»Flowers» Moss for growing orchids - what functions does
0
89
Article rating
Moss for orchids is a source of nutrients necessary for full growth and flowering. It is used to protect the root system from waterlogging and to insulate the stems.

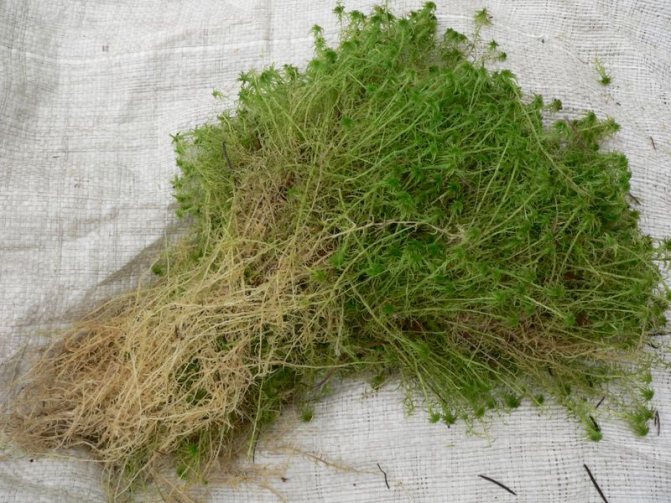
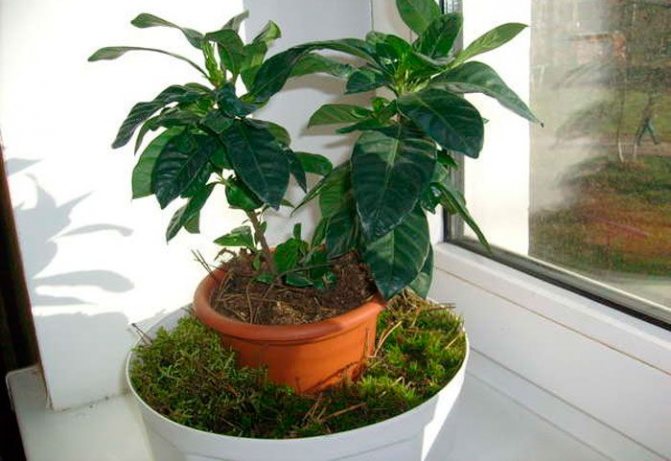
Moss for growing orchids
What is it used for?
Attention: When growing orchids, moss can be used as a stand alone substrate or as a useful supplement.
Main purposes of application:


Increase in moisture... Using moss as a casing layer will keep the substrate constantly moist without increasing watering.- Getting babies... If a peduncle cut and treated with cytokinin paste is placed in a container with wet moss, a shoot will appear from the "dormant" bud over time.
- Raising children... The cut shoots are placed in clean moss or in a mixture of moss and bark.
- Rescue of a dying plant... An orchid with rotten roots must be planted in a moss substrate and greenhouse conditions created.
- Engraftment of roots to the block... To fix the roots on the block, you need to put moss under them. In six months, algae will begin to grow, a precipitate of salts will appear, the moss will begin to crumble, but the orchid will already be tightly attached to the block.
- Prevention of drying out of young roots that have appeared above the soil... For this, the surface of the soil must be covered with moss. The amount of moss depends on the number of holes in the flowerpot.
With the correct application of moss, orchids will reward the grower with stable growth and lush flowering.
Sphagnum: medicinal properties


White marsh moss is very popular in both traditional and folk medicine. In addition to bactericidal properties, sphagnum is also famous for its antifungal effect.
With bedsores
Fresh or dried moss was used as bedding by our ancestors. Sphagnum allows air to pass through well, and also removes an unpleasant odor. All this is due to the bactericidal effect.
With osteochondrosis, radiculitis, rheumatism

For the preparation of a healing agent, dry moss is used. In a deep container, it is necessary to place 1 part of the raw material and pour 10 parts of boiling water. Cover with a lid and keep at room temperature until it cools completely. Then strain and pour into a warm bath. Lie in this broth for no more than 40 minutes. After taking a bath, all problem areas will need to be rubbed with a warming ointment.
To prepare a compress, you need 1 tbsp. l. combine moss in 0.5 l. boiling water. Strain the cooled liquid.
With colitis, acute respiratory infections


To get rid of colitis and enterocolitis, you need to take dry crushed moss (1 tsp) 30 minutes before meals.
Sphagnum is also used to prevent respiratory diseases. In this case, daily washing with moss infusion and gargling will help. Also, the nasal passages are washed with the prepared agent.
For cuts and burns
In order for the festering wounds to heal faster, it is necessary to grind a small amount of dry moss and pour boiling water over it. You should get a gruel, which is applied to the problem area.
Gruel compresses will also help with burns and fresh cuts. Dry moss powder is used for disinfection. They are sprinkled with wet wounds.It should be kept in this state for several minutes, then everything is thoroughly washed off with the infusion from the plant.
For dermatological problems


