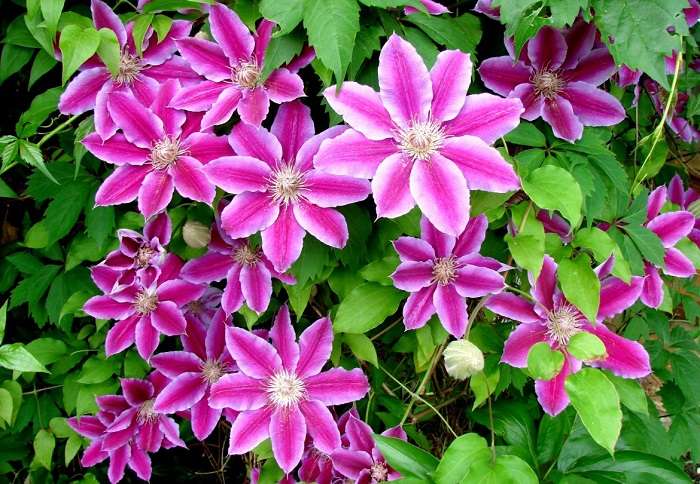
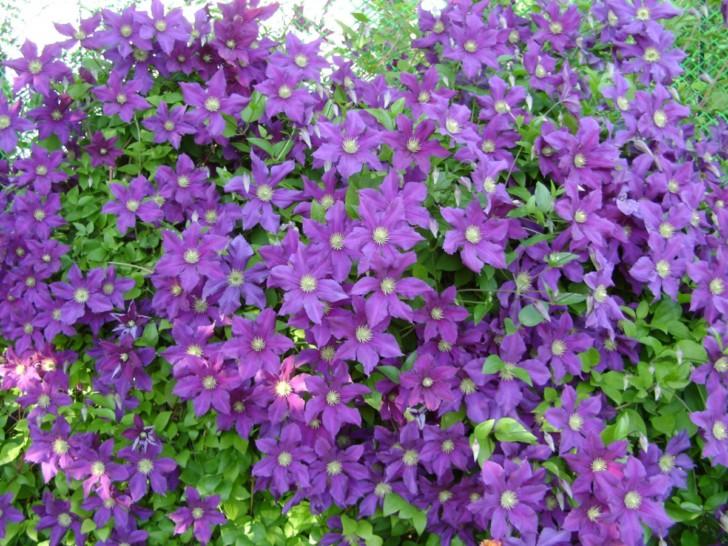
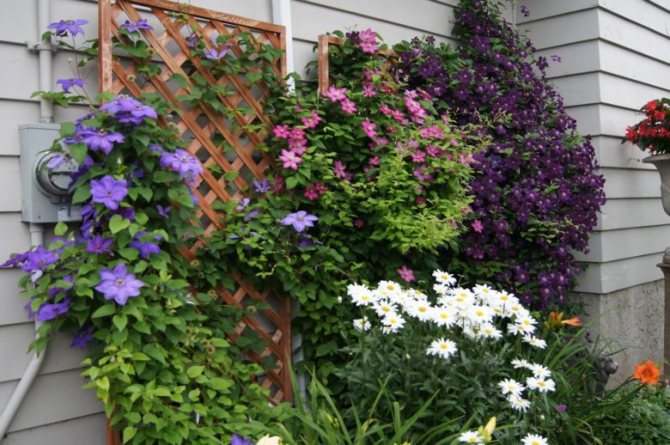
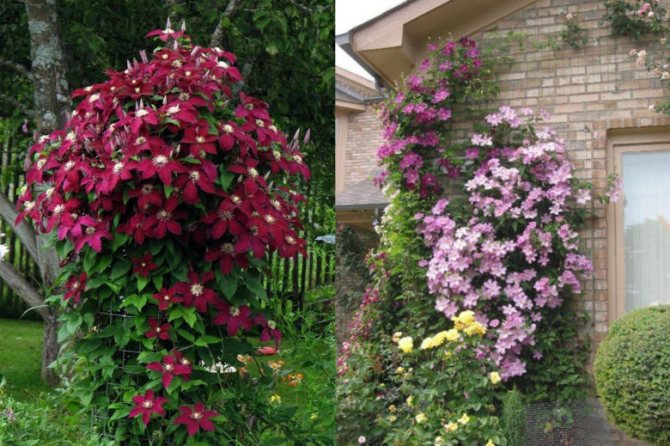
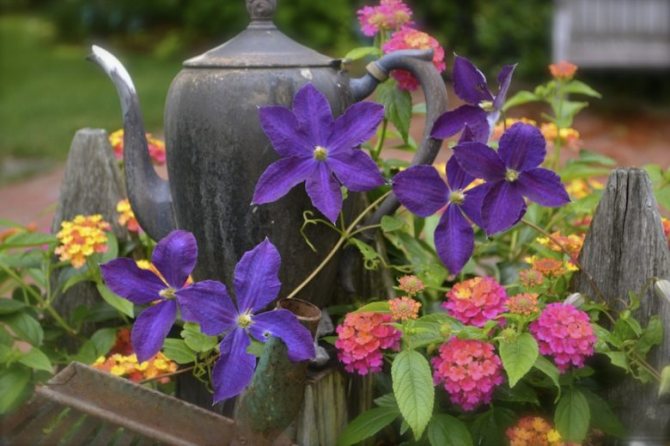
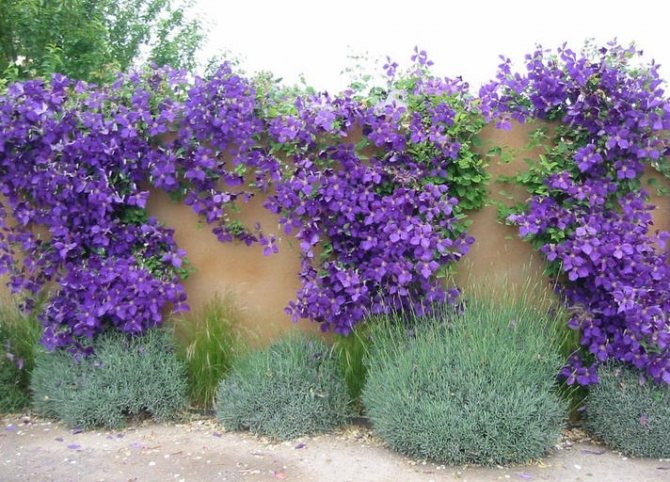
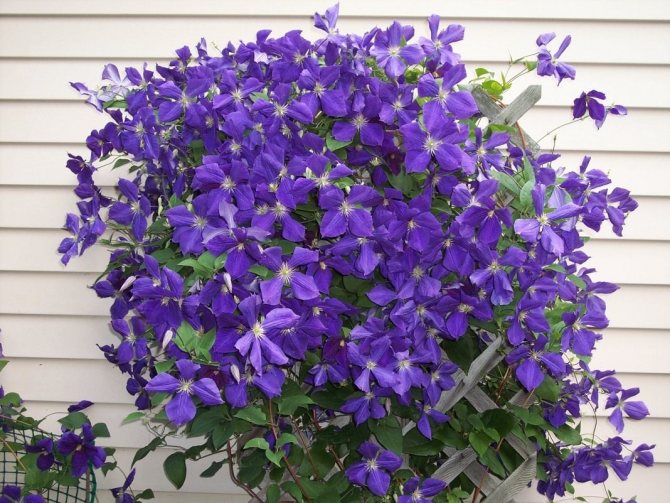
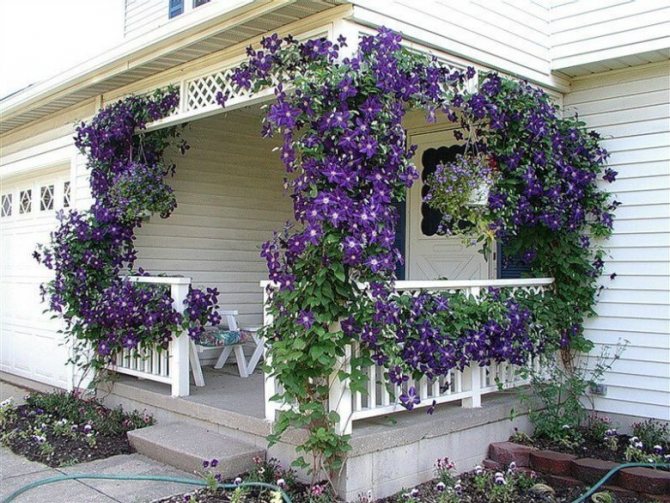
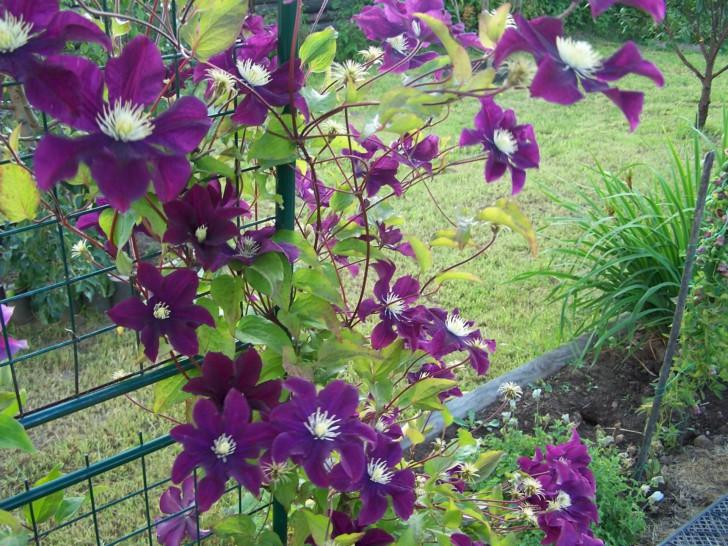
Clematis Is a wonderful perennial decorative liana. Perfect for landscaping and decorating any vertical surfaces. If you want to create a flowering wall or decorate a gazebo, choose clematis. This plant will not give you much trouble, but will give a lot of joy and delight to those around you. The variety of colors, double and simple flowers, different heights of lianas, flexibility and power of the shoots, and at the same time the lightness of the mass of the bush - all this makes clematis an excellent plant for landscaping the garden.
In addition, caring for this vine is not difficult, and the flowering is abundant and very beautiful.
Clematis is quite frost-hardy, can be grown in regions with cold climates, but, of course, with shelter. And you can plant it in the spring and autumn.
Brief instructions for planting and caring for clematis
- Almost all species and varieties prefer well-lit areas, some need protection from the midday sun. When grown in southern regions, it is strongly recommended to shade the "legs" - the lower part of the shoots and the soil around them.
- The optimal planting time is in the spring at the very beginning of the growing season or in the fall, at the end of September-October. After the buds have swollen, the plants can only be transferred with a lump and very carefully.
- The soils are necessarily light, well-drained, preferably fertile, slightly acidic, neutral or slightly alkaline. Some species require slightly alkaline soil (for example, Tangut clematis), others prefer slightly acidic, in neutral all grow well.
