Sometimes soil analysis shows that there is enough nutrients in the soil, but the plants do not develop. What is the reason? It turns out that one of the reasons is the accumulation in the soil as a result of chemical reactions of an excessive amount of free hydrogen ions. They determine the acidity of the soil. In an acidic environment, many vegetable and horticultural crops cannot grow and develop, since as a result of reactions, compounds are formed that are inaccessible for absorption by plant roots. It turns out that nutrients are present in the soil, but the roots of plants "do not see" them, begin to "starve", which means they stop growing and developing.
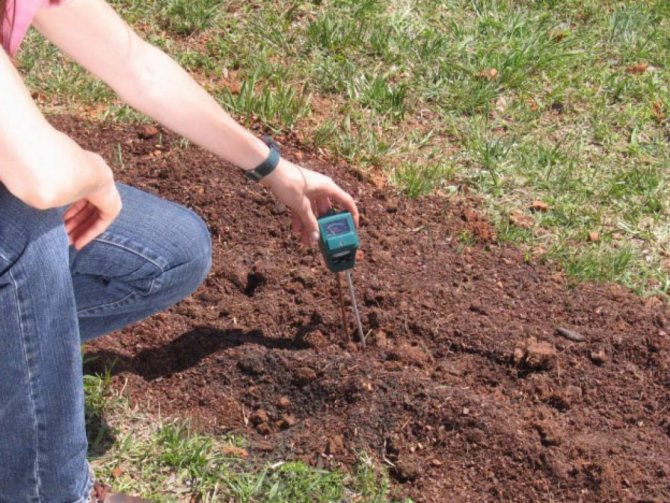

Determination of soil acidity with a special device
Part of the soluble salts is carried away by rain and melt water outside the root system of plants, in turn, depleting the soil. Long-term application of some mineral fertilizers also acidifies the soil. The total impact on the soil of all negative processes will increase acidity and, in this case, neither additional fertilizing, nor irrigation, nor other agronomic techniques will help. The soil will need to be deacidified.
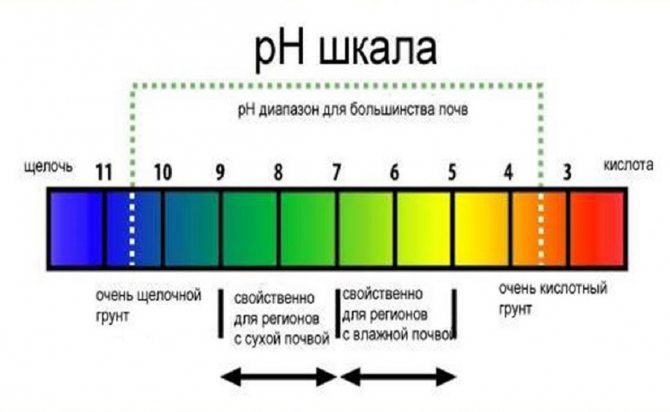
Soil acidity
The acidity index of the soil is influenced by the amount and composition of chemical elements. The acidity level is indicated by the pH icon. The pH value depends on the amount and composition of chemical elements in the soil. According to the results of chemical experiments, it was found that nutrients are optimally available to vegetable and horticultural crops at pH = 6.0 ... 7.0. Soil pH equal to 7.0 is considered to be neutral.
All values below 7.0 are considered acidic and the lower the number, the higher the acidity. Like acidity, biological processes in plants are also influenced by alkalinity, which is caused by alkaline elements contained in the soil. Alkalinity is reflected in pH values above 7.0 units (Table 1).
Both deviations from the neutral indicator indicate the degree of availability of certain elements to plants, which can decrease or, conversely, increase so much that nutrients become toxic and the plant dies.
Table 1. Types of soils by acidity
| Soil acidity | pH, units | Soil types |
| strongly acidic | 3,5 – 4,5 | bog soils, low-lying peat |
| sour | 4,6 – 5,3 | peaty, coniferous, clayey - soddy |
| slightly acidic | 5,4 – 6,3 | heather, turf |
| neutral | 6,4 – 7,3 | sod, humus, deciduous |
| weakly alkaline | 7,4 – 8,0 | carbonate |
| alkaline | 8,1 – 8,5 | carbonate |
| strongly alkaline | 8,5 – 9,0 | carbonate |


Determination of soil acidity and its deoxidation
How pH affects nutrient absorption
At very low pH values, the absorption of such nutrients and trace elements as molybdenum, phosphorus, potassium, sulfur, magnesium deteriorates, as a result of which chlorosis of the leaves appears.


