Aymeriosis or coccidiosis in chickens is one of the most common parasitic diseases, accompanied by impaired digestion, inflammation of the intestinal mucosa and intoxication. It affects chickens of all ages, but young animals are most susceptible to it. The infection spreads quickly throughout the farm and can wipe out most of the livestock in a matter of days. Every poultry farmer should be able to recognize the symptoms of coccidiosis and know how to treat the disease.
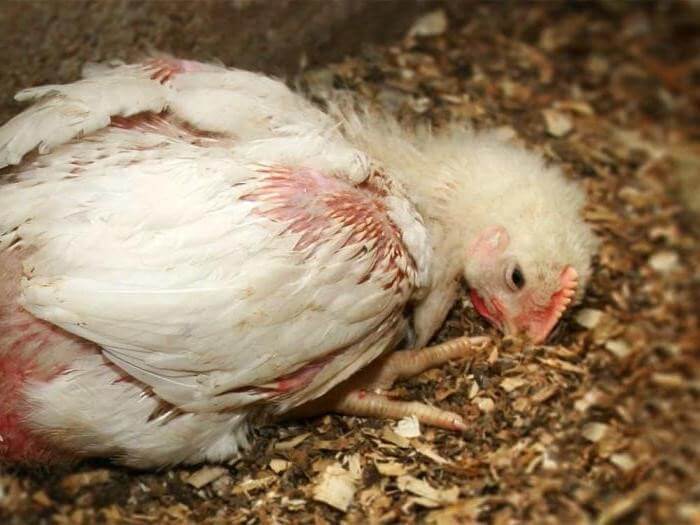

The chicken got sick
What is coccidiosis
TOoccidiosis (second name eimeriosis) - a parasitic disease caused by the simplest eimeria (coccidia). They multiply actively in the intestinal tract of chickens and lead to damage and damage to its mucous membrane.
As a result, inflammation and intestinal bleeding develop. Poultry digestion is impaired, and immunity falls, from which bacterial intestinal damage often joins.


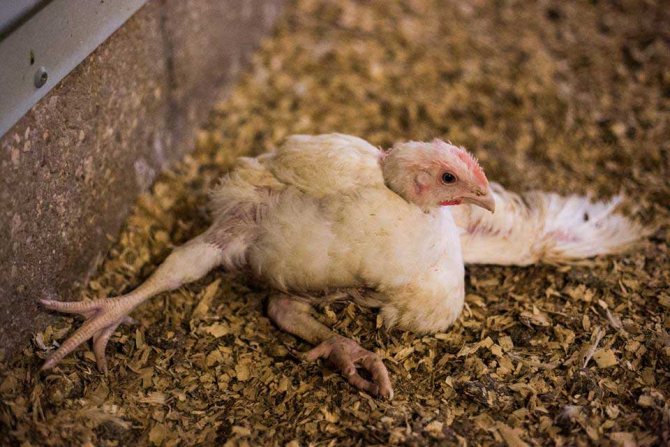
With coccidiosis in chickens, diarrhea is observed with an admixture of blood
The parasite gives up to 2 million new protozoa per week, and the usual antiseptic drugs are ineffective against it. Simple house disinfectants fail to deal with the pathogen, and its oocysts persist on the floor and litter. Coccidia can be brought to the chicken coop with shoes, equipment, or with the hay used for nests.
Chickens are most susceptible to the parasite at the age of 10 to 90 days.
Pathogens in the intestine first multiply asexually. When their number becomes significant, and the limit of asexual reproduction is exhausted, they reproduce sexually.


The parasite gives up to 2 million new protozoa per week, and the usual antiseptic drugs against it are ineffective
With the droppings of chickens, oocysts of the pathogen are released into the environment. The bird becomes infected with them for the second time. If re-infection with the parasite is excluded, then the chances of recovery for the chicken increase. No irreversible tissue damage occurs during the first infection with the parasite.
Features of the disease in chickens and young animals
The course of the disease in young animals has its own characteristics. This is due to insufficient immunity of chicks and young birds. At the onset of the disease, it is impossible to notice infection. The infected chick appears to be completely healthy on the outside.
During the incubation period of the disease, it is a source of infection for the rest, and the parasite actively multiplies in the body. Symptoms appear in severe lesions, when treatment is no longer always effective.
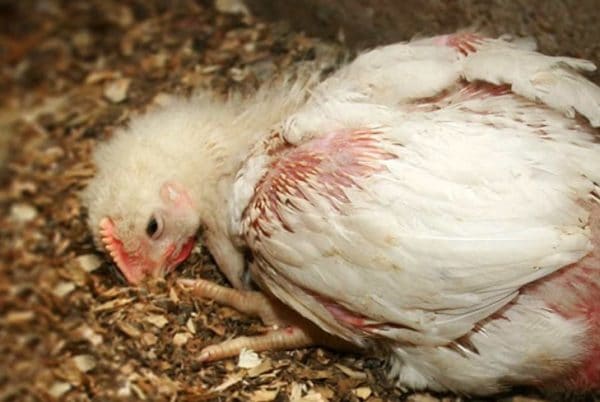


