Vegetable growing »Pumpkin
3
349
Article rating
Planting a pumpkin requires a gardener to follow a number of rules. Vegetable crops are planted by seed and seedling methods, differing from each other in technology. Proper care after planting will help you achieve the best yields and produce large, strong fruits.
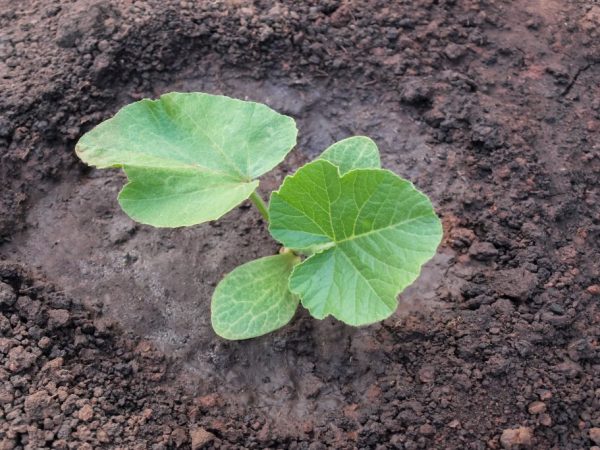

Planting pumpkin seeds and seedlings
Pumpkin planting dates


Before sowing pumpkin seeds outdoors, make sure the timing and timing are right. Pumpkin is a heat-loving plant, the seeds of which may not sprout in cold after winter or excessively humid and damp ground. Also, it is worth taking into account the possibility of frost return after the first warming.
After the end of the frost, as soon as the air temperature rises to + 18 ° C, the time comes when you can plant a pumpkin. Seeds are planted in the ground when it warms up to 12-13 ° C at a depth of 7-8 centimeters. The optimum temperature for pumpkin development is + 25 ° С. The plant stops growing if the air temperature drops to + 14 ° C.
To get a good harvest, you need to start sowing pumpkin in May. Favorable days for planting seeds in open ground are different for each region: they depend on the climatic conditions of the area. In the northern part of Russia, the first days of June are favorable for sowing pumpkin seeds in open ground.
Residents of the southern regions can plant seeds outdoors in mid-May. Some gardeners in the southern part start planting seeds from May 10. For those who live in the middle lane, the most favorable days for sowing pumpkin seeds in open ground come at the end of May, from about the 25th.
According to folk traditions, the best day for planting a pumpkin is Yuri's day, from the very morning. If circumstances do not allow you to plant seeds on this particular day, do not be upset. A pumpkin planted in moist, warm soil enriched with fertilizers, regardless of the day of planting, will give an excellent harvest.
Pumpkin: a description of the garden culture
Common pumpkin (Cucurbita pepo), or hard-barked, is an annual herbaceous creeping plant of the Pumpkin family, with thin pentahedral sharp-ribbed and prickly stems, reaching 8-10 m in length. branched superficial periphery.


Five-part or five-lobed large leaves up to 25-30 cm in diameter, cordate at the base, alternate, sitting on long petioles and covered with stiff, spiny, short hairs. Large monoecious unisexual bell-shaped flowers of bright yellow or orange-yellow color on ribbed pedicels bloom in June-July, cross-pollinated, most often by bees.
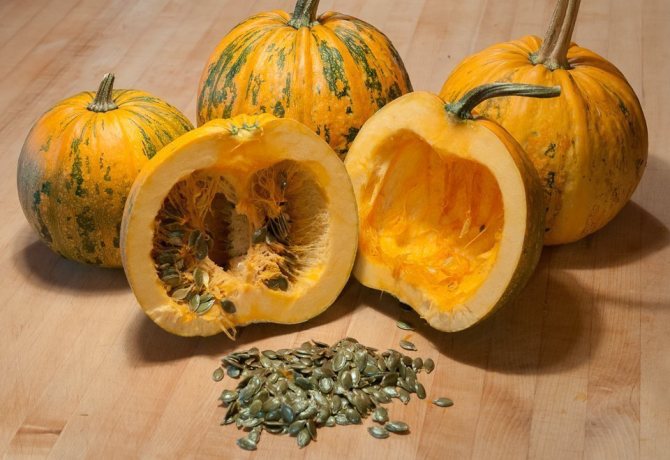
Berry-like polyspermous hard-bore fruits with an average diameter of 15-40 cm and weighing about 20 kg (specimens of more than 100 kg are found) ripen in a melon, a vegetable garden or in a summer cottage in the open field in August-September. The shape, size and color of pumpkins varies and depends greatly on the variety. Flat oval seeds 1-3 cm long are covered with a woody yellowish-white shell, have a pronounced rim along the edge.


Experienced growers recommend the following outdoor pumpkin varieties that are suitable for growing in almost all regions:
- Smile.Bushy high-yielding early maturing (85-90 days after germination) with a large number of small bright orange striped fruits weighing up to 1.5 kg. The pulp is sweet, crunchy, with a melon flavor. Stored at room temperature for up to 5 months.
- Freckle. An early ripe variety with rounded-flattened small (up to 3 kg) light green spotted fruits. The orange pulp tastes sweet and resembles a pear. It tolerates sharp temperature drops, keeping quality is good.
- Russian woman. An early ripening cold-resistant climbing bush with shiny dark orange fruits weighing 3-4 kg, inside which is a delicious sweet orange pulp. It tastes like a melon.
- Dawn. Medium early ripening with dark gray segmented fruits weighing about 5 kg, covered with bright orange-pinkish spots. Juicy bright orange pulp is sweet, tasty, with a high content of carotene. The variety is distinguished by its increased resistance to various diseases.
- Therapeutic. An early variety (90 days), large flattened fruits weighing from 3 to 5 kg, gray with a lighter shade of mesh. It can last until spring.
- Vitamin. A late-ripening nutmeg variety with elongated oval green fruits weighing up to 6-6.5 kg.
- Butternut. Small-fruited (up to 1 kg) nutmeg pear-shaped late-ripening variety with light gray fruits.


Choosing a place on the site
The correct selection of the site for the pumpkin is an important condition for obtaining a rich harvest. It is advisable to place the bed in a warm area warmed up by the sun's rays. The pumpkin also tolerates shading well. For a plant, the most preferred loamy or sandy soil, which is good because it warms up quickly.
Perennial grasses, corn, or winter wheat are good precursors for pumpkin in the garden. You can plant it after carrots, cabbage, beets, tomatoes, onions, peas, beans, peanuts, lentils, green manure. After cucumbers, zucchini, squash, watermelons and melons, it is advisable to plant a pumpkin only after 5 years.
Features of growing pumpkin: how to choose a site for planting
It is not difficult to cultivate pumpkin outdoors, but some rules must be followed to obtain a bountiful harvest. Special requirements are imposed on the alternation or crop rotation; it is impossible to plant any melons (watermelons, zucchini, melons, cucumbers) after the pumpkin. The best precursors for pumpkin seeds are cruciferous or legumes (cabbage, beets, tomatoes, onions). They can be planted again in the same place no earlier than after 5-6 years.


Lighting requirements
Growing pumpkin is best in open, well-lit, sunny, ventilated and dry areas. A heat-loving culture cannot stand gusty cold winds. Therefore, it is recommended to plant it on the southern side of buildings, along a fence or wall, which will protect from the wind during the daytime, and will give away the heat accumulated during the day at night.
In this case, the long lashes of the plant can be directed to the vertical surface of the fence, house or barn, since the fruits will ripen faster and better when they are well lit by the sun. Pumpkin needs direct sunlight for at least 6-7 hours a day.


Optimum temperature for seedlings or seeds
Planting pumpkin seedlings and sowing seeds in the ground on the site is carried out only after the soil at a depth of 10-12 cm warms up to + 10 ° C. At the same time, the daytime temperature should remain above the mark of + 8 ... + 10 ° С, with the seed method of planting, this indicator should be more than + 13 ... + 15 ° С. At night, the air should not cool below +3 ° C. In other cases, it is required to cover the seedlings at night.
See also
How to grow and care for squash outdoorsRead
The landing time is determined by the climatic features of the region.Sowing dates in the Moscow region most often fall in the first ten days of May; when growing pumpkins in the Urals and Siberia, they shift closer to the middle of the month.


What should be the soil for planting?
Pumpkin crops develop well and give a bountiful harvest on rich, fertile, drained and warmed soils. This plant will not grow in clay, heavy and too damp soil. The soil for the pumpkin should be neutral or slightly alkaline.
Acidic soils are categorically unsuitable, they must be deoxidized with fluff or dolomite flour, you can use crushed wood ash.
In order to properly grow a pumpkin in a summer cottage in the middle lane, it is recommended to prepare a bed for it in advance in the fall. The area cleared of previous crops and weeds must be well fertilized. When digging to a depth of at least 20-25 cm, the following components are added per 1 m²:


- humus - 5 kg or manure - 7 kg;
- potassium chloride - 15 g;
- superphosphate - 30 g.
If the post is heavy, then it is loosened by the introduction of coarse river sand. All components must be mixed, then the bed must be spilled with hot water at a temperature of about +80 ° C for disinfection.


