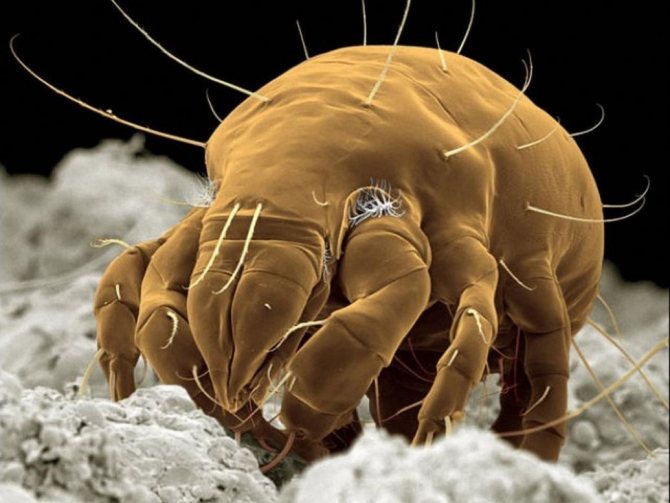
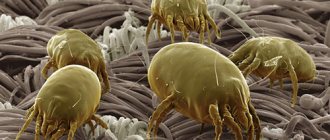
Are ticks dangerous in winter
When the temperature drops below + 3 ° C, parasites are not dangerous at all. Some of them remain awake, but they no longer pose a threat to animals and humans. They simply do not have enough strength to even cling to the victim's body with their paws.

Mites in winter
When the arrow on the thermometer drops below zero, the ticks are inactive, they hibernate, in which they will remain until more favorable weather conditions.
A small amount of snow or its complete absence, severe frosts will become fatal for parasites, under such conditions, up to 30% of both larvae and nymphs die. Adult sexually mature individuals freeze out by 20%. An important point will be that hungry ticks tolerate cold better than those that previously drank blood.
A tick bite during this period is possible only if the parasite has previously entered the dwelling and, gradually warming up, began to actively search for something to profit from. It is impossible to bring a parasite from the forest or park on oneself in winter; it will sneak into the house with sticks, hay, leaves from the street. However, there were cases during abnormally warm winters, when the tick attacked a person, the air temperature during this period was higher than + 8 ° C.
The activity of ticks directly depends on temperature indicators; + 18 ° С are optimal for their development. Lower temperatures make the tick sluggish and passive. Decrease in indicators to -15 ° C and below become destructive. With little snow in the winter and without proper shelter, the bloodsucker will die. Ticks live at a temperature of about zero, but you should not expect active action from them, their metabolism is practically zero.
Where do they live in winter?
Mostly, ticks live in forests and parks in winter, but not always. As soon as the air temperature gets low, they start looking for the nearest suitable shelter for themselves to sleep. If the animal brings the tick into the house in late autumn, it will overwinter there. There are several other sources where mites can appear in your home in winter. If you run a subsistence economy and stock up on hay or straw for animals for the winter, ticks also live very comfortably in such deposits in winter. Sometimes ticks hibernate in the bark of trees, which is why you can bring the tick into the house yourself on the Christmas tree or along with the firewood. True, in coniferous forests, these parasites rarely hibernate, because the absence of leaf cover reduces their chances of survival in a snowless winter.
Note! At freezing temperatures, the tick will not sleep, even if it is winter outside. Once in a warm room, these parasites come to life and resume their livelihoods, looking for food.
A little about the pest
It is quite difficult to remove spider mites. After all, it is not always possible to notice a small, 0.2 to 1 mm in size, brown or greenish-gray insect with the naked eye, not to mention its eggs. But the size of the damage caused by the pest is quite impressive, since the spider mite feeds on the cell sap of plants. An enzyme secreted from the salivary gland destroys the chloroplasts of plant cells. Why the leaves begin to turn yellow, dry out and eventually fall off. As a result, the plants stagnate and sometimes even die.
Most often, bushes and deciduous trees are susceptible to pest attacks: ticks settle on cherries, apples, plums. They often live on conifers. Cucumbers, seedlings, melons and gourds, cotton, ornamental plants in greenhouses and open ground can also suffer from massive attacks of plant parasites. The favorite target of the pest is roses. Of indoor plants, the spider mite yucca and orchid are very fond of, it is also found on ficus, cactus and lemon (decorative).
However, before looking for methods to combat a plant parasite, it is necessary to know what conditions are favorable for its spread, as well as at what temperature the spider mite dies. As a place of residence, arthropods select dry and warm places (the most comfortable for them is the air temperature above +27 degrees). When the air humidity rises, they experience depression, so that indoor flowers do not become a treat for the pest, they must be regularly sprayed.
During her short life, and the red spider mite lives for about 45 days, the female lays more than one hundred eggs. Of which, after a maximum of 5 days, young individuals are born. This fact should be taken into account, coinciding with the period of persecution of pests.
Recipes from the people
Despite the effectiveness of chemicals, many gardeners and summer residents prefer to use folk remedies for spider mites, the main advantages of which are safety and availability.
Decoctions and infusions
Herbal decoctions and infusions are widely used in pest control.
- Garlic (2 heads) is finely chopped, poured with water (1l), insisted for 5 days in a dark place. The resulting infusion is filtered, the same amount of water is added and used to spray the infected plants.
- It is good to remove parasites with mustard, the smell of which is very disliked by the spider mite. 60 g of dry powder is diluted in 1 liter of water, infused for 3 days.
- Onion peel (100 g) is filled with water (5 l), infused for 5 days. After that, the infusion is filtered and used to treat mite-affected plants.
- Dry or fresh alder leaves (200 g) are poured into 2 liters of water, boiled over low heat for 30 minutes. Then the broth is infused for 12 hours, filtered and used for spraying.
- Dandelion leaves and roots (100 g) are poured with hot water (1 l) and left to infuse for 3 hours. The filtered infusion is used in a similar way.
An effective effect in the fight against spider mites is provided by a soap solution (20 g of soap per 1 liter of water). It is better to use ordinary laundry or green soap to prepare the solution. It is necessary to wash the leaves on both sides with a cloth soaked in soapy water, preventing the composition from getting on the roots of the plant.
Sulfur tar soap (100 g of soap per 10 liters of water) can also be used to spray flowers and garden plants. The procedure is carried out 2-3 times a week.
I think that poisoning for cultivating garden crops is not the best option. I use soap and garlic solution periodically. In the early stages of plant infection, nothing better is needed.
Hydrogen peroxide and potassium permanganate
To combat spider mites at home, use a solution of hydrogen peroxide, which is prepared at the rate of 2 tbsp. l. (3%) means for 1 liter of water. Spraying is carried out once a week for a month, which allows over time to destroy the entire harmful family. A weak solution of potassium permanganate is used for soil cultivation.
Ammonia
Ammonia has similar properties. The solution is prepared in a ratio of 1 tbsp. l. 10 liters of water. The resulting composition treats the leaves on both sides, which will allow not only to remove ticks, but also to saturate the plant with nitrogen.
Afraid of cold water spider mites. It is necessary to put the plants under a cold shower every day for a week and the parasites will no longer disturb them.
To prevent the spread of pests on indoor flowers or seedlings, their regular inspection and compliance with the rules for caring for them will help: regular watering, timely weeding and feeding of plants, as well as the use of folk remedies for prevention.
Now the time of the year has come when even a tick can easily "blow" with the wind from an open window into an apartment. Those who have trees near the window / balcony are especially susceptible to this. Also, ticks can be "stray" from neighbors from above, because they are so light that they are carried by the wind like dust particles. They can be brought in with the newly purchased plant, if you do not first quarantine it.
The biggest problem is dealing with a tick, so, of course, it is better to prevent this matter.
I have not known problems with the mite for several years, since we moved to a new apartment, but this year I found a cobweb on a rose, and upon a detailed examination of the plants adjacent to it, I also noticed disgusting living creatures.
The clinical picture of allergy to household dust
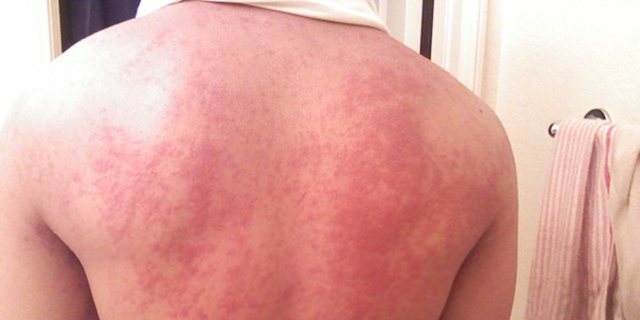

