Side effects
Usually, the vaccine is well tolerated by the child's body, as evidenced by numerous reviews of parents. But side effects of a biologically active drug are still possible, especially for domestic vaccines. Immunity after the introduction of the protein membranes of the virus begins to work more actively, concomitant reactions are possible.
The injection site turns red, there is a local reaction, swelling, the child may complain of itching, burning sensation. These unpleasant sensations usually disappear within 1-3 days after vaccination, you should not be afraid. At the time of the manifestation of the reaction, it is forbidden to smear the injection site with anything, make lotions, seal it with a plaster
It is important to ensure that the child does not itch. You can swim and wet the injection site, but you should not rub it with a washcloth
Rapid heartbeat, nausea, bloating, vomiting, and diarrhea. These manifestations can be associated with the side effects listed above, in this case they will be a direct consequence - at a temperature, the child often has a rapid heartbeat, and urticaria can occur with diarrhea and nausea. Adult help is symptomatic.

Vaccine preparations
In Russia, 4 vaccines against the TBE virus have been registered for children. They contain formalin-inactivated TBE viruses reproduced in the primary cell culture of chicken embryos. These are the most dangerous strains of the TBE virus circulating in the territory of the Russian Federation.
Tick-E-Vak
Active ingredient: TBE virus antigen (Sof'in strain) with a titer of at least 1: 128. The minimum age of administration is 3 years, the childhood vaccination dose is 0.25 ml.
The drug is produced by the Scientific Center for Research and Development of Immunobiological Preparations. M.P. Chumakova (Moscow).
EnceVir Neo
Active substance: TBE virus antigen (Far Eastern strain) from 0.3 to 1.5 μg. The drug is recommended for ages from 3 to 17 years.
This is a new vaccine produced by FSUE NPO Microgen. Until 2011, the drug EnceVir was used, which was banned in pediatrics due to its reactogenicity for the child's body.
FSME-Immun Junior
The inoculation dose of 0.25 ml contains the antigen of the TBE virus (Neudorfl strain) 1.19 μg. The drug is designed for children and adolescents from 1 to 16 years old.
The developer and manufacturer of the vaccine is the pharmaceutical concern Baxter (USA).
Encepur
One dose of the drug 0.25 ml contains the antigen of the TBE virus (strain K23) 0.75 μg. It is used from the age of 1 to 16 years.
Manufacturer - Novartis Vaccines and Diagnostics GmbH & Co. KG, Germany.
Which drug is better?
Regardless of the manufacturer, the drugs create the same level of immunization with a duration of up to 3 years. When choosing a vaccine, reactogenicity and the recommended age for use are assessed.
The main factors of reactogenicity of the vaccine are foreign proteins. In the preparations used for TBE, these are proteins of the chicken embryo, human albumin and specific proteins of the TBE virus antigen.
To reduce the negative effects on the body, vaccines are purified from protein inclusions to a safe norm for humans.
The Encepur vaccine has the highest degree of purification. According to research data, children vaccinated with this drug have developed:
- temperature reaction in 1.4%;
- malaise in 4.1%;
- muscle soreness in 6.1%;
- hyperemia and edema in 14.2%.
The FSME-Immun Junior vaccine also has a low reactogenicity. Since the child's body is more sensitive, experts recommend vaccinating with imported drugs.
