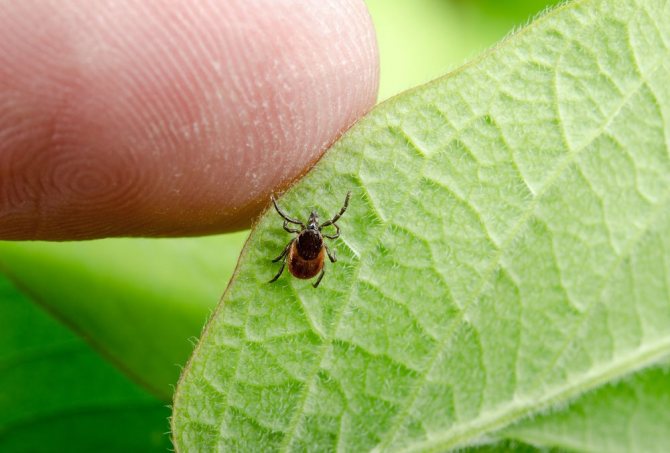
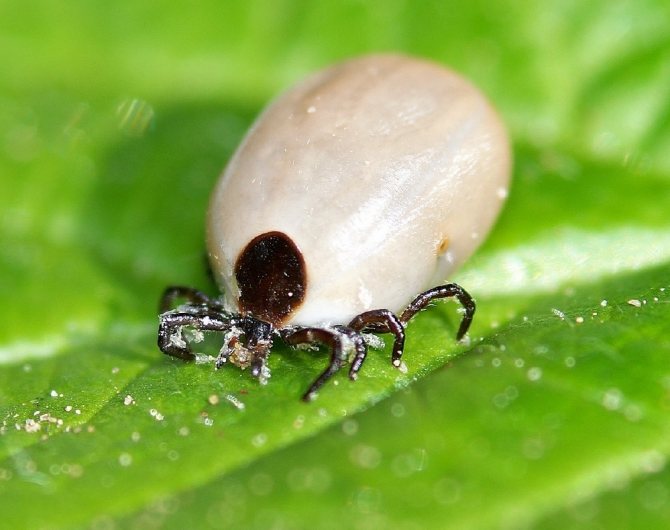
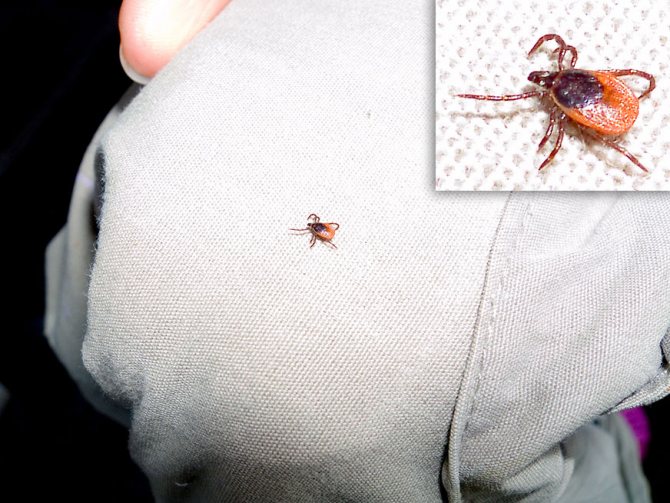
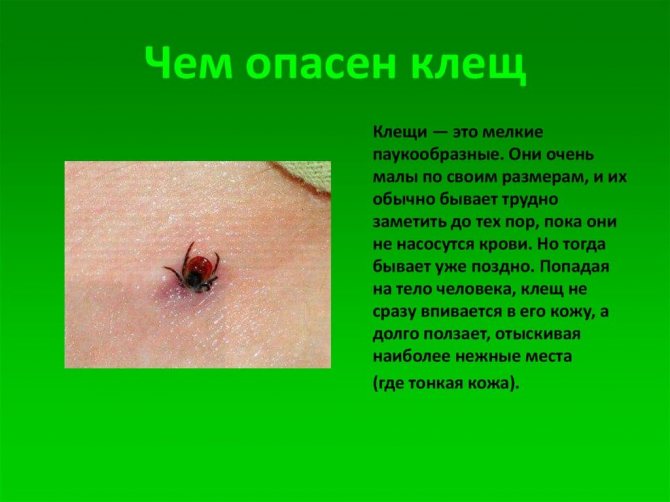
Encephalitis is one of the most dangerous viral diseases that is still incurable. The vector of encephalitis can be any "reusable" bloodsucker, who first drank the blood of an infected animal, and then "had a snack" by a person. But the main danger is carried by ticks, popularly called encephalitis. There is no separate type of "encephalitis mite" in nature. The main carriers of this disease among arachnopods are two types of ixodid ticks at once: dog and taiga.
Description of ticks
Many people think that ticks are insect species, but actually ticks are arachnids. As mentioned above, there is no separate species that can infect a person with such a dangerous ailment, therefore there is no image of it either.
The tick is called "encephalitis" because it is potentially dangerous to humans. Based on this fact, other species can be considered dangerous as well. If the facts indicate otherwise, then the risk of contracting the virus is minimal.
Consequences of a bite
The structure of the sucking proboscis of mites is a functional engineering structure, with which they literally dig into the skin. As in a complex drilling rig, the biting tick synchronously operates a deepening proboscis, a lower lip with fixing reverse notches and jaw ties, gradually expanding the edges of the wound. Thus, the tick takes a comfortable position to suck the victim's blood for several days.
The saliva of encephalitis mites is known to relieve pain, so the bite is not felt. Redness appears around the wound, and more serious skin inflammation due to an allergic reaction is possible.
An encephalitis tick bite can have different consequences. Their severity depends on the human body, the state of immunity, as well as how quickly it was possible to detect and extract the parasite.
The incubation period lasts from 4 days to 2 weeks. If the immune system has cleared the virus on its own, symptoms may not appear. Otherwise, the first sign of infection will be a flu-like condition: high fever, weakness, muscle aches, fever, and nausea.
If the virus breaks through further protective barriers of the body, it threatens with serious complications associated with damage to the central nervous system. Among the most severe consequences are impaired consciousness, mental disorders, seizures and paralysis.
If a person is bitten by a tick, you must immediately contact an institution that is engaged in the prevention of tick-borne infections. A timely visit to the seroprophylaxis center will allow you to avoid pathologies carried by these arthropods. If a person has not previously been vaccinated against tick-borne encephalitis, an immunoglobulin will be administered after testing the blood and insect. The action must be completed 3 days after the bite. In this situation, the development of the disease can be avoided, even if the tick was infected with encephalitis.
Noticing a sucked tick on yourself, you first need to pull it out. This will reduce the risk of infection and reduce the chances of developing an allergic reaction. The remaining wound is treated with disinfectants.It can be 5% iodine, vodka or alcohol. After the procedure is completed, you must wash your hands well.
The extracted tick must not be thrown away. It must be placed in a vial or jar with a wet swab, and then taken to the laboratory. If there is no seroprophylaxis nearby, or the person does not know where he is, to prevent infection of others from the insect, it is necessary to get rid of the insect. To do this, you need to burn it or drown it in boiling water.
Encephalitis can lead to many complications. The disease can result in:
- incontinence of urine and feces;
- meningitis;
- deterioration of vision and hearing;
- occurrence of mental problems;
- headaches that bother the patient constantly;
- disruption of the musculoskeletal system.
If rehabilitation is carried out correctly, the negative consequences gradually disappear. However, this will take time. In a severe form of pathology, recovery may take several years.
What to do with a tick bite? It is important to follow a strict sequence of actions. First of all, you must carefully remove the parasite. It is desirable for a specialist to do this, but such an opportunity does not always exist.
Do not pick up the tick with your bare hands
In such cases, you will have to do it yourself with the help of improvised means. The main thing is to follow a few rules:
- do not take the tick with bare hands;
- do not use oil;
- act carefully.
The last two rules are aimed at preserving the life of the tick for the purpose of its further research in the laboratory. Dead insects are not suitable for analysis. There are 3 ways to remove ticks from the skin:
- With tweezers. Ideally, this is a special tool designed to remove ticks. This first aid kit may include a flask for transporting an insect and instructions. The tick is pushed on from both sides with teeth and slowly unscrewed. In the absence of professional tweezers, you can use a cosmetic one. In this case, it is important not to crush the tick during extraction.
- With a thread. The main requirement for a thread is strength. A loop is formed from it around the tick (as close as possible to the proboscis). It is necessary to get the insect without haste, slowly loosening it and pulling it up.
- With your hands. It is highly advisable to wrap your fingers in a clean bandage. The extraction is carried out strictly perpendicular to the skin surface.
Next, the bite site is disinfected with any alcohol-containing agent. After the procedure, you should thoroughly wash your hands with soap and water. If you see a black dot at the site of the bite, this indicates that part of the tick has remained inside. The principle of its extraction is the same as that of removing a splinter. All instruments used must be disinfected. As soon as possible, you should consult a doctor, and deliver live ticks to the laboratory within two days.
During a tick bite, or for several hours or days, a person may feel worse and develop various symptoms, which can be associated both with the bite itself and with diseases that the tick could transmit.
The most common of them are:
- Increase in body temperature to 37-38 degrees
- Excessive tactile sensitivity
- Pain in the eyes from the light
- Weakness, body aches
- Pressure surges
- Allergic reactions to the bite
- Pain, irritation, and itching around the bite
- Poor blood clotting at the site of the bite
These symptoms may appear one at a time, in arbitrary combinations, or they may not appear at all. It all depends on the state of the human body and the individual characteristics of immunity.
However, the main thing that makes an encephalitis tick dangerous is the transmission of the virus, the consequences of a bite in humans in this case will be expressed through the symptoms of encephalitis.
- Temperature from 39 degrees and above
- Severe headaches
- Constant pain in muscles and joints
- Symptoms similar to body intoxication
The disease affects the brain, spinal cord and nervous system, resulting in neurological and mental disorders. According to the Moscow Department of Health, 25-30% of cases of encephalitis are fatal. The outcome in the form of disability in motor activity and mental activity is also very likely.
We suggest that you familiarize yourself with: How to kill cockroaches in an apartment
In order to avoid the consequences of encephalitis tick bites, it is necessary, first of all, not to hope, according to tradition, that everything will somehow go by itself, and to do everything possible to identify the disease in the early stages of its penetration into the body. What to do if bitten by an encephalitis tick?
By the appearance of a tick, it is impossible to determine whether it is encephalitic or not, this can only be shown by laboratory analysis. Immediately after you pull out the tick yourself or you will have it removed at the nearest trauma center, the parasite must be placed in a container for analysis and taken to a laboratory, where specialists will check whether it was a carrier of any diseases. In Moscow, a tick can be tested for:
- In the Center for Hygiene and Epidemiology of the city of Moscow in Grafsky Lane, 4/9.
The tick must be tested on the day it is removed or the next day. If the analysis reveals that a tick is a carrier of encephalitis, laboratory specialists will immediately inform you about this.
If a tick has bitten you in a territory endemic for encephalitis, you can, without waiting for the result of the analysis, make an emergency immunoglobulin vaccination:
- For adults in the infectious diseases clinical hospital No. 2 on Sokolinaya Gora street, 15.
- For children in the Children's Clinical Hospital No. 13 named after NF Filatov at 15 Sadovo-Kudrinskaya Street.
Vaccinations in these institutions can be done around the clock. The injection must be made immediately after the bite, but no later than 96 hours later.
Only a doctor should monitor the state of the body further and determine the treatment, since the disease in each case proceeds individually.
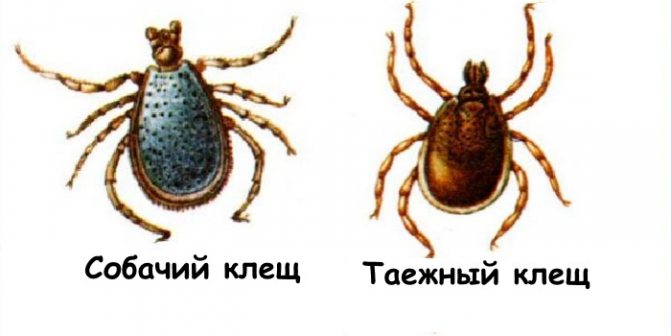
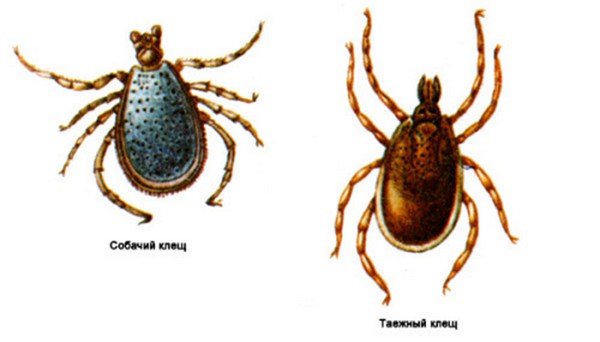
Dog tick
These parasites attack almost all animals. Dog owners are well aware of the danger posed by this species, as they can infect a pet with a very serious disease, piroplasmosis. Regarding the size of the parasite, they may differ depending on what period they eat. At the developmental stage, nymphs and larvae need nutrition for further development and transition to the next stage. Compared to an adult, they are much smaller.

