Alkaline Soil: Improvement
In the previous article, we learned which flowers will take root in acidic soil (read here). The opposite problem is high alkalinity, which also negatively affects many representatives of the flora. Alkaline soil is characterized by a high Ph (7 and higher) and salinity. Usually such soils are considered "heavy" due to the high content of calcium salts, large doses of which interfere with the absorption of iron and other beneficial trace elements, which weakens plants and leads to chlorosis.
On a note: How to measure the acidity of the earth at home - read here.
Alkalized soil does not differ in fertility and air permeability, in a wet state it becomes viscous, and when dry it takes the form of a "crust", and this prevents the flow of air to the roots, as a result of which they quickly wither away. It is especially difficult for young plants and seedlings, which lose their ability to form chlorophyll and become susceptible to disease. Of course, the ideal growing medium is neutral or slightly acidic, but more often than not, you do not have to choose. Therefore, it is in our power to acidify the soil. What methods are there?

Soil improvement:
- The introduction of high-moor (brown) peat is an excellent opportunity to improve the structure of the soil in general. After all, peat itself has an acidic reaction, and its presence makes the soil looser, "breathing", and susceptible to fertilizers. In small doses, peat is good even for acidic soils, and on heavy clay soils it is absolutely necessary. But it is important to remember that peat is not a fertilizer! Application rate - approx. 1.5 kg. 1 sq.m. soil.
- Among organic matter, fresh manure is called the best deoxidizer. It not only fertilizes the soil and saturates it with trace elements, but also increases acidity. The dose of fresh manure should be three times less than that of rotted manure, because fresh manure is much more active! Application rate, exclusively for digging - no more than 1 kg. 1 sq.m. soil.
- Overripe coniferous litter is a good organic component that does not give quick results, but provides a gradual and gentle acidification of the soil. This additive decomposes well, and also serves as a mulch. You can use coniferous sawdust, or coniferous forest bedding. Application rate - approx. 3 kg. 1 sq.m. soil. Similarly to needles, leaf compost is used, which has a relatively low acidity, but with prolonged application it improves the acid balance.
- Urea, or carbamide, is a chemical compound that already belongs to mineral fertilizers. A significant nitrogen content improves the growth and development of plants in the early stages, therefore it is advised to apply urea in early spring at the beginning of the growing season. Fertilizing garden flowers: florist's memo. When digging, the urea is sealed to a depth of 3-4 cm, and a water-based solution is prepared for feeding the plants. Application rate - approx. 50 gr. 1 sq. m. soil.
Attention! Urea impairs the germination of seeds, therefore, before sowing, the fertilizer must be absorbed by the soil. Do not plant seeds right away, wait 1-2 weeks.
- Ammonium nitrate, or ammonium nitrate, is also a chemical fertilizer based on nitrogen and sulfur, which, acting together, improve the absorption of active substances from the soil, strengthen the immunity of plants.Sulfur in the composition of macrofertilizer helps nitrogen to be better absorbed and at the same time enhances its effect. However, strictly follow the instructions, in large doses, saltpeter is dangerous to plants! Application rate - approx. 20-30 gr. 1 sq.m. soil.
- If you are just planning to set up a flower bed on the site, the site advises to prepare the soil by planting green manure - plants that improve the properties of the earth, maintain the balance of acids, enrich the soil with nitrogen, make it loose and well-drained. These beneficial plants include rapeseed, oats, white mustard, rape, as well as lupine, soy and vetch.
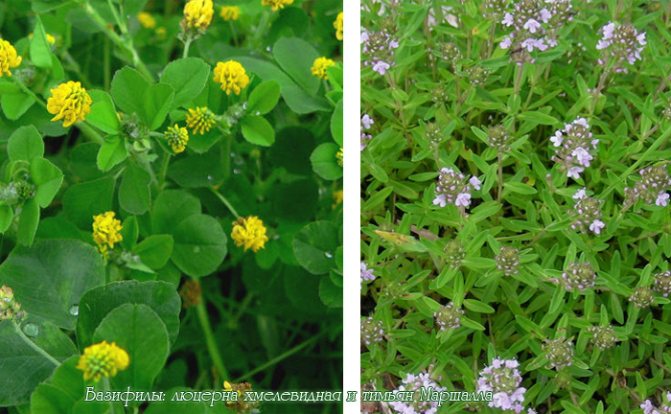
Even on alkaline soils, some plants can tell by their presence what kind of soil you are dealing with. Such plants are called calcephiles, they include: tenaciousness, white doze, rough elm, mullein, yarrow, wormwood, smolens. From the observations of gardeners, it can be noted that on acidic soils, lungwort has pink flowers, and on alkaline soils, purple flowers.
