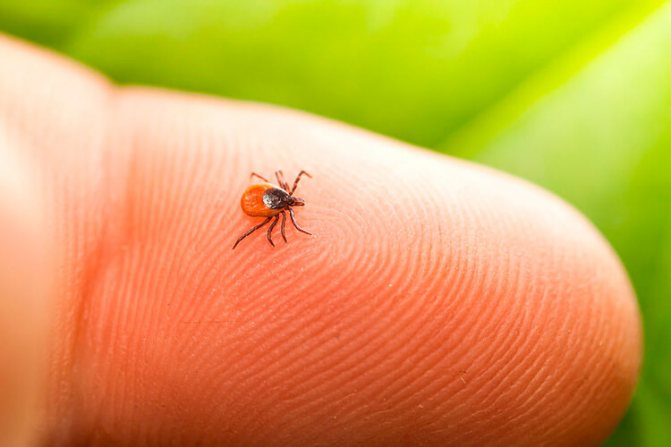
Lyme disease (Borreliosis) is a vector-borne disease. The most common carriers of the infection are deer bloodsuckers, black-footed and forest ticks. Borreliosis can also be caused by insects and spiders.
The immune system reacts to a certain type of bacteria that enters the body when bitten. Once in the bloodstream, the infection spreads to all organs (heart, brain, lungs), joints. Immature ticks (nymphs) are especially dangerous. They are smaller in size, their bite is almost imperceptible, which is why the tick can contact the skin for hours or even days. The longer such contact is maintained, the higher the likelihood of infection.
Stages of borroleosis disease

The classification of tick-borne borreliosis according to ICD-10 has three stages:
Stage I and II
Stages I and II refer to the early period of the disease.
During the 1st period, the patient feels:
- chills;
- his temperature rises;
- the patient has a headache;
- he has muscle aches;
- weakness and fatigue are clearly expressed.
At this stage of the disease, some patients are susceptible to some of the symptoms without icteric hepatitis:
- anorexia;
- nausea;
- vomiting;
- pain in the liver area;
- there is a slight increase in the liver.
During the second period, the causative agent of the disease, along with blood and lymph, is carried throughout the patient's body. During this period of the disease, neurological symptoms are characteristic, which can be expressed:
- meningitis;
- meningoencephalitis with lymphocytic pleocytosis of cerebrospinal fluid, and some others.
In addition to the above symptoms, at this stage of the disease, neuritis of the oculomotor, optic and auditory nerves can be observed.
At this stage of the disease, the cardiovascular system is damaged, but this happens less often than a violation of the nervous system.
Stage III
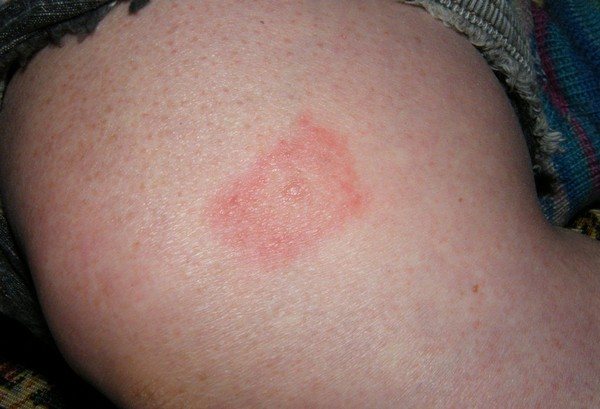

At the third stage of the patient, the joints are affected and the following are possible:
- benign recurrent arthritis;
- chronic progressive arthritis;
- chronic arthritis is possible.
Is an infected person dangerous?
Lyme disease cannot spread between people, for example through touch, kissing, or sexual contact.
Dogs and cats can contract Lyme disease, but they cannot infect humans - no such case has been reported.
Lyme disease cannot be spread through air, food, or water.
Lice, mosquitoes, fleas, or flies also do not transmit Lyme disease.