In a hungry state, the nymph has a body size of about 1.5 mm. Female adults are much larger than males. The male in a hungry state reaches 2.5 mm, and the female 4 mm. In a saturated state, the female reaches sizes up to 1 cm and more.
They have an oval egg-shaped body. The back is protected by a brown carapace, in males it covers almost the entire back, in females it is smaller. On the head there is a mouth apparatus with a proboscis. When saturated with blood, the parasite increases in size and changes its color, becomes gray.
Carriers of the disease - who should be feared
Outside the city, in summer cottages and in the forests, people are in danger in the form of small blood-sucking parasites. They hide in tall grass and on the leaves of trees, waiting for a potential host. The main danger of ticks is the spread of many diseases: borreliosis, relapsing fever, tick-borne encephalitis. The latter ailment leads to serious disorders of the nervous system, and in some cases to the death of a person.
Attention. There are two ways of infection with the virus - transmissible (tick bite), alimentary - eating raw milk from goats or cows carrying the disease.

Dangerous types of ticks
The tick-borne encephalitis pathogen is carried by ixodid ticks Ixodidae. There are up to 650 species of them, in Russia the taiga and dog ticks are dangerous. The first species is widespread in the forests of Siberia, the Urals and the Far East. The second is in the European strip. In late spring and early summer, their number reaches peak levels, so the number of bites increases dramatically. The virus is carried by adults, nymphs and larvae. The victims are not only people, but also animals.
Attention. Despite the name of the species - a dog tick, the parasite attacks other animals, as well as humans, with the same frequency.
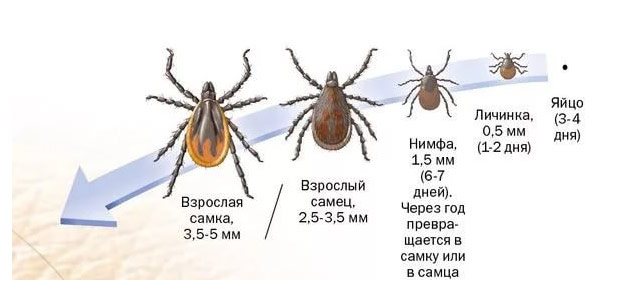
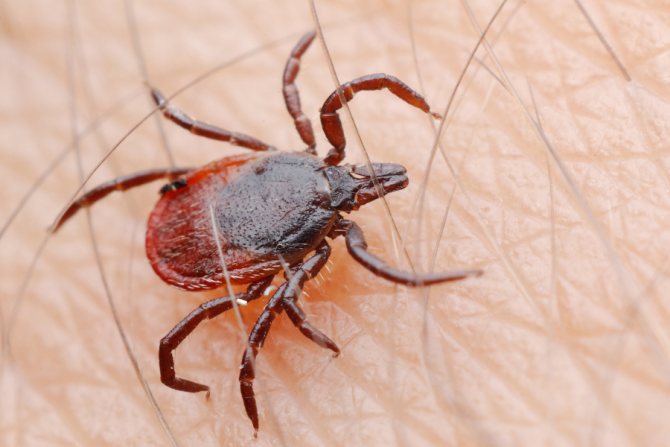
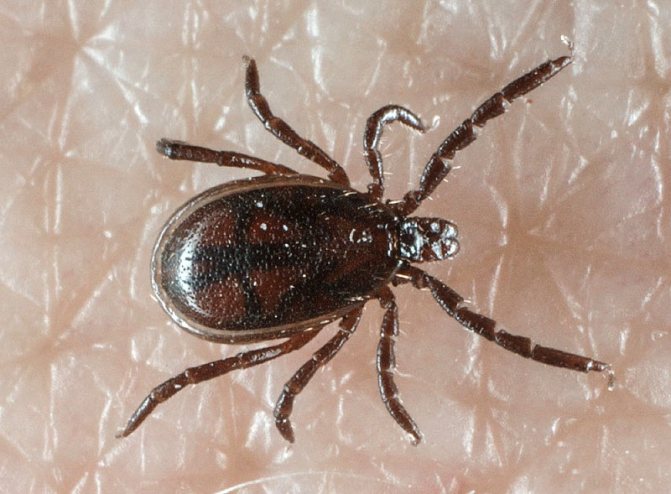
What does an encephalitis tick look like? The parasites have a rounded flat brown body. Females differ in their larger size - 3-4 mm, males no more than 2-3 mm. In adulthood, females are covered with a chitinous shell by a third of their backs, while males have a completely closed back. The parasite has 4 pairs of legs with suction cups that allow it to move along a vertical surface. The female lays up to 17 thousand eggs, but a small part of the offspring survives. Ticks go through several stages of development:
- egg;
- larva - feeds once on small rodents;
- nymph;
- an adult.
The transition from one phase to the next is accompanied by molting. At the end of summer, nymphs become sexually mature, saturated with blood, females mate with males and lay eggs and die. Males die immediately after fertilization.
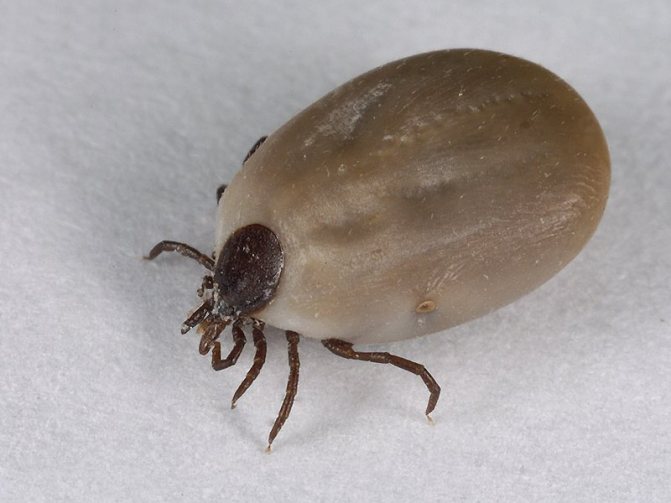
Attention. The female can stay on the human body for up to 2 days. It gets drunk with blood and grows to a size of 10 mm. The bloated body changes color to light gray. The male sucks blood for 4-5 hours, then falls off, its size changes insignificantly.
Taiga tick
In terms of appearance, this view is practically no different from the previous view. The only difference is the red color of the abdomen when the individual is in a hungry state. Already at the larval stage, it needs nutrition. Most often, rodents become its victims. And since the larva is already attacking the victims, accordingly at this stage it is dangerous.


