In some of our previous articles, we have often mentioned the different types of ticks and the harm they can do to humans. Today we will talk about another species of these arachnids - gamasid mites, which are much less common, but they harm us no less.
There is relatively little information about these parasites, and many online sources present everything in a very confusing way, and many conclusions are more mythical than informational. Let's try to look into the official entomological encyclopedias, as well as talk with practicing veterinary and medical parasitologists to finally find out what gamasid mites are, how to deal with them, and what harm they can bring.
Rat mites: description
Rat tick (Ornithonyssus bacoti) is a temporary hematophage that predominantly attacks rats. They can be carriers of a number of diseases of bacterial origin. During a period of lack of familiar hosts, they can attack other small mammals, as well as humans.
It is also useful to read: Chicken mites
Appearance
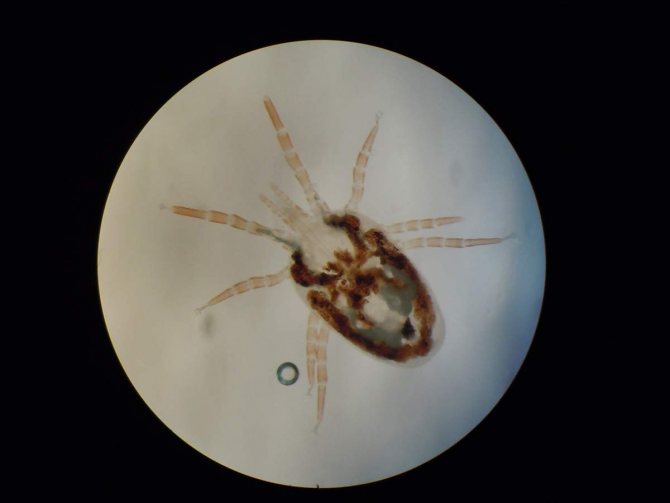
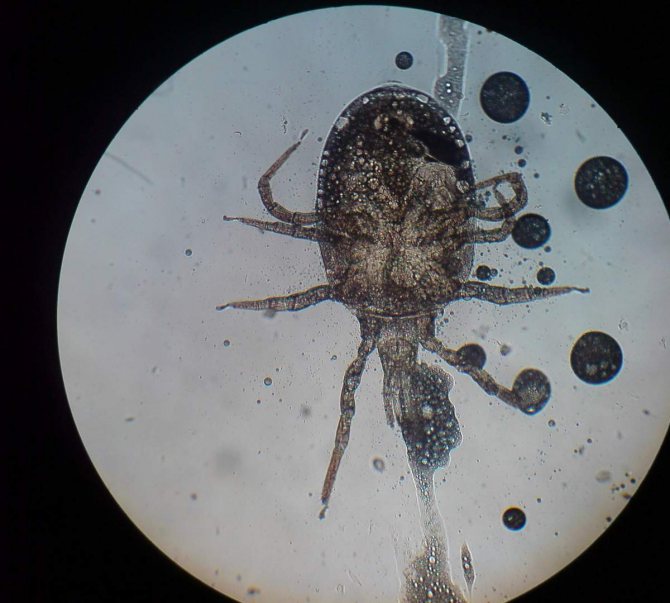
The rat mite is a parasite 0.75 to 1.45 mm, has undivided chelicerae (used to capture the host's coat). Color varies from light gray to dark brown, after a portion of blood, the parasite turns red. It has a sharp caudal scutum, an oval genital shield, and an anus located cranially.
Photo
These photos show what rat mites look like under a microscope:
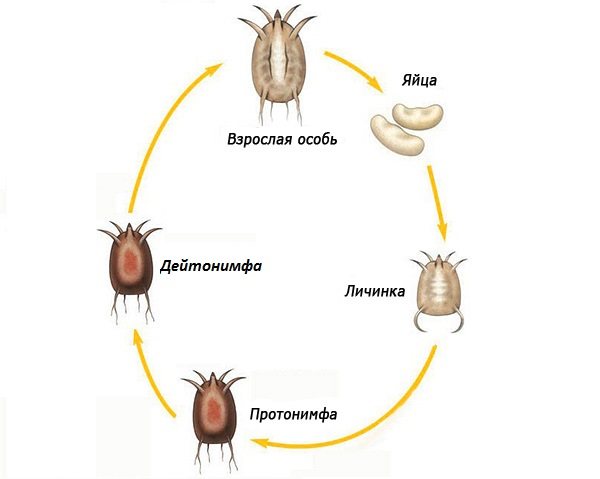
Development life cycle
The life cycle of a rat mite includes 5 stages:
- egg;
- larva;
- protonymph;
- deutonymph;
- an adult.
