Author rating
The author of the article
Yakov Pavlovich
Professor, Head of the Department of Vegetable Growing
Articles written
153
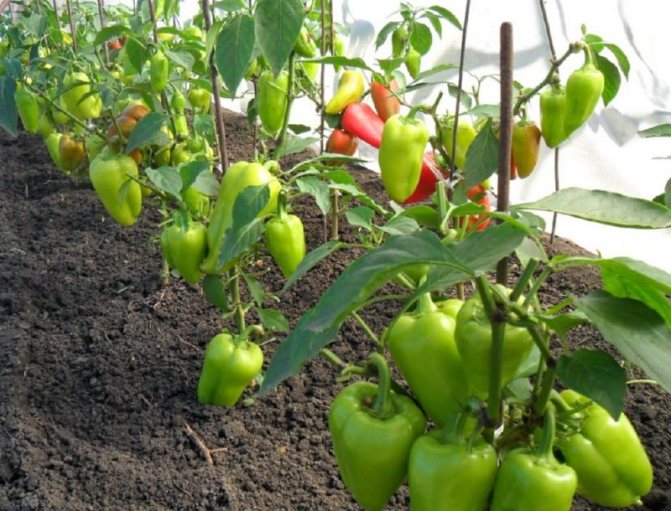
Bell peppers are a favorite of many gardeners. With its compact size and relative unpretentiousness, it gives a good harvest. The fruits are rich in vitamins C, K, A, micro- and macroelements. They are kept fresh for a long time, used for canning. Applying the knowledge of how to form pepper bushes in the greenhouse and in the open field will increase the yield and improve the quality of the fruit. And this is exactly what every owner of a personal plot dreams of.
Why mold pepper bushes
Sometimes gardeners underestimate the formation of bell pepper bushes, ignoring this agricultural technique. They believe that it is enough to simply remove dry leaves and drying shoots from the bushes.
In fact, with the correct formation of pepper bushes, you can achieve many goals:
- shoots and barren flowers are removed, on the formation of which the plant also spends strength;
- removing unnecessary ovaries and shoots relieves unnecessary stress on the bushes;
- vegetables ripen more evenly;
- sunlight enters all parts of the bushes evenly;
- bushes become neat and beautiful;
- the risk of diseases and pests is minimized (it is easier to deal with them, since the bushes are clearly visible);
- the fruits retain their commercial characteristics.
On a note!
Almost all varieties of peppers need to be shaped. There are some low-growing plants that do not have lush vegetation that do not require shaping. Sometimes it is enough for them to remove dry leaves.
Possible mistakes of gardeners

There are several major mistakes that gardeners do not get the expected harvest.
When forming bushes, a certain balance is observed. Too much pruning makes it difficult to synthesize enough energy to produce a large crop. Therefore, it is necessary to remove excess shoots and foliage gradually and in reasonable quantities.
Pepper grazing is not carried out if the plants are planted too rarely. The distance between the bushes should be 25 centimeters or more. On plants, near which there are no neighboring pepper bushes, dense greens are left, as it protects the fruits from burning out, and the soil from drying out.
Pepper formation is not carried out if the weather is dry and too hot for several days. By removing excess shoots and leaves, the soil and plants are deprived of additional protection from the sun.
Do not pinch shoots and remove leaves in wet weather. The procedure is carried out only in dry weather. This promotes rapid drying of injured areas and reduces the risk of infection.
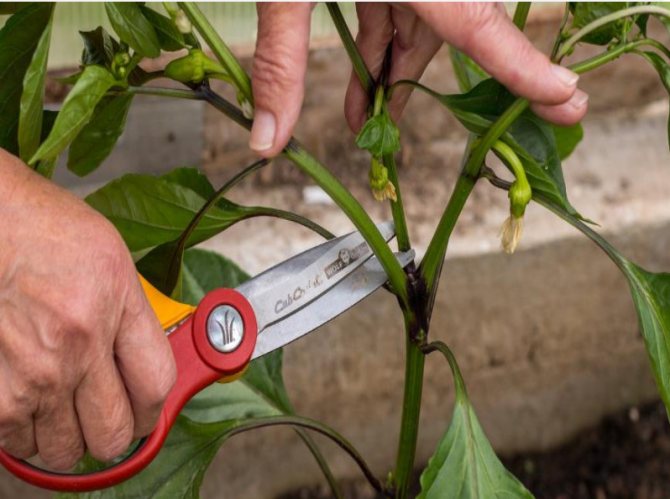
It is possible to form bushes in the complete absence of diseases on the plants. If at least one plant is sick, when pruning, the disease will spread to other bushes through the pruning shears, knife or scissors with which this procedure was carried out. For trimming, only clean, disinfected, sharp, rust-free tools are taken.