It is believed that soil acidification is a shorter process than deoxidation. But be prepared for the fact that soil improvement measures will have to be carried out more than once, and having achieved persistent ph values, it is important to maintain this level.
Plants-indicators of groundwater
Soil moisture
Plants are xerophytes. They easily tolerate drought, are able to do without moisture for a long time:
|
|
Plants are mesophytes. Forest and meadow grasses growing on moist soils, but not waterlogged:
|
|
Plants are hygrophytes. Prefer abundantly moist, waterlogged soils:
|
|
A place with abundantly moistened soil, if the territory allows, it is better to equip it as a decorative part of the site, for example, to make a secluded corner for rest with a small pond. In the absence of such an opportunity for growing vegetables, you will have to work hard on drainage.
Such a place is not suitable for trees and shrubs; for good growth, they need a groundwater level no closer than one and a half or even two meters from the soil surface.
Groundwater level
The owners of the site, especially the new one, are wondering about the availability of water, for example, for arranging a well or a well, an automatic irrigation system or distributing plants. Plant indicators will come to the rescue in this. Explore the area and find plants that detect the presence of groundwater.
The depth of water occurrence from 10 cm will be indicated by sedge of two types - turfy and bubbly, 10–50 cm sharp sedge and purple reed grass, from 50 cm to a meter tall meadowsweet and canary grass. When the water passes at a depth of 1–1.5 m, the plant indicators will be grass sagittarius, meadow fescue, multiflorous vetch and field grass, more than 1.5 m - creeping wheatgrass, red clover, large plantain and a sharp fire.
What to plant on alkaline soil
Alkaline soil is found in areas with calcareous and chalk deposits. Therefore, it is unlikely that it will be possible to radically affect the composition of the soil.But, in order to get a beautiful flower bed, you can pay attention to plants for alkaline soils. The list is large enough!
Note In parentheses are data on plant height and flowering period.
Adonis (30 cm, April-May) is referred to as primroses, first from under the snow its bright yellow flowers appear, and only then the leaves. It is replaced by evening primrose, or primrose (30-100 cm, Jun-Aug) - a bushy frost-resistant plant with corollas of yellow, white, or pink flowers.
Plants that are not indicators
Not all plant species can identify the soil, the best in this matter are those that are adapted to certain conditions, and are intolerant to any changes in them (stenobionts). Plant species that easily adapt to changes in the composition of soils and the environment (eurybionts) cannot be called indicators.
Plants whose seeds were accidentally added to the site are not indicators. Usually they give single shoots, and with timely harvesting they no longer appear.
It turns out that most of the plants with which we fight and are used to calling weeds can be indispensable helpers in soil diagnostics. Indicator plants allow you to save time and effort on complex experiments, because all you need to do is just find them on your site and recognize them.
How to know if the soil is alkaline
The first sign of an alkaline soil in the area may be yellowing of the leaves of the crops planted on it. The presence of such indicator plants as alfalfa, toadflax, yarrow, wormwood and field violet also speaks of the low acidity of the soil. The pink flowers of large-leaved hydrangea and purple lungwort also indicate alkaline soil.
A simple experiment will help determine the acidity of the soil: pour 1 tsp. land from the site with 9% vinegar. In the absence of a reaction, the soil is acidic, and when abundant foam appears, it is alkaline. Very little foam is formed on neutral soil.