When an adult is infected, it gives birth to an already infected offspring. Therefore, it is necessary to be afraid not only of adult ticks, but also of individuals at the stage of development of nymphs and larvae.
Possible complications of encephalitis
The disease is dangerous not only by manifestations in the active phase, but also by possible complications. These include:
- meningitis;
- mental problems;
- violation of the functioning of the musculoskeletal system;
- hearing and vision impairment;
- persistent headaches;
- fecal and urinary incontinence.
With proper rehabilitation, the negative consequences gradually disappear, but this takes time. After a severe form of the disease, they disappear within a few years, after an average - two to three months, a mild one - in 2–5 weeks.
Life cycle
Tick activity begins with the arrival of heat. As soon as frosts give way to above-zero temperatures, the parasites wake up after a long winter sleep and go in search of food.
Regarding the life cycle of these small blood-sucking animals, much depends on external factors. The maximum period of their life is 4 years. They hibernate in the upper layers of the soil, forest floor and other secluded corners.

When they wake up after a long winter, the main goal is to satisfy hunger and reproduce. The peak of their activity is in May-June, but much depends on the weather, so no one can say the exact time interval when they are most aggressive.
These parasites can go without food for a very long time. With regard to their nutrition, they need it in order to continue the population. The female is unable to lay eggs without being saturated with blood. In addition, she needs much more food than the male. If the male can be on the victim's body for several hours, then the female can suck for several days.
Treatment of the disease
The treatment regimen directly depends on the symptoms manifested in the patient, and even the vaccinated should consult a doctor. During the acute period, you need to lie in bed under medical supervision until the symptoms disappear. It is important to follow the diet, developed by the doctor, depending on the degree of damage to the liver and gastrointestinal tract, as well as to take ascorbic acid to improve the adrenal glands and liver.
The cause of the disease can be overcome by antiencephalitis immunoglobulin. It gives a positive effect after one or two days: the temperature drops to normal, the general condition improves, the meningeal symptoms become weaker. You can replace it:
- leukinferon;
- homologous polyglobulin;
- reaferon;
- serum immunoglobulin;
- ribonuclease.
To rid the body of toxins, vitamins, sodium chloride and glucose solutions are injected intravenously. If the patient suffers from poliomyelitis, meningoencephalitic and polyradiculoneuritic forms of the disease, additional treatments are needed. If the cranial nerves are not affected and there are no disturbances of consciousness, prednisolone is prescribed. Simultaneously with glucocorticoid, a sparing diet and potassium salts are prescribed.
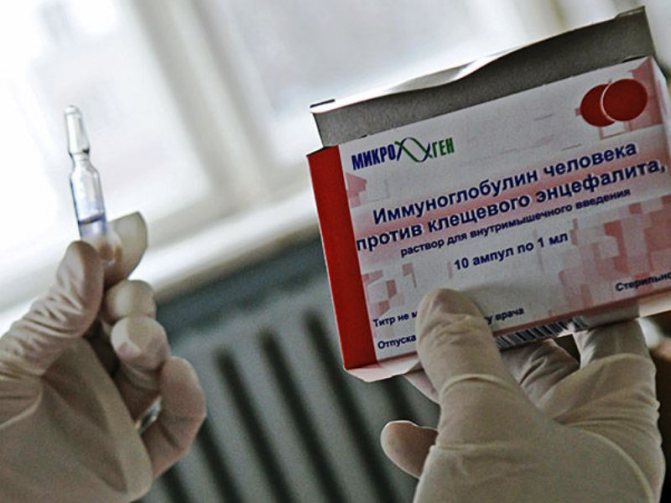

For the treatment of encephalitis, antiencephalitis immunoglobulin and its substitutes are used
Infection with parasites
Of course, nature has not created them with a dangerous disease, they get an infection through the blood when they attack a sick animal. For this reason, not all individuals are dangerous vectors. Also, as mentioned earlier, the new generation may already have the encephalitis virus, even if they did not feed on blood. This happens when the offspring is laid by an infected female.


Outwardly, it is impossible to determine whether the parasite is a carrier of the virus or not. In order to find out whether a tick that has adhered to the body is dangerous, special studies can be carried out. For this, the sucked parasite must be carefully removed from the body and placed in any airtight container. Then take it to the laboratory for analysis.
How to distinguish an encephalitis tick
The encephalitis virus is transmitted to ticks when the blood of a sick animal is absorbed and hereditarily. Individuals of any age and sex can be infected. It is visually impossible to distinguish the parasite-carrier of the encephalitis virus and other diseases, it looks absolutely normal.
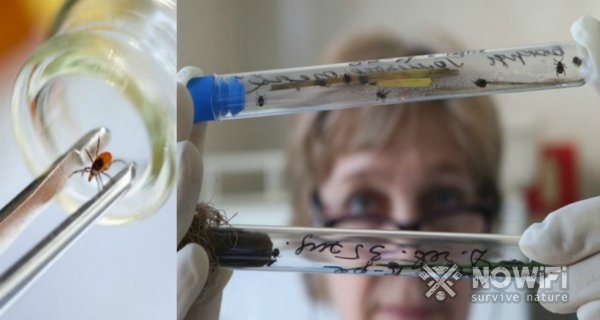

Figure 5. Laboratory tests of ticks
For detection, laboratory tests are carried out by the following methods:
- A live tick is examined for the presence of tick-borne encephalitis virus antigen (Figure 5).
- Viral RNA is detected by a fragment of the parasite.
- If the tick has already bitten a person, but itself is lost, then the blood, tissue or cerebrospinal fluid of a potential patient is examined.
You should know that in accordance with the studies of the Siberian Branch of the Russian Academy of Sciences, only 6 ticks out of 100 are infected with the encephalitis virus. Moreover, if you take 100 carrier parasites and release them on 100 people, then only a small part (2-6%) will get sick.
The reasons are complex, the main ones:
- The amount of injected virus (before tick removal).
- The subtype of the bitten parasite (Far Eastern is considered the most dangerous).
- The main one is the state of the victim's immune system (it is obvious that the weaker the body's immunity, the higher the likelihood of the disease).
Those who are not sick will begin to develop antibodies of the tick-borne encephalitis virus, i.e. natural immunity will appear. As a rule, they are possessed by: hunters, lumberjacks, fishermen, gamekeepers, avid tourists, etc., who spend a lot of time in the wild. The presence of natural immunity is determined by laboratory tests.
Protection against encephalitis
You always need to remember what danger these small bloodsuckers pose and take all possible actions to minimize the likelihood of a bite.Most often, they wait for their victims in shaded places, because they cannot stand direct sunlight. They can hide in the grass, in bushes, in thickets. Therefore, when visiting the forest, you should adhere to open areas, trodden paths. For a picnic, stop on the lawns, where there is a lot of sun.
The wardrobe is very important, which is chosen for walks in nature. Remember that these insects cannot jump and fly, they are rather slow and cannot travel long distances in a short time. They don't jump from treetops. Therefore, the more carefully your equipment is thought out, the less chance the parasite has to inflict a bite.
You must put on your pants and tuck them into your socks. Wear a sweater or jacket that has cuffs that fit tightly to the body. Be sure to wear hats. When the parasite hits the clothes, it goes to look for a way to the body. Due to its small size, it is impossible to completely exclude the possibility of penetration, but it is possible to significantly reduce its chances for a wave.


