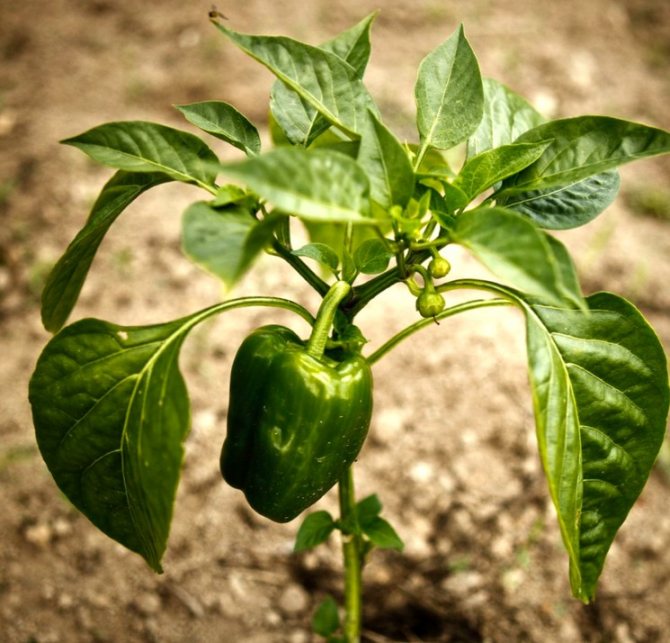
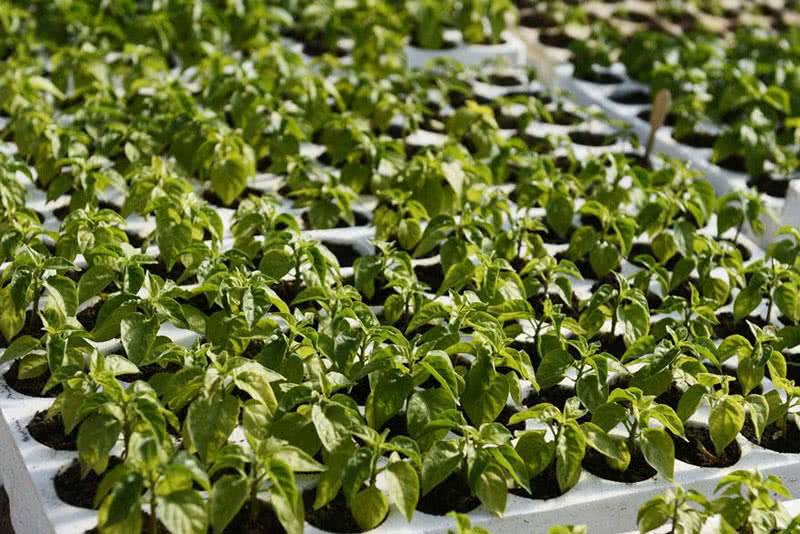
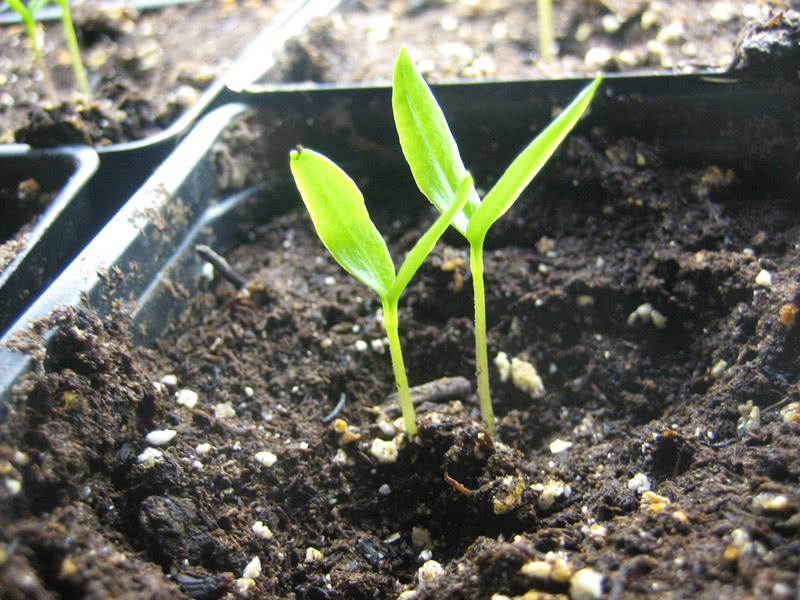
To get a chic harvest of sweet peppers, you first need to properly grow strong seedlings at home. The procedure for growing a crop is in many ways similar to eggplant and partly to tomatoes, but there are also fundamental differences. Pepper reacts sharply to temperature fluctuations (sharp drops) and an unsuccessful transplant (picking), due to which the level of its vitality decreases sharply and it slows down in growth.
Therefore, before you start sowing pepper seeds for seedlings, you need to familiarize yourself with the main features and rules of its cultivation. Next, you will find detailed step-by-step instructions on the preparation and direct planting of pepper seeds for seedlings at home, as well as useful photo and video materials.
Here you will find out:
How is pepper planting carried out, depending on the regions
In the vast majority of regions, bell peppers have to be planted in greenhouses. Even in the latitudes of Voronezh or Saratov, where the summer is quite warm, pepper is not always planted in unprotected soil. This culture is more thermophilic than its related tomatoes. In addition to real warmth, peppers need sunlight, fertile soil, and adequate moisture.
It has become much easier to grow peppers with the advent of polycarbonate greenhouses, which hold heat better and have higher diffuse sunlight permeability than conventional materials. But even in ordinary film greenhouses in the latitudes of Moscow and to the north, most varieties of pepper feel fine. In the south (from the Volgograd region), greenhouses are used only if they want to get especially early harvests.
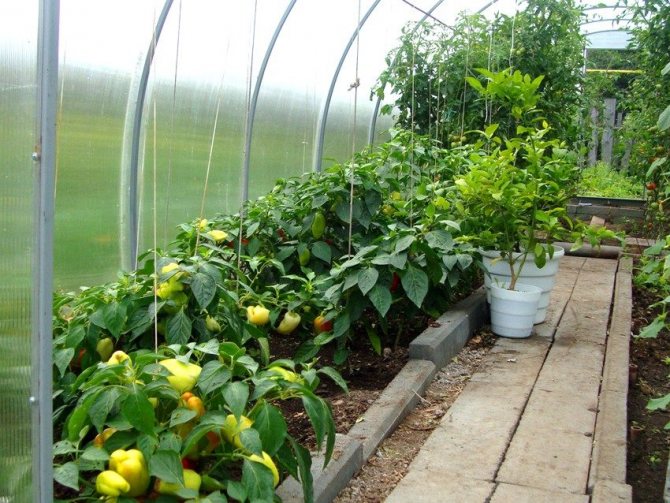