- Watering is rare but abundant. Young plants about 5 liters once a week, adults - two buckets every two weeks. Both young and adult plants very poorly tolerate overflow and stagnation of moisture in the soil.
- Top dressing - ideally at least three times per season. In the spring, a complex with a predominance of nitrogen, before the beginning of spring flowering (if any) - a complex with a predominance of phosphorus and potassium, before the start of the second - only phosphorus and potassium. At the end of the years, spraying with a solution of phosphorus and potassium fertilizers is recommended to increase the winter hardiness of the shoots.
- Garter: Requires most varieties and species. Some can cling to the supports with petioles.
- Pruning - carried out in the fall. Depending on the pruning group, the plants are not pruned at all (group 1), pruned at a height of about 60 ... 100 cm (group 2) or at a height of 30 cm (group 3)
- Reproduction: green and lignified cuttings, layering, dividing the bush. Many species of clematis can be propagated by cuttings.
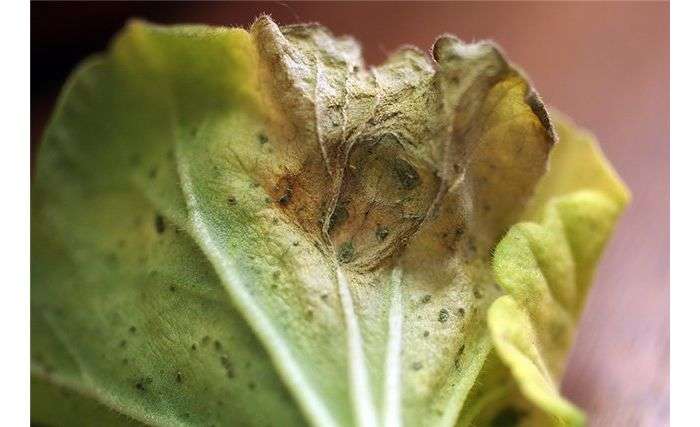
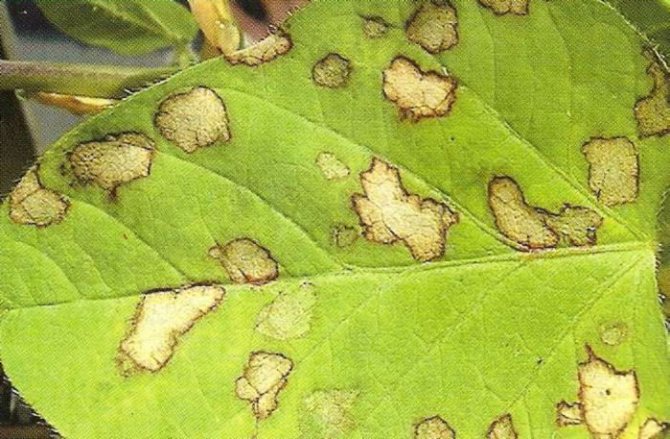
- Diseases: from critical wilt caused by some soil fungi. Sometimes there are also powdery mildew, ascochitosis and some other spots, but rarely and they are not dangerous.
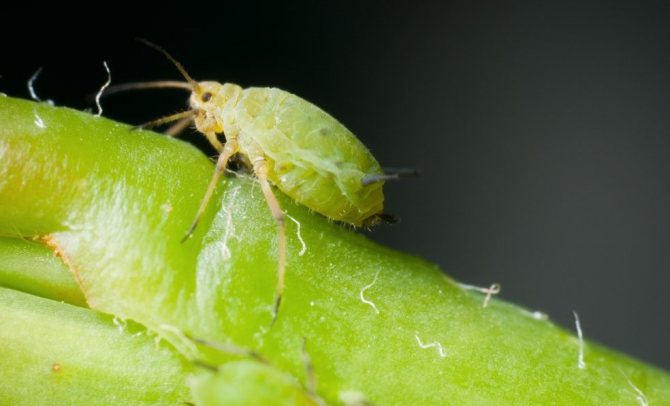
- Pests: nematodes, aphids are also mentioned in the literature.
Suitable varieties
Many varieties with frost resistance and high decorative effect are successfully grown in Siberia.
Elegy
Purple beauties with a flower size up to 13 centimeters. Shoots grow up to 3.5 meters. It has been cultivated in Siberia for many years.
Luther Burbank
The Luther Burbank variety is not afraid of frost, blooms all summer months. The flowers are purple-violet with yellow anthers (16-20 centimeters).
Anastasia Anisimova
A strong bush (1-1.5 meters) does not need support, it is strewn with blue flowers with delicate veins.

