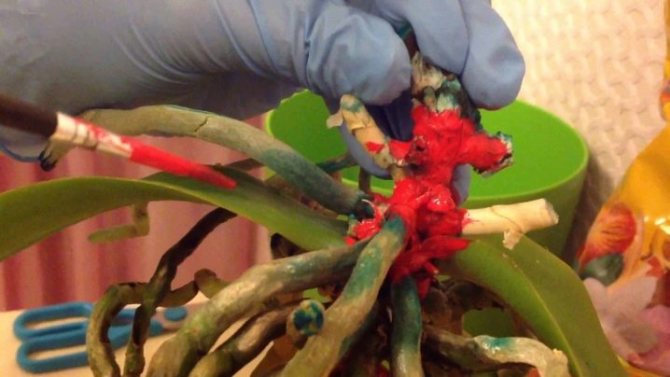
Orchids are beautiful tropical epiphytes common among many flower growers. However, these plants are extremely demanding for care, without which they quickly die. The fact that the flower does not feel well is evidenced by the lack of budding or the fall of not yet blossoming buds, sluggish, withered leaves, instability of the trunk in the pot.
To save the orchid from decay, urgent measures must be taken.
Growing an orchid. Illustration for this article is used under a standard license <179
Why does an orchid rot?
Putrefactive processes in any part of the plant are mainly associated with high and prolonged humidity at low ambient temperatures... This is especially true for inexperienced florists.
Without experience, without knowing the physiological characteristics of tropical orchids, they take too much care of their pets, not realizing that they are only harming the plant.
The reasons
The main reasonswhy does an orchid rot when grown at home, are:
- excessive watering;
- poor quality soil;
- Greenhouse effect;
- sunburn;
- hypothermia;
- organic fertilizers;
- oversupply of fertilizers;
- weakened plant;
- pests.

Often the cause of decay is excessive watering.
Which plant organs are under attack?
The most vulnerable part for putrefactive processes is root system... From the overflow, the soil becomes compacted, decomposes, and in the absence of good ventilation, rapidly spreading foci of decay are formed.
The second place belongs to plant leaves... Damage by direct rays of the sun or pests opens the flow of air to the intercellular tissues, where the process of decay begins.
Third place belongs to pith or stem... Inaccurate watering, irrigation or pests quickly enough bring this part to the center of the spread of the fungus.
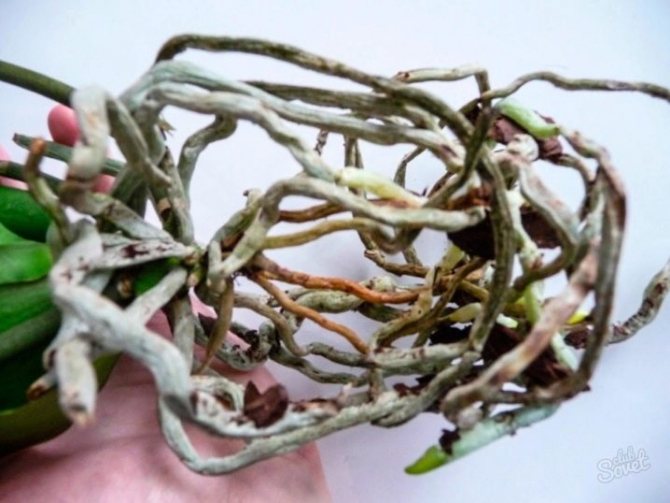
How to recognize root rot
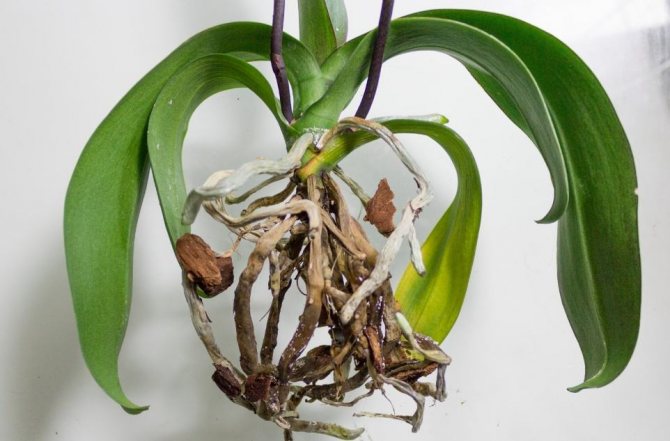
When the root system of an orchid decays, the leaves of the plant droop due to a lack of nutrients. At first, the green part simply withers, even with increased watering, and then completely dies off. The second significant sign is the appearance of a white or green plaque on the ground and containers. This means that there is too much moisture, and the air penetrates into the soil worse.
A flower with decaying roots "sits" loosely in the pot. It can stagger in different directions. In parallel with this, the aerial roots become dry and take on a dark color. Experienced flower growers recommend replanting orchids in a container with transparent walls in order to observe the growth of the plant.
Types of rot
Gray
Fungal disease caused by the fungus Botrytis cinerea. Ideal educational conditions - cold, humid atmosphere with poor air ventilation... Initial appearance on flowers as small brown spots.
With progression spots increase and are framed by a pale pink halo... The final phase of spreading is the merging of the spots into one and the appearance of gray membranous shoots (mycelium) of the fungus.


Gray rot on orchids.
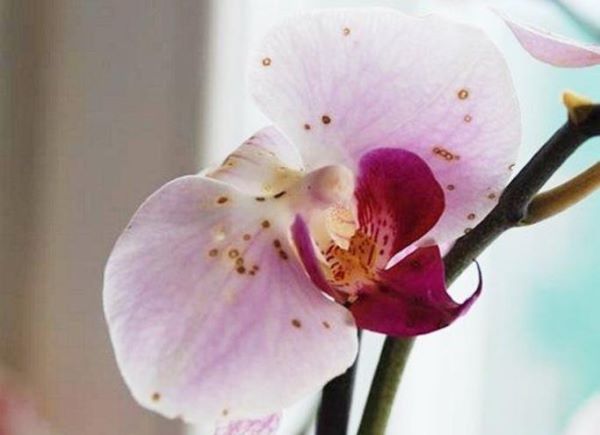


Gray rot on the petals.
An infected plant is capable of releasing spores into the environment under ideal conditions. At a temperature of 18 to 23 ° C and a humidity of at least 90%, the spread of infection to healthy tissues occurs rather quickly - within 12-15 hours. The most susceptible to the fungus are Phalaenopsis and Cattleya.
Attention! In 90% of cases, a weakened plant is affected.
Brown or bacterial rot
The causative agents are bacteria of the Erwinia family, Pseudomonas and others. Most often they are affected young leaves and shoots... Lesions appear wet brown spots, which cover the entire area of the plant part before our eyes. If the stem or growth point is affected by brown rot, it dies.
The action of bacteria progresses if the humidity is above 60%, and the ambient temperature is 15 ° and below.
Susceptible to this type of rot:
- Phalaenopsis;
- Cattleya;
- Cymbidium;
- Paphiopedilum.


