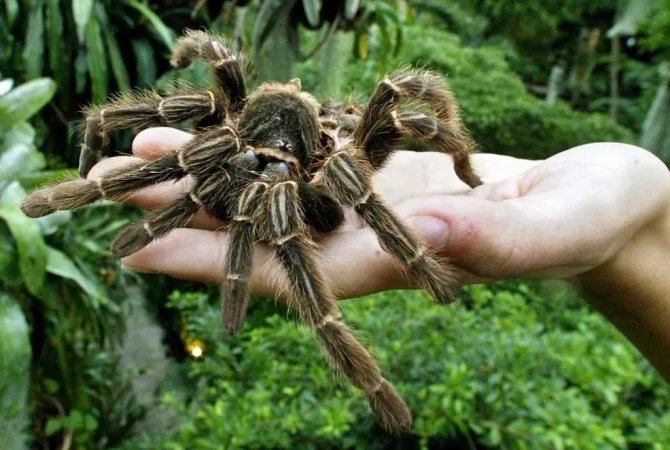
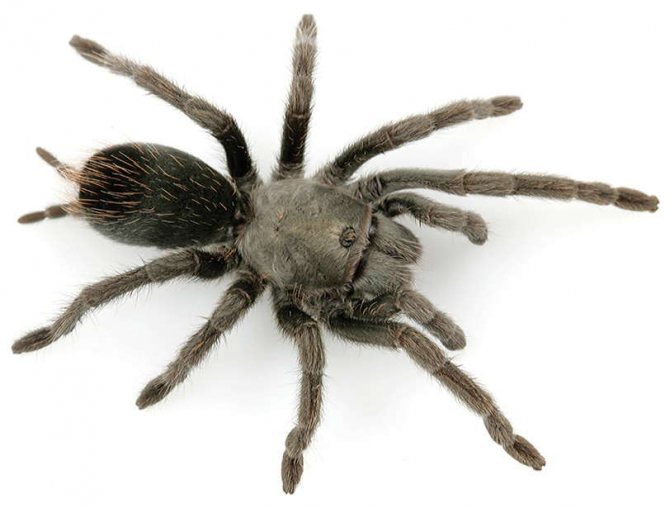
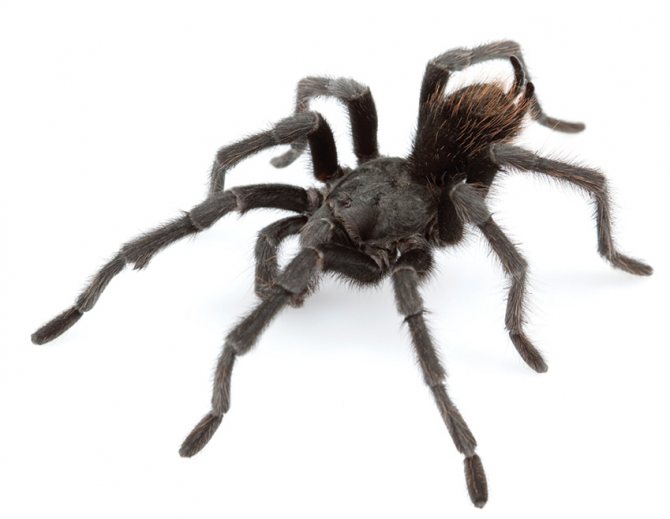
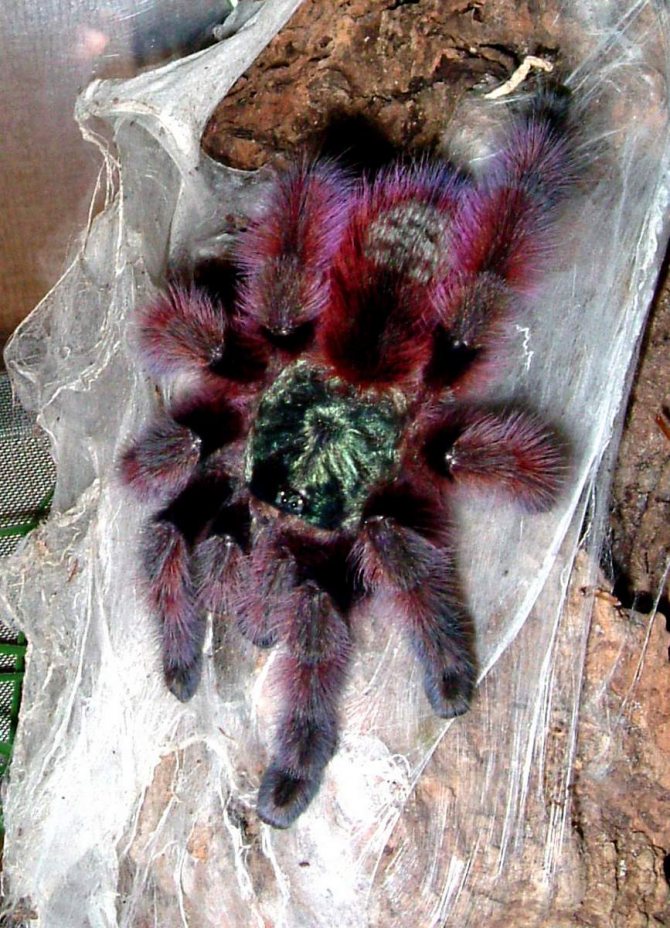
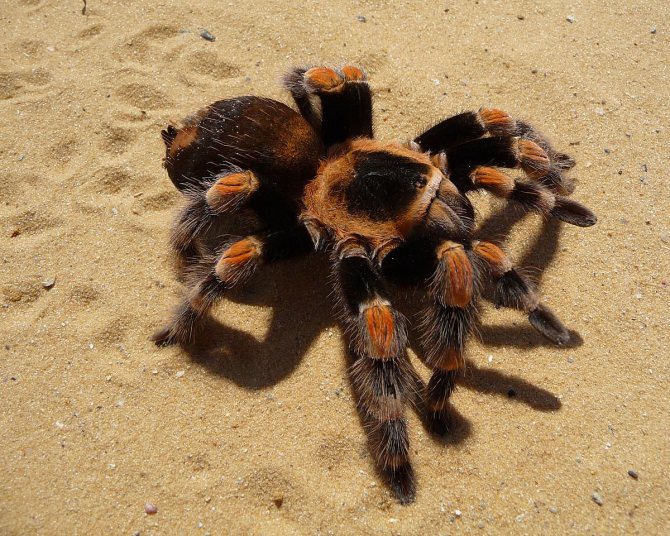
The tarantula spider is a large arthropod animal that lovers of exoticism increasingly start at home. The actual question arises as to why the spider is so called. The tarantula got its name at the end of the 18th century, when a team of scientists discovered a large spider in the tropical forests of Venezuela that was eating a hummingbird.
