The black widow is a very unusual spider and in some way is a collective term, since about 30 species of arthropods are hidden under it. These creatures gained fame, because some representatives of this genus are distinguished by their ability to secrete an extremely toxic poison that can cause severe intoxication in a person and even cause death. Wherever this articulate lives, people are well aware of the degree of its danger.
Black Widow is a very unusual spider
Representatives of this order are found almost everywhere where the climatic conditions are rather mild. They are widespread in the countries of East and South Asia, America, North Africa. Some of them are found in Australia and Oceania. In the northern regions, only a few species can live, which are not as dangerous as their thermophilic counterparts.
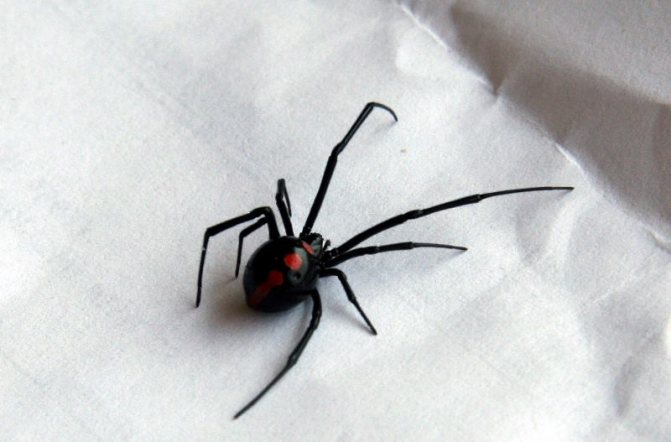

What makes the black widow stand out?
Such a big name speaks for itself. The black widow spider is special in that the female eats her gentleman during mating. At the same time, the naive boyfriend does not even suspect about his intended fate.
And although similar behavior was observed in other animals, for example, in praying mantises, nevertheless, the nominal black widow became the most famous killer of their own kind. What caused this family misunderstanding? Scientists believe that during this period, the female needs a large amount of food, and the best option for her prey is to eat the males.
Habitat
This type of spider is distributed all over the world. They live in regions with a temperate climate, incl. in the USA, South Europe, Asia, Australia, Africa and much of South America. Can be found in dark, dry shelters, dimly lit areas such as sheds, garages, basements, toilets, hollow tree stumps, rodent burrows, and dense vineyard vegetation. They seek to hide in warm dwellings in winter.
Although previously the black widow spider was not known in Russia, in recent years they have been found in the South Urals and in the Rostov region. Migration is explained by an increase in air temperature.
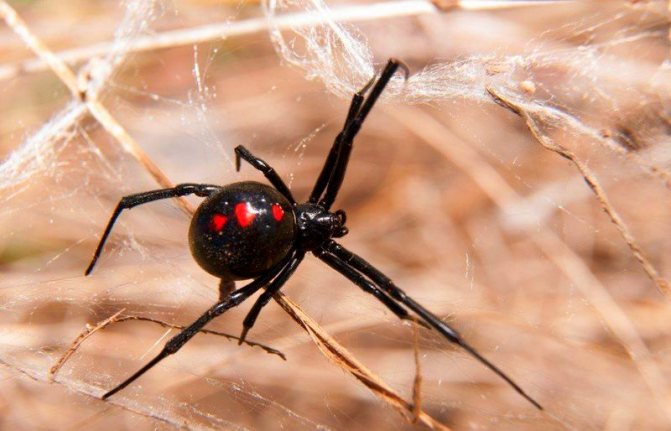


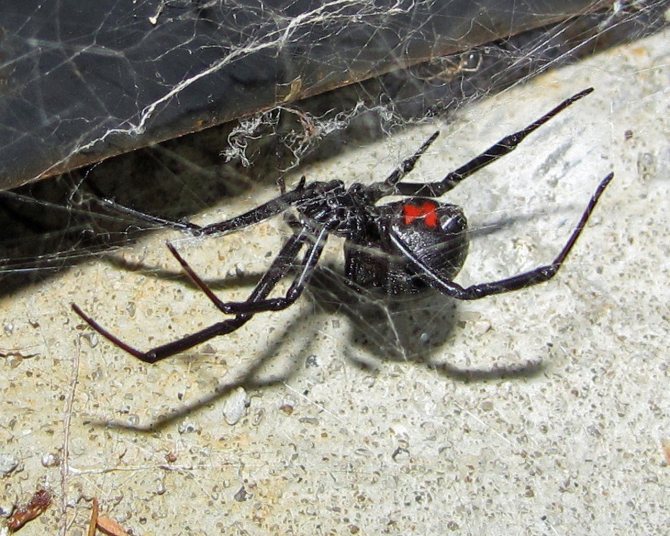
An important characteristic of the black widow is its shaggy combs. A row of strong, curved bristles are located on the back pair of legs and are used to pull cobwebs over captured prey
What does a black widow spider look like?
