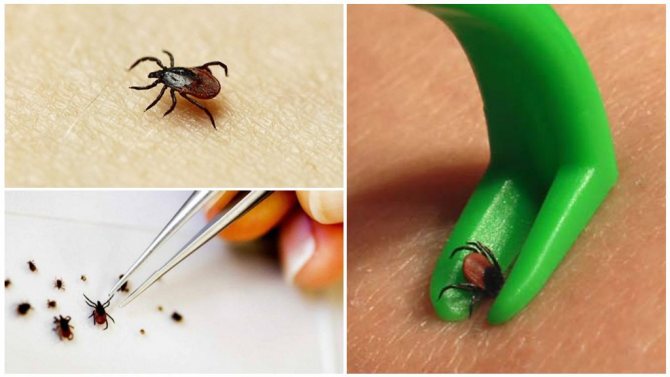
How can you pull out a tick? There are special hooks with a bifurcated end. They are the most convenient for getting them, but not all of them have them. In this case, tweezers or thread will do. But keep in mind that you need to work very carefully, you cannot press or separate the body from the head. Use tweezers or a crochet hook to gently grasp the tick. Do not apply too much pressure. Try to reach it as deep as possible.
But do not pick out the wound specially for this purpose. And then twist the tick in a smooth circular motion clockwise. The threading process is both easier and more difficult. The thread is folded and wound on the tick and then, gradually twisting it, pull out the tick. It is quite difficult to do this without experience. It is easy to pinch or cut the tick, which will cause saliva to flow. How to treat a tick bite? Alcohol, antiseptic will do. After a bite, you need to check the blood and observe your body. If you have any symptoms, see your doctor right away. What to do after removing the tick? The tick, as mentioned above, is not thrown away. It must be placed in a tight jar with a lid and left in the refrigerator, and then taken to the laboratory. Be sure to wear rubber gloves. If the poison gets on your hands, you can also get infected. The tick remains dangerous even after it has already sucked on one victim. If you still do not want to take it away, then dispose of it correctly. You cannot throw it into the water or crush it. You need to drown it in alcohol, you can still burn it or scald it with boiling water.


When the head remains in the body, then you need to get it only with the help of a doctor. But if there are antennae or paws, then it's okay. They themselves will then disappear. If the child has been bitten by a tick, then do not try to remove it yourself. Children are very mobile, and it is difficult to get it. Without skill, even with a moving child, it is almost impossible to do this without damaging the parasite. Be sure to talk to your child about this topic. Explain to him that under no circumstances should you touch or crush him. You need to immediately seek help from your parents.
Treatment and prevention
For a doctor, the tactics of treating a patient depends, first of all, on his general condition and the identified infectious disease. The most common pathologies are tick-borne encephalitis and borreliosis. With tick-borne encephalitis, hospitalization is indicated in an infectious diseases hospital (or an infectious diseases department of a hospital). The patient needs strict bed rest
throughout the entire period of fever and for 7 days at normal body temperature. The main etiotropic drug is human immunoglobulin, which doctors inject to combat the causative agent of the infection. Antibiotic therapy is indicated in the presence of concomitant bacterial complications (drugs are prescribed exclusively by a doctor).
In Lyme disease, doctors hospitalize patients with severe nervous system dysfunctions. Antibacterial drugs (a group of penicillins, cephalosporins) must be included in the course of treatment. In the case of a pronounced inflammatory and allergic reaction, prednisolone, the introduction of infusion solutions, vitamins are used.
In order to prevent a tick bite and the development of associated complications, you need to follow the simple recommendations of doctors:
- When outdoors, wear clothing that covers as much of your exposed body as possible.
- Use a tick repellent.
- Vaccinations should be given to people living in areas where outbreaks of infections transmitted through insect bites often occur.
If a tick bite does occur, then you need to go to a specialist in a timely manner. It is also important to send the tick for examination to a special laboratory.
Save the link, or share useful information in social. networks
In spring and summer, the risk of being bitten by a tick increases. This issue must be approached responsibly, since insects are carriers of dangerous infections. Knowing the rules of action and where to go if bitten by a tick will help maintain health. In the article, we talk about which doctor treats the consequences of a tick bite - encephalitis and borrliasis.
If bitten by a tick, it is important to go to the clinic or hospital as soon as possible, preferably no later than 72 hours after the bite. In the emergency room, the doctor will remove the tick and disinfect the damaged area of the skin and send the parasite to the laboratory for research, and possibly give you a referral for the administration of immunoglobulin.
What to do after removing the tick?
Did you manage to get the tick out? Excellent! Moreover, it does not matter whether he remained alive and whole or not, it is advisable to preserve it and transfer it for research to a laboratory at a hospital, SES or a private clinic. To do this, place the bloodsucker in an airtight container.