The advent of polycarbonate greenhouses made a small revolution in vegetable growing
Unlike tomatoes familiar to all gardeners, most varieties of sweet peppers have a longer growing season. Rare varieties can yield earlier than four months after sowing the seeds. Therefore, almost everywhere, peppers are grown through the seedling stage.
This is done even in sunny Bulgaria: there, for autumn consumption, peppers are sown directly in the garden, but in order to remove the fruits in early summer, soon after the New Year, they begin to work with seedlings.
Preparing the seeds
How to plant peppers on seedlings to avoid further infections? For sowing seeds, you must prepare them in advance. Preparing pepper seeds for seedlings may include:
- soaking in a saline solution: 30 g of salt is used for 1 liter of water. The seed is soaked for 60 minutes: floating seeds are thrown away, those that drowned are used for further planting;
- preliminary soaking in warm water: the seed is placed in a humid environment for 48 hours;
- treatment with special growth stimulants: zircon, epin, humate - dilute the drug in accordance with the manufacturer's instructions, use as directed;
- preliminary hardening of seeds: germinated seeds are first kept in the refrigerator, then at room temperature. The procedure time should not exceed 12 hours, the temperature in the refrigerator should be at least 2 degrees;
- bubbling seeds: a popular procedure for professional gardeners.The seed is placed in a gauze bag and placed in a container with water, into which oxygen is supplied with the help of a compressor. The oxygen saturation procedure is carried out for 6 hours;
- treatment with disinfectants: soak the seed in a solution of potassium permanganate for 60 minutes.
Many vegetable seeds are soaked in fresh aloe juice. It is not recommended to soak peppers in this biostimulant, as these two plants are incompatible.
Preparing purchased pepper seeds for planting seedlings does not need a decontamination measure. Such seed has already passed all processing procedures.


Planting sweet peppers for seedlings
All operations for planting peppers are similar to those in the case of tomatoes, but each has some nuances. Maybe a novice gardener will not succeed in everything right away, but with due diligence, there should be no problems.
When to sow sweet peppers for seedlings
Unlike the aforementioned Bulgaria, in our country it has long been considered generally accepted that seeds for seedlings should be sown in February. Now another theory prevails, based on the fact that modern varieties and hybrids are more resistant, plants develop faster, and there is no need to endure the difficulties of a lack of heat and light in the winter months. Most gardeners get used to sowing in the first half of March. However, early varieties for open ground can be sown in boxes until the end of the month.
For greenhouse cultivation, the reference point is mid-March: these are the last dates when growing your own seedlings makes sense. Didn't have time - it is better to buy seedlings in the market in May.
Features of planting seeds
Seedlings are transplanted into the garden bed when real heat comes, at which time it should be about 2.5 months old. The fact is that at first the seedlings grow slowly, and they need comfortable conditions. Peppers are not very fond of transplanting, so they often try to grow their seedlings without picking, sowing seeds immediately into individual containers. But in order to save at least a little space on the windowsill, many amateurs sow seeds in a box, and only then dive the seedlings in individual dwellings.
Since many gardeners believe that hybrids are always better, they buy seeds from the store; as a rule, these seeds are already ready for sowing and are sown “as is”. You can only take your seeds from varieties (not F1), they should be prepared:
- calibrate;
- disinfect;
- harden.
These operations are well known to gardeners. The first is carried out in a jar with a salt solution, the second - in a dark solution of potassium permanganate, the third - in the refrigerator. Hardening, no more than a day, may not be carried out if the peppers are grown in a greenhouse. It makes sense to harden swollen seeds: for this, they must be held in a damp cloth until the very first ones hatch, and only then sent to the cold.
I consider advice such as bubbling seeds or using ultrasound completely superfluous.
It is important to use high-quality soil for seedlings, the first land that comes across will not work. It should be:
- air and moisture permeable;
- do not form a crust on its surface after watering;
- very nutritious;
- neutral in acidity.
Those who want to make a mixture on their own can mix compost, coarse sand and good soil in a ratio of 2: 1: 1 and add a handful of ash to the bucket of the mixture. After that, the soil must be disinfected. However, it is much easier and more reliable to buy a suitable soil for planting a dozen bushes.


When buying soil, you should give preference to the one that is intended specifically for pepper
If it is planned to grow seedlings with a pick, the seeds are sown in any small box with a height of 5 cm. To do this, drainage is placed on its bottom (a small layer of clean sand is enough), then soil is poured. Thereafter:
- Make grooves about 2 cm deep, placing them every 4 cm, watered.
- Seeds are placed 2-3 cm apart.
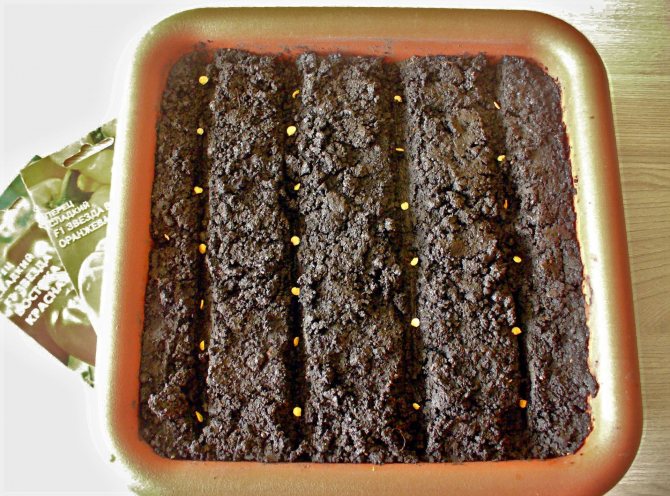


The seeds of the pepper are large, it is easy to spread them evenly
- Sprinkle the seeds with soil, tamp them a little.
- Cover the box with glass and put it in a warm place.