The president
A flower in the shape of a star with wavy petals.Blossoming - twice a season, the color of the flowers can change from dark to light purple.
Multi Blue
Lush double flowers ranging in color from purple to blue and up to 20 centimeters in size. In the absence of early frosts, the bush can bloom again in the fall.
Miss Bateman
White and delicate, like an English miss, flowers grow up to 15-17 centimeters. They are grown in Siberia due to their unpretentiousness and resistance to adverse conditions.
Cholmondeli
Clematis of this variety produce flowers in shades from lilac to lilac. On old shoots - semi-double, on young ones - simple.


Madame le Cultre
A bush with lily-white flowers withstands frosts down to -35 ° in winter.
Varshavska Nike
The petals, which are dark purple in the center and lighter towards the edges, do not fade in the sun. Blossom twice.
Dr. Ruppel
Flowers of exquisite shape and color with lush anthers. The petals are pale pink with a brighter stripe in the center.
See also
Symptoms and treatment of clematis diseases, causes and how to get rid ofRead
Nelly Moser
Star-shaped flowers with 6-8 petals with pointed tips. The color of the petals is light pink with a bright purple stripe in the center.


Zhakman
4-6 petals of clematis are colored dark purple with a tendency to discoloration to a bluish tint.
Rouge Cardinal
Velvety bright purple or burgundy flowers will adorn any area. Abundant flowering, June-August.
Huldin
Late variety with large white flowers with a pearly sheen.
Hegley Hybrid
English miracle with heads up to 18 centimeters. Petals are pink-lilac, anthers are claret-lilac.


John Paul 2
Clematis blooms with snow-white buds with a pale pink unexpressed stripe in the center of the petal.
Ernest Markham
1936 variety. It is famous for its colors of bright shades of red - from pink-purple to red-burgundy.
Purpurea Plena Elegance
Small flowers cover the bush with a purple-violet blanket.
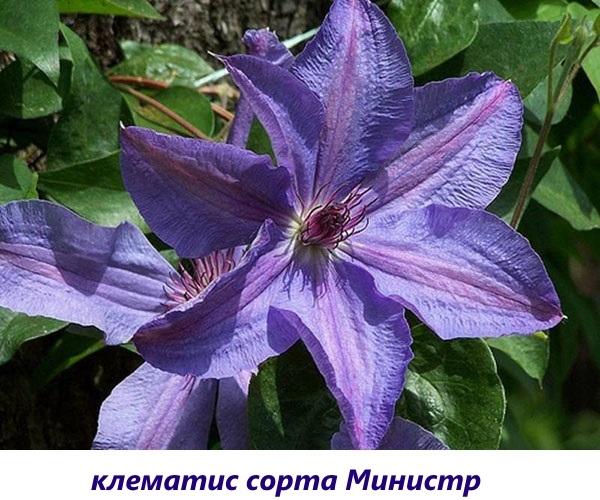
The minister
On the bluish lavender petals there is a pink-purple stripe in the center.


Cosmic melody
The flowers are strongly open, cherry-colored with velvety petals. The flowering is profuse and long lasting.
Ville de Lyon
Pink-red flowers with a pronounced border around the edge.
Forest opera
White petals almost close together, form a circle. Blooms until frost.
Dawn
A rare variety with snow-white flowers, which are pale pink at the beginning of blooming.
Climber
Clematis of the Alpinist variety has light lilac petals of an elongated rhomboid shape.