Then, under the impression of what had happened, Maria Merian, a member of the expedition, depicted this situation on paper. Soon the sketch hit the pages of newspapers, the animals gained popularity and the corresponding name.
Classification and habitat
Tarantula spiders belong to the family of obligate infraorder migalomorphic predators. Their main difference - in the structural features of the oral appendages and sizes - is much larger than other spiders.
Primary animals prefer to live in places with a warm climate. They are found throughout the United States, Mexico. Distributed in Africa, in most of Asia, throughout Australia. In Europe, they are seen infrequently, mainly in Portugal, the Kingdom of Spain, Turkey, southern Italy, and Cyprus.
Some species prefer an equatorial climate, others prefer deserted steppes. Natural habitat includes grasslands, tropical and common forests, shrubs, mountains.
Interesting facts about tarantulas
Although tarantulas inspire fear in many people, they are still peace-loving creatures. You can find the largest of them, the size of which is not less than an average plate.
The directors instilled fear in people to a greater extent with their horror films with tarantulas in the lead role. So named spiders were in honor of the city in Italy Tarento. There were many of these creatures. A variety of diseases have been attributed to their bites. Experts recommended that a spider bite be smeared with its own blood, which contains an antidote.
Behavior in the wild
Arthropods hunt for prey in trees, on the ground, in burrows. They are capable of producing a protein-crystalline substance and weaving a cobweb. But more often predators look for the prey and attack it. With a web, they strengthen burrows, nests and provide faster ascent and descent along it into the dwelling.
Behavior can change throughout life. Larvae spend most of their time in burrows; adults are busy looking for food and consuming it on the surface.
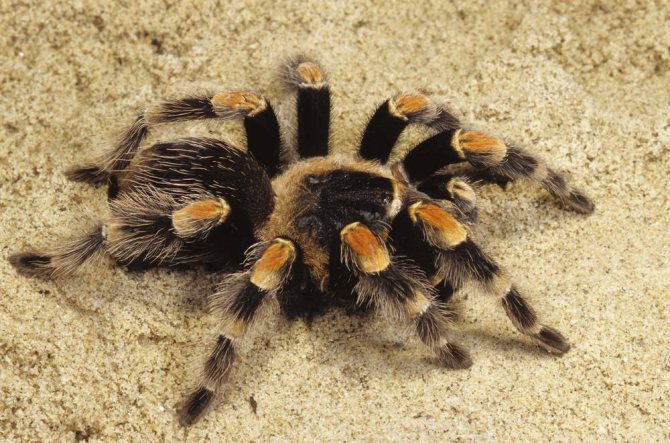

Tarantulas have natural enemies. The hawk wasps paralyze the arthropod, then drag it into their hole. The insect lays eggs in the victim's belly and seals them. The hatched larvae feed on the remains of the spider. The representative of migalomorphs is attacked by predatory scolopendra, scorpions, spiders of the genus Lycosidae.
Cerbal arabian
This arthropod species lives in Israel and Jordan. The individual was discovered relatively recently - in 2003.
Its size ranges from 20 to 25 cm. The color of the spider is adapted to the shade of sand, among which it spends most of its time. It attacks the victim only at night, during the day it hides among small stones.
It lives mainly on the territory of Arabia, which is where its name came from - the Arabian Cerbalus. For humans, it is completely safe, therefore it is often found at home.