Soil preparation


Fertile soil rich in nutrients is the key to a good pumpkin harvest.
Preparing the soil for planting should be done in the fall:
- Remove weeds and plant debris from the area.
- Shallowly loosen the ground with a hoe.
- After 2-3 weeks, dig up the soil, collecting the roots of the weeds.
In the spring, a day before planting or on the same day, the earth must be dug up again. After that, the site is leveled with a rake.
Starting to develop actively, the pumpkin builds up the aerial part, so the plant needs a lot of nutrients. When digging up the ground, you should definitely apply fertilizers to it. The best option is rotted compost, humus, or manure. They are introduced at the rate of 5-10 kilograms per 1 square meter to a depth of 15-20 centimeters in light soils and 10-15 centimeters in heavy soils.
It is not always possible to apply such an amount of manure. Then it can be put into the holes at the rate of 1-2 kilograms per plant. In addition to manure, it is worth adding 20 grams of superphosphate and 10 grams of potassium sulfate to each well.
Some gardeners add a handful of humus, a glass of ash and 50 grams of superphosphate to each hole. You can use mineral and organic fertilizers (for one plant - 1 tablespoon). All introduced components must be thoroughly mixed with the ground before planting seeds.
Some gardeners grow pumpkin on compost heaps. This method allows you not only to get a high yield, but also to improve the compost heap.
It is beneficial to plant pumpkin on compost for several reasons:
- The green mass of the pumpkin prevents weeds from growing on the compost.
- Pumpkin planted in compost accelerates the decomposition of coarse plant residues (sunflower stalks, cabbage stalks).
- Leavings covered with greenery improve the appearance of the compost heap.
- The pumpkin protects the compost from drying out.
Pumpkin transplant
Many gardeners often have a question whether it is possible to transplant a pumpkin from one place to another, because the realization that the wrong site has been selected for a vegetable crop sometimes comes late, when the seeds with seedlings have already been planted in a permanent place of growth.
The need for transplanting appears when too many pathogenic microorganisms accumulate in the place where the culture is grown, or the occurrence of groundwater does not allow the vegetable to fully develop.
There is no unambiguous answer to this question, tk. pumpkin culture does not tolerate transplantation.Compliance with the rules allows you to transplant it without negative consequences during that period until 2-3 real leaves have completely blossomed.
If the threat to the harvest is great and requires an immediate plant transplant, they do it as carefully as possible, digging the vegetable around the perimeter and transferring it along with the soil.
2-3 days before the planned transplantation date, the plant is stopped to water, so that the roots can be easier to get out of the dried soil.
Pumpkin roots with the remnants of the earth are disinfected and only then they are added dropwise to a new place of growth. After transplanting, the vegetable is watered abundantly with water and fed.
Seed selection


There are more than three dozen pumpkin varieties. Almond, Mozoleevskaya 49, Gossemennaya, Freckling are hard-bodied large-fruited varieties that ripen early and are stored for a long time. Large-fruited varieties Smile, Winter sweet, Kroshka, Winter dining are good for winter storage. Early ripening portioned pumpkins are distinguished by a sweet taste: Butter crumpet, Amazon, Winter sweet, orange bush.
Many pumpkin varieties can be grown from seeds in the garden. For seed growing, it is not recommended to choose only nutmeg varieties, since the seeds may simply not sprout. Pumpkin seeds can be stored for 1 to 4 years.
When choosing a seed, you need to pay attention to its freshness, checking in advance for germination. This is easy to do: just take a few seeds and germinate them on wet gauze. By looking at how many seeds from all have sprouted, you can determine the approximate percentage of their germination. This will help in the future easier to know how many seeds to put in the holes.
For a good pumpkin harvest, you need to choose only full-weight seeds. To select the best, you need to prepare a 3-5% salt solution and dip the seeds into it. The ones that have surfaced are unsuitable for planting, and the rest can be planted. These seeds must be collected, washed and dried.
What seeds you throw into the ground - you will get such a crop
Pumpkin seeds must be tested for germination before planting. To determine the germination, take as many seeds as you do not mind and germinate them. The more seeds were taken, the more accurate the germination percentage will be. If out of 18-20 seeds 15-16 have sprouted, then the germination rate is 80%.
To prevent the development of fungal diseases, seeds are etched in a bright red solution of potassium permanganate (1 g n 100 ml of water) for no more than half an hour.
Preparing seeds for planting
For growing pumpkin in the open field, it is important not only to choose the right seeds, but also to prepare them for further sowing. It takes a little time, but has a positive effect on the harvest.
For friendly shoots, before planting pumpkin, it is recommended to warm up the seeds for 2 hours at a temperature of about 60 ° C. To prevent fungal diseases, after that they are kept in a 1% solution of potassium permanganate for 12 hours.
To ensure the sprout easy penetration through the hard skin of the seed, use a solution, for the preparation of which 2 tablespoons of wood ash are diluted in 1 liter of boiling water with stirring. Gauze folded in several layers is abundantly moistened with an ash solution and the seeds are wrapped in it for 12 hours.
Treated seeds can be sown directly into the ground, or you can germinate first at home and then plant. For those who choose the second method, it is better to prepare a box of sawdust for this procedure in advance.
You can do it this way: place sawdust on the bottom of any convenient deep container, then pour boiling water over them several times and cover them in 2-3 layers with gauze. Having laid out the seeds there, cover them with several layers of gauze and a layer of sawdust, and tighten the box with foil. In a home greenhouse arranged in this way, the seeds will germinate in 2-3 days and will be ready for planting.
You can do without these procedures, but the ripening period of the pumpkin in this case is significantly increased. A pumpkin whose seeds have not undergone pre-sowing treatment, in areas with a cool, short summer, may not have time to ripen until frost.
How to protect pumpkin from pests and diseases?
Growing pumpkin in the open field is fraught with the risk of developing fungal diseases caused by excessive dampness, among them:
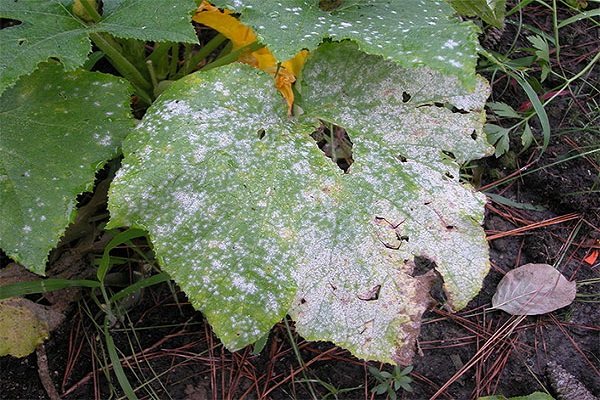
- Powdery mildew. The leaf plates are covered with a white bloom, which passes over to the petioles and stems. Spray with a solution of copper sulfate (2 g per bucket of water), potassium permanganate (3 g per bucket) or Bordeaux liquid (1%).
- Bacteriosis Brown spots and sores appear on the leaves and fruits. Spraying with Bordeaux liquid (1%) and zinc sulfate solution (0.02%) helps.
- White rot. A bold white bloom covers all the ground parts of the plant, gradually the bush decays. Landings are sprinkled with crushed charcoal or fluff.
- Root rot. Leaves and whips turn yellow, then crumble. For prevention, the bushes are treated with Previkur every 2-3 weeks.


Of the insect pests, pumpkin is most often attacked by spider mites and aphids. To combat them, an infusion of potato tops and onion husks, a solution of sodium chloride or soap, and wormwood broth are used. In case of severe damage, they are sprayed with insecticides (Karbofos, Actellik, Tsitkor and others). When buying seeds, it is recommended to take into account the characteristics of the variety, depending on the local climate. In regions with high humidity, varieties of pumpkin that are resistant to diseases are planted.
Technology of planting pumpkin seeds in open ground