An allergic reaction to dust is rare. This reaction occurs only in predisposed individuals and is no different from allergies to food or cosmetics. Symptoms of a dust mite allergy on the skin:
- Severe itching that occurs immediately after or some time after contact with an infected surface. Itching can be localized in one area of the body or have a generalized character.
- Redness and rash. An itchy rash that rises above the surface of the body usually appears on the skin at the site of contact. The elements of the rash are prone to fusion with the formation of giant foci. After taking an antihistamine or on its own, after a while, the involution of the rash occurs without residual effects (pigmentation, scars, and others).
- Combing. Appear due to intense scratching of the skin during itching. Pathogens can enter the wounds, which leads to suppuration and worsening of the condition.
- Conjunctivitis. There is a sensation of a foreign body in the eyes, photophobia, lacrimation. Allergic conjunctivitis quickly turns into bacterial, which is dangerous for the development of complications (keratitis, uveitis, and others).


Attacks of bronchial asthma with allergies to household dust are seasonal: the process is usually exacerbated in the spring and autumn months, at night. The attack of suffocation is protracted, the frequency and duration of attacks decrease with a change of housing or regular wet cleaning.
Control methods


Preparations for treating the area from ticks
You can scare off with a cologne with a pungent smell, essential oils of citronella, lavender, and cloves. Sprays, aerosols are used - Gardeks, Reftamid Antiklesch, Raptor, Raid, Taiga, Off, Moskitol. Thoroughly spray clothes, some products are allowed to be applied directly to the skin.
To rid their land of parasites, to ensure safe outdoor recreation, smoke bombs are used - Quiet Evening, Whirlwind, Fomor. Use solutions for spraying grass, trees based on insectoacaricides. You can poison with the drug Tsifox, Sinuzan, Executioner, Medilis-Tsiper, Forsyth.
Mites are not massively poisoned, as this increases the chances of the death of natural enemies - birds, animals, insects. This explains the fact why there are a lot of ticks. Initially, after using chemicals, pests disappear, but along with them, natural enemies. Over time, the population of pests increases, but there are no “destroyers”. A situation arises when people say that there were no ticks before, now there are a lot of them.
Pests can become more active at the end of March, end their activities in November. Therefore, you should always remember about safety, but you should not be afraid of panic.Not all ticks are contagious; with timely access to specialists, the risk of the disease decreases or the disease proceeds without complications. In advance, you should protect yourself with clothes, drugs against ticks, get vaccinated when visiting dangerous territories and regions.
Will the wasps return to the roofed hive in the spring?
After winter, female wasps wake up. This happens when the air warms up to +15 degrees. Now they need to find a home for a warm period in order to settle their offspring in it. Their appearance will not be immediately noticeable. At first, the wasps will equip the home and actively reproduce. And by the middle of summer you can see a full hive of young individuals.
The natural instinct calls the females to return to their native land. Therefore, if the houses of striped insects are not destroyed in winter, while they are empty, then in the spring a new family will settle there. How to effectively destroy a hornet's nest:
- remove and throw away from home;
- burn;
- treat with "Dichlorvos" or boric acid;
- sprinkle with bleach or a special deterrent compound (Raptor, Getom, Alatar).
Important: even if the nest was physically destroyed, the place where it was located must also be treated with a chemical composition. Otherwise, the wasps can simply build new housing on the site of the old one in their usual territory.