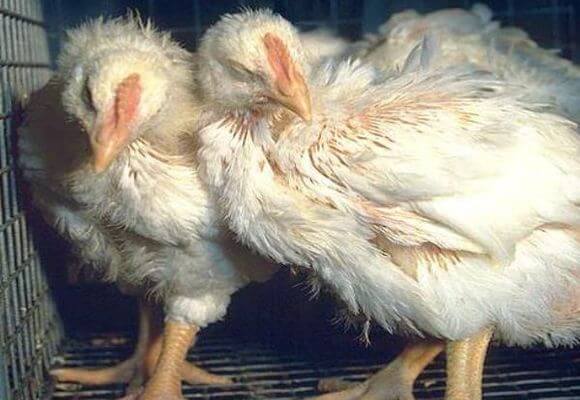
Coccidiosis is the leader among parasitic diseases in poultry farming
The death of chickens occurs in 3-7 days. Some individuals live for 10-14 days. The disease progresses rapidly. Chickens do not eat or hardly eat, they develop hungry edema. Autopsy of dead chicks reveals overflow of the stomach with liquid droppings mixed with blood.
Important! Broiler chickens begin to eat more actively during illness, but they are rapidly losing weight.
Features of the disease in adult chickens
Adult chickens can only get coccidiosis if they are not kept properly or if there is a particularly strong outbreak of the disease. The disease lasts longer than in chickens, and the survival rate of the bird is higher. Without treatment, in acute lesions, about 80% of adult birds die, and among chickens, the mortality rate is almost 100%.


Infection with coccidiosis occurs through dirty troughs and drinkers
In adult chickens, pathology can have a subacute course, and then the mortality rate is 10%. Coccidiosis with a subacute course is characterized by a long course.
Important! For humans, chicken coccidia do not pose a danger, and infection from a sick bird cannot occur.
A bird with strong immunity does not get sick when the parasite enters the body, but becomes its carrier and infects others. Chickens that have recovered from an illness are also carriers, and it is extremely undesirable to let them breed.


Be sure to read:
How to treat mycoplasmosis in chickens quickly and effectively, symptoms of the disease, is it possible to get infected
Development of coccidiosis in broiler chickens
The disease proceeds quickly, covering a significant number of birds. Bacteria rapidly multiply in the intestinal area; on the second or third day, there may be more than one thousand harmful microorganisms.
Affected broilers are in a sluggish state, without appetite, the plumage changes its structure. They can eat a lot, but body weight will not increase. Red blood cells in the blood are reduced. Useful substances are poorly absorbed. Leukopenia is possible. Hungry edema and poultry may occur.
Symptoms and course of the disease
The symptoms of the disease depend on its shape and the age of the bird. They appear at a time when the chicken is already in a rather serious condition, and its treatment turns out to be difficult.
With the subacute course of coccidiosis, the prognosis is better, the chicken is not so much depleted and its digestion is not catastrophically disturbed.
In the acute form of the disease, symptoms are observed:
- loss of appetite to its complete loss;
- deterioration of the pen;
- excessive thirst;
- drop in egg production until it stops completely;
- diarrhea with foam and blood;
- dirt on the feathers near the cloaca;
- blue skin;
- general lethargy;
- lack of coordination in chickens.
If left untreated, the chicken's condition worsens. She ceases to be active, her movement is difficult. The sick bird mostly sits motionless in the corner, eyes closed.