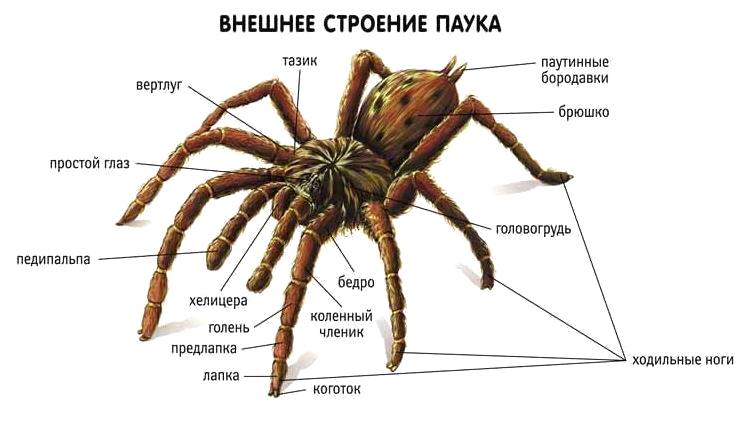
Body size and structure
In the imaginations of children who first heard the name of an arthropod, different images are drawn in their heads.To confirm or refute fantasies, you should tell what a tarantula spider looks like.
The primorsome is large, up to 4 inches long. Some large species weigh more than 85 g. The largest representative is Heteropoda maxima, weighs 170 g and has a leg span of up to 30 cm. It was entered in the Guinness Book of Records. Males are longer and females have larger girth.
Arthropods are invertebrates. Instead of an internal skeleton, they have an external skeleton called an exoskeleton. The body consists of two sections: the cephalothorax (prosoma), the abdomen (abdomen).
Head
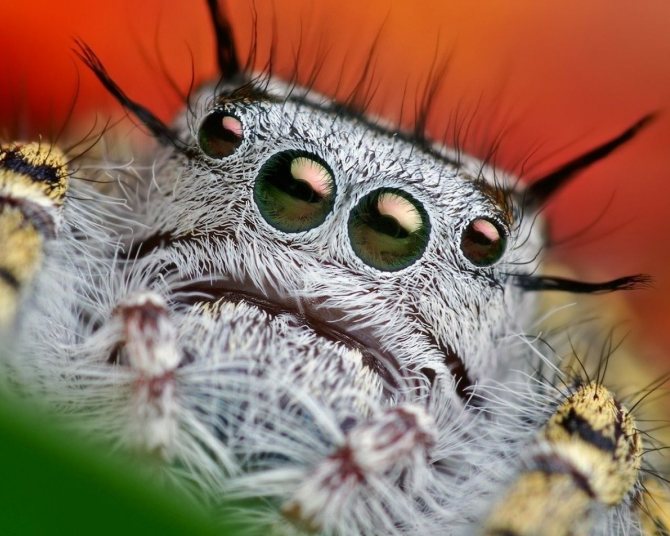
Prosoma is an important part of the body of an arthropod. It contains the medulla and muscles, which are responsible for the motor function and the muscles that control the chelicerae and the sucking stomach. Almost all parts of the body are attached to the head.
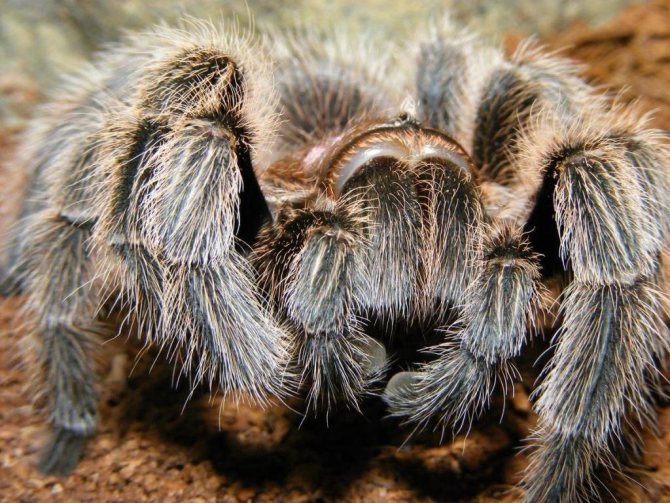


There are 8 simple eyes on the dais. They are small, poorly developed. In arboreal inhabitants, vision is better developed than in terrestrial ones. Two-segment processes (chelicera) are located between the visual organs and the mouth. They contain venom glands that exit through the canines. Through them, the toxin enters the victim or animal when the spider begins to bite - during defense, attack.
A representative of the infraorder migalomorphic has four pairs of legs and two additional pairs of appendages. Each leg consists of segments and ends with three claws. They are used to grip the climbing surface.
Abdomen
The opistosome contains various organs responsible for digestion, excretory function, and reproduction.
At the base of the abdomen, in the lower part, there is an epiginal platform, separated by an epigastric groove located between the first pair of stigmas. At the end of the abdomen are two small arachnoid appendages (spinnerettes). The anus is located even lower.
Cervical part
The internal organs are enclosed in an exoskeleton.
In arthropods, exogenous digestion. Bird-eaters are the only spiders capable of chewing food. The stomach is a tube that runs the entire length of the prosoma. Through the sucking stomach, food enters the true stomach. Digestion is completed in the intestines, with the help of the malpighian tubules. Nutrients are accumulated in the scratch pocket. Unprocessed particles come out in the form of white and dark excrement.