Of all the above stages, parasites can attack hosts only in the form of a protonymph and an adult. After drinking blood, the protonymph goes through a molting period, and the adult goes to the ovipositor.
Reference. Ticks lay about 100 eggs at a time.
It takes about a day and a half to hatch the larva from the egg, which then attaches to the wool, and then goes through the molting stage within 1-2 days with the transition to protonymph. Having taken a portion of blood, the protonymph goes through a molting stage with the formation of a deutonymph. The latter is transferred to the new owner. The duration of the entire life cycle of a tick is about 7-16 days. The life span of the female does not exceed 2.5 months, of the male - 1.5-2.
Habitat
Most frequent localization of tick populations - old, unused buildings with a large number of rats. The main habitat of the parasite is rat nests. They are able to move in space in search of a new owner.
There are industrial foci of the described parasites - these are points related to the maintenance and breeding of various animals (for example, laboratories, zoos), processing and storage of products (for example, meat processing plants, markets).
Important! Mites can penetrate into apartments through the slots of the ventilation ducts, from the side of the entrance door from the corridor.
Reproduction
Reproduction occurs through partogenesis - a type of reproduction in which female reproductive cells develop into an adult organism without a previous fertilization process.
If the protonymph attaches to the owner and drinks blood once before the next molt, then a male develops from it. If the protonymph molts to the deutonymph and sheds again after a few hours, then the development of the female occurs.
Food
The main food for rat mites is blood and serum... They can withstand without power for up to six months.
Danger to humans


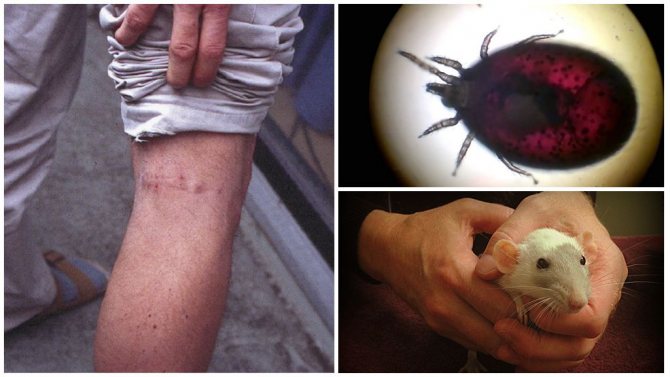
The described parasites are one of the most dangerous for humans. The bites of these ticks are fraught with the development of a number of pathological conditions.
In most cases, contact with this parasite causes contact tick-borne dermatitis, which is manifested by local changes in the skin.
Also, after being bitten by a rat tick, transmission of some infectious diseases is possible, one of which is tick-borne rickettsitosis. The following types of rickettsitosis are distinguished:
- rat typhus;
- Japanese river fever;
- smallpox rickettsitosis;
- Q fever with renal syndrome.
Attention! Lack of timely treatment for these pathologies can lead to death.
It is also useful to read: Fish mite
Preventive actions
Of course, the most common cause of the spread of parasites are rats and mice, which can enter living quarters, thereby significantly increasing the risk of human infection. Therefore, preventive actions should be aimed at maximizing the protection of premises from rodents. It is also very important to adhere to sanitary standards and maintain cleanliness.
It should be remembered that pets are also susceptible to attack and infection from these parasites, they can bring insects to their living quarters. Be sure to monitor the condition of your pet, conduct regular examinations, and take preventive actions. From the beginning of spring to autumn, you need to use protective equipment that does not allow infection of animals.
Signs of rat tick bites
The favorite localization of bites is places with the most delicate and thin skin. Most often, bites can be found in the following areas:
- under close-fitting clothing: belt area, collar area, cuffs;
- depressions on the body: armpits, navel area, auricles;
- in skin folds: inguinal folds, on the abdomen, under the mammary glands.
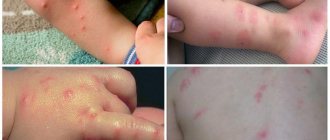
The symptoms of a tick bite include the following:
- feeling of crawling something on the body, stirring;
- itching of the skin in the area of the bite;
- hyperemia of the skin;
- a point of black or brown color if the parasite has adhered to the body;
- a point of red tint if the tick has disappeared;
- rashes on the skin;
- rise in body temperature to individually high numbers.