Due to diarrhea in chickens and chickens, feathers around the cloaca stick together or fall out
Instead of droppings, almost one blood is released. Changes in the intestine become irreversible, the tissues of the organ become necrotic and completely cease to perform their functions. Treatment is no longer possible, and the chicken is sent to slaughter.
In the subacute form, it is more difficult to establish coccidiosis due to the worn out symptoms. The presence of pathology is indicated by such manifestations of a violation of the condition of the bird:
- weight loss;
- lack of weight gain with the maximum high-calorie diet;
- untidiness of the bird in a clean house;
- lack of improvement in productivity from the use of stimulants;
- improving the condition of the bird with the use of drugs against coccidiosis.
Important! In adult laying hens, the disease can have a completely latent course, and its presence is indicated only by an improvement in egg production after a course of premixes with anti-coccidial components.
The body of chickens is able to secrete antibodies against the parasite, which, with a weak infection, acts as a vaccine. The bird does not develop symptoms and, after expelling the pathogen, no longer gets sick with this form of coccidiosis.
The main signs of the disease in chickens
The diagnosis of the disease is usually established by examining bird droppings and scraping the intestinal mucosa. In a mild form, the disease is very rarely seen by symptoms.
Signs of the disease in chickens in acute form:
- oppression of the condition of the bird;
- poor or no appetite;
- constant thirst against the background of severe dehydration and weight loss;
- the appearance of the bird is unkempt, the plumage is ruffled, feathers stick out in all directions;
- weakness and unsteadiness when walking;
- diarrhea mixed with mucus and blood;
- an increase in goiter.
In a latent form, the disease proceeds as follows - the bird gains weight poorly, due to poor absorption of food, often on the contrary - it loses weight, its productivity decreases. An increase in the quantity and quality of feed or the addition of vitamin supplements does not bring any visible improvement.
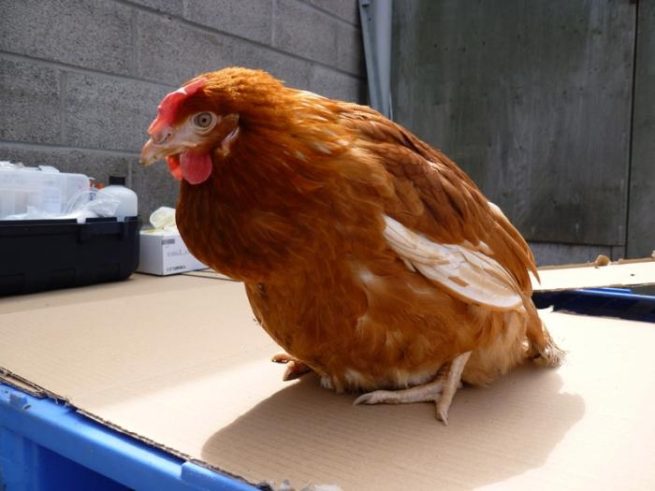


In young individuals, mortality can reach 70 - 80%, the course of the disease is aggravated by the fact that the resistance of the immune system to other infectious diseases decreases.
If you suspect this disease, you need to pay attention to the state of the litter in the chicken coop, sticky and wet litter is also a sign of coccidiosis.
In some cases, the disease can be determined by the therapeutic effect of the use of a premix with coccidistatics.
Reasons for the appearance
The cause of the disease is the penetration of the pathogen of the pathology into the body of the chicken. In the presence of factors predisposing to the disease, the immune system will not cope with the attack of the parasite.
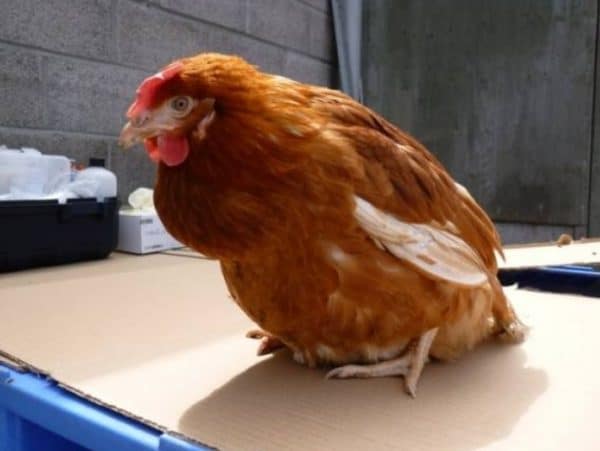


The body of chickens is able to secrete antibodies against the parasite
Coccidiosis develops under the following conditions:
- feeding poultry with spoiled feed;
- non-observance of the rules for disinfection of feeders and drinkers;
- the presence of a person in the poultry house in shoes in which he walks outside the farm area;
- keeping birds on dirty litter;
- keeping poultry unvaccinated against disease;
- cold, dark house.
The elimination of predisposing factors reduces the likelihood of coccidiosis in chickens.
Sources of infection
The source of infection is a sick bird. Oocysts are brought to the hen house from another house on his feet or with equipment for caring for the bird. The disease can be brought in after visiting pet markets and poultry farms.