Glass allows you to maintain humidity conditions
- After the first shoots appear, the temperature is lowered to 18–20 ° C for 5–6 days, and the box must be placed in a well-lit place..
After the indicated time, the temperature is raised to 22–25 ° C (a little colder at night) and two or three true leaves are expected, after which the seedlings are planted in pots.
Planting pepper in the "snail"
Sowing seeds in a snail, which allows you to save space for 2-3 weeks, is rarely used in the case of pepper, since it provides for a subsequent transplant, during which the roots can be injured, and the pepper does not tolerate this well... The technique is as follows.
- A piece 15 cm wide and about a meter long is cut out of linoleum or thick film, covered with toilet paper, after which about 1.5 cm of soil is poured.
- Spread the seeds 1.5 cm from the long edge every 4 cm, cover them with another layer of paper.
- Roll the structure into a roll, put it vertically with the seeds up, cover with polyethylene and place in a warm place. Periodically remove the cover and spray the roll with water.
After the emergence of shoots, the "snail" is looked after in the usual way: the temperature is lowered for 5-6 days, after which it is raised. With the appearance of the second or third true leaf, the seedlings are seated in cups.
Video: a variant of making a "snail"
Planting in a peat cup or peat tablet
If you sow seeds in a peat cup (pot), picking is not required: this is the most common way to grow pepper seedlings. Peppers are sown in medium-sized pots. For a safety net, 2-3 seeds are placed in each pot, after the emergence of shoots, one, the strongest, is left.
The use of peat tablets has become very popular. In addition to peat, nutrients are added to them during the manufacturing process. For pepper, it is better to take tablets with a diameter of 7 cm. Fill the tablets with water and wait for them to swell: at the same time, they increase significantly in height without changing the diameter. Seeds are placed in a special dimple at the end, they are embedded in peat and watered. Pepper tablets are usually kept in transparent plastic boxes. Pouring pills "through the bottom", pouring water into the box.
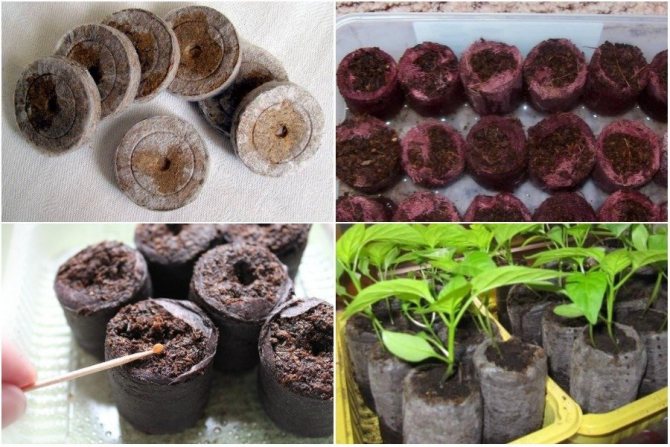


Peat tablets are a very convenient invention
Growing conditions for seedlings
- After passing the "critical" 5-6 days, when they are kept cool in order to avoid stretching the seedlings, a temperature of about 25 ° C is created for the peppers during the day and no higher than 20 ° C at night.
- If sowing was carried out in a common box, do not forget to plant the plants in time.
- Daylight hours - at least 12 hours.
- Watered sparingly, at the root, without soaking the leaves.
- At the age of one month and 2 weeks before disembarkation, they are fed with ash infusion.
Temperature regime and watering
Immediately after sowing containers or pots are placed in a warm place... The optimum temperature for germination is 27-28 degrees. Some gardeners specifically warm up the soil before planting, placing it closer to the battery. A decrease in temperature delays germination and often causes seed death.
When shoots appear on the surface of the soil, the seedlings are placed in the brightest place. It is good if a lamp for additional lighting is mounted above the plantings. The ideal daylight hours for peppers are 12 hours. Overnight planting can be covered with an opaque cloth.
After germination, the room temperature drops to 20-25 degrees. Watering pepper seedlings should be done once every 5-6 days., first from a spray bottle, and then from a watering can.The seedling container is rotated periodically so that the seedlings grow evenly. After the appearance of the first 2 leaves, the plants are ready for picking.
Peppers planted in peat tablets must be transferred to pre-prepared pots filled with a nutrient substrate.
Seedlings planted on time grow well, do not get sick and do not need special care. Strictly observing the irrigation regime and maintaining the desired temperature in the room, you do not have to worry about young plantings.
It is important not to keep it in the house for too long and plant it on a permanent place of residence before the onset of the flowering phase, otherwise the fruiting process will slow down.
So, we figured out how to plant pepper seedlings at home, do it correctly and effectively, sowing rules, how and when to sow seeds, care after sowing.
REFERENCE! Learn about the different methods of growing peppers: in peat pots or tablets, outdoors and without picking, and even on toilet paper. Learn the tricky snail planting method, and what diseases and pests can attack your seedlings?
Picking: is it obligatory and how to plant bell peppers without picking
Pepper picking is an optional procedure, you can do without it... That is why the seeds are often sown immediately in individual containers. If you went the other way, then when 2-3 true leaves appear, the seedlings are planted. Unlike many crops, this stretch operation can be called a pick. The day before, the seedlings are well watered so that they can be removed from the box with a clod of earth.