Of all the melons and gourds, pumpkin is the most resistant to cold weather, but it also loves heat. Better to plant it in late spring when there is no frost. In cold soil, seeds planted too early can simply rot. To feed one plant, an area of 1-4 square meters is required. It may be slightly less for early maturing varieties and more for late maturing.
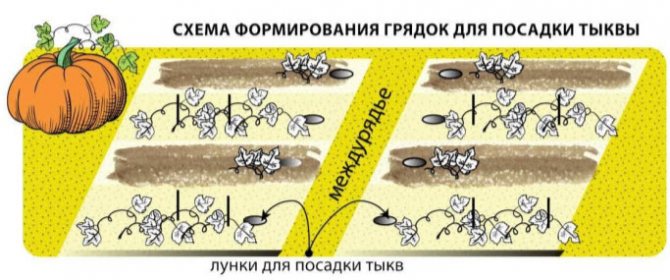
A melon seeder is used to plant pumpkin seeds in large areas. In an ordinary vegetable garden, seeds most often have to be planted by hand. Before planting the pumpkin, rows are marked on the site and holes are made in them with a diameter of 30 centimeters.
If, after a snowless winter, the land on the site is dry, about 2 liters of water with a temperature of 50 ° C must be poured into each hole. Seeds can only be planted when the water is absorbed.
It is very important to keep the distance between plants when planting. For long-plaited varieties, 1.5-2 meters are left between the holes, 1.4-2 meters between the rows. Bush pumpkin varieties can be planted in the nesting method according to the scheme 80x80 centimeters or 1.2x1.2 meters.
In light soils, seeds are sown to a depth of 5-8 centimeters, in heavy ones - by 4-5 centimeters. It is recommended to put 2-5 seeds in one hole: in large-fruited varieties it is possible less, in nutmeg - more. Place the seeds with their beak down at a distance of 3-4 centimeters from each other.
Having sprinkled the seeds with fertile soil, the site is mulched with humus or peat crumbs. Experienced gardeners install a homemade greenhouse made of film with slots over the planted seeds to accelerate growth.
Pumpkin: when and how to harvest
Ripe fruits are cut with a sharp knife, leaving 5-6 cm of the stalk. Ripeness is determined by the following criteria:


- the stalk is lignified;
- the foliage is yellow and dry;
- the crust became hard and bright.
You need to harvest on a dry sunny day, before the onset of frost. Not quite ripe specimens are immediately eaten or processed. Ripe fruits are stored, pumpkin in winter at home can be kept in an apartment at room temperature (under the bed, in the closet).


Plant care field planting


Pumpkin sprouts should hatch a week after planting in the ground. Further care of the plants includes loosening the earth, regular watering, feeding, and combating diseases and pests.
Watering
The large leaves of the pumpkin contribute to the rapid evaporation of moisture, so the plant requires regular watering, and only with warm water. As the pumpkin grows, the amount of water for irrigation must be increased.
It is recommended to slightly reduce the amount of watering during the flowering period: the fruits will be tied better. The pumpkin patch is re-hydrated when the fruits begin to gain weight. Before harvesting, about 10 liters of water should be used to water one plant. When the pumpkins reach their full size, you can stop watering the plants.
Loosening and thinning
The soil around the plants must be loosened and cleaned of weeds after rain or watering. With the emergence of seedlings, the first loosening is carried out to a depth of 6-8 centimeters. It is better to loosen the row spacing before watering to a depth of 12-18 centimeters in order to ensure rapid penetration of water to the roots of plants. During loosening, it is recommended to slightly huddle the plants, increasing their resistance.
After the formation of two true leaves in the seedlings, it is necessary to thin them out, leaving in one hole two sprouts of nutmeg or hard-bore pumpkin and one at a time - large-fruited.
When 3-4 leaves are formed in seedlings, the second thinning is carried out. In order not to damage the root system of the remaining seedlings, it is not necessary to pull out the extra seedlings. It is enough just to cut off an unnecessary seedling at the level of the ground surface.
Top dressing
Pumpkin forms a large amount of vegetative mass (leaves, stems) and fruits, so it needs frequent feeding, preferably with liquid fertilizers.
3 weeks after sowing the seeds in the ground, it is recommended to carry out the first feeding with manure or chicken droppings diluted with water in a ratio of 1: 4. Such organic feeding should be repeated 3-4 times a month. It is good to feed the pumpkin by dissolving a glass of wood ash in 10 liters of water.
When applying the first top dressing at a distance of 10-12 centimeters around the plants, it is necessary to make grooves 6-8 centimeters deep and pour the solution into them. For further feeding, grooves 10-12 centimeters deep are placed 40 centimeters from the plants.
After fertilization, the grooves are covered with earth. If cloudy weather lasts for a long time, it is recommended to spray the pumpkin with a solution of 10 grams of urea in 10 liters of water.
Pollination
If there are not enough pollinating insects on the land plot during the pollination of plants, you will have to do it yourself. To do this, you need to learn to distinguish between female and male flowers. The males have an elongated stem, and the females are located on the stem, they have an ovary under the petals.
At about 9 o'clock in the morning, it is necessary to pick the male flower, cut off the petals and touch the pistils on the female flowers with an anther. If the male flowers have not yet blossomed, the male flowers of a closely related plant such as a squash can be used to pollinate the pumpkin. The pumpkin harvest will be good, but it will no longer be possible to use the seeds for sowing.
Seedling planting technology
Planting pumpkin can be carried out not only by seed, but also by seedling. This method is especially good for gardeners in the northern regions.
Site selection and soil preparation
A well-lit windowsill or another warm place where the temperature is maintained at 20-25 ° C during the day and 15-20 ° C at night is chosen for home seedlings.
The nutrient substrate is made from a mixture of peat, rotted sawdust and humus, taken in a ratio of 2: 1: 1, respectively. If there is no sawdust, a soil mixture is made from equal parts of peat and humus.
For growing seedlings, a ready-made mixture is suitable for planting a pumpkin culture.
The substrate, disinfected with a weak solution of potassium permanganate, is filled in containers with a volume of 0.2 to 0.5 liters. In this case, the volume of filling should be equal to ½, so that it was possible to add soil mixture during the growth of seedlings.
In the future, the choice of a place and the preparation of the soil for transplanting seedlings is carried out according to the rules for planting a vegetable crop with seeds.
Sowing seedlings
In individual containers, seeds for seedlings are planted to a depth of 2-4 cm in a substrate moistened with water. The plantings are covered with polyethylene or glass to create a greenhouse effect. Once a day, the shelter is removed to ventilate the seedlings.
The shelter is removed from the plantings as soon as the first shoots appear.
A week after the germination of the seeds, the seedlings begin to be placed in a cooler place, where the temperature level is 4-5 points lower. This will allow them to be hardened before transplanting them to the garden bed and will prevent the seedlings from pulling out.
The main care when growing seedlings is regular watering, good lighting and feeding.
Before the seedlings are transplanted to the garden, they are fed. Suitable fertilizers are nitrophoska (1 tablespoon per 10 liters of water) and mullein (50 g per 0.5 liters of water). The mixture is kept for 3-4 hours.
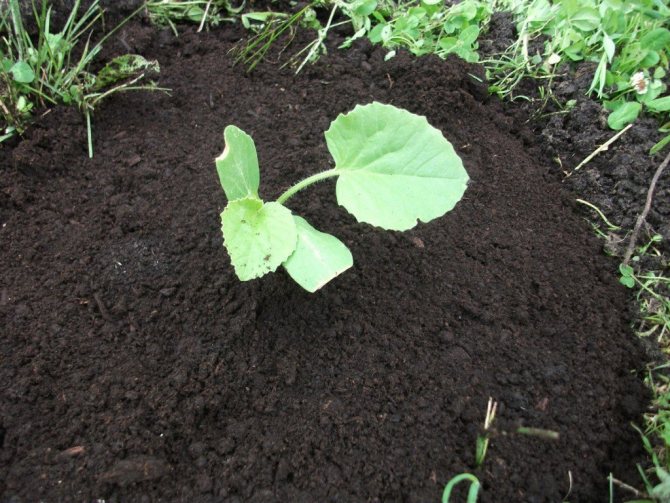
When 2-3 leaves appear in the seedlings and a height of 15-20 cm is reached, it is transplanted to the garden bed. Planting scheme - 1 × 1 m.When transplanting, the seedlings are removed from the containers together with an earthen clod so as not to damage the fragile roots.
As in the case of planting seeds, fertilizers are applied to the holes if the soil has not been prepared for planting in advance.
Harvesting and storage rules
Signs of a ripe pumpkin:
- the surface of the peduncle and the stalk that conducts food harden, become similar to the touch of a cork;
- the leaves of the whip dry up and turn yellow;
- after ripening, the texture appears on the peel more clearly;
- the crust cannot be damaged with a fingernail;
- the fruits are firm to the touch;
- a matte coating appears;
- when struck, a ringing sound is heard;
- the peduncle is easily detached.
Pluck pumpkins carefully, without damaging the rind. If lesions do appear on the skin, they are sealed with a plaster, preventing microorganisms from entering the fetus. Harvested vegetables should ripen in a dry place for 30 days.
The secret to a bountiful harvest lies in the correct selection of seeds and proper care. During the long winter, you can pamper the family with delicious pumpkin delicacies that are very healthy.
The pumpkin is not capricious in planting and care in the open field, which means, adhering to all of the above recommendations, any gardener can grow an enviable crop. This vegetable does not require special storage conditions, and it can lie until the New Year. Pumpkin is widely used in cooking, it can be used to prepare main dishes, soups, desserts, pies. It retains all its beneficial properties when preserved.
Pre-planting preparation
To grow a healthy and high-quality pumpkin, it is necessary to carry out a number of preparatory measures before planting.
The soil
A plot for planting a pumpkin is prepared in the fall:
- when digging the soil, organic matter is introduced - humus (5 kg per 1 m²) or manure (7 kg per 1 m²);
- mineral nutrition is added to organic matter - superphosphate (30 g per 1 m²), potassium chloride (15 g per 1 m²);
- provide the soil with the required looseness - they bring in peat or coarse river sand.
Seeds
Generally, seed preparation includes calibration, disinfection, pre-germination and hardening.
Calibration
Initially, the seeds are selected by their appearance, removing too thin, insufficiently filled and having mechanical damage. Then they are sorted by soaking in a saline solution. Those that remain at the bottom are suitable for sowing. Seeds that have surfaced are not used, because they have the lowest germination rates.
Disinfection
Treatment of seeds with a weak solution of potassium permanganate increases the resistance of plants to diseases and helps them withstand the attack of pests. Additionally, the seeds can be soaked in a growth stimulant, for example, "Epine", which will increase their germination.
Germination
The seeds selected for sowing are germinated, for which they are placed in water heated to 40-50 ° for 3-4 hours. Then they are wrapped in a moistened cloth and left to peck, preventing it from drying out.
Hardening
Tempering helps to increase the resistance of future sprouts to temperature changes. For this purpose, the seeds are kept in a damp cloth in a refrigerator at a temperature of 4 ° C for 3-5 days.
Description
Pumpkin is an annual plant with large fruits that is grown both commercially in the field and in summer cottages. In cooking, the pulp of the vegetable and the seeds inside are used. It is not only tasty, but also a healthy plant that is used for medicinal purposes. The fruits are notable for keeping quality and are very well stored until spring, without losing their healing properties.
The pumpkin has a powerful above-ground root system and a hairy stem creeping along the ground, reaching a length of 4 - 5 m, on which large, tough leaves are located. During the flowering period, large single flowers of white or yellow color are formed on the plant. Cross-pollination is characteristic of the pumpkin. Most varieties have fruits weighing 5-10 kg, large-fruited pumpkins weigh from 40 to 80 kg. Inside the fruit are seeds in the form of large white-yellow seeds.
How to plant a pumpkin: site preparation
If you are interested in the richest harvest, then you need to choose the right place for planting. The ridge should be located in a warm place on the sunny side. The soil can be any, but sandy or sandy loam is preferable, such a soil warms up better. It is best to plant after winter wheat, corn, or perennial grasses. You can also pick up ridges after tomato, onion, potato, cabbage or carrot. It is not recommended to plant after cucumbers or squash. You cannot plant in the same place, you need to wait 5 years after the previous planting.
Selection and preparation of a place, soil
The pumpkin grows in the form of a large bush, and most varieties also form long lashes, which spread in all directions for 2-3 meters or more. Therefore, it is problematic to allocate a good plot for her in a small summer cottage, and the owners have to be cunning, allocating a dwelling for pumpkins in old barrels, large bags or on compost heaps. If it is planted on ordinary beds, they often provide for a "second floor" for the arrangement of lashes and fruits in the form of sheds or decking over the beds, so that a place for planting other vegetables can be allocated nearby.
Since the pumpkin, like a cucumber, loves to climb any vertical obstacle, it is often planted next to a fence. If she on her own refuses to put whips on him, she just needs a little help, and then the growing fruits will hang on the fence, like toys on a Christmas tree. True, so that they do not fall, the fruits will also have to be firmly tied to the support. And since the average family needs to plant only 3-4 plants for year-round consumption, the problem of space for pumpkins with such approaches becomes not very significant.
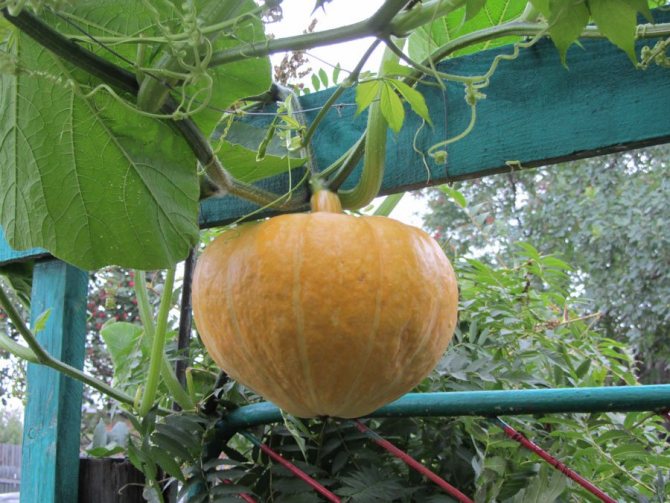