External signs are not enough for the diagnosis
Without complete disinfection, you cannot use drinkers and feeders for your poultry, both new and used.
Before settling new chickens in the poultry house, it is necessary to first carry out a complete cleaning and disinfection of the premises and walking.
This is necessary to prevent infection when there were carriers of the parasite in the old herd, which were isolated with oocyst droppings.
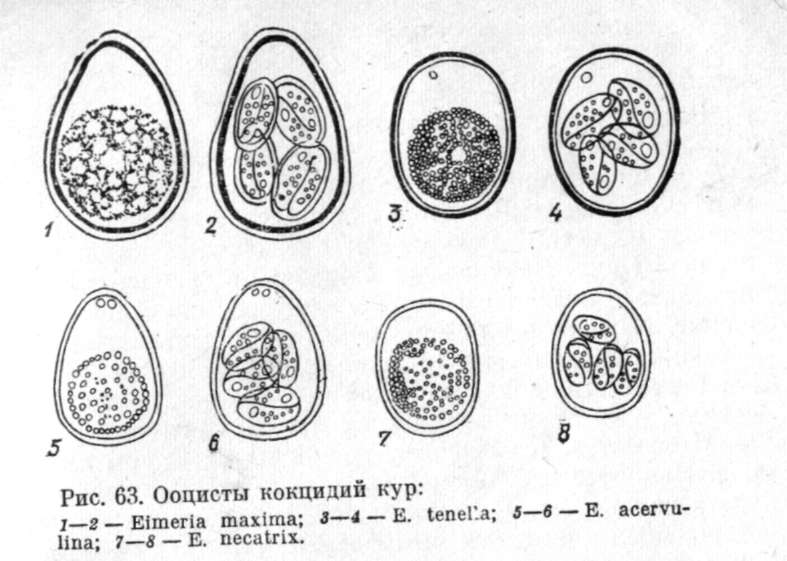
Reproduction of eimeria
Single-celled parasites differ in the degree of danger to the organism - from E.tenella to E.acervulina. They settle in different parts of the intestine - from the epithelium of its thin part to the rectum.
The primary source of infection is the discharge of a diseased individual, in which parasite oocysts are located.
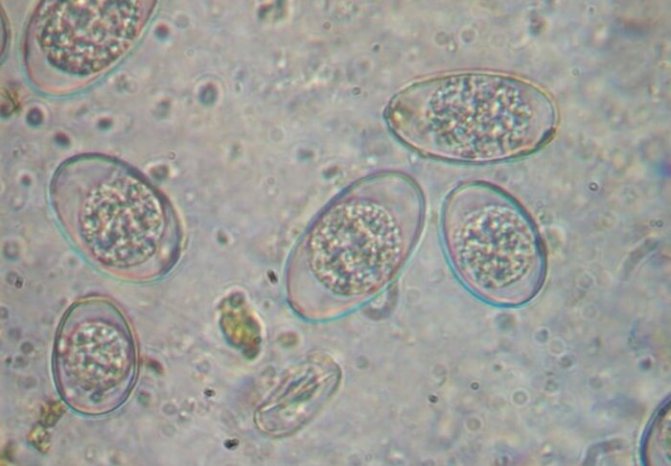
Capsules of eimeria (coccidia) are oval or elongated-ovate, cream-colored (sometimes colorless). Oocysts spread mechanically - on the soles of shoes, by animals and birds, with food.
Parasites that have entered the body of chickens begin to actively multiply and secrete oocysts, which can be stably preserved in the environment for at least ten months, in a zone with vegetation - up to one and a half years.
Single-celled, parasitizing in the body, of course, harm the body of birds, even if they do not manifest themselves clearly, stopping the rate of growth and development.
Aymeria are resistant to the main types of drugs that destroy them, which causes the elimination of external signs of the disease, but not parasites.
Diagnosis of the disease
External signs are not enough for the diagnosis.
If the presence of parasite oocysts is determined in chicken droppings, in veterinary medicine this is regarded as a sign of carriage, but not a disease. The presence of a parasite in the intestines of a bird in small quantities is considered acceptable.
The official diagnosis is made after the pathological examination of the dead chickens from the herd.
In case of illness, the intestines of a bird are inflamed, with yellow nodules; the inside of the organ contains a lot of water and liquid droppings. Poultry treatment begins when external signs of the disease appear. If mortality has begun, the prognosis for the livestock worsens.