In domestic drugs, the rates of adverse reactions are higher by an average of 10% -12%. In addition, headaches and joint aches are noted. The most reactogenic is the Mite-E-Vac vaccine.
How the vaccine is stored
Exposure to heat, sunlight, or violation of the optimal low temperature threshold and expiration date will reduce the immunogenicity of the vaccine.
Overheating and freezing the vaccine promotes protein aggregation. This can cause collaptoid reactions after drug administration.
The shelf life of EC vaccines is 1 year. The optimum temperature for transportation and storage is from + 2 ° to + 8 ° C. For storage, the drug is placed in a refrigerator with temperature control.
Vaccine is transported in thermal bags. Transportation is allowed at t from + 9 ° to + 25 ° C within 2 days.
Storing a vaccine at home is a complex process. There is no guarantee of a sudden shutdown of the light and other factors that violate the temperature regime. Therefore, for vaccination, it is better to select clinics with the presence of the selected drug.
Contraindications
Temporary contraindications for vaccination are acute infectious and somatic diseases, exacerbation of chronic pathologies. The vaccination is done 2 weeks after recovery.
Children who have had viral hepatitis or meningitis are vaccinated 6 months after recovery.
Absolute contraindications:
- sensitivity to drug components;
- allergic reactions to chicken protein (depending on the drug);
- severe reaction and complications after the initial administration of the vaccine.
Parents of children with a history of brain damage should insist on a detailed examination.
Diseases requiring medical supervision (vaccination can be combined with concomitant treatment):
- allergic dermatoses;
- localized skin infections;
- febrile seizures (taking antipyretics before the procedure and within 8 hours after);
- seizures in the hereditary line;
- cerebral disorders;
- congenital and acquired immunodeficiencies;
- pathology of the nervous system;
- systemic diseases;
- chronic diseases of internal organs.
The possibility of vaccination for children with diseases not listed in the list of contraindications is determined by the doctor, assessing the state of the body and the possible risk of infection with TBE.
In any case, you do not need to select the drug and vaccination schedule yourself. The best option for a specific child can only be offered by doctors.
Do I need to vaccinate my child?
If you live in the African savannah, there is no great need for vaccination against tick-borne encephalitis. The disease develops when a virus falls into the child's body. It is carried by encephalitis ticks, the usual habitat of which are the countries of Russia, Belarus, Ukraine, and so on. Ticks live in forests, parks, squares, in tall grass, thickets of green spaces. In most regions, the peak of their activity occurs in April – July, it is at this time that ticks multiply and migrate.
It is almost impossible to prevent a tick bite, even to notice it in time is not an easy task, therefore the risk of contracting tick-borne encephalitis in spring and summer is very high. The tick-borne encephalitis vaccine is a pharmaceutical preparation that contains particles of the virus - the causative agent of a dangerous disease. They cannot cause an independent illness, since they were previously weakened, rendered harmless.
In fact, these are only parts of the protein envelope of a real aggressive virus.But they can activate the immune system, "train" it to recognize a real virus and, if necessary, if it penetrates the body, be able to quickly deal with it.