Throwing away or burning the parasite is not worth it. It is necessary within two days (better immediately) to send the extracted tick to the laboratory, where they can determine whether it is infected with viruses that are dangerous to human life and health. By the way, if you do not have insurance against a tick bite, then the research will be paid. The average cost of checking an arthropod for available viruses is 500-600 rubles. If this is a comprehensive analysis (for 4 pathogens), then you will have to pay about 1500-2000 rubles. The test results are prepared within a day, in an emergency - several hours.
After that, be sure to contact a medical institution as soon as possible. Ideally, get an appointment with an infectious disease doctor. He will conduct an examination, prescribe drug therapy if necessary, tell you about the appearance of which symptoms should alert you, etc.
Once the parasite has been removed from the body, it cannot be destroyed! It is necessary to take the parasite to a laboratory for research. This is done in order not to blindly administer an expensive vaccination, but first to find out if the tick is infected with some viruses.
Pull out the tick in the emergency room or on your own
If possible, then after the publication of an insect that has penetrated the skin, you should immediately visit a doctor. Any nearby clinic or hospital will help to remove the tick, provided that there is an emergency room or a surgeon on duty. Further, depending on the condition, a visit to a surgeon or infectious disease specialist is appointed.
Time after defeat plays a big role. The longer the tick drinks blood, the more infection will enter the body directly. This affects the course of the pathology, the severity of its course.
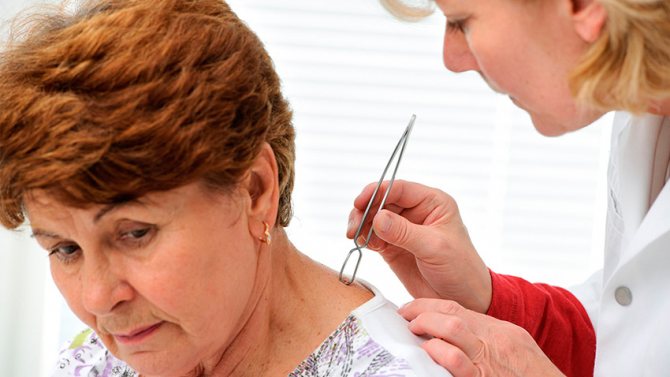

If it is not possible to consult a doctor, then pull out the tick yourself, then deliver it to the laboratory.
Leaving an insect on the skin is prohibited.
Algorithm of actions if a tick is found on the body
Where do you need to go with a tick bite? How to get it out if the bloodsucker has sunk deep into the body? These and many similar questions are very often asked by people on the Internet. There is nothing surprising in this. After all, after the discovery of this parasite, everyone wants to remove it from under the skin as soon as possible. At the same time, not everyone knows what needs to be done for this. Therefore, we will tell you in as much detail as possible how to behave in such a difficult situation:
- The first step is to contact a medical facility. In which? You can call an ambulance (103) and ask them. Most likely, you will be sent to the nearest emergency room, clinic, emergency hospital or to the district SES. Often they offer to go and immediately to the infectious diseases department of the hospital in order to pass all the tests there and send the tick itself for research. At the same time, wherever you go, even if it is a private clinic, do not forget to bring your identity documents and a medical certificate (if possible).

- If the tick has sucked, then you cannot try to tear off or crush it! Remember this! Otherwise, part of the parasite (for example, the proboscis with the remnants of infected saliva) will remain under the skin, which is not good at all.
- Can you try to get the tick yourself? Let's just say, if you don't have this experience, it's not worth experimenting. Better hurry to the hospital. If there is no possibility of immediate provision of qualified medical care, then one thing remains - to try to pull out the parasite ourselves. Here you should be extremely careful and attentive, observe some rules, etc. Let's talk about this further.
The sooner you remove a stuck tick, the better. After all, the likelihood of contracting tick-borne encephalitis, borreliosis and other infections transmitted by these arachnids depends on the amount of the virus that penetrates through the bite.
Take the tick for analysis to the laboratory
It is not recommended to kill a self-removed parasite. It is necessary to hand over the tick for analysis to an epidemiological laboratory in order to diagnose the presence of infections in the insect's body: encephalitis virus, borreliosis pathogens.
After pulling out the arthropod, it must be placed in a clean container (test tube, jar). It is necessary to create conditions of high humidity in the container: put a paper napkin slightly moistened with water inside. It is recommended to put the parasite crushed during the removal on ice.


It takes two days to deliver the insect to the laboratory.
You can find the list of laboratories where you can donate a tick for research on the page "Tick analysis".
Some of the laboratories in Moscow:
Laboratory at the Center for Hygiene and Epidemiology in the city of Moscow
Krasnogvardeisky Boulevard, 17, bldg. 1
Head Center for Hygiene and Epidemiology
1st infantry lane, 6
Federal Center for Hygiene and Epidemiology, Federal Service for Surveillance on Consumer Rights Protection and Human Welfare
Varshavskoe highway, 19a
Center for Sanitary and Epidemiological Examination and Certification
Goncharnaya, 11, bldg. 2
FBUZ "Center for Hygiene and Epidemiology in the Moscow Region"
Mytishchi, st. Semashko, 2
What to do and where to go if bitten by a tick
If the tick nevertheless sucked, then the first consultation by phone can be obtained in the ambulance by dialing 103 from the cell phone, and 03 from the landline phone.
Step 1 - How to remove the tick - remove the tick as soon as possible
You will be referred to a local hospital or health center to remove the tick.
If you are in the country or in the forest, then you will have to pull out the tick yourself.
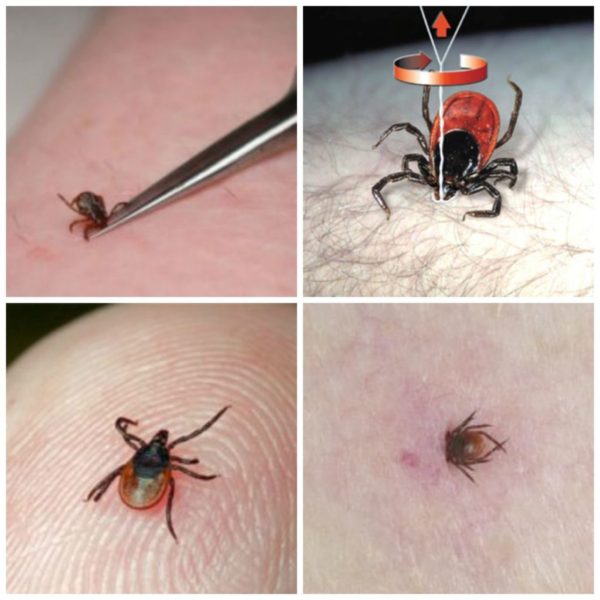