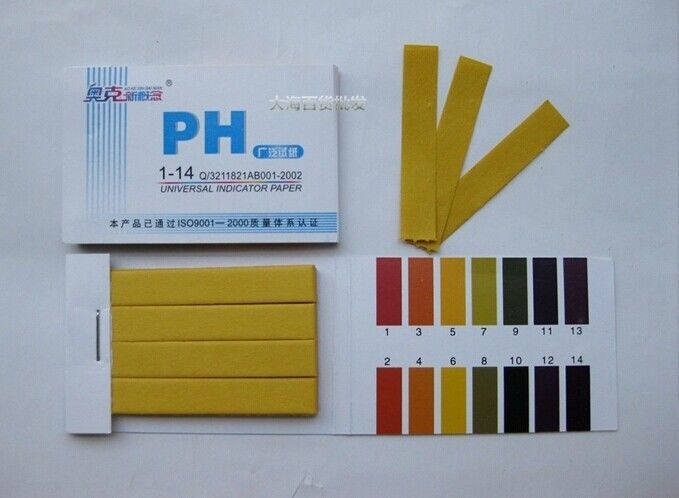
A special device, a pH meter or litmus test, which can be purchased at a garden store, will help determine the acidity of the soil.
Indicator plants in the country
To save yourself from the need for constant diagnostics of cultivated plants, you can turn to those that grow on the site without your participation, the so-called indicator plants. Look around and you will definitely find them. From year to year, they grow well on their own, no matter how often you remove them.
Determining the condition of the soil is one of the important factors for gardeners, helping to determine in advance and more accurately which fertilizers should be applied, what exactly is better to plant in one place or another.
What to plant in alkaline soils
Most plants prefer a slightly acidic and neutral environment. But there are among the crops and those that love alkaline soils. Calcephiles - this is the term these plants are called. These include many trees, shrubs and flowers.
It is in the alkaline soil that tall ornamental plums grow, as well as white and Japanese plums, berry and European yew, mountain ash, cercis, etc. From shrubs on soil with a high (> 7.5) pH, hibiscus, spirea, cotoneaster, chubushnik and etc. The choice of flowers for alkaline soil is also quite extensive: adonis, hellebore, mountain cornflower, saxifrage, gypsophila. Let's tell you more about calciphiles, which can be planted in the garden, on the flower garden and in the vegetable garden.
What to plant in alkaline soils in the garden
Ornamental trees and shrubs are mainly suitable for planting in the garden on alkaline soils. They are planted both individually and as a hedge. For the latter, in particular, barberry and hawthorn, black elderberry and dogwood, forsythia and tamarisk are suitable. Some of these shrubs can be eaten.
The common bean, honeysuckle, honeysuckle or clematis will help to decorate a pergola or a gazebo in the garden. Privet, medicinal rosemary, boxwood are good in border plantings, which can also be used to decorate flower beds or beds.
Among fruit trees, some varieties of plums yield crops on alkaline soils, for example, white plum and Japanese plum (ume). If the pH of the soil is less than 7.5, pears, cherries, peaches, apricots, walnuts, mulberries and quince will take root in the garden and will bear fruit. Lilac also grows on slightly alkaline soil.
Some areas have a thin soil layer above the limestone, which makes it difficult to grow trees on them. However, mountain ash and viburnum, berry yew and European yew feel good in such conditions. Of the coniferous crops, perhaps, only the common juniper, flatworm and Crimean pine can grow on sandy, stony and calcareous soils. They are used in single and group plantings in gardens and parks.
What to plant on alkaline soils in a flower garden
With an alkaline reaction in the flower bed, you can try to neutralize the soil or plant calcephilous plants. Alkaline soils are especially fond of adonis, woodruff, asphodelin, astilbe, bindweed, gypsophila, morning glory, corydalis, lavender, sunflower, night violet, chrysanthemum and mallow.
Aster, carnation, hyacinth, sedum, iris, calendula, canna, hellebore, catnip, levkoy and bell grow well on slightly alkaline soil. And even certain varieties of the queen of flowers - roses - can decorate such a site.
Among calcephilous flowers, there are many ground cover ones, such as saxifrage, anacyclus, anagallis, saxifrage tunic, Caucasian rezuha, aubriet, which will look good in any rockery or on an alpine hill.
Calcephilous flowers differ in size, color, flowering time. Among them there are both perennial (anemone, gypsophila paniculata) and annual plants (Cape ankhusa, woodruff, tricolor bindweed). Skillfully picking up plants, you can create beautiful compositions on the flower bed.
What to plant on alkaline soils in the garden
Alkaline soils are not very suitable for growing vegetables. Most vegetable crops prefer slightly acidic, neutral and slightly alkaline soils.