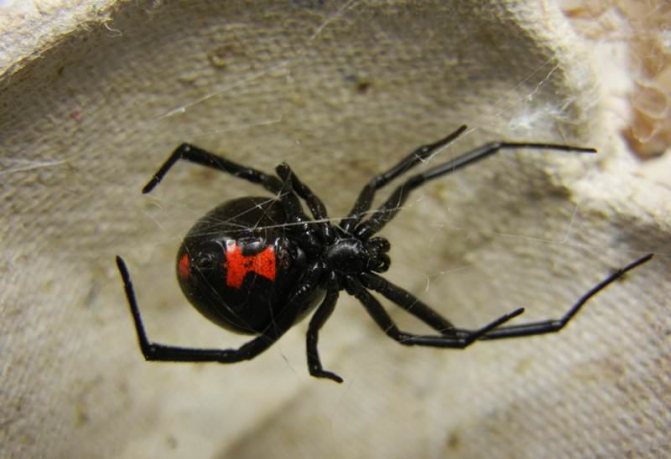
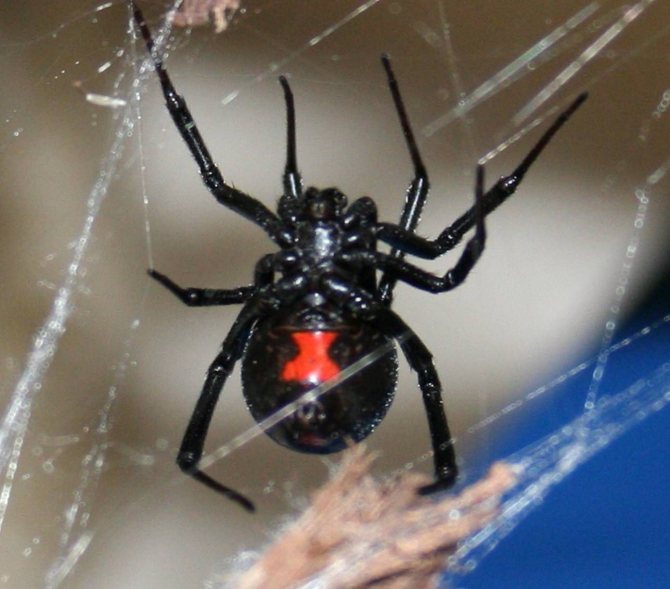
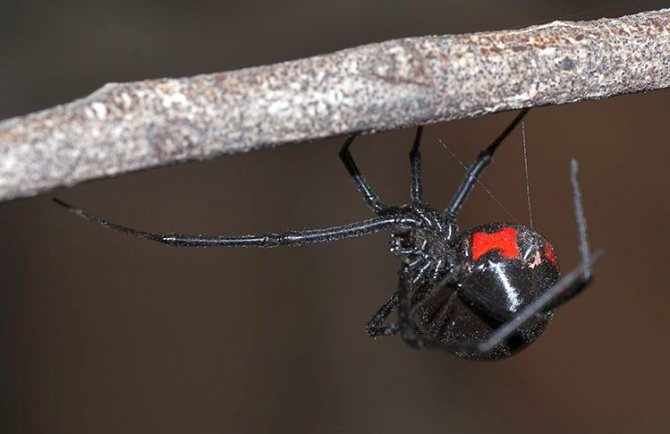
The spider itself is not very large. On average, the female's body reaches a size of 1.5-2 cm, eight legs extend from it in different directions, their length sometimes reaches 7-9 cm.The abdominal cavity is glossy black, and females also have red pigments, most often forming a symbol in in the form of an hourglass.
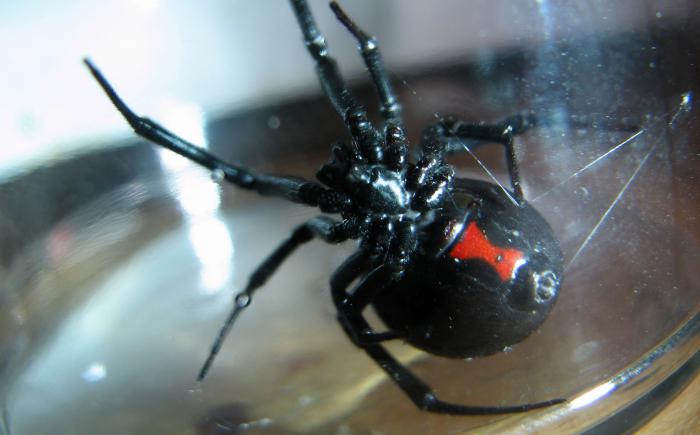


Males are much smaller, which makes them vulnerable to mates. Also, in their glands, the concentration of poison is much lower, which makes them harmless to humans. But the trouble is that in nature, males are much less common, and, therefore, the chance of running into a poisonous spider is still quite high.