Some small studies have linked Lyme disease in pregnancy to birth defects or fetal death, but there is not enough research to conclude that Lyme disease adversely affects pregnancy.
There are no reports of transmission of the disease through breastfeeding.
A woman who needs treatment for Lyme disease during pregnancy will receive a different type of antibiotic treatment than usual.
Symptoms of the disease
The symptoms of borreliosis begin to appear after a few days after the insect bite. At this time, bacteria are actively spreading throughout the body of a sick person. Symptoms at this stage of the disease:
- weakness;
- chills;
- temperature increase;
- weakness;
- headache.
Only 15% of patients have similar symptoms.
Symptoms, which are expressed in a violation of the patient's cardiac activity, are observed in only 8% of patients.
If borreliosis is not treated, then arthritis can be observed in 60% of patients. This symptom can manifest itself in a patient for several years. And only 10% of patients can develop chronic arthritis of the knee joint.
Other dangerous insects
It is not only ticks that should be feared. Fleas, lice, mosquitoes can be contagious. The Borrelia bacterium can be found in a wide variety of insects, moreover, it can be transmitted from infected people to others. Dangerous contact with contaminated saliva, blood transfusions, breast milk, intercourse, or organ transplants.
Infection from a sick person is possible through blood transfusion, unprotected sexual contact. The fetus is susceptible to infection during conception if one of the parents is sick with borreliosis. The transmission of pathogens is possible when the body fluids of an infected person get into the mucous membranes or open wounds of a healthy person.
We suggest you familiarize yourself with: Bed parasites how to get rid of at home
How to treat

Having become infected with tick-borne borreliosis, you must immediately consult a specialist. The earlier the patient see a doctor, the better the treatment will be. The treatment process is especially effective at the 1st stage of the disease.
Treatment of this disease can go in two directions:
- The first direction of treatment is etiotropic. During this method, they act directly on the causative agent of the disease, carry out it with the help of antibiotics.
- The next line of treatment is symptomatic and pathogenetic treatment. In this case, the affected organs and systems of the human body are treated (this is, as a rule, the patient's nervous system, his heart, joints).
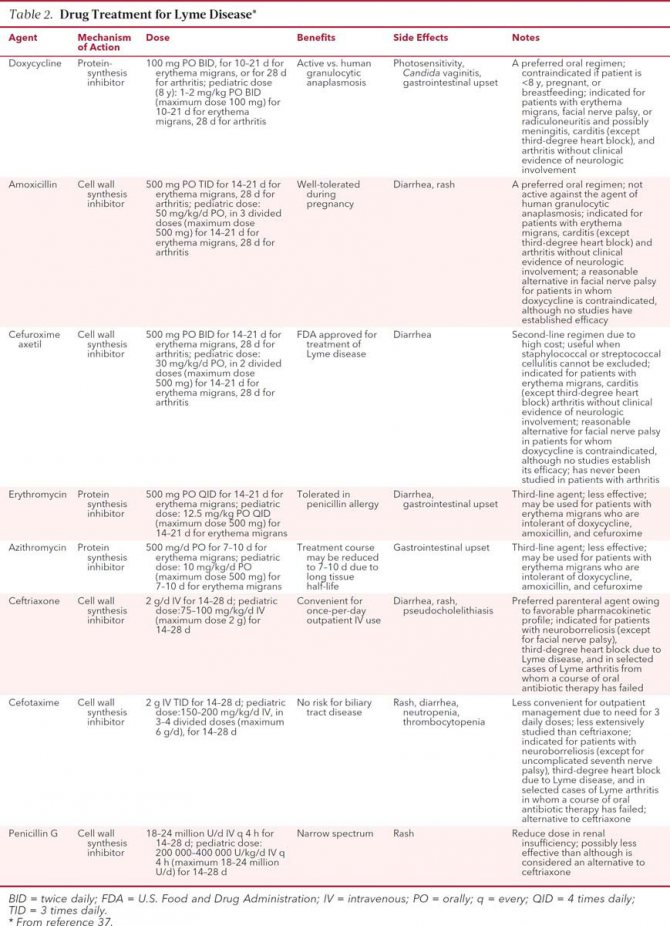
At the first stage of the disease, tetracycline, doxycillin, amoxicillin are often used for its treatment. The dosage and time of taking these drugs should be prescribed only by the attending physician.
