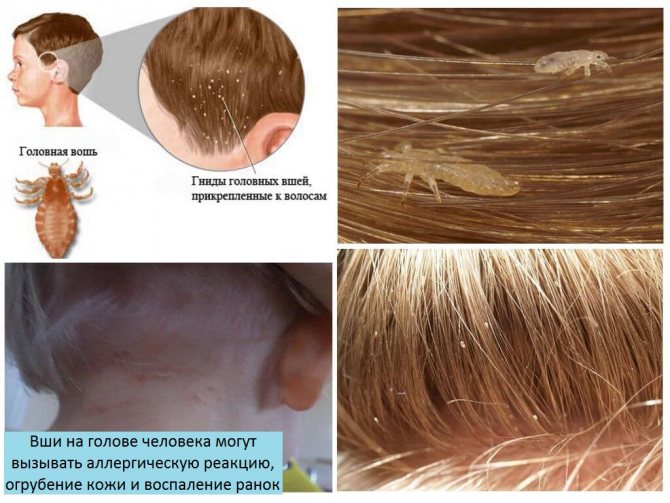
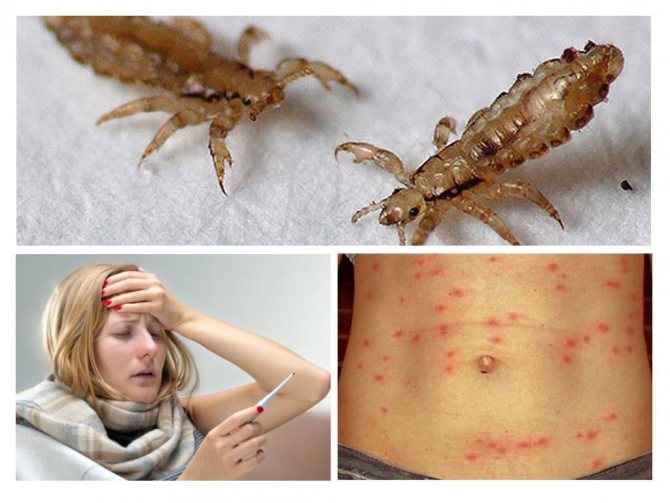
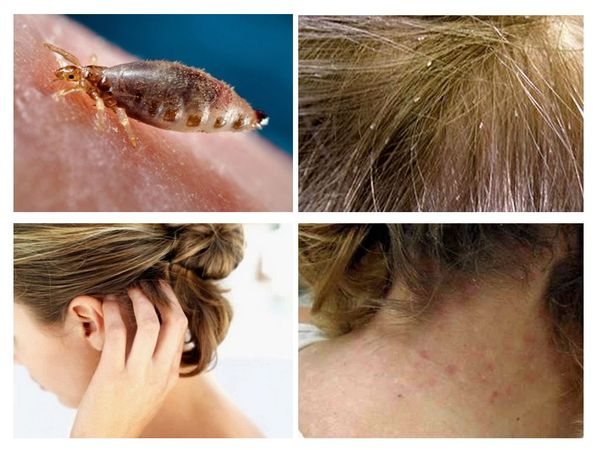
Pediculosis is a common disease throughout the world. It is characterized by many unpleasant symptoms, including severe itching and redness of the affected skin. Sometimes infected people have severe allergic reactions. Fever, severe headaches and nausea are just some of these complications.
In addition, there is an opinion that lice are carriers of severe AIDS and hepatitis viruses. But is it really so? What are these parasites really dangerous and where can they get infected? We will try to understand these issues in more detail.
How can you get infected and the symptoms of head lice?
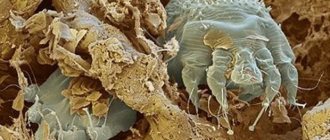
The louse, affects the scalp, travels a distance of up to 35 cm in a minute. At this speed, the parasite quickly crawls from a sick person to a healthy one. An insect can only crawl on a rough surface.... Its exoskeleton is not equipped with the necessary growths, so the louse does not move on smooth objects.
Infection with pedicles occurs when visiting public places:
- hospitals;
- camps;
- pool;
- transport;
- shopping centers;
- clothing stores;
- schools, universities, offices.