Bacterial rot.


Another photo of bact. rot.
With a large lesion, the plants are destroyed. Local, small lesions are cut out to living tissue, and the cut is disinfected with crushed activated carbon. Conditions and care are improved.
For preventive purposes, under favorable conditions for the spread of bacteria, they produce spraying with preparations based on copper.
Black
The causative agents of this fungal disease are soil-dwelling Pitya mushrooms, leading a parasitic lifestyle.
And although the main damage goes to young roots, since they are not yet protected by a reliable coating, when spreading, it goes to all parts of the exotic, regardless of age.
The greatest danger is the formation of foci of rot on the root system and in the bases of tuberidia. The danger lies in the rapid spread of lesions to healthy areas. The roots quickly turn black due to tissue necrosis, and tuberidia are mummified.
The conditions for the spread of black rot are low temperature and high humidity of the environment and soil... Under such conditions, the underground part develops slowly. Some roots do not have enough air in the soil saturated with moisture, and they gradually die off, which contributes to the easy penetration of pathogenic fungi to them.
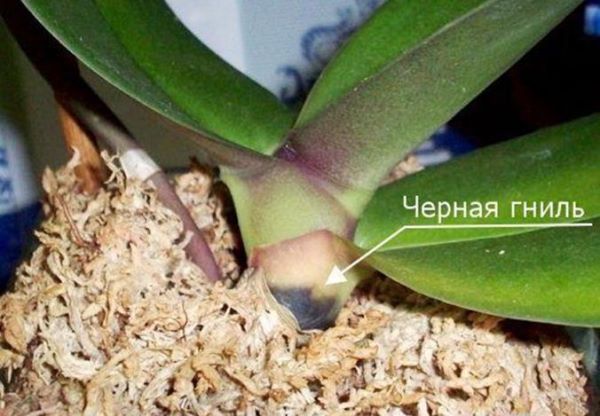


The most accessible types of black rot are orchids such as:
- cattleya;
- stangopea;
- lelia;
- leliokattley;
- papiopedilums, etc.
Even at normal temperature and humidity, fungi do not die.... Propagation processes slow down and proceed much more slowly. Extensive activation of putrefactive processes leads to the death of the tropical beauty.
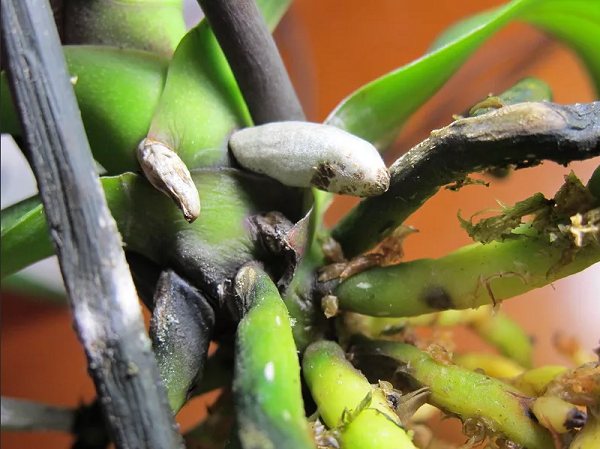


Black rot.
You can save the plant in the initial stages of damage.... Since the development takes place in foci, the optimization of hydration and treatment with copper-containing preparations will not only significantly slow down the process, but in the early stages can heal ocher.
Dry rot
On orchids, according to some sources, dry rot is nothing more than fusarium. But there is another concept of dry rot - this is southern sclerocial rot.
South sclerocial
An infectious disease caused by the fungi Sclerotium rolfsii. It appears on almost all parts, but especially the roots and stem, and at the same time.
Soil fungi that can remain viable for many years. The infection gets not only with poor-quality soil components, but also with water for irrigation.
Ideal distribution conditions are considered temperature 27-33 ° С and high humidity.
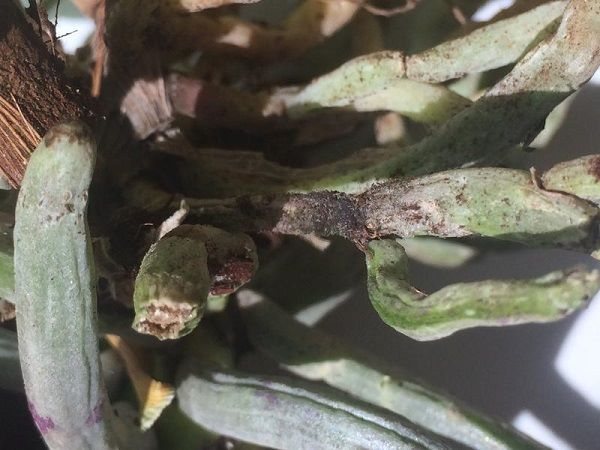


