The dietary vegetable pumpkin has taken an honorable place among not only fans of healthy eating, but also deservedly so by ordinary people. She is very tasty, and today we have an extensive selection of both dishes with her participation, and a variety of varieties of vegetables for planting.
However, experience shows that you should not rely only on luck during the cultivation process. Achieve record harvests can only be done with a lot of patience and strength.


general description
This orange vegetable is very beneficial for humans. It contains: beta-carotene, alpha-carotene, vitamins A, B, E, C, K, magnesium, calcium, manganese, iron, zinc, phosphorus, potassium.
Pumpkin is proven to:
- cleans the body of toxins and toxins;
- stabilizes metabolism;
- normalizes high blood pressure;
- increases hemoglobin;
- enhances immunity;
- improves digestion;
- evens out the glycemic profile in diabetes mellitus;
- strengthens the heart muscles, vascular walls;
- good for vision, even more than blueberries.
Pumpkin seeds, which have antiparasitic properties, are very useful for digestion.


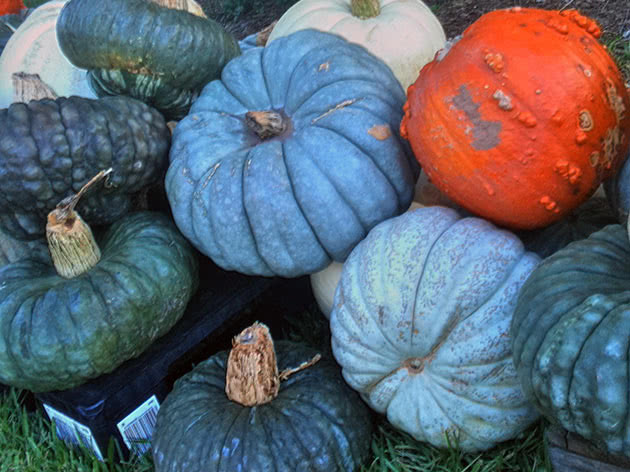
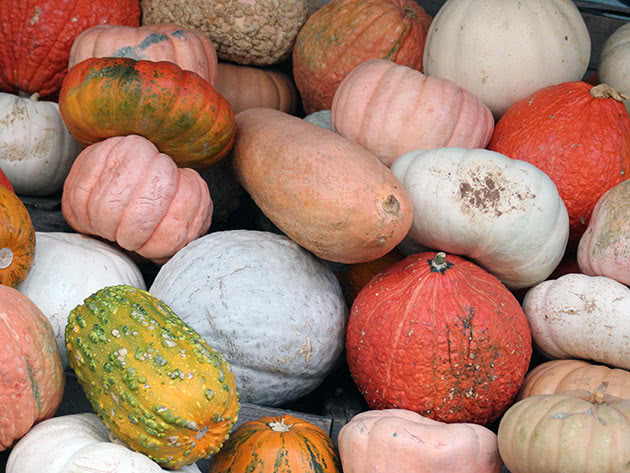
A huge variety of varieties and types of pumpkins
Pumpkin is an annual plant from the family of melons and gourds.
Interesting! Pumpkin is the most cold-resistant plant of all representatives of melons and gourds. Well-rooted bushes are able to withstand recurrent frosts.
Pumpkin fruits can grow up to 10 kg in weight. The shape of the fruit is round, oval or pear-shaped. The peel of the fruit can be bright orange, light green, deep green, grayish. The flesh is usually bright orange, but there are varieties with amber-yellow flesh.
Growing pumpkin outdoors is not at all difficult, you just need to know the rules of agricultural technology. We will tell you about them.
Pumpkin pests or diseases
Pumpkin can contract fungal diseases with black mold, powdery mildew, rot, ascochitosis and anthracnose.
Black mold is manifested by yellow-brown spots between the veins of the leaves, which, with the course of the disease, become covered with a dark coating with fungal spores. After the spots dry up, holes form in their place. Young pumpkins shrivel and stop developing.
With ascochitosis, large yellow-brown spots are first formed on the leaves, stems and in the nodes of the shoots, then light spots with a chlorotic edge, covered with black pycnidia containing the body of the pathogenic fungus. The pumpkin dries up and dies.
Powdery mildew is a real scourge of gardens and vegetable gardens, the symptoms of which look like a thick whitish coating, similar to spilled flour, which contains fungal spores. Leaves affected by powdery mildew dry, the fruits are deformed and stop developing. This disease is most active in conditions of sharp fluctuations in air humidity and temperature.


Anthracnose appears as large, watery, yellowish spots on the leaves. In wet weather, the veins of the leaves are covered with a pink bloom. Gradually, pink spots spread over the leaves, petioles, stems and fruits; by autumn, the affected areas turn black. Anthracnose is most dangerous at high humidity.
White rot develops on all parts of the plant, causing damage to the root system, drying out of fruiting stems and a decrease in yield. The pumpkin turns yellow, turns brown, becomes covered with a flocculent mold. Mucus may appear on the stems.Gray rot is manifested by brown blurry spots that quickly merge with each other and affect the entire plant. Wet bacterial rot can appear as a result of damage to ovaries and young fruits in too dense plantings by slugs or suckers.
Of insects, pumpkin is affected by melon aphids, podura, or white springtails, wireworms and slugs.
- What does the F1 marking on the seed package mean?