Products based on this plant are very useful for nail fungus. Ointments, gruels and baths are prepared from moss. They also give insoles from it, which they put in shoes and walk throughout the day.
To improve the effect, you can put a small piece of the plant in a sock so that it contacts the problem area.
Pros and cons of adding to the substrate
The use of moss in the substrate has both positive and negative sides.
pros:
- antibacterial properties;
- aesthetic appearance;
- help in saving a sick plant and growing shoots;
- moisture retention.
Minuses:
- decomposes quickly, needs to be changed 2 times a year;
- too dense a layer of moss blocks access to the roots and destroys the flower;
- it is difficult to calculate the amount of watering, which can lead to rotting of the root system;
- pests can start in the moss;
- algae formation.
Important: It is better for novice growers to grow phalaenopsis without moss.
Why orchid moss
Moss is a natural organic matter with antiseptic properties. In the process of life, as living cells die off, the lower layers are converted into peat, which serves as a donor of nutrients for indoor flowers and improves the air permeability of the soil.
The composition contains:
- phosphorus, bicarbonate, sodium and chlorine;
- sphagnol with antibacterial properties that protect plants from the reproduction of pathogens of infectious diseases.
The structure easily conducts and accumulates moisture, evenly giving off as required, thereby reducing the required amount of watering and protecting the root system of flowers from stagnant water.
Moss is capable of retaining water. The amount of moisture absorbed exceeds its original weight by 20 times.
Properties:
- transformation of heavy soils into a light structure with good hygroscopicity and air permeability;
- improving the fertile qualities of the soil mixture;
- intensive absorption of moisture and its even distribution;
- protection of the root system from decay;
- increased resistance to pathogenic microorganisms.
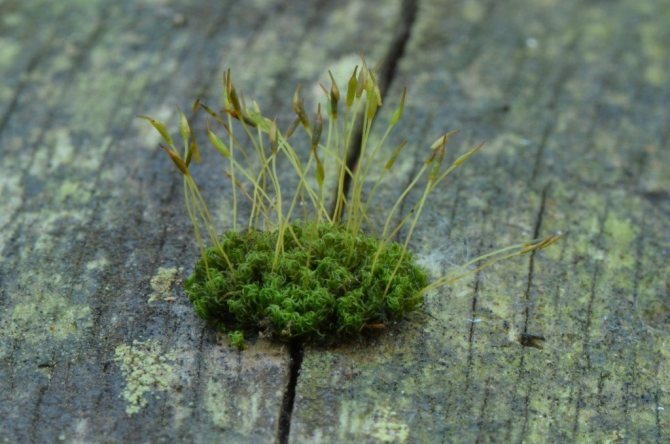
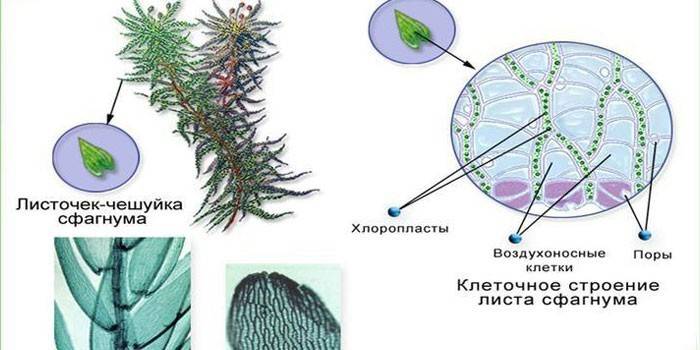
Suitable bryophytes with a photo
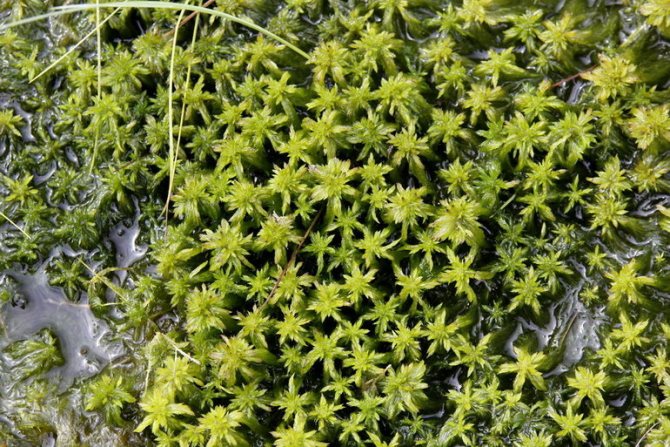
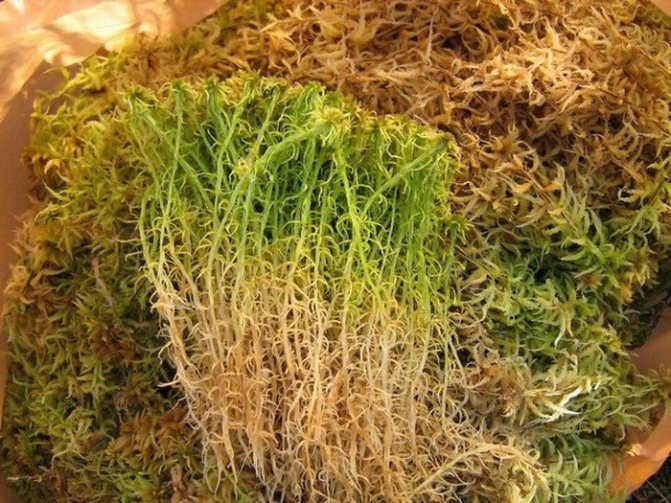
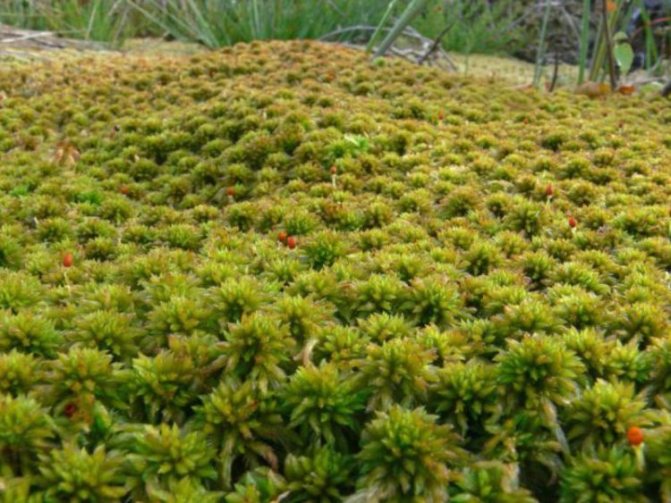
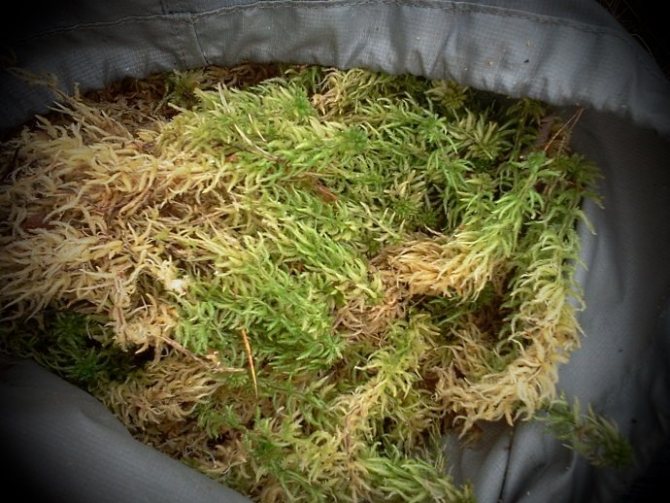
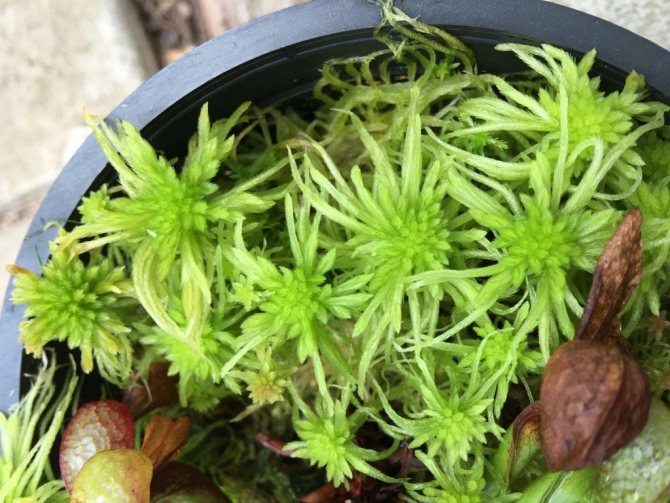
Sphagnum
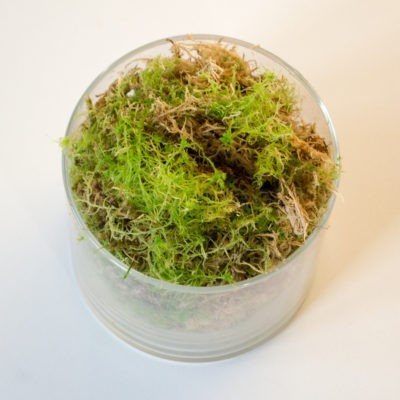


