Description of the field mouse, belonging to the animal world
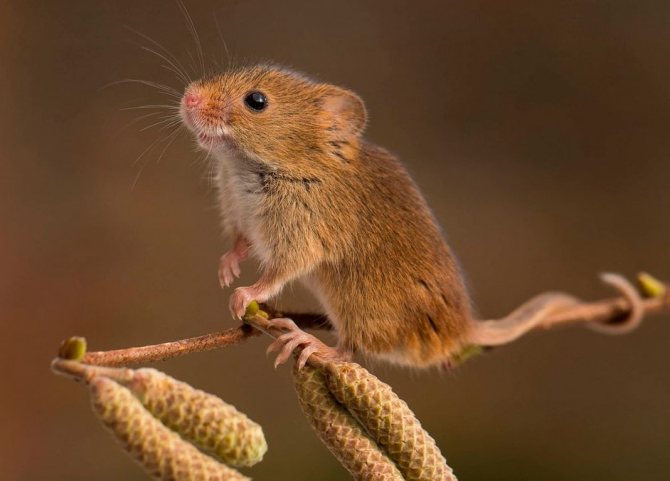
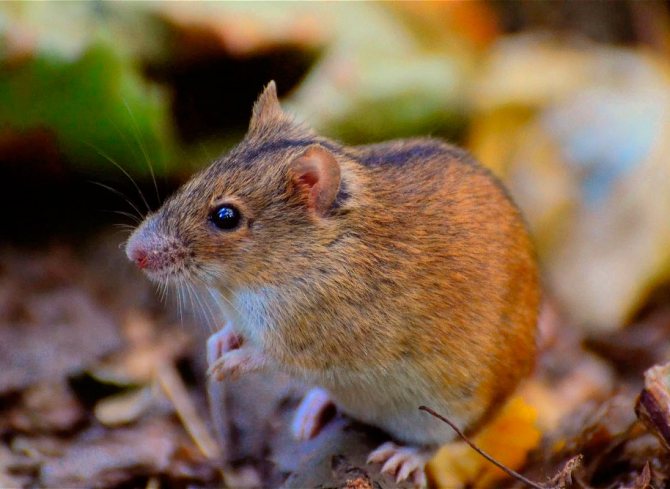
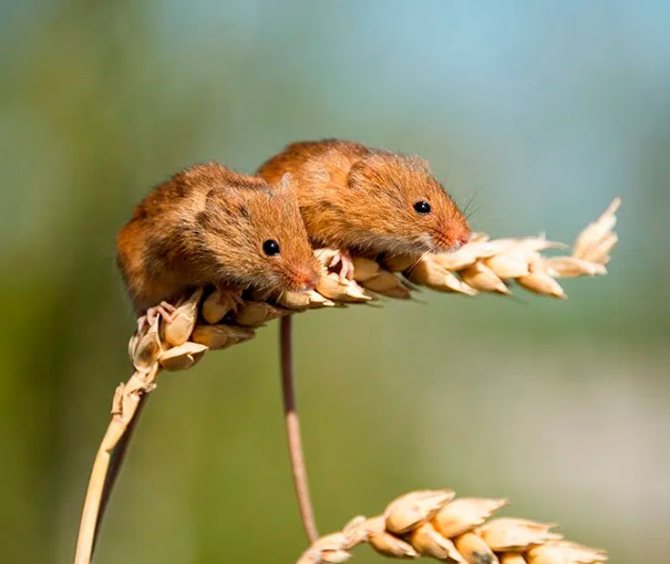
The field mouse looks almost like a house mouse, but according to many, it is much cuter. She has a more miniature muzzle, short tail, neat compact ears. The common field mouse is included in the subfamily of hamsters, which explains its external resemblance to these domesticated rodents.
This small animal has a discreet coloration, which allows it to remain inconspicuous for numerous predators. It is difficult for large birds to see the mouse from the air - it merges with packed grass, bushes, soil. And terrestrial predators hardly distinguish it in thickets of rye or wheat. A person rarely manages to find the mouse itself or offspring, but only traces of its invasion:
- spoiled grain;
- litter;
- gnawed roots.
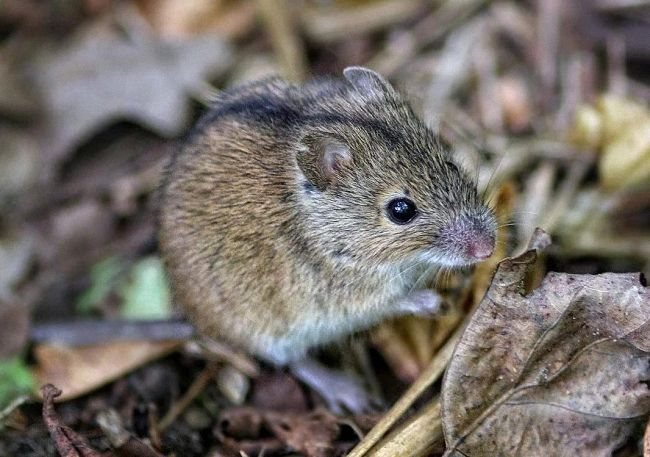

Length
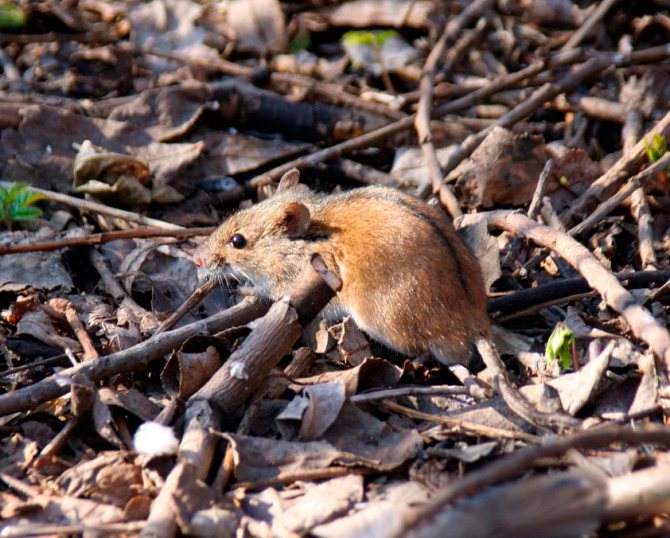
This mouse with a black wide stripe on its back is more voluminous than a rodent that lives in houses and outbuildings. With large reserves of food and the absence of predators, from which you have to constantly run away, the length of the animal can reach 12 cm. This is about 30–75% of the total size. The mouse has a flexible, mobile body, so it can easily:
- climbs trees;
- penetrates into narrow winding passages.
But the length of the rodent is not always an advantage - predators have a better chance of finding and grabbing prey.
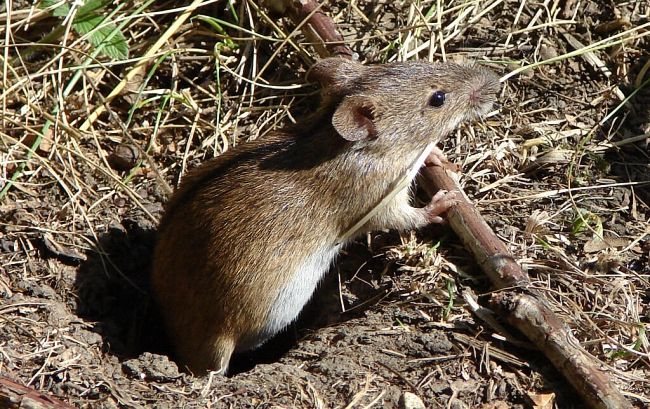


Tail
The tail of voles is long, for example, in adults it reaches 8–10 cm. From a distance it may seem that it is completely naked, but this is not so. The mouse's tail is covered with:
- durable protective leather scales;
- the smallest stiff hairs.
The fact that it is cold in rodents does not correspond to reality. His temperature is the same as that of the whole vole calf. The tail is cold, but only if the animal is frozen.
This part of the vole is a kind of temperature regulator. In hot conditions, its vessels constrict, slowing down blood circulation and helping to cool the body. In winter, on the contrary, they expand. The temperature of the blood passing through them rises. Entering the body, it quickly warms it up.
The tail also serves as a balancer for the vole, allowing it to maintain balance while crawling along the thin branches of trees. And in a fight, a rodent can use it to fight off small predators - rats and birds.