In addition, weakened, diseased plants die quickly after pruning, so they must first be cured, and then formed or removed (if the disease cannot be treated).
After pruning, some of the most developed shoots should remain on the plants, which are located at a distance from each other. They should not touch and interfere with the growth of others.
The main purpose of the formation of pepper bushes is the rational design of strong compact plants with powerful shoots, which are created by cutting off excess branches. Having carried out competent pruning, the pepper develops better, is less sick and increases the yield.
Having figured out the intricacies of the formation of pepper, any gardener, regardless of where the pepper was planted in a greenhouse or open field, gets an excellent harvest of large and tasty peppers.
What peppers require shaping


There are many varieties and hybrids of peppers, they differ from each other in the height of the bushes, the period of fruiting, the shape and color of the fruit. Many undersized varieties do not differ in a lush green part, they are rarely stepchildren and formed. But tall plants, on the contrary, require mandatory formation, since without this procedure they will not be able to grow.
Peculiarities of pinching and formation depend, first of all, on the height of the bushes. For low-growing varieties (height no more than 0.5 m), shaping is not necessary, provided that they are located at a distance from each other. If the seedlings are planted too close, then excess shoots and leaves will need to be removed.
Why are bell peppers formed?
Often gardeners (especially beginners sin this) neglect the formation of peppers, believing that sufficient lighting, feeding, watering and treatment from parasites will provide everything necessary for a good harvest. But the correct design of the bushes will give the following advantages:
- the formation of a strong plant skeleton;
- removal of barren branches;
- preservation of the strength of the plant for the ripening of large, juicy peppers;
- providing ventilation to prevent the development of diseases;
- creating good lighting;
- no overload with excess ovaries;
- uniform aging;
- aesthetic appearance.


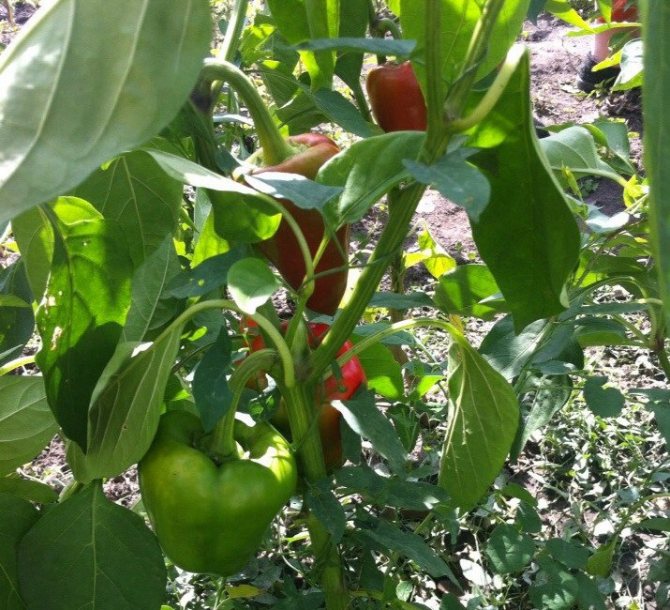
On specimens, the development of which is allowed to flow, weak peppers of different sizes will be chaotically formed, the maturation of which is difficult. On those formed at about the same time, the harvest of ripe, healthy peppers will ripen.
Important! Forming affects the presentation of the crop. Fruits from the "right" bush will be of the same size and shape, reaching biological maturity at the same time. Ideal for beautiful blanks, stuffing, as well as for sale.
Meaning for different varieties
Not all varieties are equally in need of special work. Be sure to form according to all the rules, using pinching, pinching, trimming excess leaves, tall varieties. The scheme involves one or two escapes. Medium-sized ones are subject to removal of the lower branches, as well as non-yielding, “fattening” branches. They are formed into two or three stems. Low-growing varieties with a sufficiently sparse planting do without molding. It is enough to remove the diseased, twisted and sterile twigs. And with a tight planting - extra leaves to ensure ventilation.