Inspect your clothes more often, since they do not know how to run fast, then a parasite caught on clothes can be noticed before it makes its way to the body. When you return from a walk in nature, be sure to take a shower and carefully examine your skin. Also inspect the clothes and send them to the wash.
When a bloodsucker bites through the skin and sticks to the wound, it secretes anesthetic enzymes, so a person cannot feel the attack, it is a thorough examination of the body that allows it to be detected on the body. Since males saturate quickly enough, it may not be found on the body. He attacks the victim, drinks the blood and falls off the body himself. A person may not even know that they have been bitten by a tick. A small red spot remains at the site of the attack.
If a person is attacked by an infected parasite, it is very important how to detect the virus early. Since, getting into the human body, the virus is in the incubation period, it is impossible to detect it with the help of analyzes immediately after the attack.
The only way to find out about the disease is to take the bloodsucker for tests.
The likelihood of contracting tick-borne encephalitis with a single tick bite
Interestingly, even with a bite of an encephalitis tick, the likelihood of a person becoming infected with tick-borne encephalitis is very small. This is due to many factors, among which the following are most significant:
- Usually, people detect a tick in the early stages of suction and quickly remove it, and the parasite does not have time to introduce into the tissues an amount of saliva containing an infectious dose of viral particles;
- The body's immune system suppresses the virus as soon as it enters the tissues and prevents cell infection;
- Viral particles themselves do not survive in the human body due to species characteristics. For example, the infectivity of the European subtype of tick-borne encephalitis is about 2-2.5%, and the Siberian subtype is about 6%, that is, the Siberian subtype is more virulent.
According to statistics, with the bites of infected ticks, human infection occurs on average in 4% of cases and only in some regions reaches 6%. In other words, out of 100 unvaccinated people who were bitten by encephalitis ticks, four or six will get sick with tick-borne encephalitis.
If you multiply this figure by the number of encephalitis ticks in the population itself, then the figure will be even smaller. Above, we found that, on average, throughout the distribution area of tick-borne encephalitis, the infection with the ixodid virus is about 4-6%. This means that if a person is bitten by a tick in nature, then with a 4-6 percent probability of infection of the parasite itself and an approximately 4 percent probability of infection, if the bloodsucker is encephalitic, the probability of infection from this one individual is approximately 0.2%. That is, out of 500 tick bites in nature, a bite of about one leads to the development of a disease.


Statistics say that for about 500 tick bites, only 1 can lead to infection with tick-borne encephalitis.
On average in Russia, the annual number of people infected with tick-borne encephalitis ranges from 1800 to 2200 people. Perhaps some of them are infected by other routes (for example, through the same milk of infected cows), but their proportion is insignificant.
It is interesting that the ratio of the number of people who have registered tick-borne encephalitis to the number of people who went to the hospital or emergency room for tick suction is approximately 0.48%. This is 2.5 times higher than the previously calculated figure of 0.2%, but it does not contradict the calculations in any way. The fact is that only a part of those bitten go to hospitals after tick bites, and the actual number of those who are bitten by ticks is greater, which means that the percentage of cases among them will be smaller.
Be that as it may, the likelihood of the disease with the bite of any ixodid tick (and in almost any area on the territory of Russia, Ukraine, Kazakhstan and neighboring countries) remains. Moreover, the same parasites that carry tick-borne encephalitis can also carry Lyme disease. And therefore, if such a bloodsucker is found on the skin, it should be removed immediately.
Symptoms of the disease
The first symptom that appears on the skin is redness, but this is completely unrelated to the fact that the tick is infected. Such a reaction of the body is quite normal and it is impossible to understand from it whether an infection has occurred. For each person, the reaction of the body is individual, for some the speck disappears quickly, for some it can last for several days.
When the virus enters the body, the first symptoms may appear after a few weeks. It is very important for a person to remember about the attack of the parasite, since the first symptoms of encephalitis are very easy to confuse with a cold or flu, and this cannot be allowed. Symptoms include weakness, decreased appetite, muscle pain, headache, fever, nausea, and vomiting. How long the symptoms appear, no one can say for sure, it depends on the organism, on average it will last up to 4 days.


As you can see, such symptoms in a person can appear with colds and flu, and people begin to be treated precisely for these diseases. After about a week, the symptoms disappear, the person gets better. And this condition once again confirms that the treatment for the flu was successful. But in fact, the virus does not disappear anywhere, which leads to dire consequences.
If we talk about data and numbers, then we can note the following, 75% of people who were attacked by infected ticks did not have serious consequences. But the remaining 25% have a repeated attack of the virus, which leads to very serious consequences. The danger is that the central nervous system is affected. After the primary symptoms pass, after a while the second stage of the development of the disease begins and more severe signs of tick-borne encephalitis appear.
The person develops a fever, a severe headache, and meningitis. With the development of the virus in the body, the human condition deteriorates significantly, coordination of movements is impaired, the person loses sensitivity, and consciousness is impaired, paralysis of the limbs is observed.
In areas where there is an increased risk of contracting encephalitis, the virus is carried not only by ticks, but also by other types of bloodsucking. Therefore, when visiting such areas, you need to protect yourself as much as possible, it is recommended to get vaccinated against this terrible disease.
The area of distribution of the encephalitis virus
Ticks are found throughout the Eurasian continent, but the risk of contracting encephalitis is only among residents of a rather narrow strip, which runs approximately in the middle of Eurasia.
On a note!
All three types of encephalitis virus are present in Russia.In the European part, the spread of the disease is the dog tick, in the Asian part, the taiga tick.
There is a clear division of the territory between the types of viruses: up to the Urals in the territory of the Russian Federation there is a virus of the European type, after the Ural mountains through the whole of Siberia to the Far East the Far Eastern type of encephalitis is rampant. The natural reservoir of the virus is sick animals, the blood of which these arthropod creatures feed on.
Tick infection with encephalitis is also higher in the Asian part of Russia. Behind the Ural ridge, 20 percent of ticks are infected with the virus.
First aid for a parasite attack
If you find a parasite on your body, you must immediately seek medical help, where they will correctly carry out the procedure for removing the bloodsucker and give recommendations on the following actions.
You can pass an individual for tests to detect infection, which will allow you to detect the disease at an early stage. If this is not done, then the patient is prescribed a set of tests that can identify an infection.

Remember that it is very dangerous to ignore the situation if a bite has occurred, because without proper and timely treatment, a person develops severe and irreversible complications. The virus affects the nervous system, cardiovascular, organs of sight and hearing.
Without treatment, the consequences lead to disability, in some cases to death.
The sequence of actions upon detection of an embedded tick on the body
If a tick is found on clothes or on the body, but it has not yet had time to suck, but simply crawls in search of a convenient place, it is enough to simply shake it off. If found during a picnic, it is better to kill him - while people are in one place, the parasite will be able to climb onto someone else again.
It is also useful to read: The incubation period of tick-borne encephalitis in humans
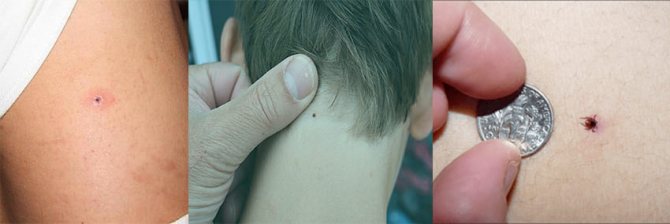
If the tick has sucked in, it must be removed immediately. Moreover, the sooner this can be done, the lower the risk of infection will be.
On a note
In many instructions and literary sources, you can find recommendations to go with a sucked tick to a polyclinic or an emergency room and entrust its removal to a doctor there. These are dangerous advice. As a rule, a tick bite occurs in nature, far from settlements and hospitals, and you will have to spend at least 1-2 hours on the way to the doctor. While the bitten person gets to the hospital, the bloodsucker will have time to inject an infectious dose of the virus under his skin. And if you remove the parasite immediately after detection, this may not happen. Therefore, you need to remove the tick as early and quickly as possible, even if it is not as aesthetically pleasing and competent as shown in numerous videos on the Internet.
In the optimal case, a person has a special tick-tipper at hand - a device with which the parasite is captured, rotates around the axis of its body and falls out entirely, without the risk of squeezing out a part of the pumped blood into the wound and without the risk of tearing off the head.
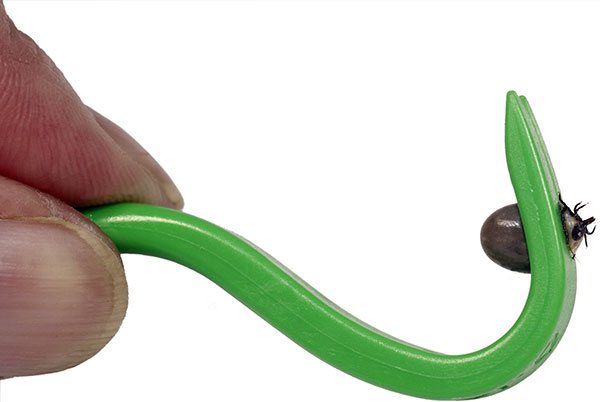