The most common type of moss, it grows mainly in the Northern Hemisphere, in coniferous forests, on marshy soils and marshes. Differs in delicate soft stems with needle-like leaves. Sphagnum contains a lot of moisture in the dead parts..
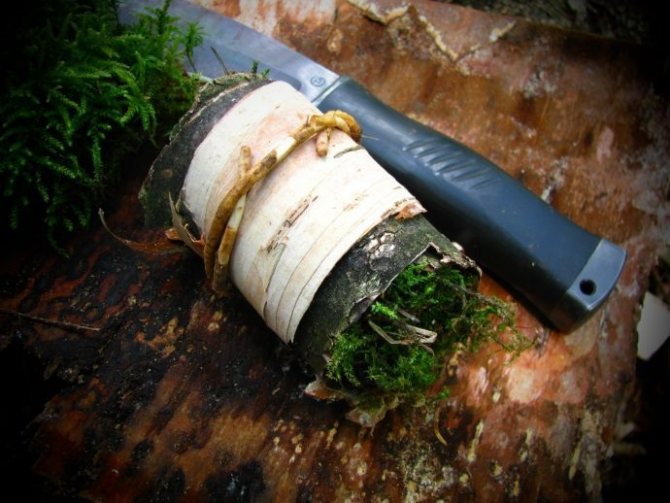
For orchids, it is used as a component of the substrate, mulch layer, drainage, root substrate when planting on a block. Sphagnum is also used as an antibacterial agent and as the main substrate for resuscitation of an orchid that has lost its roots.
When salted, sphagnum just changes... It is from this type of moss that high moor peat is formed - one of the substrate components for terrestrial orchid species.
We recommend watching a video about the features of sphagnum moss for orchids:
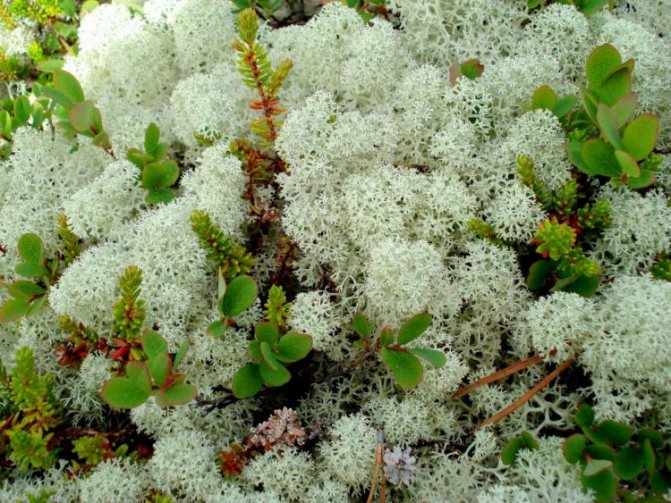
Reindeer moss
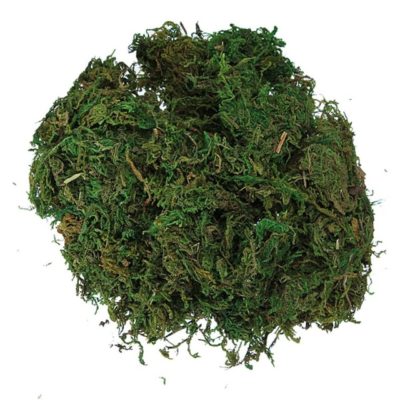