You can facilitate the relocation of the swarm to a new location, away from people. For this, comfortable platforms are created, protected from bright light, wind and moisture. You can lure them with sweet fruits, water and sugar.
In nature, the wasp did not appear for nothing. At first glance, these insects are of absolutely no benefit, rather the opposite. But in fact, striped ones destroy clouds of pests in the garden and vegetable garden in order to feed the offspring. And they also promote the reproduction of flowers and plants, carry pollen. And if you do not make them angry and do not interfere during the period of conception of offspring, then the wasps can peacefully exist next to a person. The life cycle is short, but they do a lot in a year. Until the last days, they help the offspring to survive so that the food chain is not disrupted.
Where do they spend the winter?
After fertilization, instinct stimulates females to find suitable housing in which they will spend the winter. Wild wasps choose places that are able to keep warm. A reliable shelter is the bark of trees, in which insects gnaw holes. The walls of the winter dwelling were impregnated with saliva. From this, they are strengthened in order to further protect the sleeping inhabitants from bad weather and attack. After that, they fill it with food reserves for the winter, so that there is something to feed the offspring. Public wasps (paper wasps are their second name) accumulate nutrients throughout the summer in the body, and in winter they do not wake up for snacks. Wasp shelters in winter often include old tree stumps, stocks of firewood stacked for building boards, and wooden decks under the roof. Slots in the walls of residential buildings, which are regularly heated in winter, are also suitable.
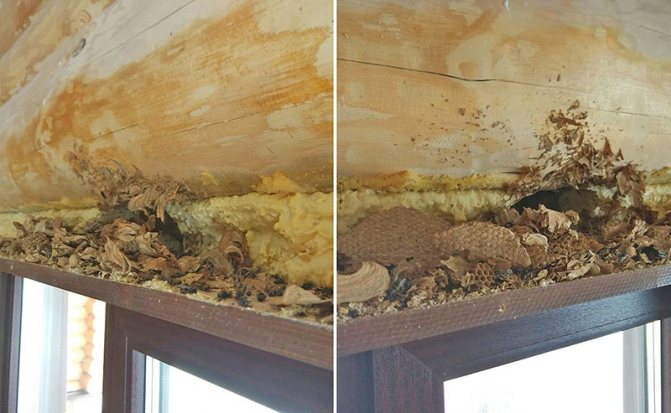


It's good if a snowy winter comes. The wasp shelters are covered with snow and the females will calmly survive the cold. But if the weather is rainy, water gets into the holes and insects die.
Expert advice: to get rid of these pests on the site, you must try to find winter shelters and destroy. Because if this is not done, but simply to destroy the empty nests, an unpleasant surprise may await the owners in the country house in the spring.
Diapause in ticks
Winter is not a typical time for tick activity. In the Moscow region and temperate climatic zones, the seasons of ticks are spring and autumn. A temperature of about 20 degrees Celsius and an air humidity of 80% are the most favorable conditions for the reproduction and life of ticks. When it gets too hot or too cold, their activity subsides. In frosts, ticks completely hibernate, the so-called diapause.
In hibernation, all metabolic processes in the body of an arthropod slow down. In this state, he can be up to 3 years. But hibernation usually lasts for several months. It begins with the onset of the first frost, and ends by the end of March, when the above-zero temperature is recorded.
As soon as it gets colder, the parasites choose a place to hibernate. They usually hide in the grass, under leaves and branches.
If the winter comes out with little snow and frosty, an insufficiently covered tick may die, so they approach the choice of a wintering place thoroughly. Once a safe hiding place is selected, the tick falls asleep and enters a phase of its life called diapause. With diapause, the tick becomes less sensitive to cold, reduces the amount of oxygen consumed, and the need to feed and reproduce is lost. Activity returns to ticks in early spring and their first victims are small rodents that are found in the forest.
How insect populations are measured
In order to better understand which periods are the most dangerous, you need to know the stages of a tick's life: from the larva it passes into a nymph, then into an adult. At the first stage, the larva drinks the blood of small creatures, at the second stage, the nymph hibernates and only in the spring feeds on the blood of small animals, falls asleep again until next spring and wakes up already ripe. Therefore, there are such years (approximately every three) when there are especially many mature ticks.
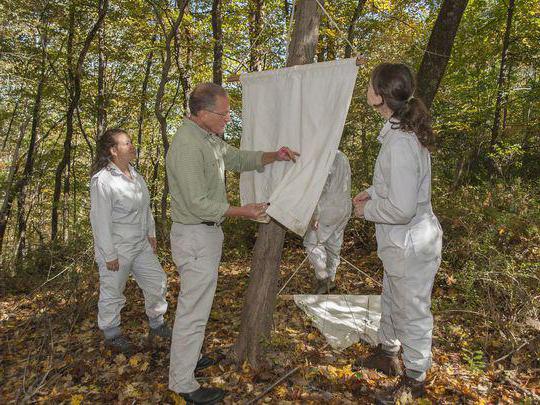
The tick population is measured to determine how dangerous the month will be using a flag clock. They take a piece of white matter about 40 by 70 cm, and place it in thickets or shrubs, so that, by the number of insects that have attached themselves, they can determine the rate of their reproduction.
It is difficult to say for sure whether ticks are dangerous in September, since the level of air humidity can change, but the threat always remains and protection means cannot be neglected.
Previously, only a few people visited forest areas: woodcutters, geologists, foresters. Today, thanks to the frequent visits of people and pets, the tick has reached urban green areas.
Where do mites come from in winter:
1. Winter thaws are above zero degrees.
For example, a couple of days ago, on January 26, it was raining for half a day in Belgorod! This means that for several days our air temperature was positive.
Veterinary parasitologist Sergei Konyaev warns that thaws above zero can lead to tick activity on thawed patches, where the ground is bare, uncleaned foliage is visible and last year's grass peeps out.
2. Areas in which ixodid ticks can maintain their activity almost all year round.
An example is the territory of heating mains. In such places, stray dogs are especially fond of huddle. which then carry ticks around the city.
3. Items brought from the street into the heat (apartment).
There are a lot of options. We can bring a Christmas tree, a bag of potatoes, or a bucket of soil for seedlings into the house, in which a sleeping tick can hide. This is a matter of chance!
Once in the warmth, he will wake up and want to "refresh", sucking on you or your pet!
4. Use of hay and straw.
Repeatedly I met stories about how dogs were insulated with hay in winter and about how puppies lived on a bed of straw, in which ticks hibernated. Warmed by the warmth of the dogs, the ticks came out of suspended animation and bit the animals, infecting them with piroplasmosis.
As a result, the dogs died, and the owners did not even have time to figure out what was going on ...
5. Ticks can "come" into the house on people's clothes or dog hair.
Cases when a half-asleep tick caught on the clothes of a hunter walking in a sunny meadow in the forest or on the fur of a dog lying down to rest on a thawed patch during a walk are, of course, isolated. But they are also possible!
Having arrived, like by bus, in a warm apartment, a hungry tick can finally wake up and take advantage of the situation by biting your dog.
Now you know that ticks can also "appear" in winter, in connection with which we want to give
How to clean the tree from bugs, spiders and ticks?
In the central part of Russia, the weather is relatively warm for winter, Euro-winter, therefore, when placing live spruce at room temperature, aphids, bugs and other insects will perceive it as the onset of spring.
You may not believe that ticks can inhabit a Christmas tree, but before installing in the living room, shake it out well above the bathroom and see how many small insects and their larvae fall off it. It is better to keep the spruce in the bathroom for several hours so that the insects that have come out of hibernation cannot scatter around the house.
Second tip: clean the bark from the bottom of the tree trunk, preferably outdoors or in a bathtub. Shake the tree well outside.
Precaution won't hurt. Do not treat the spruce with such a strong-smelling insecticide like Dichlorvos or the like.
Such an aroma will ruin the whole holiday mood, and the plant will dry out ahead of time.
Do not treat the spruce with such a strong-smelling insecticide like Dichlorvos or the like. Such an aroma will ruin the whole holiday mood, and the plant will dry out ahead of time.
The previously mentioned scientist, Bjarthe Jordal, said:
How to treat a plant for a spider mite? Means of combating spider mites.
Of course, there are a large number of drugs that guarantee almost complete elimination of spider mites - these are the so-called acaricides and insectoacaricides. I will make a reservation right away that they are effective not only against ticks, but also against other insect pests.
These drugs are both chemical (for example, Actellik and Fufanon) and biological (for example, Fitoverm and Akarin). Preparations of a chemical and biological nature have different active substances, but the principle of action is the same.
Both drugs are used three times, with a break of 5-10 days, because during the initial treatment, the poison kills adults, but the eggs are resistant to the substance and after a while they hatch from the eggs and continue to exist on the plant.
But what to do, because we are talking about indoor plants, how then to process the plants if the tick is still wound up on them?
general information
Despite the fact that insect activity decreases in summer, it increases again at the end of August. It should be remembered that in the fall. The duration of the second wave of parasite activity depends on weather conditions. If the autumn is warm and humid, then in November the ticks do not hibernate, but hunt their prey.