The effectiveness of the tick-borne encephalitis vaccine for children is estimated at 95%, which means that the vast majority of those vaccinated form a complex of antibodies to this virus. Can a child get sick with tick-borne encephalitis after vaccination? Maybe no one is immune from this, but in a vaccinated child, the disease will be mild and will not cause total brain and spinal cord lesions, serious complications that can lead to the death of the child or his disability.
Therefore, vaccination is considered important and necessary for all children who live in areas where ticks are found. In regions where the risk of tick-borne encephalitis is high, for example, in the Urals, vaccination is mandatory, in regions with moderate and low prevalence of the disease, the decision to vaccinate is made by parents
And before making this decision, it should be well understood that the risk, even moderate or low, is not justified when it comes to children. For every 600 ticks, there is one that carries the deadly virus. In 2–5% of cases of infection, medicine is powerless, the child dies. The common consequences of tick-borne encephalitis include paralysis of the limbs, upper half of the body, impaired visual function, hearing, and psyche.
The situation is further complicated by the fact that there is no effective way to treat tick-borne encephalitis in nature. Doctors provide only symptomatic help to a sick child, support his organs and systems, but they cannot predict how destructive the consequences of severe intoxication can be.
Who needs
Vaccination against encephalitis is not required. However, it is recommended when visiting CE-endemic regions. The list of regions is published and regularly updated on the Rospotrebnadzor website.
The vaccine is recommended:
- people living and visiting areas where there is a high risk of infection or cases of TBE have been reported;
- persons engaged in deratization, disinsection activities, arrangement, clearing green areas;
- the contingent working with soil;
- personnel who come into contact with the cultures of the pathogen;
- donors.
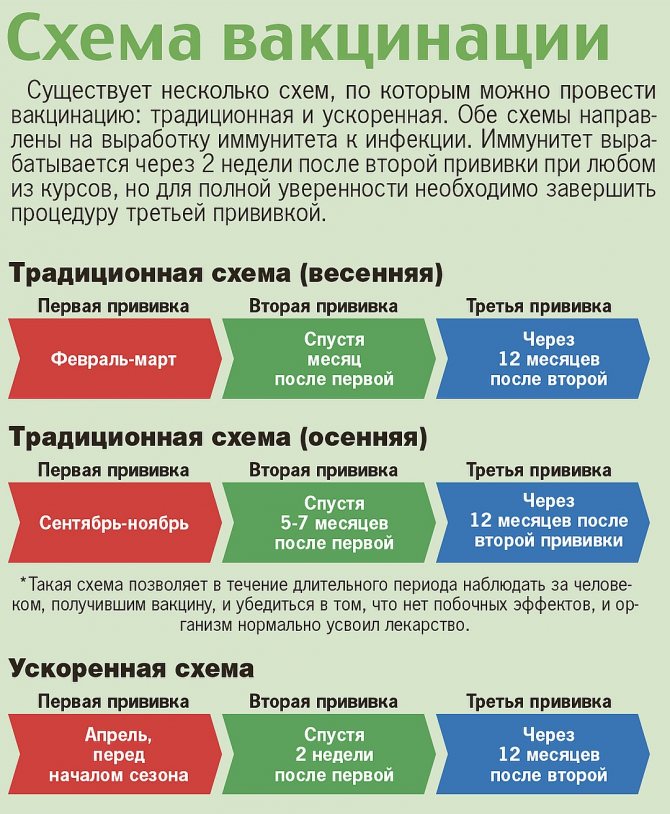
Scheme (schedule) of vaccination of adults and children
There are two types of vaccination: routine and emergency. In the first case, the injection is administered in 3 stages. The first time the vaccination is done in the autumn, the procedure is repeated in the spring. Between the first and second administration of the vaccine, it is necessary to maintain an interval of 7-12 months (according to the instructions for the drug used), then by the onset of the dangerous season, a stable immunity will develop in the body.
The third time the vaccination is done after 9-12 months, but no later than a year later. This type of vaccination is mandatory for residents of the most dangerous areas, where cases of infection with encephalitis are often noted. Vaccination helps reduce the risk of infection.
Emergency vaccination is carried out according to a different scheme - with a reduction in the intervals between vaccinations. It is carried out in exceptional cases, when a person will soon have to stay for a long time in places where the risk of getting an encephalitis tick bite is quite high. The emergency vaccination schedule requires three vaccinations. The first - 2-3 weeks before the intended departure to the unsafe area. 2-3 weeks should elapse between the first and second vaccinations. The third injection is given after 9-12 months.
In both cases, revaccination is carried out after 3 years and includes one vaccination. The above terms may vary slightly depending on the drug used.
It is important to know that the second time the vaccine should be administered a month before the start of seasonal tick activity, otherwise the immunity will be unstable. In the event that only 2 vaccinations were made, the resulting immunity will be valid for one season
To provide reliable protection for 3 years, you should not ignore the third and violate the frequency of procedures.
Vaccination schedule
How many types of vaccines are there and which one is better? Despite the well-established opinion that an imported drug is always better than a domestic one, in this situation it is not entirely true. There are several types of drugs on the vaccine market:
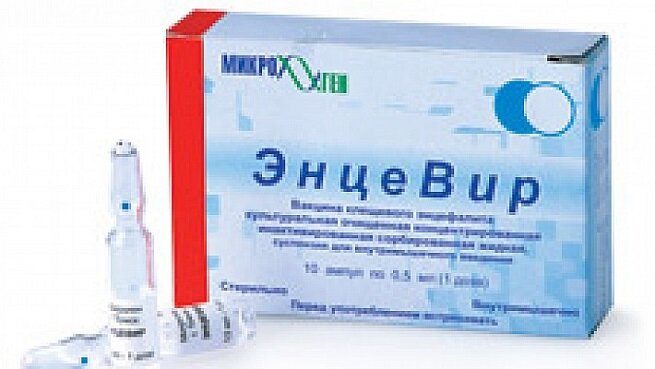
Entsevir - Russia (for adults and children over three years old).