Be sure to read:
The most common diseases of chickens, their symptoms and treatment. Photos of sick birds
Causative agents of the disease
Coccidiosis is an inflammatory disease of the intestines of birds, which is caused by the simplest parasites of eimeria (this lesion is also called eimeriosis). Reproducing in the intestines of poultry, they cause persistent damage to the intestines, accompanied by bacterial infections (salmonellosis and others).
What is eimeria? These are the simplest unicellular organisms that infect strictly one species of birds. Parasites that breed in the intestines of turkeys cannot infect chickens. It is extremely difficult to get rid of them: the ability of single-celled organisms to reproduce allows them to quickly cover the largest livestock.
The usual methods of disinfection do not affect parasites, this is due to the peculiarities of the life cycle of these unicellular organisms.
Like many parasites, the initial reproduction cycle of eimeria is carried out in the external environment, forming a capsule - an oocyst. In this form, unicellular organisms withstand numerous temperature extremes.
In the poultry house, the parasites persist in the layers of the bedding material, on the floor surfaces of the bird feeding equipment. Infection of the premises occurs through the introduction of capsules from the external environment - with materials for equipment, earth from the territory, underlying materials.
There are several types of eimeria (11) - seven of them are the most dangerous. In various parts of the chicken intestine, a separate species parasitizes, causing specific lesions. Eimeria are especially dangerous for chickens from a week to three months. Defeats of the livestock take place in the form of mass destruction of the livestock of the poultry house.


Treatment methods
Treatment for the parasite is carried out with veterinary drugs or alternative methods. Special veterinary medicines for chickens have the maximum efficiency, the action of which is directed specifically at the pathogen of the pathology and does not lead to the appearance of severe side effects.


Treatment for the parasite is carried out with veterinary drugs or alternative methods.
When treating sick chickens, they are isolated. The house is kept clean. The litter should be changed daily, not just sprinkled on it. If possible, the chicken coop is irradiated with an ultraviolet lamp.
Veterinary drugs
Veterinary coccidiostatic drugs give a quick and pronounced result. The funds do not violate the general condition of the bird, its development and further productivity. It is necessary to give veterinary drugs to sick pets in therapeutic doses, and to those at risk in preventive doses.
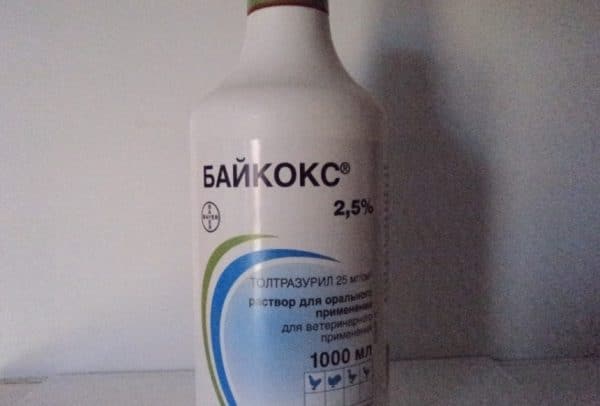