A variety of lichen that grows in different climatic zones. Yagel replace sphagnum if the latter is not nearby.
Sufficiently water-absorbing, decomposes for a long time, but very brittle. Can be used as drainage inside softer moss.
For stability, you can add broken red brick.
Kukushkin flax


It grows abundantly in the forest, in glades, alternating with sphagnum. This moss is vaguely similar to a juniper branch. Kukushkin flax does not crumble when dry, does not retain moisture for a long time, it is easy to detect and eliminate pests in it.
For an orchid, it is used as a substrate or part of it, the best option for growing plants on a block. When harvesting cuckoo flax, you need to rinse the bottom, as this moss grows moldy easily.
Description of sphagnum moss


Sphagnum or white moss, as it is also called, is a small herbaceous plant. It grows as a solid carpet, which is referred to as turf. There are many different types of sphagnum in nature. They differ among themselves in the long shoots, the shape of the leaves and their shade.
Sphagnum contains chemicals:
- triterpenes;
- cellulose;
- sugar;
- pectin;
- coumarin;
- various resins;
- phenolic acids;
- salt.
Also sphagnum contains sphagnol. It is a phenol-like substance that has antiseptic properties. Due to the huge amount of this component, plants that have sunk to the bottom of the reservoir do not decompose, thus forming peat.
Procurement recommendations
Collection or purchase
Sphagnum and cuckoo flax grow abundantly in the forest and it is better to collect them yourself - only in this way the quality of the product and the absence of pests will not be in doubt. In addition, this will save a little. It is better to choose moss, which forms peat cushions, they are useful for planting a new orchid and for fertilizing an adult flower.
Advice: Collect the top layer of the plant without touching the bottom. It is in the upper part that useful substances are contained, and new shoots are formed from the lower part.
Yagel does not grow everywhere, so it is easier to buy it... You can also buy sphagnum and cuckoo flax if they cannot be collected. Moss for orchids is easy to buy: it is sold in almost all flower shops.
We recommend watching a video about collecting sphagnum and reindeer lichen in the forest:
Processing and disinfection
When harvesting moss, one must not forget that this is an excellent breeding ground for various pests, bugs and snails. That's why moss after collection must be disassembled, inspected, washed and processed... You need to wash the green part, you can not wipe it.
Several processing options:
- Soak in plain water for about 12 hours, then treat with "Akarin" and keep it that way for another 14 days, treating the surface with water. Then dry well in the sun, letting the insecticide evaporate.
- Pour boiling water over the moss for about 5 minutes, squeeze out a little and put to dry.
Drying
If it is not possible to dry the moss in the sun, you can collect it in small bunches and hang it to dry on a rope. It is not worth using an oven or drying machine - this will not completely dry out the moss..
Varieties
Sphagnum
Spagmoss has several subspecies, combining on the basis of the absence of rhizoids (roots).
In floriculture, white peat is often used, its properties resemble river sand.
Consists of dissected stems covered with sessile ligulate leaves. Grows in bogs on bumps or in free movement on the surface of the water.
Benefits:
- characterized by increased hygroscopicity, taking water through moisture-storing cells;
- the composition contains a natural antiseptic - carbolic acid, which is detrimental to pathogenic microflora.
Disadvantages:
- leads to soil acidification;
- with excessive grinding, it quickly compresses, cakes, requiring frequent flower transplantation.
Forest
Includes several types of leafy plants growing in the forest belt (mnium, climacium, ptylium). It must be collected together with rhizoids (roots).
Benefits:
- creates a mild humid environment;
- maintains density, does not cake;
- has high breathability.
Disadvantages:
- requires careful processing before use;
- in contact with pine bark, it loses some of its beneficial properties.
Kukushkin flax