Habitat
The common habitats of parasites are mixed and deciduous forests, where there is high humidity. These insects prefer dense undergrowth and tall grass. But in recent years, they began to move into the urban area, and now they can be found in parks and forest belts, and sometimes in garden plots. In the Moscow region, ticks are often found in the fall.
Hiding in the grass and bush branches, parasites await their prey - animals and people, because they feed on their blood. Insects have a pronounced sensitivity. They sense the approach of a person at a distance of 10 meters. The tick does not descend on top of its prey, but clings when the victim passes by.
Insect activation starts early due to the mild winter. Their life cycle is accelerated thanks to the hot summer. The increased growing season affects the growth of the mite population and their activity in September and October.
Activity in the fall
The presence of an average level of humidity is the main condition for the spread and reproduction of mites. High humidity or drought is not suitable for them. The activity of females falls on the period of spring until the first days of July.Then comes a period of relative physiological rest, which lasts until mid-August. A new round of tick activity begins at the end of August and reaches its peak in September until October, and in some places even until November. But in late autumn, ticks go into hibernation.
Insects parasitize animals and are carriers of the tick-borne encephalitis virus. Usually preventive measures for destruction in early spring. But individuals who survived after processing forest areas begin to actively seek food in the fall. In places where treatment has not been carried out, there are especially many parasites.
Indian summer in October is another reason for their activity. Ticks are as dangerous in the fall as in the summer. Until the first cold weather, they are looking for their prey. They will begin to fall asleep with the onset of frost, when the thermometer shows below 5 degrees.
How to dress in September for a nature walk
The first rule is that clothes should be closed. The legs need to be tucked into the socks, there is no need to wear flared trousers. It is worth choosing a jacket with a long sleeve. It is necessary to exclude clothes with cutouts and buttons. If you have long hair, you need to collect it. We must not forget about the hat even when it is warm, as a means of protection it is necessary. High boots made of rubber and an insect net are required.
What should be the behavior in the autumn in the forest:
- you cannot climb into tall shrubs and grass unnecessarily;
- follow the trampled paths;
- avoid dry tall grass as a place of possible accumulation of ticks;
- be in the forest during the day, avoiding the morning and evening hours.
After arriving home, it is necessary to examine the body for the presence of sucked ticks. In women, parasites often target the chest and neck, in men, the groin and armpits. This is due to insects' instinct for warm places well supplied with blood. Shake the clothes, comb the hair with a fine comb.
Tick activity by month
The vital activity of ticks depends on the area of residence. In the southern regions, where the temperature does not drop below zero degrees, they can exist and reproduce all year round, reducing or increasing the degree of activity depending on weather conditions. In most of the territory of Russia, they become more active already during the spring warming up to 3 - 5 degrees.