Which pepper does not require shaping
If you do not want to engage in pinching and pinching, in addition to dwarf ones, you should pay attention to specially bred weakly branching varieties and hybrids: Florida, Dobryak, Bogatyr, Swallow, Goodwin F1, Mercury F1 and many others. They form less green mass than traditional ones and form independently.


In addition, there is no need to manipulate decorative and indoor (pot) varieties of sweet and hot peppers.
Important! If the goal is not the aesthetic component of an indoor ornamental plant, but still a harvest, it is worth forming it by removing excess shoots and timely pinching.Getting food and growing the root system in a pot is limited, therefore, without molding, the bush will not have enough strength for full fruiting.
When to start shaping


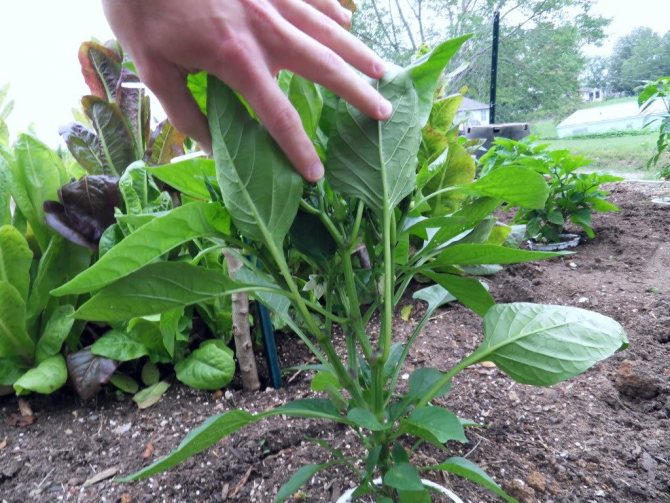
Peppers are very rarely grown directly from seeds; first, they take care of the seedlings. Therefore, even before the transfer of seedlings to the greenhouse, they begin to form young bushes. The first procedures for removing stepchildren begin when the peppers reach a height of 20 cm.
On a note!
Around the planted plants, space is left for the development of bushes. No more than 5-6 pieces are planted on each square.
The first shaping procedures are performed before planting, and then they are regularly pruned and excess shoots are removed after the seedlings take root in a new place.
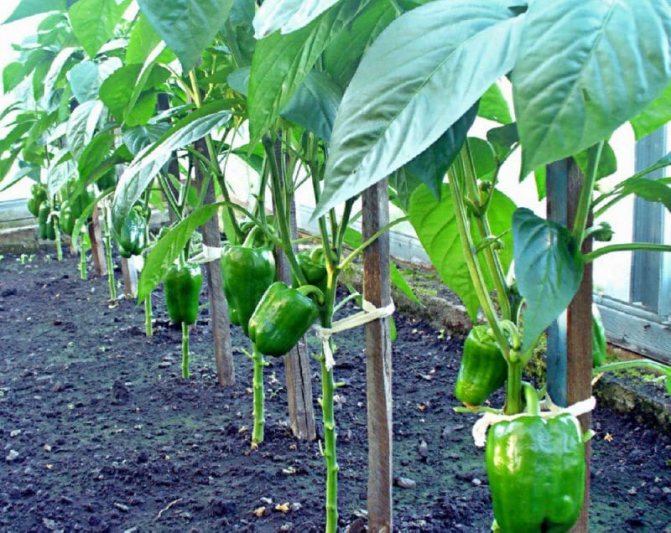
How to properly form peppers in a greenhouse and in the open field: forming schemes
Agrotechnology of sweet pepper in open and closed ground includes several components. This is timely watering, loosening, fertilizing with mineral or organic fertilizers, as well as the fight against pests and diseases. But, in addition to these standard and mandatory measures, there is one more thing - the correct formation of a plant bush. The formation of pepper in a greenhouse and on beds in the open field is an agricultural technique, which in many cases cannot be dispensed with if you want to get a decent harvest of this nightshade plant. Information on how to properly form bell pepper bushes will be useful to everyone who grows it on their plots.