Pumpkins love to grow on various supports: both naturally occurring and specially built for them
When choosing the location of the garden, it is important to ensure that it is well lit by the sun's rays: in partial shade, the plants feel worse. But the composition of the soil is of great importance: pumpkins take out a large amount of nutrients from the ground, and without high-quality fertilizers, the harvest will be scarce. True, for one plant, only about 1 m2 of a well-fertilized area is required, therefore this issue is completely resolved.
The best soil composition is light sandy loam of dark color with acidity close to neutral (pH of soil extract 6.5–7.0). The pumpkin should not be planted after any related crops (squash, squash, cucumber).If a pumpkin is planted on a flat horizontal surface or a low bed, you can not carry out a continuous digging of the site, but only dig up and fertilize the wells well in the places designated for sowing. True, these holes will be more like planting holes: each plant must be provided with an almost full bucket of humus and a half-liter jar of wood ash. Mineral fertilizers are best applied during feeding.
Often, pumpkin is planted directly on compost heaps, even not yet fully ripe, or large pits or trenches (up to half a meter deep) are specially prepared for it, which are filled with various garbage and waste (small branches, grass, tops, manure), mixing them with the ground ... In the spring, these pits are watered with warm water with a small addition of saltpeter (up to 20 g / m2), and by the time of sowing the seeds they warm up well due to rotting organic matter.
Video: sowing pumpkin by the fence
Useful properties of pumpkin
Regular consumption of pumpkin helps to prevent diseases of the cardiovascular system, kidneys, liver, atherosclerosis, anemia, oncology, diabetes, hypertension. The carotene contained in the pulp of the fruit improves metabolism, contributing to the growth of the body, increasing the body's resistance to infections. The beta-carotene contained in fruits has anticarcinogenic properties. The dose of beta-carotene consumption for prophylactic purposes is 20 mg per day.
The biological significance of pectins is manifested in their ability to bind radioactive particles, heavy metals and remove them from the body. Fiber has a beneficial effect on the work of the intestines, removes cholesterol from the body.
Pumpkin seeds also have healing properties. Useful properties of which are the presence in pumpkin seed oil of such important acids as palmetic, steoric, oleic, linoleic. The content of tocopherols (vitamin E) in 100 g of oil is about 150 mg.
With atherosclerosis, diseases of the liver, kidneys, gallbladder, gout, it is recommended to drink 1/3 cup of fresh juice 2-3 times a day. A decoction of pumpkin stalks is a good diuretic.
The ripening time of the vegetable and its collection