The peak of tick activity falls on a temperature regime of 5 to 20 degrees, in the middle lane it is the end of April, May and June. If a not hot summer is established, then the period of insect activity does not stop until the onset of cold weather. Under the normal course of the temperature regime, the second wave falls on the time of the heat leaving, that is, September, early October.
Thus, the period of tick activity in Siberia, Karelia, the Moscow region or other regions is not so much a calendar phenomenon as a weather one. And if comfortable (approximately 85-95%) humidity is added to warm, cool weather, this will be ideal for reproduction, and therefore for tick feeding.
An adult tick can go without food for three months to a year. The activity of ticks in the heat drops sharply and can temporarily disappear to zero. Already when the air temperature reaches 20 degrees, the process of their vital activity begins to subside noticeably.
External features of ixodid ticks
Ixodid ticks pose the greatest danger to humans. They are carriers of tick-borne encephalitis and borreliosis. All over the world there are over 6.5 hundred species of them. However, on the territory of Russia, most often there are only two:
- taiga;
- European forest.


Both species are united under one name - pasture.
Encephalitis is an acute viral disease that affects the central nervous system. Its carrier is the taiga tick. The European forest tick is also capable of infecting humans with encephalitis, but in a different form, which proceeds more easily.
The body of ixodid ticks consists of a trunk and a head. Its length in a hungry state reaches 4 mm.When this creature sucks blood, the body is able to grow up to 4 cm. The female is somewhat larger than the male. You can distinguish between heterosexual individuals by the shield located on the back. In females, a third of the back is covered with it, the back of males is completely covered by it.
The pliers have four pairs of legs. Three pairs of legs are intended for movement, the uppermost pair is for attachment to the victim (animal or human). Only females suck blood. Full saturation occurs in 7-10 days. Males can stick to humans, but not for long. They do not pose a threat of infection with encephalitis.
Ticks breathe through the breathing plates located at the back. They have no eyes, but arachnids are perfectly oriented thanks to their sensitive sense of smell. Tick saliva contains a special secret that has an anesthetic effect. The victim may be unaware of the danger for a long time.
Viruses are found in the salivary glands of arachnids. They enter the human blood along with saliva.
The life cycle of ticks
Ticks belong to the class of arachnids, their torso consists of two parts - the head and the torso. Small parasites have 6 pairs of limbs, the front ones are modified into pincer-like appendages. The rest of the limbs are used for movement, each leg consists of 6 segments, ending in claws and suction cups, which allow it to be held on the host.
Among the many species, ixodid ticks are dangerous to humans and animals. They are carriers of viral diseases - tick-borne encephalitis and borreliosis. Adults are divided into two sexes - the male is small (2-2.5 mm), his back is covered with a chitinous shell, the female reaches 3-4 mm, she is covered by a shield by a third. After drinking blood, the parasite increases several times. After mating, the female lays up to 17 thousand eggs.
The development of arthropods includes several phases:
- egg;
- larva;
- nymph;
- an adult (female or male).
Attention. Blood-sucking parasites move to the next stage of development after feeding. In the process of a bite, a virus of encephalitis or other disease enters the bloodstream.
Security measures
The activity of ticks by month is very conditional, so you need to make it a rule to take precautions at any time you are in nature. Although isolated cases of tick attacks in the city are also observed
- Dress properly before going to the forest or meadow. Consider your wardrobe to cover all tick-borne areas. The sleeves of the shirt should be long with fastened cuffs, it is better to tuck the trousers into high boots or boots, and put on an adjoining hood or other headdress covering the neck.
- Treat the places of clothing that the tick can catch with a repellent several times during the walk. These are, first of all, legs: trousers, boots. Remember that ticks hunt, sitting in the grass, do not rise to a height of more than one meter. They are inactive, and in their entire life they crawl only a few meters. But when caught on clothing, they will travel through it in search of an exposed area of skin.
- Examine yourself periodically. It is easier to see a tick clinging to clothing if it is light in color.
What is the danger to humans and animals posed by wintering parasites
Most people believe that ticks lie in wait for the victim, sitting in a tree, and they fall on a person from above. However, these creatures are so small that it is very difficult for them to climb to the height.
The mite is often found on the neck and head
- When a tick hits a potential feeder, it begins to move along it with the help of claws and suction cups.
- He is looking for an unprotected area of skin to which he can suck. In a person, the most endangered places, which, when examined, pay attention first of all, are considered: the neck, chest, armpits and inguinal cavities.
- Having sucked in, the tick secretes an anesthetic substance. Therefore, the bite is usually not accompanied by pain symptoms. Often the victim does not even notice that a tick has clung to her. When a few hours have passed after attachment, its head will be completely immersed in the skin, and the body will swell from the sucked blood. The salivary glands of a tick are exactly the place in which the causative agent of encephalitis or other disease can be contained. Therefore, if a tick is infected, then the pathogen enters the bloodstream along with its saliva.
Protection methods
September is the time for collecting mushrooms, but it should be remembered that insect activity begins during this period
Therefore, when going for a walk in the forest, you should take precautions to avoid an unpleasant meeting with the parasite.
How to dress:
- Clothing should be of dense fabric and cover arms and legs completely.
- At the bottom of the legs on the trousers and on the sleeves of the jacket, dense elastic bands are desirable.
- Shoes should be chosen one that covers the feet completely with the ankles.
From time to time, clothing should be inspected for ticks to avoid the danger of ticks crawling under the collar or other parts of the suit. This inspection is recommended every 30-40 minutes. This measure will allow you to detect the parasite before it bites a person. It is recommended to choose light and monochromatic clothing, because insects will be clearly visible on it.
During periods of increased activity of ticks, it is better to avoid places with dense grassy vegetation. It is necessary to adhere to paths and trodden paths. All these measures will reduce the likelihood of the parasite getting on the skin.
Before walking in a park or forest belt, it is necessary to treat clothes and exposed areas of the body with chemical protection against ticks. They are divided into three groups by the method of exposure:
- killing, which include "Tornado-anti-mite" and "Refamid taiga";
- deterrent, the best of which are "Dipterol", "Permanon" and "Pretix";
- combined, including "Mite-kaput aerosol" and "Mosquito-spray - a special remedy for ticks."
Before using chemicals, you should carefully study the instructions for their use, especially paying attention to the conditions for reapplication. There are factors that can affect the duration of such funds, significantly reducing it.
This could be due to wind, heat, rain, or a particular person's sweat pattern.
Following simple recommendations and observing preventive measures will help maintain health and make it possible to enjoy a walk in the forest without unpleasant consequences.
Folk remedies in the fight against spider mites. My processing scheme.
Those who, like me, were looking for other ways to fight, I think more than once have seen recipes against spider mites based on laundry soap, onion peels, garlic or even dandelion.
You should not be skeptical about these methods, since they help many people quite well, and my scheme is based on one of the above components.
Let me remind you that chemistry for me is not an option at all, and I was ready for anything, just not to poison myself and my household with her. Therefore, at first, I tried to follow the advice from the forums and having treated the plants with soapy water, wrapped them in a bag for several days (so that the solution would work), but after such treatment, the ticks crawled out again. It was foolish to hope that I would get them out the first time, but I still wanted to believe.
I will not write to you about my sufferings and different options, I’ll move on, perhaps, to the scheme that I reached by trial and error.
There are a lot of plants in my collection, so I had to ask for help in implementing it.
All you need is laundry soap, water, and a soft sponge. No packages needed!
- Transfer the infected plants to the tub.
- Be sure to remove and wash the curtains asthey come into contact with infected plants and may also harbor these pests.
Since I had a lot of plants, I had to wash in parts: while one portion was washing in the bathroom, the rest were waiting nearby. Thus, I treated for ticks: drymiopsis, ficus, hibiscus, indoor rose, sour cherry, begonias, fuchsias, chlorophytums, tradescantia, lemons and even mangoes.
Drimiopsis is completely soapy. Even crumbs of fuchsia easily survived soapy procedures. The fuchsia buds were not damaged by the soap treatment, and the fuchsia bloomed a couple of days later.
I wash it off like this: I lay the plant neatly on its side, and wash off the soap with a sponge, I also wash off the pot and the top layer of soil (then you can add a new one). I carry out such manipulations with all plants, except for thick-skinned ones, which cannot be washed (for example, not my haworthia, because water must not be allowed to enter the outlet). Plants that cannot be washed (I have succulents), I treat them with high quality alcohol, wash them in a pot with soap.
But what is the scheme? Everything is very simple. Remember, above we analyzed the life cycle of a tick?
So, after a week there is a chance that mites that have not been washed off will hatch, so you need to repeat the treatment of plants and pots. This time I no longer wash the curtains or wash the windows, I just wipe the windowsill a little with soapy water. And I cover the soil with cling film so that the soap does not get on the roots.
The cling film prevents soap from getting on the soil and roots.
It is much easier to wash off the plants, because the film protects the soil from soapy water.
Natural factors that have a negative impact on the survival of parasites in the cold season
The most common reason for the death of the forest tick population is the early November frost, when the thickness of the snow cover is minimal or absent altogether.
Snowless winters reduce the number of ticks in the natural focus by 60-70%. It takes 2-3 years to restore the population to the previous level (under favorable climatic conditions).
Plots of meadows covered with short herbaceous vegetation do not provide reliable thermal insulation of places where ticks hibernate; therefore, pasture ixodids, with the onset of cold weather, penetrate deep into cracks in the soil and burrows of rodents.
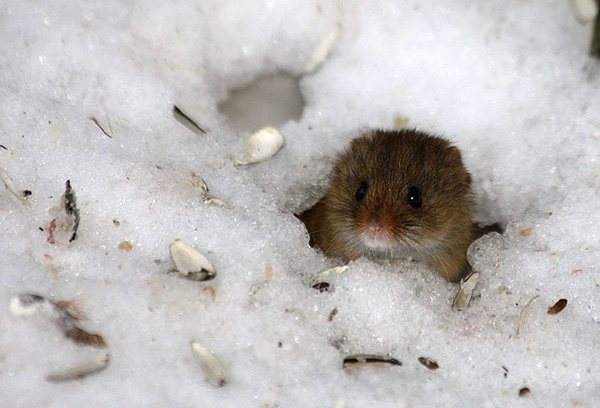