Basic shaping techniques
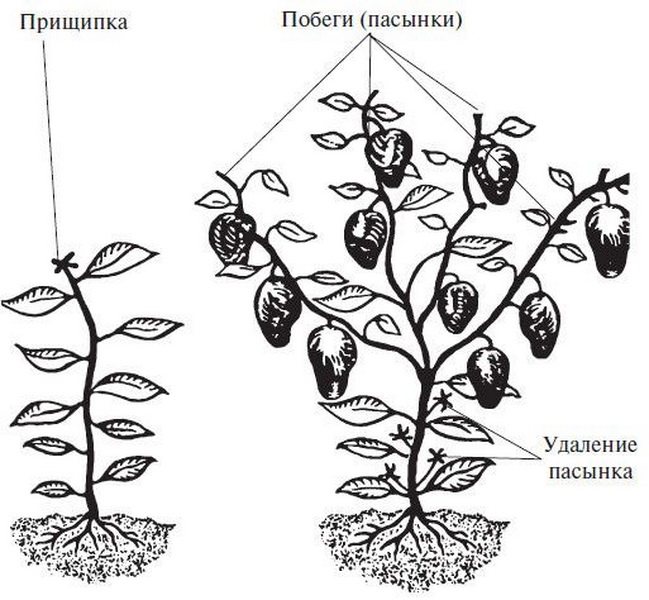
When forming bushes of sweet pepper, 3 basic techniques are used: pinching, pruning, pinching. Rules are used for each procedure.
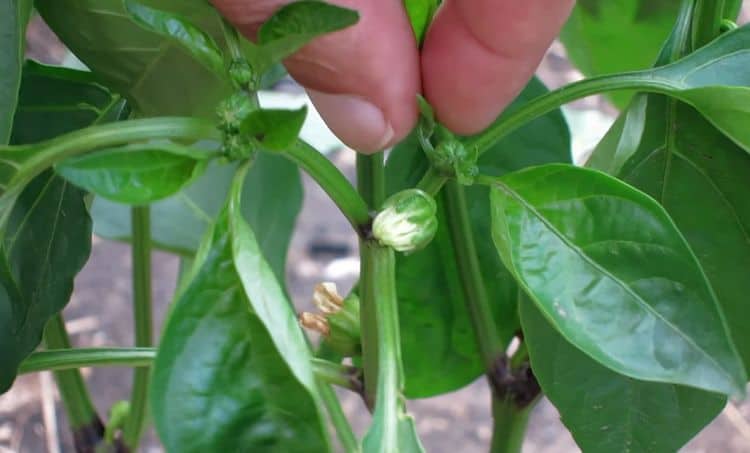
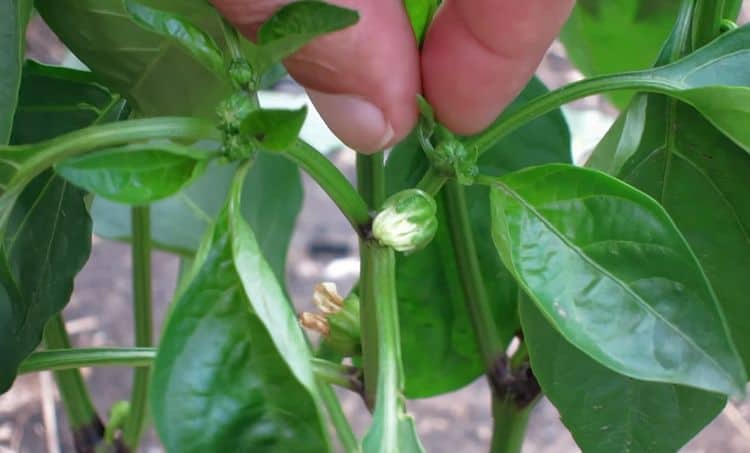
Steying


This technique involves cutting off additional lateral processes that grow in the sinuses of the leaves. If you leave all the additional branches, then the plant will spend a lot of energy on their growth, and not on the formation of vegetables and their ripening.
Is it possible and necessary to pick off the lower leaves
You can pick off the lower leaves of the pepper bush, and in some cases it is necessary... The feasibility of this measure largely depends on weather conditions. So, in hot and dry weather, the lower leaves are not removed, since they protect the soil from drying out. The sun's rays will destroy the plant without leaves in a short time.
If the weather is wet, the lower part of the pepper bush is exposed, since excess moisture accumulates in the leaves, which, in turn, provokes the development of bacterial and fungal infections.