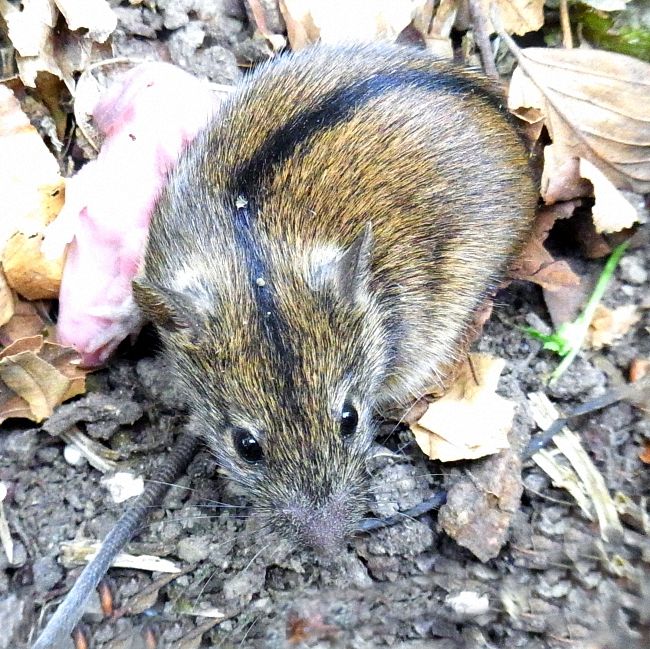
Wool and color
According to the zoological description, the vole differs from other species of mice by a wide stripe on its back. It starts between the ears, runs all over the body and ends at the tail. In the area of the brown stripe, the longest, thickest hairs are. They are quite tough, unlike those located on the belly of the vole. There are hairs:
- grayish;
- softer;
- short.
Therefore, it is much more difficult to see a vole from above than from below. The color of the animal varies somewhat depending on the genus. So in a vole living in the middle zone of our country, the coat has a reddish tint. The mouse of this species remains inaccessible to predators in wheat and rye crops, on loamy soil and on the banks of water bodies. Even in a photo taken at a distance of 4–5 meters, it is almost impossible to see a rodent against this background.


Torso and limbs
Even a small vole has a mobile, muscular body. The mouse easily climbs the stalks of cereals, flexible branches of shrubs and trees, perfectly maintaining balance.The mouse begins to lay fat closer to autumn in order to wait out the harsh winter without problems. The rodent's limbs are short - the length of the largest specimen does not exceed 3 cm.
Each paw is equipped with claws dull from regular digging in search of food. They are powerful enough to resist a predator attack. With the help of claws, the vole easily climbs not only trees, but also brickwork of houses and barns. In newborn mice, they are thin and sharp, but as they grow older they become flat and wide.
Head
The ears of the field mouse are round, small, and the black eyes are set close to each other. The muzzle is pointed, but not as much as in rodents living in houses, barns, yard buildings. The hair on the head of the vole is shorter, resembling bristles when touched. In some species, the hairs on this part of the body are somewhat lighter and thinner.
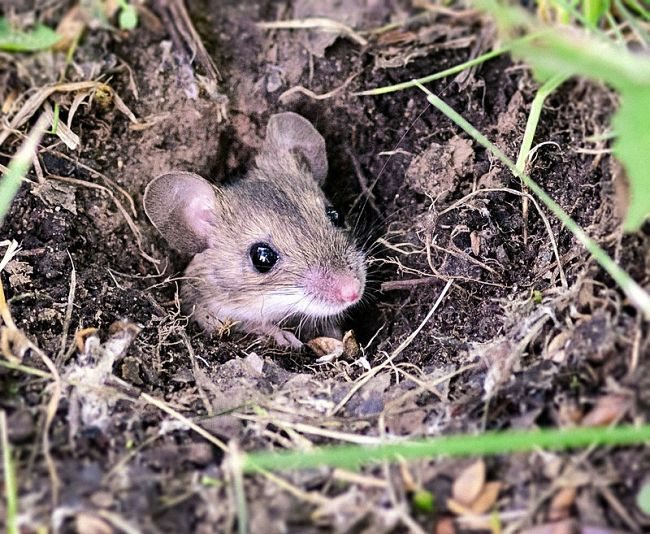


In general, it is impossible to distinguish a male field mouse from a female by appearance. They do not differ in the length of the body and tail, the shape of the head or ears. The only difference is 4 pairs of nipples on the belly of a female vole.
Wood mouse appearance
Rodents are very similar to each other. It is difficult for an ordinary person to notice the difference between animals. But each type of mouse has its own individual traits. It is enough to study in detail the structure of the mouse body, as it becomes clear that the forest animal is practically unlike a domestic or field inhabitant.
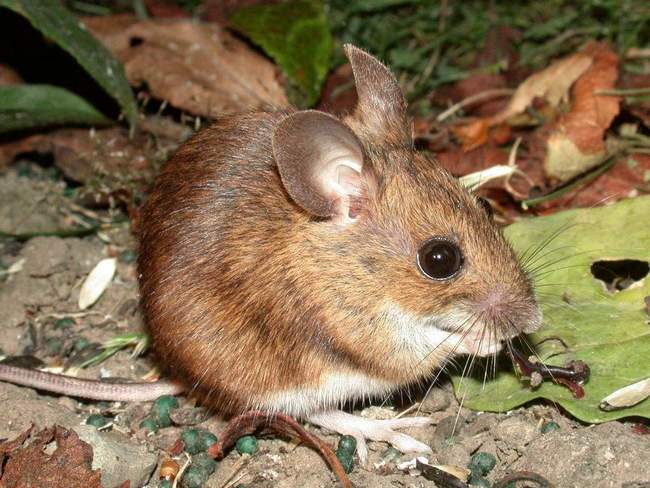


Length
This type of rodent is larger than those individuals that live next to humans. In length, the mouse grows up to 10–12 cm. In a rare case, the animal grows only up to 8 cm. In this case, the young offspring reaches the size of an adult by four months.
Tail
The length of the tail is proportional to the length of the body. But in some cases it differs up or down. This factor does not depend on the health of the rodent or other factors. The tail color matches the body color.
Wool and color
Most often there are red forest mice, on the back of which there is a brown spot that does not have obvious outlines. On the belly, white color predominates, but the shade can be yellowish. A distinctive feature in the description of a forest mouse is the presence of a bright yellow spot on the breast, which has the form of a strip or a small oval.
Important! In winter, the rodent is covered with thicker fur, and the color changes to dark.
Torso and limbs
The weight of the rodent is on average 200 g. Some individuals grow up to 300 grams. Compared to the body, the head is large. The muzzle is pointed. It has large bulging eyes that look like peppercorns.
Important! The main feature is the size of the ears - they reach 2.2 cm in length.
What do decorative mice eat?
All animals from the Mouse family are prone to obesity, so you need to know what the decorative mouse eats. The basis of the animal's diet is cereals: barley, wheat, corn, sorghum. The grain should not be ground. Usually domestic mice are very small and eat up to 1 tsp a day. stern.