Important! If a tick is found, remove it as quickly as possible. Since the tick manages to pump the infection in the first minutes of blood absorption, therefore, the longer it sticks, the greater the dose and the higher the risk of disease.
We take out the tick with tweezers - step by step instructions
- Take TWEEZERS.
- Grab the tick as close to its head as possible. Keep it strictly perpendicular to your skin.
- Rotate around the axis clockwise, carefully remove it by pulling up.
- Removing the tick must be done with caution, without squeezing its body, otherwise you can crush the insect and the infection will enter the wound.
- It is important not to break the tick. Often the head remains in the wound. If, when removing the tick, its head comes off, which looks like a black dot, then the wound is moistened with alcohol and the head is removed, like a splinter, with a disinfected needle.
- Wipe the bite with alcohol or iodine so that bacteria do not get into the wound and it does not fester. It is better to process the bite once daily for 5-7 days.
- After removing the tick, wash your hands with soap and water.
- Place the tick in a hermetically sealed container and take it to the laboratory for analysis, the addresses of which will be indicated later in the article.
Important! no need to drip oil on it or smear with ointments. The tick breathes with its "bottom", the respiratory organs are on the opposite side of the head. The oil can clog the respiratory system and the mite will die unrecovered.
Important! An infection test is performed only if the tick is alive.
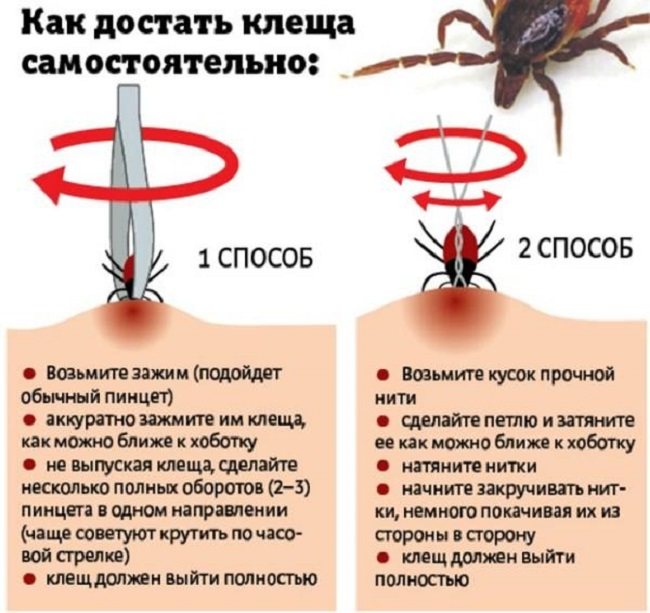

We take out a tick with a thread - step by step instructions
- Take a piece of sturdy thread and make a loop.
- Tighten the loop as close to the proboscis as possible.
- Begin to twist the threads, wiggling them slightly from side to side.
- The tick should come out completely.
After getting the tick, if a person is allergic, he may develop an allergic reaction, accompanied by swelling of the face and limbs.
In this case, you need to give an antihistamine, for example, Suprastin, Diazolin, Zodak, etc. and call an ambulance.


Watch the video! Emergency tick bite treatment
What is the threat of a tick bite?
Even if the tick bite was short-lived, the risk of infection remains.
In addition to encephalitis, there are three infections that a person can contract from a tick: borreliosis, anaplasmosis and orlechiasis (diseases of the circulatory system).
Therefore, after removing the tick, you need to save and place it in a hermetically sealed container and take it to the laboratory for analysis, then the addresses will be indicated.
Tick analysis is needed for peace of mind in case of a negative result and vigilance in case of a positive result.
If a tick turns out to be a carrier of infections, this does not mean that the bitten person will get sick.
The surest way to find out if a person has become infected is to have a blood test for infections. But donating blood immediately after the bite will not show anything.
It is more expedient to donate blood 14 days after a tick bite for antibodies (IgM) to tick-borne encephalitis virus, and three weeks later for antibodies (IgM) to borrelia (tick-borne borreliosis).
Tick-borne diseases
The main danger of ticks is that, when bitten with saliva, they transmit pathogens of infectious diseases, such as tick-borne encephalitis, borreliosis, anaplasmosis and orlechiasis (diseases of the circulatory system).
- tick-borne encephalitis - the virus damages the central nervous system, which can lead to paralysis of the limbs and other serious complications. After a person is ill, immunity to the disease is acquired.
Emergency prevention of tick-borne encephalitis should be done as early as possible, preferably on the first day.
For this, antiviral drugs or immunoglobulin are used.
TO antiviral drugs relate:
- Yodantipyrine for adults and children over 14 years old.
- Anaferon for children for children under 14 years old.
If these drugs are not found, you can use their analogues and replace them with cycloferon, arbidol, ergoferon, remantadine.
Immunoglobulin is advisable only during the first three days. After 14 days, you need to send a blood test for antibodies to tick-borne encephalitis virus.
Important! If the bitten person is vaccinated against the tick-borne encephalitis virus, no action is required.
The second most common infection by ticks is Borreliosis (Lyme disease) - transmitted by bacteria through the blood, causing inflammation in the human body, negatively affects the functioning of the cardiovascular system, joints and skin.
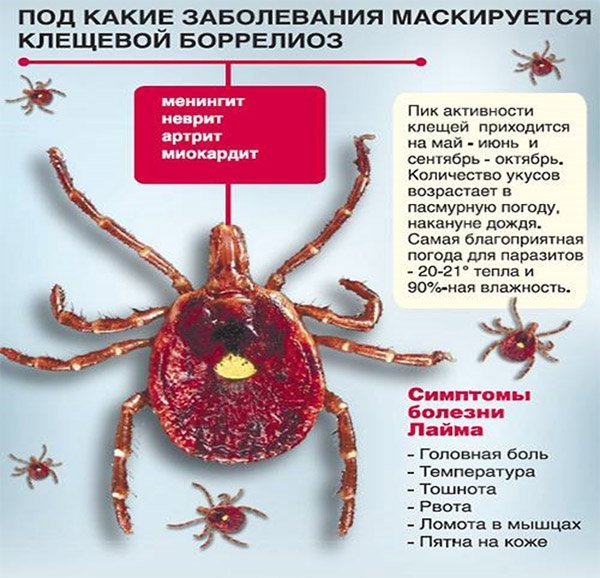