Slugs eat up the leaves of plants, sometimes leaving only a net of veins from them. There are especially many of them during rainy seasons. In addition, they are able to live and harm plants for several years.
The melon aphid damages the shoots, flowers, ovaries and the underside of the leaves, causing them to curl and shrivel.
Podura are the smallest white insects with a cylindrical body up to 2 mm long, feeding on seeds and underground parts of plants. The greatest harm podura bring to plants in cold, wet weather.
Wireworms are the larvae of click beetles that gnaw at the root collar of young seedlings, which leads to the death of plants. Most of all, wireworms like to congregate in wet lowlands.


Pumpkin processing
The fight against pumpkin diseases is carried out in fact and prophylactically, which is undoubtedly preferable, since the disease is much easier to prevent than to cure. To protect the pumpkin melon from fungal diseases, it is necessary to observe crop rotation, fulfill agrotechnical requirements, take a responsible attitude to each type of work, and especially to the pre-sowing treatment of seeds. At the first sign of illness, spray the plants and area with 1% Bordeaux liquid or other fungicide. And try to make the spring and autumn processing of melons with Fitosporin mandatory - this will help you avoid many unpleasant surprises.
Slugs will have to be collected by hand or set up beer traps for them: place bowls with beer on the site and from time to time collect shellfish that have crawled onto its smell. Wireworms are also caught with bait, digging holes 50 cm deep in different places around the site, placing roots cut into pieces - carrots or beets - and covering the holes with boards, wooden boards or roofing felt. After a while, the traps are checked and the wireworms gathered there are destroyed. They fight fools by dusting the soil around the plants with wood ash. Aphids are destroyed with Phosphamide, Karbofos or a solution of 300 g of soap in 10 liters of water.


And yet, let us remind you that diseases and pests, as a rule, affect weak and unkempt plants, so observe crop rotation, follow agrotechnical requirements, take good care of your plants, and you will not have to heal and save them.
The best predecessors and neighbors of the pumpkin
In the plant world, like humans, there are friends and enemies. With some plants, the pumpkin gets along well, and some do only harm. To grow a pumpkin in the country in the open field, this is important to consider.
| Good predecessors | Bad predecessors | Good neighbors | Bad neighbors |
| Corn, legumes, mint, radish. | Potatoes, other melons and gourds (due to similar diseases). | Potatoes, herbs, legumes, cauliflower, onions, garlic. | Late cabbage, carrots, tomatoes. |
By planning the planting correctly, you use the area rationally and get an excellent harvest.
Seedling care
For the active development of pumpkin seedlings, daily care is required. This is not only irrigation, but the observance of the temperature regime, the introduction of fertilizer mixtures.
An important nuance is considered to be daily ventilation, the removal of condensation from the covering material.
Excessive moisture significantly harms the seeds, contributes to the appearance of rot on the soil. Water droplets that form on the film are checked with a dry cloth.
After the procedure, the rag is washed well, additionally rinsed in a weak manganese solution.
Requirements for growing conditions
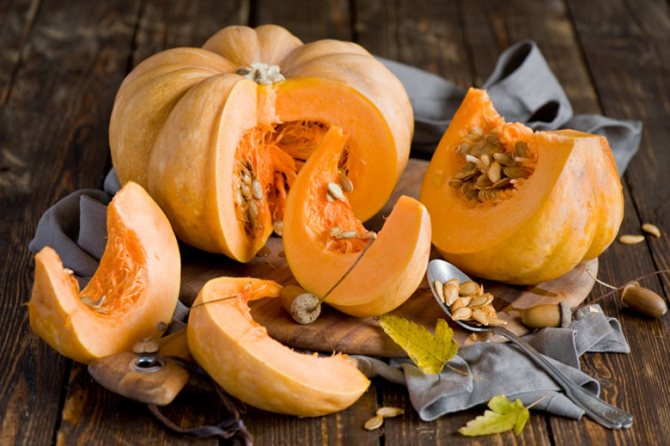


Pumpkin fruit
Pumpkin belongs to melons and gourds, which means it requires a lot of space. This vegetable has long creeping lashes, can spread up to 7 meters from the root, large wide leaves, large fruits. You need to plant the plant so that it can be at ease on the melon, and you should be comfortable looking after the plantings. One of the important conditions for growing this crop is soil.
The soil
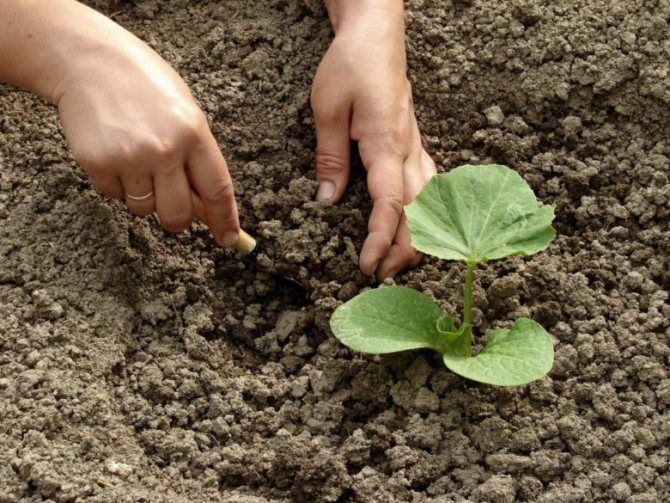