Harvest before the first frost
The ripening period of the pumpkin depends on the climatic conditions of the region. In latitudes with a temperate climate, this is approximately the first days of October, in the south - early September. The main reference point for harvesting is the drying stalk, which acquires a grayish color. The collection must be carried out in dry, not cloudy weather.
In hard-bore varieties of garden pumpkin, with full ripening of the fruit, the pattern on the peel changes. To check maturity, press on the crusts with your finger, and if they do not squeeze, then you can remove. Also, when tapping, a ringing sound should be heard.
You can remove large-fruited fruits a little ahead of time and place in a cool and well-ventilated room, then they will ripen in a couple of weeks. The main thing is that there is no damage on the surface.
If we talk about the ripening time, then it occurs 85-120 days after the appearance of the first shoots. Ripe vegetables should have a bright orange color and matte bloom, and the tops by this time turn yellow and dry out.
In order not to damage the fruit, cut the stalk carefully. If chips and scratches are found on the barrels, it is necessary to treat with brilliant green and seal the defects with adhesive plaster so that the infection does not penetrate inside.
back to menu ↑
See also: Pepper: description, growing from seeds, planting in open ground and care + Reviews
Pumpkin pests and ways to fight
The main pests of all melons and gourds:
- melon aphid;
- bear;
- slugs.
The melon aphid is a small insect that damages the aboveground part of the plant. The insect sucks juice from shoots and flowers. Leaves wrinkle, ovaries crumble. Soap solution works well against aphids.Stir 100 g of laundry soap grated on a coarse grater in a bucket of warm water and spray the plants.
Medvedka makes moves in the soil and gnaws at the stems and roots of plants. When planting, you need to put several granules of Medvedox into each well. You can put boiled grain mixed with Bankol into the holes.
Slugs cause significant harm in the main young plants. Their invasion during the rainy season is massive. Several generations of slugs develop during the season. If there are a lot of slugs on the site, then wet rags are laid out and insects are robbed from them every morning.
Fertilizers for pumpkin when planting
In terms of soil nutrient requirements, pumpkin is very similar to cucumbers. The pumpkin feels great on a heap of ready-made compost, where various waste was dumped last season, as well as in places where manure used to lie.
You can grow pumpkins in specially prepared trenches, covered with chopped branches, green or dry grass, manure, various household waste, which are mixed with the ground and a layer of fertile soil is poured on top. The depth and width of the trench is up to half a meter.
The greatest effect is obtained with the combined use of organo-mineral fertilizers per 1 m2: for digging 4–5 kg of manure and for top dressing (when 5–6 leaves appear) 20 g of ammonium nitrate, 30 g of superphosphate and 15 g of potassium chloride. Nitrogen fertilizers (nitrate, urea) can also be applied during spring loosening of the beds.
Pumpkin pests or diseases
Pumpkin can contract fungal diseases with black mold, powdery mildew, rot, ascochitosis and anthracnose.
Black mold is manifested by yellow-brown spots between the veins of the leaves, which, with the course of the disease, become covered with a dark coating with fungal spores. After the spots dry up, holes form in their place. Young pumpkins shrivel and stop developing.
With ascochitosis, large yellow-brown spots are first formed on the leaves, stems and in the nodes of the shoots, then light spots with a chlorotic edge, covered with black pycnidia containing the body of the pathogenic fungus. The pumpkin dries up and dies.
Powdery mildew is a real scourge of gardens and vegetable gardens, the symptoms of which look like a thick whitish coating, similar to spilled flour, which contains fungal spores. Leaves affected by powdery mildew dry, the fruits are deformed and stop developing. This disease is most active in conditions of sharp fluctuations in air humidity and temperature.
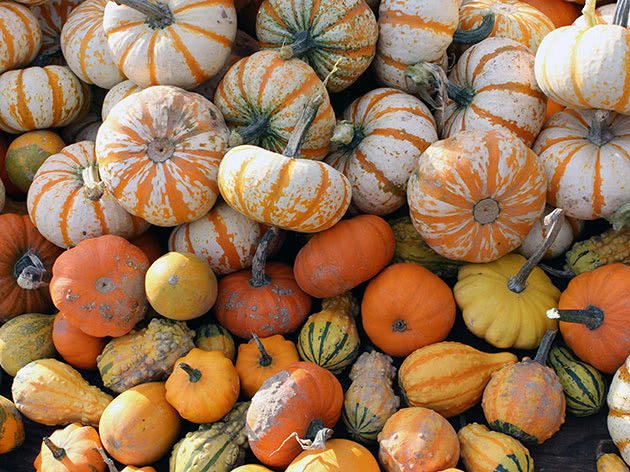


Anthracnose appears as large, watery, yellowish spots on the leaves. In wet weather, the veins of the leaves are covered with a pink bloom. Gradually, pink spots spread over the leaves, petioles, stems and fruits; by autumn, the affected areas turn black. Anthracnose is most dangerous at high humidity.
White rot develops on all parts of the plant, causing damage to the root system, drying out of fruiting stems and a decrease in yield. The pumpkin turns yellow, turns brown, becomes covered with a flocculent mold. Mucus may appear on the stems. Gray rot is manifested by brown blurry spots that quickly merge with each other and affect the entire plant. Wet bacterial rot can appear as a result of slugs or sucker damage to ovaries and young fruits in too dense plantings.
Of insects, pumpkin is affected by melon aphids, podura, or white springtails, wireworms and slugs.
- Savoy cabbage: outdoor cultivation, planting and care
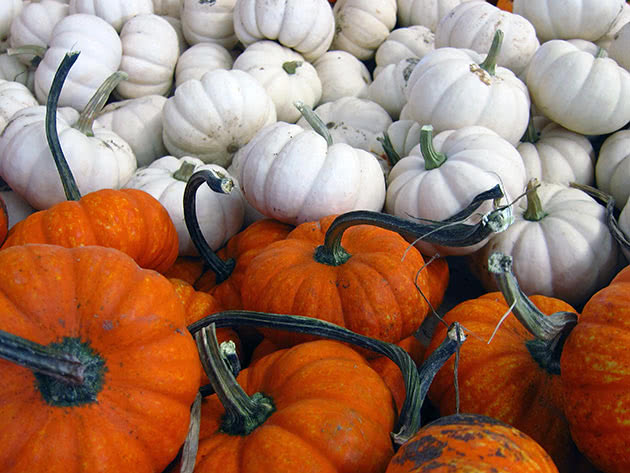


Slugs eat up the leaves of plants, sometimes leaving only a net of veins from them. There are especially many of them during rainy seasons. In addition, they are able to live and harm plants for several years.
The melon aphid damages the shoots, flowers, ovaries and the underside of the leaves, from which they curl and shrivel.
Podura are the smallest white insects with a cylindrical body up to 2 mm long, feeding on seeds and underground parts of plants.The greatest harm podura bring to plants in cold, wet weather.
Wireworms are the larvae of click beetles that gnaw at the root collar of young seedlings, which leads to the death of plants. Most of all, wireworms like to congregate in wet lowlands.
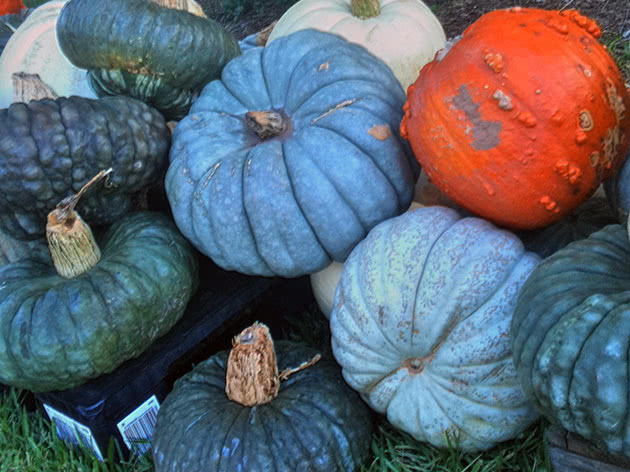


Pumpkin processing
The fight against pumpkin diseases is carried out in fact and prophylactically, which is undoubtedly preferable, since the disease is much easier to prevent than to cure. To protect the pumpkin melon from fungal diseases, it is necessary to observe crop rotation, fulfill agrotechnical requirements, take a responsible attitude to each type of work, and especially to pre-sowing seed treatment. At the first sign of illness, spray the plants and area with 1% Bordeaux liquid or other fungicide. And try to make the spring and autumn processing of melons with Fitosporin mandatory - this will help you avoid many unpleasant surprises.
Slugs will have to be collected by hand or set up beer traps for them: place bowls with beer on the site and from time to time collect shellfish that have crawled onto its smell. Wireworms are also caught with bait, digging holes 50 cm deep in different places around the site, placing roots cut into pieces - carrots or beets - and covering the holes with boards, wooden boards or roofing felt. After a while, the traps are checked and the wireworms gathered there are destroyed. They fight fools by dusting the soil around the plants with wood ash. Aphids are destroyed with Phosphamide, Karbofos or a solution of 300 g of soap in 10 liters of water.
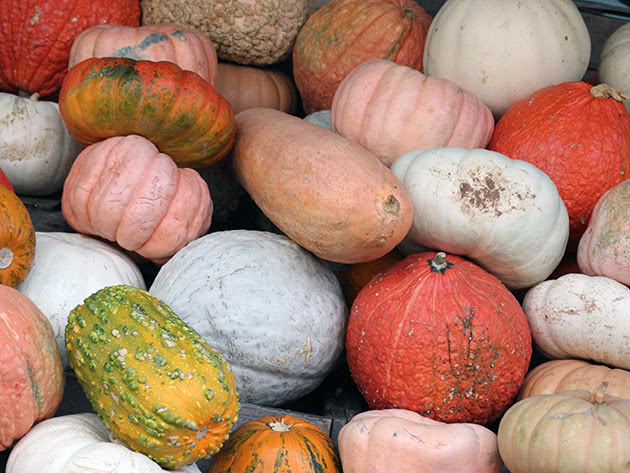


And yet, let us remind you that diseases and pests, as a rule, affect weak and unkempt plants, so observe crop rotation, follow agrotechnical requirements, take good care of your plants, and you will not have to heal and save them.
Follow-up care