The scheme of the formation of bell pepper
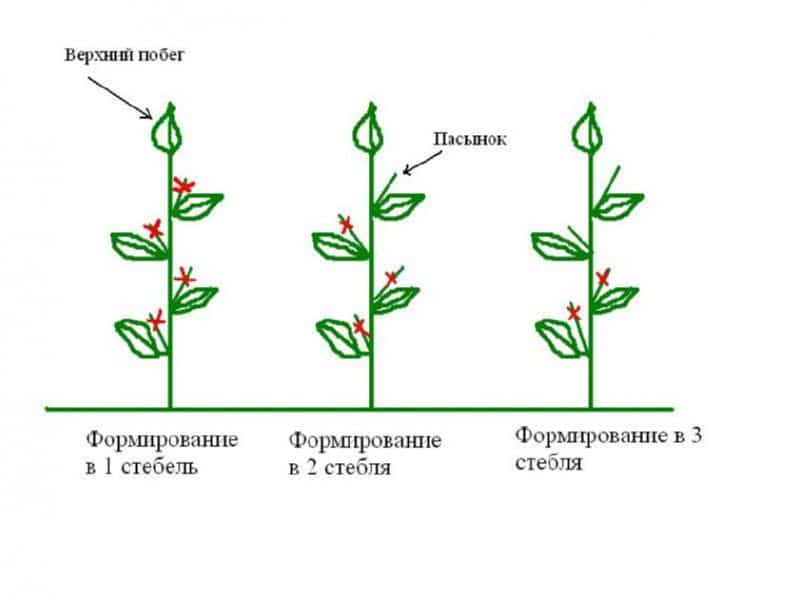
They are engaged in the formation of peppers so as not to overload the plants with excess green mass, as well as to make up the forces for the formation of vegetables and their ripening. But in order not to harm the bushes with too active pruning, the procedure is performed according to the rules in compliance with the selected scheme. Variants of the formation of peppers in 1-3 stalks are common. The choice depends on the density of planting in the greenhouse.
On a note!
You can take a closer look at the features of each scheme in the photo and in video tutorials.
One stem
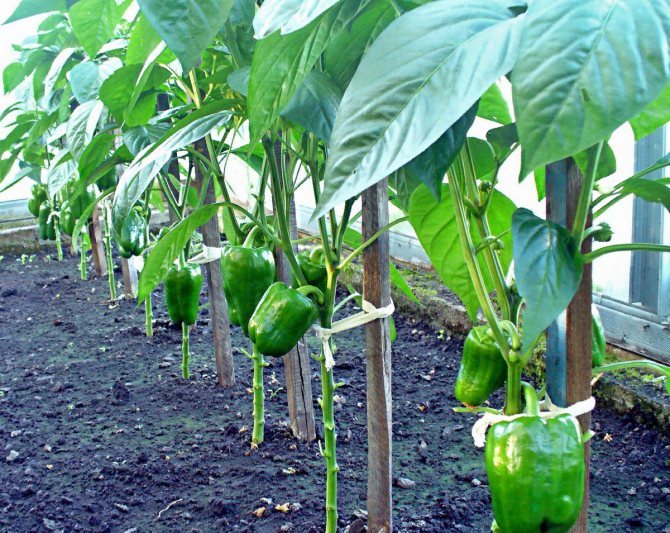


If the seedlings are planted close, then the bushes form into one stem. In such conditions, it will not be possible to get a harvest from voluminous bushes.
Step-by-step instructions for pinching are as follows.
- The first stage of formation is performed when the main stem forks.
- Remove shoots from the side, leaving one. Cutting is carried out in such a way as to create a bush with one straight shoot.
- When additional forks are formed on the main stem, they are carefully cut off.
- After about 12 vegetables appear on the plant, pinch the crown.
After removing the growth point, the bush will stop growing, all its strength will be spent on the growth and ripening of vegetables.