Planting pumpkins in open ground
This bright beauty is rather unpretentious. But it is better to grow it on light, fertile soils. Sandy soil, light loam is suitable, black soil is ideal. If you have heavy clay soil in your country house, you need to add sand. Conversely, loam is added to too sandy soil. The acidity of the soil should be neutral.
It is important that the site is dry, without stagnant water and flooding.
The pumpkin is a large plant, the taproot reaches a depth of 3 meters, and can grow up to 4 meters wide. She needs a lot of nutrition, so fertilizing the soil is necessary.
The site needs to be cultivated in advance:
- dig up and clear the area of weeds in the fall;
- dig up again in the spring;
- add fertilizers to the soil, ideally rotted compost, manure or humus. Mineral fertilizers are also applied: superphosphate, potassium sulfate. You can fertilize the land with a complex, balanced fertilizer for vegetable crops.
- the earth is leveled with a rake.
Good, nutritious soil is the key to an excellent harvest.
It is important to choose the right place for outdoor planting.
Lighting
The pumpkin is a thermophilic plant. She loves a lot of sun. You need to plant this culture in the sunniest place, where there is no shade and the sun all day long. There are varieties that grow well in shady areas, but mostly the plant prefers sunlight. Then this culture will delight you with large and sweet fruits.


Large pumpkin
Temperature regime
An orange vegetable grows and develops well at temperatures of +25 degrees and above. It stops growing if the temperature drops below +14 degrees. The ideal temperature regime is over +25 degrees, then the pumpkin fruits will be juicy, with a rich taste, and a pleasant aroma. Consider the thermophilicity of the plant when sowing seeds in the ground.
Growing pumpkin through sowing seedlings
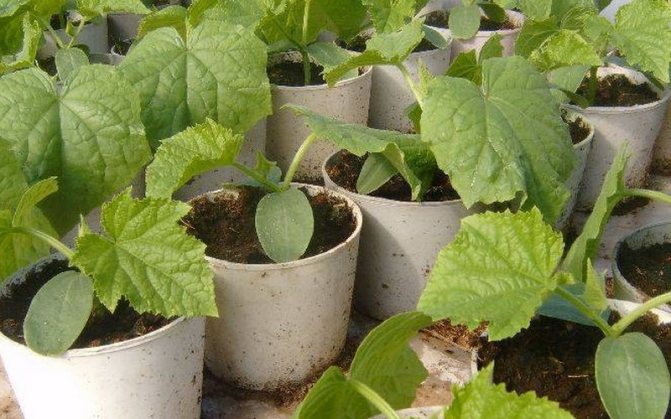
Planting tanks and soil
Containers for planting and growing pumpkin seedlings should be individual: pumpkin does not tolerate picks, therefore, special peat cups, ordinary disposable plastic cups (0.2 or 0.5 liters), plastic pots or any other small containers, of which it will be easy to get seedlings when planting in the garden.
Pumpkin loves nutritious soil. You can prepare the soil mixture yourself or buy ready-made soil for vegetable seedlings (or cucumbers). If you decide to make it yourself, then you should mix peat, rotted sawdust and humus in a ratio of 2: 1: 1, or take peat and humus in equal proportions.
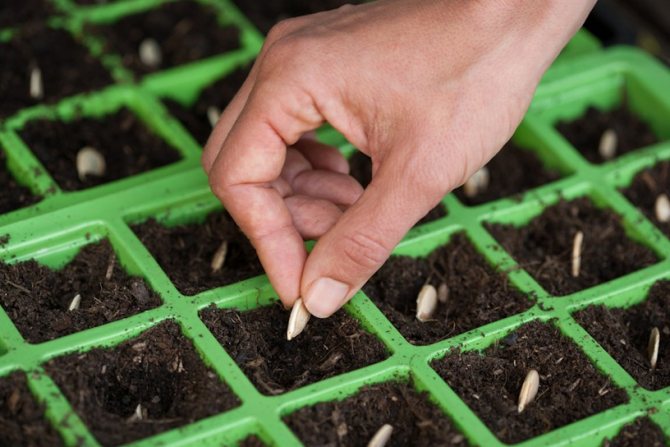
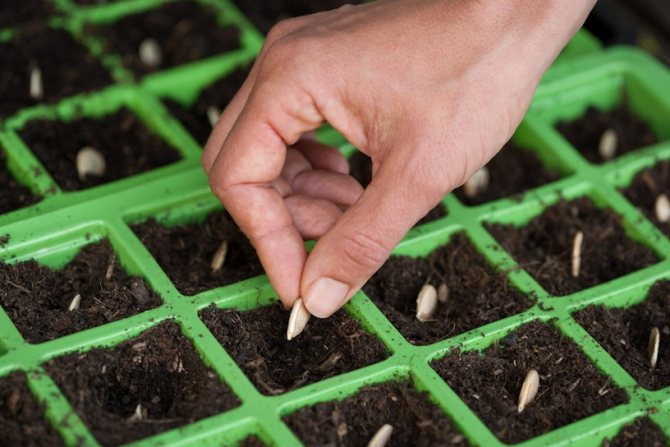
Sowing seeds for seedlings
Step-by-step instructions for sowing pumpkin seeds for seedlings:
- Prepare planting containers and fill them with soil a little more than half, so that as you grow, you can add soil to the seedlings.
- Spill liberally.
- Sow seeds to a depth of 2-4 centimeters.
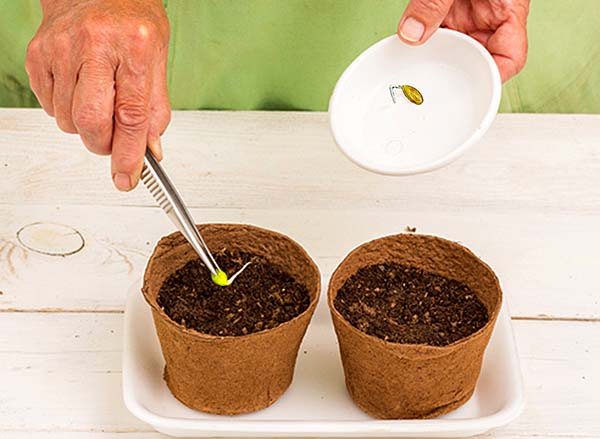