Ballerina
In their whiteness and shape, the opened flowers resemble a ballet tutu. Blooms again in August.
Ball of flowers
Rounded petals of clematis are painted in a pale purple color, in the center there is a brighter stripe.
Golden jubilee
Violet-purple pointed petals of clematis gradually brighten in the sun.
Blue flame
One of the most reliable varieties for Siberia with purple petals.


Lilac star
The mauve flowers do not fade in the sun, flowering June-August.
Gray bird
The slightly bent down and outstretched petals of a violet-blue color give the flowers the appearance of a bird.
Nikolay Rubtsov
Abundant flowering along the entire height of the bush with pink-lilac buds.
Texa
Buds with a complex color of petals - a blue background with a stripe and strokes of pink and white shades.
Blue angel
Clematis blooms in a lush cloud of pale blue flowers.


Koduehe
Delicate lilac color of the petals with a darker stripe in the center.
Lituanica
A variety bred by Lithuanian breeders with red anthers, wavy pink-white petals.
Niobe
Highly decorative flower of bright purple color with short yellow anthers.
Gypsy Queen
Purple flowers can fade in the sun; a shaded area is chosen for planting.


Victoria
Delicate clematis with a purple-pink color and a yellow heart are bred in Estonia.
Description of clematis is the most important
Most varietal clematis have thick succulent roots that are easily attacked by pathogenic fungi if there is a lot of water and little air in the soil. Thin roots in shrub species and varieties of the Atragene group (princes). They suffer from overflow a little less.
Herbaceous clematis vines have very brittle green shoots. Therefore, they must be tied up well and, if possible, not disturbed until autumn. In autumn, the shoots are lignified on the outside, but remain green on the inside. If we bend them down to cover, this must be done carefully so as not to break the shoot at the very base.
Clematis leaves are ordinary - green, with petioles. Depending on the type and variety, they can be simple, triple or separate. Many varieties, up to 9 knots, have one leaf shape, and above another. The shape of the leaf and leaf blade is one of the varietal traits, in some cases it can help identify the variety.
Clematis flowers are very different, but always bisexual. Depending on the species and variety, they can be single or collected in inflorescences. Small flowers are mainly found in the species clematis and in the Atragene group varieties. Large in varietal forms. What seems to us to be petals are actually sepals. Usually there are from 4 to 8. Terry flowers are formed not only due to sepals, but also due to staminodes - modified stamens. In double varieties, double and semi-double flowers are usually formed on the shoots of the last year and with a sufficient amount of active temperatures. Flowers on the shoots of the current year are usually simple.
The fruit of clematis is a multi-nut with a long nose. In some varieties and species, fruits in the Moscow region do not have time to fully form.
Features of decorative culture
When growing any plant, you must first familiarize yourself with its characteristics and features.
The native edges of clematis are subtropics and temperate zone of the Northern Hemisphere... A plant of the Buttercup family can be herbaceous or woody, but most often gardeners grow vines with weaving shoots.
Leaf climbers can be characterized by a taproot or fibrous root system. Faceted shoots, distinguished by their subtlety, are formed from underground parts or above-ground points of a tree. Simple or compound leaves can be lanceolate or ovoid. Lianas are characterized by green foliage, but there are varieties that have equally attractive purple leaves.
Bisexual flowers can grow one at a time or gather in panicle, scutellum or semi-umbellate inflorescences. Simple flowers have 4, 6 and 8 petals; double species may have several dozen. A large number of stamens and pistils form a furry center, similar to a spider. Clematis are characterized by a variety of shades: they are white, yellow, pink, purple, blue, etc. Fluffy fruits, collected in compound fruits, are characterized by a nut-like shape.
Vines bloom for 3-4 months. Flowering of high clematis, reaching 3-4 m in height, occurs in the upper part of the shoots. This nuance should be taken into account when choosing a place for planting and installing a support for a vine. Usually the shoots are tied up so that they tilt down. Such an organization of the plant allows you to beautifully decorate arches and fences. In low species, there is an almost complete combination of the vegetative and generative parts. During flowering, almost the entire tree is covered with beautiful flowers. But this feature prevents cuttings, since only the vegetative elements of the plant go to the cuttings.
Growing clematis from seeds


From the point of view of growing from seeds, all clematis can be divided into three groups:
- with small seeds - germinate within a few weeks, have good germination. These are species clematis - Tangut, grape-leaved, serrate-leaved;
- with medium seeds - germinate from a month to six months, many do not germinate without stratification. These are clematis six-lobed, Manchurian, whole-leaved;
- with large seeds - germinate for at least three months, and some for a year. Germination and germination energy are ugly, stratification is almost always required. These are varietal large-flowered clematis, woolly, Texas and others.
The best germination rate is with fresh clematis seeds, recently harvested and dried. However, if the seeds were stored in a dry place at a temperature of about 20 degrees, they will remain viable for 3 ... 5 years, although the proportion of those capable of germination will decrease every year.
Sowing dates depend on the group: small seeds are sown in March, medium ones at the end of December, and large ones a couple of weeks after harvest (they germinate so slowly that in the first year they may not even get to the pick).
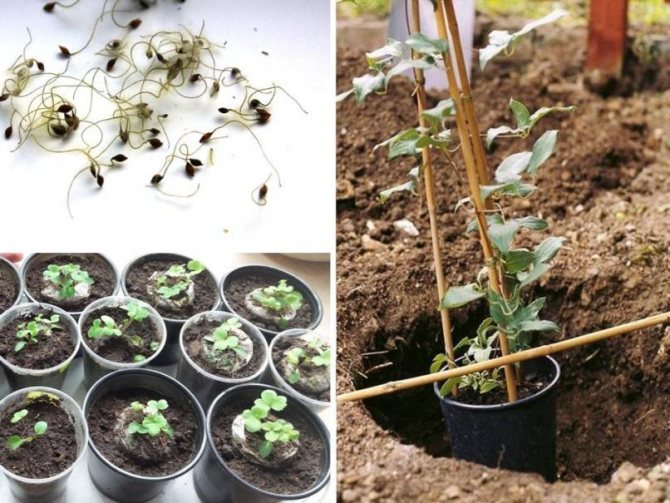
Many seeds do not germinate or germinate poorly without prior soaking or stratification. The seeds are soaked for 7 ... 10 days in clean water, which is changed several times a day. seeds are stratified in the refrigerator for 10 ... 30 days at a temperature of about 4 degrees.
After soaking or sowing, the seeds are sown in a light nutritious soil with a neutral soil solution. they are spread over the surface of the soil and sprinkled with wet sand. The thickness of the sand layer is 2 ... 3 diameters of seeds. after that, the containers are covered with glass or foil and placed in a warm place.