Ticksheater is one of the most effective devices for removing ticks.
However, in most situations, such a tick ticker is not at hand. In this case, you need to pick up the tick with your nails under the body, turn it at least 90-180 degrees and pull it out. Almost always this can be done without tearing the head off, but even if the mouth organs come off and remain in the skin, they can be removed with a needle in the same way as a splinter is removed.
It is important to understand that it is more dangerous to carry a tick in the skin to the hospital for an hour or two than, even in the worst case, to tear off the tick's head and pick it out with a needle. If the body of the tick breaks off from the gnathosoma, the mouth organs remaining in the skin no longer pose an infectious danger to humans: there are no salivary glands in them (they remain in the body) and there is no virus. Already such a head can be removed for a long time and thoroughly, without risking infection.If you are afraid to break the tick, then during the time a person gets to the doctor or makes a homemade tick-grabber, the parasite will already have time to infect him with tick-borne encephalitis or borreliosis.
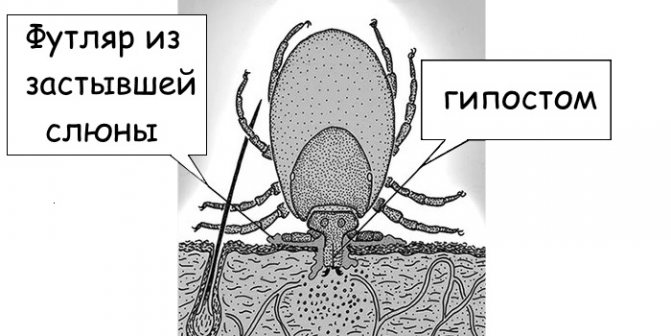
Moreover, cases of detachment of the parasite's torso from the head are very rare. Both the most common vectors of tick-borne encephalitis - canine and taiga ticks - do not form a cement sheath around the hypostome in the skin when bitten, and therefore their jaws are easily pulled out and this requires less effort than tearing the body of the parasite. That is, if you just take and tear off a tick, almost certainly no jaws will remain in the skin.
Further actions depend on whether the bitten was vaccinated against tick-borne encephalitis. It is enough for a vaccinated person to remember the date of the bite in order to be tested for infection with Lyme borreliosis in about a month. If there is no vaccination, then the sequence of actions should be as follows:
- After removing the tick from the skin, it must be placed in any tightly closed container, in extreme cases - in a bag, which is then tightly tied;
- After that, you need to find out if the region in which the bite occurred is dangerous for tick-borne encephalitis. In fact, you can get infected with this infection anywhere in the temperate zone of Eurasia, from Sochi to Vorkuta, but in some areas the epidemiological threshold is relatively low, and the likelihood of infection is higher than in others. You can find out by using special cards, they can be easily found on the Internet. If the bite occurred in a dangerous region, the tick must be taken to a special laboratory, where it is examined for infection with the virus. Further actions will depend on the result of the research;
- If a tick is infected with a virus, the bitten must be administered anti-encephalitis serum (the so-called emergency prevention of tick-borne encephalitis). It reduces the risk of developing the disease (although it does not completely protect against it), and if it develops, the disease will be milder and most likely will not lead to serious consequences. If the virus could not be detected, it means that the tick is not encephalitis and there is no danger of developing the disease for a person. Nothing else needs to be done in the near future.
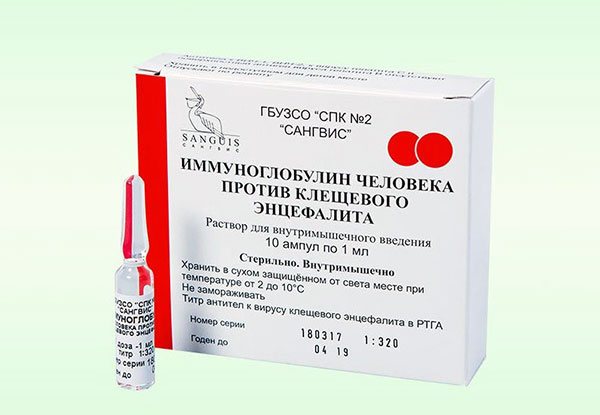

This serum is sometimes used for emergency prevention of TBE.
In any case, after a bite, it is necessary to observe your own condition for a month. If any nonspecific symptoms of the disease develop, it is necessary to consult a doctor and inform when the bite occurred.
Prevention measures
There are two types of prevention, specific and general. If we talk about the general, then it consists in providing protective measures against bloodsucking. This is choosing the right clothes, shoes, hats. Also, the use of specialized means, repellents, which are designed to repel insects.
Frequent examination of clothing and body is also a general prophylaxis. If a sucked insect is found, it must be removed as soon as possible. The longer the bloodsucking is on the human body, the more the likelihood of transmission of a dangerous virus increases. Remember that in endemic regions, milk must not be drunk unboiled, as the virus may be in that product.
Specific prophylaxis includes vaccination against tick-borne encephalitis. Vaccination is necessary for people who live in the outbreaks of the epidemic. Also, vaccinations must be given to people who visit these areas for work, vacationers and tourists, and other groups of people who plan to visit these areas.
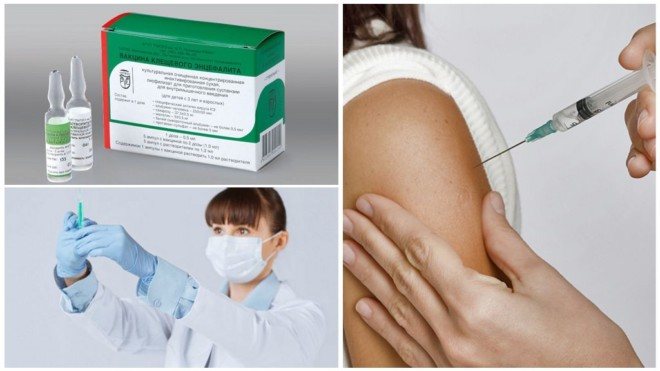

You can get vaccinated in medical institutions, both public and private. It should be remembered that for maximum protection against disease, it takes time to develop immunity. Therefore, the vaccination is done 1.5 months before traveling to a dangerous territory, or 1.5 months before the start of the tick activity period.
If the vaccination was not carried out on time or for some reason it is impossible to carry out, it is necessary to adhere to simple rules to minimize the likelihood of infection. In nature, wear clothes of light shades, since an insect will immediately be noticeable on it. Cover the body as much as possible and exclude access to blood sucking.
Do not walk through thickets and tall grass, stick to paths. Use repellents and check more frequently.
How to remove a tick
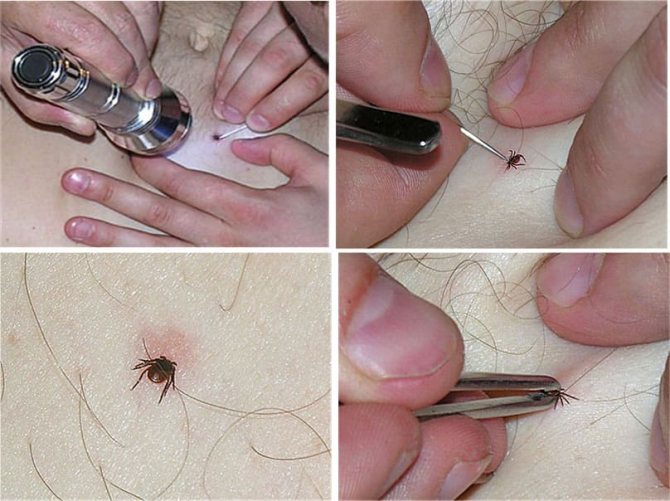
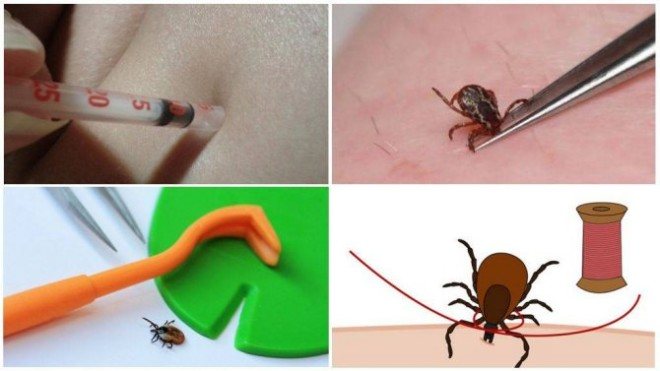
If, during the examination, a sucked parasite was found on the human body, it must be removed. To do this, you can use the tools at hand:
- cosmetic tweezers;
- strong thread;
- a special device for removing the tick (sold at the pharmacy).
The main thing is to get the individual completely together with the proboscis, without crushing the abdomen. It is necessary to capture the tick as close to the surface of the skin as possible. Pull out by rotating counterclockwise. So the coiled proboscis comes out more easily. When using the thread, a loop is made that tightens on the parasite. The two ends of the thread are also twisted clockwise, the loop rotates the body of the tick. Filling with oil is not advisable, the parasite dies from this, and for laboratory analysis for encephalitis, it needs a live one.
Outwardly, it is impossible to recognize whether or not a tick is a carrier of viral diseases. It is placed in a glass jar and delivered to the laboratory within 2-3 days. If this is not possible, then they burn it. The wound is disinfected with alcohol or iodine. When the proboscis is separated, it is pulled out of the wound like a splinter.
Attention. It is not advisable to remove the sucked individual with your fingers, if there is nothing at hand, it is advisable to wrap them with a bandage or scarf.
Vaccination
Today, vaccination is the most effective preventive method against tick-borne encephalitis. In order to be able to protect yourself as much as possible, you need to contact a medical institution, where you will be provided with all the information regarding the procedure itself, the action of the vaccine and additional measures.