Symptoms of the disease are the appearance of a red spot at the site of the bite. The disease, if left untreated, can become chronic and also fatal.
Those who have had Lyme disease can become infected again after 7 years of interruption.
3 weeks after the bite, you need to donate blood for antibodies to tick-borne borreliosis (IgM). In case of a positive result, contact an infectious disease specialist.
Watch the video! Tick-borne borreliosis (Lyme disease)
A tick bite can also lead to infection
- monocytic orlichiosis - an infection caused by microorganisms of the genus Ehrlichia, which affects the skin, liver, central nervous system and bone marrow, where infectious granulomas form.
- granulocytic anaplasmosisom - an acute febrile illness, which is transmitted by pathogens Anaplasma phagocytophillum, microorganisms act on neutrophils, which causes a decrease in the body's immune defense response.
- Astrakhan, Crimean fever (etc.) - symptoms of infection - the appearance of papules at the site of the bite, rash, itching and fever, insomnia, headache, joint pain. It is mandatory to take antiviral drugs iodantipyrine, cycloferon, arbidol, remantadine, anaferon for children.
Symptoms of these diseases do not appear immediately, they may appear after 72 hours, but the incubation period lasts from 14 to 40 days.
Step 2: go to the nearest medical facility
You don't have much time to protect yourself from the unpleasant consequences of infection.
Remember: you only have 72 hours. Provided that the analysis of the tick itself is carried out within 24 hours. Therefore, you do not have much time.
If you have money to buy immunoglobulin, this is about 5000-6000 rubles (1 ampoule per 10 kg of weight at an average price of 900 rubles per ampoule), then you can take your time: buy a medicine, inject within the same 72 hours after the bite and count on successful outcome. In the district hospital or clinic at the place of residence, the immunoglobulin you have acquired will be administered if the tick is a carrier of encephalitis.
Children under 17 will receive immunoglobulin free of charge.
First of all, you need to contact the children's clinic at the place of residence. If the working day in the hospital is over, then in the evening and at night - to the admission department of children's hospitals. You must have your passport and policy with you.
If there is no extra money for immunoglobulin, and there is no desire to inject it unnecessarily, then we are waiting for the result of the analysis of the tick.
Step 3 - We send the tick to the laboratory for analysis, preferably within 24 hours
If you do not have insurance against a tick bite, insect research will be paid. For one infection, 300-400 rubles. It is better to investigate immediately for 4 infections - the price is about 1300 rubles. depending on the region.
Important! Better not to skimp on laboratory research.
The analysis result can be obtained the next day. In case of a negative result, you can breathe a sigh of relief and forget everything like a bad dream. In case of positive - follow the further instructions.
Where to take a tick for analysis in a laboratory, where the tick will be checked for infections?
The addresses of such clinics are as follows:
In Moscow and the Moscow region
- FBUZ "Center for Hygiene and Epidemiology in the City of Moscow": Grafsky Lane, 4/9 (entrance to the institution from the courtyard, second floor). Phone: 952-40-98. Reception from 9:00 to 15:30 (break from 13:00 to 13:30);
- Institute of Poliomyelitis and Viral Encephalitis: Moscow Region, Vnukovo, Moskovsky settlement. Phone: 8 (498) 540-90-96;
- Children's Clinical Hospital No. 13 named after Filatov: Sadovaya-Kudrinskaya Street, Building 15. Fixed phone: (499) 254-34-30;
- Infectious Diseases Clinical Hospital No. 2: Sokolinaya Gora Street, 15.Landline telephones, backup number (495) 365-01-47;
- branch of FGUZ "Center for Hygiene and Epidemiology in Moscow": Krasnogvardeisky Boulevard, 17, the first microbiological laboratory. Landline phone. Reception is from 9:30 to 15:00 daily.
In Izhevsk:
- FBUZ "Center for Hygiene and Epidemiology in the Udmurt Republic"
- Address: Izhevsk, st. Kirov, 46;
- Phone: 7- (3412) -43-23-11;
- BUZ UR "RKIB MZ UR"
- Address: Izhevsk, st. Labor, 17;
- Phone: 8- (3412) -21-96-51;
- Medical
- Address: Izhevsk, st. Shumaylova, 20A;
- Phone: 7- (3412) -65-51-51;
- Medical
- Address: Izhevsk, Pushkinskaya str., 136A;
- Phone: 7- (3412) -60-11-11;
- Medical
- Address: Izhevsk, st. Labor, 17;
- Phone: 8- (3412) -21-96-51;
- Medical
- Address: Izhevsk, st. Spring, 6;
- Phone: 7- (3412) -24-54-54;
- Republican Center for Vaccine Prevention
- Address: Izhevsk, st. Petrov, 6.
If there is insurance, the tick will be accepted for free,
Tick research prices:
Tick removal - 90-140 rubles, a test for tick-borne encephalitis - 280-430 rubles, for borreliosis - 430-485 rubles, for ehrlichiosis and anaplasmosis - 490-520 rubles, if not - a test for four infections - 1300 rubles ...
in St. Petersburg
FBUZ Center for Hygiene and Epidemiology in St. Petersburg
st. Malaya Sadovaya, 1, st. Defense, 35, lit. BUT
8
Center for Hygiene and Epidemiology in the Leningrad Region.
st. Olminsky, 27, (station M "Elizarovskaya")
8
Clinical Hospital Botkin,
Outpatient clinic: Piskarevsky pr., 49 Reception dep. hospital at the addresses: Piskarevsky pr., 49 and st. Mirgorodskaya, 3
Research and Production Enterprise ImmunoBioService Moscow highway, 30, building 2; st. Kirochnaya, 3 8 (812) 273-03-03
BALT MED Vyborgskoe highway, 40 8 (812) 670-03-03
Hemotest There are many medical offices, you need to check by phone.
Invitro There are many medical offices, you need to check by phone.
The results will be available the next day.
At any trauma center, you will be given the exact address where you need to go for the study. Watch the video! What should I do if bitten by a tick? How to get it out? Why is he dangerous
Step 3 - Injection of immunoglobulin injection
If the test is positive and the tick turned out to be infectious, then no later than 72 hours, seek help from a local polyclinic or a private clinic to a therapist or infectious disease specialist.
If a tick infected with encephalitis sticks to an unvaccinated person, an immunoglobulin preparation is administered to the victim as an emergency measure (at the rate of 1 ampoule per 10 kg of weight). This must be done within 72 hours. After the introduction of immunoglobulin, the doctor prescribes antiviral drugs, antiviral drugs of the interferon group and vitamin C to stimulate immunity.
If it was not possible to introduce immunoglobulin on time, the bitten one is prescribed a course of immunostimulating drugs, for example, the antiviral drug iodantipyrine.
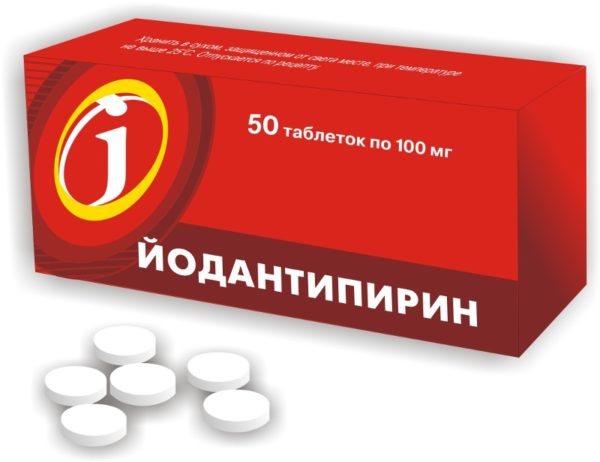