At the II stage, the patient is prescribed drugs for parenteral administration. This is done in order to achieve the maximum concentration of the drug in the patient's blood. During this period of treatment, the doctor prescribes to the patient: penicillin, ceftriaxone. As in the previous stage of treatment, only the attending physician determines the dosage and duration of the medication.
In the treatment of stage II, the same penicillin series of antibiotics is used. The patient must take drugs under the strict supervision of the attending physician. Which, if necessary, can replace one drug with another. This is due to the fact that the originally prescribed drug does not bring the desired result.
For symptomatic and pathogenetic treatment of the disease, antipyretic drugs are mainly used.
In addition to them, the doctor prescribes detoxification, anti-inflammatory drugs to the patient. Perhaps the patient will be prescribed heart medications, fortifying. A vitamin complex may be prescribed.
It is unacceptable to self-medicate for such a serious illness. The patient can receive the most effective treatment only in an infectious diseases hospital. Only there a person will receive the whole complex of treatment aimed at the complete destruction of barrels. If a sick person does not receive the necessary treatment, then this can lead to disability, and in some difficult cases, even death.
Borreliosis treatment
Diagnosis is difficult because the manifestations of Lyme disease are similar to those of autoimmune diseases (lupus, rheumatoid arthritis, fibromyalgia).
In addition to a specific skin rash, an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay helps in the diagnosis.Although in the first phase of the disease in half of the cases, it does not allow the detection of pathogens, and the blood sampling must be repeated after 20 days.
Treatment is usually carried out in a hospital. Therapy includes taking antibiotics (tetracycline, amoxicillin, doxycycline, cefuroxime). Depending on the symptoms, it can be supplemented with corticosteroids, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (indomethacin, naproxen, chlotazole), pain relievers, immunosuppressants.
Side effects of antibiotics and other medicines include cramps in the legs and body, digestive problems, drop in blood pressure, memory impairment, constant fatigue, body numbness.
Barrel in children
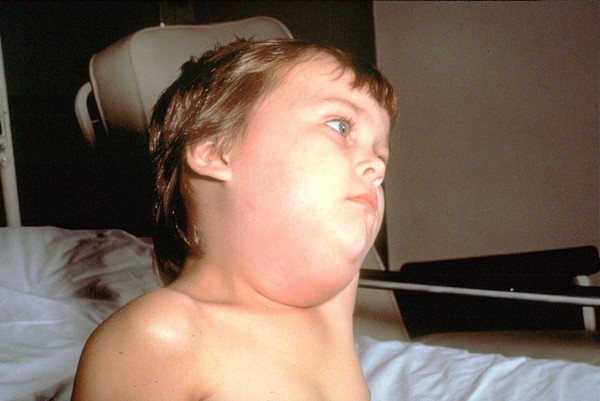

When infected with borreliosis in children and adolescents, the head hurts more often, the whole body aches, the child has a fever, he feels weak, the child has nausea, ringing in the ears, a severe rash at the site of the bite.
If the disease develops in a more severe form, then the child has:
- he will be dizzy;
- speech impairment is possible;
- concentration may be impaired;
- sometimes stuttering appears.
If the disease proceeds with complications, then the child:
- depression may occur;
- sudden mood swings;
- the child can observe the nakedness of the nation;
- paralysis of the facial nerve may occur.
Spread of infection throughout the body
Borrelia, penetrating the body with the saliva of a blood-sucking beetle, gradually penetrate the lymph nodes that are in the immediate vicinity of the bite. They multiply in them, and after 3 days the rest of the tissues begin to become infected, since the infection will spread through the bloodstream. The nervous and cardiovascular system, muscles and joints suffer from borreliosis.