Moss improves soil quality
Refers to leafy plants with long and stiff stems, growing up to 40 cm. There are weak rhizoids. It grows in the taiga and on damp lawns.
Benefits:
- maintains breathability for a long time without decay.
Disadvantages:
- rough structure;
- does not absorb water well.
New Zealand
Tropical leafy variety without rhizoids with long stems.
Benefits:
- suitable for any purpose when growing orchids;
- retains its original appearance, dry sprouts do not crumble, do not break;
- does not cake;
- has a large and loose fiber structure, characterized by increased aeration;
- does not lose air permeability when tamped.
Disadvantage:
- lack of availability for purchase.
Step by step instructions: how to use


You can add moss to the pot if the top of the soil dries quickly and the roots dry out on the surface. In the case of growing an orchid in a basket, you need to cover it with moss on all sides. It is important to remember the rules:- moss should not lie close to the orchid;
- it should not be tamped tightly;
- the moss layer should be no more than 4 cm.
- Crushed moss can be one of the components of the substrate: the moss must be treated with mineral fertilizer, then crushed and added to the mixture, which can be poured under the root system, but not placed on top.
- You can put moss and bark in the pot in layers, starting with the bark.
- Sometimes the orchid is grown only in moss, then the gaps between the roots in the pot must be filled with moss, and drainage must be placed on the bottom of the flowerpot.
The choice of soil for an orchid is an important nuance for further growing a flower. We will tell you whether it is possible to plant a plant in ordinary soil, what types of soil there are and how to choose them, how to choose the right soil composition with your own hands. Also on our website there is detailed information about what kind of bark is needed, how to select and process it.
Features of the plant and its life cycle
it perennial spore plant that does not have a root system. In the process of development and growth, they form straight, non-branching shoots, which are collected in a dense sod, reminiscent of "pillows".
Instead of a stem, phyllidia and caulidia are formed. The gaps that form between the elements have the property of absorbing moisture, which ensures the life cycle.
In addition to phyllidia, which consist of only one cell layer, there is also a third element. These are rhizoids, which formally are the root part. The thinnest filaments of rhizoids branch very strongly and absorb moisture from the soil layer. One of their features is that over time, the absorption process stops and the rhizoids perform only the function of support.
The life cycle is based on the alternation of the sex generation with asexual... Gametophyte is a sexual generation that has male and female gametes that give rise to asexual sporophytes. Gametophyte is a photosynthesizing green plant.
The sporophyte is a spore-bearing generation that feeds on the gametophyte. Each sporophyte cell has a double set of chromosomes, while in gametes there is only one of them. Sporophyte development occurs due to cell division during meiosis. The result of the process becomes a dispute, but having sex, becoming a single gametophyte. This is how it goes constant, endless, life cycle.
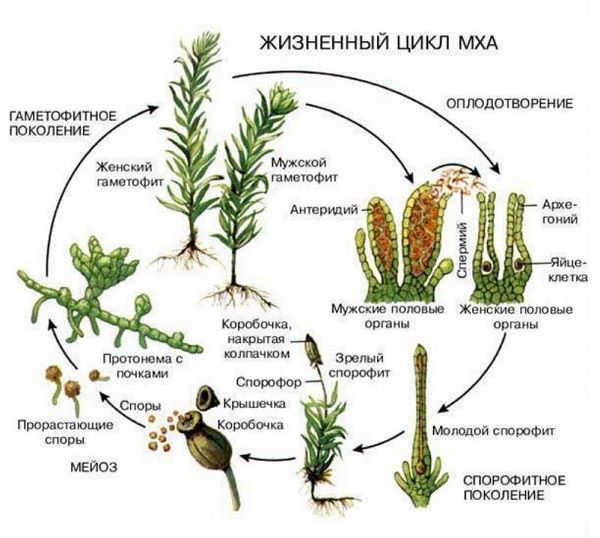