Iodantipyrine tablets are taken orally after meals:
- 300 mg (3 tablets) - 3 times a day for the first 2 days;
- 200 mg (2 tablets) - 3 times a day for the next 2 days;
- 100 mg (1 tablet) - 3 times a day for the next 5 days.
Only 45 tablets in 9 days.
Important! It is not recommended to take immunoglobulin and iodantipyrine together.
Continuing to monitor his condition for a month. The incubation period for diseases ranges from 14 days to 40 days.
It is also possible that the disease will not develop at all or develop in a mild form - it all depends on the body's immune system. If the tick is a carrier of Lyme borreliosis, then antibiotics are prescribed to the bitten person, even if no symptoms have yet appeared - this is also a measure of emergency prevention. At the same time, the body is insured against the development of other bacterial infections.
Antibiotics are used to suppress spirochetes, the causative agents of the disease. The most commonly used drugs are the penicillin series and cephalosporins. To stop erythema, antimicrobial agents of the tetracycline group are prescribed. Use:
- Doxycycline (0.1 g orally for 5 days),


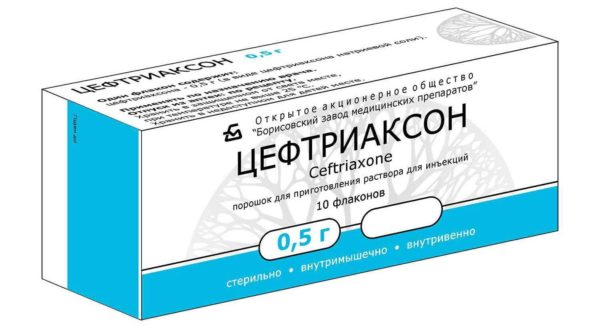
- Ciftriaxone (according to the instructions for 3 days),

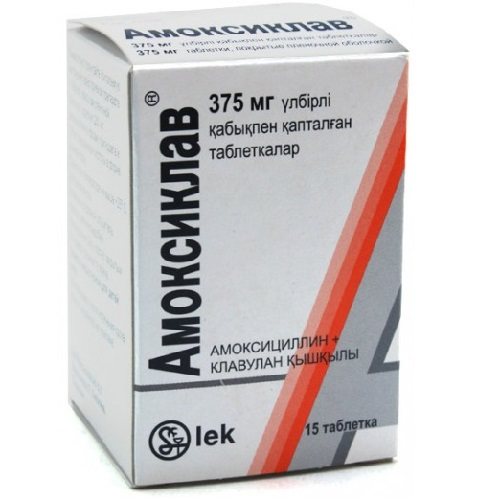
- Amoxicillin (0.375 g three times a day for 5 days),

- Retarpen (once per instructions).
Step 4 - Where to donate blood for analysis?
It is not advisable to donate blood immediately after the bite, blood is donated for infections that the tick carries:
- by PCR for borreliosis and encephalitis (by PCR it is possible to determine the presence of tick-borne encephalitis, tick-borne borreliosis, granulocytic anaplasmosis, monocytic ehrlichiosis) - after 10 days;
- for IgM antibodies against tick-borne encephalitis virus - 14 days after the bite,
- for antibodies of the IgM type against the causative agent of borreliosis - after 21-30 days.