Remember that there are contraindications for which vaccination cannot be carried out. In rare cases, the procedure causes side effects. Adverse reactions can manifest as redness and pain at the injection site. A more complex manifestation is possible in the form of an increase in body temperature up to 38 ° C and fever. But these manifestations do not pose a threat to human health and quickly disappear.
Vaccination against encephalitis
By itself, the bite of a small parasite does not harm people, the danger lies in the infections that it carries. Among the ways to combat the consequences of a bite, an encephalitis tick vaccine plays an important role. In a person who has been vaccinated, the production of immunity is stimulated. The tick-borne encephalitis virus in the vaccine is inactive. It poses no danger to people, and the body learns to fight the disease and produce immunoglobulin.
Several types of vaccines are used in the country, they are divided by the age of the patients. Children are injected with special drugs designed for the age of 1-11 years.
Who should be vaccinated?
Vaccination against tick-borne encephalitis is optional. It is recommended for residents of areas with a high prevalence of encephalitis and those who are going to visit this area. In Russia, such regions include Siberia, the Urals, the Far East, the North-West region and the Volga region. This applies not only to recreation in the country or in the forest, but also to work on agricultural plots, construction and surveys.
Vaccinations can be done at any time, preferably before the peak tick season (April, May). The scheme of the event depends on the type of drug chosen. The standard schedule provides for the introduction of 3 doses - the first in the fall, the second in 1-3 or 5-7 months, and the third in a year. Revaccination is carried out after 3 years.
Attention.Like any medical procedure, tick-borne encephalitis vaccination may have contraindications. They include: a period of exacerbation of chronic diseases, general malaise, pregnancy, allergy to vaccination.
Summing up
Speaking about the danger from these small blood-sucking animals, it is worth saying that not every individual is infected. But if we consider what serious consequences tick-borne encephalitis brings, then every bite is necessary to beware and afraid.
Do not ignore the attack of the tick and hope that it was not infected; you must take all possible actions to prevent serious consequences. Also, do not forget that the further development of events depends on how well you prepared for a walk in nature.
Features of the bite
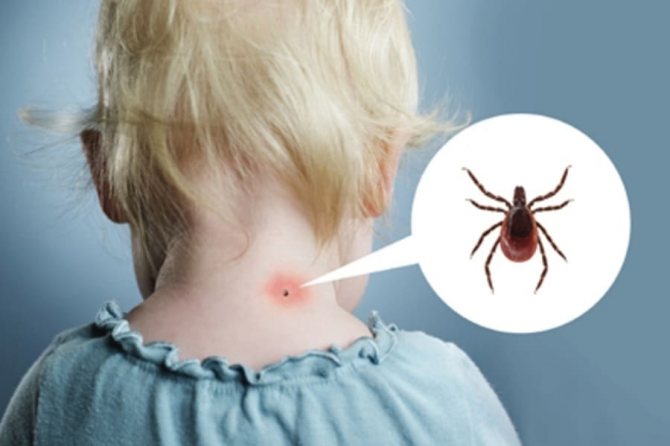
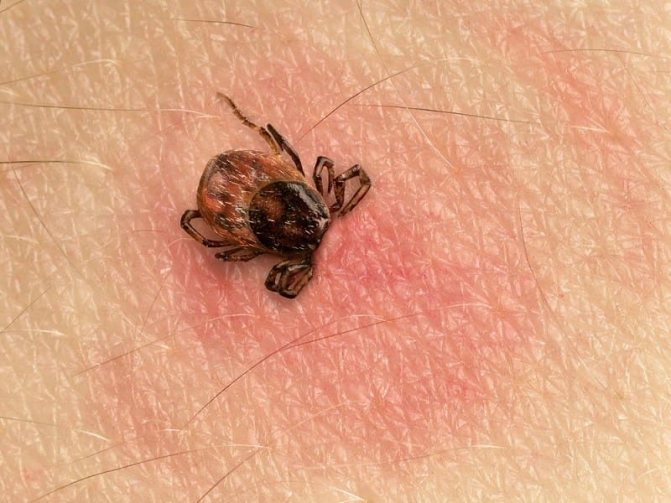
The parasite bites using a hypostome, which looks like a proboscis and allows it to attach to and feed from the victim. It is also a sense organ. Most often, the tick bites in the groin, lower back and armpits, abdomen, neck, chest and ears. On the affected area, due to the action of the saliva of the parasite, a local inflammatory process and an allergic reaction in the form of redness occur. No pain. Sometimes the skin at the site of the bite does not change. But the evidence that he was is a sucked insect.
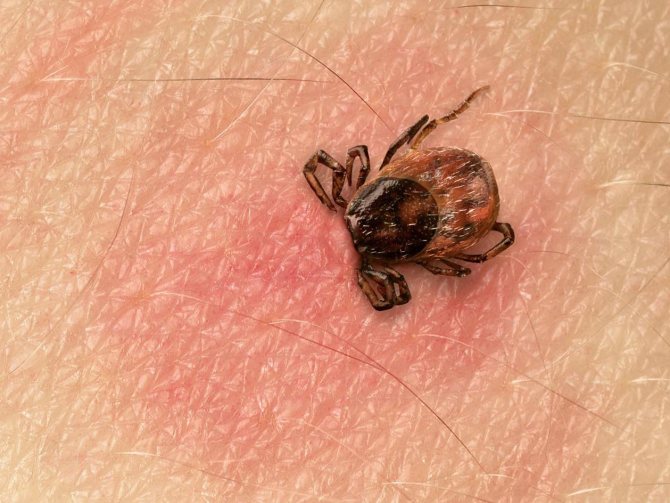

The site of the tick bite is characterized by slight redness.
To determine when to fear tick bites, you need to focus not so much on the season as on temperature and humidity. The weather is most favorable for them from +5 ° C and air humidity from 80%. Such conditions are typical for May-June, as well as late August and early September. If the temperature exceeds 22 ° C, parasites rarely crawl out of the shelters.
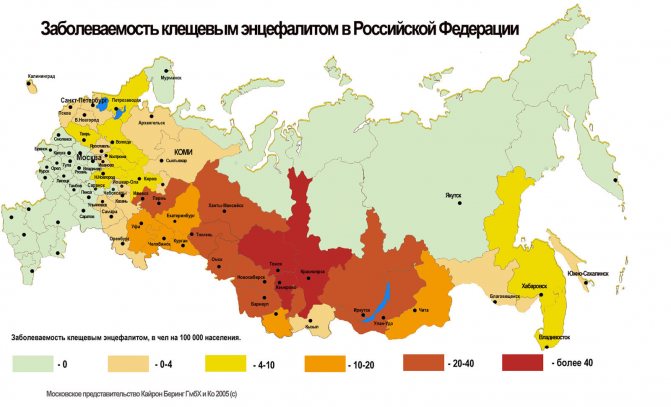

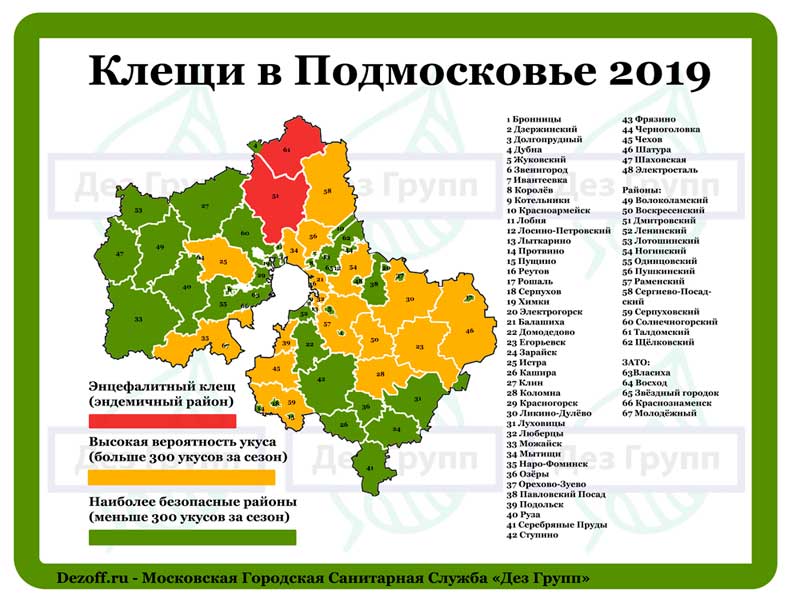
Having studied in advance the incidence map of tick-borne encephalitis, you can decide whether it is advisable to vaccinate
Usually insects bite in cloudy weather before rain. They should be feared before 8 am and at the end of the day - after 19-22 hours. Ticks do not rise to a height of more than 50 cm, so they jump onto the victim from grass or bushes. The parasite takes a long time to find a place for a bite. Sometimes you can remove it even before biting through the skin.
The male tick does not stick, but quickly bites, feeds and falls off. But the female sits on the victim until full saturation and increases in weight almost 100 times.
Saprophytes
These are arthropods that feed on decaying organic matter. Saprophyte mites are relatively harmless. Most of them recycle rotting organic matter, improving the quality of the soil like earthworms. But the "dust allergy" known to many actually arises from the presence of Dermatophagoides farinae dust mites in the house.
These are microscopic creatures 0.1-0.5 mm in size. They feed on scales of the epidermis, particles of lost hair and animal hair, and waste products.
"Dust allergies" are not actually caused by house dust, but by the excrement of dust mites and particles of the shells of dead arthropods. Dermatophagoides farinae live in uncleaned dust in corners and under furniture, in sofas, pillows, mattresses. To get rid of this type of arachnids, they carry out regular thorough cleaning and processing of upholstered furniture.
Signs of a bite