Pumpkin especially needs moisture during flowering
Caring for a pumpkin is easy, since it is an unpretentious plant. The vegetable does not belong to particularly moisture-loving representatives, despite the voluminous leaves, due to which intensive evaporation of moisture occurs.
Moisture reserves are found in fleshy stems and cuttings, which allows the plant to survive dry periods safely. With abundant watering, the vegetative component begins to rot and is more susceptible to fungal attack.
In drought and during active growth, the pumpkin is watered every day in the evenings. During the ripening of the fruit, watering is reduced so that the vegetable does not grow watery. It is better to underfill than to overfill - this is the basic rule.
Pumpkin is especially prone to organic feeding. Therefore, it is recommended to make them, both before and after planting. The following options will work:
- real manure
- chicken droppings
- vegetable compost
- humus
- potassium humate
Of the mineral compositions, preference is given to those in which potassium, phosphorus and nitrogen are present in the composition. In the absence of such, potassium salt, ammonium nitrate and nitrophoska are suitable. And you can also add wood ash to the soil.
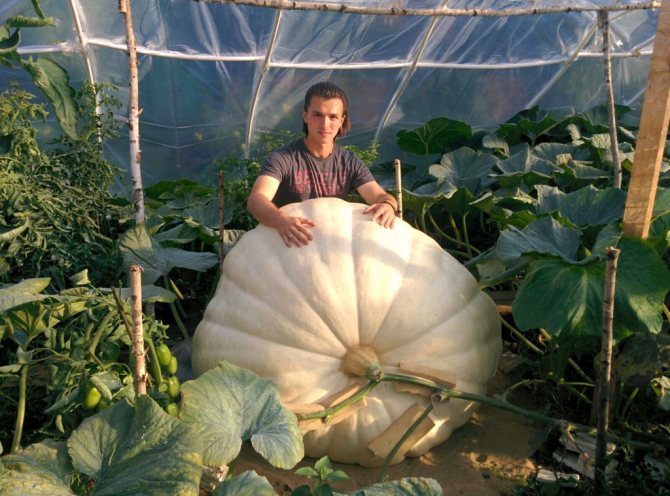


Miracle pumpkin
In early spring, you can plant on the site for planting siderat pumpkin. Until the end of May, they will have time to build up a rich green mass, which, when mowed, is slightly sunk into the soil. This will further serve as an ideal fertilizer for the pumpkin.
When full-fledged 2-3 leaves appear on young seedlings, thinning of the plantings should be done. The peculiarities of growing large-fruited pumpkin are that only 1 sprout is left in the garden. When nutmeg or hard-barked variety, 2 seedlings are left.
Pumpkin needs more than watering. Loosening, mulching, removing weeds, weeding are additional activities. Similar actions are carried out after setting the first fruits, but no later than the beginning of August.
It is necessary to loosen as the weeds grow. Sawdust or peat is suitable as mulch. For better formation of adventitious roots, plants are spud with moistened earth.
You should also pinch the side shoots and the central stem. There are two ways to form a bush:
- in one stem - extra ovaries should be removed, leaving only 3 on the bush, on which there are 3-4 leaves
- in two stems - it is necessary to cut off the tops of the shoots so that 2 fruits remain on the center, and one on the side
In wet weather, boards are placed under the pumpkins, so they don't start to rot.
back to menu ↑
See also: Zucchini: diet vegetables of the pumpkin family. Planting seeds in open ground and care, growing seedlings (15 Photos & Videos) + Reviews
The best option for pumpkin is to plant seeds for seedlings
Today even southerners complain about the delay in spring and the quickness of autumn. The cold weather suddenly returns, and the vegetable garden, which has been crumpled in the sun, mercilessly crushes the frost. That is why gardeners began to plant not seeds on the beds, but seedlings grown in home heat, waiting for the time of frost to pass.
Pumpkin is a healthy, tasty plant, but very thermophilic. The optimum average daily temperature for plant well-being is 20–23 ° С, the lower limit is 16 ° С. If the thermometer drops to 14 ° C, the pumpkin will stop growing. So seedling is the best option for her.


Pumpkin is a very beautiful vegetable and, most importantly, healthy
In addition to those intended for food purposes, there is a large detachment of decorative pumpkins. In shape, they are warty, pear-shaped with a two-tone color; turban-like with a red cap, there are pumpkins, the shape and color of tangerines. Nature has worked especially well on the coloring of the two-tone species: various fringes, stripes, droplets, lines that are in very good harmony with each other. The fruits of the decorative pumpkin are not very edible, but they are very beautiful and varied, they are happily grown in flower beds.
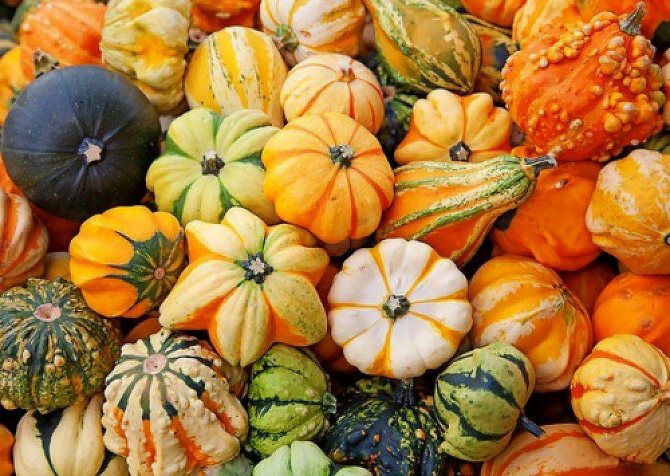


Varieties of decorative pumpkin are characterized by extremely diverse shapes, colors and textures, the effectiveness of which is emphasized by the miniature size.
How to calculate sowing time
Pumpkin seedlings, the age of which has exceeded 30 days, take root in the garden bed, so the germinated seeds are placed in the soil about 25 days before planting in the ground. In the middle and central zone, favorable weather for this is usually established in mid-May, in Siberia - not earlier than the end of the first decade of June.
Containers and soil for planting seedlings
If the seedlings will be grown in soil purchased in a store, then it is recommended to give preference to the soil for melons, which will suit the pumpkin much better than the universal one. You can prepare the mixture yourself by combining one part of rotted sawdust and leaf humus with two parts of peat.
If seeds for seedlings are planted in a common box, then often sawdust is simply spread four centimeters thick directly to the bottom, and a layer of 8 cm is poured on top of the remaining ingredients. Accordingly, the depth of the seedling box should be at least 14-16 cm.
It is a good idea to leave a margin for sprinkling the stems, which grow very intensively and often stretch out, while the sprinkling allows them to grow stronger.
Pumpkin seedlings do not like transplanting very much, therefore they never dive, and when sowing seeds, it must be borne in mind that it is in this container and in this soil that shoots will develop within four weeks.


Peat pots - ideal containers for growing pumpkin seedlings
Of course, it is best to sow pumpkin seeds right away in separate cups, peat tablets or pots.... The volume of the container should be about 10 cm3. When placing seedlings in a common box, it is necessary to adhere to a sowing pattern of about 15x15 cm so that the grown plants do not crowd each other.
Video: how to plant pumpkin seeds in peat cassettes
Growing seedlings
Pumpkin seedlings are planted in late April - early May, when the air temperature exceeds +10 degrees.Transplanting seedlings into open ground is carried out 20 - 25 days after sowing. Seedlings older than 30 days do not take root well in the open field. You can sow pumpkin at home, as well as in greenhouses and hotbeds.
Before sowing, the seed is germinated by soaking it in water for several hours, and then placing it in a damp cloth until sprouts appear. Seeds are planted in pre-prepared soil, the same as for planting ornamental varieties.
It is worth noting that the culture does not tolerate transplantation. Experienced gardeners recommend planting seedlings in peat pots or tablets so as not to injure the root system by removing the seedlings from the pot.
If sowing is carried out in boxes, the distance between the seeds should be 10 - 12 cm. The close placement of seedlings helps to stretch the stems. If the plant is elongated, the stem is rolled up into a ring and covered with wet soil. After a while, the pumpkin will form lateral roots.
For the first few days, containers with pumpkin seedlings are kept at a temperature of + 20 ... + 22 degrees in the daytime and + 15 ... + 18 degrees at night. Then the daytime temperature is reduced to +18 degrees, and the nighttime temperature to + 12 ... + 13 degrees. After 7 to 10 days, the plant is returned to its original temperature conditions.
A week after the emergence of seedlings, the seedlings are fertilized with nitrogen fertilizers. When 3 - 4 true leaves are formed on the plant, you can transplant it into open ground. A few days before the procedure, the seedlings are fed with nitrophos. Watering is stopped 7 days before transplanting.
Planting seedlings allows you to grow healthy and strong plants from which you can harvest a rich harvest in the fall.
Breeding conditions
The heat-loving pumpkin has a powerful root system and a long stem that grows up to 7 m.Nourishment occurs through a branched root system, in which the central root grows to a depth of 6-7 m, and the lateral ones - up to 3-4 m. the structure is five-toed, bright green. The fruits form on the main stem.
The rules that must be observed when choosing the conditions for growing it depend on these features of a vegetable crop:
- temperature. Sown pumpkin seeds germinate in 2-3 days at a temperature of 30 ° C, germinate for a long time at 20 ° C and do not germinate at 10 ° C or lower. The optimal mode for further cultivation is 25 ° С during the day and up to 13 ° С at night. At this temperature, the vegetable crop quickly grows foliage, the area of which sometimes reaches 40 m², and intensively forms large fruits;
- humidity. In addition to warmth, pumpkin long roots require increased moisture, especially during the flowering stage. Properly organized watering is important here;
- lighting. A heat-loving vegetable crop requires a lot of sunlight, so the place for planting it must be chosen so that the sun gets there for 6 hours or more. It is better to plant the plant so that from the north it is protected from cold winds by a fence (fence, building wall, etc.). As the pumpkin grows, it will be able to act as a support for the whips;
- priming. A powerful root system is responsible for plant nutrition and does its job well in loose and fertile soils. A vegetable crop does not bear fruit well on heavy clayey soils, especially with a high level of groundwater, which soak its roots. Slightly acidic and slightly alkaline soils are acceptable;
- "Predecessors". Plant pumpkin well after beans, onions, cabbage and garlic. Vegetable crops grow and bear fruit poorly after carrots and tomatoes. You can grow corn, beets, beans and radishes in the neighborhood. Potatoes, cucumbers and salad greens do not affect the development of the vegetable in any way.
How to grow a large pumpkin?
Gardeners make several mistakes, believing that a vegetable can grow anywhere. Yes, it grows everywhere, but only tops.The pumpkin does not like the shade, because there the fruits grow smaller, and the taste is worse. Try to plant the same variety in the sun, in many cases you simply won't recognize it.
- Some novice gardeners begin to feed seedlings intensively with nitrogen fertilizers, rejoicing that the lashes are beginning to grow actively. But this is not entirely good, since burdock leaves begin to grow, and very few fruit ovaries are formed. The plant needs fertilizing only at first. We saw that the plant started and began to grow, no more fertilizing is carried out. Carry out the first feeding with herbal infusion, it will play its role and the pumpkin will have enough nutrition.
- For a vegetable to be tasty, it needs potassium. Make an infusion of wood ash (1-2 glasses of ash for 1 bucket) and pour the plant under the root. Or use potassium fertilizers - potassium humate, or potassium sulfate.
- When the fruits begin to grow, put a plank, a piece of plywood, linoleum, etc. under them. This is necessary so that the pumpkin barrel, which is closer to the ground, does not rot.
- The culture is grown by direct sowing of seeds in open ground, or by planting seedlings. The pumpkin prefers open, sunny places, since in insufficient light, the number of ovaries decreases, the lashes are stretched. In addition, the risk of fungal diseases and pest attacks increases. Adequate lighting contributes to more female flowers formation, and therefore a larger harvest. The duration of daylight hours during the period of active growth should be at least 10-12 hours.