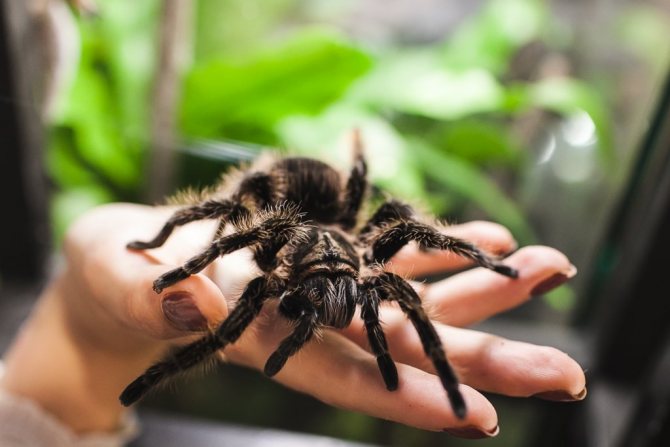


Spider size
Theraphosidae range in size from as small as a fingernail to as large as a dinner plate when the legs are fully extended. Depending on the species, the length ranges from 2.5 to 10 cm, with a leg span of 8-30 cm. The parameter is determined by measuring from the tip of the hind leg to the tip of the front leg on the opposite side.
Reproduction


The sex of the tarantula spider is easy to determine if you follow the recommendations of experts. Young spiders begin to shed after about a month. After molting, the skin is taken and carefully examined. In the posterior region of females there is a depression, while males have something like two tubercles. If individuals are adults, then sex can be determined by appearance. In males, the legs are somewhat slimmer, and they are higher, while the body is much smaller in size than the body of the female.
After mating, eggs develop inside the female for 2 months. During this period, she must form a special cocoon. At a time, she can lay up to 500 pieces of eggs, while about 50 spiders remain alive. In order for the juveniles to develop actively, the cocoon moves to a separate terrarium, while creating certain temperature conditions.
For the first month, baby spiders do not eat anything until the first molt. Until this moment, they can be together, after which they are deposited one by one. The female tarantula spider molts up to 12 times during its entire life period. Males stop shedding immediately after puberty.
Interesting to know! The tarantula spider is constantly growing and maturing, which is why it needs to shed its "old clothes". Before molting, individuals turn onto their backs, trying to remove old skin from themselves. At the same time, he completely stops eating.After molting, the spider gets a new color, and the pile is completely renewed.
Varieties
In 1802, Charles Valkener separated the migalomorph spiders into a separate infraorder. Despite this, their numbers are large. All are poisonous, but to varying degrees. The World Spider Directory includes about 143 Theraphosidae species from all over the planet. In Russia, animals are found only as exotic pets or in zoos.
The most famous types of tarantula spiders:
- Acanthoscuria brocklehursti;
- Brachypelma
- Caribena;
- Caratogyrus darlingi;
- Grammostola rosea.
Brazilian black and white
Acanthoscuria brocklehursti inhabits most of Costa Rica and is distributed in Central and South America. They live in semi-arid shrubs, deep burrows. Underground dwellings protect from the scorching sun, maintaining normal temperature and humidity.
Arthropods reach sizes of 10-13 cm, with legs up to 18-22 cm. Color - from dark brown to black. The limbs are painted with white stripes at the transition points of the segments.
Females live up to 20 years. The age of the male is shorter - about five years. The diet consists of a variety of insects. In the wild, they feed on grasshoppers, praying mantises.
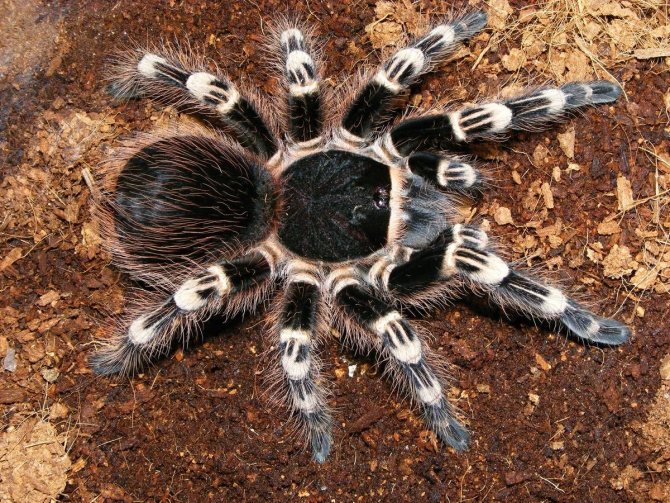


Brachypelma Smith
It should be said right away that the representatives of Brachypelma are proposed to be included in the Red Book. Trade in them is regulated by the Convention on the Movement of Endangered Species.
Brachipelma is found in Mexico, Central America. They are known for their large size, colorfulness, and docility in captivity. In length they reach 4.5-6 cm, with legs up to 7 cm. Females are larger than males.
The leg segments close to the body are black, and the patella, tibia, and metatarsal bones are red or bright orange. They live in burrows in the form of dividing tunnels. In one part, the arthropod rests, in the other it eats. Animals wait for prey that passes by the hole, carry it inside, where they eat it.
Brachypelma Smith - long-lived, the maximum life expectancy in captivity was recorded at the Berlin Zoo, which was 12 years. In the wild, females take 9-10 years to become sexually mature, after which they can live another 10 years. Males reach maturity in 7-8 years, after which they die within a year.
Avicularia purpurea
This species is common in South America. They live in pastures, in agricultural conditions. Sometimes found in the crevices of the walls of buildings or in places under the roof.