The body's natural defense (immunity) gradually develops antibodies against borreliosis, but it will not be possible to completely defeat it. If untreated, against the background of the rapid multiplication of infection, pathology can cause an autoimmune failure. It is characterized by the destruction of its own cells by antibodies synthesized by the immune system against borrelia. As a result of this development of events, ixodic tick-borne borreliosis often develops into a chronic form, which is difficult to eliminate. The danger from pathology lies not at all in a bite or bacteria, but in their toxin. It gradually destroys body tissues and the human condition worsens.

After a tick bite, both children and adults develop Lyme disease in stages, and each stage has its own symptoms. Focusing on them, the patient may suspect that he has this serious ailment. You should not panic in such a situation, since the disease cannot be transmitted from a person, which means there is time to go through all the examinations and get the necessary medical care.
initial stage
In Lyme disease, the incubation period varies. For some patients, it lasts a week, while others noticed the first manifestations only after a month. After the incubation stage, the infected person begins to feel the symptoms of the development of the infection:
- Nausea;
- Lethargy;
- Heat;
- Rash;
- Conjunctivitis;
- Cold symptoms;
- Pain in muscle tissue and joints;
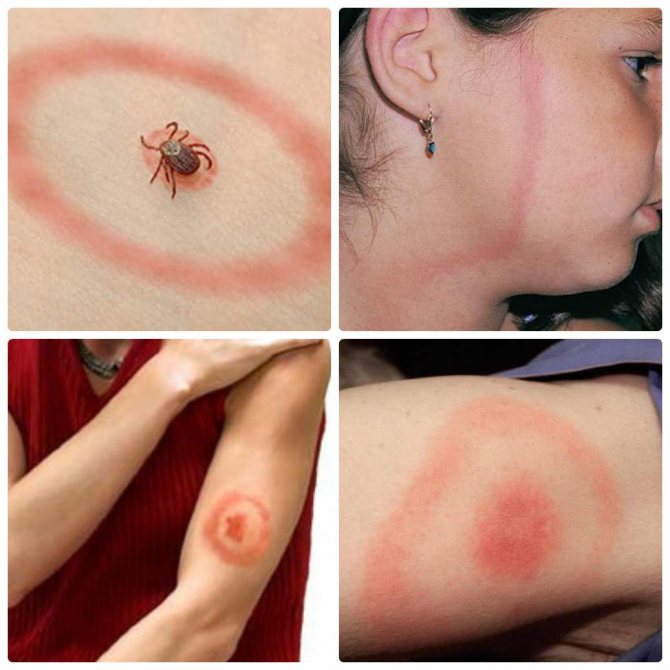
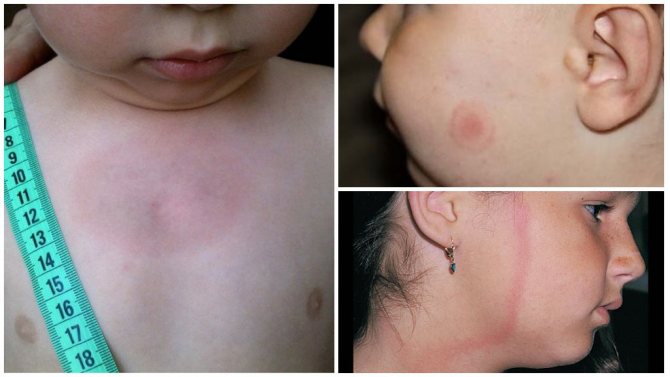
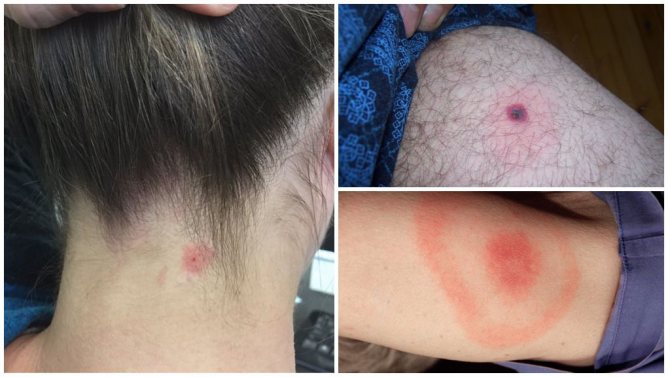
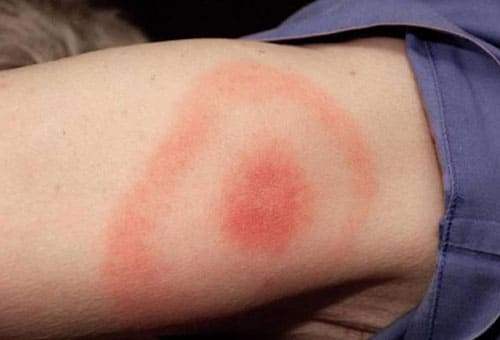
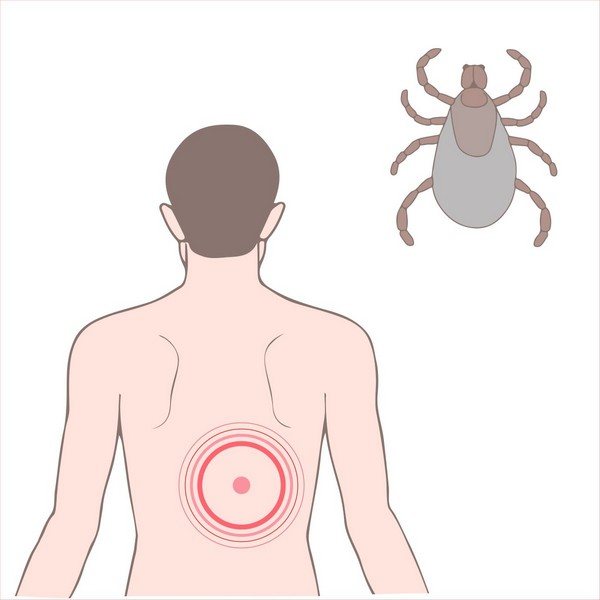
The rash is observed mainly near the site of the bite and the following signs of borreliosis are also visible here:
- Redness (erythema);
- Burning pain and itching;
- Swelling.
The basic manifestations of the disease are not immediately noticeable, and they are more like a cold. Over time, the patient notices a rash and erythema in the area of the bite. After 3 days, the red spot grows, and its center becomes light. The size of the erythema sometimes reaches 50-60 cm.
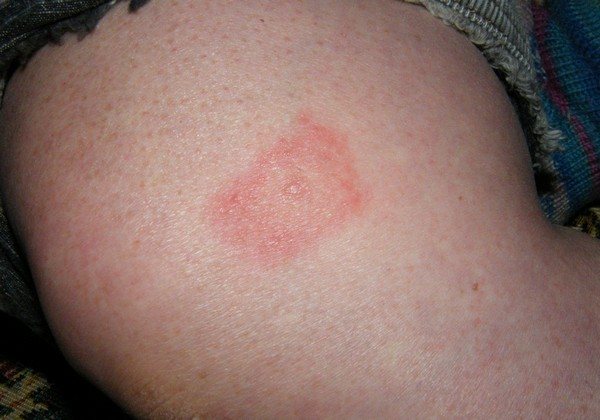

Borreliosis in a child at this stage is extremely similar to a cold, and the ring can grow over most of the baby's body. In addition to erythema, other manifestations of the disease can be distinguished:
- Overgrowth of lymph nodes;
- Fossilization of the muscles of the neck and occiput.
There have been cases when the symptoms of borreliosis after a bite did not appear. In such a situation, the infection secretly multiplies in the body until the person's condition worsens.