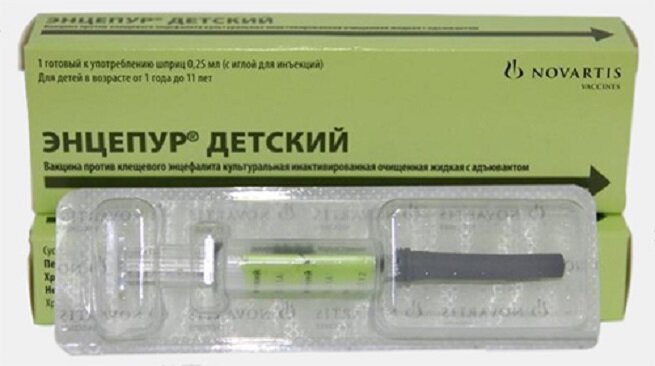
Encepur (children and adults) - Germany (for children from one to 12 years old and for adults).

FSME-IMMUN Inzhekt and FSME-IMMUN Injekt Junior - Austria (for adults over 16 years old and for children from one year old).
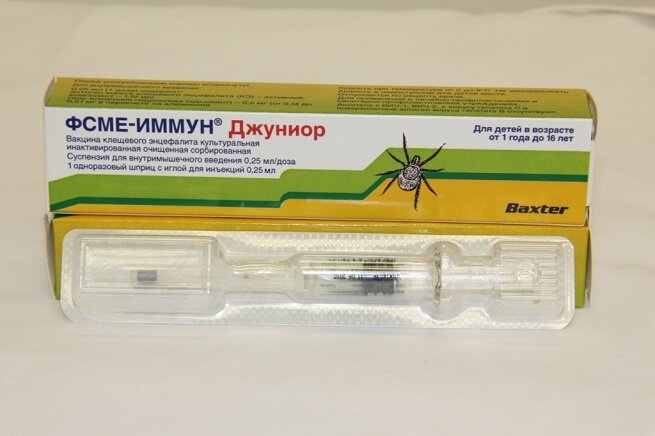

Tick E-Vak - Russia (from year).
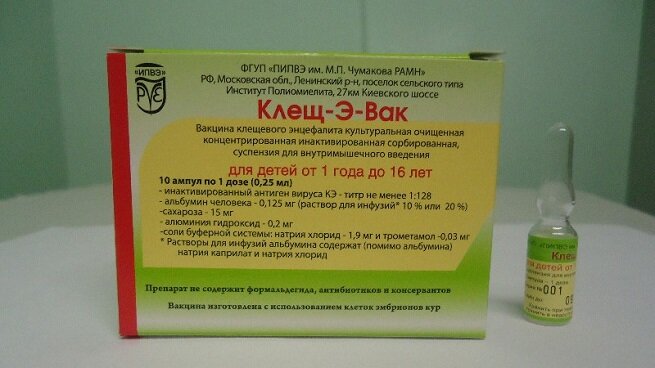

It is believed that there are no side effects in humans from imported vaccines, and this is the only advantage of this vaccine. In terms of the degree of protection reliability, they are not inferior to the Russian ones.
All of the above remedies include an inactive virus. The opinion that they contain a live vaccine is wrong. This practice has been abandoned for a long time, as it was dangerous and endangered the health of, first of all, children.
The vaccination schedule can be divided into two types:
- Two-component scheme.
- Three-component scheme.
Two-component scheme
Vaccination according to the two-component scheme differs from the three-component scheme only in time and number of vaccinations. There is a standard and an accelerated two-component scheme.