At high pH levels, plants suffer from a lack of moisture during drought, and from a lack of air during rainy periods. Therefore, mainly on alkaline soils, only corn and cereals are grown, moreover, their predecessors are sweet clover and alfalfa, which, after several years of sowing, are able to create a favorable agrobiological background.
Peas, beans, cucumbers, rutabagas, cabbage, strawberries, parsnips, parsley, beets, pumpkin, beans, garlic and spinach grow on soil with a pH level of up to 7.4 (slightly alkaline). Asparagus, leeks, white and black currants, marjoram can also be grown in alkaline soil (pH 7.4 to 7.9).
Alkaline soils are significantly less than acidic. If they are located in arid regions with calcareous and chalk deposits, then it is unlikely that it will be possible to radically affect the composition of the soil. Therefore, it is worth taking a closer look at calciphilous plants. A lover of acidic soil can be planted in a container or pot with appropriate soil. However, alkalization of land in summer cottages occurs much less frequently than acidification.
How to identify soil by weeds
The variety of weeds on the site can tell about the soil without laboratory research. Weeds will indicate the degree of soil fertility, its mineral composition, density, and how close the groundwater is. When processing the site, the growth of the same weeds is noted every year. The appearance of new plants is a signal that the composition has changed. Appropriate measures must be taken.
Important! There may be different soils on the same site, in this case the indicator herbs are indispensable.
The growth of cultivated plants is negatively affected by increased levels of acid and alkali. If the site is recently acquired, the composition can be determined by the weeds on the untreated land, and the soil can be adjusted according to the findings. Application of mineral fertilizers at a low pH will worsen the situation, so weeds are, to some extent, useful on the site.
What flowers like acidic soil?


The personal plot does not always have the necessary acidity. Some gardens are pH neutral, others are acidic. Not all plants can live on such soils, but they emit a number of flowers that cannot live on alkaline or neutral environments, they need increased soil acidity:
- Lupine loves acidic soil. With a good pH environment, its growth can reach up to 1.2 meters at the time of flowering in June. In addition, lupine is an excellent green manure, which not only independently saturates the soil with nitrogen during growth, but also after flowering and digging it up together with the soil, contributes to an increase in nutrients in the ground.
The beautiful hydrangea does not lag behind the lupine. To get a rich pink shade or an original dark blue, the plant should be fed with special additives that increase the acidic environment in the soil.
Read also: Where to buy champignon mycelium
In addition to these bright representatives of the acidic pH of the environment, there is a list of plants that are unable to germinate on alkaline soil substrates:
- Peonies - they prefer moisture-consuming, highly acidic soils, they stretch to such an area up to 1.5 in height.
- Sunflower (real and decorative) - can reach up to 2 m high, while such a garden decoration will become a real highlight of the personal plot.
- Nasturtiums - the better the environment for them, the brighter the flowers and the richer the leaf plate, and the trunk will curl throughout the summer.
- Roses - This may come as a surprise to many, but the queen of the garden loves the increased pH in the garden.
- Garden poppy - on this kind of soil will riot not only with flowering, but also with gorgeous green leaves.
- Purslane is ground cover - its bright inflorescences will completely braid all free areas of the acidic territory.
In addition to these well-known flowers and plants, ferns, Cassiopeia, various types of chrysanthemums, elegant zinnias, cornflowers, forget-me-nots, heather grow with pleasure on acidic soils. Magnolia does not see its existence without increased pH. Thus, a large number of plants grow on acidic soil, you just need to know which species they are and plant them correctly.