The optimum temperature for seed germination is 25 ... 28 degrees. During the entire time of germination, the soil is moistened by pouring water into the pan. You can also water from above through a strainer. After the emergence of seedlings, the temperature is reduced to 18 ... 21 degrees and placed in a well-lit place.
Care of clematis seedlings
Until the appearance of the first pair of true leaves, the seedlings are kept in a common container and watered rarely, but abundantly. After the appearance of true leaves, the plants are planted in individual pots and grown until the end of May-beginning of June. After that, they are transplanted into open ground.


For disembarkation, it is better to choose a calm, well-lit, but protected from the midday sun, a place with light, well-cultivated soil. If the nights are not very warm, the plants can be covered overnight in the first weeks. They need to be watered as the soil dries out, abundantly, but rarely, one complex feeding is desirable, 2 weeks after planting.
For the winter, the seedlings are covered, and in the spring they are transferred to a permanent place.
Planting clematis
How to plant clematis
For the cultivation of clematis, light, well-cultivated soils with a reaction of the soil solution from slightly acidic to slightly alkaline are suitable. The best landing site is well lit in the morning and evening hours, but slightly shaded at noon and as calm as possible.

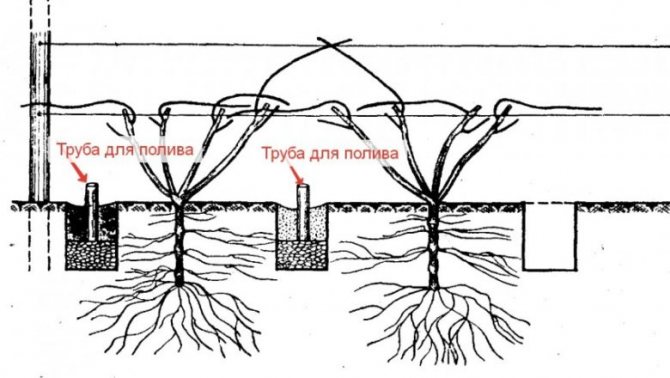
Clematis are often planted against a fence or wall. This is normal, but the distance from the wall to the landing point should be at least 50 cm, and it should not get water from the roof. Exposition is also important. In the description of clematis varieties on the Estate, it is almost always indicated at which wall they can be grown. Without exception, all varieties grow well near the east or west wall, many can grow near the south, and some even near the north. However, with the northern exposure, the plant always has fewer flowers.
Clematis Tangut, mountain, alpine, oriental and large-petal need alkaline soils, but in general they are undemanding and can bloom well on any soil if properly prepared. Grafted on Clematis viticella, it is advisable to plant in acidic soil so that they move on to their own roots.
Timing
Planting clematis is possible in spring, summer (only from pots and keeping a lump) and autumn. In the spring, it must be planted before the start of the active growing season. If you are late planning to plant the purchased clematis after the start of vegetation, you must wait until the shoots begin to lignify and pinch the growing point. For summer planting, you also need to pinch the growth point or cut off part of the shoot if it is long. It is best to plant in autumn, when the intensive growth of green mass has stopped, but the roots are still growing.
What if the seedlings are bought too late?