- Cover the container with glass, plastic wrap or shoe cover.
- Put in a warm and dark place, where the air temperature is 20-25 degrees during the day and 15-20 at night.
Video: planting pumpkin seedlings with germinated seeds
Video: sowing dry seeds for seedlings
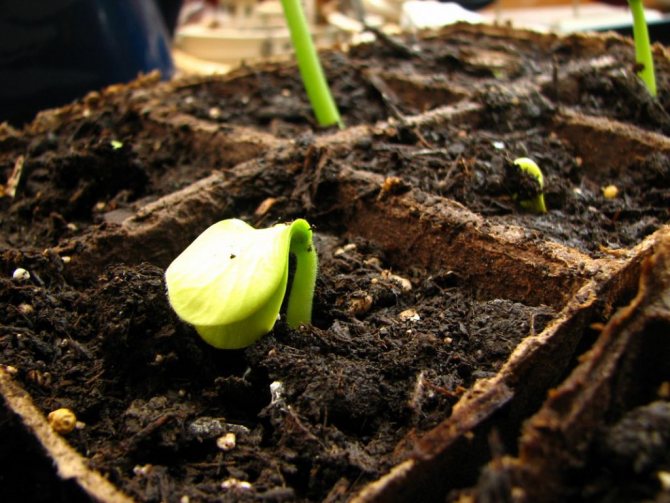
Further care of seedlings at home
When the pumpkin seedlings hatch and seedlings appear, the shelter must be promptly removed. Before that, it is worth at least 1-2 times a day to open the containers for airing for 10-15 minutes.On the 5-7th day after germination, the container with plantings can be placed in a cooler place (where the temperature is 4-5 degrees lower), and then returned to the previous temperature conditions. Such a procedure will help young seedlings not to stretch out.
Pumpkin seedlings need good lighting for normal growth, so the containers should be placed on a brightly lit windowsill, ideally south. Adequate daylight hours are your protection against pulling out seedlings.


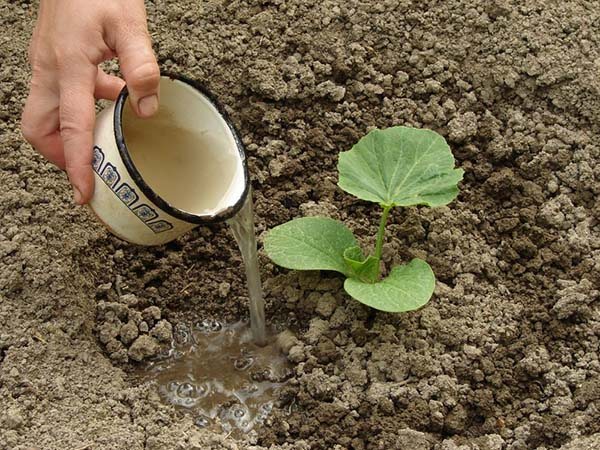
Pumpkin loves moisture, so it needs regular watering. But it should be done in moderation, without overflowing the plant.
Advice! If suddenly the seedlings begin to stretch, then be sure to add a little earth to the cups.
After 2 weeks as shoots appear, pumpkin seedlings can be fed. For this, both nitrophoska solution (0.5 tablespoon per 5 liters of water) and mullein (dilute 100 grams in 1 liter of water, let it brew for 3-4 hours, and then add another 5 liters of water) are perfect.
Video: growing pumpkin seedlings
Planting seedlings in open ground
The signal for planting pumpkin seedlings in open ground is the appearance of sufficiently developed 2-3 true leaves and the achievement of a seedling height of 15-20 centimeters.
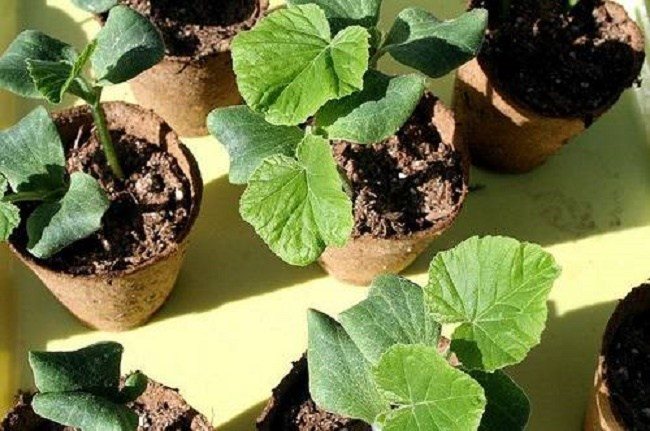