Addresses of medical institutions where you can donate blood for analysis after a tick bite.
in Moscow and the Moscow region:
- State Research Institute GISK named after L. A. Tarasevich, Moscow address: Sivtsev Vrazhek lane, house 41. Fixed telephones, reserve numbers 241-99-78 and 241-31-77.
- State Institution of Research Institute of Epidemiology and Microbiology named after N.F. Gamaleya RAMS, Moscow address: Gamaleya Street, house 18. Stationary phone: 8 (499) 193-30-01.
- Medical Center for Immunoprophylaxis "MEDEP": Kutuzovsky Avenue, house 33. Phone.
- Medical: Grokholsky lane, house 31. Phone: 8 (495) 937-5757.
- Tick transport for analysis should be carried out in a dry container (preferably sterile).
At the same addresses, you can carry out immunization (vaccination) against tick-borne encephalitis for children and adults.
Blood for analysis after a tick bite can also be donated at any infectious diseases hospital.
The average cost of a blood test to detect IgG and IgM antibodies is 430 rubles. The analysis will be given in 2 days, in case of emergency - about 3-5 hours.
The cost of testing a tick for additional diseases (borreliosis, anaplasmosis, ehrlichiosis) is on average 430 (price of analysis for encephalitis) + 700 rubles.
In Izhevsk:
- Hemotest, medical laboratory
8-800-550-13-13, Izhevsk city, Krasnogeroyskaya street, 38a
- Mira-plus, clinical diagnostic laboratory (3412) 513189, city of Izhevsk, Borodin street, 7
- MedLab Express, LLC, medical laboratory
+7 (3412) 66-50-66 ,, Izhevsk city, Lenin street, 17
- Laboratory, City Clinical Hospital No. 1
(3412) 510787, city of Izhevsk, Pushkinskaya street, 158
- Invitro, an independent laboratory
88002003630,
Izhevsk city, Pushkinskaya street, 270,
(3412)412525
Izhevsk city, street named after Petrov, 7
(3412)508989
So that you never need these tips, follow the precautions and preventive measures.
Since April, residents of different regions of Russia and not only have been attacked and bitten by ticks. To protect yourself and your loved ones, you need to follow certain rules, we will consider them in this article.
According to epidemiologists, tick activity begins after the snow melts. The peak of activity is in May and June.
The most dangerous areas to pick up a tick are:
- Garden massifs;
- The woods;
- Cemetery zones;
- Parks and squares in the city.
The most dangerous to humans are ixodid ticks (Latin Ixodoidea).
You can read more about them here.
Important! Ticks can't jump!
The ticks do not rise above 1.5 m from the ground.
After the snow melts from the forest litter, in which the ticks have wintered, they come out of hibernation. They are in an aggressive search for warm-blooded animals or humans.
Ticks love wet, warm springs and rainy summers.
Signs of a tick bite
In the case when it was not possible to immediately detect and remove the insect, its bite is easy to notice by the following signs:
- increased body temperature;
- inflammation of the lymph nodes;
- headache and muscle pain;
- redness at the site of arthropod lesions;
- rash on the skin.
In a person prone to allergic reactions, a bite can lead to the development of a strong reaction of the body: swelling of the face and neck, breathing problems.
Attacked by a safe or infected tick, it is impossible to determine independently. But the risk of infection is directly proportional to the duration of the insect's stay under the skin.
Who treats a tick bite
First of all, if a bite is found, carefully try to remove the pest from the skin. Take your time to throw out the tick - it should be sent to the laboratory for a thorough examination.This is necessary in order to determine whether the insect is a carrier of diseases such as borreliosis and tick-borne encephalitis.
If the removal of a tick is impossible, you should consult an infectious disease doctor. Using special tools to extract the insect, he will rid you of the parasite, and the tick will be sent to the laboratory for testing. If the hospital does not have such a doctor, the surgeon or the doctor on duty can help.
First aid after a bite
First aid immediately after a bite is to remove the parasite. This can be done in the following ways:
- pick up the parasite with forceps / tweezers, then, turning the instrument, remove it. During the process, the instrument must be kept parallel to the skin;
- build a loop from a strong thread, grab the arthropod and pull it out, slowly swinging it. The procedure takes about three minutes;
- if, during the removal, the body of the tick came out, and the head remained under the skin, it is necessary to decontaminate the bite site and remove it with a needle;
- it is forbidden to leave the head of an insect in the tissues of the skin, as this can serve as a continuation of infection or the development of an inflammatory process;
- disinfect the area after an arthropod bite - with an alcohol-containing agent / iodine;
- hands should also be treated with an antiseptic, since tick-borne encephalitis is transmitted by the household;
- if the insect does not come out on its own or there is no disinfectant at hand, visit a doctor immediately to receive first aid.
We remove the tick ourselves
Usually, if a person goes to the hospital with a request to remove a sucked tick, then the surgeon takes over. It is this doctor who will easily remove the tick so that the head or proboscis does not remain in the skin. But who will help if there is no way to get qualified medical care? In this case, you can get and remove the tick yourself or someone from those people who are next to you. True, you need to adhere to the following plan:
- Wear medical gloves or protect your hands and fingers with several layers of gauze, a rag, etc.
- Using tweezers, a surgical clamp, or a strong suture (line) with a loop, grab the tick as close to the head and trunk as possible. By the way, there are also special tools for removing such parasites. The Uniclean Tick Twister is popular today. It is inexpensive, and if you are an avid tourist, fisherman or hunter, then such a device will not be superfluous in your arsenal.
- Then gently pulling towards you, start pulling out the bloodsucker. You can slightly rotate the parasite around the axis. At the same time, do not make sudden movements, jerks and do not put pressure on him! Otherwise, you can provoke a more intense release of the contents of the tick along with pathogens into the wound at the site of the bite.
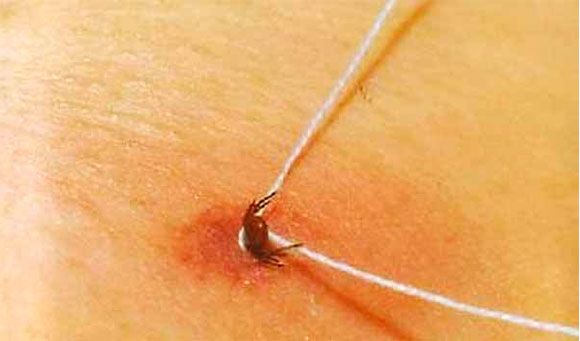