Caring for offspring
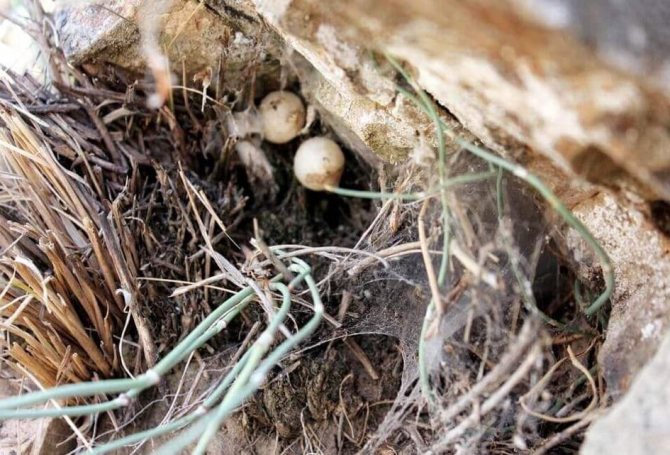


Karakurt nest
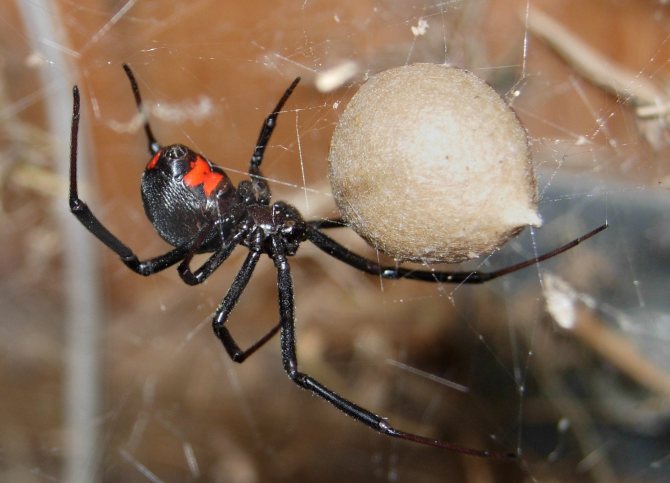
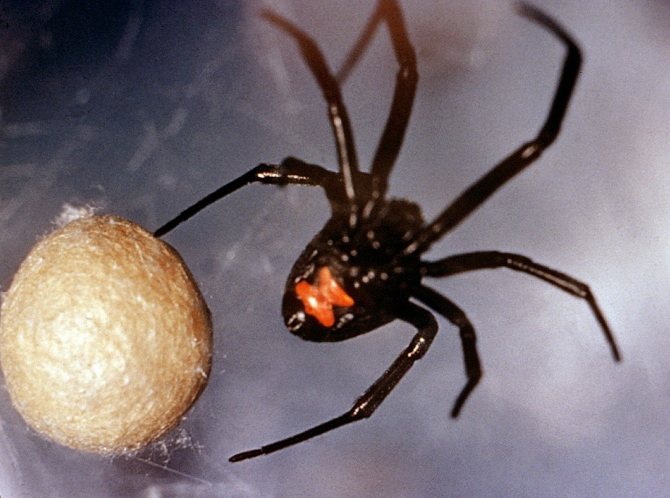
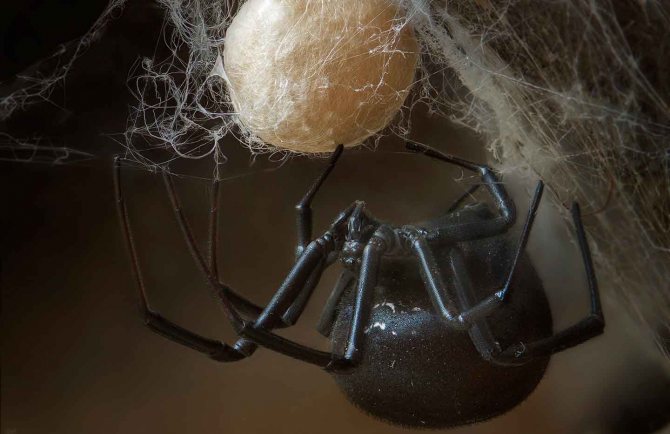
Caring for offspring in karakurt females is pronounced during the incubation period. First of all, they look for a place for future laying, digging a nest in the ground, or adapting for this the abandoned burrows of rodents. Before entering the nest, she pulls on trapping nets. And only then they lay cocoons with eggs.Females remain in the nest for the entire incubation period. Usually fry appear in April.
Interesting:
Why do camels spit?
With the appearance of the offspring, the maternal functions of the female are fulfilled and the juveniles attached to the cobwebs are carried by the wind. By the beginning of summer, young karakurt reach maturity and are capable of mating.
Where does the spider live?
North America is considered the homeland of this arthropod. There and now their number is the highest, just like the number of cases of attacks on people.
With the development of trade routes, the black widow spider managed to move to other continents. Now they can be found everywhere, even in Australia, which is considered the most isolated continent.