Almost all calcium is spent on neutralizing the acid, so its amount is insufficient for plant nutrition. Due to the lack of carbonates, crops are threatened with fungal infection of the aerial part.
Vegetable plants lose microscopic hairs on the roots, which are responsible for absorbing water. Because of this, crops suffer even more, as they do not have the ability to absorb moisture. In this case, the top of the plant is usually damaged, since the liquid does not enter there.
The root system develops poorly due to a lack of phosphorus, which is not absorbed at a low pH value, therefore, dwarfism of shoots, leaves and fruits appears.
Did you like the article? Share with your friends:
What does the acidity of the soil affect?
Soil acidity affects the solubility, availability and absorption of nutrients by plants. So, on moderately acidic and acidic soils, phosphorus, iron, manganese, zinc, boron and other elements are more accessible and better absorbed by some plants. If the acidity is increased (pH = 3.5-4.0), then instead of even greater assimilation of nutrients, inhibition of the growth of roots and the activity of their work will be observed, the plants become sick from a lack of supply of necessary nutrients to the organs.
In strongly acidic soils, the aluminum content increases, which prevents the entry of phosphorus, potassium, magnesium, and calcium into plants. Substances that negatively affect the beneficial microflora begin to accumulate in the soil. The processes of processing organic matter into humic substances and then into mineral compounds available to plants will practically stop.
The alkaline environment also significantly influences many biological processes. Interferes with the assimilation of some macro- and microelements necessary for plants. Phosphorus, magnesium, boron and zinc become inaccessible to plants. In some plants, the opposite effect is observed: in an alkaline environment, the root system of plants intensively absorbs the applied mineral fertilizers, up to toxicity.
Experimentally, in agrochemical studies, the optimal limits of soil acidity were determined for various agricultural crops, ornamental-park and flowering plants (Table 2). For vegetable crops, the most favorable is soil acidity within neutral or slightly acidic (pH = 6.0-7.0).
Table 2. The optimal level of soil acidity for garden crops in the country
| soil pH | Name of crops |
| 5,0 – 6,0 | watermelon, potatoes, pumpkin, parsnip, sorrel |
| 5,5 – 7,0 | tomato, white cabbage, carrot, corn, garlic, cucumber, pepper, parsnip, rhubarb, beetroot, peas |
| 6,0 – 7,0 | lettuce, onion, legumes, pumpkin, spinach, beets, beans, eggplants, garlic, collard greens, Brussels sprouts, radishes, zucchini, beets, carrots, foliage, turnips, tomatoes, chives, shallots, leeks, cantaloupe, chicory, cucumbers, horseradish, spinach, rhubarb |
| 7,0 – 7,8. | cauliflower, artichoke, celery, lettuce, onion, asparagus, parsley |
| 4,0 – 5,0 | heather, hydrangea, erica |
| 5,0 – 5,6 | juniper |
| 5,0 – 6,0 | Pine |
| 6,0 – 7,0. | 1 - woody ornamental, ornamental herbaceous perennials and annuals, lawn grasses 2 - fruit crops (plum, cherry) |
| 5,5 – 7,0 | apple, strawberry, pear. |
| 7,0 – 7,8 | clematis |
| 4,0 – 5,0 | blueberries, cranberries, currants, gooseberries, raspberries |
| 5,0 – 6,0 | lily, phlox |
| 5,5 – 7,0 | carnation, iris, rose |
| 7,0 – 7,8 | peony, delphinium |
What plants love acidic soil and why?
Lovers of medium and strongly acidic soils include acidophilic plants. The area of their natural growth is wetlands, peat bogs, coniferous forests.
Over the years of evolution, the root system of plants has adapted to assimilate nutrients from an aggressive soil environment. A distinctive feature of acidophytes is the absence of suction root hairs. They are replaced by microscopic fungi that invade the root tissue and act as a supplier of moisture and trace elements.
This symbiosis in botany is called mycorrhiza - mushroom + rhizome (rhizome). They cannot live and develop normally without each other, and the condition for the existence of mycelium is an acidic environment.
White bloom on the roots is not a disease, but mycorrhiza, through which the plant receives nutrition
Garden ornamental acidophytes
The group of ornamental plants that need acidification of the soil is quite extensive:
- shrubs - heathers, azaleas, rhododendrons, wild rosemary;
- conifers - spruce, pines, junipers, fir;
- berry crops - cranberries, blueberries, blueberries, lingonberries;
- perennials - primroses, gravilat, dicentra, ferns.