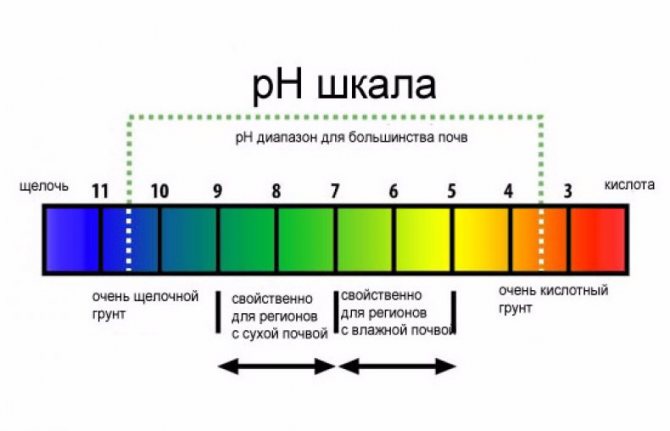
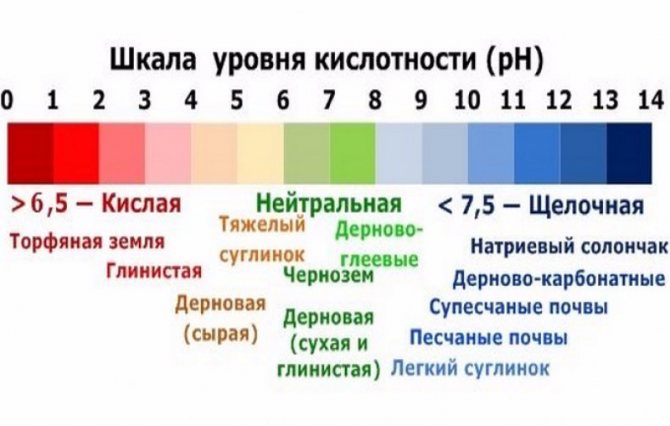
The pH scale - what is it and how do you understand it?
The acid-base balance scale ranges from 0 to 14. The neutral pH is considered to be pH 7. Low pH indicates that the environment is acidic, and tall - that it is alkaline. Accordingly, pH 0 will be the most acidic and pH 14 the most alkaline.
In the case of determining the acidity of the soil, ideal commonly referred to as pH 6.0-6.5. However, neutral soils with a pH value between 5.5 and 7.5 are considered. Acidic soils have a pH of 4.6-5.0, strongly sour - pH 4.5. Alkaline soils have a pH of 7.5-7.9, strongly alkaline - pH 8 or more.
A pH difference of 0.5-1 may seem insignificant, but it is actually significant. For example, the acidity of a medium with a pH of 7 is 10 times less than a medium with a pH of 6!
Air temperature and humidity for nephrolepis


Nephrolepis does not tolerate dry air and long exposure to cool temperatures below +12 ° C. Most plants of humid subtropical forests and tropics would not be able to triple comfortably in a city apartment. However, this genus of ferns is very hardy. If artificially maintain high humidity, the temperature for nephrolepis can be + 16-25 ° C.In hotter air, the plant looks depressed, but comes to life if it is regularly sprayed or irrigated the crown.
In winter, when growth activity decreases, the temperature is lowered and the pot must be removed away from radiators and other heat sources. The big enemy of the fern is the draft. So that caring for nephrolepis is not in vain, you should not put the plant under an open transom or near a balcony door.
As in summer, in winter, a warm shower with soft water is regularly arranged for the fern. Before "water procedures", the soil is covered with a film or other moisture-proof material.
Why is the acidity of the soil changing
A slightly acidic or neutral soil medium with a pH of 5-7 is suitable for many crops. But the formation of soil acidity comes from the effect of the chemical composition of the material in it. For example, if it is calcareous shale or soil with limestone, then the pH will initially have high alkali values. It takes a long time for the soil to become acidic, more than the sandstone or soils formed on the granite will need. The geological age of the earth also affects the acid-base balance, as well as annual precipitation: water evaporation and residual moisture. With the accumulation of moisture in the ground, leaching of soluble salts and minerals occurs, which increases the acidity of the soil within the plant roots.

Each crop takes out calcium, potassium and magnesium from the soil, which makes it more acidic. In wet soils, organic material tends to decompose, which also increases acid readings, especially carbonic acid. If there is little oxygen in wet ground, carbon dioxide will react with water and carbonic acid will form. It takes a long time for the pH values to change naturally. This process can be accelerated by yourself, that is, manually.
The harm of excess acidity and alkalinity
Soil acidification negatively affects its fertility and negatively affects the vegetation of most plants.
- Due to the strong concentration of organic acids in the cells, protein metabolism is disturbed, the development of roots slows down, and their gradual death occurs.
- Excessive acidity inhibits the movement of phosphorus into the aerial part of the plant, which provokes phosphorus starvation.