Do we have a black widow spider? In Russia, unfortunately, these creatures are also found. And if earlier they could be seen only in the Caucasus or in the Crimea, then with a change in climate they began to move closer. For example, an official case was recorded when a black widow was found in Taganrog.


Antidote
The poison of the black widow spreads rapidly throughout the body. It is important to get to the hospital as soon as possible. The most effective method of overcoming the effects of a bite is the introduction of an anticaracourt serum.
The injection is given intramuscularly. You need 5-10 cubes of the drug. However, the vaccine is not available in all medical institutions.
Usually they are engaged in buying it only in those areas where black widows are often found. The cost of one vaccine is about $ 150. In addition, the shelf life of the antidote is very limited.
First aid for a black widow bite:
- the patient can be given pain relievers;
- a cold compress is applied to the bite site;
- a person should drink a little, but often;
- the affected part of the body must be immobilized so that the poison does not spread so quickly throughout the body.
In the first minutes, you can try to suck the poison. But this can only be done by a person who does not have any damage to the oral cavity. Otherwise, he can also be poisoned.
When bitten by a spider, avoid doing the following:
- make an incision at the site of the bite;
- apply a tourniquet to the injured limb.
In the hospital, in order to reduce the harmful effect of toxins on the body, they make an internal administration of calcium chloride, novocaine and magnesium hydrogen sulfate.
Features of behavior and methods of hunting
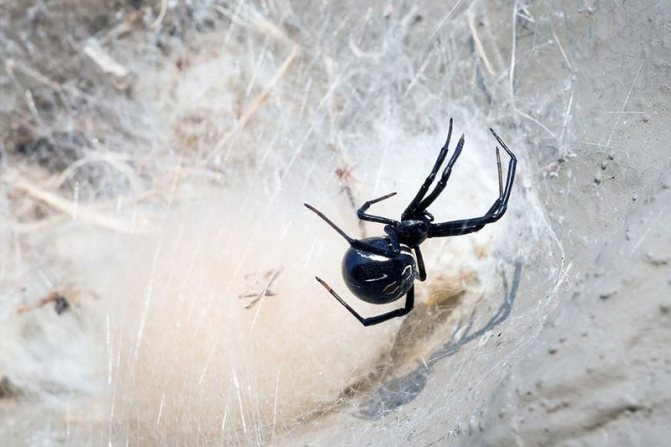
The black widow spider leads a closed lifestyle. To arrange a den, he looks for a quiet area where uninvited guests rarely appear. There it weaves a net that can become a good lasso for small insects. Often it is located at a height of 30-40 cm and has an arbitrary shape.
Although this predator has eight eyes, it practically does not use them when hunting. He uses the net as his main weapon. As soon as the victim touches it, the spider is already on the alert, and at the first convenient opportunity it will attack its prey.
Lifestyle
Karakurt: male and female
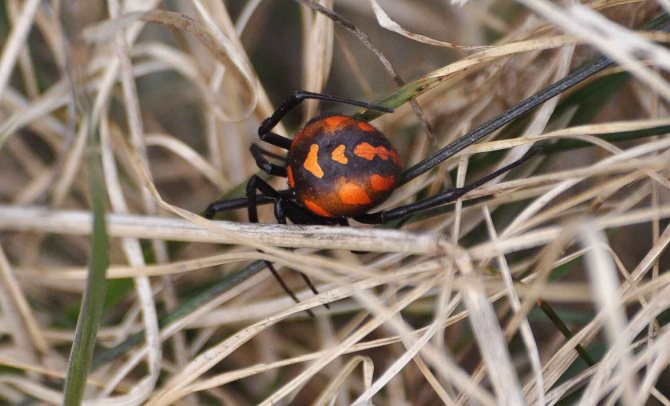
The main difference between the male and the female in karakurt is the size. The female is almost twice the size of the male. She can reach two centimeters in length, while the male does not grow more than seven millimeters. In addition, the male has red spots on its abdomen. In the female, the body is painted deep black. Karakurt, like other spiders, are good runners, and can cover quite large distances and at high speed. This is all the more surprising, because muscle fibers are completely absent in the spider's limbs.
In addition to movement, the spider uses legs for digging minks and weaving nets. There are also olfactory and tactile organs on the legs.
Karakurt, like all spiders, are predators. They catch their prey with cobwebs. Spiders plunge into the caught prey chelicerae, releasing poison and digestive juices. Having entangled the victim with a web, they leave it for a while.Digestive juices quickly digest the prey, after which the spiders suck out the resulting broth.
Mating season
With the arrival of heat, spiders begin the mating season, during which males begin to actively search for a mate. It is curious that a gentleman, having entered the web of his chosen one, begins to emit special vibrations. Thanks to this, the spider realizes that she has a welcome guest.