The animals' favorite treats are sunflower seeds, pumpkin seeds, caraway seeds, walnuts, peanuts and hazelnuts. Vegetables and fruits are necessary in the animal's diet. It is better if the vegetables are green: cauliflower, lettuce, cucumber, zucchini, broccoli, parsley. And the fruits are not very sweet and juicy: apple, banana, quince, pear, plum. Bread and egg whites can be given occasionally.
What mice don't eat: citrus fruits, smoked meats, meat, food for cats and dogs.
Population and status of the species


According to scientists, there are more than 60 species and subspecies of such rodents in the world. At the same time, it is quite difficult to distinguish a species from a species, if the method of gene analysis is not used.
Until now, the genome of this rodent has not been deciphered, since the genetic material is located chaotically, and the bulk of the information is located in the sex chromosomes.The number of chromosomes can be at the level of 17-64, and in females and males, their number may be different. Despite this fact, all mice in the same litter are genetic clones.
The mouse population has one unique property that is associated with the "self-transplant" of genes into the nucleus from cells (mitochondria) of other organs. Scientists have been struggling with this problem for many years to no avail, which is associated with gene transplantation in humans, while a similar process in mice has been working for millennia. Scientists explain this by the fact that mice have made a sharp evolutionary leap in the next few million years.
The size of the vole mouse population depends on the year and season, while the cycle of birth rates is about 3 - 5 years. Under favorable natural conditions, there can be up to 2 thousand individuals per hectare of territory, and in unfavorable years - only a hundred individuals.
Lemmings and muskrats, like mice, also belong to the rodent family.
What cubs, reproduction and offspring look like
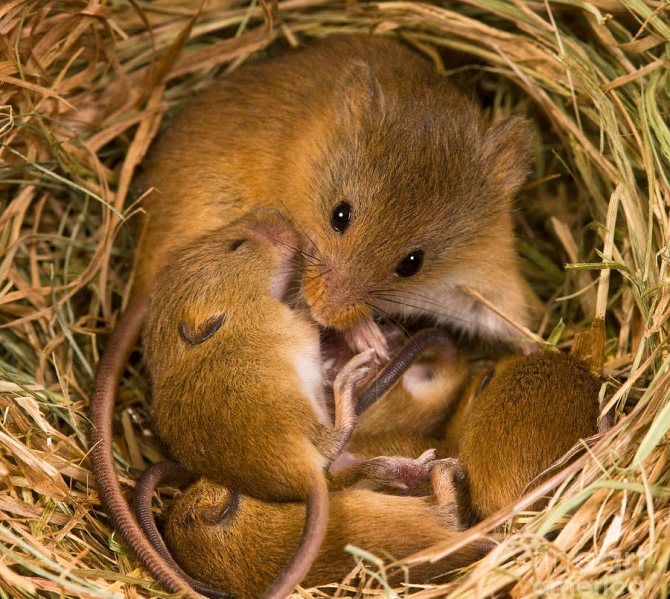
Voles are fertile animals. Females give birth to offspring up to six times a year, while up to 7 cubs can be born. They are born absolutely helpless, hairless, unable to distinguish between objects. The female takes care of the offspring - she warms it with her body, feeds it, protects it from the attack of predators who like to feast on tender little mice.
Vole pregnancy lasts about three weeks. And ten days later, the mouse is again ready for fertilization, even despite the helplessness of the newborns. Cubs reach sexual maturity in three months. But long before that, they learn the skills of finding food and defending themselves from predators.
Danger to humans
Humanity has been waging its war with rodents for a very long time, and such a struggle even managed to get a special name - deratization. Nevertheless, in the east, rats symbolize wisdom and wealth, fertility and prosperity, therefore the image of rodents in such countries is purely positive. In the western territories, such representatives of the Mouse family are treated with disgust and some apprehension. To create an extremely negative image, it was enough for people to recall several plague epidemics associated with the rat, the carrier of the pathogen.
Also, some types of rats cause colossal damage to agricultural activities. Rodents often eat crops. As a result, a wide variety of methods of struggle have now been developed and continue to be developed, including scare off and destruction. Rats are currently one of the dangerous natural reservoirs of many anthropozoonotic and zoonotic infections.
Such rodents carry the causative agents of tularemia, plague, rabies, toxoplasmosis, typhus, leptospirosis, as well as rickettsioses, sodoku and many other diseases dangerous to humans and domestic animals. Imperceptibly for people, representatives of the Mouse family are able to penetrate into the most hidden corners of the human home, using sewer and ventilation ducts for this purpose.
It is generally accepted that it is simply impossible to destroy any rodents, including rats, one hundred percent. A quarter of a century ago, the main criteria for deratization were introduced, and the optimal permissible percentage of areas freed from rodents was indicated:
- 80% - the result is satisfactory;
- 90% - the result is good;
- 95% - the result is very good.
Thus, the main goal of deratization is to establish and maintain quality indicators of the permissible level of the number of rodents, at which there will be no complaints from people.
Rodent control
The increase in the number of mice in the field threatens serious losses for agricultural workers. No less damage from rodents in the garden, in the garden. To destroy pests, poisonous baits, poison for mice, mousetrap cages are used.They fight with folk remedies, professional drugs. Indoors, ultrasonic rodent repellents, products with a pungent odor, and plant repellents are used. Preventive measures are also important.
Artworks
- Shards - uncategorized, 12/01/2018 00:16
- Isola di Vulcano - landscape lyrics, 20.08.2018 13:01
- Cold Edge - Uncategorized, 05/14/2018 01:01
- April - love lyrics, 04/09/2018 17:02
- Sintra - landscape lyrics, 27.10.2017 13:57
- Evening - love lyrics, 10/21/2017 01:28
- The past is love lyrics, 08/10/2017 17:09
- Moscow - uncategorized, 08/10/2017 16:47
- Palanga - uncategorized, 06/23/2017 17:30
- Twilight - love lyrics, 05/24/2017 01:06
- March 2020 - love lyrics, 06.03.2017 08:00
- Amateur - uncategorized, 09/01/2016 19:04
- String - love lyrics, 09/01/2016 18:40
- Again - uncategorized, 09/01/2016 09:03
- About the white horse - love lyrics, 07/27/2016 11:13
- Omnia transeout - uncategorized, 06/03/2016 12:28
- Multicolored - love lyrics, 03/20/2016 11:58
- March 1st - love lyrics, 03/01/2016 17:37
- The morning of this day - uncategorized, 02/21/2016 19:48
- To the village, grandfather. - uncategorized, 12/18/2015 12:09
- Ill - love lyrics, 06/10/2011 01:34 PM
- 495 ... - love lyrics, 09/20/2008 16:40
- Alternative antiquity - uncategorized, 06/14/2011 01:54
- New Clarissa, or I'll tell you about love ... - uncategorized, 09.12.2006 08:36
- Milk and honey - uncategorized, 12.12.2005 08:10
- Charybdis. Hexameters - love lyrics, 07.10.2005 18:27
- Song not included in the soundtrack of the Iliad - uncategorized, 01/21/2006 10:12
- A song about an inhuman competition, as an attempt to osm - uncategorized, 06/17/2006 08:04
- November. Thaw - landscape lyrics, 18.01.2006 11:24
- October. Rain. - love lyrics, 12.10.2005 13:31
- October. The sun. - love lyrics, 10/29/2005 07:19
- I don't love you, summer ... - love lyrics, 11.02.2006 11:02
- Waiting - love lyrics, 14.10.2005 08:26
- Aynurka - love lyrics, 17.10.2005 09:03
- The war is over ... - uncategorized, 11/26/2005 08:59
- Add Legend - uncategorized, 10/14/2006 09:42
- Rock - love lyrics, 11.10.2005 11:47
- Ballad about the rules of hunting for wild boars, or How widows - without a heading, 04/15/2006 08:26
- Marriage Blanchefleur, or Something about courtly love - without heading, 06/08/2006 00:23
- Ballad about Elinore of Aquitaine - love lyrics, 03.11.2005 11:34
- Ballad of Beatrix de Clermont-Beauvais, Countess de Beaumont - love lyrics, 01.10.2005 19:45
- The Ballad of the Crusade, or All Misfortunes Count - Uncategorized, 01/30/2006 10:43
- Malbrook is going on a hike ... - uncategorized, 05.12.2005 09:55
- Act 5, scene 5 - love lyrics, 24.10.2005 09:59
- Blank sheet - no heading, 07.01.2006 20:08
- Blah is love lyrics, 02/27/2006 09:40
- Mute - uncategorized, 09.09.2007 14:47
- Dialing the number ... - love lyrics, 04/01/2006 12:44
- Crimea Evening - uncategorized, 11/04/2006 08:39
- Pamponsky forest Broceliande - uncategorized, 03/21/2006 17:08
continued: 1-50
51-72
Food
The wood mouse prefers to eat nuts and acorns. The basis of the rodent's diet is plant food: grains and seeds, foliage, berries, mushrooms. But sometimes the animal arranges a hunt for small insects or can attack a clutch of bird eggs. Mouse nutrition directly depends on the season:
- During the shedding of acorns, the rodent eats them exclusively.
- During the ripening period of hazelnuts, the individual tries to go out to the trees more often and pick up the fallen fruits.
- In the absence of nutritious food, the mouse can eat mushrooms. Toadstools, fly agarics and poisonous fruiting bodies, the rodent bypasses, giving preference to russules, boletus, chanterelles and other noble mushrooms.