Room-decorative acidophytes
Many indoor plants come to us from tropical and subtropical regions. Heat and high humidity levels provoke rapid decomposition of organic matter and predominantly acidic soil environment. This determines which flowers like acidic soil, including indoor crops. Among those who prefer pH in the range of 4.5–5 units are azaleas, camellias, fuchsia, monstera, cyclamen. They love the acidic soil of Saintpaulia (violets), representatives of the numerous myrtle family.
The substrate for indoor plants of this group is prepared on the basis of peat, vegetable compost obtained from rotted coniferous and leaf (preferably oak) litter. Sphagnum moss is added as an acidifier.
Note! High moor peat is suitable for acidification. Its distinctive feature is brown. Low-lying peat has a higher degree of humification, it is much darker.


Coniferous-heather garden on acidic soil - an example of stylish landscape design
Methods for determining the acidity of the soil
When receiving a land plot for temporary or permanent possession, it is necessary to analyze the soil and determine the level of its fertility, acidification, the need for processing to reduce acidity, alkalinity, etc. The most accurate data can be obtained by taking soil samples for chemical analysis. If this is not possible, you can roughly determine the level of acidity using home methods:
- using litmus test strips of paper;
- on weeds growing on the site;
- a solution of vinegar;
- decoctions of the leaves of some berry and horticultural crops;
- device (pH meter or soil probe).
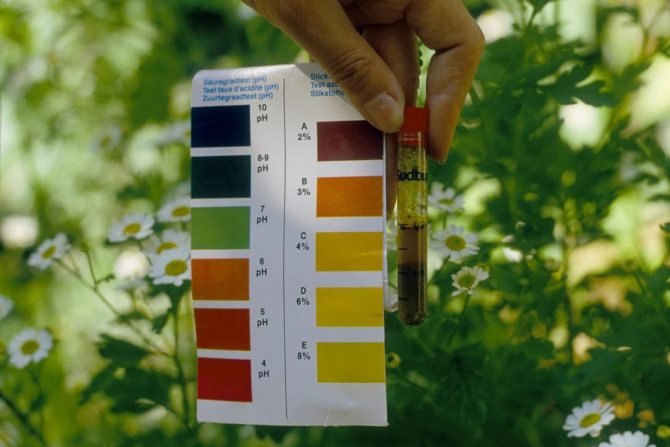
Determination of soil acidity with indicator paper
Dig holes with a smooth wall along the diagonal of the site on the bayonet of the shovel. Remove a thin layer of soil along the entire depth of the straight wall, mix on a film and take a sample at 15-20 g. Stir the samples separately in a glass of water, allow to settle and immerse the indicator paper in water. Along with the indicator strips, the packaging contains a scale of color changes with numerical values. When changing the color of the strip (the color range can be of different shades):
- red - acidic soil;
- orange - medium acid;
- yellow - slightly acidic;
- slightly greenish - neutral;
- all shades of blue are alkaline.
For a more accurate determination of soil acidity, compare the color reading with the digital (on the package) indicating the digital pH value.


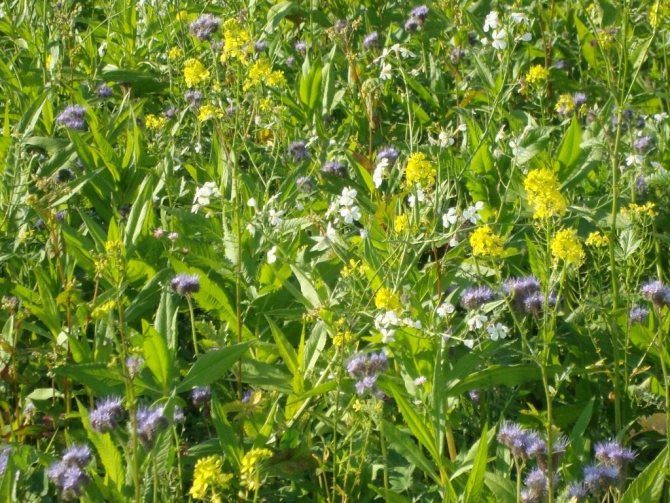
Determination of soil acidity by growing weeds
Determination of soil acidity by weeds
On acidic soils grow:
- horse sorrel;
- plantain large and lanceolate;
- horsetail;
- common mint;
- ivan da marya;
- wood lice;
- heather;
- mosses;
- sedge;
- slender bent;
- wild mustard;
- bloodroot;
- the highlander is cheeky;
- lupine blue;
- creeping buttercup.