At the end of autumn, garden centers reduce prices for seedlings by 2-3 times. It's time to buy - for example, the “The President” sapling in this photo in C2 cost only 300 rubles. The trouble is that it is no longer possible to plant them in November and even more so in December - you must keep them until spring. It is best to use the bottom shelf of the refrigerator for this - it is dark and cool. During thaws, it is better to take out the seedlings for a couple of hours to ventilate.
Video on this topic
Planting clematis in spring
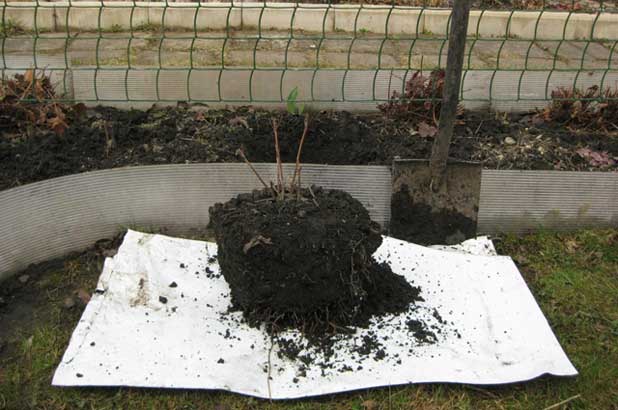
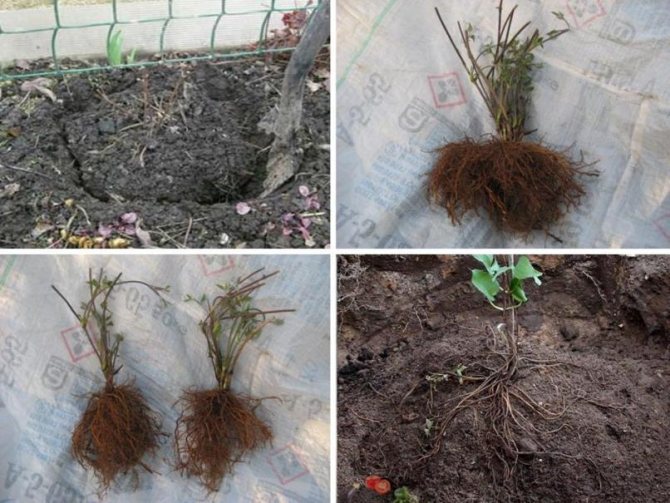
It is best to plant clematis in the spring at the very beginning of the growing season - depending on the region, this is the second half of April or the first decade of May. If the leaves on the seedling have not blossomed, it is highly advisable to remove it from the pot, rinse the roots and remove rotten and damaged ones. If possible, it is better not to plant with an old clod: as a rule, the supply of nutrients in the soil has already been exhausted. In addition, wireworms and other pests are often found there.
It is better to prepare the planting hole in advance, as soon as the soil thaws or even in the fall. If possible, the pit should be deep and wide - about a cube with a side of 50 ... 60 cm.It should be filled with the same soil that was taken out of it, but filled: It is mixed with 10 ... 12 liters of humus or compost (not manure), add 50 ... 60 grams of simple superphosphate and about the same amount of potassium sulfate. In no case should you fill the hole in an area with more loose soil and lay drainage down: you will get a drainage well into which water from the entire area will be collected.
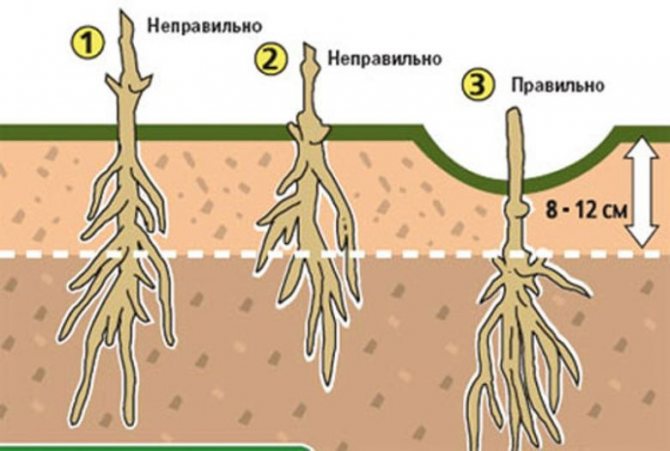
Planting depth is very important. In terms of developmental features, clematis are very close to herbaceous plants. The center of tillering, where new buds and shoots are formed, is in the soil: therefore, when planting, the plant must be buried. Deeper plants form a powerful tillering center, they suffer less from frost in winter and from heat in summer. Bushes from buried seedlings are more powerful and durable, although they develop more slowly in the early years. Annual plants can only be buried one node so that the buds are no more than 8 cm deep. Biennial and older plants can be buried 2-3 nodes. If internodes are long, and in some varieties they are longer than 25 cm, you can plant not vertically, but diagonally. Sometimes it is necessary to plant clematis, in which only the lowest part of the shoot is lignified - approximately to the first internode. In this case, the plant is planted in a hole so that three nodes are below the zero mark, but only the darkened ripe part of the shoot is filled up. The plant will be in the moon. In the fall, when the shoot is ripe, the pits are completely filled up.
How it's done
- Dig a planting hole deep enough to hold the estimated number of nodes in the soil.
- Place a small mound of earth in the middle of the hole.
- Place the seedling carefully and spread the roots along the slopes of the mound so that they do not curl upwards.
- Water the mound and roots liberally to keep them moist for a long time. If you need to add earth to the mound, add it.
- Sprinkle the roots and the buried knot with clean sand and ash to protect them from pathogenic soil fungi. Fill the hole to the top and water it again.


Planting clematis in the fall
Early autumn, when the growth of the aboveground part has already ended, and the roots are still actively growing, is the best time to plant normally developed clematis seedlings. If the plant has a month or more before the frost sets in, it will have time to root and prepare for winter. You just have to cover it to protect it from frost.
Clematis care
Clematis care after planting and in subsequent years is different. During the planting season, plants need to be watered regularly. Watered at least once a week, and in dry and sunny weather - every 5 days. The amount of water when watering should be such that it gets to the roots. In subsequent years, watering is carried out rarely, but abundantly: young plants are watered once a week, pouring about 5 ... 8 liters of water under the root, adults - once every 2 weeks in a volume of about 20 liters. The water should be warm, ideally rainwater. Tap water and well water should be allowed to settle for 6 ... 12 hours.
If clematis has a long shoot, and you did not cut it off when planting, this can and should be done later. About two-thirds should remain from the escape. If the shoot is short, only pinching is needed to awaken the dormant buds and the plant to form more lateral shoots.
The second, the same pruning is carried out in the summer before budding: with spring planting - in the year of planting, with autumn planting - the next year. The shoot is cut by about half. The third pruning is done before the first hibernation after the second. It is needed so that clematis is better prepared for winter. It can be done according to the trimming group, but it is better to trim the entire aerial part to the first true leaf. In the future, trimming is carried out in accordance with the group.
After planting, you need to feed at least once with a complex fertilizer with a predominance of nitrogen. This top dressing can be timed to coincide with the second pruning.
Top dressing of clematis
Clematis every year almost completely restore the entire above-ground part and therefore remove a large amount of nutrients from the soil. This take-out must be replenished in a timely manner.
I recommend the following scheme for feeding clematis:
- At the very beginning of the growing season, the introduction of 5 ... 10 grams of ammonium nitrate in the trunk circle. Can be replaced with 4..8 grams of carbamide (urea).
- 10 days after the first feeding, the second application of ammonium nitrate in the same dosage.
- Two weeks after the second feeding - a full range of fertilizers with microelements. By dosage - about 5 grams of NPK for the active ingredient per plant.
- The same feeding is carried out at the beginning of the first and second flowering.
- In September, shoots are sprayed with a 0.5% solution of phosphorus and potassium fertilizers to accelerate the ripening of shoots and increase winter hardiness.
Fertilizer