Sphagnum life cycle.
What to do with green bloom in a pot?
Sometimes in the spring and summer, a green bloom forms in the orchid flowerpot. This is algae or moss that grows on its own. They themselves are not dangerous for the flower, but they serve as a signal that the environment in the pot is too damp and warm. This plaque can form due to excessive watering, caked substrate, or if the flowerpot is too large. To solve the problem, you must:
- transplant the orchid into a new substrate;
- rinse and dry the roots;
- rinse and dry the pot;
- reduce watering.
We recommend watching a video about the causes of green plaque on an orchid pot and getting rid of it:
Terms of use
Sphagnum mosses before use it is recommended to scald with boiling water and, bringing to room temperature, squeeze. Then put in a plastic bag for 4-5 days.
Some growers are unhappy with the result of using sphagnum, citing a stop in the development of the orchid or rotting of the root system.
This happens due to improper watering and ignorance of the biological structure:
- watering should be carried out with a small amount of water;
- withstand the next watering until completely dry;
- do not allow completely dried moss to remain without watering for a long time;
- provide sufficient lighting;
- do not allow connection with the root collar;
- do not compact the layer.
Possible problems


The most common problem when using moss, especially when growing an orchid under a lamp, is soil salinity. Moss takes a lot of liquid and evaporates it from the surface., this cannot be avoided, even using distilled water for irrigation.
In this case, it is necessary to replace the moss or transplant the entire orchid, and rinse the leaves with liquid fertilizer.
Salinization of moss can occur not only in the pot, but also on the block... In this situation, replacing moss or transplanting an orchid must be done very carefully so as not to damage the root system that has sprouted into the block.
Which to choose
It is best to opt for live sphagnum moss, which can be used not only for orchids, but also for other indoor plants. It, unlike dry, does not need to be soaked and treated with an insecticide for a long time. In addition, it can be stored perfectly in bags in a cold place for several months. Even after freezing, which allows the plant to be preserved for a longer time, it does not lose its beneficial properties.
Dry sphagnum perfectly retains moisture and provides ventilation. It can be placed at the very bottom of the container with a plant, and in the soil, and from above. Sphagnum will perfectly retain the moisture your orchid needs, even if you cannot water the flower in time, and keep the heat it needs.


Growing zones
To find the places where sphagnum grows, it is enough to determine the wettest areas of the area. Most of all, he loves swampy, shaded and damp areas. Its reproduction contributes to the acceleration of the process of waterlogging of the area. Therefore, it is better to look for sphagnum in a raised bog.
Note. Sphagnum moss thrives on poorly ventilated soil. In order to prevent its large-scale growth in the personal plot, it is necessary to organize high-quality ventilation of the soil.
The hygroscopic sphagnum moss is most common in the temperate regions of the Northern Hemisphere. On the territory of Russia, there are about 42 different species that love wet areas.
Useful qualities
White moss is a unique substrate with amazing properties. The most familiar product to most people is peat.


First of all, peat is used in the form of a known fuel. The second way to use the characteristics of peat is to grow all kinds of seedlings. Peat is an excellent additive for improving soil performance in garden plots. Also, peat is a source of chemical raw materials used for the production of substances with various characteristics, the most famous substance from peat is medical alcohol. But this list does not allow to fully assess all the characteristics that correctly reflect the facts for which the prepared raw materials are used.
Attention! Cotton wool absorbs 20–25 times less moisture than sphagnum moss, which, even when wet, perfectly permits air through itself.
A unique combination of biological characteristics of sphagnum, is used with particular success in various spheres of human life.
Medication use
In medical practice, biological properties are actively used:
- high hygroscopicity due to the special structure of each cell of a biological substance;
- high antibacteriality: special substances that make up the plant have high properties to counteract fungi, microbes and other harmful substances that are important for medicines.
These high properties make it possible with particular success to use the substance as a drug for dressing, which has high-quality antibacterial and disinfecting properties. As a medicine, sphagnum can be used
:
- with superficial skin lesions (cuts, burns and frostbite);
- in case of fractures as a quality medical pad between the body and the applied splint.
Historical facts show that as early as the 11th century, doctors knew how to use the "natural sponge" in medicine to treat patients.
Construction site use
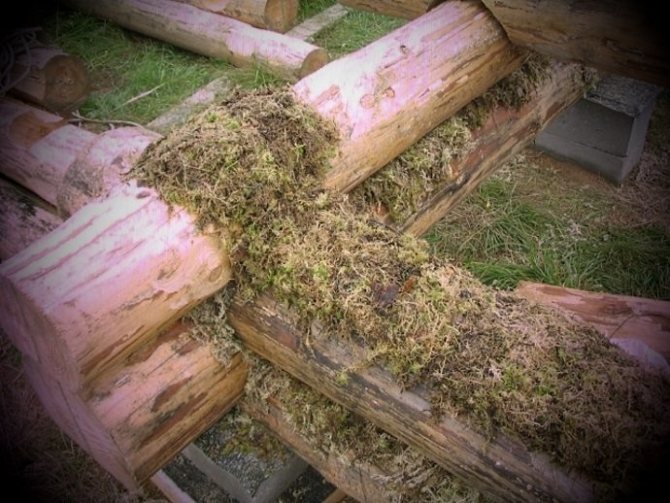
Builders also love the antibacterial and hygroscopic properties of the material. It is used as a heater, which is laid between the rows of logs, when building wooden log cabins. Despite the large assortment of high-quality modern materials used in the production of construction work, moss occupies one of the leading places among the highest quality and environmentally friendly insulation materials that do not allow decay.
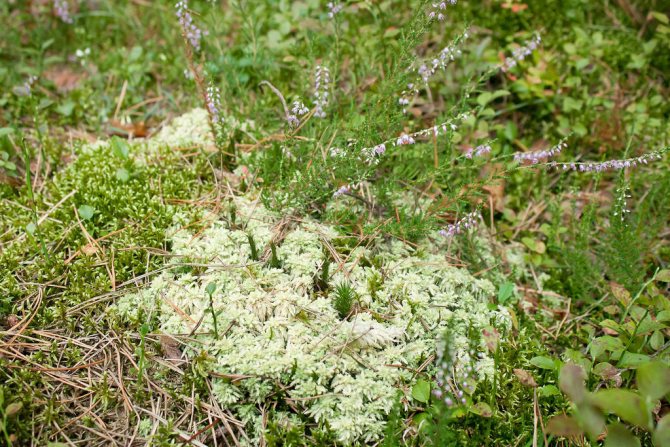