Excessive soil moisture significantly impairs the thermal insulation properties of tick habitats. Heavy autumn showers, followed by frosts, often lead to hypothermia and death of parasites.
But the greatest natural danger to the wintering of parasites is represented by thaws with complete snow melting and subsequent frosts. Such phenomena cause a significant decrease in the thickness of the snow cover and freezing of the soil to a great depth.
Is it possible to protect yourself from tick-borne encephalitis?
Prevention of the disease consists in carrying out anti-tick protection of a person and increasing the resistance of his body to the pathogen. Anti-mite protection methods are divided into individual and collective.
Personal protective equipment.
When visiting the forest, it is necessary to strictly observe the conditions that prevent the crawling and penetration of ticks under the clothes. For this purpose, you need to wear special protective clothing - a jacket with a hood and trousers made of dense fabric. You can turn ordinary clothes into protective ones, if you tightly fasten the collar and cuffs, tuck the shirt into trousers, and trousers into boots or socks, put a hood over your head. But it is difficult to work in such a suit in hot weather. And yet, where it is urgently needed, such clothing should be worn.
During the day, it is necessary to carry out thorough self-and mutual examinations in 1-2 hours. This measure is simple, reliable and accessible to everyone.
When examining, special attention should be paid to the hairy parts of the body, skin folds, auricles, armpits and inguinal cavities.Returning home, you need to carefully examine all the folds and seams of clothes, as ticks can crawl into them, which did not have time to suck.
And, only after making sure that there are no ticks, you can go into the room. It is better to leave the suit, boots outside the living quarters. It is recommended to change the underwear at home, and remove the removed from the living rooms to the balcony, to the shed, or fill it with warm water and wash. Nice to take a shower. These simple and effective measures are available to everyone.
Well, if, despite the observance of precautionary measures, the tick still sucked, how to remove it together with the head? To do this, you need to lubricate the tick and the area of the skin around it with cream, petroleum jelly, vegetable oil, any fat, and after 30-60 seconds, throwing the tick back onto the dorsal side, grab it near the skin with tweezers (you can use two fingers - thumb and forefinger) and fast, pull out with a sharp movement. Fat closes the respiratory openings - and the tick relaxes the muscles of the proboscis for a while
It can be painlessly removed together with the head, which is very important, since the rest of the tick's body can cause an inflammatory process
PI Marikovsky proposes to use a thread to extract the tick: they tie up the front end of the body at the very surface of the skin and, pulling the ends of the thread up and to the sides, pull out the tick.
If the head of the tick comes off and remains in the place of suction, it is removed with a pre-calcined needle or pin. The wound is disinfected with iodine.
All mites found on the body, non-sucked and removed from the integument of the skin must be destroyed: they are placed in any disinfectant solution (lysol, kerosene, alcohol, etc.) or burned.
Never push the ticks with your hands! Splashes of the cavity fluid and salivary glands of the tick can get on the mucous membranes of the mouth, nasal cavity, small wounds on the skin of the hands and cause tick-borne encephalitis. After removing the tick, wash your hands thoroughly.
The implementation of these simple and accessible techniques to everyone will help to reliably protect yourself from tick-borne encephalitis.
Along with protective clothing, there are special deterrent chemicals called repellents. DEET (diethyltoluamide), carboxyde, kuzol, etc. have proven themselves well. DEET is available in the form of a 40% solution in alcohol, cream, and also in an aerosol package. To protect humans from blood-sucking arthropods, repellents are applied to open skin areas - face, neck, hands.
Recently, another, more convenient and safer method has been increasingly used - soaking clothes and head covers with repellents. On clothes, the drugs retain their repellent properties much longer than when applied to the skin. It should be remembered, however, that there are negative reactions from individuals to repellent odors. Some of them irritate integuments, mucous membranes and cause other side effects. Therefore, it is necessary to use repellents, strictly observing the rules for their use.
Removing the parasite
If, after going into the forest, a tick is found on the body, it is necessary to remove it. The main thing is not to panic and do everything right. Pressing or pulling is strictly prohibited. The best option is to contact the clinic for qualified help.
It is impossible to determine by the type of insect whether it is a carrier of the disease. Therefore, you should put it in a bag and take it to a medical laboratory for research in order to make sure that it is not a source of infectious disease.
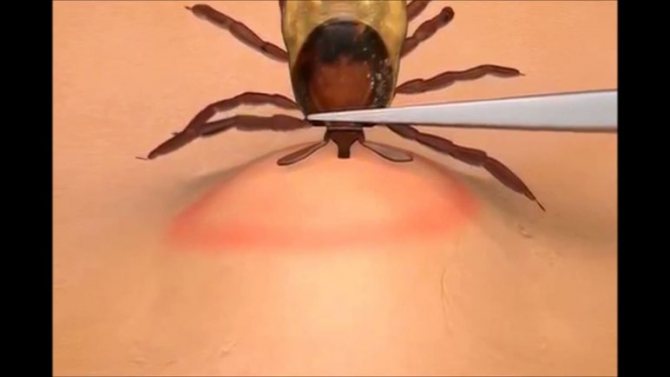