Middle stage
As it develops, a disease such as borreliosis enters the bloodstream and from there begins its harmful effect on muscle tissue, nerve fibers, joints and the cardiovascular system as a whole. By that time, the primary erythema of borreliosis has actually disappeared and the patient's local symptoms are almost not disturbing. This stage of development lasts from a week to 3 months.
Stage 2 manifestations resemble the following pathologies:
- Inflammation of the lining of the brain (meningitis);
- Damage to the nerve tissues of the brain;
- Clamping of the nerve roots in the spine.

The first disease is characterized by the following symptoms:
- Sleep disturbance;
- Pain in the head;
- Fear of light;
- Excessive sensitivity to sound;
- Weakness, rapid loss of strength;
- Sudden mood swings;
- Lack of concentration of attention;
- Poor memory;
- Fossilization of the occipital muscles;
- Increase in the level of lymphocytes and protein in the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF).
Often, the facial nerve is injured, less often the nerve tissues responsible for the sensory organs are damaged. This phenomenon is accompanied by characteristic symptoms:
- Pathological changes in facial features;
- Problems with food intake (due to loss of food from the mouth);
- Non-closing eye;
- Weakening of vision and hearing;
- Strabismus development;
- Incorrect eye movement.
Basically, doctors diagnosed cases of bilateral damage to the nervous tissue. In case of unilateral damage to the nerves, the other side was also touched after 7-10 days.
For the third pathological process, the following symptoms are characteristic:
- Deterioration or excessive sensitization;
- Shooting pains;
- Deterioration of tendon reflexes;
- Weakening (paresis) of muscles.

All signs of Lyme borreliosis in the second stage are often combined, which brings additional difficulties in diagnosis. As the disease progresses, the infection damages the nervous system more and more and the characteristic neurological symptoms appear:
- Epileptic seizures;
- Disruptions in the swallowing process;
- Indistinct speech;
- Movement coordination disorders;
- Swimming gait;
- Various involuntary movements;
- Tremor (trembling).
In patients with borreliosis, 2-3 months after the bite, problems with the joints appear and most often the elbow, ankle, knee and hip joints are affected. The problem manifests itself in the form of pain when flexing and extending the limbs.
The cardiovascular system suffers primarily as the infection spreads through the bloodstream. A person has signs of pericarditis and myocarditis, antifreeze blockade:
- Pain in the chest;
- Dyspnea;
- Developing heart failure;
- Rapid heart rate.
The site of the bite is already extremely difficult to find, but such skin manifestations remain:
- Secondary erythema;
- Lymphocytoma;
- Hives.
Lymphocytoma is not particularly dangerous and consists of an accumulation of lymph cells. Its size is usually at least 2 mm and no more than 2 cm. There is a tumor in the nipple, groin or near the auricle.
Running stage


The third stage is rare, since the infection can reach it no earlier than 1-2 years after the bite. This stage is most clearly expressed in such pathological processes:
- Chronic atrophic acrodermatitis;
- Chronic arthritis;
- Severe damage to nerve tissues with the development of encephalopathy and polyneuropathy.
In most cases, Lyme disease in stages 3 damages one of the body systems. This is expressed in serious violations:
- Chronic arthritis. The launched pathological process concerns not only large joints, but also small ones.Chronic arthritis is characterized by constant relapses that occur due to changes in the weather or health problems. This constant inflammation leads to changes in the structure of cartilage tissue and bones. Sometimes the problem affects the skeletal muscles as a result of which myositis develops;
- Atrophic acrodermatitis. The disease with borreliosis stage 3 has a chronic course. Acrodermatitis manifests itself in the form of spots of a red and bluish tint. You can see them on the extensor part of the arms and legs, sometimes on the other side of the feet and hands. Places where acrodermatitis manifests itself harden, swell, and the skin begins to atrophy;
- Damage to nerve tissues is expressed by the following symptoms: Paresis of muscle tissue;
- Problems with the pelvic organs;
- Weakening of mental abilities;
- Impaired coordination;
- Numbness, tingling, and creeping on the skin in various parts of the body;
- Increased or decreased sensitivity of the skin;
- Pains of various kinds in muscle tissues.