Alkaline is dominated by:
- larkspur;
- wild poppy;
- field mustard;
- fluffy purse;
- beans.
On neutral or slightly acidic soil, suitable for growing most garden crops grow:
- mother and stepmother;
- field bindweed;
- field radish;
- field cornflower;
- chamomile;
- meadow and mountain clover;
- meadow fescue;
- wheatgrass;
- quinoa;
- stinging nettle;
- garden thistle;
- soapwort medicinal;
- drooping resin;
- rank is meadow;
- erythematosus is flat-leaved.
Determination of soil acidity by improvised means
Table vinegar
This definition is quite approximate, but it will show in which direction to conduct further work on the site. Diagonally, the plot is collected in separate containers for a handful of earth. Selected soil samples are poured onto a film and a few drops of vinegar (6 or 9%) are dripped.If you hear hiss or the soil "boils", bubbles appear - it means that the soil is neutral and suitable for use without the use of deoxidation.
Cherry or currant leaf tea
Pour boiling water over a few leaves, let it brew for up to 15-20 minutes. Add a lump of earth. If the solution becomes bluish - the soil is acidic, changed color to green - it can be neutral or alkaline.
Grape juice (not wine)
This analysis can be done in early spring or late autumn when there are no green plants. A lump of earth is thrown into a glass of juice. If the juice has changed color and bubbles are released, the soil is neutral acidity.
Soda
In a small container, gruel is prepared from soil and water. Pour generously with baking soda on top. There was a hiss - the soil is acidified. The degree of acidity must be determined more accurately in order to take the necessary measures.
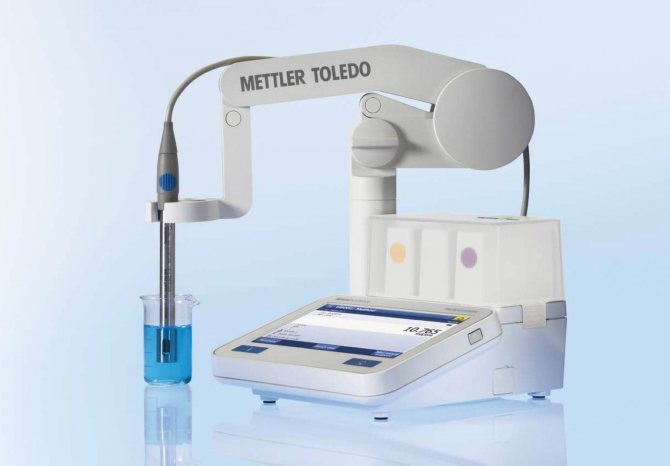
Determination of soil acidity with special devices
The most accurate result at home can be obtained using analyzer instruments: pH meters, acid meters, soil probes. They are very easy to use. It is enough to stick the probe with the sharp end into the soil and after a few minutes the scale will display the level of soil acidity.
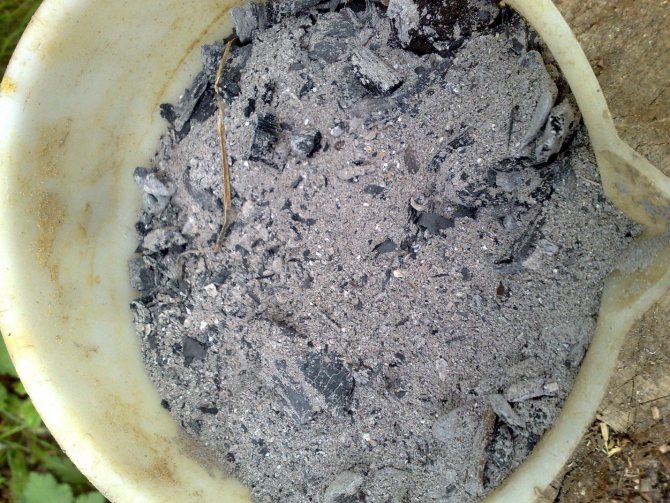
Ash


The most common way to reduce the acidity level in the soil is the introduction of wood ash into the soil. In addition to this useful property, it also has a lot of advantages. Ash structures the soil well, and also enriches the soil with useful microelements. After applying the ash, the soil becomes soft and loose, which means that the plants will be able to breathe well, and moisture will get directly to the root system. Wood ash is excellent at reducing soil acidity. It also makes up for the lack of calcium in the earth. Therefore, it is especially needed by potatoes. Summer residents recommend adding ash to the soil when planting tomatoes and peppers. However, it must be mixed with earth, and also used in combination with other drugs. Usually, ash is mixed with water and watered with it. Remember that ash is mixed with water, and not dissolved, since a sediment always forms at the bottom of the bucket.
