Wolf spiders: description
Their amazing ability to disguise keeps these creatures from prying eyes. They are practically indistinguishable in dense vegetation, make holes in secluded corners, hunt only when there is no danger nearby. This spider looks unremarkable.

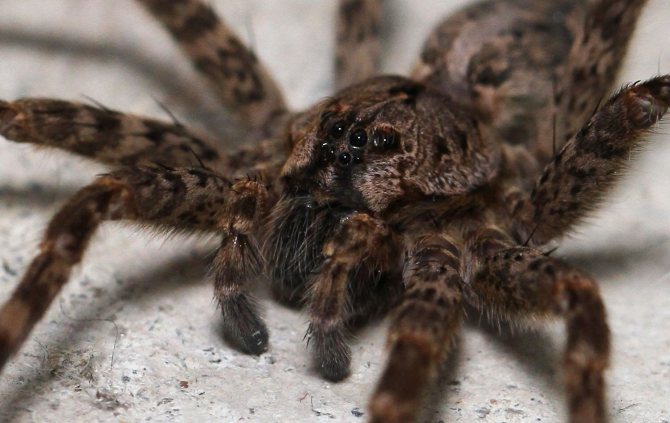
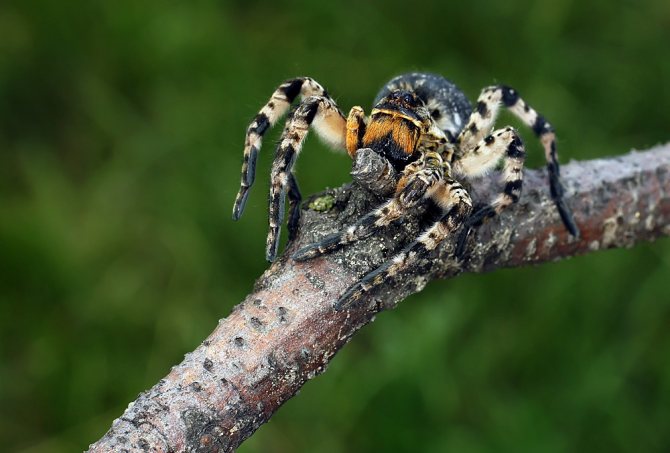
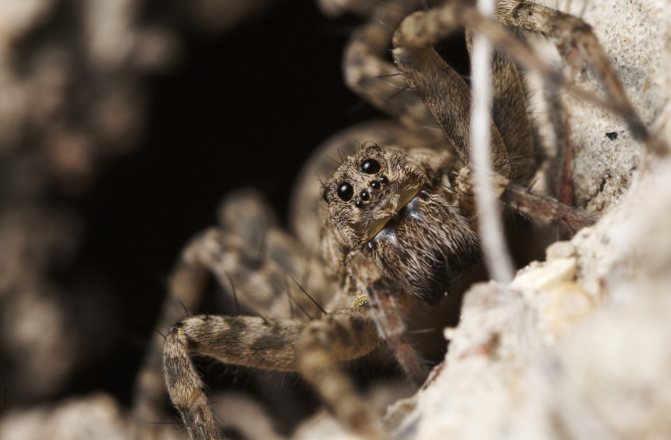
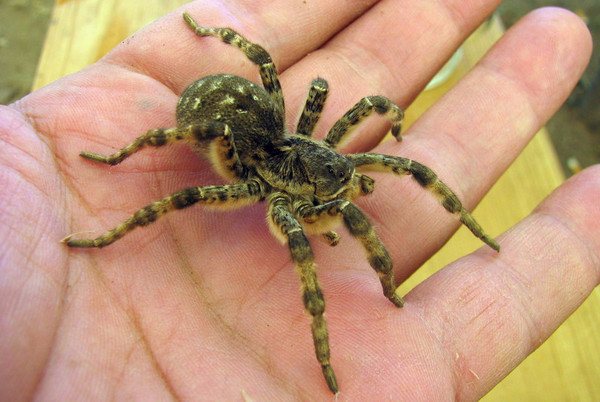
He has a primitive body structure - the cephalothorax is used as a place for the organs of vision, mouth and respiratory organs. The internal organs of the spider are located in the abdominal part, and long articulated legs extend from it. Its color is brownish-gray, earthy, so the description of a wolf spider can be confused with a hermit spider. They differ only in a special spot on the back in the shape of a violin, which the wolf does not have.