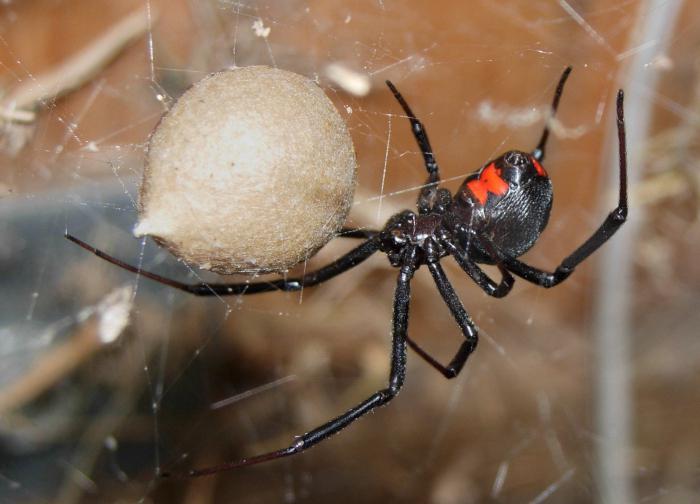
As soon as the sexual intercourse ends, and sometimes even during it, the female stings her companion and wraps him in a web, in order to then satisfy her hunger. Then she prepares for laying eggs, for which she looks for a secluded place and begins to weave cocoons.
One cocoon can hold from 20 to 350 eggs, but only a few will crawl out of it. Since the mother does not feed her children, after a while they begin to eat each other. And now, after 3-4 weeks, no more than a dozen spiders appear outside.


The structure of karakurt
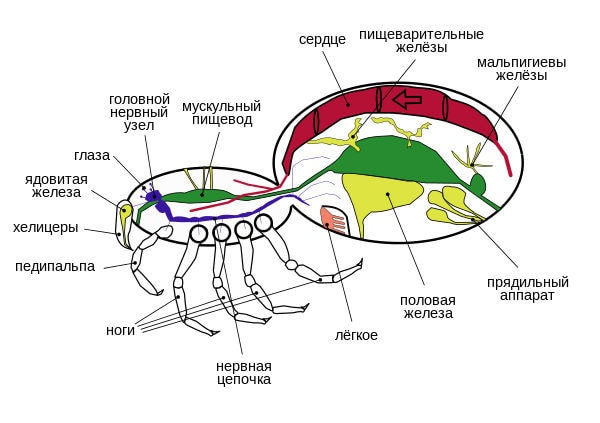

The structure of karakurt
The structure of karakurt is practically no different from the structure of other spiders. Its body is divided into two sections: the front section of the torso, with four pairs of eyes, is covered with a hard chitinous shield. The second section is the abdomen, which is covered with an elastic membrane. The spider glands are located in this section of the trunk. On the head of the body there are two pairs of modified limbs - chelicerae and pedipalps, behind which are walking legs. Spiders have eight of them.
Chelicerae consist of one limb, at the end of which there is a claw, where the poisonous gland opens. They are designed to grab and hold prey, as well as to defend against enemies.
Interesting:
Why does the dog growl at the owner?
Pedipalps are similar to legs, but shorter. They are the organ of touch; they usually do not take part in movement. In sexually mature males. They are somewhat modified.
How dangerous is the bite
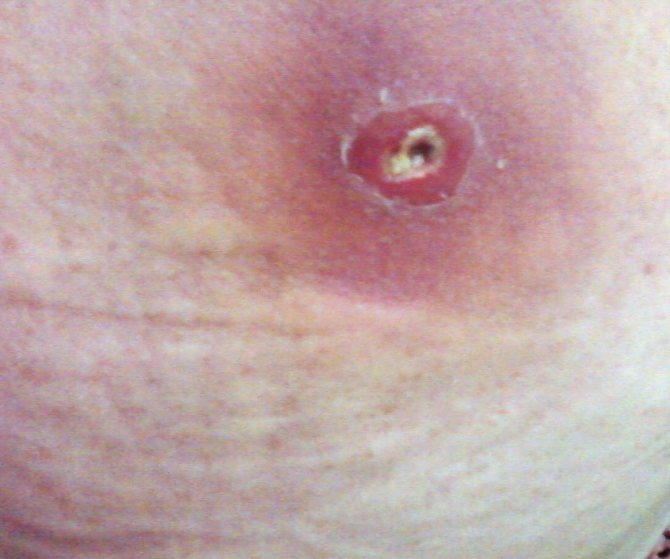
Many are interested in how deadly the black widow spider is? The bite of this creature is dangerous, since the secret contains poison, the strength of which exceeds that found in the glands of the rattlesnake. But the good thing is that when bitten, not so many toxins enter the human body, because the spider itself is much smaller than a snake. And yet, painful sensations cannot be avoided.