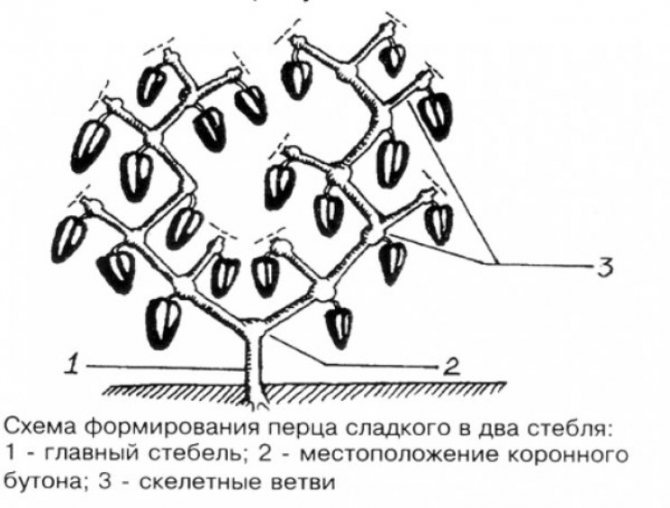
2 stems

The most common option for forming peppers into two stalks.The result is a V-shaped plant that ripens up to 25 vegetables.
The step-by-step process is as follows.
- Formation begins after the branching of the central stem.
- All stepsons of the first order are removed, a bush with two shoots should turn out.
- After the formation of branching on the shoots of the first level, remove all additional, except for one of the strongest.
- The previous step is repeated for all new shoots.
- After the formation of about 20-25 vegetables on the bush, pinch all the growing tops.
After the pinching, the plant will stop growing and will devote all its strength to the formation of vegetables.
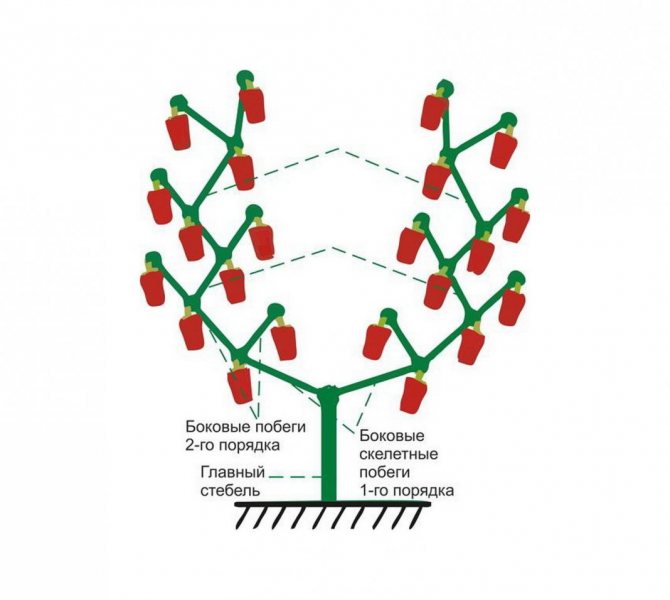
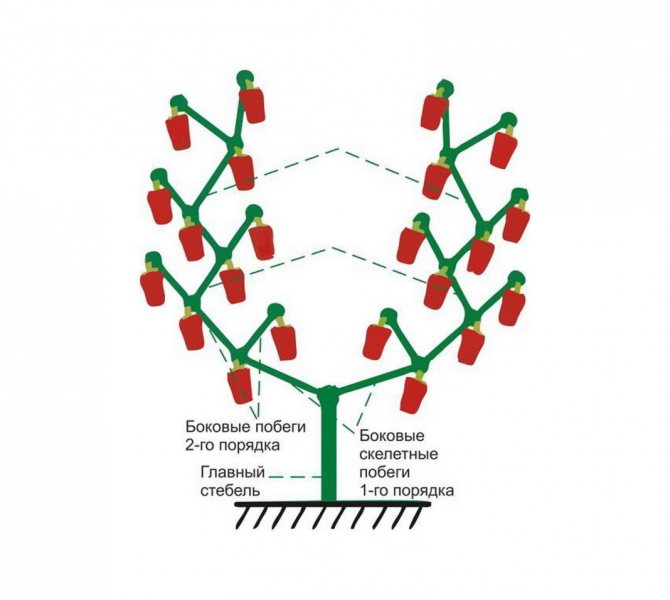
3 stems

A bush formed into three stalks requires more space but results in a richer crop. With this option, better lighting is achieved.
Step-by-step description of the "3-stem" forming scheme:
- Formation begins after branching.
- If there are more than 3 shoots in the branch, then the extra ones are removed.
- If the fork is formed from only 2 shoots, then the lower shoots on the main stem are not removed. When they grow up, choose the strongest, and pinch the rest.
- On the skeletal stems of the first level, after the fork appears, all the weak are pinched, leaving one of the most powerful ones.