In length, individuals reach 5 cm, and therefore are among the smaller representatives of the genus Avicularia. In daylight, the arachnid shimmers with purple and blue hues. The color is given by numerous villi located on the legs, palps, chelicera. The hair on the metatarsal segments is dark brown, on the chest is pale cream. The abdomen is covered with stinging hairs of a velvety black hue.
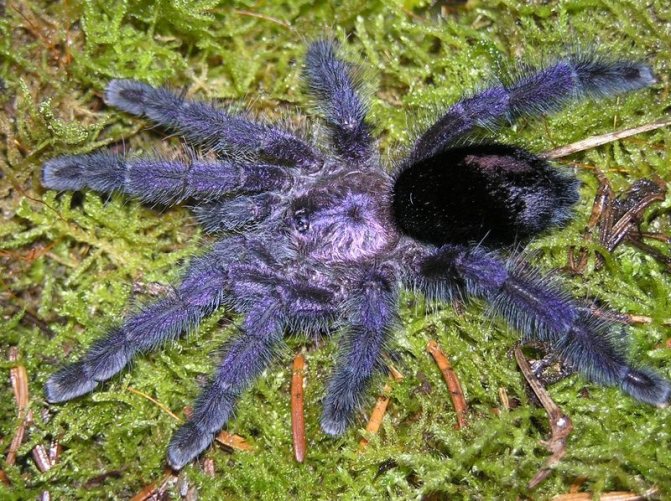


Arthropods live primarily in trees. Nests are built in hollows or next to epiphid plants.
Avicularia versicolor
The species is found on the mainland of South and Central America. Differs in the presence of longer and thinner urticating hairs. Males have palpable organs. They are located on the last segment of the forelimbs.
The length of the specimen is 5-6 cm, with paws - up to 17 cm. Arthropods are of deep blue color, with a characteristic pattern on the abdomen for the species. After each molt, the color changes, the shell turns green, the abdomen is red, the hairs on the legs become pink and purple.
In 2020, Avicularia versicolor was transferred to the genus Caribena. In the World Spider Catalog, the species is called Caribena versicolor.
Aphonopelma seemanni
Arthropods are common in North and South America. They have fewer hairs than other species. The total size with a leg span is from 11.5-16 cm. The color is brown or black, with light, beige stripes on the legs.
In the wild, they consume crickets, grasshoppers, cockroaches, praying mantises, and beetles. In captivity, they feed on crickets.
Brachypelma boehmei
The spider is popularly called the Mexican fiery leg. He received such a nickname due to the rich orange color of the shell and lower legs. The feet look brighter due to the upper black part and the same color of the feet.
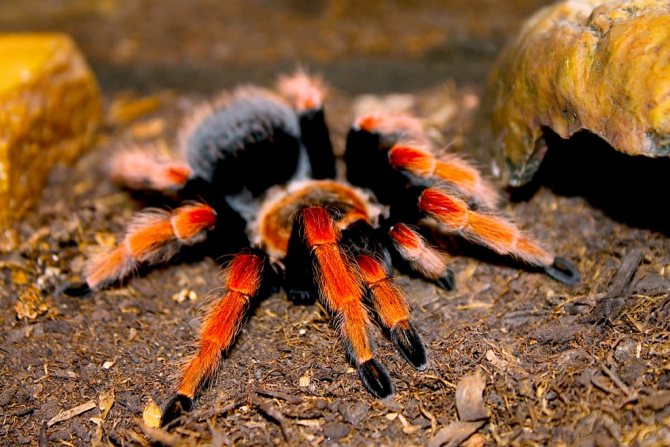


In length, arthropods reach 13-15 cm.The species is characterized by slow growth and average lifespan. Males reach maturity at the age of seven to eight years, females at 9-10. After the last molt, males live for about a year, females - up to 10 years.
Representatives are common in southern Mexico, along the central Pacific coast. They are found in dry shrubs, homemade or rodent-abandoned burrows.
Chilean pink tarantula
Grammostola rosea, also known as the pink hair tarantula, is the most common. In pet stores in America and Europe, it is often delivered illegally from its native Chile, Bolivia and Argentina.
Some descriptions confuse it with Grammostola porter. Chilean pink is brown to chestnut in color, with occasional brown and pink spots. The average size is 15-16 cm. They live in burrows, are more active at night.
They eat grasshoppers, moths, beetles, cockroaches, mealworms, small lizards.
Goliath tarantula
Theraphosa blondi is the largest representative of its class in the world in terms of weight and size. Lives in the northern part of South America. The body length is 11.9, with a leg span of up to 28 cm, and can weigh up to 175 g. This species is one of the few that does not have tibial spurs located on the first pair of legs of most adult males.
The habitat of Goliath is the mountainous regions of the forests of the south of America, Brazil and Venezuela. They feed on rodents, frogs, toads and snakes.
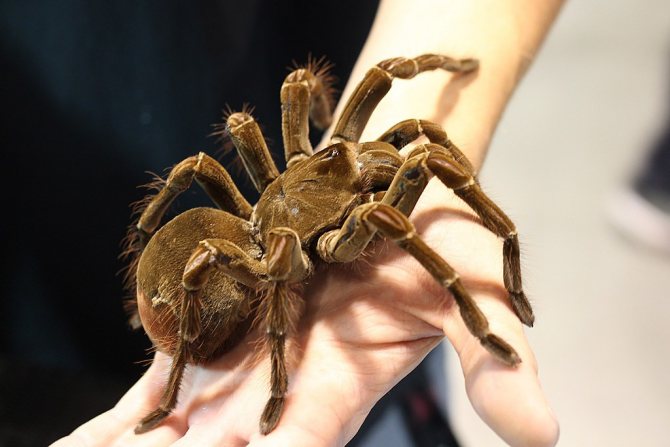


Females reach maturity in 3-6 years. After mating, 100-200 eggs are laid, of which the larvae hatch after 6-8 weeks.