Bite symptoms:
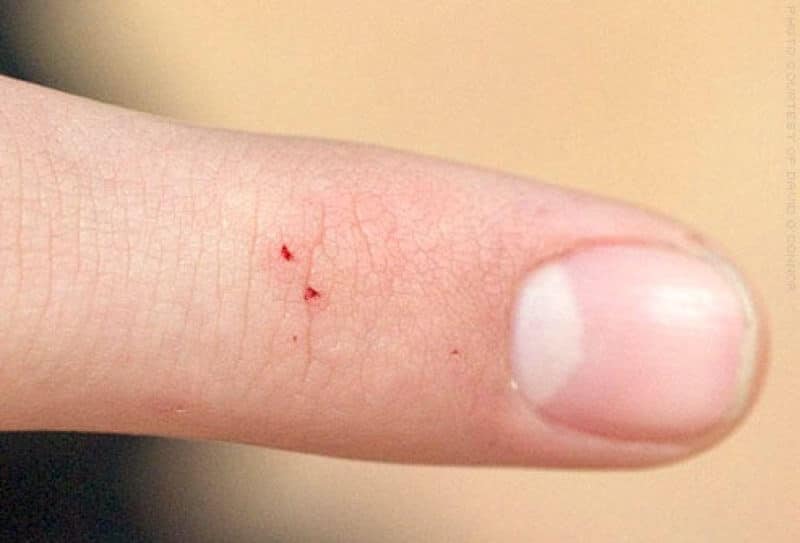
- It is impossible to miss the moment of injection of the poison, as it looks like a sharp prick from a sharp object. After that, two points will be visible on the body, which are difficult to confuse with something else.
- After 20-30 minutes, the muscles around the bite will begin to contract, and pain is felt.
- The muscle spasm will spread throughout the body. Toxins in the blood lead to fever, and sometimes even nausea and chills.
- Only after 24 hours, the effect of the bite begins to recede. Full recovery occurs only after one week.
It is important that when you are bitten, you should definitely see a doctor. Ideally, he should inject a serum that neutralizes the effects of toxins. And remember: if an adult gets off with an unpleasant experience, then such a bite can be fatal for children and the elderly. The same goes for people who are allergic to certain toxins or have health problems.
Karakurt and man
The poison of karakurt contains a neurotoxin and is close in action to the venom of rattlesnakes. At the site of the bite, hyperemia occurs, which quickly disappears. A quarter of an hour later, there are sharp pains in the abdomen, chest, legs go numb. All this is accompanied by mental agitation, convulsions, headache. The heartbeat slows down, arrhythmia appears, blood and protein appear in the urine. The victim's condition becomes critical. The most effective remedy is anticaracourt serum. With timely administration, the patient's condition will quickly return to normal.
It should be noted that karakurt are never the first to attack... Spiders are aggressive only if disturbed.The most dangerous are female bites. The largest number of bites occurs in June-July, the time of annual migrations.
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl + Enter.
Share this:
What does a spider eat?
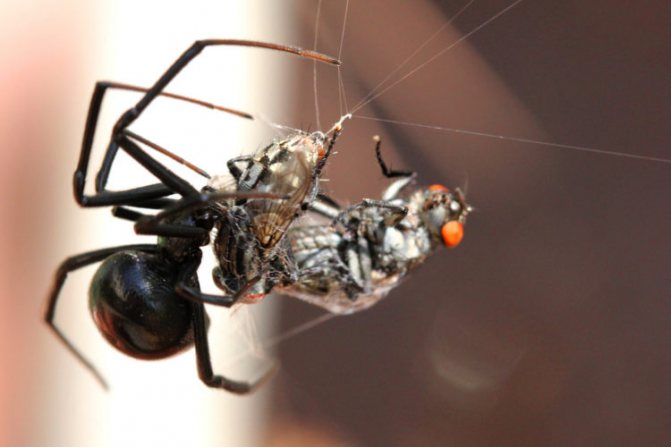


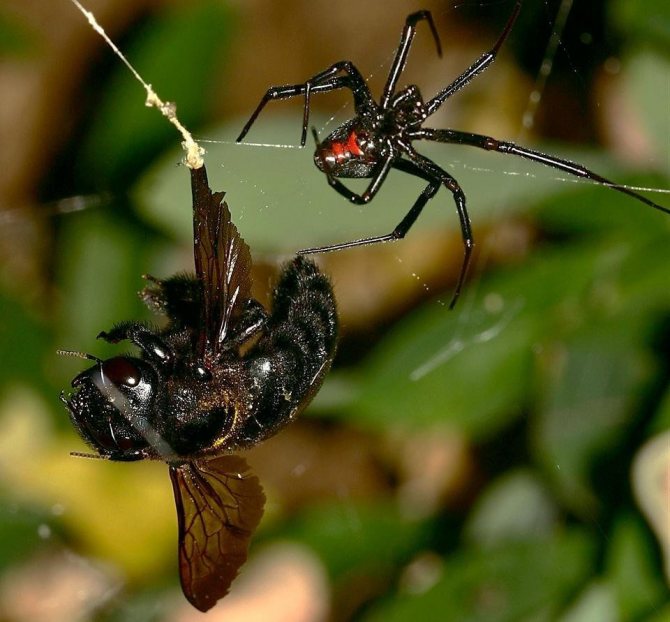
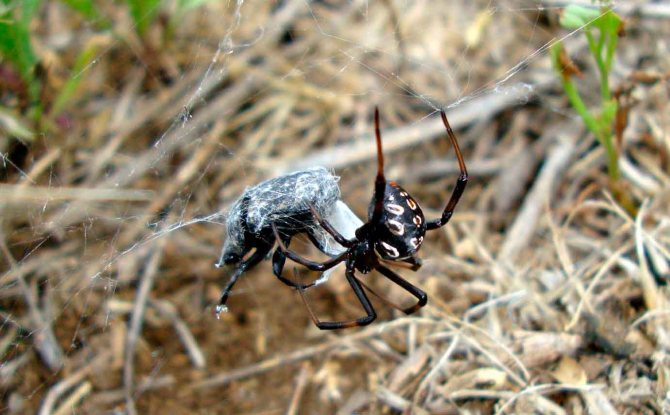
The black widow feeds on flies, moths and other flying insects, as well as ants, beetles and even other species of spiders. She makes a disordered, three-dimensional web, very often with a short "cap", in which she hides herself, waiting for prey.