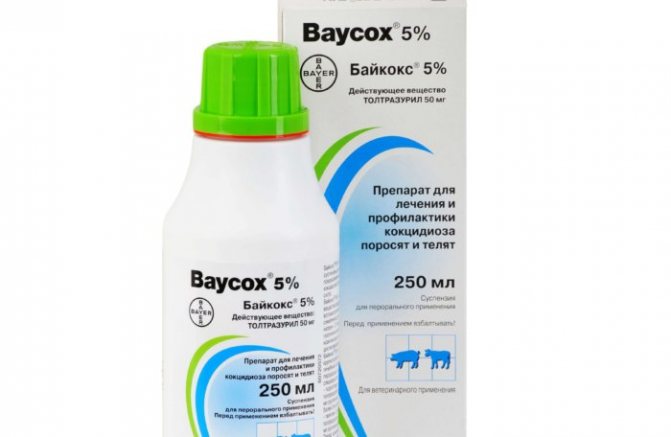
Baycox is an effective drug for the prevention and treatment of coccidiosis
All chickens in the poultry house are treated.
List of commonly used drugs:
- Baycox 2.5%. Use diluted with water. The therapeutic dose is 1 ml / 1 liter of water. This portion is drunk in two days. The prophylactic dose is reduced by 2 times. For prevention, it is necessary to water chickens once a day.
- Amprolium. Added to feed. For medicinal purposes, 0.25 g of the product is added per 1 kg of feed. For prophylaxis, the dose is halved. The treatment course lasts 1 week. Chickens are given medication to prevent disease from birth to 4 months.
- Koktsidiovitis. Preparation for addition to feed. For preventive purposes, add 1.25 g of the product to chicks up to 4 months per 1 kg of food. Treatment requires a 2-fold increase in dosage. Give the medicine for 1 week.
- Avatek 15% SS. It is added to food for the prevention of illness. The dosage is 5 g per 10 kg of feed. In areas unfavorable for coccidiosis, the drug is given to chickens from the first day. Stop using the product 5 days before slaughtering chickens.
- Sulfadimezin. Medicinal drug. Not used for prophylaxis. Dose 1 mg per 1 kg of feed. They give the medicine for 3 days.
It is unreasonable to treat chickens in serious condition.


It is unreasonable to treat chickens in serious condition
Even if the chicken survives, it will be weak, with low productivity.
Home treatments
For the treatment of eimiriosis, special drugs are used - coccidiostatics. There are many of them, so you should not self-medicate. It is best to consult a veterinarian who will prescribe the correct medication.
Koktsidiovitis


The form of the drug is powder. 2.5 g of the substance is mixed with a kilogram of feed and given to the birds. If you plan to slaughter chickens, this is done no earlier than a week after stopping treatment.
During diarrhea in chickens, not only infection is dangerous, but also dehydration and loss of minerals. Protracted ...
Coccyprodin

Coccyprodin changes the structure of eimiria and does not affect the quality of immunity. Broilers and any young animals are treated with it. For treatment, 1 ml of the substance must be dissolved in 1 liter of water and sick birds should be drunk. The course of treatment is 2 days, but if the disease is started, it is repeated. Coccyprodin is successfully treated for both broilers and babies, but it should not be given to laying hens, otherwise they will stop laying eggs.


Like Coccyprodin, Baycox is used for two days. The concentrated liquid preparation is diluted in 1 liter of water. With a severe form of infection, the course of treatment is repeated after 5 days.


Avatek effectively removes toxins from the body of birds. It is given together with feed at the rate of 5 g of substance per 10 g of compound feed. Applied from the onset of the disease, up to four months of age.


Acts on all types of coccidia. The active pharmacological substance of the drug is 5% semduramycin. The course of treatment is 5 days. 1 g of Aviax is added to 1 kg of compound feed.
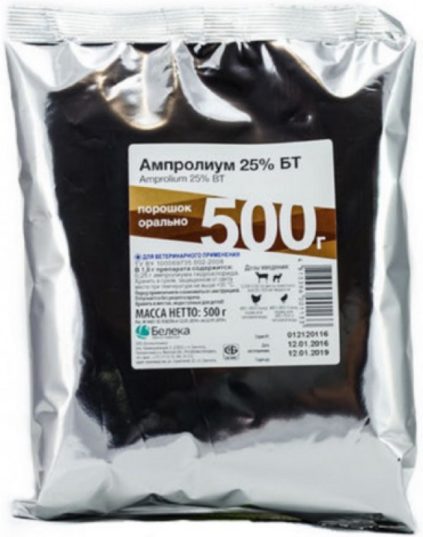


The course of treatment of birds with Antrolium is a week, if you adhere to the daily rate: from 400 to 420 g of substance per half liter of water. If you need to cure a large number of chickens, add 850 g of the drug to a ton of compound feed. The course of treatment is from 8 to 12 days. During drinking water without medicine should not be given to "patients".


It is a broad-spectrum drug. It kills all coccidia and is effective for both chickens and adults. The active ingredient is toluamide. For treatment, 1 g of coccidin is added to 1 kg of feed and mixed thoroughly. The treatment time for birds is 5-7 days.