Important! This type of arthropod does not practice deliberate attacks on warm-blooded creatures. In order not to engage in a fight with them, he rolls over onto his back and remains in this position without movement until the threat disappears.
The entire body of this arachnid is covered with hairs similar to wool. Eight eyes are located on the head, two of which are especially large - the vision of this creature is much sharper than that of representatives of other subspecies. He needs a good ability to see at long distances for free hunting, since this spider does not weave webs, but catches prey moving along the territory adjacent to its burrow.
Check out the features of the tarantula, tarantula and black widow spider.
This spider has three claws at the tips of each articulated paw, they help it move faster on different surfaces and overtake its prey. The front legs of males are much more noticeable than those of females, and they are three to four times smaller in size than females, since females are designed so as to carry and feed offspring.
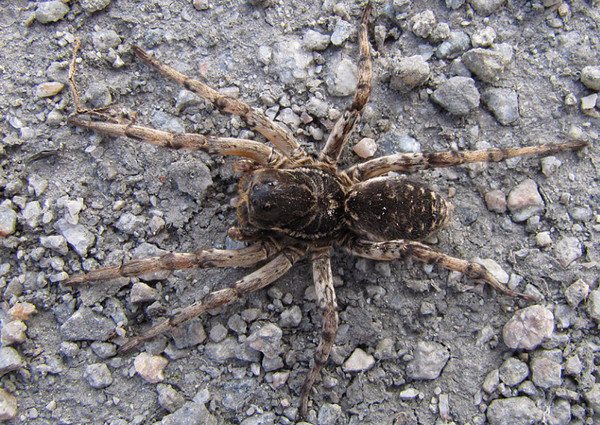


Characteristic
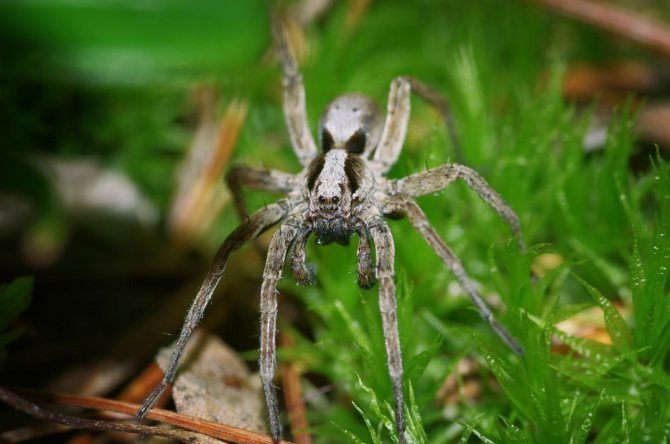
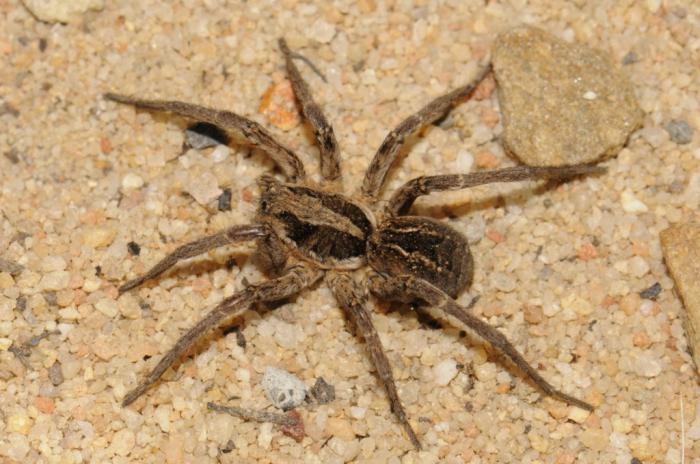
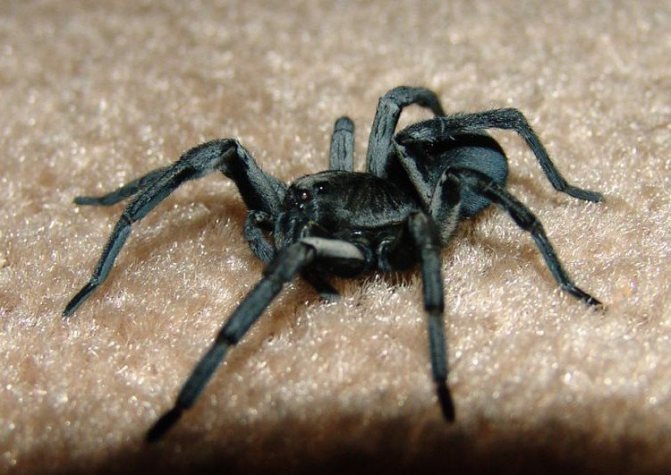
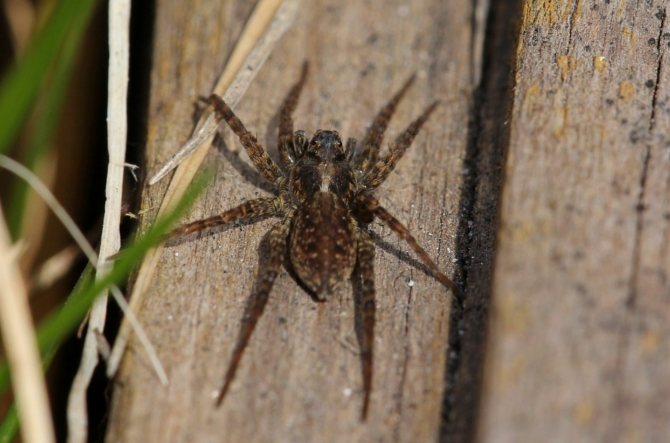
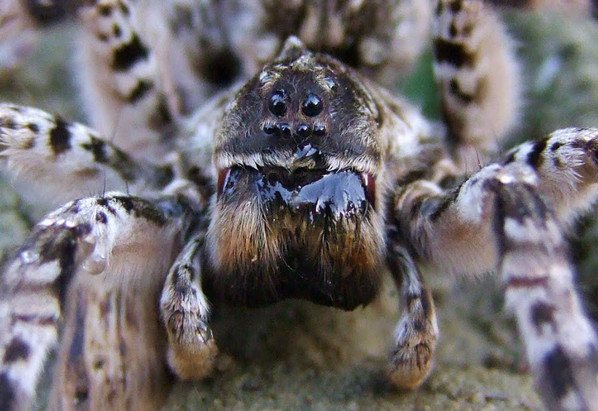
As you can see in the photo, the wolf spider has a primitive body structure - it is divided into the cephalothorax and abdomen. The covers are usually dark and black, brown or dark gray. Light-colored individuals are extremely rare. Due to their color, wolf spiders can perfectly disguise themselves - they almost completely merge with the environment. In representatives of this family, sexual dimorphism is expressed: females are much larger than males, while the latter have darker integuments, and a pair of forelimbs is much better developed. The front legs are used by males to attract the attention of females and during mating.
As for the vision, it is comparatively good for wolf spiders. They have 4 pairs of eyes arranged in 3 rows: on the bottom row there are two pairs of small eyes, in the middle - a pair of the largest ones, in the upper - two lateral eyes, which are slightly higher than the middle pair.
It is interesting! Thanks to good eyesight and a perfectly developed sense of smell, wolf spiders are able to detect a potential victim from a rather impressive distance - about 30 cm. But at the same time, it is believed that these creatures are not able to distinguish form!
The interconnection between the organs of the wolf spider's body is provided by a transparent hemolymph, which acts as blood. It has one feature - as soon as the spider goes out into the open air, the hemolymph becomes blue.