It is also useful to read: The consequences of a tick bite in humans
Room processing procedure
If a large number of gamasid mites are found in the room or cases of rat or mouse tick-borne dermatitis in humans are noted, first of all it is necessary to close all the cracks in the room. The gaps under window sills, skirting boards, at the joints of panels, at the pipe entrances are sealed with cement.
If the infection with ticks came from rodents, first they carry out deacarization, and then deratization of the premises, that is, the destruction of rodents. Deacarization (elimination of ticks) is carried out using acaricides - preparations designed to kill ticks. Acaricides are most effective at temperatures above 20 degrees.
Household premises can be treated with liquid preparations of insecticides approved for use against ticks. These drugs are used to treat the places where rodents and mites penetrate most often (kitchens, bathrooms). If there are pets in the house, it is necessary to treat their bedding and sleeping places. Hosts should kill ticks on their cats or dogs with pet shampoos or insecticides.
If the living quarters are infected with chicken mites, which usually happens on the first and last floors, it is necessary to get rid of the nests of swallows, pigeons, sparrows, where ticks live in large numbers. In poultry houses, double spraying with acaricides is used.
But if you want to keep your dog free of ticks, try treating it with essential oils, such as clove, lavender, or tea tree oil, before walking. Dissolve the oil in water (10 drops per 50 ml) and spray the dog with a spray bottle.
Rat tick bite remedies


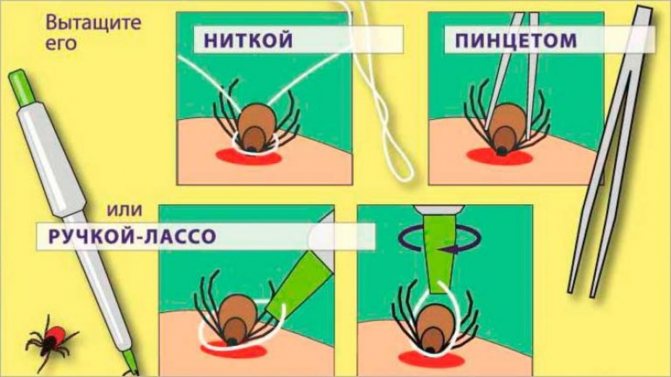
Before using any tick bite remedies, the tick itself must be removed directly. To do this, follow these steps:
- steam the affected area, soften the skin with a cream;
- disinfect the skin by treating them, for example, with alcohol, Chlorhexidine, Septocide;
- remove the tick with a special twist;
- see a doctor.
After removal of the parasite, antihistamines are prescribed (for example, Cetrin, Loratadin). Also, medications with antiparasitic, antiseptic effects are used.
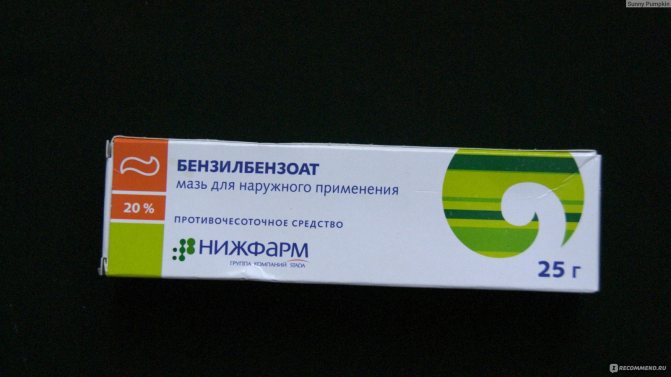
Benzyl benzoate ointment 10%
It is an antiparasitic drug used topically. It is produced in the form of an ointment in metal tubes or glass jars.
Duration of treatment is about 4 days.
The first treatment with ointment is done in the evening before going to bed. The skin of the arms, trunk, legs is processed, not excluding the soles and fingers. Processing is done on clean skin. After processing, put on clean linen and clothing. In the next 2 days, it is necessary to take a break in therapy, while it is forbidden to wash off the remnants of the medication from the skin. On the 4th day in the evening, repeated processing is performed, similar to that on the first day. On the 5th day, the ointment is washed off.

Sulfuric ointment
It is an anti-scab and is used externally. The release is carried out in the form of an ointment in metal tubes.
Duration of treatment - from 7 to 10 days.
The drug is applied in a thin layer to the affected areas of the skin 2-3 times a day during the specified duration of treatment. After the end of therapy, it is allowed to take a bath, it is necessary to change underwear and bed linen.