South sclerocial rot.
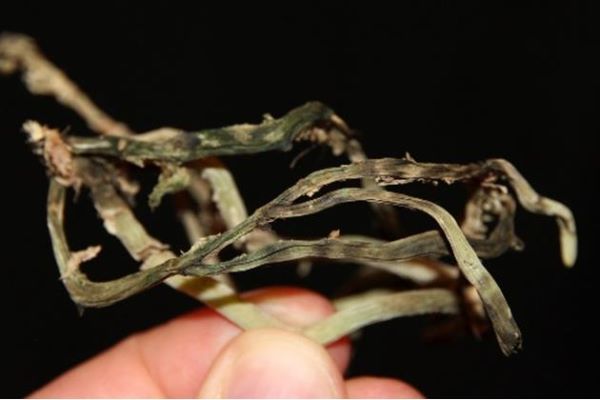


More photos.
Important! At low humidity, the disease multiplies also quickly, differing only in a different development process.
If wet rot is in many ways similar to various kinds of root rot, then dry rot mainly affects orchid plants growing on blocks.
Fusarium
Fungal disease caused by fungi Fusarium moniliforme var. Lactis. Spotting on yellowed leaves and curling - the main symptom of fusarium. The tissues of the leaf plate lose their structure, soften and become covered with a whitish-pink bloom formed by the spores of the fungus.
The orchid quickly takes on a nondescript gray appearance. Rotting occurs with the central shoot and subsequently dies off.
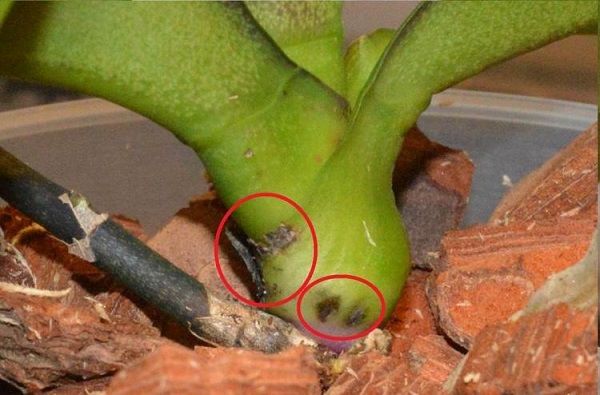

Fusarium.


It is quite difficult and long-term to fight the disease. 7-10 days, he repeatedly per day is subject by treatment with the preparation foundationol.
Causes of root rot on an orchid
First of all, root rotting begins in a waterlogged substrate - excess watering will immediately affect the state of the root system. However, there are other possible reasons that are not directly related to the irrigation regime:
- as a result of prolonged use, the substrate has lost its air permeability and looseness, has become dense;
- feeding with a fertilizer solution prepared with an overestimated dose;
- damage to the root system during transplantation in the absence of disinfection of the wounds;
- colonization of the substrate by root-eating pests;
- fungal infections - late blight, southern sclerocial rot, rhizoctonia or brown rot.


Course of the disease
Different types of orchids are affected by pathogenic fungi parasites in different ways and under different conditions. Also, the clinical picture looks different.
Pathogenic fungi enter plant tissues due to the presence of certain enzymes. Having penetrated inside, toxins are released, which provoke the formation of rot that decomposes the tissue.
Any, even small damage on the roots, leaves or stem, promotes the penetration of air into the wound and, accordingly, the development of pathogens. Moisture oversaturation leads to tissue destruction, which is the main culprit in the development of fungal diseases.
Output
But what if water accidentally flooded the orchid? Roots rotted, what to do? Now many growers recognize themselves. After all, almost everyone has encountered this problem.
Improper plant care may be the cause of this phenomenon. Most often, the flower can be brought back to life. Following all the advice of experienced florists, you can enjoy the view of blooming bright and noble orchids in your home.
It is not difficult to notice that the orchid is sick. Her flowers and buds fall off, the leaves become flabby and lethargic, the bush staggers. Most often this happens because the roots of the orchid rot. If you find out the cause of the root system disease in time, you can successfully cure the indoor beauty.
Terms of distribution
Fungal diseases caused by various kinds fungi that develop and spread under certain conditions... But mostly, conditions are related to temperature, humidity and lighting.
Some types of fungi, such as Phytophtora cactorum, require high humidity and temperature, while others require dry air and lower temperatures.
Therefore, it is desirable for flower growers to know the physiological and biological characteristics and characteristics of the type of orchids grown at home.
Exactly proper care, the creation of the necessary conditions, the absence of "excessive" care and the implementation of the recommendations of experienced orchid growers will ensure the health of exotic beauties.
How to revive an orchid without leaves at home
When phalaenopsis receives less moisture, the roots and peduncles begin to dry, the casting wither or rot. Sometimes the yellowed plates fall off, and the roots remain unharmed, this phenomenon may be associated with the wrong choice of meta or with a violation of the light regime.Phalaenopsis sheds old leaves, it is easy to distinguish the natural process - only the lower plates turned yellow and fell off, the rest are strong, saturated color with a glossy surface. How to save an orchid without leaves, but with roots:
- check the roots for damage and rot, remove damaged areas, process them and transplant the flower (if possible, put it in a greenhouse for a while);
- normalize the irrigation system, light and temperature conditions;
- exclude cold drafts;
- use fertilizer in a timely manner, in small quantities.
It is possible to save an orchid without leaves only if all the rules for growing an epiphyte are observed; the restoration process can take a little more than 3 months. It often happens that the leaves begin to wither in only purchased orchids; when grown in greenhouses, plants are susceptible to pest damage. It is necessary to immediately transplant the purchased flower into a new substrate with the obligatory processing of the leaves, stem and roots with Fitoverm.


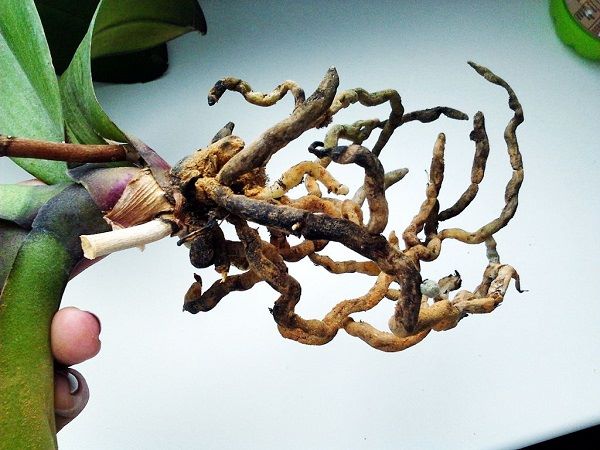
External signs of defeat
Rot is the process of decomposition or destruction of intercellular substances, tissue cell walls and all plant cell contents. Such pathological processes are caused by semi-parasitic and saprophytic fungi or bacteria. The process of tissue disintegration into cells proceeds, which weaken, cease to function, as a result of which the work of tissues and organs stops.


External signs of putrefactive processes, both aboveground and underground, may differ, depending on the type of fungi, but, one way or another, they form initial, local foci of damage:
- the appearance on young leaves and shoots of watery light brown spots, quickly darkening and increasing in size, before merging into one continuous spot;
- spots of brown and black, covered with a terry gray bloom;
- dark brown shades on roots and leaves;
- yellowness, darkening, the appearance of oozing ulcers on the leaf plates;
- brown spots on flowers;
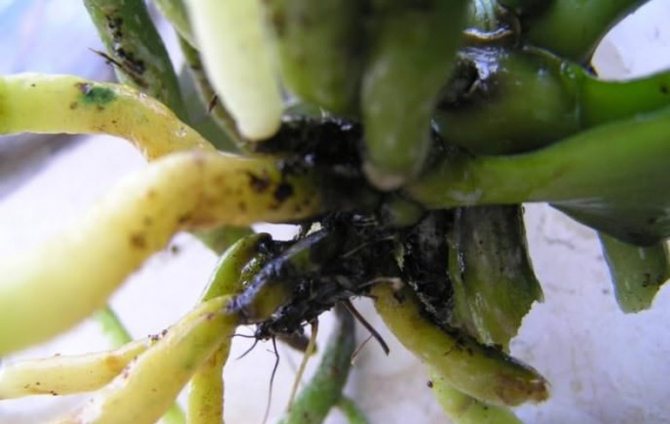
- blackening of the root system.