Its use prevents wood logs from smoldering, and its high ability to regulate humidity allows it to be successfully used in the construction of baths, the humidity of which is often high. The culture absorbs excess vapors and prevents wood from rotting.
Distribution of moss in agriculture
Lovers of bees and livestock breeders, the amazing properties of the plant were also not spared. The compressed dry product is used to make biological insulation for hives. But of particular interest for professionals is the ability to maintain the desired humidity level.
For this, the biological material dried at room temperature is laid out under the hive. When the humidity rises, moss absorbs liquid particles abundantly accumulated in the air. When it is lowered, it releases the accumulated moisture from its composition, increasing the moisture content and preventing sugaring, which causes significant harm to the quality of healthy honey.
Chemical methods
In the fight against the growth of moss, fertilizers can also help. For this, mixtures are suitable that help reduce the acidity of the soil. Experts recommend giving preference to complex products for the treatment of decorative lawns. These fertilizers usually contain three components: nitrogen, potassium and phosphorus. Such mixtures have a double effect. First of all, due to the properties of iron sulfate, the death of mossy growths occurs. Secondly, due to the presence of nitrogen, the growth of the grass is activated. If you apply fertilizer to moist soil, then the death of mosses occurs faster. As practice shows, a decrease in soil acidity is noted already two days after treatment. In spring or summer, sprinkle only on mossy areas. In case of extensive spread of plants, the entire area should be fertilized. Nevertheless, fertilizers should not be overused. You can use the mixture no more than once every 2 months. Experts advise to engage in lowering the acidity of the soil in the autumn. As a result, the alkaline composition of the soil will be provided throughout the winter.


Appearance
Now it's worth telling what sphagnum moss looks like - the photos still give only a rather superficial idea.
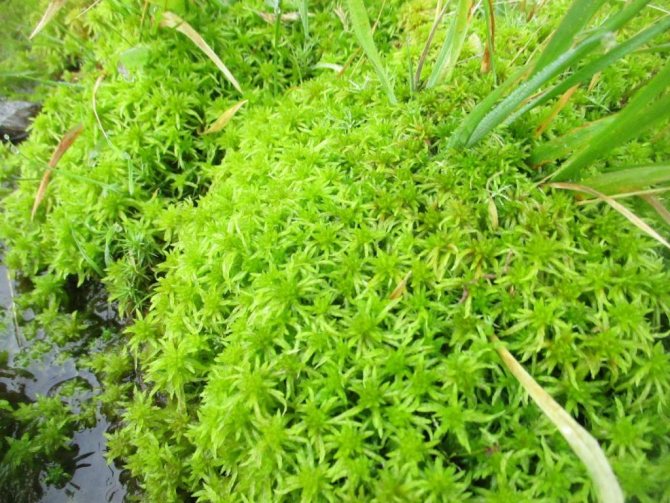