Since clematis are pruned every year in the fall and begin to re-grow the green mass in the spring, they require constant nutrition. Those fertilizers that were laid in the planting hole when planting a seedling will perform their nutritional functions for one year, therefore, starting from the second or third year, it is necessary to regularly apply new fertilizer for good growth and flowering of the plant.
Preparations need to be made different, containing a variety of elements and nutrients. In spring, as a rule, nitrogen-containing preparations are introduced, which stimulate the growth of stems and leaves. In the summer, during the further growth of the plant and the formation of buds, it will be necessary to fertilize clematis at least three times with organic fertilizers and mineral fertilizers. Here, everyone chooses the fertilization scheme that is convenient for him. Some alternate between mineral and organic solutions. You can use humus as mulch, and then fertilize the plant with only mineral preparations. You can add dry powders while watering the plant.The only period that does not require any fertilization is the flowering of the plant. If the clematis variety blooms in two periods, then after the first period has passed, it is necessary to pluck the shoots on which the flowers have already bloomed so that the plant does not waste energy on the formation of fruits.
Garter
In the spring, when the buds begin to swell on the preserved clematis shoots, they must be carefully lifted and tied to the supports. It is better to do this at the very beginning of the growing season, because then the shoots will become very brittle. When the average daily temperature rises to about 10 degrees, the shoots will begin to grow very quickly, up to 10 cm per day. At the same time, shoots with leaves that have not unfolded cling poorly to the supports, but good - to each other. If you do not follow the growth of the shoots, they will weave into dense tangles, where the leaves will not have enough light. To avoid plexus, clematis must be straightened and tied regularly.
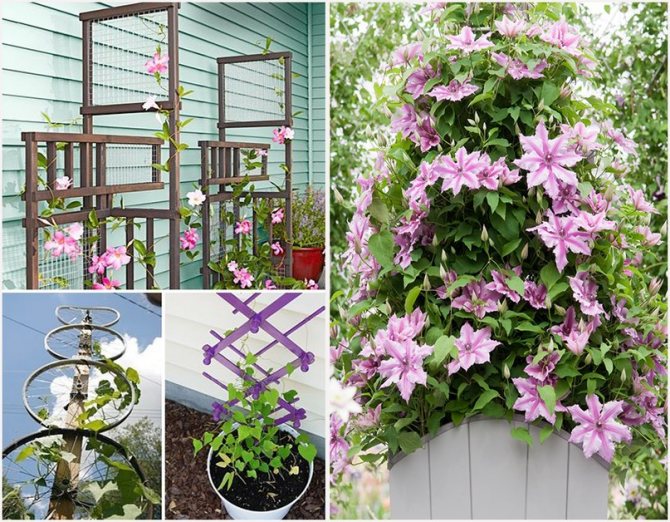
Supports for clematis
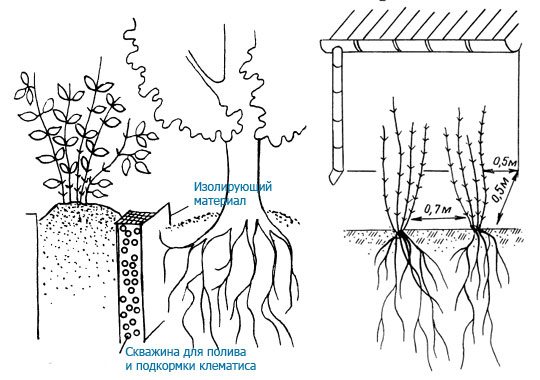
Most varieties either do not cling to supports at all, or only cling to natural ones, but they also cannot cling if the support diameter exceeds 1.5 cm.At the same time, the weight of an adult clematis is decent, and a light wooden or bamboo structure can collapse. Welded metal supports and wooden supports with a stretched mesh made of metal or nylon ropes proved to be the best.