In winter, rodents eat the reserves. Each individual can store about 5 kg of food in the house. Among the products are berries and fruits, a large number of grains, seeds, mushrooms and even cones. In this case, the mouse stores only fresh, undamaged products that can lie in the mink until spring.
Habitat
A favorite place of residence is a deciduous forest, its sunny edges, open areas. Mice prefer to live where there is a body of water nearby - a river, a swamp, a lake. In such conditions, the wood mouse feels the best.
Burrows are built by a rodent in the ground. The deepest chambers go 2 m into the soil. The animal hibernates there. The labyrinth has several chambers for storing supplies, a nest for resting, reproduction of offspring. Occasionally, forest mice climb a tree, settle in old hollows, bird nests.
Vole family (Arvicolidae)
The muzzle of the voles is rounded, the ears are small, the eyes are also small. The main difference from mice is the length of the tail, it never exceeds half the length of the body, but more often it is shorter.Unlike mice, voles prefer not seeds, but green parts of plants, and thus they are not competitors to each other and are found simultaneously in the same places. The most common in our country are the meadow vole (Microtus laevis) and the field vole (Microtus arvalis). In winter, they often settle in haystacks and can breed there. They are pests of crops, seedlings of tree crops, in winter they damage young trees and shrubs. Sometimes they make stocks of fodder from grain and succulent roots of plants, harm the underground parts of flowers - they destroy bulbs and rhizomes. Voles, like mice, dig holes. Only in mice, at one of the entrances to the burrow, there is a mound of soil discharges from one side, and in voles, the entrances to the burrow are without mounds.
What does a vole mouse eat
The rodent does not deny itself food and shows not weak gluttony: in a day it can eat as much as it weighs, which in one season is equivalent to about 10 kilograms of food. In addition, they store food for the winter, storing it in special compartments of their home, but this instinct is much less pronounced in them than, for example, in wood mice.
If we talk about what the vole mouse eats, then it is mainly plant foods: nuts, berries, grains and herbs. The peculiarity of their diet is that, unlike many other representatives of the mouse family, they prefer green parts of plants, while most of their relatives are greedy for seeds and grains. This helps voles and other members of the rodent squad to live peacefully on the same territory. Various larvae and small insects are often found in their diet.
Eating plants, mice do not disdain either roots or flower bulbs, which often leads to serious negative consequences for the garden.
There are many popular signs based on the behavior of rodents. One of them says that if winter is coming, then the mice will run from the fields. Indeed, with the onset of cold weather, when the search for food becomes a difficult task, these rodents leave the inhabited meadows, settling in food, grain warehouses and in cellars, thereby significantly undermining production and bringing irreparable damage with them. Due to this behavior of the vole mouse, many are thinking how to get rid of these pests. And if you add to this the spread of various infections, then few people will be delighted with such a neighborhood.
Origin of the species and description
Photo: Water Rat
The water rat or water vole (Arvicola amphibius) is a small mammal that belongs to the order of rodents, the vole family. The genus Water voles includes only one species, Water voles.
Rodents are very ancient and extremely widespread animals. Rodents inhabited our planet during the Cretaceous period. The oldest rodent fossils are attributed to the Pleocene period, while animals inhabited the territory of modern America. Over time, the appearance of animals has undergone changes, animals have successfully adapted to environmental changes, and at the moment only in our country there are 11 families of the order of rodents.
Video: Water Rat
The vole family includes 15 genera. Most species of the vole family are small rodents with a small snout, small ears, short paws and a tail. There are strong teeth in the mouth, with which they are able to gnaw through rather hard wood. The coat of most rodents is short, the water rat is long and thick. The Water Rat has an especially long tail, which is slightly flattened from the sides; there are no membranes on the toes of its hind legs. Water rats differ from other rats by small, almost non-protruding auricles, differ from gray voles in large size, and differ from muskrat in tail shape.
Palevaceae are one of the most numerous groups of rodents that can easily tolerate the harsh environmental conditions and eat poorly nutritious food, such as greens, bark and roots of trees and shrubs, grains. Water rats settle near water bodies, but they can also live in the field next to the water body and in the forest. Animals of this species are active around the clock, living in burrows. They do not hibernate.
conclusions
Mice are animals that are pests. They are able to destroy crops, damage garden trees and other plants. Large populations of rodents can eat the seeds of deciduous trees, eventually leading to environmental problems. In addition, rodents are carriers of dangerous diseases.
A person who is bitten by a forest mouse may be at risk of contracting the following infections:
- tularemia;
- erysipelas;
- paratyphoid, etc.
Rodents pose a danger to people and nature, but their complete destruction is strictly prohibited. Mice are the basis of the diet of snakes, foxes and birds of prey. With a lack of rodents, predatory animals can die of hunger, which will also lead to an environmental disaster. Therefore, a balance must be maintained in nature.
Identifying holes from a vole: the difference from a mole
Since voles are not the only pests responsible for stripes on the grass, they are often confused with moles. Since both are rare, it makes sense to distinguish them according to the characteristics that are left, and not on how they look. You may never come face to face with these secretive furry foes.
Moles do two types of destruction. One goes just below the surface. These are tunnels that look like elevated ridges running across the lawn. The second type goes deeper and allows moles to connect tunnels into networks. This is the land, folded into mounds, reminiscent of small volcanoes.
These mounds are a sign that the problem is not with mice, but with moles. Voles do not leave embankments at all.
You may have made a positive identification of the culprit: you have voles. Or, they are not, but want to know how to save it. Prevention trumps pest control. When taking preventive measures, stick to natural methods that are good for both your health and the environment. Natural control will save you money as you don't have to buy expensive products.
Voles can penetrate into the root system of shrubs, trees, they die off or begin to bend over. These rodent pests gnaw the trunk of the tree, the base of the bush.
In addition, voles damage the roots of perennial plants such as hosta, spring bulbs, root crops, and potatoes. However, they prefer to eat stems, blades of grass. The streaks that are left in the process make the lawn unsightly.
Mouse family (Muridae)
This family includes mice and rats. Their muzzle is pointed, the eyes are rather large, the ears are large, the tail is long, its length is at least 70% of the body length. The size of mice ranges from 7-13 cm. All mice are granivorous, feed on seeds of cultivated and wild cereals, and additionally use underground parts of plants and insects for food. The most harmful to humans are field mice, house mice, forest mice, yellow-breasted mice.
The field mouse (Apodemus agrarius) differs from its relatives by a dark dorsal stripe, the upper body is brownish-red, the abdomen is white, and does not make any reserves. The house mouse (Mus musculus) has a dark gray, gray-brown upper coloration, a gray abdomen with a yellowish tinge. The color of the abdomen differs well from forest mice. In addition, the house mouse has a well-developed musky gland, which is why it emits a strong "mouse" smell. Makes supplies for the winter, lives both indoors and out.Small mice (a group of closely related sibling species, of which the most common Ural mouse (Sylvaemus uralensis) is reddish-brown in color, the abdomen is white, some have a noticeably small yellow spot between the forepaws. Perhaps the largest of the mice is the yellow-chested mouse (Sylvaemus tauricus). It is similar to wood mice, but larger in size, and the spot between the legs is large, well pronounced. This mouse can settle in hollows, climbs trees perfectly, makes reserves for the winter from seeds of tree crops, on occasion can attack small congeners and eat them.Other species of mice are found in summer cottages much less often.All mice are twilight and nocturnal and are serious pests of fields, vegetable gardens and stocks made by us.
Sabotage
Field mice, if left unchecked, wreak havoc on agriculture. At the same time, they not only eat up the harvest, but also dig holes, moreover, numerous, damaging the root system of various crops.
With the arrival of winter, if the mice made their way into the warehouse, which is not a big deal, then they can destroy up to a third of the stocks. At the same time, they contaminate food products with urine and faeces, making them unfit for human consumption.
It's important to know! The vole mouse does not bite and at the first danger it tries to quickly hide in its shelter. But if the animal is driven into a corner, then it will definitely defend itself. At the same time, it must be remembered that rodents are capable of infecting a person with viruses, bacteria and infections, as well as serious ailments.
Types of mice. Mouse: an overview of species, nutrition and life, the way of life of mice (93 photos)
Scientists were able to identify a lot of different rodents, they live in different parts of the planet. They are absent only on the coldest continents, but they live on the rest.