You can also use tweezers to remove the tick. After the procedure, the wound should be treated with a disinfectant solution. If a situation arises when the insect's proboscis remains in the bite site, nothing else needs to be done. The remains will be excreted by the body itself. After removing the tick, you should wash your hands with soap and water.
If bitten by a tick. First steps
About 13% of ticks are capable of infecting humans.But if, nevertheless, you found an insect on yourself or in a pet, then it is visually impossible to determine whether it is dangerous or harmless. Taking the insect's body out of the wound with a rotating motion, make sure that there is no head left inside. Otherwise, the infection will continue. Wash the wound with a disinfectant solution, and take the removed tick to the nearest department of the Rospotrebnadzor laboratory. Only a laboratory examination can establish the truth.
Within 24 hours after the bite, an injection of immunoglobulin should be given there, which will serve as a prophylaxis against encephalitis. If more than 48 hours have passed since the bite, the injection is useless. The drug is administered intramuscularly, according to the doctor's prescription, who selects the dose of the drug individually.


Winter is not tick time
With some certainty, we can absolutely say for sure that winter for a tick is a time of hibernation and waiting. Such is the nature of this blood-sucking parasite, there is nothing to be done. Tick activity begins in spring, maybe in early-early spring, when even in February it suddenly becomes +10, and at night the thermometer does not drop below zero. Only warmth allows the tick to start its activity. As long as the frosty, dank and dry weather persists, the tick can be almost not afraid. Why almost? Well, firstly, spring does not come on schedule throughout our country, and it is not always as cold everywhere as in the central part and in the north. It is likely that in some southern regions ticks will annoy most often and most of all. Especially when the weather changes from week to week.
The tick is a parasite, arthropod blood-sucking, feeding on the blood of animals and people. If we talk about the very ticks that annoy us and our pets, then we definitely mean the Ixodid species. Although there are a lot of tick species, it is the Ixodidae that are the most dangerous and numerous.
The period of activity of ixodid ticks, in temperate climates, affects the spring-summer-autumn. Depending on the weather, ticks can be most active in April (sometimes in February) and also in March. At the moment of awakening, they will search for food with all their might. Further, the activity will systematically increase with the growth of the tick population, but by the middle of summer it will subside. Ticks dislike not only frost and cold, but also heat.