Separately, we can note the deterioration of vision and hearing. The patient is increasingly experiencing seizures of epilepsy. Signs characteristic of other stages of development are aggravated.
Chronic stage
Chronic borreliosis occurs about 2-3 years after the bite. It is characterized by relapses, so the patient's condition gradually becomes worse. Pathological changes are exacerbated and the chances of irreversible consequences become much higher.
For such a disease as chronic borreliosis, the development of certain pathological processes is characteristic:
- Multiple lymphocytomas;
- Generalized joint damage;
- Numerous sites of damage to the nervous tissue.
What can be the consequences
The consequences will manifest themselves only if the disease is not treated. Then the patient has chronic changes in the human nervous system, in his cardiovascular system. At the last stage of the development of the disease, inflammation of the joints is observed as a consequence. Even a lethal outcome is possible.
As complications of borreliosis according to ICD-10, there can be:
- all mental functions are disturbed in the patient, in rare cases dementia develops;
- possible paralysis of peripheral nerves;
- the patient may lose hearing and vision;
- severe cardiac arrhythmias may occur;
- the patient has arthritis;
- in the place where the tick has penetrated, the patient may develop benign tumors.
How is Lyme disease spread?
Lyme disease is transmitted through the bite of an infected tick and does not spread from person to person. However, Lyme disease can spread in a community if the tall grass areas that surround homes or other places are large and where people congregate become areas where infected ticks live. Mowing tall grasses and cleaning areas where mites like to live will help control the spread of Lyme disease. People can protect themselves from tick bites by using repellent sprays and by wearing long pants and long-sleeved shirts to prevent ticks from entering exposed skin.
Disease prevention

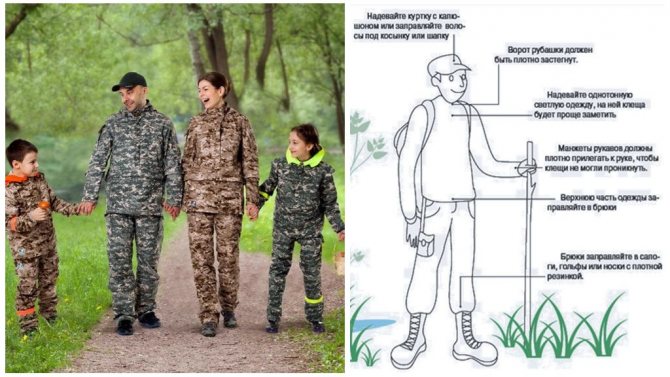
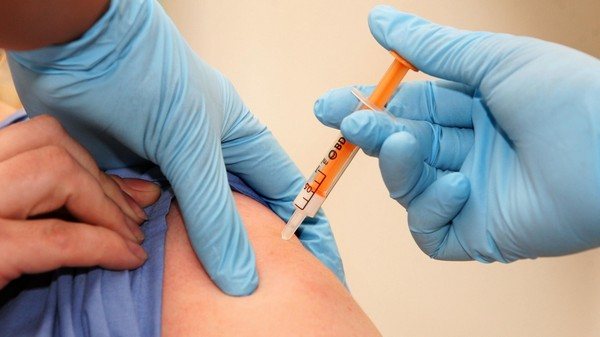
To prevent this disease, it is impossible to apply a vaccine, since it does not exist in the world. Therefore, it is very important to observe some precautions:
- when going out into nature, you need to take care of protective clothing;
- you need to stock up on, and do not forget to use, insect repellent;
- you need to take tweezers with you;
- know how to properly remove a tick (a tick is twisted out of a person's body by the head);
- in no case should the tick be pulled vertically;
- after the tick has been removed, the wound must be thoroughly disinfected;
- noticing that he was bitten by a tick, you urgently need to move towards the hospital and be sure to see a doctor.