- In an acidic environment, the availability of nutrients decreases, especially phosphorus, potassium, calcium, magnesium. But the concentration of iron, aluminum, boron, zinc reaches a toxic level for the roots.
- Unlike neutral soil, the increased acidity of the soil suppresses the activity of beneficial microorganisms that enrich the fertile layer with nitrogen. In parallel, it provokes the growth of pathogenic microflora (fungi, viruses, pathogenic bacteria).
An excessively alkaline medium (pH> 7.5–8) is no less destructive for plants. In it, most of the trace elements necessary for growth (phosphorus, iron, manganese, boron, magnesium) pass into insoluble hydroxides and become inaccessible for nutrition.
Hydrangea
Hydrangea (Hydrangea) is petioled, paniculate, ash or gray, tree-like, Bretschneider and many other species grow well on slightly acidic soils, and large-leaved hydrangea feels great already at 4 pH. These are sprawling dense shrubs or small trees. Their inflorescences attract everyone's attention. It's easy to look after her, more about this in the article Hortense: Planting and Care.
Hydrangea
I have slightly acidic soils. Treelike hydrangeas are planted almost throughout the site. Large snow-white inflorescences and strongly growing bushes look very beautiful along the fence. And how many unusual things can be created using these plants, the article Garden of hydrangeas in the Aivazovskoye health center will tell you.
We invite you to choose hydrangea seedlings to our market. Section Hydrangea seedlings. There are also separate selections: Paniculata hydrangeas and Large-leaved hydrangeas.
Heather
Heather (Calluna vulgaris) is a small shrub or shrub. All year round, the colorful heather gives a festive mood and a well-groomed appearance to the place where it grows. The plant loves bright sun and good hydration. It grows on acidic soils, so it is often found in nature near peat bogs and swamps. Planting heather in different regions of our country (especially the south of Russia) can be fraught with some difficulties. For more information on growing it on the site, see the article Heather - a healing honey plant in the garden.
In the middle lane, heathers can be grown in containers
Common heather flowers can be white, pink, red or purple. Currently, there are a huge number of unusual varieties and varieties.
What you need to know about soil pH for a flowering garden and a productive vegetable garden
Adding an article to a new collection
Determining and timely adjusting the soil pH level is an important skill of a real professional summer resident. We will tell you how to understand the acid-base balance of the soil and change it for the benefit of the garden and vegetable garden.
We all know perfectly well that pH is the pH value, in which the acidity of a particular environment is expressed. Which crops will grow well, bloom and bear fruit on your site, and which will not, largely depend on the acidity of the soil, therefore it is important to know and take note of this indicator for any grower - both an amateur and a professional.
Read also: Treatment of Kalanchoe: healing properties of Kalanchoe Degremon
Of course, going against nature is difficult, but nevertheless, it is possible and even necessary to make some adjustments to the pH level.
Ways to eliminate high acidity
There are a huge number of effective agrotechnical methods for lowering soil acidity. To deacidify the beds in your garden, choose one of the following methods.
- To properly use slaked lime, dilute it with dechlorinated water for irrigation. The slaked lime dosage will vary depending on the severity of the problem. If your soil in the beds is especially acidic, apply up to 75 grams per hundred square meters, and if you are just trying to avoid problems, you will need up to 35 grams;
- Plantations can be put in order by adding crushed chalk (100-300 grams per square meter) to the soil. Peat ash, wood ash are also suitable. The fact is that these substances contain a lot of calcium and cope with the function of a deoxidizer;
- Drywall is called lime from ancient reservoirs. It needs to be crushed and added to the soil, this tool is considered the most effective. The problem is the price of drywall and poor availability in small towns. It is a little easier to find dolomite flour, the substance rate is 400-600 grams per square meter.
Moderately resistant to salinity:


Herbaceous: sweet corn, flax, various types of sunflowers, ryegrass and meadow fescue, hedgehog, rarely found in cultivated form, alfalfa and variegated sweet clover
Vegetables: tomatoes, cucumbers and peppers, carrots, potatoes, onions, cabbage and cabbage, and cauliflower, peas and pumpkin.
Fruit and berry: grapes, both dessert and table, as well as figs and pomegranates.
Shrubs: eastern thuja and junipers.
Low acidity - what to do?