Pruning clematis
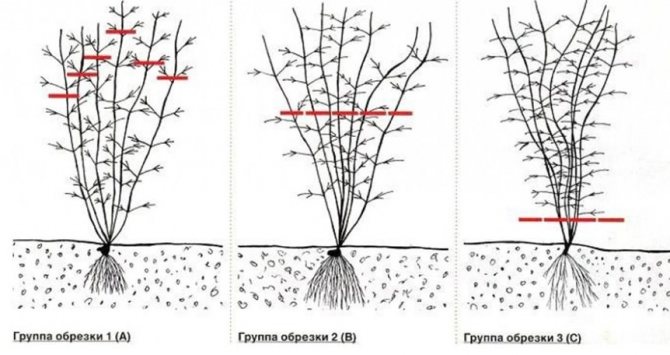
Depending on the type of flowering and winter hardiness, clematis are divided into three pruning groups:
- 1- very winter-hardy and blooming on the shoots of the last year. They don't need pruning or shelter, they just hibernate on supports.
- 2 - the least winter-hardy and blooming for the first time on the shoots of the last year, and the second time on the shoots of the current year. They are cut at a height of 60 ... 100 cm above a pair of strong buds and the remaining shoot is carefully covered.
- 3 - blooming on the shoots of the current year and usually quite winter hardy. Clematis of the third group of pruning are cut at about a height of 30 cm and also covered. However, many varieties are quite winter-hardy, and they have enough buckets of peat, with which they fill the tillering node.
Use in landscape design
Fast-growing clematis with abundant long flowering are used in landscape design in different ways:
- Combined with other plants. The bushes look harmonious and grow together without interfering with each other, with conifers and roses. Clematis is complemented by other liana-like species - honeysuckle, hops, maiden grapes, lemongrass.
- Clematis of different varieties are planted to create a "flowering wave" - representatives of different species gradually bloom. The site is decorated with blooming clematis in turn throughout the season.
- As a groundcover in rocky and gravel gardens.
- For decorating buildings, gazebos, pillars, dried trees with flowers.
- In containers for decorating verandas, recreation areas with the ability to replace and move flowers if necessary.
- For single planting, using decorative supports. The imagination of flower growers is endless - umbrellas, trellises, arches, obelisks.
Often they combine 2-3 types of clematis in a general composition. When combined, some flowers dominate in size and beauty, while others are smaller, playing the role of a background.
Clematis require regular care and care, they need to be watered, fertilized, tied up, a bush should be formed so that the shoots are placed harmoniously, do not interfere with each other. In response, blooming clematis will give a unique beauty to the site, dissolve a sea of flowers that delight the eye and cheer up.
Reproduction of clematis
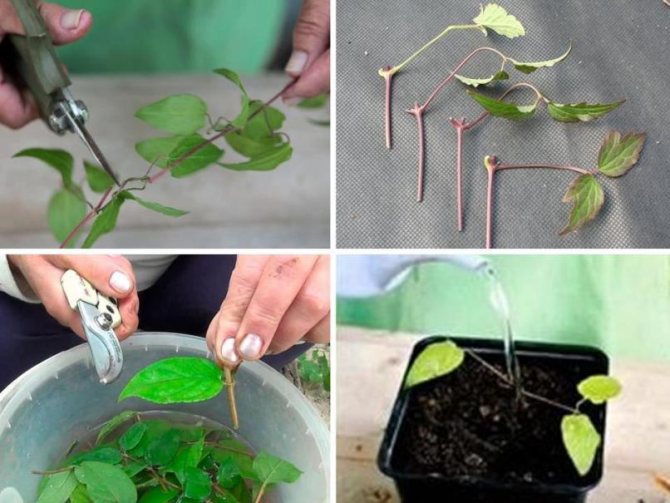
Reproduction of clematis is a very extensive topic and deserves a separate article. In general, clematis can be propagated by seeds (about how to grow clematis from seeds, written above) and vegetatively - by dividing the bush, layering and cuttings.
The easiest way to reproduce is to divide the bush, but this requires an adult strong bush, and you won't be able to get many new plants.In the fall, the bush is dug up and divided with a pruner or knife into several parts so that each has a shoot with buds.
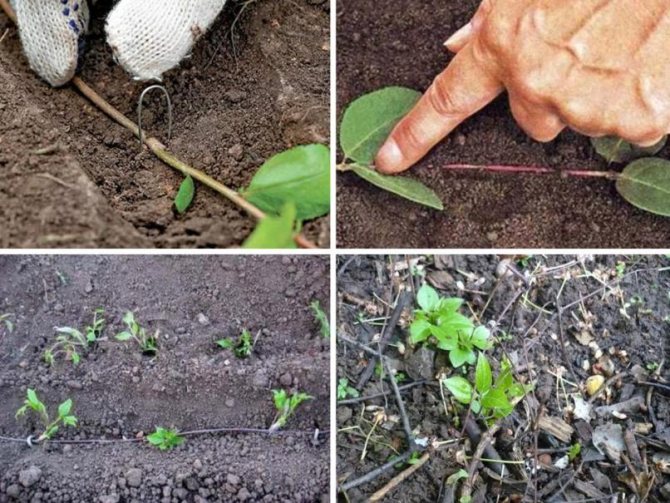
Reproduction by layering is a little more difficult, but it allows you to get more plants. In the place of future rooting, the earth is sprinkled with a mixture of sand and ash and moistened. Then the shoot is simply pinned to the ground next to the knot and a bump of wet sand is poured over the top. The leaves from the sprinkled knot are removed. On each shoot, you can make several such pinning. In the future, the bumps should be regularly moistened. In about a month and a half, the shoot will form adventitious roots and new shoots from the sprinkled buds.
Reproduction by cuttings is quite complex and is described here.
Pests and diseases of clematis
With proper planting and care, clematis rarely get sick. These are generally very hardy plants, it is not easy to kill clematis. If at least one living kidney remains in the soil, even a sleeping one, it will wake up sooner or later and give an escape. Sometimes it takes 3 ... 4 years, but the plant is still recovering.
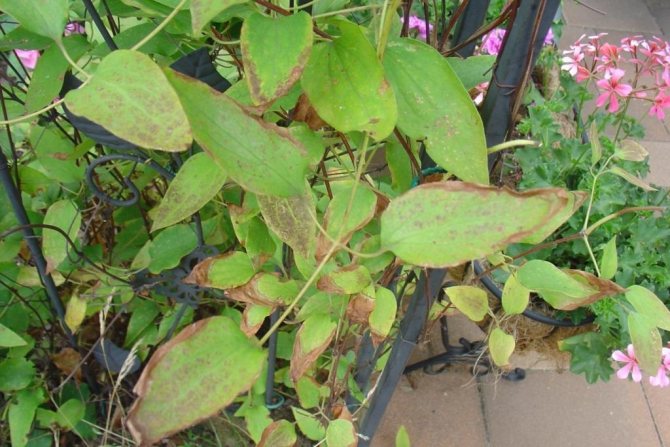
The most dangerous disease of clematis is infectious wilting, which can be caused by some soil fungi. Fungi enter through damaged or rotten roots or buds and begin to multiply intensively, spreading through the vessels and blocking the movement of water from the roots. The affected shoot quickly fades and dies. It is impossible to completely get rid of the causative agents of wilt in the soil, and the affected shoot cannot be cured either. Therefore, it is best to do this:
- When planting, the root and shoot with a growing point must be sprinkled with a mixture of calcined sand and ash. The soil around the shoot can also be sprinkled with this mixture.
- Watering clematis should be abundant, but rare: this creates conditions unfavorable for the development of soil fungi.
- Liming the soil also reduces the number of pathogenic soil fungi, but some clematis do not grow well in alkaline soil.
- If the shoot is wilted, it should be removed as soon as possible, and the soil around the clematis should be shed with phytosporin. Its efficiency is not very high, but it is better than nothing.
Other clematis diseases include ascochitis, powdery mildew and rust. They are rare and rarely do much harm. For prophylaxis, copper-containing fungicides are used, for treatment, systemic ones. Measures to protect specifically clematis from these diseases have not been developed: therefore, fungicides are used by analogy with other ornamental crops.
Clematis rarely suffer from pests: only nematodes provide a serious threat. Outwardly, damage by namatodes manifests itself in the form of a gradual wilting of the plant. The deceased clematis must be dug up and the roots examined. If swelling is found on them, it is a nematode. It is impossible to destroy it in the soil, and in the plant - only with the plant itself. Therefore, for planting clematis in the area infected with nematodes, quarantine is declared for 4 ... 5 years.
How to choose a landing site?
In order for the crops to take root and grow well, when choosing a place for planting, the following requirements must be taken into account:
- Lighting... The plant loves sunlight, so the planting site should be well lit throughout the day.
- The wind should not interfere with growth. It can break the stems and flowers of a rather fragile plant. Therefore, the place must be sheltered from the wind.
- Soil for planting by biological composition slightly alkaline, well fertilized and loose.
- Landing near bodies of water is prohibited, the accumulation of moisture will harm, and the roots begin to rot immediately, and the flower will die.
- A flower bed should have supports, on which the vines will begin to curl as the flowers grow.
- Cannot be planted tightly against walls or fences plant, the minimum distance should be 30 cm. This is due to the fact that the soil at the foundation is not very favorable for the growth of flowers. Waste water from the roof during rains should not wash over the plant.In this case, the plant will not give a beautiful weaving, but on the contrary, it will grow poorly. The most successful will be the southern wall.
- Plant does not like drafts.
With a well-chosen place and proper care, clematis grow up to 20 years in one place.