Distribution and habitat
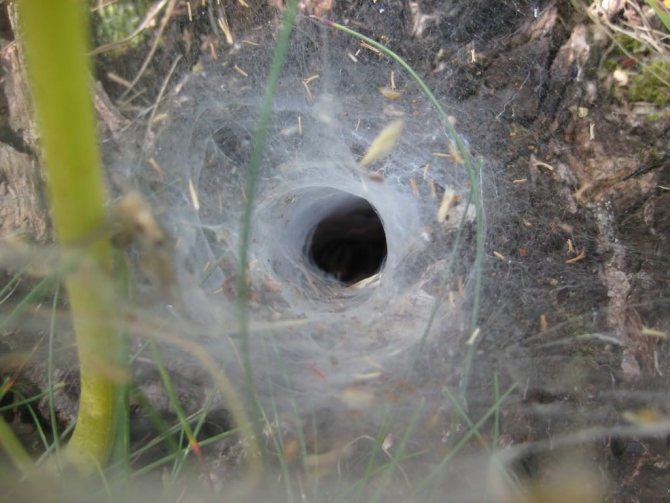
These arachnids live on all continents and in all countries, except for areas of permafrost.The warmer the climate of the country, the higher the likelihood of meeting this creature there. Humidity is another favorable condition for wolf spiders, so they massively nest in damp deciduous litter, on rocks near water bodies. What they are, everyone knows, despite the fact that wolf spiders try to hide and remain invisible, and therefore live alone in dense bushes and flower beds, in blockages of stones, woodpiles, in old sheds and warehouses.
Behavior and lifestyle
It is believed that this spider was named a wolf not only for the thick hair on the abdomen, but also for the habit of living and hunting alone, and not by the method of weaving trapping nets, but by real races after the escaping prey. He hunts mainly for small insects. Catches flies, beetles, other spiders and finds larvae laid by beetles.
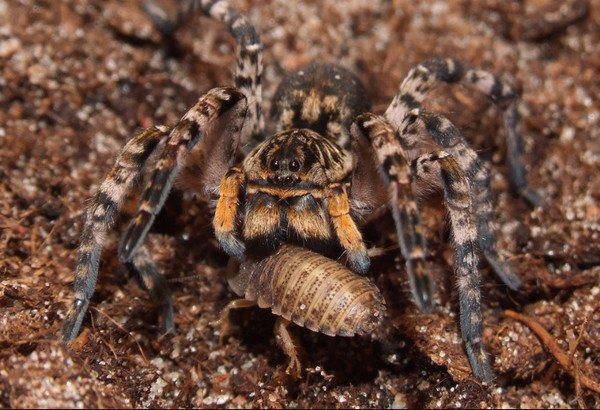


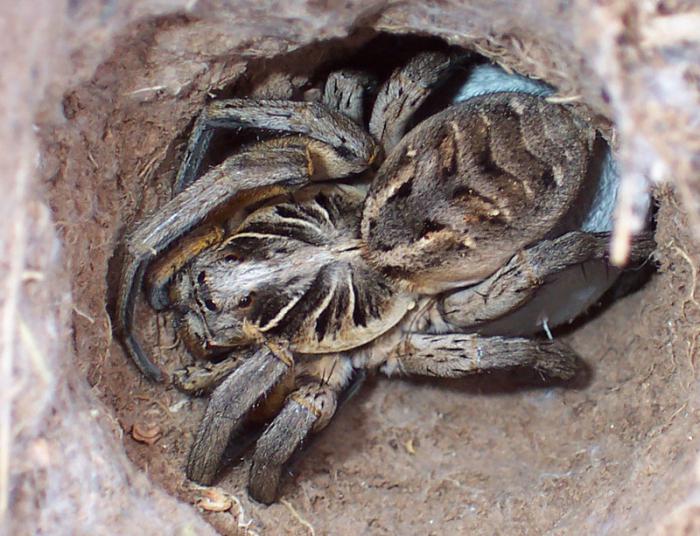
At night, these creatures sit in burrows and catch insects running by, and in the daytime they move near the mink on their own and, seeing potential prey, jump on it with all their weight, pre-attaching the web to the place from which the jump was made. Wolf spiders eat their victims, pressing them to the ground or other surface with their front paws, which look like articulated harpoons. It is a predatory arachnid, so it can immobilize large victims by injecting a poisonous substance with a bite.