Among them, the favorites of people in the person of hamsters stand out, since they are often found at home, although they live freely in nature, as well as rats, which are also often pets or living in people's homes without their permission, voles and ordinary mice.
The latter are especially disliked by people, since they often destroy winter supplies and are considered dangerous carriers of diseases.


Usually, people have difficulty distinguishing between rodents and can not always tell exactly who is in front of them. But for mice, this is not surprising, since there are about 400 different species among them.
Outwardly, they are all very similar, and behave almost identical. The animal mouse is famous for its incredible cunning and it is difficult to catch it. For centuries, people have been fighting, first of all, with this representative of rodents.


What are the external features of the mouse?
Nowadays, many photos of mice have been taken, and it is easy to find them on the net. Due to this, it is possible to accurately determine which species the mouse that appeared on the territory of a person belongs to.
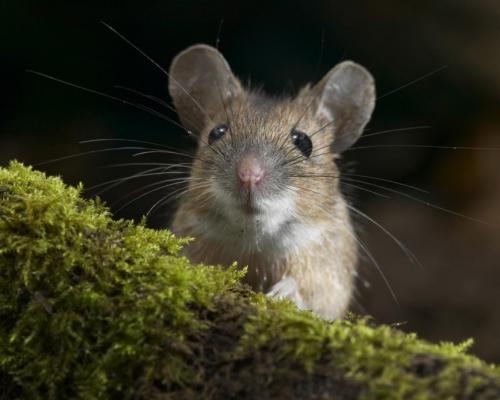


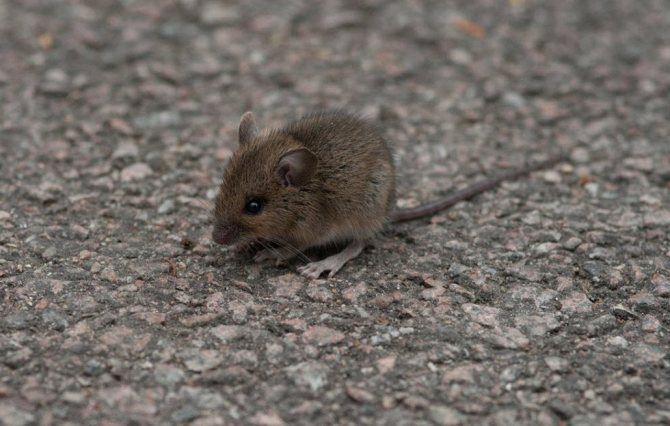
Usually her body does not exceed 10 cm, moreover, the tail is about half the size. This small process is always naked, it is difficult to detect the presence of hairs on it. At the same time, the body is completely covered with hair of a uniform color.


Mice are brown, sometimes brown, and gray individuals are often found. Scientists have found mice with stripes running along their backs.
However, there are two unique species with needles that replace wool. We are talking about Elliot's mouse and the so-called needle-like form. The hair of these strange creatures is replaced by needles that look like thorns, like a cactus.


What are the features of a needle mouse?
The types of mice are very diverse, however, this mouse stands out among them, because, in addition to the unique coating, it has almost no neck, and its legs, although they are short in size, have fingers that help to hold on to various surfaces.


How do mice differ from other rodents?
In a detailed description of mice, it is important to note that they have excellent hearing, allowing them to pick up sounds of different tonalities.To do this, they use rounded ears.


On a small, pointed muzzle, you can notice the presence of antennae, called vibrissae
Due to this important organ, mice are able to orient themselves perfectly, even when they are in the dark. However, they do not have pouches behind their cheeks.
Most species of mice do not like to climb trees, however, they move easily based on the stems of grass growing in meadows. And also for this they use reeds or small branches of shrubs.


Among them, the smallest individual was identified, it received the name - baby, since it has a body size of only 5 cm.


Where do different types of mice live?
Due to the characteristics of the organism, this animal was able to take root in any place. In most cases, they use the surface of the earth for life, however, some species have good skills in moving on vertical surfaces.


Where do mice live and how can a person meet them? Usually, people most often meet with two species of these rodents, since only the Cairo or house mouse lives near human buildings.
Some mice like to live near various bodies of water, and they swim tolerably well. They do not like to have couples and usually live alone.


However, a subspecies of the house mouse, called the kurganchik mouse, loves to start a family of up to 20 individuals living in a common burrow. They are engaged in the creation of general reserves for wintering and build nests necessary for life.


Most mice like to live in a permanent place. They leave the inhabited area only if necessary due to some environmental changes. However, they usually do not move far, since they have no desire to look for a new place to live for a long time.