It is optimal to plant a pumpkin in the garden in the evening or during the day, but in cloudy weather, in other words, when the sun has gone or hid behind the clouds.
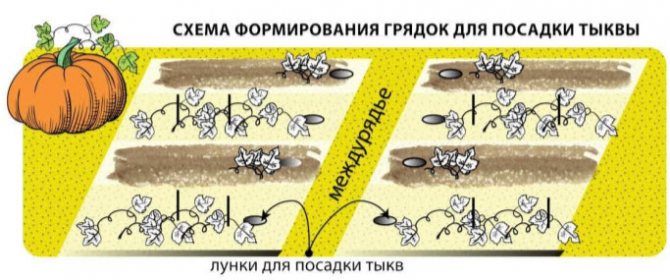

Pumpkin seedlings are planted according to the scheme 100 by 100 centimeters.


The transplant should be done carefully, slowly taking out the seedlings along with the lump, in no way damaging the plant's root system. It is better to make the hole large enough: pour humus and ash on the bottom, spill it with warm water, put the seedling (moreover, preferably not vertically), and then cover it with garden soil. As soon as the landing is carried out, the planting must be mulched with humus.
Video: planting pumpkin seedlings in open ground
Planting pumpkin seedlings in Siberia, the Urals and the Far East is similar:
Pumpkin planting dates
The pumpkin is the most cold-resistant of its fellows of the pumpkin family, but there is no need to rush to planting. This vegetable is usually planted as seed outdoors in the spring. Planting in the country is carried out at a stable daytime temperature of +18 degrees, the soil should be warmed up to +12. +13 degrees. In different regions, depending on the climate, you need to plant a pumpkin in open ground at different times:
- for southern regions - this is the second half of April;
- for Moscow suburbs - mid-May;
- Ural and northern regions - end of May, beginning of June.
We select varieties in accordance with the region. It makes no sense to plant large varieties in a cold region, the fruits simply do not have time to ripen.
Let's take a look at the best varieties of this vegetable.
Choosing a landing site
The place of cultivation also significantly affects the yield indicators - it must be well lit.
It is recommended to give preference to loamy or sandy soils. It is believed that they warm up as quickly as possible after frost.
Try to plant your pumpkin after the following crops:
- carrots;
- beans and other legumes;
- cabbage;
- beets;
- tomato.
Don't plant seeds after cucumbers, squash, or watermelon. The soil should rest for about 3-5 years.
Preparing seeds for planting
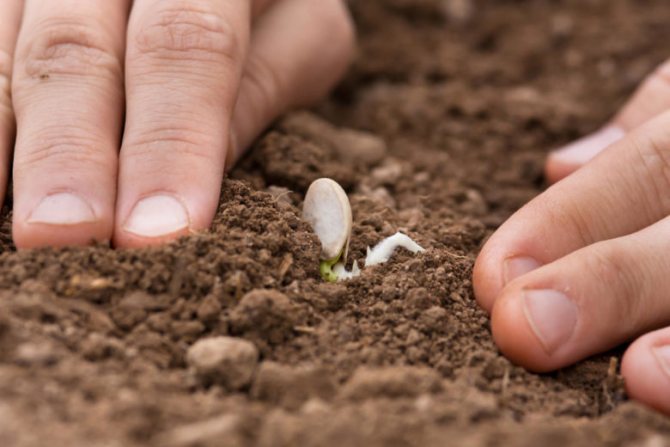


Sprouted pumpkin seeds
Planting pumpkin seeds in open ground is not a tricky business, the main thing is to choose good seeds. When buying seeds from the store, choose varieties that taste good. You do not need to take varieties of giants, they are difficult to transport, especially if you are carrying crops from a summer cottage. In addition, do not eat a large pumpkin at a time, and small pumpkins are usually tastier.
To immediately reject empty, unusable seeds, place them in water. We throw away the seeds that have appeared on the surface - they are empty. Then you can immediately sow seeds on the site, or you can germinate first.
What does the germination method give?
- Firstly, you are testing seeds for germination.
- Secondly, such seeds will start growing faster.
Germinating seeds is easy. Take a cloth moistened with warm water, put it on a plate, spread the seeds in the middle of the cloth. Place the seed plate in a warm place, not in the sun. The first shoots will appear within 2-3 days. You can plant them directly into the ground on the site. If there is no opportunity to plant immediately, the hatched seeds can be refrigerated for several days to slow down growth. It is not necessary that the sprouts be large, then it is easy to break them when planting.
Let the seeds of the "slow-witted" lie still in the warmth, if within a week the sprouts do not hatch, you can safely throw these seeds away.
Some varieties need to be grown through seedlings. To get an earlier harvest, you can grow seedlings from the hatched seeds, and then plant them on the site.
Testing pumpkin seeds for planting suitability
Next, read how to properly plant pumpkin seeds in open ground.
Harvesting and storage
Regardless of the varietal affiliation, the pumpkin must be removed from the site before the onset of the first frost. But early ripening varieties are best removed in the summer and immediately processed - they do not lie well.
How to determine the ripeness of a pumpkin?
Pay attention to the following signs of readiness for cleaning:
- The color of the leaves turns pale, then they turn yellow and dry.
- The fruit, on the contrary, becomes brighter in color, its rind hardens.
- The stalk becomes stiff and dry.
Plucked unripe fruits can get the required degree of ripeness when stored for another month. To do this, they need a cool, dark place. When collecting, 4-5 cm of the stalk is left. Only fruits that do not have external damage and bedsores are put into storage.
Many might say they grow pumpkin without all the hassle. Indeed, this is a rather patient plant, ready to forgive a lot to its owner. However, following these simple rules of agricultural technology allows you to get a much better, tasty and bountiful harvest when using much more modest areas of the summer cottage.
Planting methods and arrangement of pumpkin melons