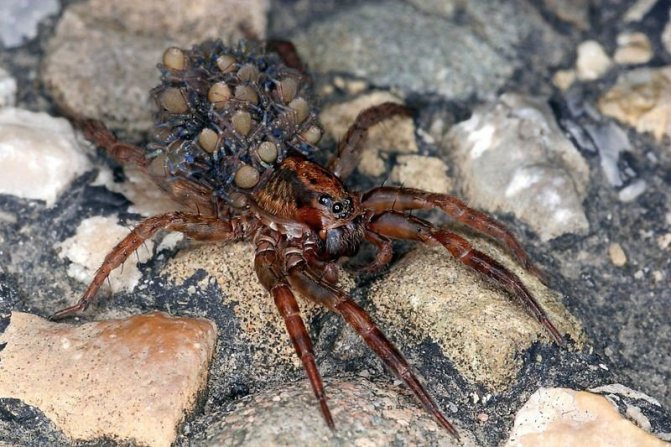
Did you know? This species of arachnids has such a strong maternal instinct that the female, from which the cocoon with the cubs was taken, loses peace and can wander aimlessly for hours in search of it. If the cocoon cannot be found, it clings to its place, that is, to the abdomen, any object similar to it. There are cases when a female wolf spider replaced the cocoon with tiny pieces of cotton wool or balls of cotton fibers to create the illusion of bearing offspring.
Female wolf spiders mate exclusively with male specimens they like. Most often, mating takes place in the warm season - thus, in a temperate climate, this process occurs in the spring, and in a tropical climate it takes place all year round. The male attracts the female's attention by swaying on elongated forepaws and slowly approaching her with a swinging gait. If the female decides that such a male is suitable for her, she helps him climb onto his back. If the male is small, the female turns the abdomen so that it is convenient for him to introduce sperm into her genitals with the help of her genital organ (cymbium).


Immediately after mating, the female begins to look for a cozy corner in order to settle in it and start spinning a cocoon for fertilized eggs. In the resulting multilayer ball, she carries eggs for two to three weeks, while the baby spiders mature in them. This tangle is attached to the female's spinning organ, from which she secretes a web to strengthen the cocoon. The cocoon ripens well only in sunny and warm weather, so the female looks for the warmest places for it and, due to the evaporation of moisture from the surface of her body, loses up to 30% of the total mass.
If you are no longer interested in popular pets such as cats, dogs, hamsters and guinea pigs, you might want to get a salamander, newt, lemur, squirrel, degu, monkey, or raccoon.
As soon as new spiders begin to hatch, the spider mom senses this, throws off the cocoon and tears it apart, freeing the spiders from the web. She carries the offspring on herself for the next three to four weeks and feeds them until the babies begin to feed on their own. Depending on the size of the female, from forty to one hundred babies are placed on her abdomen - sometimes there are so many spiders that only the eyes remain free on the mother's body.
Housekeeping rules
As a pet, this creature does not cause much trouble. Despite the slight toxicity and nervousness, the spider moves by jumping only when it is about to attack a possible prey, and practically does not move on vertical surfaces due to the weak coupling of its clawed legs.A glass aquarium with a volume of ten to twenty liters is quite suitable for its maintenance. To make the arachnid comfortable, it must be filled with soil mixture to a height of ten centimeters. In the aquarium, you need to maintain a constant temperature at 28-30 degrees - such warmth is especially necessary for females during the maturation of the cocoon. High humidity is another prerequisite for a comfortable stay of this pet. To prevent the humidity in the aquarium from becoming equal to room humidity, cover it with cling film.