When transplanting, they try to choose not the smallest containers.
When transplanting, they try not to injure the roots, and only if the central root has managed to grow very strongly, it is slightly pinched.
When planting pepper seedlings, unlike tomatoes or cabbage, they hardly deepen it, they try to place the seedlings at the same depth so that they hardly feel the process. Water the seedlings with warm water and remove for a couple of days in partial shade.
If there is room, it is better to grow pepper seedlings without picking. For this, the seeds are sown immediately in individual cups, and preferably peat pots or peat tablets, as described above.
Is it possible to keep peppers in a common box until summer? After all, you can often observe how seedlings are sold in the markets in this way. The answer to this question is easy. In principle, it is possible, but one must be aware that when planting seedlings, in this case, the root system will be severely injured, the plants will be sick for a long time, slow down in development, and without constant care in the first weeks they may die. Whether it makes sense to take risks, saving space, everyone decides for himself.
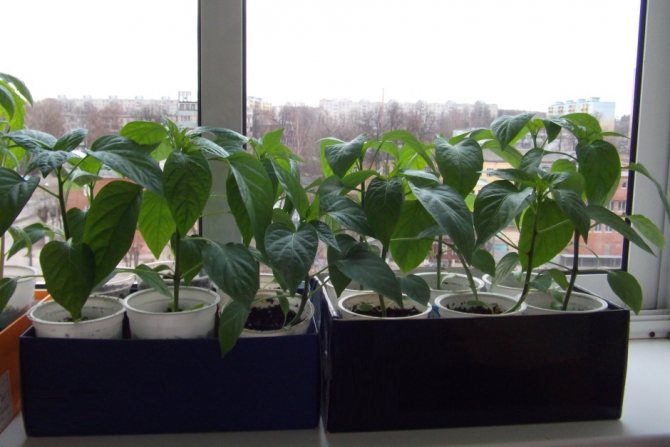
Necessary care of pepper seedlings
In order for the plants to develop normally, they need only occasionally be watered and illuminated with a phytolamp. Water should be used when the soil is completely dry - it is worth trying it with your fingers. It is enough to water the sprouts once a day or every other day. The backlight can be turned on if the weather is cloudy for a long time.
It is necessary to carefully protect the seedlings from drafts and cold weather. If it is on the window, then make sure that there is no blow from the cracks between the frames.
Important. Shortly before planting in the ground, it is worth feeding the plants with mineral additives especially for peppers. They are easy to purchase from the store. When it gets completely warmer outside, the seedlings should be taken out to the balcony for hardening.


Seedlings can be taken out to the balcony for hardening
How to properly plant bell peppers in open ground
Before planting seedlings in a garden bed, they must be hardened, 5-7 days before that they start to take it out into the street, accustom it to the breeze and low temperatures. The time for "walks" should be at first 10-15 minutes, then up to several hours.
Dates of planting in open ground
It is impossible to talk about calendar dates: they completely depend on the climate of the region and the current weather. So, in the Moscow region, planting peppers without shelter before June 5 is dangerous, in the Urals and Siberia, these dates are shifted closer to the middle of the month, and, for example, in the Lower Volga region, transplanting is possible after May 15. It is important that night temperatures do not drop to 12-14 ° C, and during the day it is really warm.
What soil does bell pepper like
In a word, we can say that the soil needs perfect pepper. It does not differ much from the soil at the seedling stage: it must pass air well and absorb moisture, be loose so that the roots breathe, and nutritious so that the bushes grow and bear fruit well. The place should be warm and well-lit, protected from the winds. The soil is neutral in acidity. Both sands and clay are bad. Better - loam, sandy loam, black soil. Since autumn, the bed is well filled with rotted manure and superphosphate, in doses of 1.5–2 buckets and 60–80 g per 1 m2, respectively. You can add a lot of ash. Acidic soils are corrected in advance with lime or dolomite flour.
After what crops can bell peppers be planted, after which - not
Peppers can have any predecessors, with the exception of nightshade crops: potatoes, tomatoes, eggplants. You should not plant pepper after pepper, including bitter. Peppers grow best after legumes, cabbage, onions, garlic, cucumbers. Normal predecessors will be root crops, cereals, green crops. Pepper has an indifferent attitude to the rest of the vegetables. The best option is if you manage to sow siderata before the pepper.
Is it possible to plant sweet peppers next to bitters
Planting sweet and bitter peppers together is one of the common mistakes of a novice gardener. There are such combinations of varieties in which nothing terrible will happen. But in most cases, everything is very unpredictable. Most likely, bell peppers on most bushes will grow bitter, while bitter peppers will not be quite bitter. Perhaps this effect will affect only the next year, when sowing seeds from their harvest. How far should landings be located? Better that it was not 2-3 meters, but more. The most ingenious answer: "So that a bee from one variety does not fly to another." Really - at different ends of the site. But in one greenhouse - very undesirable.
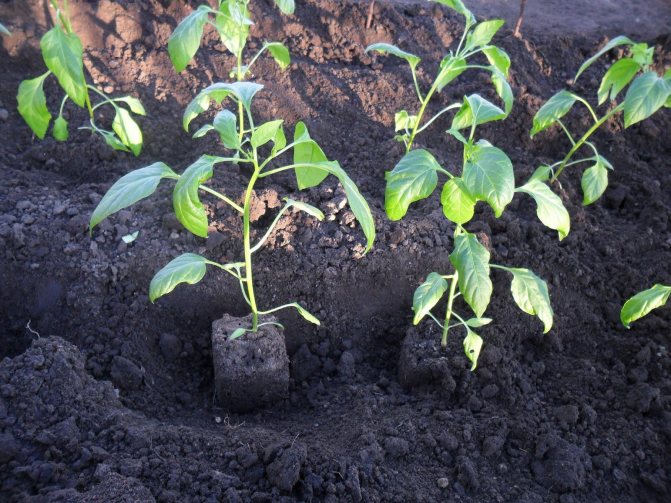
How deep can seedlings be planted
Planting pepper seedlings is carried out in the usual way: digging holes, watering, planting seedlings with a clod of earth (a peat tablet or a peat pot is planted entirely), watered with warm water, mulched. Is it necessary to deepen the seedlings compared to how they grew at home? In most cases, this should not be done. Only if the seedlings are clearly elongated can they be deepened by 2-3 cm, but not along the cotyledon, as some amateurs advise.
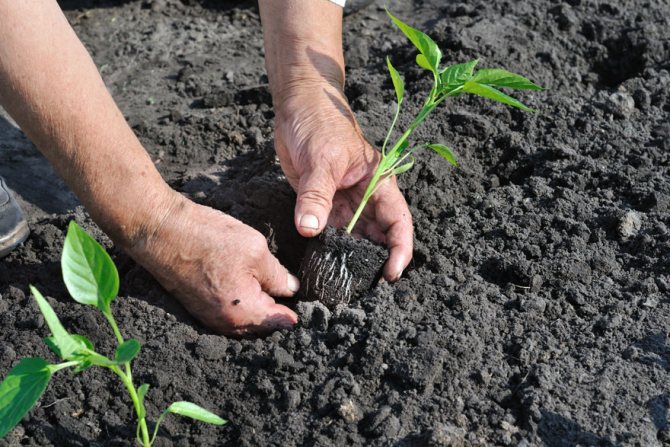