The course of therapy

What to do with Lyme disease should be told by the doctor after diagnosis. The main task of treatment is to eliminate all borrelia from the body. The result is usually achieved due to the characteristics of the course of therapy:
- To eliminate borrelia at stages 1-3, tetracycline antibiotics of the Doxycycline type are usually used;
- Chronic disease is treated with penicillin antibiotics, for example, Amoxiclav or Amoxicillin;
- When you get Lyme disease and encephalitis, gamma globulin is used at the same time.
Doxycycline tablets are more commonly used to treat borreliosis. The drug has its effect by destroying the core of the virus from the inside. Borrelia stops multiplying and is then destroyed by the immune system. Doxycycline is thoroughly purified, so it actually does not cause toxic reactions. The drug differs from other antibiotics from the tetracycline group for its long-term effect and high-quality absorption. The half-life of Doxycycline is approximately 3 hours.
Separately, you will need to take care of the affected body systems, since antibiotics are aimed only at destroying the infection. In this situation, the treatment is symptomatic and it is performed against the background of strengthening the immune system.
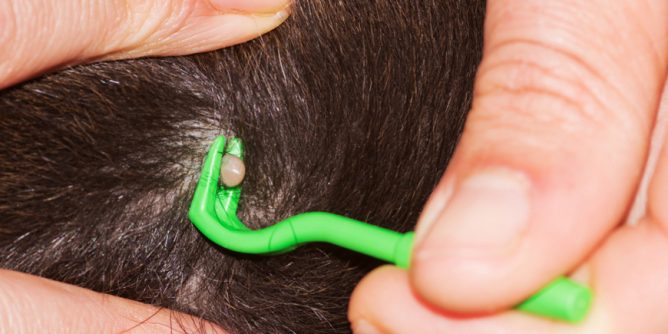
Pets as a source of infection
Dogs are very susceptible to tick bites and diseases transmitted by parasites, and there are no vaccines for animals against all tick-borne infections. You also need to remember that dogs or cats returning from a walk can carry ticks on themselves, which subsequently attack the residents of the house.
For these reasons, it is imperative to consider the role of dogs in infecting themselves and their owners with Lyme disease.
Keep in mind, among other things, that tick bites on dogs can be difficult to detect, and disease symptoms usually appear within 7-21 days or longer after a tick bite. During this time, everyone has time to forget that the problems that have arisen may be associated with a tick bite.
- In order to reduce the role of pets in infection with borreliosis, the following instructions must be followed:
- Check pets for ticks daily, especially after spending time outdoors.
- If a tick is found on a dog, it must be removed immediately.
- You need to be informed about what tick-borne diseases are common in the region where the animal is kept.
- If you have your own yard, you need to take measures to reduce the concentration of mites on its territory.
- Today, there are many different products on sale that repel ticks for animals, but you should not use them thoughtlessly, which can negatively affect the health of the pet and not bring any beneficial effect. Prior consultation with a veterinarian is required.
As for cats, you need to know that this type of animal is extremely sensitive to various chemicals. Do not use acaricides or cat repellents without first consulting your veterinarian.

In addition, the main points that any pet owner should know should be highlighted:
- Dogs infected with the causative agent of Lyme disease show no symptoms in 95% of all cases.
- The main symptoms of borreliosis in dogs include fever, lack of appetite, lameness, and joint swelling.
- A vaccine is available to prevent Lyme disease in dogs. It does not protect against other tick-borne diseases such as Rocky Mountain spotted fever, ehrlichiosis, anaplasmosis, or babesiosis (piroplasmosis). Therefore, additional preventive measures against these diseases are still needed.
- Clinical signs of Lyme disease in cats have not been described, although the species suffers from tick diseases such as ehrlichiosis, anaplasmosis and some forms of babesiosis.
- You should never use dog tick repellents on cats.