Important! Individuals that carried offspring in the warm season, as well as young spiders that appeared in the warm season, are able to winter. They pupate or simply lie in dark secluded places - it is better not to disturb such spiders in vain.
For home keeping, it is better to take a female than a male. Firstly, it is larger, so it will be more interesting for you to look after it. Secondly, it is less whimsical in its content - it is not disturbed by temperature fluctuations up to five degrees in both directions. In captivity, the female lives up to four years, while the male lives up to two years - the age of puberty and dies almost immediately after that. A domestic female spider can give numerous offspring, captivity only benefits her in matters of nutrition and comfort, however, you need to be careful with her during the period of bearing cubs, because she can bite. To do this, you will need to plant a male spider that is capable of breeding.
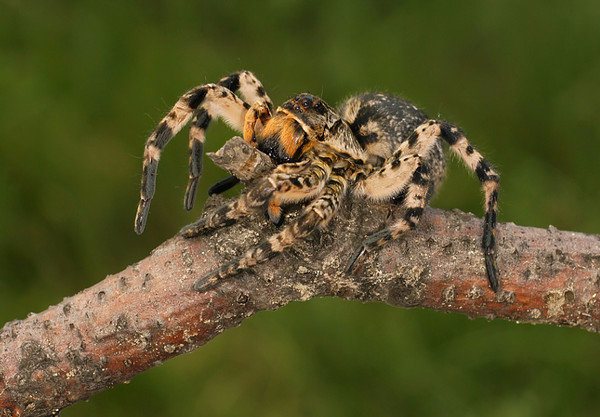


Views
In total, this spider family has more than two thousand species, which are divided into one hundred and sixteen genera. Between themselves, these species differ in the way of hunting - running or burrowing, and the time of hunting - day or night. The most common type is called ampoule tarantula... This is a rather large arachnid, it reaches at least seven centimeters in length. Lives on the slopes of mountains and hills, loves to hide in fallen leaves and cover their burrows with it. Its bite is very painful and has long been considered poisonous.
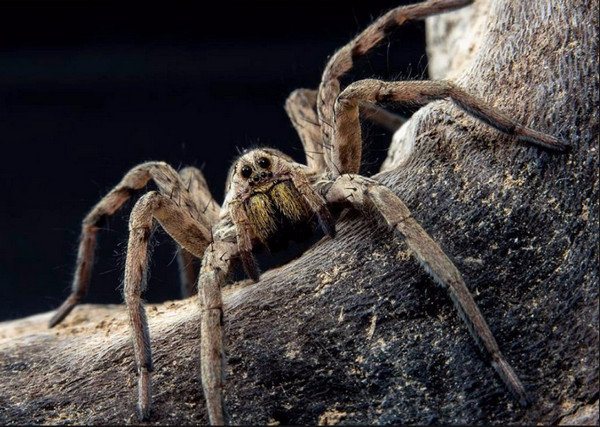


Among the species of wolf spiders that do not belong to tarantulas, in wooded areas, in private houses and in summer cottages, they are often found spider leopards and earth spiders... The former are distinguished by a bright silver stripe on the body and small size - only 0.5 cm. The latter are slightly larger, their dimensions reach one centimeter. They have similar habits and life expectancy.


Another widespread species also refers to tarantulas - this tarantula South Russian... It is not as large as the ampoule, only three centimeters, but it looks frightening and is considered the largest arachnid in the CIS. In general, about eighty species of these creatures can be found in the middle lane. The rest live in tropical and subtropical regions.


Did you know? The nervous system of this species of arthropods is better developed than the nervous systems of its other relatives. This is due to the fact that his hunting method is fundamentally different from the typical spider. While all the other representatives of the arthropod squad are sitting on their trapping nets or in burrows, waiting for the arrival of the victim, this indefatigable prey runs and searches for his prey on his own, overtaking it swiftly and suddenly. For the first time such a method of hunting a wolf spider was discovered in the 90s of the XIX century.