Prevention measures
To prevent voles from visiting the farm or summer cottage again, a number of preventive measures must be taken. These include:
- keeping the site clean (to prevent the accumulation of food and vegetable waste, old furniture and rubbish);
- periodically loosen the soil in the garden (such actions destroy the homes of voles);
- keep a cat or dog on the site (animals will scare away intruders).
Some summer residents constantly spread poison in basements and sheds, and also use adhesives to prevent rodent infestations.
It is important to carry out a set of preventive actions, then field mice will not be interested in such an economy.
Amusing clever animals and at the same time malicious "gnaws" of everything and everyone. They are often undeservedly confused with their closest sisters - house mice. However, the inhabitants of free fields bring no less anxiety and harm to agriculture and households. Animals loved by cats and not loved by females and farmers are part of the natural diversity.
The world is big enough for all species, you just need to coexist intelligently. Let's find out more about the field mouse, its habits, possible danger and methods of struggle.
What harm do parasitic animals do to humans?
The vole mouse is the most dangerous pest that damages vegetation, harvested crops and agriculture in general. Field mice live in granaries, like to settle in barns, penetrate cellars, occupy summer cottages, where they destroy everything that is planted in the garden.
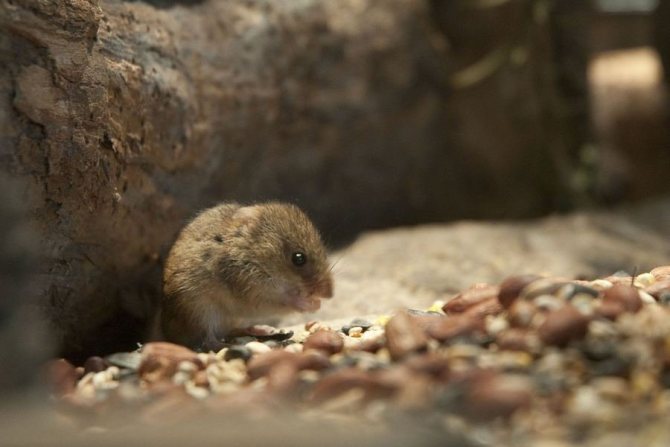


The rodent is able to destroy all the stocks stored in the cellar. With the arrival of spring, pests feed on early shoots, the bark of reviving trees, which causes irreparable damage to vegetation. These are serious arguments to wage an implacable and tough war on mice. You need to exterminate the rodents before they breed and eat everything that you grow.
Field mouse in the house. Harvest mouse. Signs of appearance and methods of struggle
Reviewed by:
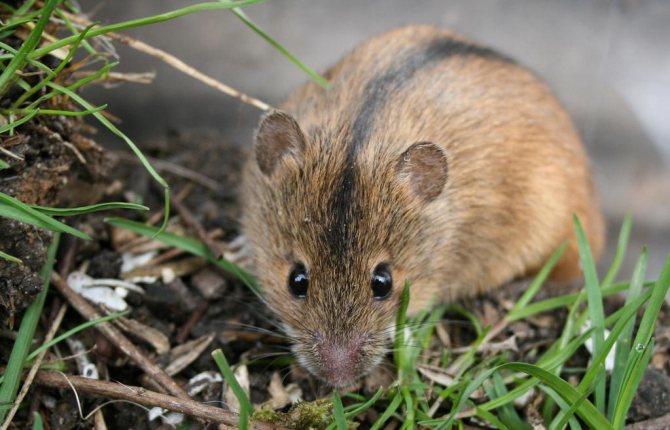
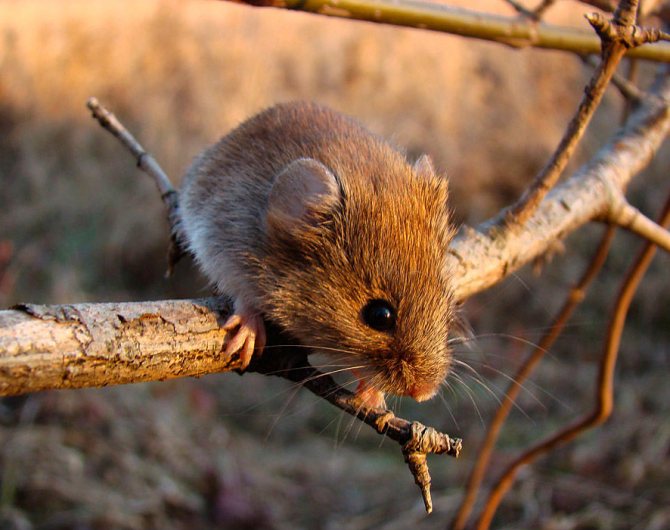
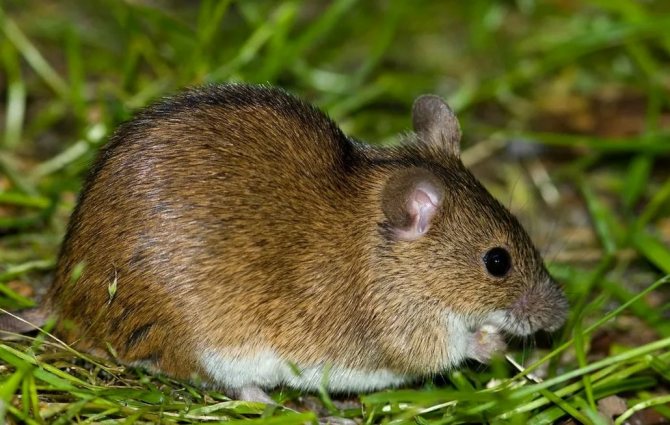
If you are the owner of a summer cottage, then you can hardly avoid getting to know the vole mouse.The vole is a small rodent, the body length of which does not exceed 12 cm. The weight of this mouse reaches 30 grams. The rodent has a rather long tail, covered with scales with sparse hairs. The vole skin has a reddish-brown tint, and the white color predominates on the abdomen. As a rule, a dark stripe runs along the spine.
The main difference between the field mouse and the house mouse is the more modest size of the vole, as well as the shorter tail and coat color.
The field mouse is very careful and swift, as soon as it senses danger, it immediately hides for cover. Moreover, this species is nocturnal - the animals rest during the day, and are active at night.
This rodent lives almost everywhere, with the exception of the northern regions. At their summer cottage, mice choose places with tall grass. In the summer, mice build their nests in the grass and bushes and raise their offspring. In winter, rodents move to houses, where they can spend the winter warm.
Signs of vole appearance
Basically, the appearance of rodents can be detected by burrows and traces of their vital activity. Also, mice leave traces of their teeth everywhere. Like most rodents, teeth


voles grow throughout life, so mice have a constant need to gnaw on something. Voles can cause huge damage to the garden, as they destroy the roots of shrubs and trees, and flower bulbs are not neglected. In just one day, an animal can eat various foods as much as it weighs itself. Such gluttony is fraught with the death of trees and shrubs in the garden. In addition, voles love to store food, for this purpose special "storage rooms" are equipped in their burrows. Thus, one individual is able to eat up to 10 kg of feed per season.
Another problem is the high fertility of rodents. For a year, a female can bring up to 4 offspring, up to 8 mice at a time. Little mice reach sexual maturity by two months. The life span of a field mouse can reach up to 7 years, but in the wild, mice usually live for a year or two. Now imagine how fast rodents can breed in just one summer season full of warmth and abundance of food.
In winter, voles do not hibernate, so in search of food they go to human housing or gnaw the bark on the bottom of trees and shrubs.
As you already understood, field mice are not at all harmless and can cause great damage to the garden and crops. Therefore, it is worth starting the fight against mice as early as possible, as soon as you notice their appearance on your territory. Otherwise, you may face a real invasion of rodents, which will not be so easy to drive away.
How to get rid of a field mouse


For a start, it is better to turn to more humane methods of struggle, simply scare away and drive away uninvited guests. Mice have a good sense of smell, so there are odors that mice do not like. For these purposes, you can use plants such as:
- Garlic,
- Imperial hazel grouse,
- Blackroot,
- Elderberry id.
To drive away rodents, it is enough to make an infusion of garlic or hazel grouse and pour it directly into the hole. For the same purposes, you can use thuja or elderberry twigs, cloves of garlic and other plants with a strong odor.
There are also chemicals that are unpleasant for voles. These include ammonia or kerosene. A cotton wool soaked in a chemical is placed in a burrow, and the vole will leave its home forever.
Scientists have found that rodents are frightened by vibrations and shaking of the soil. This property can be used. To make a repeller, it is enough to dig in wooden pegs next to the holes and hang cans on them. In windy weather, the cans will emit sound and vibration, which will surely scare the mice away.