Blackening of the roots can be a sign of decay.
Attention! Bacterial lesions occur much less frequently than fungal infections. If pathogenic fungi attack under certain conditions and in weakened places, then bacteria when the plant is completely weakened.
What parts of the plant might be affected?
Often the decay process spreads to the core, leaves or root system.
Leaves
Leaf rot develops as a result of improper watering. Most often, orchid leaves are affected by the Pythium fungus.... Usually, rotting begins at the base of the plant, after which the roots are affected. This process is rapid, the plant can die in just 2-3 days. With the Phytophthora fungus, the leaves are covered with brown dark spots. Wet rot inhibits plant development. High humidity and high air temperatures lead to this state of the flower.
At the base
If, during watering, water gets into the core of the flower (resembling a funnel), then at high humidity, high temperatures, poor lighting and other circumstances, the trunk rotting process begins.
Root
Root rot due to improper watering... This is the main reason among all considered. In second place is the rare transplant of orchids. Old soil does not allow air to pass to the root system, and moisture stagnation occurs there. And as a result, the root of the plant rotted.
We offer you to watch a video on how the affected plant looks like and what are the reasons for its infection:
The photo shows what black and gray rot looks like on orchids.
Effects
Rotten orchid very quickly loses immunity and weakens... A weak plant is unable to resist the disease, and leaves with foci of decay cease to participate in photosynthesis. With the putrefactive processes of the roots, the ground part ceases to receive nutrition and gradually dries up. Small local foci do not pose a threat if they are promptly eliminated.
General state:
- oppression and weakness of the orchis;
- loss of turgor in the leaf apparatus;
- decrease or loss of decorativeness of the plant;
- reduction in flowering duration;
- inhibition of photosynthesis processes;
- slowness or complete stop in growth and development.
The main signs, one way or another, are associated with the appearance of any spots on the leaves, stem or flowers. A flower grower should be concerned about their appearance and find out the reason... Otherwise, pathogenic fungi or bacteria will cover not only the plant itself, but also those adjacent to it.
With root rot, the ground part can remain quite healthy for a long time. But the process of rotting of the root part will make itself felt over time. The consequences can be pretty dire. If you do not take timely measures, then the plant will die pretty quickly.
Planting an orchid


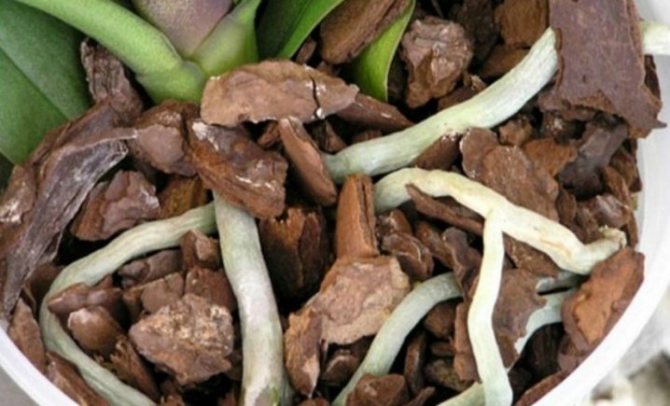
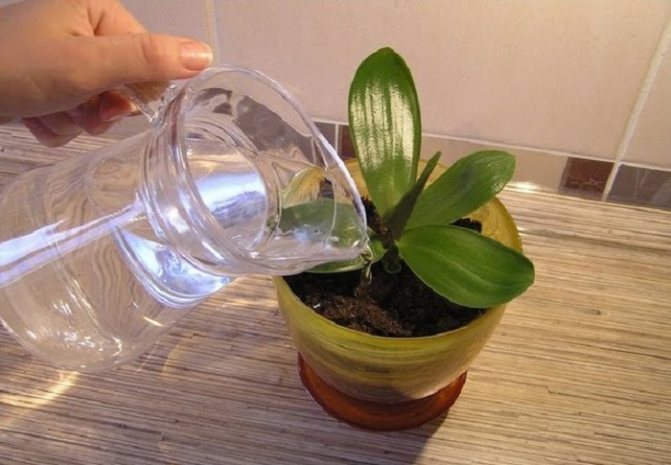
Lay a drainage layer at the bottom of the pot - it will prevent the roots from rotting from stagnant water. Pour a little dried substrate on top and set an orchid on it. Arrange the aerial roots inside the pot. If there are extra long ones that do not fit in the flowerpot, you do not need to bend or break them forcibly. Let them stay on the surface. Cover the roots in the pot with the substrate.
To speed up the process of the formation of new roots, put the flowerpot with the plant under a hood to avoid rapid evaporation of moisture and to maintain the same air temperature throughout the day. The first days it is enough to wipe the leaves with a damp sponge, watering is not necessary yet. In the future, watering should be carried out as usual.
Resuscitation of an orchid with rotten roots - video