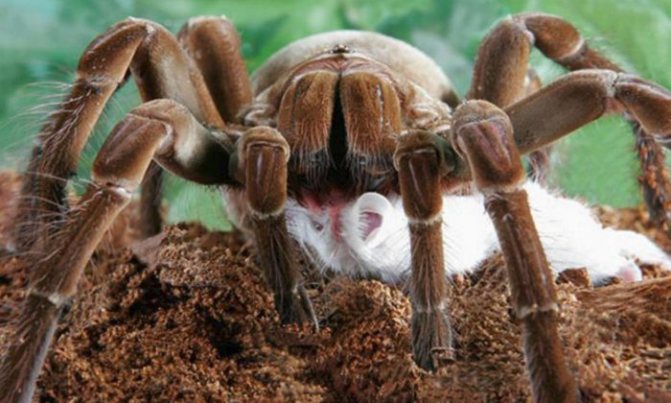
Diet
The tarantula is an obligate predator. Despite its name and the ability to chew food, the body of an animal cannot constantly consume poultry meat. The basis of the diet of all representatives of migalomorphs is large insects and other arthropods, such as centipedes and other spiders.
Arthropods are sufficiently omnivorous, and can eat a variety of food: frogs, mice, worms. Armed with their powerful chelicerae with long chitinous fangs, tarantulas are well adapted to kill other large arthropods. The largest representatives of migalomorphs kill and consume small vertebrates.
Birds
If you look at an arthropod in the wild, then birds take up a small percentage of the entire diet. Small representatives do not consume birds at all.
Protostomes received their specific name thanks to one of the members of the expedition. A group of scientists came across an unusually large arthropod that eats a hummingbird. In reality, the spider rarely eats birds. As a rule, chicks are eaten by arachnids. If accidentally stumbles upon a nest.
Small rodents
Arachnids, for the most part, are nocturnal. At this time of day, mice are also active. Many spiders, like rodents, live in burrows. In case of danger, the animals seek refuge and stumble upon the lair of an arthropod, which is waiting for the victim. He just has to bite her and start eating.
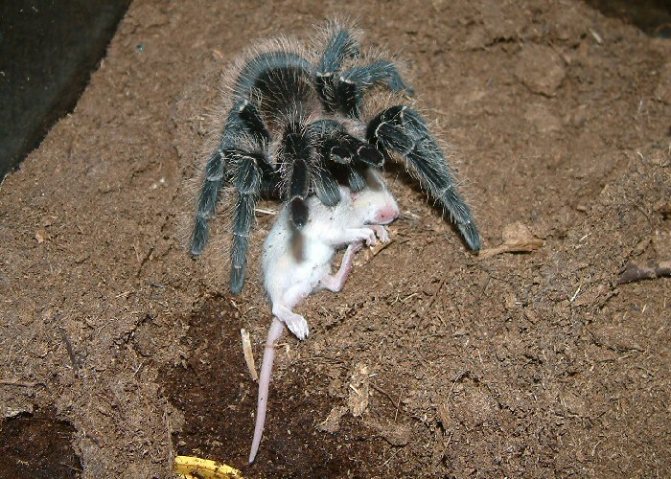


Larger species like Theraphosa blondi feed on bats.
Insects
Fowlers eat grasshoppers, cockroaches, crickets, butterflies. More precisely, this is the main diet. Insects live everywhere, especially often crawling, running and jumping, less often - flying species.
Fish
Aquatic vertebrates are included in the diet of only medium and large tarantulas. To grind fish bones, you need strong and large pedipalps and chelicerae. But even large individuals hunt only for fry, which swim to the shore in flocks.
Amphibians
Representatives of the genus Acanthoscuria eat toads and lizards. Some amphibians can defend themselves and release poison when threatened. The spider is a cautious animal, therefore, it is extremely rare to hunt these representatives of the fauna.
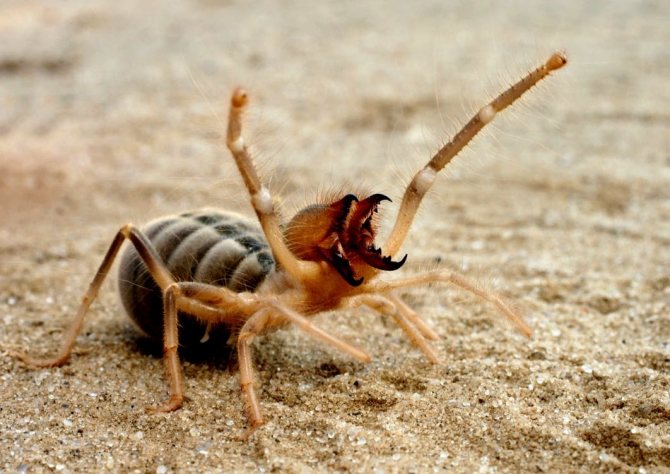
Arachnid Phalanx
This spider can also be called camel due to the hump on the back.All individuals of this species are very mobile, but are strictly nocturnal. The body and limbs are covered with hairs.