The main thing when planting seedlings is not to damage the root system.
Many tall varieties will soon require tying, so it is best to drive in the pegs right away. Whether a garter is required, you must immediately find out when buying seeds.
Preparing seeds for sowing at home
Having decided on the preliminary sowing date, it is necessary to reject the seeds. They should be examined first. All puny, damaged specimens are selected. The rest of the seeds must be pickled in a 2% solution of potassium permanganate for 20 minutes and rinsed in cold water. Instead of potassium permanganate, some choose antifungal agents for processing. The following fungicides are used:
- Fitosporin-M;
- Maxim;
- Vitaros.
After etching, they can be soaked in a solution of Epin or Zircon. These are plant growth stimulants that promote accelerated germination of seeds, activation of their defenses. 2 drops of Epin are added to 100 ml of water. When using Zircon, dissolve 1 drop in 300 ml of water.The seeds are soaked for 12-18 hours at room temperature.
When processing several varieties of pepper, which are planned to be planted separately in the future, the seeds of each type are tied in a separate gauze bag.
After the completion of the treatment with growth stimulants, the seeds are wrapped in a damp cloth and film for 2–7 days. Do not allow the tissue and seeds to dry out. They should be kept at a temperature of + 22 ... + 24 ° C. The hatched seeds are transplanted into the ground. When planting, care should be taken, the slightest damage to the roots will cause the death of the plant.
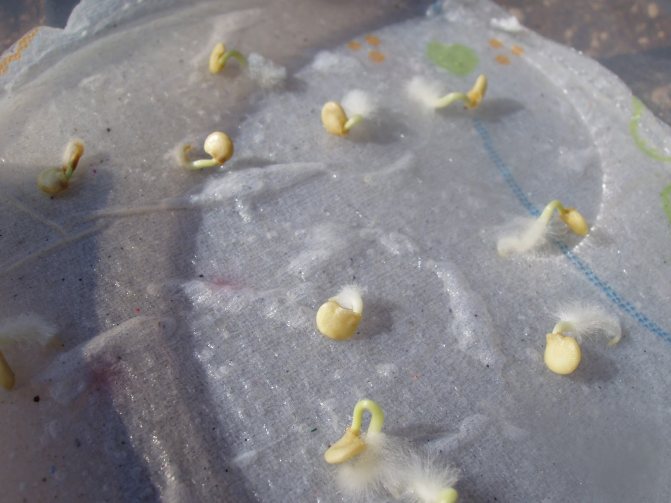


Pre-sowing preparation
Rules for the selection and preparation of soil for seeds
Home gardeners who want strong, healthy seedlings should take a responsible approach to soil preparation. He must meet the following requirements:
- absence of pests and pathogens;
- neutral or slightly acidic reaction, the optimal pH level is considered to be 6–6.5;
- high nutrient content;
- sufficient moisture capacity;
- looseness.
You can buy ready-made soil in a specialized store or prepare it yourself. For cooking you will need:
- garden land (2 parts);
- humus, rotted manure (1 part);
- wood ash (the amount is determined based on the fact that a large handful of ash is required for 1 bucket of humus);
- sawdust (1 part);
- peat (part 1).
If there is no sawdust, they are replaced with coarse sand. Garden land should be collected where no solanaceous crops (tomatoes, potatoes, eggplants, peppers) have grown over the past 3-4 years.
Also summer residents can prepare a substrate from:
- humus (3 parts);
- peat / turf (3 parts);
- river sand (1 part);
- ash (250 g per 5 liters of prepared soil).
When self-preparing the soil mixture, it must be calcined in the oven or steamed in a double boiler for an hour. This is required to kill germs and weeds.
If it is not possible to use humus and find ash, add mineral fertilizers: ammonium nitrate, superphosphate, potassium nitrate. Potassium chloride or potassium salt should not be used, these fertilizers contain a large amount of chlorine, which is harmful to the roots of young plants.
The day before planting, you can additionally disinfect the soil by watering it with boiling water.