With improper care, the orchid can begin to rot, which, of course, upsets the grower. But you can still help the plant if you navigate in time and organize the formation of new roots.
What to do and how to save an orchid if it rots:
Here we will take a closer look at what to do if the orchid is rotten. It should be borne in mind that rescue measures will differ depending on the affected plant organ.
Trunk?
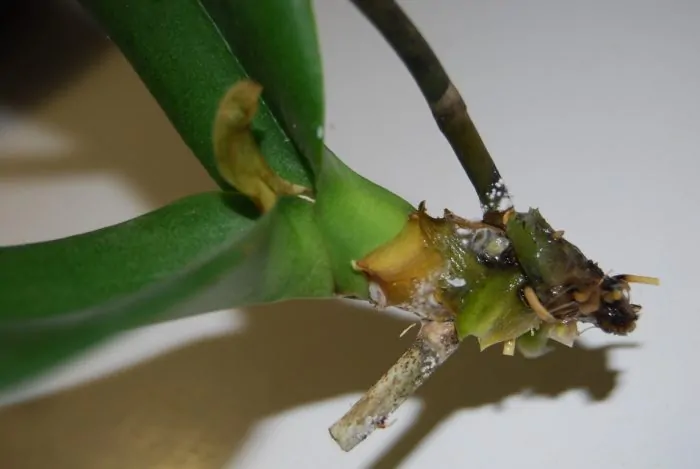
If the trunk of an orchid rots, this is one of the most dangerous processes for her life... If the hearth is too large and has captured a large part, then save such an orch almost impossible.
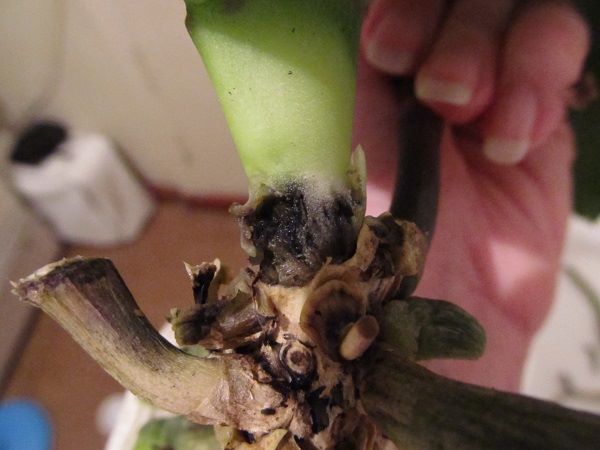


When a large section of the trunk decays, the orchid can no longer be saved.
Causes of barrel damage there may be many, ranging from frostbite and ending with mechanical damage. Black spots may appear on the trunk or it may start to turn yellow. It all depends on the cause and type of the disease.
In any case, the timely detection of a defect on the stem by an order of magnitude increases the chances of saving the tropical beauty.
Resuscitation methods are standard:
- removal of foci of decay to healthy tissue;
- processing of slices;
- transplant and special care.
Monopodial orchids have one short stem, on which all the important parts of the plant are located: roots, leaves and a growing point. For this reason, he should be given increased attention. Therefore, if the orchid rots at the base, this is a very alarming sign.
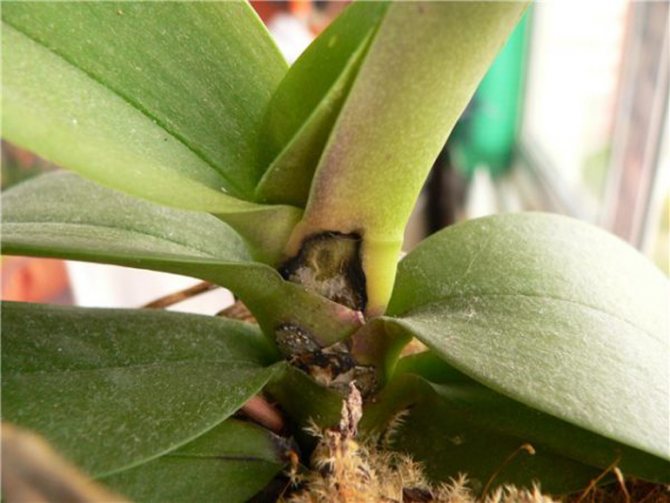
Core?
Rotting of the core (growth points) - quite a rare but common occurrence. This usually happens as a consequence of some kind of infection, rather than from the process of putrefaction caused by stagnant water. In order for the core to rot, the water must be there for at least a day.
In an apartment (hot in summer and heating in winter), this is almost unrealistic, it just evaporates. But, if a tropical monopodial beauty stands under the sun's rays, then the sun can burn out the fabric or quickly evaporate moisture, which will lead to a sharp cooling of young leaves.
Such a sharp drop is similar to frostbite, as a result of which a young leaf plate is damaged and, accordingly, open access to pathogenic microorganisms.
A completely different picture is observed in the autumn-winter period, when the heating is not yet working, and the room is cool. Water cannot evaporate for a long time, it stagnates. The destruction of tissues depends on the condition and tenderness of the leaf plates of young leaves. The softer they are, the faster the destruction of their tissues will begin.
Primarily, it is necessary to strictly observe the rules of plant care and hygiene.
Preventive actions based on the following requirements:
- lighting, temperature and humidity - three parameters defining the location;
- watering produced only with a completely dry substrate;
- regular aeration;
- removal of accumulated water after irrigation from the core with a paper napkin, within 30-40 minutes.
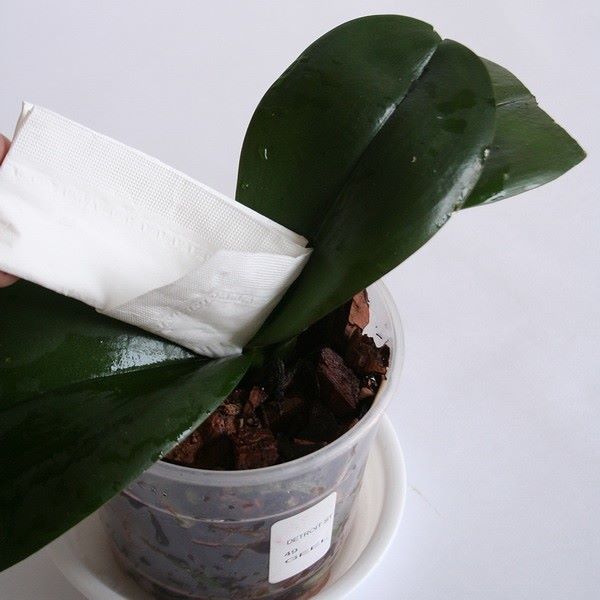