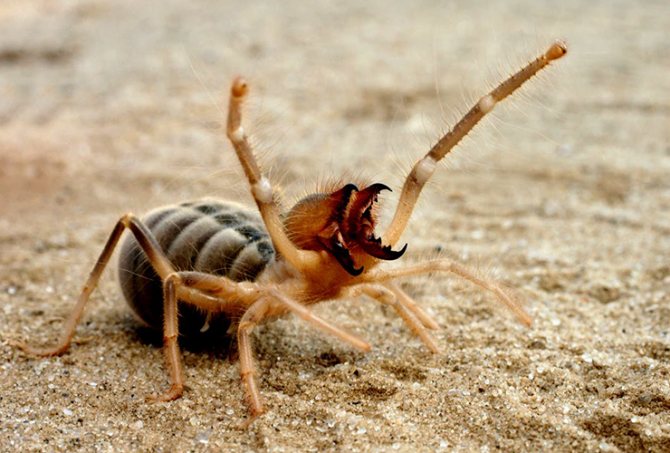


Arachnid Phalanx is characterized by a quick reaction
The eyesight of the individuals is quite remarkable. They have an additional pair of eyes on the sides, like scorpions. Spiders distinguish light, are able to react to movement. Due to this, the reaction of the arachnid is very fast. It attacks the victim with a split second delay, thanks to which the giant spider is considered not only an excellent hunter, but also an elusive creature.
Another notable feature of the spider is its chelicerae. They are so strong and durable that it can bite not only the skin, but also the human nail. Outwardly, each chelicera looks like a crab claw. It is with them that he rips off fur and feathers from his prey, and then lines his dwelling with material.
In size, it can reach 25 cm with legs. It lives mainly in desert areas, it can be found on all continents. This is the most common spider on the planet.
How many years does a spider live?
Gender influences life expectancy. Females live much longer than males. Many males do not molt after reaching maturity and die within a year.
How many years an arthropod lives also depends on the habitat, food supply, species. Some specimens, such as Brachypelma emilia, die at the age of thirty, while goliaths live to be 25 years old. The average life span is 10 years.
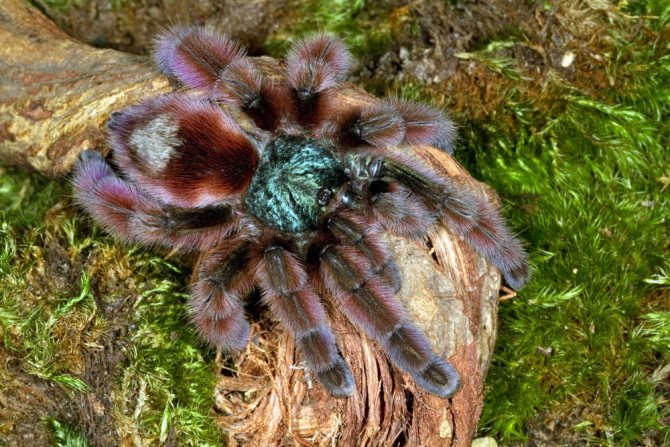


Should you be afraid of tarantulas?
It has been fashionable to have colorful Theraphosidae at home for some time now. Before buying, people are interested in - is the tarantula spider really poisonous or not for humans? This one is the largest representative of its class, like the others, poisonous. But he releases a toxic substance only in two cases. Firstly, to defeat prey, and secondly - in case of danger. If a person does not threaten him, then he is not of interest to the spider.
Bites
What happens if a tarantula spider bites you? This happens when the primary animal is kept in domestic nurseries. A bite for a person does not pose a mortal danger. There is a fever, irritation of the skin, with an allergy to the toxin, edema and severe itching may occur.
Stinging hairs
In response to threats, spiders rub the bristles on their legs, push their hind legs apart, and release hairs. They are a serious irritant to the skin and delicate mucous membranes. This bristle can be toxic to humans.
Why is this happening? Uticulating hair is one of the defense mechanisms. They cover the dorsal and posterior surface of the abdomen. In case of danger, tarantulas eject bristles from the abdominal cavity, directing them to potential intruders. If hairs get on the skin or eyes, they cause irritation.
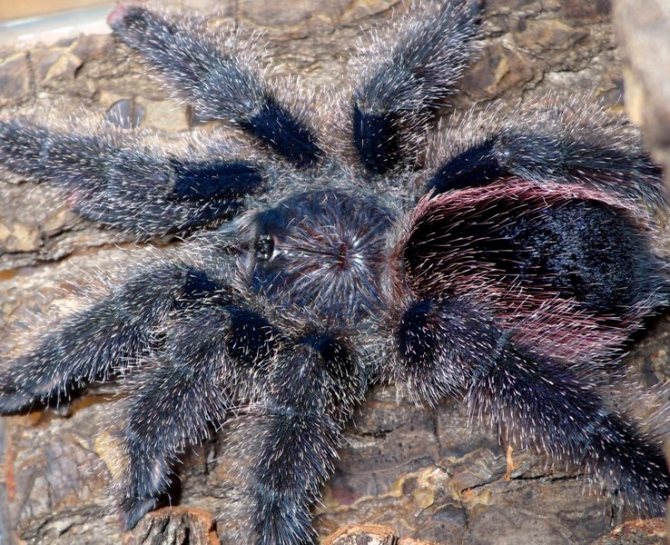


Excrement attack
Natural waste products of the arthropod can be used as a defense mechanism. They pose no danger to humans or animals. When threatened, the spider throws them out of the anus, trying to blind a potential enemy.