Notes (edit)
- Lange A.B. Subtype Chelicerata // Animal Life. Volume 3. Arthropods: trilobites, chelicerae, tracheal breathing. Onychophores / ed. M. S. Gilyarova, F. N. Pravdina, ch. ed. V.E.Sokolov. - 2nd ed. - M .: Education, 1984 .-- P. 68 .-- 463 p.
- Annotated List of Rare and Endangered Species of Invertebrates Specially Protected within Russia // 2003 * Russia * Red List of Specially Protected Rare and Endangered Animals and Plants. (2nd edition). Part 2. Invertebrates (Bulletin of the Red Book, 2/2004 (2008)) / otv. ed. V. E. Prisyazhnyuk.- M .: Laboratory of the Red Book of the All-Russian Scientific Research Institute for Nature Conservation, 2004 (2008). - S. 119 .-- 512 p. - ISBN 978-5-9243-0158-7 Full text
- Information on wolf spiders on the Australian Arachnological Society website. (English) (Retrieved November 24, 2010)
- Platnick, N. I. (2010). The number of modern genera and species of spiders. The world spider catalog, version 11.0. American Museum of Natural History. (English) (Retrieved November 24, 2010)
- Ribeiro LA, Jorge MT, Piesco RV, Nishioka SA, 1990. Wolf spider bites in Sao Paulo, Brazil: a clinical and epidemiological study of 515 cases. Toxicon 28: 715-717.
- Australian Wolf Spider Bites (Lycosidae): Clinical Effects and Influence of Species on Bite Circumstances - Clinical Toxicology
The value of wolf spiders for nature and humans
If you stumble upon this spider on your lawn or in a private house, try not to kill it, but drive it away, since the question of whether these domestic and garden creatures are dangerous can be answered in the negative. Despite their formidable appearance, they are very beneficial for the environment and your site as well. Wolf spiders do not weave webs from a web, so they are practically invisible in their habitats, but they destroy a lot of pests and parasites. Such sanitary work preserves plantings and crops from sabotage - these spiders save both garden crops and decorative compositions, controlling the population of harmful insects.
What does it eat?
All spider species have external digestion. They immobilize the prey, inject food juice into it and suck in the liquid inside the insect. This process can take more than a day. Large individuals are able to feed on backbone animals such as mice. Small ones prefer insects, larvae and beetles.
Flies
Flies are my favorite treat. They often end up in the spider web. But wolves just catch them, thanks to their speed. Flies themselves often fall into the net (which wolves do not for hunting, but to protect the nest).
Beetles
Spiders catch beetles less often. The reason is that prey can have a thick protective carapace that is difficult to bite through. But for individuals with large canines, like an adult wolf, this is not a problem. Beetles are an excellent choice as food for home spiders in the aquarium. But it is better to give them dried.
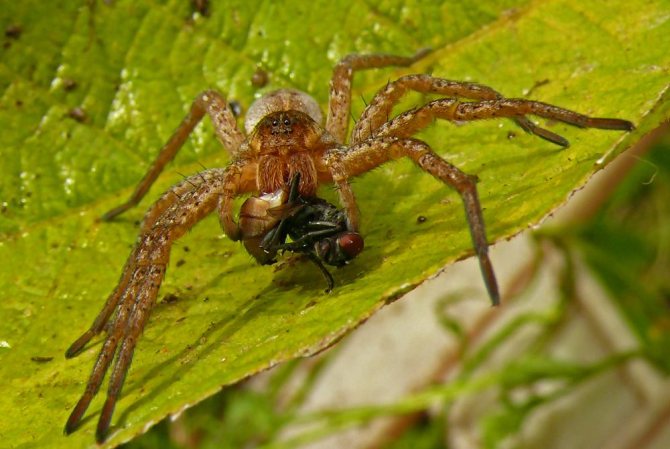


Insect larvae
Another favorite spider treat. While hunting, they can find a nest with larvae. The spider will have a real feast, because the number of individuals in such nests is large. Wolves suck the juice from the larvae.
Small spiders
Spiders often eat their own kind. They choose small individuals (no more than 1 centimeter). Choosing large individuals makes them difficult to digest.