It is impossible to feel a tick bite - the insect took care of anesthetizing the puncture of the skin by introducing saliva with a special anesthetic component. Most often, the parasite is found already embedded in the body or traces of its presence. What does the site of an encephalitis tick bite look like? A dark red spot and slight swelling forms on the skin as a local allergic irritation to a foreign substance. If an additional bordering of the bite site has formed, then this is a clear sign of infection with the Lyme disease virus, or borreliosis.
The tick, unlike other insects, bites once and plunges its head into the wound to feed on blood.
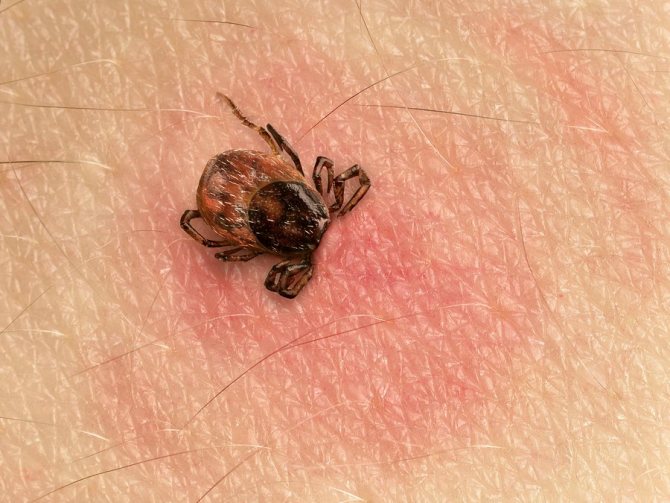

Insects choose a site for a long time and carefully - the place should be accessible for contact with a blood vessel. Favorite suction zones:
- armpits;
- abdomen and groin area;
- small of the back;
- areas behind the ears, on the neck;
- scalp.


Other parts of the body are much less likely to be affected. Ticks do not bite through the skin through clothing, they do not have enough physiological resources for this.
When an encephalitis tick attacks, what does a bite look like? The trail from the defeat is the same as from an insect not infected with viruses, bacteria. The presence of an infection can only be detected by a laboratory method; it is impossible to visually establish the presence of an infection.
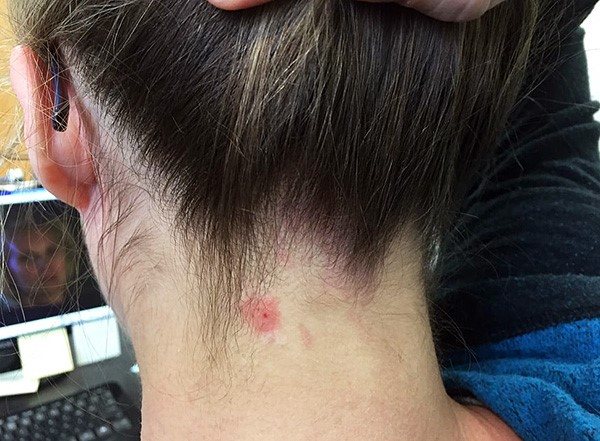

The tick proboscis is immersed only in the upper layer of the skin, the epidermis. The depth of penetration, despite the different sizes of ticks, nymphs, adults, is almost the same.
It is important to take into account that the encephalitis virus enters the body not only through the suction of a tick, but also in the case of contact with a crushed insect and skin damage.
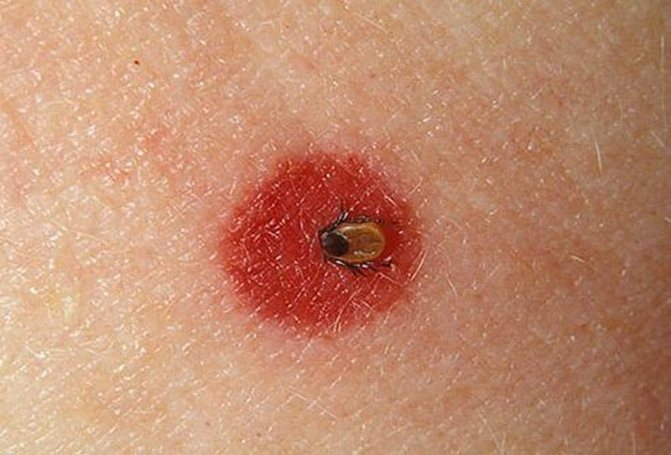
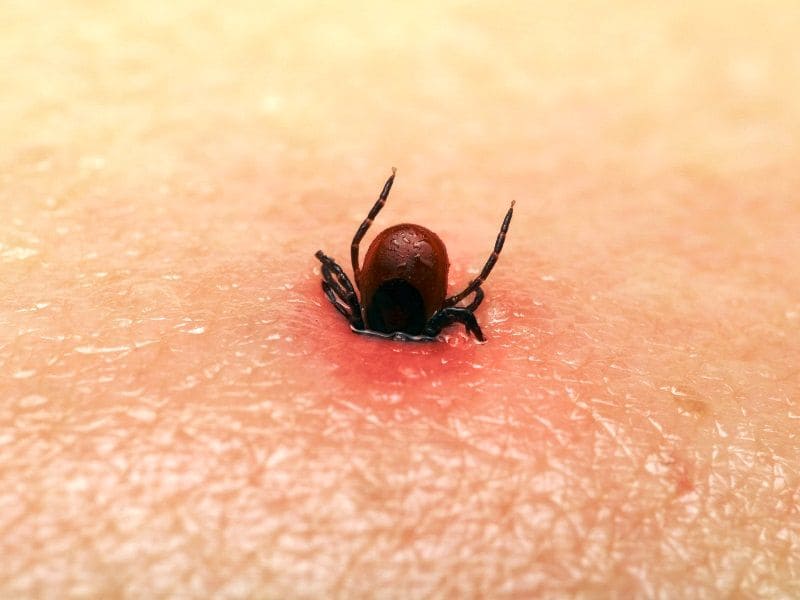
What does a tick bite look like?
The area around the bite can be pink or red, depending on the reaction of the body. A recess will be visible in the center. My husband was bitten by a tick early in the morning, when he climbed into the grass to photograph a dragonfly. Usually, Andrei (that's my husband's name) tucked jeans into his socks, if he didn't wear ankle boots. Hopefully that morning. It was lucky that I noticed the "beast" quickly and pulled it out without any problems.
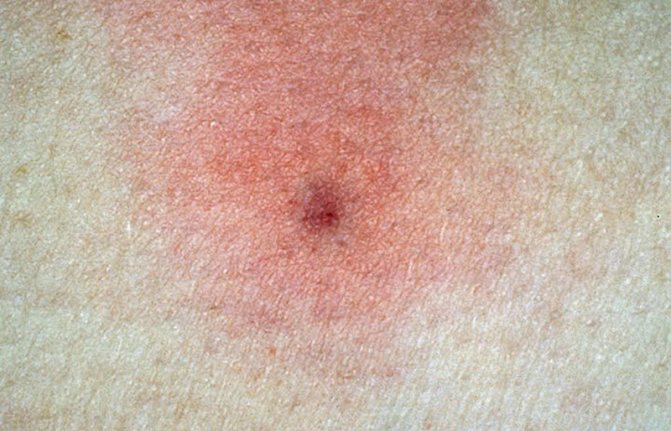

After a tick bite, a red spot formed on my husband's leg. He immediately circled it with a pen, for control, tk. if the redness increased, you would have to see a doctor again. If there is no pen, be sure to take a photo of the bite site with your phone.
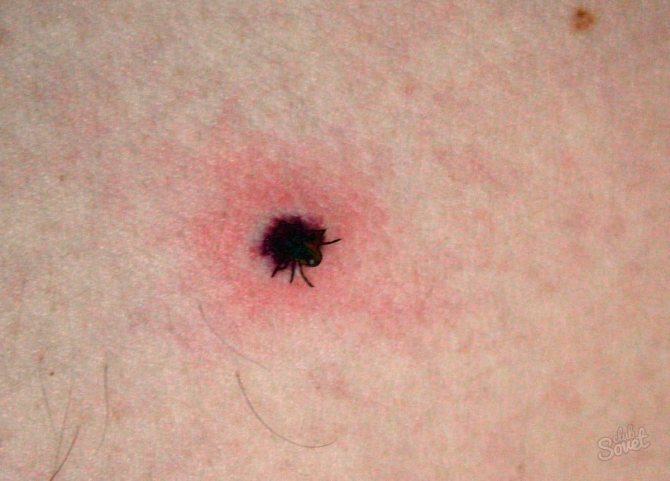
If you look closely at the previous photos of ixodid ticks, you will see the proboscis with which they pierce the skin of a person. This thing is called a hypostome. With the help of it, the tick not only sucks blood, but also "sniffs out" the victim. Usually, a sucked parasite is found in this state:


After it pierces the skin, it is immediately attached inside the wound with the help of special saliva, which simultaneously anesthetizes and fixes the proboscis in the wound. This is why a person does not feel the moment of being bitten.
What does a tick look like?
The taiga tick lives in the Asian and several regions of the European part of our country. His brother in arms, Ixodes ricinus, is more likely to meet someone who, like our family, settled in southern Russia. Here is a comparative photo of all varieties of this instance:


Ixodes Ricinus... Male, nymph, female and tick larva
I showed my husband a photo, he said that he more often removed males from trousers than females. I was also surprised why some of the ticks are black, while others have a reddish tint. All ticks of this species have a powerful shell and four pairs of legs. The reddish tint of the female is due to the fact that the integument of the rear part is able to stretch strongly and absorb hundreds of times more blood than a hungry tick weighs.