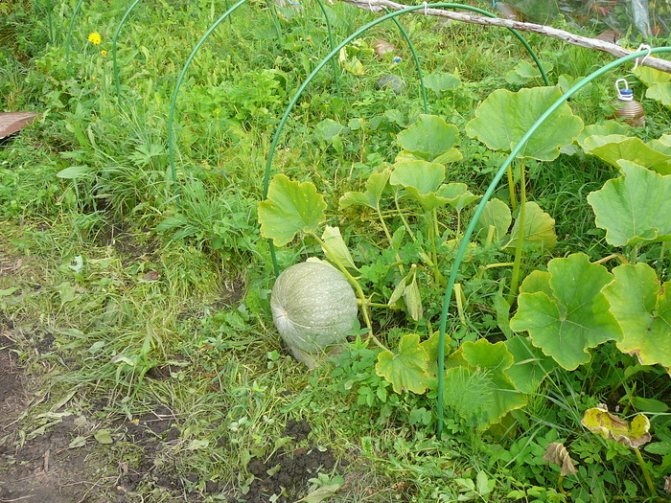
Pumpkin melon
The pumpkin is planted in open ground in spring at a stable above-zero temperature and when the soil has warmed up enough. Although pumpkins tolerate small return frosts, it is better not to take risks and do not rush to plant, especially if you are planting seeds.
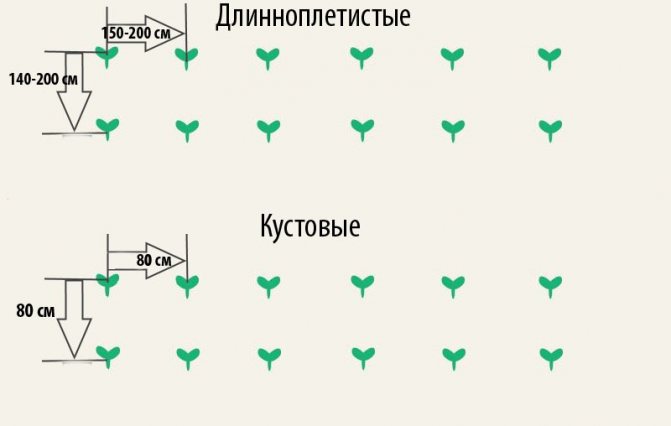
Pumpkin bushes love space and take up a lot of space, this must be taken into account when planting. The distance between plants should be 80-120 cm, row spacing 1 meter. It is better to plant the pumpkin on small swaths, the soil at the roots in this case warms up better and the plants develop well. Our soil is already ready, fertilizers have been introduced into the soil, and seeds can be planted. Make a small hole 7-8 mm deep and place the pumpkin seed. It is believed that it is better to put the seeds on the barrel, it is more convenient that way.
Important! Be careful with already germinated seeds, do not damage the sprout. Nothing will grow from a seed with a broken sprout.
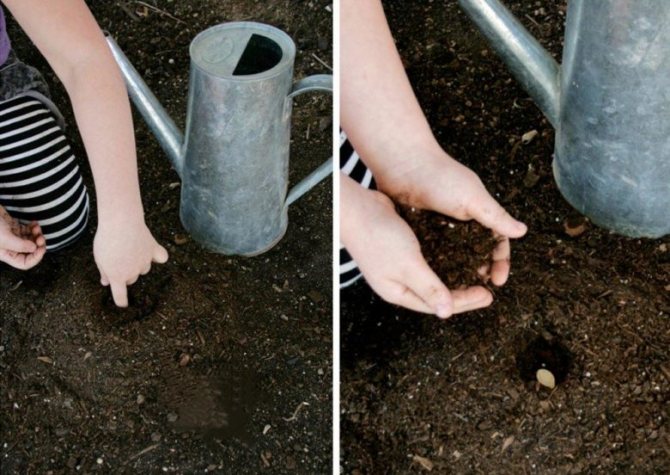


Planting pumpkin seeds in open ground
Sprinkle it with earth, without tamping it and pour it with warm water, if necessary, add the earth and spill it again. Now you need to be patient and wait for shoots and take proper care of the plant.
How to care for pumpkin outdoors
In the future, caring for the pumpkin includes watering, loosening after watering to ensure oxygen access to the roots and weeding from weeds, pinching the lashes for better fruit setting, and feeding as needed.
Watering the pumpkin is especially necessary during the period of fruit growth. However, it is worth starting to actively water only when the fruit becomes the size of a fist. All watering should be stopped at the moment when the pumpkin is finally ripe. This is necessary so that she still lies calmly and sugar, so to speak, is gathered in her pulp.