Soil preparation
Features of planting in a greenhouse, timing
There are no special changes in the technique of planting pepper in the case of a greenhouse, but the greenhouse must be carefully prepared, in the same way as for planting other heat-loving vegetables. At the time of disembarkation, it should have the same microclimate as when planting peppers on the street.
You should not think that a greenhouse is a panacea: in the event of a sharp cold snap, the temperature in it may drop below the permissible values, so the spunbond should be at hand.
In the greenhouse, they try to plant low-growing varieties against the wall so that tall bushes of other varieties do not obscure the light. Often, when growing in greenhouse, 1–2 first buds or flowers are pinched off from seedlings, which is not always done in the open field.
The dates for planting in a conventional greenhouse are about 2-3 weeks earlier than in a garden without shelter. In the south it is April, in the middle lane it is mid-May, in the Urals it is late spring.
Video: planting pepper in a greenhouse
When to Sow Pepper Seeds: Optimal Sowing Timing
This crop has too long germination time. After planting pepper seed seedlings should withstand 90-100 days and only after that it is transferred to a permanent place. Young shoots of early maturing varieties grow to the desired size within 3 months. After the earth warms up to a temperature of 16-18 degrees, they are planted in a permanent place.
The plant is transferred to the greenhouse a little earlier, and later to open ground with shelter. The landing time largely depends on the climatic conditions of the region.Usually, the planting of pepper seeds is determined taking into account the day of the future planting of seedlings in the ground.
- IN Central Russia seeds are sown in late February - early March.
- In the southern regions you can plant seeds already from January, and at the end of April, the seedlings are ready for planting in a permanent place.
- In the cold regions of Russia on Urals and Siberia and Northwest seeds are planted in trays in the last decade of March. It is better to place the plants in a greenhouse with good heating, then all the fruit ovaries will have time to ripen.
- In a greenhouse with year-round heating, the culture is planted twice a year: at the end of January-beginning of February, and then at the end of September.
Often gardeners start sowing peppers based on the data. lunar calendar... The best time for planting a culture is when the moon is under the influence of Libra, Aries, Scorpio, Sagittarius. These dates change every year, so there is a special calendar in which you can find the exact days. Here are indicated not only favorable dates for sowing pepper, but also unsuitable days. These dates change every year, so a 2019 or 2020 calendar will not work for 2019.
The packages with seeds also indicate landing dates.
- Varieties with early development can be planted in the third decade of February.
- Late varieties should be sown as early as possible.
Important! Seedlings that were sown back in January require additional lighting. The fact is that for the normal development of shoots, more daylight hours are needed than at this time.
Peppers, even the earliest varieties, have such a feature as the vegetative development time of up to 140 days. After sprouting, it takes 90 days for the fruits to ripen. The seeds can germinate for a period of 10 days to 30 days.
Therefore, seeds of early and mid-season varieties are recommended to be sown in the northern regions no later than mid-February, in warmer areas - in early March.
The germination rate of bell pepper seeds depends on the air temperature:
- 26-28 ºC - 8-10 days.
- 20-24 ºC - 13-17 days.
- 18-20 ºC - 18-20 days.
- 14-15 ºC - up to 30 days.
In order for pepper seeds to germinate in a shorter period of time, they must undergo a special preparation procedure. To do this, you need to prepare in advance:
- Seeds;
- Trays;
- Substrate;
- Cotton napkins;
- Potassium permanganate;
- Eggshell;
- Mini greenhouse for seedlings;
- Spray;
- Cling film.
Planting schemes for sweet peppers
The pepper planting scheme is less dependent on whether it is a greenhouse or unprotected soil, and mainly depends on the variety, more precisely, the future dimensions of the pepper bush. Tall varieties are planted after 35-40 cm, medium-sized ones - 25-30 cm, and the most dwarfs, sometimes, even after 15 cm. A distance of one and a half times is left between the rows. Another thing is that giants are trying to plant in greenhouses so as not to waste the useful volume in vain. Peppers are often planted in a greenhouse in a checkerboard pattern, using an approximate scheme of 30 x 30 cm.
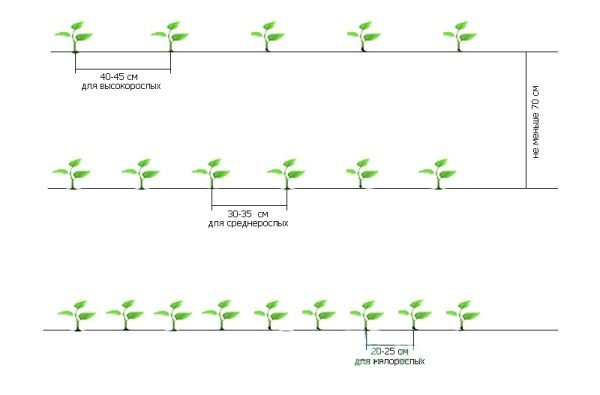

The distance between plants depends on the type of pepper
Planting bell peppers is not very difficult, although every step must be done very responsibly. Planting is followed by an equally difficult stage - caring for the plants. Only with qualified care can you get decent results.
Useful materials
Read other articles on pepper seedlings:
- Correct cultivation from seeds and should they be soaked before planting?
- How to grow black peppercorns, chili, bitter or sweet at home?
- What are growth stimulants and how to use them?
- The main reasons why leaves curl at shoots, seedlings fall or stretch, and also why can they die?
- Planting dates in the regions of Russia and the peculiarities of cultivation in the Urals, Siberia and the Moscow region.
- Learn recipes for yeast-based fertilizers.
Variety selection


The yield of peppers depends to a large extent on the variety and quality of the seeds.Often, low yields are obtained simply because seeds of unknown varieties are sown, or peppers are sown that are not intended for cultivation in the area. There are many criteria for the selection of pepper seeds, and they all affect the final figure on the harvest scales.
Selection of pepper varieties by ripening period
If all novice summer residents had the information that all varieties have their own ripening dates, then half of the problems that gardeners have on the way to a bountiful harvest of pepper could have been avoided.
So, all peppers are divided into:
- early ripening - ripen in 80-90 days;
- mid-ripening - give off the first fruits after 115 days;
- late - forming the harvest for 135-140 days.


Early varieties can be cultivated outdoors in the south of the country and in a greenhouse in the north. Peppers, which have a return already at the end of June, are preferable to grow in the middle latitudes of the country and in Siberia, where, in a short summer, this vegetable will have time to ripen.
Mid-late and late ones give the harvest at the end of summer. They have a longer and more inconsistent fruiting. It is generally recommended to plant them in southern latitudes, since autumn in such regions is milder, and peppers tolerate slightly low temperatures.
The choice of a variety according to growing conditions
Bell peppers are very fond of warmth and grows poorly in cold areas. Therefore, the best condition for its germination is a greenhouse or greenhouse. But in the south, peppers are successfully cultivated in the open field. Therefore, the manufacturer always indicates on the labels in what conditions a particular variety can grow.