- The actions are repeated for the skeletal branches of the new orders, until 25-30 vegetables are formed on the bush. After that, pinch the top, removing the growth point.
Timely removal of the growing point stops the plant, all its power will be directed to the formation of vegetables and their ripening.
Tips & Tricks
To properly form pepper bushes in open and closed ground, pay attention to the advice of experienced gardeners, who were convinced of their practical value from their own experience. So:
- If not one, but several crown buds are formed on the seedlings of peppers, all of them must be immediately removed. This will enable young bushes to grow higher fruiting shoots.
- On too densely leafy pepper plants, it is necessary to pick off excess leaves, even if they are healthy and green, so that they do not take away the juice intended for the fruit. But you should not get too carried away with this, because the leaves are important vegetative organs of plants and without them the normal existence of peppers is impossible.
- Consider the weather conditions during the growing season of the peppers. In a summer drought, it is better not to pick off the leaves of the peppers growing on the lower branches and stem to the fork - they will create a shadow and cover the ground, which will not allow it to overheat. In rainy weather, on the contrary, these leaves must be removed without fail so that the earth is well ventilated and excess moisture does not stagnate on it, which creates perfect conditions for the development of bacterial and fungal diseases.
- Carry out the most recent removal of leaves no later than 30-45 days before the expected date of collection of the last fruits, otherwise they will not ripen.
Bush formation rules


At high temperature and humidity in greenhouses and greenhouses, bushes of peppers tend to grow strongly and become covered with abundant foliage. But in such cases, not too many fruits are formed, since all efforts are spent on the formation and nutrition of greenery.
Only with the help of proper shaping will it be possible to contribute to the formation of vegetables. Peppers begin to form in greenhouses already at the seedling stage.
Formation during the seedling period
If pepper seedlings are grown on their own, they begin to form bushes when they reach a height of 15-20 cm. It is at this stage of development that the main stem is most often divided into 2 new branches.
A crown bud appears between the new shoots (first level). In order not to load the seedling ahead of time, it is pinched off.
On a note!
Leave the crown bud when planning seed collection for planting next year, for example, if it is a rare valuable variety. It is from them that vegetables are formed and grown, which have the healthiest and strongest seeds.
Forming in the greenhouse


In polycarbonate greenhouses, as well as in greenhouses with warm beds or additional heating, all conditions for rapid growth and development are created for peppers. The green mass is developing very rapidly. Often, plants do not have enough space for the full formation of vegetables.
In the greenhouse, it is necessary to plant seedlings according to the scheme 30x70 cm (3-6 pieces are obtained for each square).
The formation of bushes in the greenhouse is performed according to the following scheme:
- All leaves and stepsons that appear before the fork of the main stem are removed. This is done gradually so as not to weaken the plant.
- After the first fork, 2 strong shoots of the first level are left. This is how the pepper is formed into 2 stalks.
- Skeletal shoots will also split, leaving two stalks of the second level. On each shoot of 1 level, one strong is left (leaves and ovaries on it are not touched). The rest are pinched after the first leaf and flower.
- With shoots of the third order and higher, a similar procedure is performed.
If you plan to form sweet peppers in 2 stems, then pre-trellis are installed in the greenhouse so that each new order can be tied to the transverse bar. Tied up without fail, as the stems can break under the weight of the fruit.
Throughout the entire growing period, they not only follow the chosen formation pattern, but also constantly inspect the bushes. At the same time, unnecessary shoots and stepsons are constantly removed, especially if they grow inside the plant. All points of growth are pinched 1.5 months before harvest.
Features of shaping for open ground


When growing peppers in open ground, the formation of bushes is carried out only for medium and tall varieties. Low-growing varieties do not need to be formed.
Formation of bushes in the open field in the following sequence.
- When the peppers reach a height of 25-30 cm, the crown buds are removed from them. Also pinch buds on the shoots of the first level. This will provoke the growth of additional shoots. The seedlings will start to bush. 3-5 skeletal trunks of the first level are left.
- At each next level, a similar number of additional shoots are left. Remove the stems above the first flower and leaf.
- Tear off the lower leaves (located on the main stem), cut off those shoots that grow inward, remove all yellow and damaged leaves.
- After the required number of vegetables appears, all skeletal branches are pinched at the point of growth.