The web of males is smaller than the web woven by the female. Waiting for prey, the black widow from time to time touches the fibers with its limbs. When an insect, flying, gets caught on the sticky fibers of the net, it sticks to them. Through the web, the spider feels even the lightest movement of the victim, who is fighting for his life, so he, without losing a moment, runs out of the shelter and begins to entwine the prey with sticky threads. Then the spider injects poison into the victim's body along with saliva containing digestive enzymes, and continues to wrap a web around the paralyzed insect.
Over the next several hours, the saliva digests the victim's body, and the black widow sucks out its dissolved contents. The spider's gizzard acts as a pump. From the prey, only an empty shell remains.
What are the features of reproduction
At the time of mating, the male manually places the seminal fluid in a special organ of the female. One mating is enough for a female. The seed can be used later if needed.
You can learn more about the black widow from this video:
The insect stores eggs in a cocoon. This ensures complete safety. The new generation will hatch only in a month. The life span of a black widow is up to 5 years. This figure can depend on many extraneous factors. In the absence of a safe home, the arachnid is doomed to death.
What are the varieties of the representative
There are many subspecies of the spider. They all have specific features. The main varieties are described in the table.
| Steppe widow | Always black. Scarlet spots are present on the back and abdomen. Sometimes they can take on a yellow tint. They prefer to live in steppe conditions. Often the insect attacks rural workers who are busy improving the land. Males are much smaller than males. Females are poisonous and pose a danger to humans and animals. Cobwebs can be found almost above ground level. The insect is most active in summer. Can bite only for self-preservation. |
| Australian widow | The predator lives in Australia. The female is larger. The bite of the parasite is painful. Antivenom administration is required. |
| Western black | Lives on the American continent. The color is black. There is a bright red spot. Males are pale yellow. |
Spider at home
Not many people dare to keep such an exotic and dangerous animal in their home, but the popularity of poisonous spiders, including karakurt, as indoor pets is growing steadily. What conditions are necessary for this arthropod?
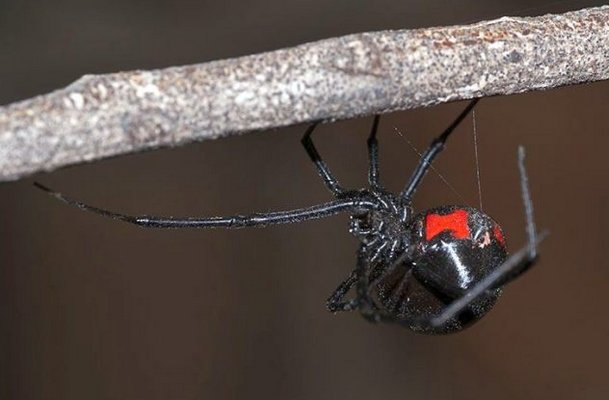


Life cycle features
Depending on environmental conditions, the life span of a spider varies from 1 to 3 years. Males live slightly less than females. Karakurt live in complete solitude, the only exception is the mating season. In winter, spiders hibernate, and in late spring they start mating.
During their life, karakurt change their skin from 7 to 9 times. After the last molt, the males mate, and even if the spider is lucky enough to survive, it soon dies of starvation anyway - after mating bonds, the male loses interest in food.
Karakurt can reproduce extremely numerous offspring - at a time, a female spider can lay from 5 to 15 large cocoons with eggs, 100-900 pieces in each.The size of the cocoons can reach one and a half centimeters.
Karakurt females are distinguished by an extremely careful and caring attitude to the offspring, carefully guarding cocoons with babies.
On average, it takes 20 days for the eggs to ripen, after hatching the spiders do not move for several more days - they are completely defenseless, cannot weave a web, and therefore get food.