Site preparation
Pumpkin loves fertile land very much. It grows poorly on clay soil. Sand is better for her, it can be brought to fertility with top dressing, and the vegetable will eat well. The plant does not like damp and moist soil, because the clay does not heat up well. If the roots are warm, then the plant itself grows better. Therefore, experienced gardeners advise planting it on raised beds or compost heaps. Make warm beds and plant her seeds there.
The best predecessors are cruciferous vegetables, legumes, and onions. It is best to plant a pumpkin in the previous place where it was previously grown not earlier than after 3-4 years.
The site is prepared in advance in the fall, organic, mineral fertilizers are applied (humus with peat or nitroamofosku) and carefully dug up. Before winter, the site is planted with green manure, which will help to further improve the fertility of the soil. In the spring, 2-3 days before planting seeds or seedlings, the bed is again dug up and loosened.


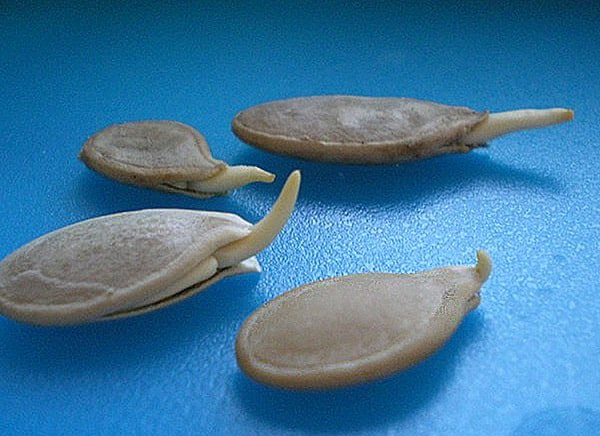
Germinating seeds
Do not buy seeds based only on the picture (orange, gray, etc.), do not try to buy only the largest varieties of seeds. But think, why do you need such large pumpkins? Cut it, you won't use it all at once, how to store the rest? Of course, you can freeze it. Opt for medium-sized seeds. This fruit can be consumed in its entirety, and such small pumpkins are usually tastier.
Before germinating seeds, test them for germination. In order for the seeds to sprout faster, they are pre-soaked. Place the cloth, folded in half, on a saucer, place the seeds between the layers, and dampen the cloth moderately with warm water. Leave for 2-3 days at a temperature of + 20-22 ° C, so that the seeds hatch. It is advisable to plant the hatched seeds in the ground immediately. If you can't plant them right away, put them in the refrigerator with a rag to slow down further germination, and in addition, the seeds will be hardened. Do not try to germinate the seeds too much, as seeds with long sprouts are easily injured when planting, leading to later germination.
Wanting to get an earlier harvest, the pumpkin is planted in open ground with seedlings. How to do it correctly, I will tell you a little later in the article.


How to plant a pumpkin correctly
If you are looking for a good harvest, you need to choose full-weight seeds.To select the best seeds, salted water is prepared, into which the seed is lowered, the floating seeds are rejected. The rest are collected, washed and dried.


Pumpkin seeds can be stored for up to four years
Duration of storage of seeds is up to 4 years. For a better germination and a healthy harvest, it is necessary to carry out preparatory measures:
- Warming up... This process will give good shoots, it is done at 60 degrees, within 2-3 hours.
- Hardening... The plant must withstand temperature extremes; for this, the seeds are kept at a temperature of +1 degrees for two days.
- Increasing disease resistance... Diseases can damage the shoots that have not yet matured, and to prevent this from happening, the seeds are treated with a solution of potassium permanganate, potassium kumate or wood ash infused in water.
- Germinating seeds... To do this, they are wrapped in damp gauze, after a couple of days the first sprouts will appear.
Selection of the type and variety of pumpkin
When choosing pumpkin seeds, do not pay attention to the picture on the package. The orange and smooth-looking fruit is not necessarily the best and necessarily sweet. Also, do not choose the largest varieties. This is due to the fact that the whole fruit at once is difficult to use somewhere, and after you cut it, there will be a problem with its storage... In addition, small pumpkin varieties are better stored and usually have a sweeter taste.
In general, pumpkins are of the following types and varieties:
- large-fruited (Gribovskaya winter, Khutoryanka, Sweet pie);


- firm or ordinary (Spaghetti, Shrub orange, Golosemyanka, Altai);


- nutmeg (Pearl, Guitar, Cello, Provencal).
The most delicious are nutmeg varieties, but they are the most thermophilic late-ripening varieties. Also hard-barked have excellent taste, they have the earliest ripening period. Large-fruited varieties are also very sweet and cold-resistant.
Video: the best pumpkin varieties
The most famous varieties
In the suburbs and the Leningrad region:
- Table pumpkin variety Premiere. It is resistant to cold weather, characterized by an elongated branched lash, sugar-rich and rather bulky fruits, reaching a weight of 6 kg. The yield does not depend on the fertility of the soil and its type.
- Dachnaya pumpkin variety. Early maturing, ripening period - 80 days. This variety has a characteristic pleasant sweet taste with pronounced vanilla notes. The weight of a mature fruit is 3-4 kg. The harvest is stored for at least 4 months. It is possible to grow table pumpkin in the open field
In the Urals:
- Russian woman. Cold-resistant variety, not susceptible to diseases of horticultural crops. The pulp is prized in cooking for its juiciness and sugar flavor. The weight of a mature pumpkin is about 3-4 kg. The crop ripens in about 120 days. The vegetables are colored in a pronounced orange color - this is the main feature of the variety.
- Butternut pumpkin Pearl. The ripening period of nutmeg gourds will be 100 days, the mass of fruits reaches 5-7 kg. The taste is distinguished by pronounced notes of nutmeg. This variety reacts perfectly to cold weather, absence and, on the contrary, abundance of precipitation, resistant to various diseases.


Butternut Pumpkin Pearl
Varieties for growing in Siberia:
- Freckle. The growing season for this variety is 80 days. The pulp of the fruit tastes like a melon, juicy and sweet. The crispy structure of the flesh remains even after cooking. Pumpkin weight - no more than 3 kg.
- Smile. This variety is bushy, resistant to sudden temperature changes, frost-resistant, tolerates high humidity well. A distinctive feature is a long shelf life, at least one year, as well as excellent taste. The growing season is about 100 days, vegetables reach a weight of 2-3 kg.
How to properly grow and care for a pumpkin
Caring for a pumpkin during cultivation primarily consists in the correct formation of the plant. The main stem is usually pinched (pinched) when it reaches 1.3 - 1.5 m in length.And leave 2 lateral shoots 60-70 cm long. On each shoot, 1 fruit is formed. Thus, one plant will have 3 fruits, one on the main one, and two on the side ones. Excess shoots are removed to speed up the pouring of the fruit.
The left shoots can be pressed to the ground with a small spear made of wood or wire and sprinkled with a layer of earth 6-7 cm. So that the fruit does not rot during growth, a plank is placed under it.
Pumpkin needs additional feeding if it does not initially grow in fertile soil. Top dressing is carried out every 15 days. Prepare a solution: dilute 1 liter of mullein and 2 tbsp. l. nitrophosphate. Consumption consumption - 3 buckets for 2 bushes.
During the growth period, the plant is watered abundantly once a week at the rate of 20-30 liters of water per plant.