On a note!
After removing the growth point on all shoots, the left ovaries will begin to actively grow and develop, and new ones will no longer appear. The last procedures for the formation of bushes are performed 1 month before the end of fruiting.
Common mistakes
A common mistake - pinching of bushes located at a distance of more than 20 cm. With such rarely planted bushes, the green mass is left.
Reference. Many gardeners are in a hurry to remove new leaves and shoots. This is also a mistake. No more than two leaves are removed per day. Otherwise, the plant will experience severe stress and may die.
Insufficient attention of the vegetable grower to the disinfection of the instrument, with the help of which pinching and pruning are performed, can cause the plant to become infected with an infection. Disinfect the instrument with alcohol and chlorine-containing preparations.
Another common mistake - pinching and pinching in wet and rainy weather, which again increases the risk of infection. The procedures are carried out in dry weather so that the sections dry out faster.
Many gardeners leave a large number of ovaries on the plant., mistakenly believing that fruits are formed from them.In fact, in this case, the plant spends energy on the development of unnecessary areas.
Plant care after formation


The process of pinching and forming shrubs is stressful for plants. After the procedure, the pepper needs proper and competent care so that the plant quickly recovers and continues to grow.
Initially, the bushes are tied to trellises and support so that the branches do not break under the weight of the ovary. Regular irrigation with warm water is carried out. Watered early in the morning or late in the evening. The next watering is combined with fertilization.
When you can do without shaping
All undersized and weakly branching varieties of pepper are not subject to forming. Therefore, when buying seeds or seedlings of peppers, do not hesitate to ask the seller about the height and bushiness of the variety you are purchasing.
Low-growing varieties include varieties with a height of 45-65 cm. It is pointless to form them - depending on the variety, from 8 to 15 fruits are tied on the bush, and then the plant stops growing, directing all forces to the development and amicable maturation of the formed ovary.
Popular undersized peppers include:
- Florida;
- Topolin;
- Alyosha Popovich;
- Ilya Muromets;
- Nikitich;
- Gift from Moldova;
- Bogatyr;
- Zodiac;
- Good man;
- Swallow;
- Belozerka, etc.
They do not need to form a variety with hot pepper - almost all of them are undersized.
Peppers with a height of 65 to 100 cm are considered to be medium-sized. It is believed that the formation of the crop in them goes in 2 waves, and then the bush stops the formation of new ovaries.
In fact, such varieties do not stop forming a new ovary, but the size and weight of new fruits are noticeably inferior to the varietal standard. Small fruits are not suitable for implementation, but they are quite suitable for the owners' own needs.
The popular varieties are medium-sized:
- California miracle;
- Atlant;
- Merchant;
- Goliath;
- Aphrodite and others.
Their formation is predominantly cosmetic in nature and consists in the removal of branches growing inside the bush. Although some gardeners prefer to carry out their full-fledged formation, claiming that in this way you can get 3 marketable waves of the crop.
The reason for this divergence of opinions among gardeners lies in the biological characteristics of medium-sized varieties. Medium-sized peppers grow up to 100-120 cm in indoor conditions, i.e. "Outgrows" average-sized standards. Therefore, if you form the bushes correctly, then you can count on a significant increase in yield.
Pepper varieties that grow above 1 m are tall. They are the most productive, but also the most demanding to care for.
Popular tall varieties include:
- Orange miracle;
- Cockatoo;
- Chord;
- Cornet;
- Hercules;
- Claudio et al.
It is the tall peppers that require careful shaping of the bush.
What varieties require formation
All varieties of pepper, but especially tall ones, need to remove some of the shoots. In medium-sized bushes, only sterile and lower shoots are disposed of. This makes it possible to free the plant from unprofitable "parasites" without fruit and to increase illumination and ventilation.
Low-growing and dwarf varieties bear fruit perfectly without forming, if the planting scheme provides for a distance of at least 45 cm between them.However, gardeners, in order to save space in the greenhouse, plant bushes much denser. Therefore, the peppers must be formed so that excessive density, lack of sufficient light and ventilation does not affect the development of plants. They are grown outdoors without forming.
Please note! Any actions for the formation of pepper are carried out on absolutely healthy bushes and with an exceptionally clean instrument. This will save the plantings from pathogens.Diseased plants are immediately removed to avoid spreading the infection.


Pepper formation increases yield