Correction of soil acidity at their summer cottage
Analysis of data on the optimal acidity of the soil under vegetables, garden and other crops showed that not all crops need neutral soil. Some plants grow normally and develop on slightly acidic and even acidic soils. If it is necessary to reduce or neutralize the acidity of the soil, then deoxidizers are used.
Soil deoxidation can be carried out in the following ways:
- liming;
- insulating;
- the use of green manure crops,
- deoxidizing drugs.
The materials used to deoxidize the soil include:
- fluff lime;
- dolomite (limestone) flour;
- lake lime (drywall);
- a piece of chalk;
- peat ash;
- wood ash;
- siderates;
- complex deoxidizing preparations.
Before proceeding with soil deoxidation, you need to zone the summer cottage area and allocate plots for a vegetable garden, a berry field, a garden, a pharmacy bed, a country house with outbuildings, a garage, a rest corner and others. Choose those that must be checked for acidity. Conduct testing and, having identified the acidity level of the soil in the selected areas, proceed with the adjustment
The most common method of deoxidation is liming with slaked fluff lime, dolomite flour, chalk, lake lime (drywall). Depending on the type of soil and the level of acidity, the rates of limestone application change (Table 3).


Soil deacidification by adding lime
Table 3. Deacidification of soils by liming
| Acidity | pH | Lime fluff, kg / sq. m | Dolomite flour, kg / sq. m | Lime fluff, kg / sq. m | Dolomite flour, drywall, chalk, kg / sq. m |
| Clay and loamy soils | Sandy and sandy loam soils | ||||
| strongly acidic | 3,5 – 4,5 | 0,5 – 0,75 | 0,5 – 0,6 | 0,30 – 0,40 | 0,30 – 0,35 |
| sour | 4,6 – 5,3 | 0,4 – 0,45 | 0,45 – 0,5 | 0,25 – 0,30 | 0,20 – 0,25 |
| slightly acidic | 5,4 – 6,3 | 0,25 – 0,35 | 0,35 – 0,45 | 0,20 – 0,40 | 0,10 – 0,20 |
| neutral | 6,4 – 7,3 | do not lime | do not lime | do not lime | |
Liming of acidified soils is usually carried out on heavy soils after 5-7 years, on light soils after 4-5 and peat soils after 3 years. The liming depth covers a 20 cm soil horizon. If lime is applied at a lower rate, then only 5-6-10 cm layer is lime. When lime is applied, it must be evenly dispersed over the soil surface. It is advisable to water the soil after application. The deoxidized soil will reach a neutral reaction in 2-3 years.
Lime is a hard deoxidizing agent and, at a high rate applied to the soil, it can burn young plant roots. Therefore, liming with lime is carried out for digging in the fall. During the autumn-winter period, lime will interact with soil acids and other compounds and reduce the negative impact on plants. In this respect, dolomite flour and chalk are softer and safer soil deoxidizers for plants. They are safe to use for deoxidation in the spring, preferably when moisture is closed.
Lime is recommended for heavy clay soils. Dolomite flour and chalk are more effective on sandy and sandy loam light soils. Dolomite flour enriches the soil with magnesium, potassium, calcium, and some trace elements. Drywall is more effective than dolomite flour in its effect on soil deoxidation.
Remember! Soil deoxidation with limestone cannot be combined with fertilization. They are bred in time: deoxidation in the fall, fertilization in the spring. Otherwise, superphosphate, urea, ammonium sulfate, ammonium nitrate and other substances enter into compounds that negatively affect the availability of nutrients to plants.


Deacidification of the soil by the introduction of ash
Soil deacidification by insulating
From ash materials, peat and wood (wood) ash is used to deoxidize the soil.
Wood ash is a wonderful natural deoxidizer. The application rate for the main deoxidation is 0.6 kg / sq. m area. If it is used as an additional deoxidizer for the next year after the main one, carried out by an incomplete deoxidation rate, then the ash is consumed 0.1-0.2 kg / sq. m.
Wood ash must be applied in the fall and not mixed with fertilizers. Being a fairly strong alkali, it enters into chemical reactions with soil nutrients, transforming them into a form inaccessible to plants. Therefore, it is possible to deacidify the soil with ash, but the harvest cannot be obtained for another reason.