If the acidity is too low, it is considered alkaline. The latter is harmful to seedlings - it stops developing, withers. Also, the leaves of fruit plants begin to turn yellow and fall off. This is characterized by a deficiency in the substrate of manganese, iron, zinc and copper, as well as phosphorus.
To increase acidity, perform the following activities:
- Peat is introduced.
- Dig up the soil together with manure or humus.
- The use of spruce branches in the form of mulch not only acidifies the soil, but also saturates it with useful substances.
- Urea has a beneficial effect - not only smoothly reduces the alkalinity index, but also is a mineral fertilizer.
It is not worth increasing the acidity in sudden jumps. This will not only adversely affect plants, but can also completely destroy trees and shrubs. Measures that increase the pH of the sphere should be carried out carefully and gradually.
What bushes and trees grow on acidic soils?


When planting garden trees and fruit and berry bushes, you need to take into account their location to the ground. Some crops do not survive at all on strongly acidic soils, others, for example, a pear, eventually get used to acidity and even give a large harvest.
The following trees are distinguished, which are not afraid of the low pH environment on the site:
Most of these plants require a pH in the range of 5.5-6.5. If a neutral or alkaline soil is selected for these plants, this most often does not suit them, which leads to the development of pathogenic bacteria.
Thus, in order for the shrub to develop correctly, the level of soil acidification should be determined before planting. In some cases, if the optimal indicator is insufficient, acidification of the soil substrate is carried out with special preparations or improvised means.
What vegetables love acidic soil?


In most cases, increased acidity adversely affects vegetable crops. On such a substrate, vegetables are often affected by various bacteria of various origins and cannot exist for a long time.
There are 4 groups that subdivide all vegetable plants into lovers of high acidity and, conversely, complete opponents:
- The first group - ardent opponents of the lowered pH level: types of cabbage, red beets.
- The second group is ideal for slightly acidic soils: legumes, eggplant, melon.
- The third group - it contains vegetables that normally feel in moderate acidity: pumpkin crops, radish, tomato plants, carrots.
- The fourth group - this list includes plants that get along well on acidic soils: greens and potatoes.
It is important if liming is carried out - to artificially increase the alkalinity of the soil, then after the planted potatoes will soon acquire an unpleasant disease - scab. Therefore, it is not recommended to carry out special work to increase the pH level of the medium in certain areas where crops that do not accept an alkaline reaction should grow.
The value of acidity for plants
There is a certain category of gardeners who do not even come close to understanding what this abbreviation is. But pH is an important metric that cannot be ignored.
For example, if the soil is too acidic for your plants, but at the same time in the soil there is enough minerals necessary for the crops, then they simply will not be absorbed. Hydrogen ions will form compounds that cannot be absorbed by plants.


Signs of an alkaline environment
The alkaline nature of the soil is determined by sodium salts, therefore the process of increasing alkalinity is also called salting. One of the main reasons for the increase in pH above 8 is intensive irrigation in arid regions, as a result of which it floats, poorly passes air, and its porosity deteriorates.
Alkaline soil is more difficult to identify by its appearance.
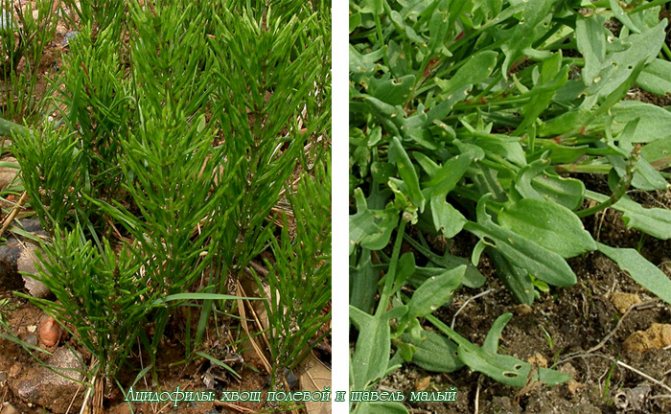
- From weeds, it is preferred by field bindweed (birch), quinoa, field mustard (rape).
- On garden plants, trees, chlorosis (yellowing) of the leaves is often manifested. This is due to a lack of iron, which becomes unavailable in alkaline bases.
Note! If nettles, clover, quinoa happily grow on the site, you are in luck. This is evidence of a neutral pH response that is optimal for agriculture.