To avoid rot, always remove water from the leaf axils.
To avoid the spread of rot deep into the trunk and on adjacent leaves the lesion is cut out to a site of healthy tissue... And the places of the cuts are disinfected and dried. The first days you need to monitor the locations of the cuts. The manifestation of new signs indicates an insufficient cut size.
Important! If the core has rotted completely, then you should not be afraid of its complete cutting. Without it, the orchid can be reanimated. With the spread of the putrefactive process throughout the ocher, there will be nothing to reanimate.
Top?
What does the top of the orchis suffer and rot from? There are two main reasons: infection or care errors.
If any rot affects the top, then it need to cut... The cut site is cleaned, treated with a fungicide or disinfected.
Further care for the remaining stump is standard, like for a regular orch, with the exception of spraying and additional nutrition. With proper care, a baby will emerge from this hemp in 50-60 days. The active growth of the baby allows feeding with a balanced diet.
Growth point?
Whatever vitality the orchid is famous for, when the growth point decays, the chances of saving it are assessed by experienced orchidists 50 to 50.
It is important to prevent the spread of infestation to the entire stem and root.
Even in the absence of a growth point, a monopodial orchid will be able to live, since it will be able to reproduce with the help of a baby.
Bulba?
The defeat of any part of the plant by rot should alert the grower. Bulba is no exception. Rotting of the base of the bulb is especially dangerous, since the infection spreads quickly enough and can damage the root system. Then only a miracle can save the exotic.
The recovery process is standard - "surgical" intervention. The putrefactive focus (or the entire bulb) is removed to living tissue, disinfected, dried and watering and feeding are temporarily stopped.
What is the core of a flower and what does it suffer from?
In the orchids of the Vanda and Phalaenopsis species, the core or point of growth is called the top leaf of the plant. Another name for it is the neck. It is no coincidence that this part is similar in appearance to a funnel, so oversights in care bring a share of troubles.
The consequences of poor care
It is enough to water the plant from above from the wide mouth of the watering can and leave it alone in the greenhouse, where there is high humidity, on the windowsill, where sunlight does not come well, for several days. Provided that you spilled the orchid from the top of your head and put it in a sunny place on a summer day, then most likely your plant will burn, so more often rot eats the leaves in autumn and winter.
As an exception, it is worth considering the cases when the epiphyte stands in a draft, a cold windowsill, or was watered at night on the day when frost suddenly came and the dwelling was not heated. The newer and more tender the top sheet, the faster the processes of its death occur.
What is the danger of the destructive process in the plant neck?
Due to excessive saturation of fluid, the tissues of the cervical surface will begin to collapse, the abscess will spread along the base to the lower sheets. If this part of the flower is significantly damaged, the orchid will be forced to either give a lateral shoot (baby), or die. To give life to a green pet, you must not overlook the disease at the initial stage.
How to determine that the growth point has begun to decay?


There is a common mistake that novice growers make: when the leaf behind the core is damaged, they decide that the neck is rotting.
If you remove such a leaf, the orchid will safely survive the loss. The point of growth is so named because the flower is the only place from which its vital upward development takes place, a new green mass is born here.
The neck can be clearly identified at the time of the birth of a small leaf. or by the type of outlet. Try to tear off the problematic part, and when a small pointed leaf remains in place, make sure in practice that it will continue the development of the orchid.
Decay of the neck is easy to identify by external signs from other diseases:
- Yellowing bottom of the upper leaf (closer to the hollow).
- Dark spot of varying intensity of shade of the color of the first leaf.
- Loose, soft gaps in the fabric of the socket.
- A falling off top sheet, after which a coal patch remains in the center.
All these symptoms indicate that the orchid needs urgent resuscitation. If you see this in the markdown department of a flower shop, think carefully about whether to get the sufferer because of the attractive price or competitive spirit.
Drugs for treatment
In this section, we will look at how to treat an orchid from rot.
Fitosporin
The basis of the microbiological Fitosporin, which is effective against fungi and bacteria, is the natural bacterial culture of Bacillus subtilis. Systemic work, the ability to spread through the vessels, allows successfully copes with the suppression of infectious agents.
Efficiency against a large sector of fungal and bacterial diseases is caused by the presence in the composition of various fillers and OD of humate, which enhances the fungicidal action and stabilizes the characteristics for a long time. Due to such characteristics the shelf life is about 2 years, and the shelf life is not limited.


Fitosporin.
The main use of Fitosporin is preventive treatments... In case of diseases in a serious stage, it is ineffective.
The use and application of the drug is made strictly according to the instructions... In orchids, it is used to treat the soil and root part before planting.
Has a low hazard rating that does not pose a threat... On contact, it sometimes causes irritation of the mucous membrane, therefore, basic hygiene is required.
Quadris
Systemic fungicide from the strobilurin group and the active ingredient Azoxystrobin. Both prophylactic and therapeutic agents are in demand.
High hazard class warns florists about careful use for indoor plants. Protects after treatment for about 2 weeks.
Foliar spraying is effective for treating fungi and bacteria.


Quadris.
Copper sulfate
Acts like fungicide and antiseptic... The main active ingredient is copper sulfate, the ions of which react to the enzyme complexes of the fungal or bacterial cell and, thereby, cause irreversible changes.
Besides treating diseases, copper is a foliar feeding... Antiseptic properties help to decontaminate the substrate and flower container.
It is used both for soil treatment and for spraying. Concentration is carried out strictly according to the instructions for ornamental indoor plants.
3 hazard class can cause severe irritation of the mucous membrane in humans, therefore, it is required to carry out the treatment with gloves and glasses. Observe all hygiene rules.
Bordeaux liquid
Included in the number the most powerful remedies against fungal and bacterial infections. It is made using special proportions of quicklime and copper sulfate (copper sulfate and calcium oxide).
Copper sulfate acts as a poison against fungi and bacteria, and calcium oxide acts as a neutralizer of an oxidizing agent, prevents burns on plants.


Bordeaux fluid is one of the most aggressive infection-fighting agents.
Important! Experienced florists do not recommend using Bordeaux mixture for the treatment of orchids, since the delicate parts of the plant can be easily burned with the product. It is better to use preparations that do not contain copper.
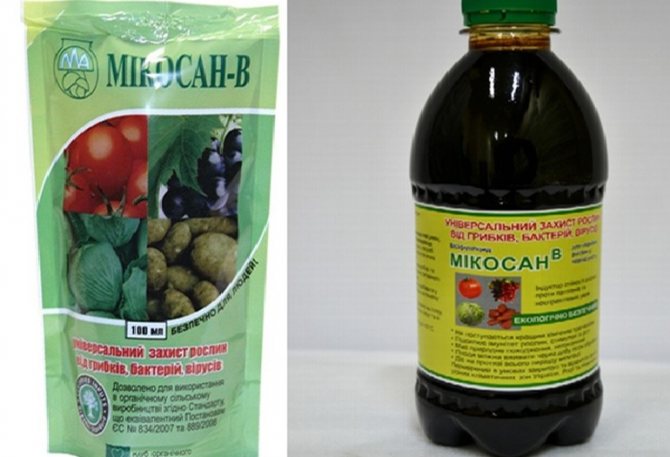
Mikosan
A biological product, the action of which is aimed at increasing plant resistance to fungal pathogens... It stimulates the production of lectins in tissues, which disrupt the growth and development of fungi and bacteria. Mikosan does not kill disease, but stimulates the plant to fight it.
The product can be used only at the initial stage of the disease, when the first spots and dots appear on the leaves. Even suspicious stains can be treated.
Attention! It is pointless to treat massive foci of rot or affected leaves with Mikosan.
Biological product of the 4th hazard class. Simple rules of hygiene are required.
Alirin
Biofungicide suppressing fungal infections in the substrate and on the orchid... The active bacteria are Bacillus subtilis.
When used, three times processing is required, with an interval of 7 days. Compatible with growth stimulants and insecticides.
4 hazard class.
Causes of leaf rot
There are a number of factors leading to diseases of the home flower. The most common mistakes made by florists in caring for a capricious plant. Rot appears due to:
- improper watering;
- low temperature and high humidity;
- wrong choice of fertilizers;
- poor lighting;
- dense soil;
- infection with fungal infections.
The reason is often mechanical damage to parts of the flower. If it is dropped or accidentally injured without providing timely first aid, this leads to rotting of the stem or leaf plate of the orchid, therefore, in case of any damage, problem areas are treated with antiseptic compounds.