Manufacturers also offer ultrasonic scarers, which you can purchase in a specialized store.It is worth considering when choosing this device where you will use it. If you need to drive off the voles on the site, then you should choose a device that works on batteries, and not from the network. If voles run into a shed or other room up to 200 m2, the budget Tornado-200 is suitable for eliminating them. There is nothing superfluous in it - only the constantly jumping frequency of ultrasound. It is these races that confuse the voles, forcing them to run away.
The above methods are absolutely safe for human health and your pets. But if you can't cope with voles, you should resort to "heavy artillery".
How to get rid of pests?
Rodent infestations are a problem for the farmer. Noticing the tricks of field mice in his area or in the basement, a person tries to get rid of uninvited guests as quickly as possible. For these purposes, you can use:
- physical methods of struggle (traps, mouse traps, scarers);
- chemical agents (poisons, poison, aerosols);
- folk recipes (essential oils, herbs, building mixtures);
- preventive actions.
Use of scarers
One of the newest measures to combat voles are scarers, which are compact and humane (mice do not die, but simply leave the room). The repeller is powered by an electrical outlet. According to the principle of operation, these devices are:
- ultrasonic (affect the rodent population with high-frequency sound more than 20,000 Hz);
- electromagnetic (devices of this type create magnetic resonance impulses that spread along all the walls of the room and scare away pests);
- combined (combine the functions of ultrasonic and electromagnetic scarers).
A very simple design can be used as homemade scarers. In the area where voles are found, you need to bury a stick. At its end, you should put on an empty tin can, which will create a loud clang when exposed to the wind. Any noise frightens the voles, and they leave their homes.
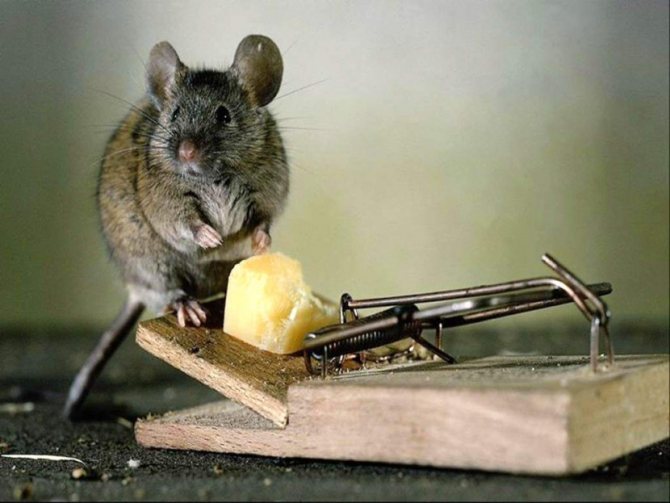
Using mousetraps
The most common way to control voles is using mousetraps. The mechanism of the device is triggered as soon as the mouse begins to feast on the bait. You can use pieces of bacon, sausage, cheese, or white bread as bait. Mousetraps are:
- metal;
- wooden;
- plastic.
Many farmers come up with homemade mouse traps that are quite effective in action. For these purposes, you can use inexpensive improvised means.
Especially popular are plastic bottles that are installed at an angle. At the bottom of such a trap, you need to pour some vegetable oil. Rodents are attracted by the attractive appetizing smell of seeds. They climb inside, but they are not able to get out back because of the slippery surface.
Farmers often use special adhesives as mousetraps. Such a tool is applied to a piece of cardboard and placed in a place where mice live. Pests simply stick to the trap.
Use of chemicals and poisons
Using all kinds of poison baits against mice remains a fairly popular way of dealing with them. This method also has its drawbacks:
- require careful use, as pets and especially children may be injured;
- backfire in the form of fetid remains that can be found everywhere.
Poisons are best laid out at the end of winter, when the rodents are hungry and eat everything. Their action is most effective when placed directly into the burrows of mice.
One of the most effective methods of getting rid of mice is the use of kerosene or ammonia. A small piece of bandage or cotton wool soaked in any of these chemicals is placed in the animal's burrow. The strong smell will drive the vole away forever.
Folk remedies
Since ancient times, people have used folk recipes in the fight against rodents.It is believed that tincture from plants with a strong odor (elderberry, garlic, hazel grouse) can save from the invasion of pests. The prepared liquid must be poured directly into the rodent's burrow.
You can stock up on aromatic herbs (wormwood, tansy, mint, wild rosemary) in the summer and dry them. Grass tied in bunches is laid out around the perimeter of the room. The pungent smell repels pests. Essential oils of citrus, conifers, tansy and mint are also used to drive mice out of minks. The principle of operation is the same: a piece of cloth soaked in essential oil is laid in the rodent's dwelling.
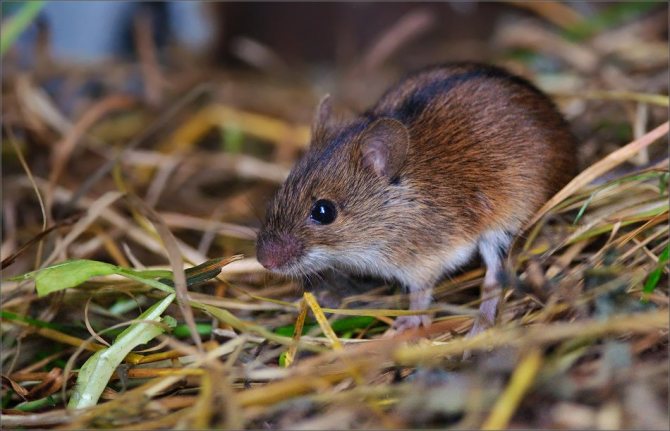
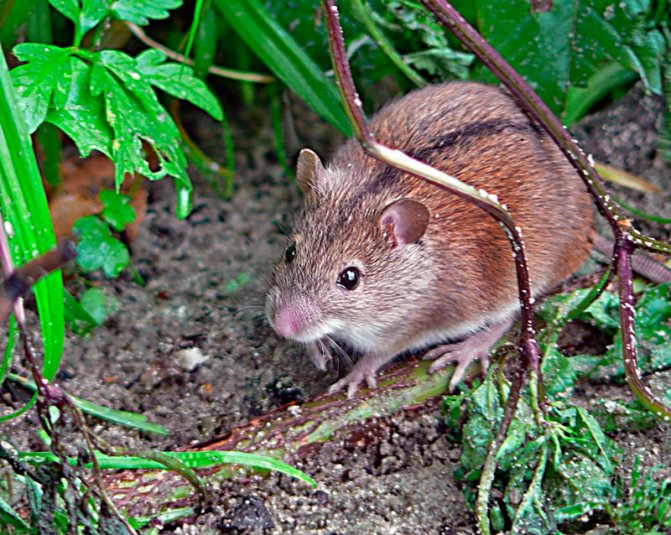
Meet the field mice
Most of the owners of summer cottages and private houses had to deal with field mice on the plots. These are small rodents, the body length of which does not exceed 12 cm, and the weight is 31 grams. A rather long tail is covered with sparse hairs and scales. The coat of the vole on the body is soft, velvety, on the back - reddish-brown, on the abdomen - whitish. A strip of dark color runs along the back. The vole differs from the common gray mouse in smaller size, coloration and a shorter tail. These rodents are widespread almost everywhere, except for the coldest northern regions. The animal moves quickly and silently. When a danger is detected, it quickly runs away and hides, it is not easy to see the mouse. Moreover, during the daytime they usually rest in their burrows, and they are active at night. They are quick-witted, cautious and resourceful creatures. The appearance of rodents is usually detected by burrows and traces of their presence (damaged plants and domestic food supplies). A vole's teeth grow throughout its life, and the animal has to constantly grind them down. These mice eat roots, tubers and bulbs of plants, seeds of various crops. In winter, they do not go into hibernation, but continue to feed actively, so they can gnaw the bark in the lower part of shrubs and trees.
During the day, the animal eats various foods as much as it weighs itself. In addition, in their holes, the voles arrange special storage chambers, where they store food for the winter. During the season, only one animal eats about 10 kg (up to 7 kg of green mass and 3 kg of grain).
Voles reproduce quickly. They reach sexual maturity at the age of two months. During the year, the female brings offspring 3-4 times, in each of which there are from 4 to 8 mice. After two weeks, young mice are already able to live independently.
Voles can live up to 5-7 years, but they have a lot of natural enemies, so the average life expectancy is about 1.5 years. In the summer, they usually live outside. If in the vicinity there are human housing or outbuildings, then with the onset of cold weather these rodents tend to penetrate into rooms where it is not only warm, but also usually has something to profit from. It should be noted that mice show considerable ingenuity and ingenuity to achieve these goals.