Standard
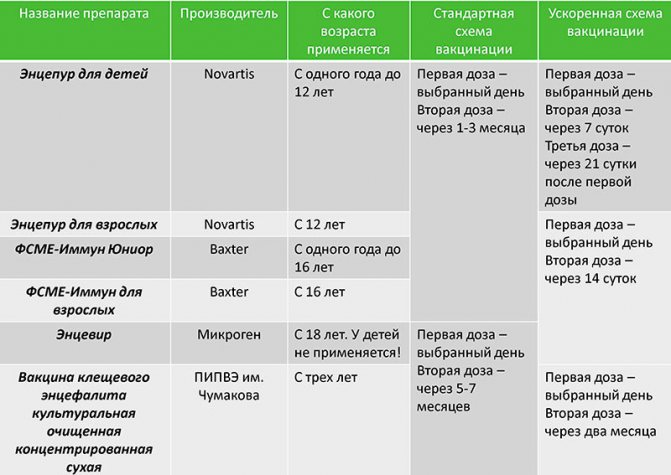
Children from one to 16 years old are vaccinated exclusively with children's drugs, in particular:
FSME-IMMUN Junior - the second dose is given 1-3 months after the first
Mite E-Vac - the second dose is given 5-7 months after the first
Encepur - the second dose is given 14 days after the first
Adults:
Encevir - the second dose is given 5-7 months after the first
Encepur - the second dose is given 1-3 months after the first
Accelerated
This scheme differs from the standard in the shortened terms of the vaccine, in particular:
Children:
Mite E-Vac - the second dose is given 1-2 months after the first
FSME-IMMUN Junior - the second dose is given 14 days after the first
Adults:
Encevir - the second dose should be given 1-3 months after the first
Encepur - the second dose is given 14 days after the first
Three-component scheme
How to vaccinate in a three-way scheme? The correct answer would be - you? No way! Only a doctor has the right to administer such vaccinations, since self-medication is a rather risky business.

In turn, the doctor prescribes this scheme to extend the period of protection of the body from the virus.
As a rule, after the second dose of the vaccine is introduced into the body of an adult or child, it becomes completely protected from this infection, and the third dose allows you to extend this immunity for another three years.
Subsequently, after the third injection, the vaccination is repeated every three years.
Price
Many vaccination clinics offer special offers and discounts when ordering group immunizations. At the same time, despite the difference in price, imported and domestic whey have approximately the same effectiveness. The table below shows the cost of one dose of tick-borne encephalitis vaccine of different production (it should be borne in mind that the procedure involves several vaccinations).
| Drug name | Cost (rubles) |
| FSME-Immun Inject | 1000 |
| EnceVir | 650 |
| Entsepur adult | 1250 |
| Entsepur for children | 1000 |
Answers to popular questions
There are a number of questions that patients are either shy or forget to ask at the doctor's appointment.Here are just a few of them:
- Is it allowed to wet the encephalitis vaccine? Modern vaccines are safe, they do not impose serious restrictions on the patient's lifestyle. The vaccine against encephalitis can be wetted, after the introduction of the vaccine, it is allowed to swim, do not just rub, scratch or shuffle the injection site so as not to infect the infection.
- Is it allowed to drink alcohol after the procedure? No, after the introduction of the vaccine against encephalitis, you should refrain from drinking alcohol. Alcohol weakens the body's defenses and can lead to an allergic reaction.
- Can I exercise after the procedure? It is undesirable, since active physical exercise depletes the body, placing additional stress on it.
- Are walks allowed? After the introduction of the vaccine against encephalitis, the body is weakened and open to various infections. Walking by itself will not harm the patient, but it is better to play it safe so as not to catch any viral infection.
- What should I do if my arm hurts or the temperature rises after the procedure? Most likely, in this way, a local reaction to the drug is manifested. These symptoms do not require special treatment. As a rule, all unpleasant sensations disappear in 1-3 days, if this has not happened, you should consult a doctor.
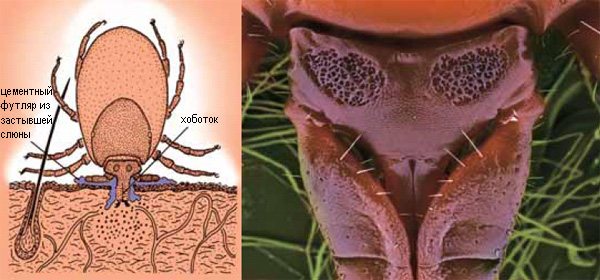

Despite the presence of contraindications and inconveniences caused by the introduction of the vaccine against encephalitis, vaccination is the only truly reliable means of protection.
How to protect yourself from bites
To protect yourself from the bites of these insects, it is recommended to wear a long-sleeved shirt, trousers, and a scarf for a walk in the forest or park. Today, there are special products (repellents) on sale that are applied to clothing and repel ticks. After walking in the forest, you should very carefully examine your clothes and skin for the presence of insects.