Here is such a pretty female of the genus Ixodes
To our great happiness, we have not met a female drunk with blood, but I will also show the photo. For comparison and a greater accent. God forbid you to face this:


Females of ticks feed from 6 to 10 days. Now let's take a look at the male. It is smaller and not as bloodthirsty as its "weak" half - it sticks for a short time (less than an hour). Take a close look at these photos and remember what the male and female Ixodes ricinus look like. They have no eyes, but their sense of smell is the strongest: they can smell prey ten meters away.


By the way, if you were bitten by a male and you didn't notice him right away, then the situation may become more complicated. After drinking blood, the tick disappears and you get a reddened spot on the skin as a reward, the origin of which you can only guess. Without finding out the nature of this spot in time, you run the risk of being in a dangerous position.
What does the tick eat?


Photo: Tick in the forest
Ticks also differ in the way they feed.
On this basis, they can be divided into two groups:
- saprophages;
- predators.
Saprophages consume organic residues. That is why such mites are recognized as very useful for nature and humanity, since they make a certain contribution to the creation of humus. However, there are saprophagous mites that feed on plant sap. These are parasitic mites. This type of animal causes great harm to agriculture, since it can destroy the harvest of grain crops.
There are mites that eat exfoliated particles of human skin - the epidermis. These mites are called dust mites or scabies. Barn mites are suitable for feeding on plant residues that decompose, incl. rotting flour and grain.
For a subcutaneous mite, the ideal option is subcutaneous fat, which it takes in human hair follicles, and for an ear mite, the fat of the ear canals. Predatory mites parasitize other animals and plants. With the help of its legs, the blood-sucking mite attaches itself to its prey, and then purposefully moves to the place of feeding.
Interesting fact: The blood-sucking tick can choose its relative, the herbivorous tick, as its victim.
Tick-borne encephalitis virus
Affiliation of tick-borne encephalitis virus:
- genus - Flavivirus (group B),
- family - togaviruses,
- ecological group - arboviruses.
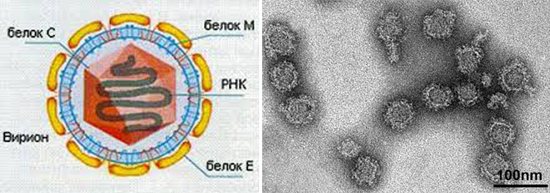

Fig. 2. In the photo, the tick-borne encephalitis virus. On the left is a diagram of the structure of the virion, on the right is the view of viruses under an electron microscope.
- The virus is resistant to low temperatures and desiccation, but quickly loses its biological properties at room temperature.
- When boiled, the virus is inactivated after 2 minutes, and at a temperature of 60 ° C (temperature of hot milk), the virus dies only after 20 minutes. For up to 10 days, the virus remains at a temperature of 16-18 ° C. In dairy products, the virus persists for up to 2 months.
- Rapid inactivation of viruses occurs under the influence of disinfectants (phenol, alcohol, formalin). Ultraviolet radiation has a detrimental effect on pathogens.
Tick-borne encephalitis viruses have a tropism for the tissues of the brain and spinal cord
Forms of encephalitis
Despite the fact that the signs of tick-borne encephalitis in the acute stage of the disease are diverse, each case allows us to distinguish a certain set of them ─ syndrome. Taking into account it, as well as the severity and persistence of neurological manifestations, 5 clinical forms of the disease can be distinguished.
- Feverish form. For this form of the disease, encephalitis has a favorable course that does not affect the nervous system, as well as a quick recovery. Among the first signs of febrile tick-borne encephalitis are: weakness, nausea, headache. It is diagnosed in about 1/3 of all recorded cases of the disease.
- The meningeal form is the most common. The primary symptoms of tick-borne encephalitis coincide with the clinical picture of the febrile form. In the future, the symptomatology has a more pronounced character of intoxication.
- The meningoencephalitic form is characterized by a severe course of the disease. Possible symptoms of encephalitis after a bite: hallucinations, delirium, psychomotor agitation, disorientation, epileptic seizures.
- Poliomyelitis form. Signs of an encephalitis tick bite: sudden weakness in any limb, its numbness, flaccid paresis in the neck and shoulders, arms. The tick-borne encephalitis virus of the poliomyelitis form is characterized by an increase in disorders of the musculoskeletal system, after which the muscles atrophy. Such symptoms occur in about a third of all infections, which indicates a high degree of spread.
- The polyradiculoneuritic form affects the peripheral nerves and roots.The following symptoms of an encephalitis tick bite are traced: pain along the nerve trunks, a feeling of numbness, tingling, chills, Wasserman and Lasegue symptoms, impaired limb sensitivity.
How can you get encephalitis?
What is tick-borne encephalitis? This disease is referred to as natural focal human diseases. Ixodid ticks are the main vectors of the virus. Many types of domestic and wild animals serve as carriers - ticks become infected from them, subsequently transmitting the virus to humans. The second method of infection - alimentary (through the milk of animal carriers), is rare.
- stomach;
- groin area;
- small of the back;
- chest;
- neck;
- armpits;
- behind the ears.
After entering the body, the virus spreads through the circulatory system and quickly reaches the brain, where it fixes its cells. Along with the accumulation of the virus, changes in the vessels and membranes of the brain of an inflammatory nature occur.
Clinical features depend on how the virus spreads throughout the body. Meningeal and meningoencephalitic syndromes are characteristic of the hematogenous pathway, and polio and radiculoneuritic syndromes are characteristic of the lymphatic pathway.
What are ticks
The classification of living organisms in biology is based on phylogenesis - the evolutionary origin and development of species. But the debate among scientists about the phylogeny of ticks continues, and the data may change in the future.
On a note!
To date, the suborder of ticks is divided into two large groups: parasitiform and acariform.
The first group includes parasites, predators and saprophages (organic processors). In the second group, all of the above are also present, but these animals are capable of completing the segments in the process of life.
Tick bite symptoms


Under the influence of tick saliva and microtrauma, rounded redness may appear on the skin of a bitten person. Sometimes, if a person is prone to allergies, Quincke's edema or anaphylactic shock occurs. The most common symptoms that can be noticed after 2-3 hours after being bitten by a tick:
- redness of the bite site;
- weakness, drowsiness;
- chills;
- joint aches;
- photophobia.
But in general, everything is individual, and depends, to a greater extent, on your physical condition. In healthy adults, everything does not go away, until they find a tick on themselves. Changes that may occur later: fever, swollen lymph nodes, headaches or muscle pains, rash throughout the body. Different tick-borne infections have different symptoms, so symptoms appear from a few days to two weeks after infection. By the way, it is impossible to distinguish a seemingly healthy tick from an infected one, and the longer it sucks blood, the higher the risk of infection.
How best and guaranteed to eliminate a tick

Such mites can live not only in layers of dust on the surface of cabinets and other inaccessible places where there has been no cleaning for a long time. Their places where they like to settle are also those that are closer to the source of food, human skin. Accordingly, where there is often a person in the house, dust mites are also found there:
- in upholstered furniture;
- in carpets;
- inside the pillows or on their surface;
- on towels, especially terry products;
- in mattresses;
- in bedding and so on.
The disease begins when the number of these insect-like organisms is exceeded in layers of dust or in upholstered furniture. If there are about 500 or 1000 individuals per 1 gram of mite dust, then a person will surely have an acute allergic reaction, expressed by a rash, similar in places, like tick bites.

It is almost impossible to completely remove dust mites from the house by 100%. But on the other hand, you can regularly reduce their number, which is not dangerous to human health. This requires:
- Ventilate the room more often.
- Always iron clean bed linen, personal and other linen, home textiles with a hot iron;
- It is advisable to put pillows, carpets, rugs, paths, soft toys, and so on in the winter in the cold (and in the summer - in the sun).
- Frequent wet cleaning with brine.
- The humidity in the rooms should not exceed the norm for the living quarters.
- Laundry and clothes should be washed regularly.
Herpetic encephalitis
Herpetic encephalitis is a disease characterized by acute brain damage and arising from the herpes simplex virus. It is registered in about 10% of all cases. Most common in young children.
Herpetic encephalitis is caused by the herpes virus
With herpetic encephalitis, the symptoms can be of different severity and are similar to the classic disease, so diagnosis is difficult. The main indicator is the presence of herpes simplex virus in the cerebrospinal fluid. Acyclovir is actively used in therapy.