So that you do not have to worry about artificial pollination of the pumpkin, it is worth planting plants and flowers that bees love next to it.
Pollination
If the fruit does not set, then most likely you will have to artificially pollinate the pumpkin. This is pretty easy to do. First you need to choose a dry and warm day. Next, cut off the male flowers (they have long pedicels and have several stamens), remove the petals and press the stamens against the pistil of the female flower.
Shaping (pinching)
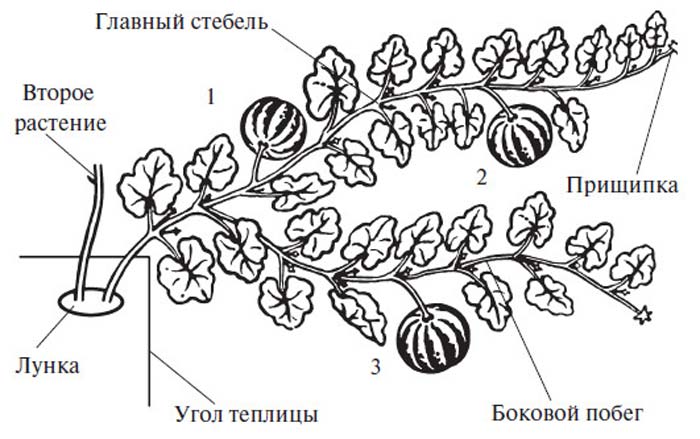
When the pumpkins are pollinated, in other words, the first small ovaries begin to appear, you will need to leave 3 whips (sleeves) on each plant. And as soon as the first pumpkin is tied, the whip behind it must be pinched. If you do not pinch, then the lash will continue to grow and another ovary will form, and the previous fruit will stop developing.
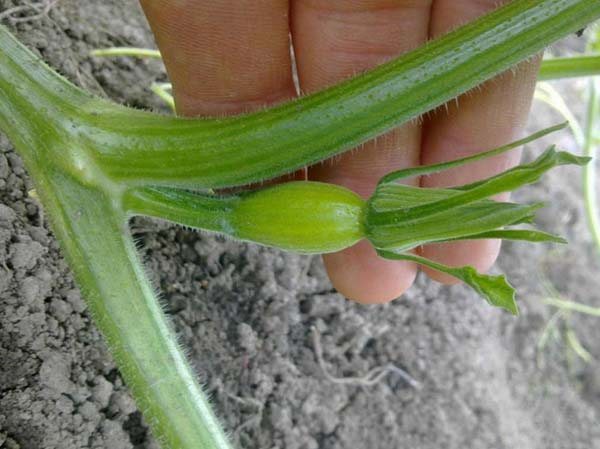


Remember! Different varieties require different shaping.


In large-fruited varieties, it is necessary to pinch the tops above the 5-6 leaf, which is located after the fruit. This should usually be done as early as June. In small and medium-sized ones, only whips with barren flowers should be removed. They are usually pinched in late July-early August, leaving 3-4 leaves after the fruit.
Video: shaping and pinching a pumpkin
Top dressing
Top dressing with manure and nitrogen fertilizers should be performed only at the first stages of active growth and development of seedlings, otherwise it will begin to fatten, increase the green mass, and you may not see the ovaries. For example, organic fertilizers such as chicken manure, which should be diluted with water in a 1: 5 ratio, are perfect for this.
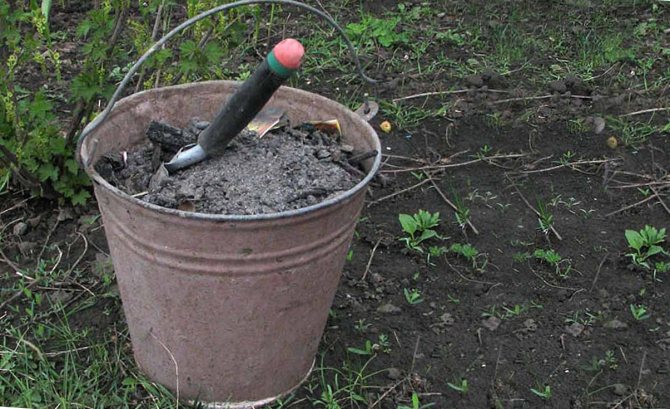
In order for the pumpkin to grow tasty and sweet, it needs potassium supplements. You can use either a more popular remedy - wood ash, dissolving 1-2 glasses of ash in water in a bucket of water, or you can purchase ready-made potash fertilizers, for example, humate or potassium sulfate.


The leaves should not cover the fruit from the sun's rays, so the excess must be trimmed or carefully torn off.
To prevent the lower part of the pumpkin from rotting even at the initial stage of fruit development, place a wooden plank under it or place it on a box. If you grow it on trellises, then the hanging fruits can be put in nets and tied to supports.