The owners of summer cottages can treat their lands with protective solutions. Vaccination is considered one of the most effective ways to protect against the effects of an insect bite.
Vaccination reactions and complications
As a rule, the reaction to the vaccine against encephalitis does not become very acute and severe if the vaccine is stored correctly and the rules for its administration are not violated. That is, the number of complications after such injections is minimal.

All side effects of vaccination in adults can be divided into two groups: general and local.
- Local manifestations are redness of the injection site, possibly induration. After 5 days, all these symptoms disappear on their own without additional treatment.
- The temperature after tick vaccination rarely rises. In addition, its growth is usually not critical, therefore it does not threaten the health and life of the patient, does not need to be adjusted or taken antipyretic drugs. As a rule, the temperature rises in the range of 1-1.5 ℃.
- Common manifestations in adults include joint pain, migraines, general weakness and loss of strength. Typically, these symptoms are similar to the onset of a cold, so it is best to consult a therapist.
- Among the complications that tick vaccination can cause is allergy. It can manifest itself in the form of a rash, urticaria, less often - anaphylaxis or angioedema.
- Alarming symptoms that require the attention of a specialist include suppuration of the injection site, high fever, which lasts several days in adults, convulsions, and some other neurological manifestations. As a rule, the reason for such a reaction of the body is the improper storage of the vaccine, including the expiration of the expiration date, as well as the violation of the rules for administering the drug.
In the presence of local reactions that do not cause significant discomfort to a person, for example, a rise in temperature, general malaise or loss of strength, no medical attention is required.
Harm
In order not to become infected with encephalitis, it is strongly recommended to carry out preventive measures in a timely manner. As a rule, the vaccination against encephalitis is well tolerated by people, without any negative effects. Nevertheless, in about 5% of patients, allergic reactions are recorded in the form of a rash in the area of serum injection. Some vaccinated people may have a rise in body temperature and a general deterioration in well-being. Such symptoms go away on their own after 1-2 days.

Which vaccine against tick-borne encephalitis is better
Children are vaccinated against encephalitis with weakened live or inactivated vaccines. Which vaccine is best for you depends on your age. If you get vaccinated at a state medical institution, they use domestic vaccines, which are much cheaper than imported ones. Therefore, there is not much to choose from.
Let's consider the main options:
- Produced in the Russian Federation. " Although these drugs are generally well tolerated, young children may experience adverse reactions after encephalitis vaccination with these drugs. Therefore, it is better for them to use other options.
- Children from 3 years old are allowed to be vaccinated with the domestic drug "Encevir Neo".
- Imported drugs "FSME-Immun" (Germany) and "Encepur" (Austria) are produced in different dosages for both adults and children. There are practically no side effects after such vaccinations. They are suitable for vaccinating children from 1 year old. Vaccines are packaged in special disposable syringes, but their cost is very high.
Thus, in order to determine which of the vaccines is better, you need to be guided by the situation. For the youngest children, it is better to choose imported vaccines rather than risk or expose them to an increased risk of complications. For adults, this issue is not so acute. Therefore, if there is no opportunity to purchase expensive foreign drugs, you can stop at domestic vaccines.


In some cases, vaccination is strictly contraindicated. To such conditions, doctors include exacerbations of chronic pathologies, the presence of bronchial asthma, lupus erythematosus, rheumatoid arthritis or rheumatism.
In addition, contraindications also include:
- the period of pregnancy and breastfeeding;
- children's age up to 1 year;
- the course of infectious diseases in the acute stage;
- taking a large amount of alcohol on the eve of the vaccination;
- allergy to chicken, eggs, gentamicin, protamine sulfate, formaldehyde;
- anaphylactic shock reported during primary vaccination.
Usually, tick vaccination is tolerated by children and adults well and without complications. Allergic reactions to the vaccine occur in only 5% of patients who received serum. An increase in temperature and general malaise are recorded in 7% of cases. As a rule, unpleasant manifestations appear within 12 hours after vaccination. After 1-2 days, all unpleasant symptoms will disappear. According to statistics, the frequency of adverse reactions after the use of imported vaccines is significantly lower than after vaccination with domestic drugs.