Peat ash is much poorer in active components that enter into chemical reactions with soil acids. Therefore, the application rate of peat ash is increased 3-4 times with the main application and 1.5-2.0 times - with the additional one. Application rules are the same as for liming.
The use of green manure for soil deacidification
To deoxidize the soil, some gardeners use green manure crops. One- and perennial plants sown in autumn with their deeply penetrating roots plow the soil, lift nutrients into the upper layers from the depths. Forming a large green biomass, they practically replace manure, which has deoxidizing properties. Of the siderates, soil deoxidizing properties are:
- lupine;
- alfalfa;
- phacelia;
- oats;
- rye;
- legumes;
- Vika.
In general, all green manure, increasing the content of organic matter in the soil, contributes to the correction of soil acidity. You can read more about how to use green manure in the article "What green manures to sow before winter". The best preparation for maintaining the soil at a neutral level in terms of acid content is the constant use of green manure. The soil will become fluffy, fertile, with neutral reactions without the use of deoxidizers.


Soil deoxidation with green manure
The use of ready-made soil deoxidizing preparations
Recently, complex preparations-soil deoxidizers have appeared on store shelves. They are very convenient, as they drastically reduce the amount of physical work. In addition, they contain, in addition to deoxidizing substances, useful components that contribute to an increase in the fertility of deoxidized soils:
- calcium;
- magnesium;
- phosphorus;
- boron;
- zinc;
- copper;
- manganese;
- cobalt;
- molybdenum
and other elements necessary for plants during the growing season.
These drugs are introduced in the fall for digging followed by watering. The neutral reaction of the soil appears in the 2nd - 3rd year.
How to determine acidity?
It is quite easy to establish this indicator at home. To do this, in a specialized store you need to buy a kit for measuring the acidity of the soil, which includes a certain amount of litmus papers. In addition, you need to prepare the so-called soil extractor (add five parts of water to one part of the soil). The container with this hood must be shaken well, left alone for a while in order for it to settle. Now you can put a litmus paper in the liquid above the sediment. Upon contact with liquid, it changes its color, which is compared with the template.
The acidic soil, the signs of which are described in this article, are characterized by the following colors on the piece of paper: green, blue-green, and blue.


The mechanical composition of the soil
This is one of the most important indicators, and at the same time - one of the easiest to understand and to define.
Soils are subdivided according to their mechanical composition into:
- light (sandy and sandy loam)
- medium-heavy (loamy)
- heavy (clayey).
Sometimes gravel and stony soils are also distinguished as independent types, but they are still much less common, so we will not dwell on them now.
The mechanical composition of the soil is easy to determine
To find out what kind of soil is on the site, take a handful of earth, evenly moisten it so that it looks like a thick paste in consistency, and roll a "sausage" about 3 mm thick. Then we try to roll it into a ring and evaluate what came of it:
- the soil rolls well, is flexible, the ring rolls up easily and keeps its shape - clayey, heavy;
- the soil rolls into a "sausage", but cracks when you try to fold it in a ring - loamy;
- the soil crumbles, it is not possible to roll something whole from it, it is impossible to fold the ring - sandy or sandy loam, light.
This is a simplified version: the same loams, for example, are also subdivided into light, medium and heavy. But from an applied point of view, we will be confident enough to navigate these three types. Each of them has its pros and cons, and if you approach the processing correctly, good yields can be obtained on soil of any mechanical composition.
Why is it important to understand this? The mechanical composition of the soil determines its density, water and air permeability, moisture capacity. Different types of soils are supplied in different ways with the necessary nutrients for plants and require a different approach.
Different soils need a different approach
So, heavy soils richer in nutrition than the lungs. But they quickly compact, after rain their surface is seized by a crust. Water often stagnates on them, and plant roots suffer from waterlogging. In such soils, beneficial microorganisms do not work well, organic matter slowly decomposes, and therefore nutritional deficiencies may occur. In spring, areas with a similar soil warm up longer, and melt water leaves them later, so you have to start planting with some delay.
How to fix the situation? The main method is the introduction of loosening materials (usually sawdust or sand).Sand can be applied both in spring and in autumn, but sawdust - preferably in autumn, and before using them it is useful to moisten them with a solution of nitrogen fertilizer. The volumes and proportions are selected in each specific case, depending on the requirements of the crops that are planned to be planted, and the characteristics of the soil.