Reproduction
Sexual maturity in representatives of this species occurs at the age of 2.5 months, usually at 75 days of age. The mating season in most regions lasts from early spring to late autumn, usually from April to September. During this time, the female manages to bring offspring 2-5 times, depending on weather conditions and the availability of food.
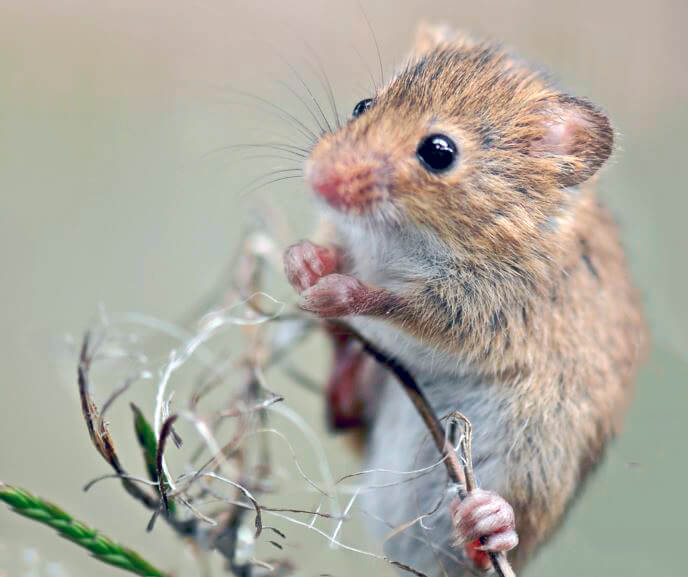


Males and females meet only for mating, leading a solitary lifestyle. The fathers are not interested in the fate of their offspring.
Pregnancy lasts 22-23 days. In one litter, on average, there are 3-6 mice. After birth, they weigh only about 2 g. They are born blind and naked in the mother's nest, which is located in an underground burrow.
The eyes of babies open at the beginning of the third week, and by the end of it, milk feeding has already stopped. After a few days, the mice become completely independent and go in search of their own home plot.
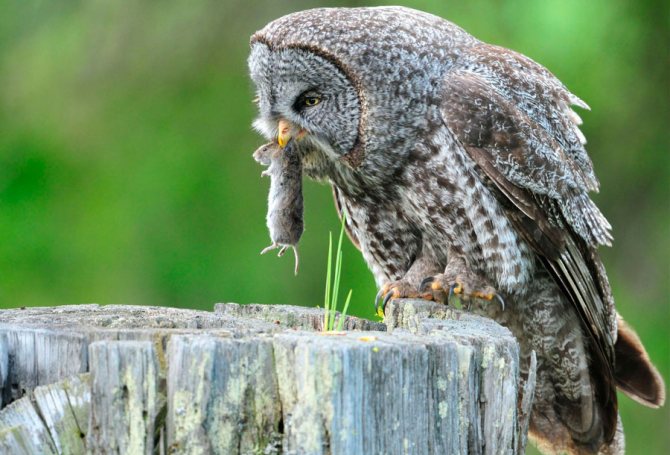
Field mice play an important role in the ecosystem, being the main food for many predators, in particular for wolves and.
The nature and lifestyle of the vole
Interestingly, little pests do not like being alone. They live in large colonies in shallow burrows. Most of all, mice are afraid of such predators as ferret, fox, owl and marten. In their homes, the cat becomes their main enemy.


In the photo, the mouse is a red vole
Rodents prepare in advance for cold weather. Field mice do not hibernate and lead an active lifestyle all year round. In winter, voles feed on supplies from their pantries. It can be seeds, grains, nuts. Most often, the animals do not have enough of their own preparations, which is why they run to people's houses.
However, they do not always get into the house by accident. Sometimes rodents are kept as decorative pets. The animal vole can live in a small cage with a metal trellis filled with sawdust.
There are usually 2-3 females per male. In winter, mice are recommended to be transferred to larger cages and left in unheated rooms.
Experts recommend that the animal be shown to the veterinarian from time to time; field mice are often carriers of infectious diseases (including tularemia and hemorrhagic fever).


In the photo there is a bank vole
Also, these rodents are used for scientific purposes. Biological and medical experiments are most often carried out on the bank and steppe voles. If in the apartment the mice are bred "illegally", it is worth contacting the sanitary and epidemiological station. Voles reproduce very actively and can significantly damage property.
Interesting facts about mice
- Mice don't like cheese at all. Rather, animals will prefer whole grains or seeds. A favorite treat for these little rodents is smoked bacon. It is he who is often used as bait in a mousetrap.
- Just one year - that's how long a male marsupial mouse lives. For reproduction of these animals, nature took only 2 weeks. After mating, which lasts 10-13 hours, the male dies to give birth to his babies.
- Smell is of great importance in communication between mice. With the help of "odorous" marks (from feces, urine, secretions from the glands), rodents delimit the territory, orient themselves in space, transmit information to each other. Each mouse family has its own unique smell, which speaks of the animal's genetic makeup.
- A cheerful, goggle-eyed mouse, a restless baby - the invariable heroine of the modern multimedia world. Fun tablet and phone games offer to catch the mouse on the screen; for a domestic cat it can become a real drug, and for its owner it can be a reason to laugh heartily.
Mice are the smallest rodents on the planet, bringing both benefits and harm to people. They spoil crop supplies and are carriers of dangerous infections. But the use of mice in scientific research helps save lives.