If the variety is endowed with strong immunity, tolerates temperature extremes and has iron resistance, then it can be grown in an open garden. In the greenhouse, mainly those varieties and hybrids are grown that perceive cold snaps and lack of light too sharply. It is better not to take risks with such varieties and not even try to plant them in an open area.
Selection of a variety by external characteristics
Choosing a type of pepper "according to the picture" is not the best solution. Initially, other criteria should be given priority. However, when there is something to mark (that is, you have decided where you will grow peppers and when you want to get a harvest), then the last thing that remains is to choose the most "beautiful" variety.
Peppers come in different shapes, colors, contents. Housewives who like to stuff or canned peppers usually pay attention to these factors, and therefore they need ideal sizes.
For stuffing, for example, thick cubic or cone-shaped peppers are suitable. For winter blanks, varieties with an average thickness of sandpaper are suitable.


For summer salads and adding to the main courses, thin peppers will also work.
Biological features
Pepper plants are determinate, semi-determinate, and indeterminate. In simple terms, the bushes of some varieties grow no more than 50 centimeters in height, while there are giant peppers that can rise to the two-meter mark. Usually undersized and medium-sized peppers are cultivated in open beds. They give small yields. Their fruits are usually medium in size. Fruiting occurs instantly and does not last long.
Tall varieties have a long growing season. They are very productive. Fruiting usually begins later than early and bear fruit for several months.
Hybrid or variety


Another important criterion for the selection of peppers for seedlings. Distinguish between pure varieties that are naturally bred and hybrid varieties - obtained by crossing a healthy productive varietal pair.
Cultivars and hybrids differ in terms of growing conditions and care. Normal varieties adapt more quickly to environmental conditions, but they are more likely to get sick.Hybrids bring better yields, but react rather hard to unfavorable conditions.
Moreover, seeds from an ordinary variety have the same qualities as the mother's, and therefore they can be sown next year. The seeds of the hybrids do not repeat the maternal properties.
Tips from experienced gardeners


In the north of the country, it is recommended to plant seedlings in advance, so that the seedlings have time to gain growth. Before planting, containers, seeds and soil are thoroughly disinfected. The most popular remedy is a solution of potassium permanganate. Powder is sold in every pharmacy at a low price.
Also, farmers are advised to observe the following recommendations:
- check seeds for germination;
- do not plant peppers too close to each other;
- if possible, plant the vegetable immediately in a larger container to avoid picking;
- prepare labeling;
- pour warm water at room temperature;
- avoid getting water on stems and leaves;
- feed seedlings in a timely manner;
- monitor the level of moisture in the soil.
Bush formation.
Growing such a fruit plant as pepper on the balcony will allow you to get delicious vegetables as quickly as possible. In order for the bush to form correctly, you must:
- Remove the lower leaves on the stem of the plant.
- Form a bush of two shoots.
- Remove the first, unblown flowers.
- Pinch the top of the plant after compacting its trunk.
Important! Tall plant varieties need additional support. Therefore, pegs are installed in the container, to which the trunk of the bush is tied.


Pegs make the plant resilient
Possible infections and how to deal with them
Bell pepper is a relatively delicate plant that is prone to infectious diseases. The plant can be exposed to:
- yellowing of cotyledon leaves in which the stem of the culture is affected. The plant turns black and lays down. The cause of the turmoil is the Blackleg. As a rule, the causative agent of this infection is in untreated soil. Less commonly, seeds are infected with a black leg. That is why, bowls, soil and seed must be disinfected with special agents or a solution of potassium permanganate. The infection develops rapidly with improper care of crops: insufficient watering or waterlogging of the soil, poor illumination of plants, low temperatures contribute to the death of the plant. You can get rid of the bacteria with the help of preparations containing copper. It is also necessary to provide crops with sufficient light. At the first manifestations of the disease, infected plants are removed;
- fusarium, in which the seedlings stop growing, withers without changing color. A characteristic sign of infection is the acquisition of yellow leaves from the bottom up. You can fight the disease using the same means as the "black leg" - disinfection of sowing material, soil and containers for crops is the best way of prevention;
- gray rot, which manifests itself in the form of plaque on seedlings and the side walls of flowerpots. To avoid trouble, it is recommended to spray seedlings with a weak solution of potassium permanganate once every 10 days. Fighting gray mold is not easy. To eliminate the infection, it is necessary to remove the infected specimens and treat the crops with a special fungicidal preparation;
- late blight is a disease that affects adult plants. The trouble manifests itself in the form of white spots on the stems, which turn black over time. As a rule, the soil is the source of contamination. At the first manifestations of infection, it is recommended to spray the crops with an iodine solution: 5 ml of iodine is added to 1 liter of warm water. With a stronger infection, it is necessary to treat the culture with a special fungicidal preparation, after removing the diseased pepper;
- Powdery mildew is a disease of pepper that affects both young and adult specimens.The infection manifests itself in the form of white spots and plaque on the leaves and contributes to the arrest of development. A bactericidal fungicide or iodine solution will help get rid of the trouble.
Timely identification of an infectious disease and the implementation of preventive actions will help grow a strong culture. Inspect crops regularly and, if necessary, do not hesitate to process with special preparations.
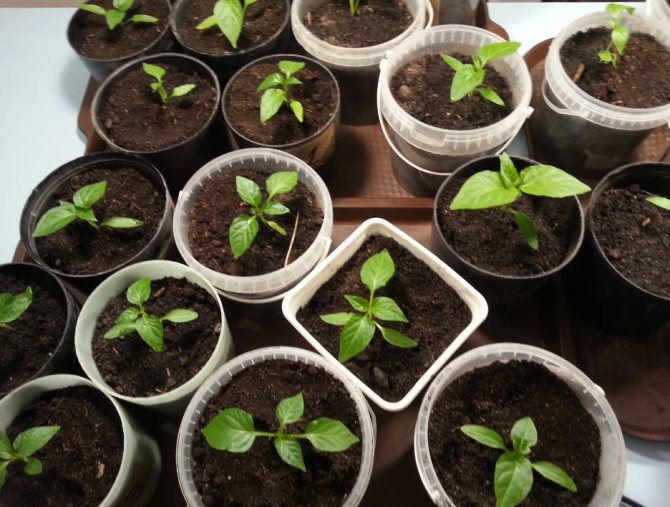