Their main comfort zone: air temperature from +5 to +15, as well as low humidity. As soon as the air becomes dry and the air temperature warms up to +20 and + 30 degrees, the population of ticks will begin to decline sharply. Literally in a week of heat, their number will sharply drop to 10-15% of active individuals. As a rule, by mid-July there are almost no ticks on the fields we are used to, sunny paths, etc. All remaining individuals are in places that are still humid and less warmed by the sun: near ponds, in trees and in tall grass, near hollows and forest edges, where the sun's rays almost never break through the foliage.
Nevertheless, the activity of the tick is maintained throughout the spring-autumn period. Even in autumn, when the temperature drops again, the vegetation withers, and at night it can be too cold, even at this time the ticks are active. Only with the onset of frost, as well as at low night temperatures, their activity subsides by almost 99%. In rare cases, bites are recorded in December and November, but often in climatic zones in which there are no severe frosts and early cold weather. By the way, ticks are also in resort places. In Turkey, ticks are active for a long time, so all vacationers should be careful.
Tick bites in winter
However, tick bites are sometimes reported in winter. How this happens is not clear to anyone. In some cases, the tick was brought home by hunters and fishermen who returned from nature in the autumn. He was messing around for a long time, and then he still sucked. Bite cases are reported in those who keep large greenhouses in their summer cottages.People not only grow vegetables, but just keep a small home garden for the soul, so to speak. It does not occur to them that even such a tiny flower garden can become a habitat for a tick.
But how he got there is an even more complicated question. In general, scientists agreed that the tick can be brought along with the earth or grasses that summer residents drag home. The individual was in captivity and hibernation for a long time, but when it came to life in the home garden, it immediately fulfilled its natural role - it found a victim and sucked. There are also cases when ticks enter homes with the help of animals. There are no statistics on this, but some dog owners complain that they found a tick on their pets already far past December, when it was snowing in the yard for a month.
* * *
In winter, the tick is inactive. His time will come in spring and before autumn, but all the frosts and snowfalls will make him hibernate. You can get a tick bite in winter only if this parasite somehow settled in your home and all year round heated garden, or when it “came on the dog” or was lying around in clothes. Otherwise, winter is the safest time.
⇒ Our knowledge base:
- Tick removal devices.
- Ticks in Europe?
- Ticks in the forest.
- The main types of ticks in the Russian Federation.
- Types and varieties of ticks: list
Winter diapause
Many people know that the time of activity of parasites falls on May - June, but are there ticks in winter? The onset of cold weather forces them to seek shelter and freeze until spring. Warm and humid places are a favorable environment for bloodsucking. They settle in ravines, tall grass, more often forests. They do not tolerate hot dry air, so activity decreases in summer. With the onset of frost, the parasites hide in the upper layer of the soil, under the leaves, and clog under the bark.
Diapause manifestations
In the cold season, the life processes of ticks are significantly inhibited. A decrease in metabolism allows them to survive a low temperature and lack of nutrition without consequences. The parasite freezes at the stage of development at which it was in the fall. Most larvae, not finding a host before frost, will not become nymphs until next year. Only in regions with hot climates, the life cycle of ticks is 1 year.
Where do ticks hibernate? Their favorite wintering place is under the cover of leaves and grass, where the temperature does not drop to negative values. The thicker the forest carpet, the more the blood-sucking parasites will survive and wait for the warm April days. With the onset of a stable temperature above +3, ticks come to life on the first thawed patches. The activity of individuals depends on weather conditions and terrain. General warming increases the season in which parasites are dangerous to humans and animals. Sucking individuals are removed from the dogs in October-November.
At the beginning of autumn, females, having drunk blood, crawl into the thickness of the deciduous litter to lay eggs. This process, depending on the temperature, begins in 2-3 weeks. The amount of clutch directly depends on the volume of blood consumed. Eggs can remain until spring or small larvae have time to appear from them. They stay overwintering in the foliage where they were born. The activity of parasites will manifest itself in the spring with the appearance of rodents - voles, wood mice.


Ixodid ticks
Spider mite science
Spider mites are rather small arachnids of the spider family. The largest specimens reach approximately 1 mm in length (0.3-0.5 mm on average) and have an elongated-oval body, the color of which depends on the season.
Females of summer generations are grayish-yellowish-green, with dark, sometimes almost black, spots on the sides; winter diapausing females have an even orange-red color.
Fertilized females hibernate under fallen leaves and plant debris, in cracks in the soil, crevices of greenhouses, greenhouse trees and greenhouse frames.4-6 days after emergence, the overwintering females of the tick lay (scattered) very small (with the naked eye it is difficult to see without a magnifying glass), spherical, greenish-yellow, translucent eggs.
Adult females live 2-4 weeks and during this time they are able to lay up to 100 eggs. After 2-4 days, they give birth to larvae 0.13-0.14 mm long, with a rounded body and three pairs of legs. They feed in the same way as adult ticks.
It should be noted that eggs can be kept alive for up to 5 years in the soil, in the crevices of window frames and in the windowsill. At a temperature of 24-28 ° C and low air humidity (35-50%), ticks multiply very quickly.
At high relative humidity (85-90%) and temperatures above 32 ° C, 25-30% of the eggs die. For the development of one generation of the pest, it takes from 7 to 20-22 days, therefore, up to 20 generations of the pest can develop in greenhouses per season.
Usually the mite settles on the underside of the leaves, entangling them with the finest cobwebs. The pest pierces the leaves and sucks the juice out of them. The lesions are clearly visible on the upper side of the leaf, separate small whitish dots are formed in the feeding places of the ticks, which later merge and discolored areas (marbling) appear on the leaf blade. First, part of the leaf turns yellow, then the whole leaf, and after a while, if measures are not taken in time, the heavily damaged leaves dry up and die off. Plants stunted and prematurely end the growing season.
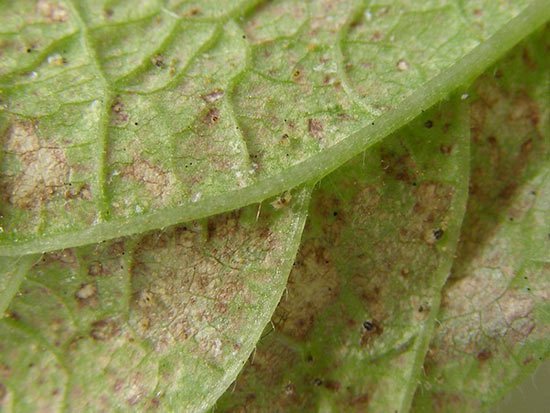


Signs of spider mite infestation
Ticks are also dangerous because, under unfavorable conditions, females burrow into the soil or secluded places and fall into diapause. At this moment, all their vital processes are inhibited. But as soon as favorable conditions are created, ticks come out of this state, intensively develop and multiply. These processes are accelerated by warm and dry air in the greenhouse.