He cannot boast of a particularly outstanding appearance. It has a very thin green stem, originating at the root and extending upward. Differs in emerald green color. The upper part is covered with small leaves arranged in a spiral. By the way, for the sake of clarity, it should be noted that this moss actually has no roots.And that brown part, which not too experienced botanists perceive as a root, is an old, dead part of the plant.
Sphagnum, despite its small size, is a perennial plant. With the approach of cold weather, he freezes to continue life in the spring. It only grows upward, not to the side. The lower part dies off over time, decays, becoming peat.
The stems grow very densely, most often in damp places. Because of this, only the upper part receives the light necessary for the development of green plants. And in the lower, shaded, chlorophyll is destroyed over time, and it turns white. Over time, it rots, acquiring a brown color.
It reproduces, like most mosses, with the help of spores. They are contained by sex cells that have grown on the stem. After ripening, the bag bursts, and thanks to water and wind, light spores are carried a decent distance.
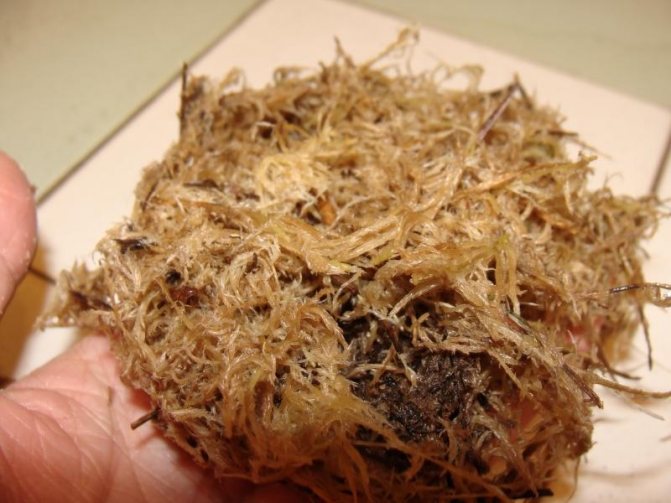
We store it correctly
Moss storage rules depend, first of all, on how you plan to use it.
Do you need dry sphagnum used in medicine? Then the easiest way is to use a cord or strong thread and hang the stems in a thin layer in a warm place with good ventilation. Well, or at least spread it out on a towel or newspaper and leave it on a windowsill, well-lit by the sun. Stir the moss a couple of times a day to dry evenly. Otherwise, the top will dry out and form a crust. Inside, the stems will remain moist and over time mold may appear here, making the use of moss for medicinal purposes impossible.
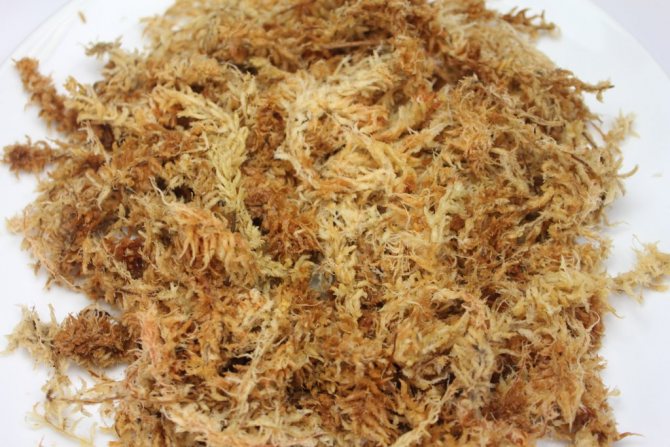


A completely different storage method should be chosen if your goal is to keep it alive for as long as possible. Coping with this task is not at all difficult. Rinse the moss well, then put it in a paper or cloth bag to put in the refrigerator or freezer. In such conditions, it will easily persist for several years. When sphagnum is needed, simply remove it from the refrigerator and leave it in a warm, slightly damp place. After a few hours, the stems will thaw, and after a few days they will continue to grow, as if nothing had happened. But here it is worth considering that the longer the sphagnum lays frozen, the fewer stems will remain alive. It is advisable to remove the rest as soon as it becomes clear that they died. It is not difficult to determine this - they will dry out pretty quickly.
Taxonomy [edit | edit code]
Sphagnum is the only modern genus of the family Sphagnaceae
(which also includes the fossil genus
Sphagnophyllites
). In order
Sphagnales
three more modern genera are distinguished:
Ambuchanania
,
Flatbergium
and
Eosphagnum
.
List of species [edit | edit code]
According to database information The plant list
(as of July 2016) the genus includes 382 species [9], some of them:
Mechanical methods of dealing with the "sponge" in the personal plot
Insufficient soil ventilation is considered one of the main reasons for the growth of moss. To ensure ventilation, you should penetrate deep into the ground, while providing air access to the lower layers. If the weed has not spread very much, then you can remove it manually. To do this, it is enough to dig out each of its bush. Correct mowing of the lawn is of great importance in preventing the spread of moss. It is she who affects the ability of the turf lying at a depth of about 8 cm to retain air, moisture and fertilizers. As mentioned above, high humidity creates a very favorable environment for the spread of the "sponge".


Carbolic acid


This substance is contained in the tissues of sphagnum moss, has a pronounced antiseptic effect... The result of this effect is the absence of bacteria that cause decay. It is this fact that explains the fact that sphagnum moss practically does not rot, and peat is formed from the fragments separating from the main plant.The thickness of the layer formed throughout the year ranges from 1 to 2 mm.
The presence of this broad-spectrum antiseptic substance makes it possible to use the plant for medicinal purposes. For example, sphagnum can be considered a suitable material for an antiseptic hygroscopic dressing in the field.