Possible adverse reactions after vaccination include:
- Strong headache;
- chills and high fever;
- muscle pain and cramps;
- inflammation of the injection site, soreness and itching of the skin;
- sleep disorders;
- nausea and vomiting;
- lack of appetite;
- indigestion;
- enlarged lymph nodes;
- tachycardia;
- loss of strength and absent-mindedness.
Possible complications after vaccination
As a rule, any of the approved vaccines is well tolerated by the patient if stored and used correctly. Of course, the vaccine must be of adequate quality.
Vaccination against ticks usually does not cause severe reactions or complications, it is well tolerated regardless of which manufacturer is chosen. What complications can arise after the procedure:
- Minor problems with local reactions: redness or infiltration. All this should not alarm the patient, it will disappear by itself somewhere in 5 days after the introduction. Local reactions also include allergic rashes or other allergic skin problems.
- For almost all immunizations, a general reaction such as fever can develop. It won't be that big, just a degree or one and a half. It does not manifest itself in everyone, but if it does, then there is no need to bring down such a temperature.
- Swelling, headaches, or fatigue may also occur. Such symptoms require a doctor's consultation, as this means that a viral infection has appeared in the body.
- In case of improper administration, storage or poor-quality vaccine, serious consequences can occur in the form of suppuration of the injection site, convulsions or other serious problems. It does not depend on the level of immunity, the presence or absence of contraindications to vaccination, or the name of the drug. In case of manifestation of such symptoms, it is necessary to consult a doctor as soon as possible, explaining to him where, when and with what vaccine the immunization was carried out.
In the case of mild types of ailments, the patient does not need to do anything to get rid of it, the side effects will quickly go away on their own. However, if serious disturbances in the functioning of the body appear, then you need to immediately consult a doctor who can either eliminate these consequences, or minimize their effect on the body.
In the case of such a vaccination, it will be much more correct to protect yourself from the disease in advance, even if you have to spend money or experience skin redness. But as a result, tick bites will not have fatal consequences for the vaccinated person that cannot be cured during life. Remember that the mildest form of encephalitis is always worse than the side effects of the vaccine. Therefore, it is best if you provide protection for yourself and your children in time.
Contraindications
There is a fairly impressive list of contraindications to this vaccine. The patient needs to carefully study it and track the state of his health, making sure that he does not fall under any of the points:
Tick injections are not given if the previous vaccination has caused a vivid reaction or any health problems for the patient. Vaccination takes place with a live pathogen that is weakened. Therefore, any diseases with a decrease in the level of immunity (especially sharp) are a contraindication to the introduction. For example, they include colds. As a result, any acute infectious diseases or chronic diseases in the acute stage are also an absolute contraindication. Vaccination in this condition is best postponed until health improves. Pregnancy is also a contraindication. There is no information how, although a weakened, but still a living pathogen can behave in a pregnant woman's body. It is not known how it will affect the health of the unborn child. Often a woman's immune system can be weakened during pregnancy, which creates additional problems with vaccination. Some vaccines also have an indication on the list that the drug is contraindicated for people who have allergic reactions to chicken protein. But not all vaccines contain this protein. The patient needs to carefully study the composition of what he will be injected. This composition is written in the annotation that goes with each vaccine. Little patients. Children should also be protected while ticks spread.Most often, vaccination is allowed for a 4-year-old baby, but certain childhood vaccine options are allowed for use from 3 years of age, and some even from 1 year of age. Disorders in the liver and kidneys. This is especially true for severe renal and hepatic insufficiency, chronic diseases or acute stages of such diseases.
In this case, it is best to make every effort to minimize possible contact with ticks by taking precautions.
Indications for use
Tick-borne prevention should be carried out by people living in areas with a forest landscape and a humid climate. In addition, indications for immunoglobulin injections are:
- planned trips to endemic areas (especially in summer and spring when ticks are at peak activity);
- work in the environmental sphere, on farms, logging, military bases;
- frequent hikes, hunting.