- It is imperative not to sever this dangerous arachnid when removed. After all, the remaining part of the tick in the body can cause inflammation and suppuration. This is also fraught with the fact that the process of infection will continue, since a significant concentration of viruses is present in the salivary glands and ducts of this animal.
- It is not recommended to lubricate the tick with oil, cologne, vodka, alcohol, etc. before pulling out. There is an opinion that such substances will make the parasite disappear on its own. But this is not at all the case. From this, the bloodsucker will only suffocate and inject an even larger amount of the contents of its abdomen into the human blood. And this will significantly increase the likelihood of infection.
- After removing the tick, thoroughly rinse the bite site with warm water. When the skin and the wound are dry, treat it with antiseptic agents - alcohol, brilliant green, iodine, etc. It is not necessary to glue it with adhesive plaster or wrap it with a bandage. Everything that you have done above is enough for the first emergency aid to the victim.
- What if part of the tick remains under the skin? Then heat the needle and remove everything with it, like a common splinter. Then treat the bite site.
Note that you cannot touch the tick with unprotected hands. Otherwise, there is a risk of infecting yourself, since there have been cases when a person was infected with the contents of the abdomen or the saliva of an arthropod through microcracks in the skin.
Do I need to go to the doctor if there are no symptoms?
It makes no sense to go to a specialist immediately after a tick bite. Make an appointment after receiving the results of the laboratory analysis of the tick. If an infection was found in the insect's body, then the specialist will prescribe a course of antibiotic treatment (with the risk of infection with tick-borne encephalitis - antiencephalitis immunoglobulin).
If laboratory diagnosis of a tick has not been performed, symptoms of the disease after a tick bite do not appear, and it is impossible to speak about the absence of infection. The disease may appear later, due to the long incubation period, or it may be asymptomatic for a long time. Be sure to go to the doctor, tell about what happened. The specialist will give full instructions for further actions.
Tick bites in questions and answers
Q: I was bitten by a tick, what should I do?
О .: Read the article: "What to do if bitten by a tick", the issues discussed in the article will not be considered below.
Q: How to find out an encephalitis tick or not?
A: Tick-borne encephalitis is a virus that is transmitted by ixodid ticks - but not every tick carries it. In appearance, it is impossible to determine whether a tick is encephalitic or not - this can only be done in a laboratory. In almost all cities where there is a risk of contracting tick-borne encephalitis, it is possible to take a tick for analysis (usually a tick can also be checked for other infections common in the region). On our website, for a number of cities, the addresses and phone numbers of such laboratories are indicated.
Q: I took off the tick, it looks like it just started to stick, is there a risk of getting sick and what?
A: There is a risk of getting sick with tick-borne infections even with a short-term tick suction. It will not be possible to unequivocally answer the question of what can be infected, since ticks carry different infections in different regions. Tick-borne encephalitis is considered the most dangerous disease transmitted by ticks, annually Rospotrebnadzor publishes lists of territories of the Russian Federation endemic for tick-borne encephalitis, unfortunately, such information is not published for other infections. Tick-borne borreliosis (Lyme) is a very insidious disease, as it often proceeds latently, becomes chronic and leads to disability. Ticks infected with borrelia are found to a greater or lesser extent in most of the territories of the Russian Federation, as well as in the countries of Europe, Asia and North America. A common sign of tick-borne borreliosis disease at the initial stage is the occurrence of migrating annular erythema at the site of tick suction. In the southern regions of Russia, the most dangerous disease carried by ticks is Crimea-Congo hemorrhagic fever. There are other diseases, so if you feel unwell, see your doctor right away.
Q: I was bitten by a tick, two weeks have passed since the bite, I felt good, and today my temperature rose, what should I do?
A: Feeling unwell may not be associated with a tick bite, but tick-borne infections cannot be ruled out. Be sure to see a doctor.
Which doctor treats tick-borne encephalitis and borreliosis?
Treats tick-borne encephalitis and borreliosis infectious disease physician.
It is not necessary to donate blood for pathogens the next day after the bite of the parasite. Important: even if infection has occurred, antibodies in the blood are formed only after two to three weeks. To assess the dynamics of the body's immune response, two analyzes are assigned with a difference in time of delivery of 21 days.
Tick-borne encephalitis
Tick-borne encephalitis is a viral infection that affects the brain and spinal cord.It can proceed in various forms and most often ends with a person's recovery, but with the development of complications of various severity: convulsions, paralysis, paresis, blindness, hearing and vision loss.
After an insect bite, 8-22 days pass, usually 10-12 days before the first manifestations of the disease appear. In the early stages:
- feeling of weakness
- nausea,
- migraine,
- feeling of numbness of the skin in the head and neck area.
Tick-borne encephalitis can be acute, starting with a rise in body temperature to 39-40 ° C, which is observed for 2-10 days. Pains appear in the muscles, head, arms and legs. There may be clouding of consciousness, coma.
Tick-borne borreliosis
The causative agents of tick-borne borreliosis (Lyme disease) are carried by ixodid ticks. Borrelia, after entering the human bloodstream, can be in the body for years. In the initial stages, when the infection is detected during tests and by external signs, therapy with antibacterial agents ends in absolute recovery.
If, after infection, a person does not visit a doctor, self-medicates and diagnostics is carried out at the last stages, then the result of the disease is extremely serious, its complications are irreversible, and it is very difficult to achieve recovery.
Pathogens enter the body during a tick bite, which can be overlooked. Immunity, being activated for the formation of antibodies against borrelia, is not able to cause a complete suppression of the infection. Damage to body tissues occurs, the formation of immune inflammation, which destroys the heart muscle, nervous system and joints.
From a bite to the first signs of pathology, it takes up to a month. During this period, the skin and internal organs are absolutely healthy externally, in view of this disease it is difficult to identify.
The early stage is characterized by a period of active reproduction of Borrelia under the skin and their attack on the lymphatic system. General signs at this time are not specific:
- headaches with general weakness,
- fever up to 38-39 ℃,
- nausea with vomiting.
Sometimes signs of pathologies of the respiratory system develop with a cough, a sore throat, a runny nose.
A distinctive feature is changes in the skin in the area of the bite: there is swelling and soreness, redness and itching, in 75% of cases of infection, erythema is formed in the form of a ring measuring 20-100 mm or more. The site of the lesion may itch and burn, but it happens that it does not cause inconvenience. It lasts up to 30 days on the skin.
Important! Tick-borne borreliosis is not dangerous to others. You cannot get infected from a person with a disease.
The dangerous consequences of a parasite bite can be prevented if the tick is removed in a timely manner, seek help from a medical institution and, if necessary, undergo a course of treatment. It is important to remember that a sucked insect does not immediately transmit infectious agents. Time spent on the body increases the risk of contracting tick-borne encephalitis or Lyme disease.
Why ticks can be dangerous
In the conditions of the modern climate, insects become active already in the earliest spring and continue their activity until the first frost. Ticks freely fall on a person's clothes, look for a favorable place before the bite, and then dig into the body. Therefore, you need to be very careful, especially if you are often outdoors.
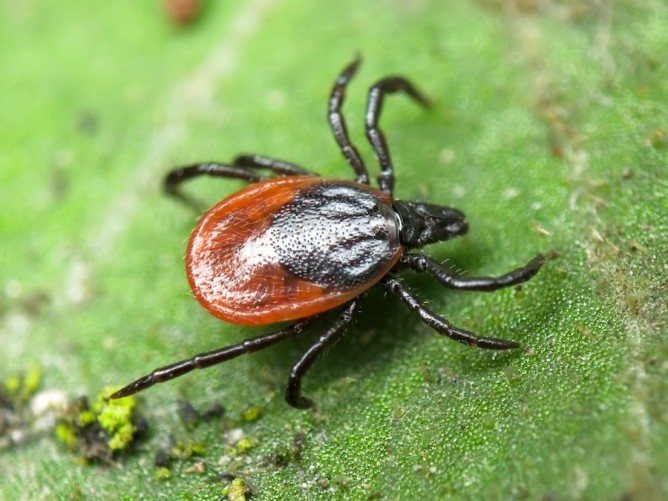