Problems of growing pumpkin seedlings
Beginners in growing pumpkin seedlings can face problems that can negate all their efforts. What dangers can small plants face?
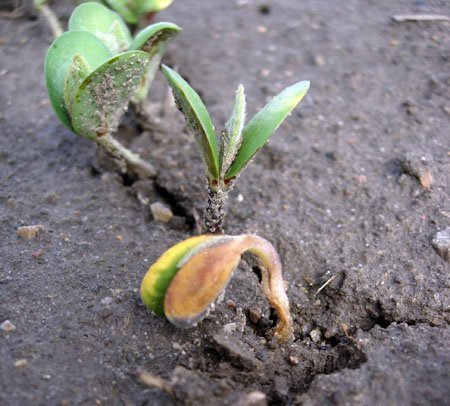
Pulling
The most common problem that can occur with seedlings when grown on a windowsill is stretching. At the very beginning of development, when the shoots have just made their way through the ground and, as if having escaped to freedom, actively went into growth, there is a slight stretching of the shoots, which is easy to eliminate. Elongated plants are poured at the base with earth and, having put down lateral roots, they stop excess growth, get stronger due to the development of the root system.


Elongated pumpkin sprouts are common
The seedlings can stretch out for other reasons, for example, when there is little light, but enough moisture and nutrition. In search of sunlight, the shoots spend all the accumulated nutrients on vertical development and become weak and thin, like blades of grass. These may not take root in the ground, so the lighting must be intense. And if there is not enough natural light, artificial lighting should be provided.
Pumpkin seedlings will also begin to strive upward when the plantings are thickened or receive too much moisture. To prevent this from happening, you must initially follow the recommended seed planting scheme and carefully monitor the correct soil moisture.
Blackleg
It is especially important to observe the irrigation schedule also because their excess entails consequences much more serious than usual stretching - we are talking about a black leg. If the elongated shoot can be, neatly folded into a ring, dug in with earth so that it puts out lateral roots and returns to normal, then the problem with the black leg cannot be corrected so quickly.


The black leg can ruin all the work of the gardener at the very beginning of the journey.
The root collar of the plant becomes brown when infected, the plant tissue rots and the seedlings die, it is almost impossible to stop this process. But not only an excess of moisture in the soil provokes this trouble, often the infected soil becomes the culprit of the disease. This can only be avoided by first disinfecting the soil. Most often it is frozen on the balcony or calcined in the oven..
Having laid out the soil mixture on a baking sheet, set the temperature in the oven to 200 degrees and ignite the soil for two to three hours
If it is enough to heat the ground for two hours, then it needs to be frozen for about two months, which means that you have to take care of this in advance. The soil thaws after freezing at room temperature for about a week, then on the day of planting it is spilled with a hot solution of light crimson potassium permanganate.
Landing patterns
The root system of all types of pumpkins is well developed, penetrates to a depth of 1.5 m. Nevertheless, it requires a lot of space: the pumpkin spreads roots not only deep into the ground, but also to the sides, and the growing lashes reach a length of several meters.
Pumpkin feeding areas are perhaps the largest of the well-known gardeners.The following planting patterns are recommended: 2 x 1 m, one plant per hole, or 3 x 2 m, two plants per nest.

If there is space, you can plant pumpkins along the path, and lay out the whips in directions from it.
Conditions
The plant is considered thermophilic, but does not impose special requirements, although it loves moist soil during flowering. This is due to the fact that during this period the root system begins to develop, which needs to get stronger. If there is not enough moisture, the ovaries will fall off.
As a "sunny" crop, pumpkin requires ample light. It does not tolerate strong winds and cold, so there should be a fence / building from the northern part of the garden.
Lighting
It is advisable to plant a crop in areas open to sunlight. This is almost the only plant that easily tolerates exposure to direct sunlight, and for 6-8 hours. Despite this, insignificant shading is acceptable, so many gardeners compact crops with corn.
Temperature
The pumpkin loves warmth, therefore, the optimal temperature can be considered as +25 degrees. Features:
- if the temperature drops below + 8-10 degrees, the seeds do not germinate;
- at a temperature of + 15-20, germination is slow;
- at a temperature of + 25-30 degrees, the seeds hatch in a couple of days.
Soil requirements
Soil for pumpkin crops should be saturated with humus, which will allow you to get tasty and aromatic fruits of high yields. It is advisable to drain the land and fertilize with compost. pH acidity should be 6-6.5. The upper soil layers should not be soaked, and groundwater can pass through the lower soil layers.
If we talk about crop rotation, then the best predecessors are beans, cabbage (necessarily early) cabbage, onions, garlic. It is undesirable to plant pumpkin after tomatoes, carrots and cabbage of late varieties. Beets, herbs, cucumber are considered neutral. Pumpkin can be adjacent to beans, radishes, beets, corn. It is forbidden to plant next to potatoes and tomatoes.
Home care
Seedlings that appear at home require follow-up care. Containers with seedlings are kept at a temperature of + 20 ... + 22 degrees during the day and + 15 ... + 18 degrees at night.
Pumpkin is a fairly light-loving plant, so it is better to place seedlings near windows on the south or southeast side. In this case, additional lighting is not required.
Do not expose the pots in direct sunlight so that fragile seedlings do not get burned and burn out. If it is too hot on the windowsill or the window panes heat up under the influence of the sun, it is better to place the containers on the table next to the window.
Watering
Watering the culture must be carried out competently, avoiding both stagnant water and drying out of the soil. Excessive watering can lead to rotting of seeds and the root system of plants, from an excess of moisture, seedlings can stretch out, which will affect their stability and subsequent fruiting. The plant should be irrigated as the soil dries out. When the soil in the pot has dried out to a depth of 1 - 2 cm, you can water it.
You can check the dryness of the soil with your finger or a wooden stick, deepening it to the desired depth. It is advisable to water in the morning or evening.
Water for irrigation should be separated, at room temperature. Heavy metals in tap water are detrimental to plant health.
The first feeding of decorative pumpkin is carried out a week after the emergence of shoots. For these purposes, nitrogen fertilizers or a complex of fertilizers for indoor plants containing nitrogen are used. The second feeding is carried out after 20 - 30 days with complex mineral fertilizers. To speed up growth and fruiting, once a week, you can water the pumpkin with an infusion of chicken droppings or manure.During flowering, fertilizer for flowering plants is introduced along with watering, which can be purchased at a flower shop.
Pollination
For a pumpkin growing at home, pollination must be done independently, since pollinating insects are rare guests on balconies, and even more so in apartments. To carry out the procedure correctly, it is necessary to distinguish between female and male flowers, evenly located on the whip of the plant. Inside the male flower there are long pedicels, and in the female, the rudiments of the ovary are formed.
To carry out pollination, you need to carefully collect the pollen from the male flower with a soft brush and transfer it to the pistil located inside the female flower. The procedure is performed several times to achieve a good result. If the ovary begins to grow in size, then the process went right.
There are more male flowers than female flowers, so the excess must be cut off so that the pumpkin does not waste energy and nutrients on the development of barren flowers.
Pumpkin compatibility with other plants when planting
If we talk about what can be planted next to the pumpkin, first of all we must think that it does not drown out its neighbors: the bushes of the pumpkin are huge, and the whips stretch far. Therefore, if, for example, she climbs into a garden with carrots, you will not have to expect any harvest of carrots. Therefore, the question of neighbors should be asked to yourself only after it becomes clear which area will limit the distribution of pumpkin lashes.
From a biological point of view, anything can grow next to a pumpkin patch: it, except for its geometry, does not interfere with anything or anything.
Pumpkin feels very good near corn, beans, onions, various salads. It is undesirable to plant it not far from the cabbage. Sometimes you can read that potatoes are also an undesirable neighbor, but the practice of planting pumpkins in potato fields has long been known, and both plants coexist normally. Although, perhaps, in this matter it is better to listen to agronomists and limit the possibility of such a neighborhood.
Pumpkin can be grown both by sowing seeds in a garden bed, and by pre-preparing seedlings. Options are selected based on the climate of the region, pumpkin variety and gardener preferences. In any case, pumpkin is an unpretentious vegetable, and, besides good doses of fertilizers, it does not require anything special, and the planting process itself will not complicate the most unskilled gardener.