The release form of Koktsisan is a fine-grained brown powder. The active ingredient of the drug is sodium salinomycin. It effectively destroys coccidia and prevents them from developing in the bird's body. For treatment, you need to add 120 mg of Koktsisan in 1 kg of feed and give the chickens during feeding. The effect of the drug is calculated for a day, so every day you will have to prepare a new medicinal mixture. The course of treatment lasts a week.
Madikox is a gray-brown powder, poorly soluble in water. Sometimes it is gray and white. It is a broad-spectrum drug that kills all possible types of coccidia. To prepare a therapeutic feed mixture, from 0.5 to 1 g of Madikox is added to the compound feed and thoroughly mixed. The course of treatment is a week.
Sulfadimezin


A well-known anti-inflammatory agent. 0.1% sulfadimezin is dissolved in 1 kg of feed and given to the birds for three days.
Furazolidone

The proportions of Furazolidone for the treatment of coccidiosis in chickens are 5 g of the substance per 1000 individuals. Instead of furazolidone, you can use its analogue - norsulfazole.
Folk remedies
Folk remedies are less effective than veterinary remedies. They help at the very beginning of the disease and with strong immunity in chickens. It is undesirable to waste time using them.
List of popular products:
- Iodine or iodinol. An antiseptic solution with food is recommended to be given to chickens and chickens in the morning. The concentration of the solution is 0.01%. The dose for chickens up to 40 days old is 2 ml of solution per head, from day 40 to 60 - 5 ml. After three months, iodine is no longer added to the feed. An antiseptic is used in the same way for prevention and treatment.
- Osarol. The product is given with feed at the rate of 10g / 1kg of chicken weight.The dose is fed in 2 doses during the day. The treatment lasts 5 days, followed by a break of 3 days and a repetition of the course. In total, giving the medicine will be repeated 4 times.
- Fodder sulfur. It is added to poultry food in the amount of 2% of the feed portion. Give no more than 2 weeks. An overdose of the substance causes rickets in chickens.
Important! Recommendations to drink vodka for chickens are wrong. Alcohol will only make the bird worse, and it will be impossible to save it.
Food
Feed the bird at the onset of the disease in small portions with a drug... When the chicken completely refuses to eat, the food is mixed with the medicine, a small ball is formed from it and forcibly thrown into the beak.


Be sure to read:
Chicken fleas: how to get rid of parasites with folk remedies and chemistry?
During treatment, chickens should not be given dry grains and raw chopped vegetables, which additionally damage the affected intestines. To prevent rickets, vitamin complexes must be introduced into the diet of poultry.


Feed the bird at the onset of the disease in small portions with a drug
If the hens' appetite is not disturbed, which is observed in broilers, foods that cause internal fermentation and raw grass and vegetables are excluded from the diet. New portions of the parasite can be introduced with them.
Chickens should eat semi-liquid feed. In the early days, bran is added to one of the feedings to speed up bowel cleansing. If the bird is fed with compound feed, then its nutrition does not change.
Premixes with coccidiostatics
Premixes with coccidiostatic content are quite effective, but in severe cases they will not help.
They are easy to use and are recommended as a medicine for mild injury and for prophylaxis.
A premix is a powder that is easy to dispense into food. Compound feeds with premixes against coccidiosis are also produced. Their use is preventive.
The drugs are produced in industrial packaging in bags of 30 kg, and for a private courtyard in packages from 500 g to 3 kg. Chickens can be given the drug from 5 days.


Premixes with coccidiostatic content are quite effective, but in severe cases they will not help
When feeding with premixes, there are no restrictions on the type of feed, they are combined with all food for poultry.
How to treat coccidiosis in broilers


Coccidiosis is treated with ionophores, coccidiostatics and iodine
For therapy, coccidiostatics, iodine, premixes and folk remedies are used.