Seedling picking
A pick is necessary if the seeds originally grew in small containers. Over time, the root system needs more space for development, so the seedlings are transplanted into larger containers.
As a rule, peppers dive 15-20 days after germination. Watering is stopped five days before the procedure.
How to make a pick:
- Pour soil into a larger container and pour warm water. Make a hole 4-5 cm deep.
- Use a spatula to scoop out the sprout and place in a new container.
- Plant the seedlings up to the cotyledonous leaves, gently pressing the soil to the roots with your fingers.
- Drizzle the pepper with water at room temperature.
Composition and usefulness
Sweet pepper has a rich mineral and vitamin composition. He is rich:
- thiamine;
- folic acid;
- riboflavin;
- niacin;
- pyridoxine;
- vitamins A, E, K, C, B;
- trace elements: sodium, potassium, calcium, iron, manganese, phosphorus, magnesium, zinc, copper and selenium.
Since pepper has a low energy value (only 25 kcal), it is widely used in weight loss diets. Dried and ground seeds are used as a spice. And also, yellow fruits, rich in potassium, strengthen the heart muscle, which is important for the older generation. The red color indicates the presence of vitamins A, C. Green peppers prevent the appearance of cancer, as they contain phytosterol, which binds and removes bad cholesterol from the body.


Sweet peppers are good for blood formation and brain activity.
Folic acid is very necessary for the adult body, since its deficiency causes malignant anemia, and pregnant women have a risk of defects in the neural tube of the child.
Moreover:
- Riboflavin (B2) is required for the regulation of reproduction and growth; for hair, nails and skin; for the thyroid gland.
- Thiamine (B2) is involved in the metabolism of proteins, fats and carbohydrates.
- Lack of niacin (niacin PP) leads to diarrhea, dermatitis and dementia.
- Pyridoxine (B 6) is involved in the production of hemoglobin.
There is no need to talk about the need for microelements - without them, the normal life of the body is impossible.
Stage number 3: Saturation of seeds with microelements

The next step in preparing seeds for sowing is soaking them in a nutrient-rich solution. However, this procedure is optional. There are summer residents who use mineral mixtures purchased in a special store for this purpose, and there are those who use exclusively folk remedies. The most popular among folk remedies is a solution prepared on the basis of wood ash. The composition of such ash contains 30 trace elements, which are necessary for the normal growth and development of pepper.
To prepare the solution, you will need to mix a liter of water with 20 grams of wood ash. This mixture must be put on for 24 hours so that it can settle well. Place the seeds in a cloth bag and place in the resulting nutrient solution. The seeds should stay there for 5 hours. After the time is up, the seeds must be pulled out and dried on a sheet of paper. They should be soaked just before sowing.
Possible problems with seedlings and solutions
Absolutely not difficult growing home seedlings inspires gardeners to harvest them on their own, and not spend money on purchasing ready-made ones.In addition, a seller who does not differ in honesty may report incorrect data about seedlings.
However, inexperienced novice gardeners sometimes have problems:
| Problem | Cause | How Correctavit |
| The seeds did not sprout | Poor quality material; omissions in disinfection of seeds, containers, soil | Do not store seeds for more than 4 years; Pay due attention to the quality of disinfection |
| Slow growth of seedlings | Insufficient lighting; lack of food; poor soil; waterlogging; exposure to light on roots | Provide plants with extra light; shade roots; do regular feeding; balance watering |
| Pulling seedlings after picking | Insufficient lighting; early disembarkation was carried out; climatic satiety | Reconsider disembarkation dates; increase daylight hours; reduce the room temperature |
Sometimes young and tender pepper seedlings can be affected by diseases:
Blackleg
The disease most often affects peppers in the cotyledonous leaf phase. The sprouts become yellow, and the hypocotal stem becomes dark near the ground. After a while, a black constriction forms on it. The seedlings lodge.
The causative agent of the black leg could hide in an insufficiently disinfected container, soil, even on seeds. The appearance of the disease is provoked by a large density of crops, a lack or excess of moisture, sharp temperature changes.
Fusarium and gray rot
In seedlings that already have 4 leaves, another enemy may be found - Fusarium. At the same time, the color of the plants does not change, they just suddenly stop growing. And only then, when the fungus hits the seedling almost completely, yellowness immediately appears.
Sometimes the soil, sides of the container and even the peppers themselves are covered with gray fluff. It is gray rot. She oppresses the seedlings by drinking their juices.
For prevention, every decade peppers are treated with manganese. For treatment, fungicides are used.
Soil preparation
The yield of garden crops largely depends on the quality of the soil used. The soil substrate should be light, loose and nutritious. An earthy mixture is prepared from various components that meet all the requirements for the successful growth of seedlings.
The soil for pepper seedlings should include sifted compost (you can also use peat or sand) in half with humus. Add two glasses of ash to the bucket of the mixture. There must be microelements in the soil substrate. To do this, add turf soil to the mixture or replace it with superphosphate fertilizers (60 grams per bucket) and potassium sulfate (20 grams).


Before sowing, the soil must be disinfected, since harmful microorganisms often remain in its pores, which are activated in a humid and warm environment. They are capable of destroying the crop even at the stage of seed germination. To do this, the earth is spilled with boiling water with the addition of potassium permanganate or calcined in an oven at a high temperature.
Tip: we recommend decontaminating potting mix purchased from a store.