In our country, the most common forest tick
In the vastness of our country, one of the most popular species of insect is the forest tick, the second name of which is the taiga tick. It is considered the main carrier of such a terrible disease as encephalitis. This disease is dangerous because it affects, first of all, the central nervous system. Encephalitis is most often fatal if treatment is not started in a timely manner. Also, due to encephalitis, paralysis can occur, deafness, blindness can develop.The incubation period for this fatal disease is approximately 14 days. After this time, a person may suddenly feel fatigue, dizziness, weakness, nausea. Often the body temperature is elevated, muscle pain appears. These symptoms can go away for a short time, and then appear again, and in an already more severe form. The danger of this disease is that the death of brain cells begins, therefore, the earlier it is diagnosed and treatment begins, the more chances of a favorable outcome are.
In addition to encephalitis, ticks can be carriers of barreliosis, which not only affects the nervous system, but also disrupts the work of the heart. A tick bite can infect typhus, anaplasmosis, ehrlichiosis, fever, and also provoke severe allergic reactions.
The tick, sensing its prey, crawls onto clothes, but does not dig into the skin immediately, but looks for a more favorable place to bite. He is attracted to those places on the body on which thin skin, and it is easy to bite through: groin, armpits, collarbones, abdomen or back. Also, the tick can dig into the scalp or neck. A person does not feel the moment when the tick bites him, because the insect's saliva contains a substance that acts as a natural anesthesia. Further, the tick sucks blood, its body becomes ten times larger than its usual size. Infection after a tick bite begins to occur instantly, as soon as it is absorbed into the victim's body.


The tick is a carrier of many dangerous diseases.
First aid for infection
- First you need to remove the tick. This can be done both independently and with the help of a professional. It is difficult to get rid of an insect on your own. If you do not remove it immediately, then a white and then a red halo will form at the site of the bite. It is not recommended to eliminate the pest with your bare hands; you should take some kind of device with which you can carefully carry out this procedure. For this, a lasso pen or curved tweezers may be suitable, and a coarse thread will help, from which you need to make a loop for the tick. Use a twisting motion to remove the parasite from the skin. A special proboscis with hooks helps him to bite a person. It is the hooks that prevent the tick from being pulled out at a stroke. It has to be twisted and pulled to remove the proboscis from the wound, otherwise an inflammatory process may begin, aggravating the situation. After successful removal, the bite site is treated with a disinfectant, this is done so that suppuration does not begin. The wound is wiped with cotton wool soaked in alcohol or iodine. In this case, you should not apply a bandage. It is forbidden to water the tick with oil. This method is considered a popular method of getting rid of parasites, but you need to know that the oil will simply kill the tick, and it will remain on the skin. The likelihood of leaving the proboscis in the human body when removing a dead pest increases many times over. You can then remove the trunk only with the help of specialists. Most laboratories do not accept dead ticks killed by this popular method for analysis. Do not pour alcohol or sprinkle the parasite with salt, as this will also not help to get rid of it according to the rules.
- The pest should be taken to a medical laboratory for research. Experts will determine if the parasite was a carrier of an infectious disease. Based on the results obtained, a further action plan will be outlined.
- Emergency seroprophylaxis. The patient is injected with immunoglobulin to prevent tick-borne encephalitis. This must be done in the first 3-4 days after the bite, only then it will make sense.
- During the first 10 days, you need to be tested for infections. If the results are positive, go to the infectious disease doctor.