Be sure to read:
What internal and external (skin) parasites look like in chickens, symptoms and treatment
Coccidiosis is treated with ionophores, coccidiostatics and iodine.
For the treatment of chickens, special preparations for coccidiosis are used. They contain various vitamins (K, PP), folic acid, as well as positive bacteria that destroy the bacteria coccidins.
Among the popular means are Koktsidin, Avatek, Dekoks. In the composition of these drugs there are various enzymes that increase immunity, after 2-3 days the drug can completely eliminate the disease, and after 5 days of prophylaxis, the disease recedes. Usually, medications for treatment are changed periodically to avoid addiction.
Preparations must be prescribed by a veterinarian, depending on the age and type of chickens.
During treatment, it is worth adding to the diet an increased dose of vitamins A and E. It is advised to vaccinate young chickens every month, if they are sick with coccidiosis, to give injections once a week.
The diagnosis is made quickly, according to the results of the analysis, and treatment is immediately prescribed. To a greater extent, coccidiosis is treated with chemicals that further affect the work of the intestines. Such drugs are added to water or chicken food; care should be taken to ensure that the sick bird takes the drug. Poultry can also be treated with these products, but
You may also find it helpful to learn about turkey farming as a business.
At home, the drug Koktsiprodin is used.The medicine is used for both prevention and treatment of the disease.
Once in the body, it eliminates harmful bacteria, at the same time, the drug is toxic and affects the microflora. If you have few animals, it is better to feed them with simpler preparations and only in difficult cases use chemical preparations.
What are the sizes of cages for quails and how to make them yourself, read this link.
Effects
Lack of treatment for poultry leads to significant material damage. The mortality rate among chickens from the disease is almost 100%.
For breeders of thoroughbred poultry who breed them for commercial purposes, the transferred coccidiosis in chickens is the reason for a change in livestock, with a preliminary complete disinfection of the entire backyard. You cannot get healthy, strong chickens from recovered chickens.
In broiler chickens, due to the characteristics of their body, treatment is ineffective and the disease leads to the death of the bird. It is important for the owner to prevent the onset of the disease by constantly giving protective drugs.
What to do to prevent the spread of infection in the chicken coop
If an outbreak of a disease occurs on the farm, the premises and all equipment should be processed.


The litter from the chicken coop is removed and burned.
The litter from the chicken coop is removed and burned. Walls, floors, feeders and drinkers are treated with steam, iodine monochloride solution (you can use a smoke bomb), 7% ammonia solution. This procedure must be carried out twice a year.
Preventive measures
The main prevention of the disease is vaccination of poultry.
The drugs are available in the form of an emulsion or aerosol. They are used more in poultry farms for breeding broiler chickens. At home, because of the difficulty of obtaining the vaccine, premixes are usually added to the food of chickens to prevent disease.


Prevention of coccidiosis in chickens is carried out up to 9 days of age
The rest of the preventive measures against the disease are as follows:
- giving high-quality feed;
- maintaining cleanliness in the poultry house;
- prevention of crowded keeping of adult and young birds;
- regular treatment of the chicken coop and inventory with an antiseptic (heat-resistant objects and surfaces are scorched with a blowtorch);
- urgent isolation from a herd of sick birds.
With the cellular content of chickens, coccidiosis rarely occurs, since they are not on the walk and the risk of getting the pathogen is less.
Prophylaxis
The main method of dealing with coccidiosis is prevention. Due to the high virulence of the pathogen, it is impossible to use the same agent for prophylaxis for a long time (in conditions of mass keeping of birds, it is mandatory to change the drug every 2 years).
Usually, for broilers, the developed systemic prophylaxis of coccidiosis uses up to four drugs, which have different active substances and mechanisms of action on parasitic unicellular organisms.
The preparations are used for 60–120 days during the development of young birds to stop the possibility of carriage by adding them to the feed. High-cost vaccines are used to prevent young productive birds - meat hens and egg-laying hens. Young animals are subjected to the procedure after 10-14 days of development.
It is important to maintain sanitary standards for keeping young stock, cleanliness of the poultry house and prevention of crowding.
For the prevention of coccidiosis in broilers, it is important not only to keep the poultry houses clean and to regularly disinfect them, but also to use medicines for the treatment and prevention of the disease.
Is it possible to eat the meat of chickens with coccidiosis
Meat from sick chickens does not pose a danger to humans. Coccidia, which infects birds, does not parasitize in humans.
After the end of treatment, the chickens are sent to the slaughter after 5 days so that their body is cleared of drugs. The remaining pathogens die when the meat is frozen or cooked.


Prevention of coccidiosis is to maintain cleanliness in the chicken coop and on the walk
You should not eat meat from chickens that died from illness, or slaughtered at a time when they were in agony. Such meat is disposed of by burning it.
Important! You can eat an egg from recovered chickens without fear. Chickens are given it by boiling for 10 minutes.
How does coccidiosis of young chickens develop?
It is most dangerous when chickens suffer from coccidiosis. Epithelial cells die off under the influence of coccidia accumulated in the intestine. The integral structure of the walls in the intestine is disrupted, which leads to necrosis.
Peristalsis is disturbed, nutrients are poorly absorbed, this causes hungry edema. The pathogen matures within 2 or three days. The bird is at risk during feed changes, in stressful situations. It is easiest for chicks to get sick in warm weather and during rains.