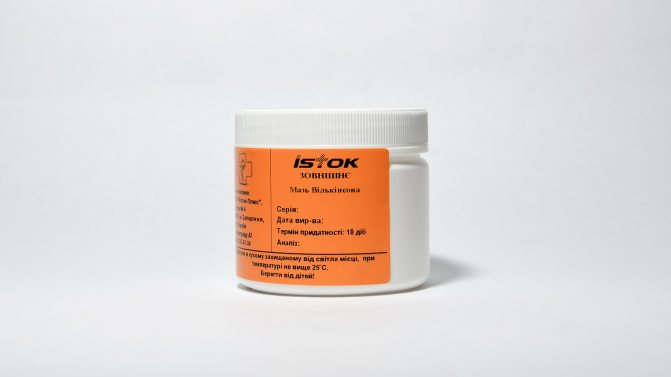
Wilkinson's ointment
It is a product for external use, which includes tar, sulfur, Naftalan oil. It has anti-inflammatory, antiseptic, antiparasitic effects. The release is carried out in the form of an ointment in tubes and glass jars.
Used externally. Once a day, the ointment is rubbed into the skin of the whole body, excluding the face and scalp. Duration of treatment - 3 days.

It is also useful to read: Steeloral "Tick Allergen"
Appearance and lifestyle
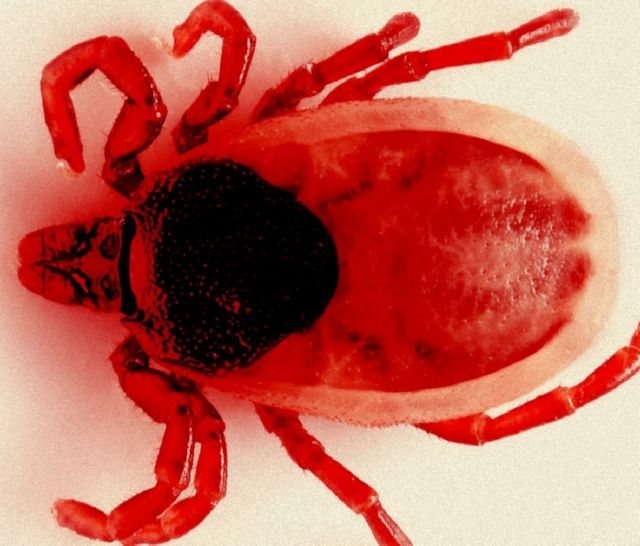

Gamasid mites are very small animals, ranging in length from 0.2 to 3.5 mm. The body is ovoid or oval in shape and yellowish or brownish in color. Having just drunk blood, the parasites have a scarlet color. The body is divided into two parts - into the body itself, or the body, covered with a dense chitinous cover, and the oral apparatus. An adult tick has 4 pairs of limbs on its body.
The oral apparatus of parasitic mites has the form of a proboscis and is designed to pierce the skin of victims. Sharp chelicerae pierce the skin, and on the sides of them are pedipalps designed for touch. Ticks breathe with the help of the trachea, the airways are located on the sides of the body.
In their development, gamasid mites go through several stages:
- egg,
- larva,
- nymph I (protonymph),
- nymph II (deuteronymph),
- an adult.
We suggest that you familiarize yourself with: How to get rid of small flies in an apartment
Fertilization occurs as follows: the male with his chelicerae attaches a spermatophore (sperm bag) to the corresponding hole in the female's body. There are species that can reproduce by parthenogenesis. In parthenogenesis, unfertilized females lay eggs, from which viable larvae emerge. Viviparous species of gamasid mites are also known.
Representatives of different stages of development are easily distinguished from each other. The larvae have only six legs and do not feed. The protonymph has a fourth pair of legs, they have a whitish color, soft integument and are very active. Deuteronymphs have dense integuments and are yellowish or brownish in color. Protonymphs and deuteronymphs eat. The developmental cycle is very fast, on average, the time from oviposition to the appearance of an adult takes ten days.
Adult ticks usually live for six to nine months.
Rat mite in an apartment: how to get rid of
In order to carry out disinfection in an apartment, you need to make sure that it was rat mites that were affected. The supposed habitat of the ticks should be examined by a disinfectologist. If the presence of these parasites is confirmed, then deratization and disinsection of the premises are carried out.