Causes of the disease of the home flower
Fungal and bacterial infections
The most common orchid diseases that cause flower rot are wet, gray and brown bacterial rot and fusarium. All these diseases are distinguished by the appearance of pronounced spotting and active growth of spots on healthy tissues.
The fight against all these diseases is based on the removal of rot-damaged areas of the flower and its treatment with fungicides. The orchid should be quarantined to avoid contamination of other domestic flowers with diseases.
Application of unsuitable fertilizers
Some flower growers use complex mineral compositions for feeding orchids. This cannot be done: such fertilizers contain a large amount of nitrogen, which negatively affects the immunity of the flower.
Use only specialized formulations for fertilizing orchids, and fertilization is carried out according to the instructions.
Excess moisture
The basic rule for watering orchids is moistening the soil, which is carried out if the substrate is completely dry. Excessive watering creates pathological conditions for the rotting of the roots of the flower.
They also pay attention to temperature, water quality and air humidity. It should be well-kept and not cold. If the air humidity is high, spraying should be abandoned. The flower will have enough moisture in the soil.
Dense soil
The wrong choice of soil also leads to rotting of the flower. If it is heavy and dense, it may be difficult to ventilate the roots. Another reason is the waste of excess moisture in the pallet.


The wrong choice of soil also leads to rotting of the flower.
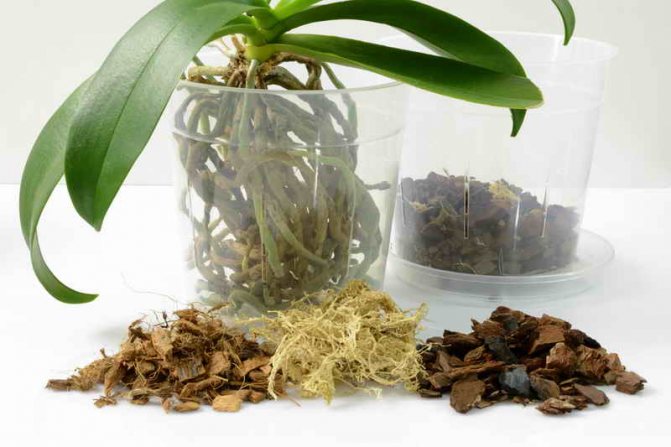
To restore an orchid grown in dense soil, the plant is transplanted into a specialized light granulate of zeolite or bark, as a result the plant comes to life.
Lighting and temperature
For the development of fungal infections, the ideal conditions are lack of sunlight, as well as coolness. They take care of natural light, for which a pot with an orchid is placed on a windowsill. On cloudy days, use a phytolamp.
The favorable temperature for growing orchids is 18 ° C-24 ° C. For any deviations from the norm, the conditions of detention affect the flower negatively.
Folk methods of deliverance
In general, only strong chemicals can cope with fungal or bacterial infections. Alternative methods can help if the focus of decay is insignificant and identified at the very initial stage.
Iodine solution
Used as a spraying, based on: 5 drops of iodine in 5 liters of warm water.
Garlic tincture
Garlic husk in quantity 100 g is infused in a bucket of water for 20-24 hours... The plant is treated with a ready-made, strained solution.


For the preparation of garlic tincture, only the husk is used.
Mustard infusion
Taken 50 g of dry mustard and infused with 5 liters of hot water for 48 hours in a dark, warm place. The masterbatch is diluted with water in a 1: 1 ratio before processing.
Important! Folk recipes are not harmful, not toxic, but even with the slightest development of fungal or bacterial infections, they are practically ineffective. You cannot do without chemistry in the fight against rot.
Folk remedies have shown themselves well as preventive drugs.
Step-by-step instructions on what to do if certain parts of the flower have rotted?
But at the same time, there should be enough daylight in the room. You need to check the orchid pan, maybe moisture has accumulated there. Bordeaux liquid or fungicide is suitable for spraying the leaves. Regular feeding with complex fertilizers for the orchid is also important.
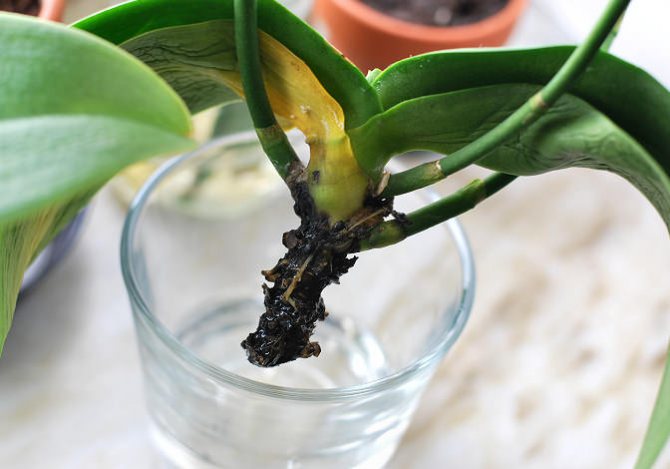
Root