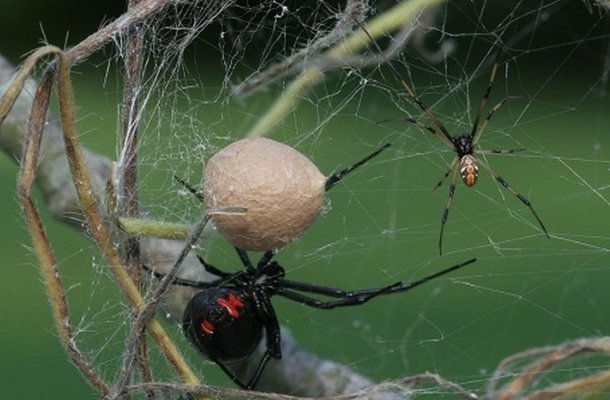


The first molt occurs a week after birth. Soon the spiders get out of their cocoons and begin their independent life. Under natural conditions, a very small percentage of spiders survive from the clutch.
At home, however, you can resort to "transplanting" the young in separate dwellings - in this case, it will be possible to preserve almost all the offspring. For transplant, you can use small glass bottles, vials, small plastic containers.
You will probably be interested in reading about the keeping of a eublefar, a chameleon, a maize snake, a red-eared turtle, an iguana, a noses, a possum, a manul, a capybara and a crocodile in the house.
The peak of the karakurt attack is in the middle of summer. - just at this moment young spiders mature, besides the warm weather at the height of the season contributes to the high activity of spiders.
How to feed karakurt
The diet of karakurt is quite diverse: it can be flies and cockroaches, crickets, locusts, small beetles, goose, midges and mosquitoes, in general - karakurt is not averse to feasting on all small insects.
Since the spider's activity stops in winter and it hibernates, the arthropod does not need food, but at this time it needs to provide a slightly higher temperature of the terrarium.
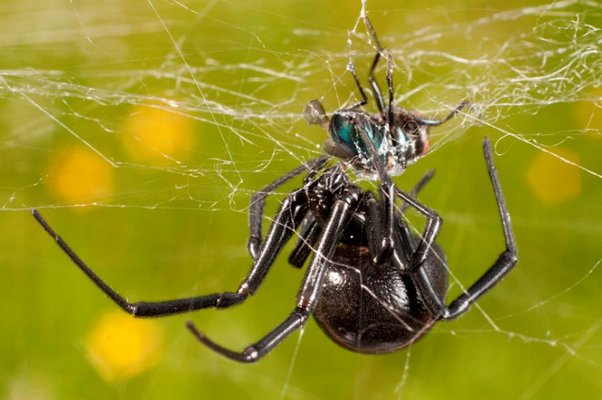


In natural conditions, the spider receives food in the following way: it is located on the edge of the web, holding a pair of legs on signal threads that go to the farthest ends of the snare.
As soon as the victim falls into the trap, the spider receives a signal, gets close to the insect and envelops it in nets, which instantly stick together to form a strong cocoon. The victim can no longer move in the cocoon.
Then karakurt makes a bite, the active substances of which turn the victim into a kind of liquid "broth". On average, eating an insect can take more than a day.
Important! Periodically, spiders refuse to eat; this can occur during molting. In this case, be sure to provide your pet with water. A small plastic container will work well as a drinker.
It is interesting that karakurt can go without food for a very long time, in some cases they may not eat for 6-12 months. However, if you keep a spider in your home terrarium, there is no need to check how long the arthropod will last without food.
You need to feed an adult once every 7-10 days, young spiders need to be given food more often - once every 3 days. If you feed young animals, give them slightly "crushed", not particularly active insects, as a young immature spider may not be able to cope with it.
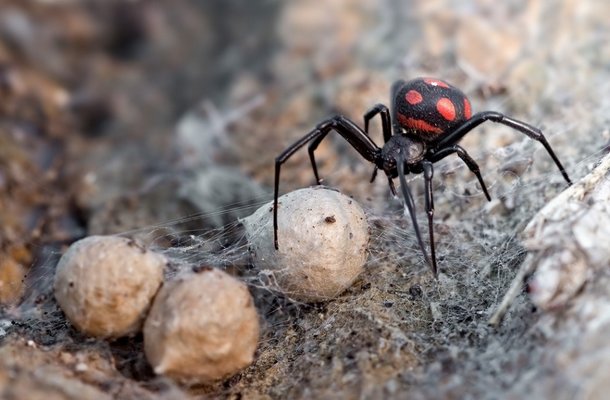


Terrarium care
Perhaps spiders are the most undemanding pets to care for. To keep karakurt, you need to equip with a terrarium. For this, a regular aquarium is suitable, on the bottom of which you need to place sand or small pebbles, as well as leaves, stems, dry branches and moss.
To maintain a warm temperature, you can heat the spider's home with a special lamp. Fix a container of water in the corner. The terrarium does not require frequent cleaning - it is enough to change the sand once a year.
It is best to do this in the spring, after the winter sleep of the arthropod. Also, be sure to take care of the cover for the terrarium so that one day you do not find an escaped spider in the house. However, the lid should be finely perforated to allow air to enter the enclosure.