The disinfestation process implies the treatment with special preparations of those places through which rats can enter the room, as well as the possible ways of their movement - plinths, manholes and many others.
Reference. If pets live in the room, then their resting places are subject to treatment with acarcides.
After three days, the necessary actions are taken to destroy the source of the parasites.
It is also useful to read: Acaricidal treatment against ticks
Habitat
As can be understood from the name of these insects, they parasitize mainly on rats and mice. Therefore, they are most often localized in mouse and rat nests. These can be basements, abandoned houses, warehouses, garbage dumps.
Due to the fact that mice and rats are not always in the same territory, but move in search of food, they carry parasites with them. Residential buildings are no exception, where they can equip themselves with nests in basements and attics. This is the reason that people and pets are attacked by dangerous parasites.
Prevention of the appearance of parasites
Preventive measures for the appearance of rat mites are as follows:
- getting rid of rodents;
- control over rat populations, constant vermin control in their habitats;
- isolation of premises from the penetration of rodents;
- maintaining the proper sanitary and technical condition of the premises.
Rat mites are parasites, the main hosts of which are rats, but they can also infect humans. The main place of their localization is where there is a high population of rats. When bitten by this parasite, a number of clinical symptoms arise, when they appear, it is necessary to consult a specialist, as well as to disinfect the premises.
Varieties
The most common types of gamasid mites encountered are mouse mites, rat mites, and chicken mites.
Mouse
Mouse mites feed mainly on house mice, but they can also bite humans. These mites are carriers of vesicular rickettsiosis.
Rat


Rat mites feed on the blood of black and gray rats, house mice and other rodents, but they attack both domestic animals (cats and dogs) and humans, causing rat tick-borne dermatosis.
Rat ticks carry many diseases: vesicular rickettsiosis, Q fever, hemorrhagic fever. They can also be carriers of tick-borne encephalitis viruses, lymphocytic choriomeningitis. Rat ticks can even spread the plague and tularemia.
Chicken
Chicken mites feed on domestic and wild birds, and attacking humans can cause dermatitis. This species of ticks lives mainly in nests; it attacks birds only for food. Chicken mites are very harmful to the poultry industry. With a massive attack of ticks, egg production decreases, body weight gain decreases, and chickens die.
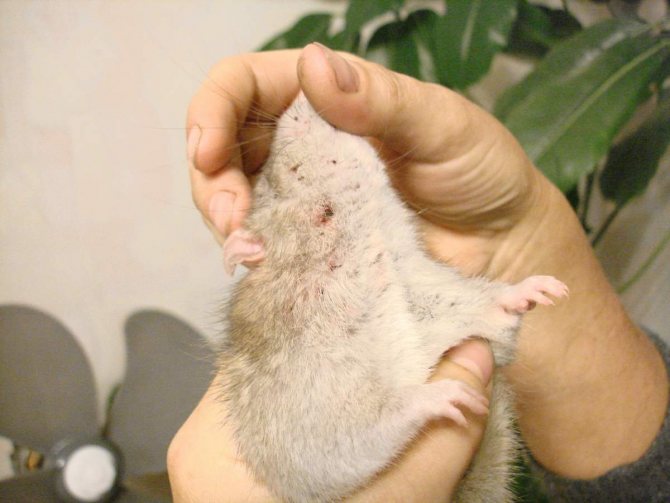
Treating an infected rat
Clarification of the type of parasite and the appointment of treatment should be carried out by a specialist in a veterinary clinic, since different drugs are used to destroy external and subcutaneous parasites. In case of complications, the animal is prescribed anti-inflammatory ointments, immunostimulating drugs and a course of vitamins and antibiotics.
Insecticidal preparations are highly toxic, with improper processing or exceeding the dosage, there is a likelihood of poisoning a decorative rat. It is advisable that the animal is treated by a veterinarian; it is also permissible to treat a fluffy pet at home in a well-ventilated area with strict adherence to the recommendations of a specialist.
Simultaneously with the treatment of the pet, it is necessary to throw away the bedding, disinfect the cage and all accessories several times, change the filler, and treat the entire room with repellents. It is advisable to discard all wooden objects from the cage, they can be places of accumulation of parasites. Rodent claws should be trimmed short during treatment to prevent scratching of the skin.
When keeping domestic rats in a group, it is necessary to repeatedly handle all individuals in order to avoid re-infection. If a pet is bitten by fleas or bugs, it is recommended to treat all pets living in the house with insecticides, as well as the room itself: carpets, upholstered furniture, mattresses, floors, etc.