Danger to humans
Tarantulas do not threaten the health and life of their owner. But when carrying out any measures for caring for a pet, you must adhere to precautions. All species of spiders are poisonous to one degree or another. If we talk about non-poisonous species, then the low degree of toxicity of the poison is implied.
The bite of the animal leads to the death of small rodents. Cases have been recorded when domestic cats died due to the fault of spiders. The bite is likely to be hazardous to the health of young children.
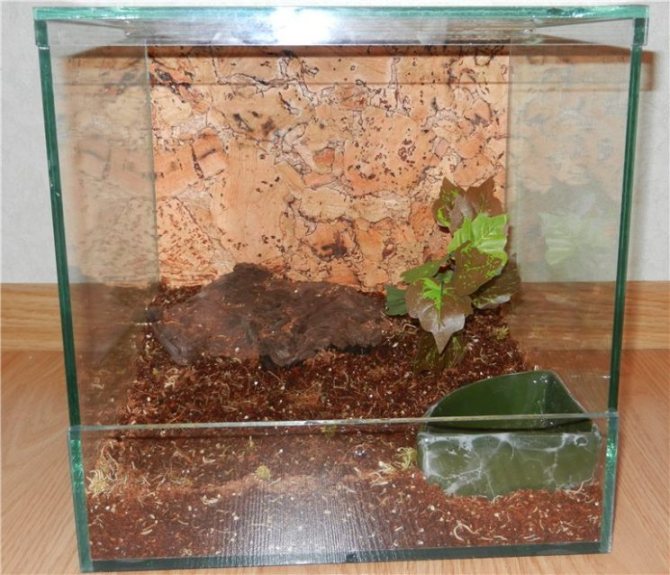
Females show increased aggression in the active stage of motherhood. But in other cases, it is impossible to predict the reaction of an arthropod to any, even the most harmless actions. That is why it is not recommended to touch them with your hands.Before purchasing a tarantula, you need to acquire a special terrarium, as well as long tweezers for carrying out all kinds of manipulations.
Toxic poison or not depends on the type of spider. For an adult, the danger of a tarantula bite will be equal to a wasp bite: burning pain is felt, edema appears. With increased sensitivity of the body to toxins, there is an increase in body temperature, fainting, muscle cramps, vomiting, and even mental disorders. When the tarantula bites through the skin, the poison is not always injected, most often the so-called "dry" bites occur.
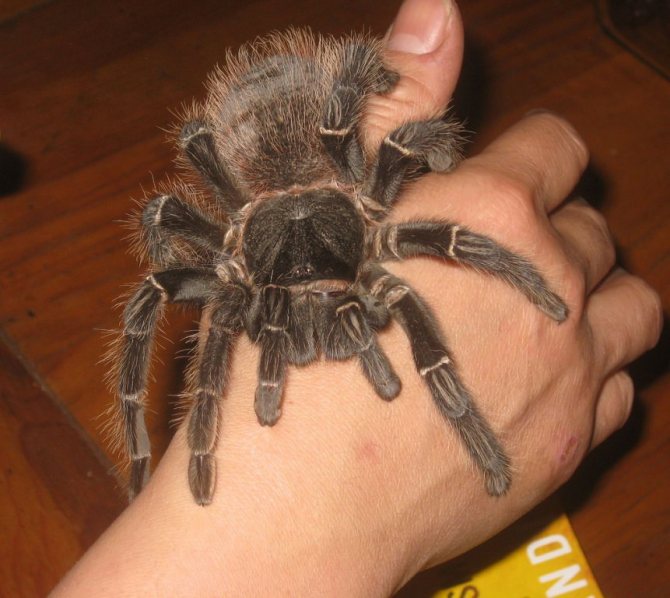


The hairs covering the legs and body of the arthropod are dangerous. Being in a stressful state, the spider is able to quickly pull out the villi with its paws, trying to throw them to the enemy.
When hairs come into contact with human skin, they provoke burns and allergic manifestations. Contact with the mucous membrane of the eyes causes severe burning and itching, which do not go away for several hours, and in some cases - days. Sometimes toxins lead to deterioration in the quality of vision for the rest of your life.
The tarantula spider is really a danger to humans. If the potential owner of such a "domestic" animal is not afraid of the threat to health, the exotic appearance of the arthropod does not repel, but attracts, you can safely start it at home. But at the same time, we must not forget about the rules for keeping a pet and safety precautions.
Is it listed in the Red Book?
Many representatives of the infraorder migalomorphic are under the protection of various organizations - conservationists. Why are some tarantula spiders listed in the Red Book?
The primitive animal has many natural ill-wishers who strive to eat it. But the most dangerous enemy is man. People are cutting down forests, burning steppes, draining natural reservoirs, disrupting the ecosystem. This leads to inadequate nutrition and poor reproduction of arthropods. Some species are on the verge of extinction and are listed in the Red Book.