Azalea, or rhododendron
Blooming azalea
Azalea (Azalea) belongs to the genus of rhododendrons, usually so called beautifully flowering rhododendrons of different species (Indian azalea - Rhododendron simsii, Japanese azalea - Rhododendron obtusum). This is a deciduous or evergreen shrub belonging to the heather family (less often small trees), it is very decorative, but rather thermophilic. It begins to bloom in early summer and simply requires acidity in the soil for good development. Medium acidity is best, providing this plant with coolness, light shade, well-drained but well-hydrated soil, and a lush bloom will come soon.
You can learn more about the peculiarities of this culture in the article Azalea - a shade-loving beauty. Azalea planting, cultivation and care. And how beautiful are rhododendrons in the Crimean park: the rhododendra kingdom in the Japanese garden. Get to know this amazing plant in the article Rhododendron - a beautiful fantasy of nature.
Rhododendrons
In the middle lane, difficulties associated with wintering may arise. Therefore, pay attention to zoned varieties and choose places for rhododendron wisely - protected from winds and direct sunlight. It is desirable on slopes, where the sun is only the first half of the day, or near not very tall spruces and pines. Heavy, clayey, always weeping soils should be avoided.
Table of the optimal acidity (pH) of the soil for various plant crops
What do the numbers after the abbreviation pH mean, which is found on packages (bags) with soil mixture (planting material) sold in specialized stores, not even every experienced summer resident will be able to explain exactly. And if you ask what is the acidity of the soil on its site, then only a few will answer. But it is precisely this characteristic of the soil that largely affects the yield of a particular garden crop. It is not for nothing that there are special tables that indicate the recommended acidity values for various plants.
The author considered it correct to place several tables in the article, although some of them repeat each other. But if you look closely, you can find differences. In addition, this gives the reader more opportunities to determine the optimal soil pH for the plant of interest, since none of the tables contains an exhaustive list of all horticultural crops.
What do the numbers after the pH symbols mean? Indeed, in many recommendations for growing plants, they are not indicated, but the characteristics of the soil - medium, strongly acidic, and so on. These tables (somewhat duplicating each other) explain everything well.
Why do you need to take into account the pH of the soil on the site? Each of the garden plants in the process of its development consumes a certain set of microelements (nutrients) from the soil. Their growth and further fruiting depends on how saturated the earth is with them.
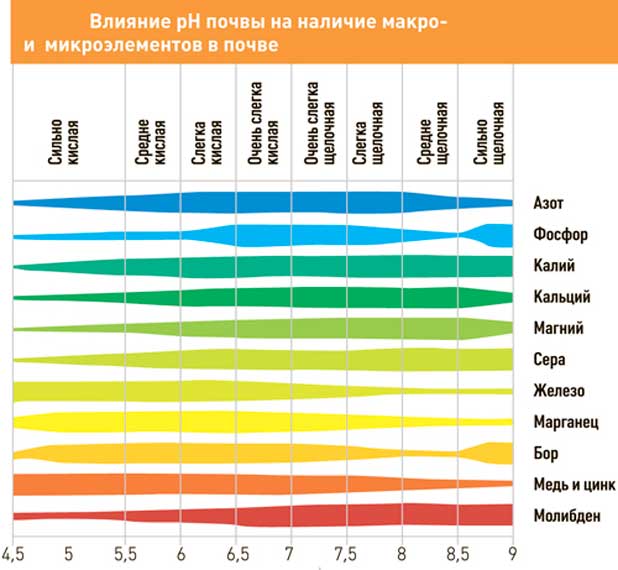

That is why good owners always not only adhere to the rules of crop rotation, but also artificially regulate the acidity of the soil. If not on the entire site, then on certain segments of it - for sure. Removal of a layer of land, delivery of fertile soil to the territory - such a technology, given the complexity of implementation, labor costs and high cost, will not be seriously considered by any summer resident. But after all, many horticultural crops are planted in pre-prepared holes. For example, berry bushes, potatoes.
Knowing what acidity the earth needs for a particular plant, it is enough to load a self-made soil mixture into these holes. Alternatively, fertilize the soil with appropriate fertilizer. With such a competent approach, you can count on high yields even on land that is not quite suitable for gardening.