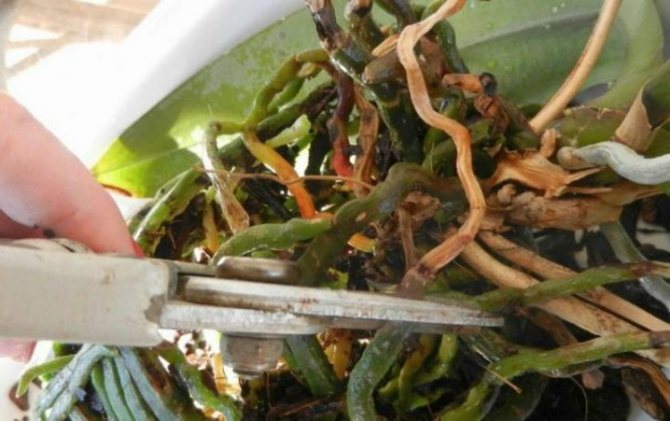
What to do if the root of the plant has begun to rot? It is necessary to remove the plant from the pot and remove all dead and rotten roots. They can be recognized by their brown, gray or yellow tint. Sick roots are cut off along the living part, otherwise the rot will begin to spread further. Places of cuts are treated with brilliant green or a solution of activated carbon.
Prevention measures
A rotting orchid is a sad sight. In order not to face it, prevention should be carried out.
Effective prevention measuresaccumulated by the experience of orchid growers:
- comfortable temperature with drops of no more than 5 ° С;
- humidity 50-60%;
- moderate watering, with drying out of the substrate;
- removing water from the leaf axils;
- diffuse and sufficient lighting;
- ventilation, avoiding drafts and cold air;
- strict adherence to the rules and concentrations of dressings.
Florists who decide to grow an exotic plant at home need to remember that a healthy, strong and well-immune plant is practically not exposed to any kind of disease. Therefore, proper care, maintaining the required growing conditions is the key to strong immunity and, accordingly, a healthy plant.
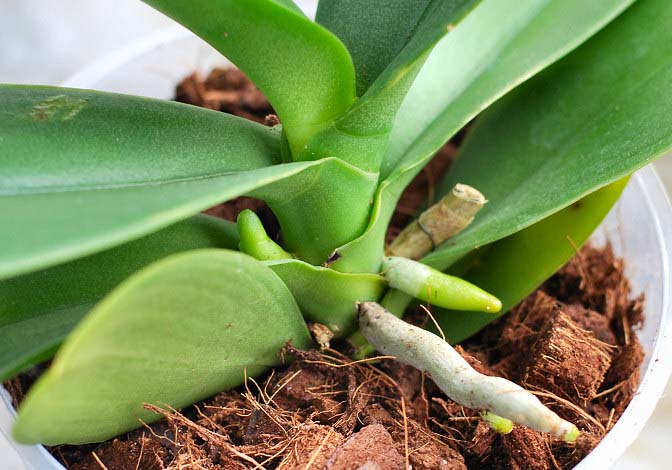
Rescue an orchid without roots and leaves
Novice florists very often ask a question about such a plant as the phalaenopsis orchid: "Roots rotted, what should I do?" This is not surprising. After all, our housewives often fill the plant. Sometimes there are such cases that the flower has lost not only the roots, but also the leaves. In order to save such a plant, it is necessary to create optimal conditions for its survival.
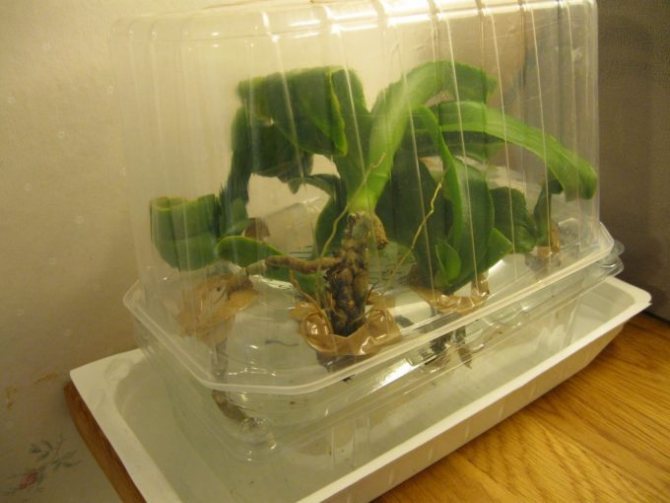
To do this, you need to plant a flower in a small greenhouse. You can buy it at a flower shop, or you can design it yourself using a transparent plastic box.
How to reanimate an orchid if the roots have rotted and the leaves have disappeared, right? At the bottom of such a greenhouse, it is necessary to put expanded clay and moss.You need to carefully place the plant here. It is imperative to take care of good lighting, so it is better to purchase a special phytolamp. If extra expenses are not provided, it is enough to place the greenhouse in a room with good lighting.
Now you can carry out the following procedures with these plants:
- Soak in nutrient solution, clean water.
- Roots and leaves can be wiped with a special solution that stimulates growth and saturates the plant with nutrients.
- The flower can be bathed in water solutions with diluted special preparations.
Experienced flower growers know how to revive an orchid if the roots have rotted. To do this, you can use the following drugs:
- Vitamins of group B. They support the vital activity of the plant during the absence of the root system. In such a solution, it is necessary to soak the orchid every month, and every week you can wipe the leaves.
- Growth regulators. These preparations contain natural phytohormones that stimulate the emergence of new roots. Monthly it is necessary to soak the base of the plant in such a solution.
- Potash and phosphate fertilizers. They accelerate the formation of the root system. It is necessary to feed the plant with this fertilizer 2 times a month.
- Glucose. The drug is added to various solutions. In a healthy plant, glucose appears spontaneously through photosynthesis. This substance is necessary for the formation of new cells.
- Iron chelate is a micronutrient fertilizer. Stimulates the growth of roots and leaves. The substance is added to solutions and the plant is treated.
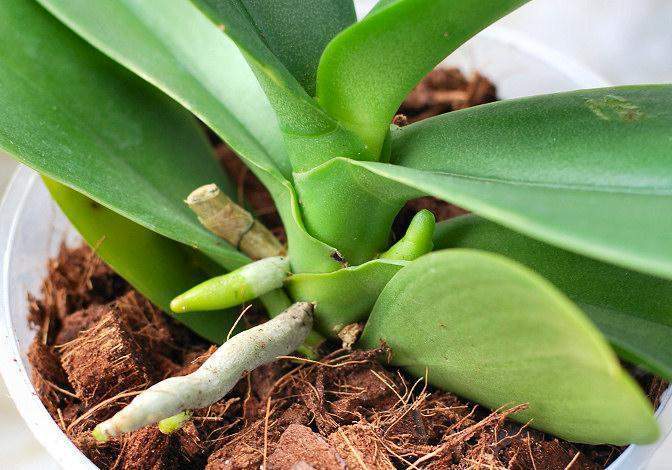


Now you know what to do if the orchid dies. The roots are rotten, but it doesn't matter. Proper care will help bring back the luxury of this noble tropical flower.