Fertilizing and feeding a growing fruit
As soon as the plant acquires a lush "head of hair", feeding should be done regularly after 7-10 days. You should not dwell on one thing, the plant needs both mineral and organic trace elements.
The first top dressing will be organic from wood ash and superphosphate in the base of the manure mixture. The second subcortex is mineral: saltpeter, superphosphate and potassium salt. After, they are alternated. Since the pumpkin has many shoots, to form a juicy fruit, it is necessary to properly pinch the fruitful shoots and remove unnecessary shoots. The main stem is pinched when there are already 2-3 fruits on it, and the other two lateral branches are also left. We delete the rest. To protect from the wind, the hinges are pinched or fixed with moist soil. If the goal is to grow a huge pumpkin, then all the other ovaries are removed, leaving the healthiest and ripeest.
Major pumpkin diseases
Among the most common diseases, you should know the following:
- powdery mildew, which first covers the leaves with powdery spots, and then the stems. Over time, the leaves turn yellow and fall off;
- olive spot is characterized by the appearance of sores on the stems of the plant, and brown spots on the leaves. Oily spots appear on the fruits themselves, in which the spores of the fungus mature over time. The edges of the affected area have a gelatinous fluid. If the disease takes possession of the ovary, then it will certainly perish;
- slugs.
Varieties for planting seedlings
In many ways, the yield of a vegetable depends on the selected variety.They all differ in the taste of the pulp, the size and shape of the fruit, the color of the peel, and susceptibility to diseases. When choosing seeds for planting, the weather conditions in the growing region are taken into account. If the climate is temperate or cool, greenhouses or greenhouses are used to grow thermophilic species.
Of all the existing types of pumpkin, only three are grown in vegetable growing:
- A common or hard-bore pumpkin has a short growing season. Fruits with a hard crust ripen within four months after germination. The plant tolerates a drop in temperature well. Its only drawback is the poor keeping quality of the fruit.
- Large-fruited pumpkins have an oval or round shape with a layer of tasty pulp of great thickness. Their crust is not woody. Under suitable conditions, the harvest is well preserved until early spring.
- Heat-loving nutmeg vegetable varieties have the sweetest flesh. They have fruits of an elongated shape, reminiscent of a pear. In regions with cool climates, nutmeg varieties are grown in greenhouses and greenhouses.
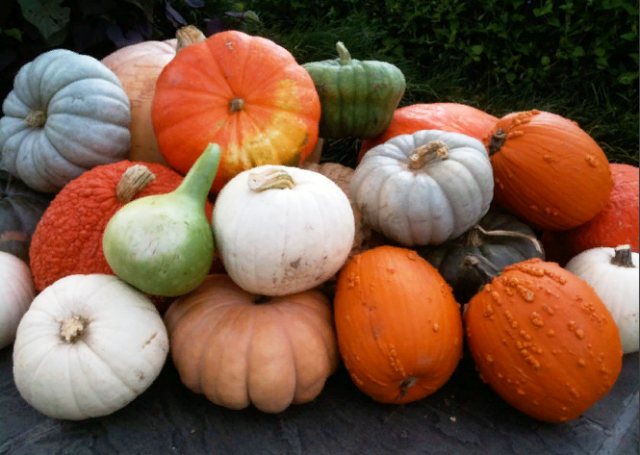


Popular varieties of common pumpkin:
- The "mushroom bush" pumpkin ripens early. It produces medium-sized fruits weighing up to 5 kg, covered with a light orange crust with green stripes. Dark yellow, firm flesh with a sweet aftertaste.
- The heat-loving variety "Kruknek Scrooge" has pear-shaped fruits with a pinkish or creamy shade of sweet and juicy flesh, covered with an orange or yellow crust with large tubercles.
- Early ripening variety "Biryuchekutskaya 27" produces oval or cylindrical fruits, covered with a thick yellow-orange crust with brownish spots. Their pulp is dense with a pleasant, delicate taste.
Common large-fruited varieties:
- Variety "Volzhskaya gray" has an average growing season. Pumpkins covered with a gray crust reach a weight of 9 kg. They have a sweetish pale yellow or orange flesh with medium density.
- Pumpkin "Barn" flat-round shape. Their weight ranges from 2 to 4 kg. The rind is dark green, covered with black stripes.
- The mid-late variety "Kroshka" forms fruits weighing up to 3 kg. They are covered with a light gray crust with small pinkish specks. Inside there is a thick layer of dense orange pulp, sweetish in taste.
Butternut pumpkin varieties:
- The late-ripening pumpkin "Vitaminnaya" has broad-shaped fruits, reaching a weight of 7 kg. They are covered with a crust of dark pink color with orange spots. Inside is a thick layer of reddish, sweet-tasting pulp.
- The "Candied" variety has an average ripening period. It produces fruits weighing up to 5 kg, covered with a light brown crust. The layer of red or orange flesh is thick and dense, pleasant to the taste.
- Pumpkin "Pearl" has an average ripening period, gives a rich harvest. It has pear-shaped fruits covered with an orange, smooth crust. The inside is dense, sweet orange pulp.