Transmission of a parasitic disease is possible when using other people's personal hygiene items or clothing: combs, towels, hats... Infection can occur if you spend in bed where the sick person slept less than 24 hours ago.
IMPORTANT. For some time, parasites can live outside the human body. Once in water, they can survive 48 hours without food. During this period, insects must find a person without a headdress.
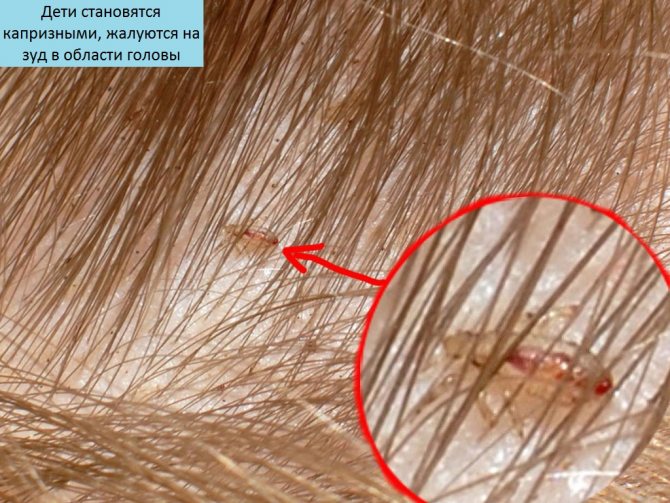
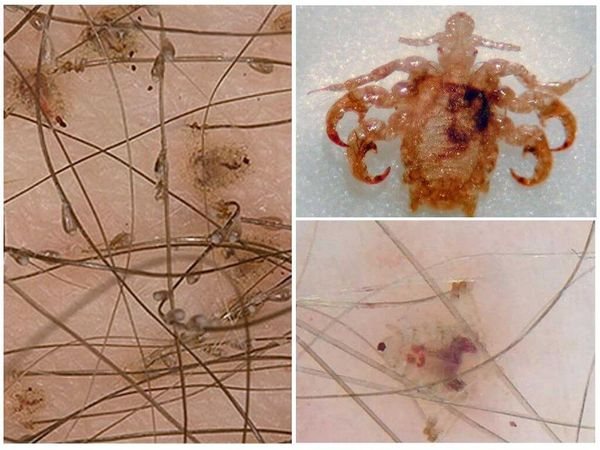
Lice can be detected with the naked eye. They can be confused with dandruff, but when squeezed by the nail plates, the insect's exoskeleton collapses and emits a specific crunch. Other symptoms of pudiculosis are:
- the presence of eggs and adults on the skin, scalp, clothing;
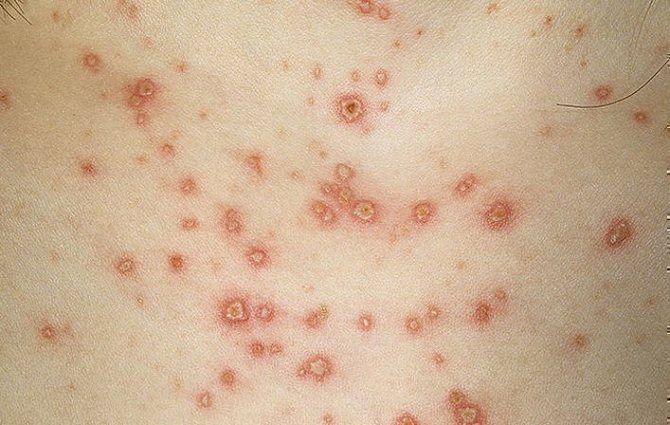
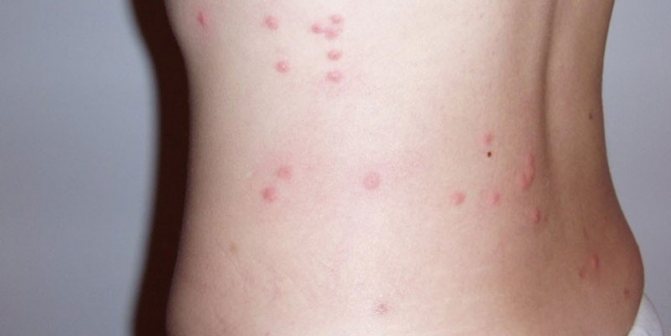
- severe itchingcaused by numerous parasite bites and an allergic reaction of the body;
- skin irritation in different parts of the body, dermatitis;
- infectious diseasesresulting from parasitic invasion;
- the appearance of ulcers on the head and body.

Itching of high intensity is observed with bites of body lice, slight irritation occurs when infection with pubic parasites... Over time, a person gets used to the bites and they become less sensitive. Lice multiply at a high rate, therefore, if at least one of the family members is affected, it is necessary to examine the head and clothes of all those present for head lice.
Tularemia

Tularemia is an infection carried by animals. The disease is transmitted to humans, including by blood-sucking insects.
The disease begins with a high fever, dizziness, headache and pain in all limbs. Next comes confusion, loss of consciousness, delirium.
Serious diseases caused by lice are very rare.
However, no one can give an absolute guarantee that they cannot get sick with the bite of a blood-sucking insect. Therefore, it is necessary to approach very seriously the prevention of head lice, as a method of transmission of such infections.
Compliance with the rules of personal hygiene, refusal to communicate with people unfamiliar and at risk, using only your own personal items is enough to ensure yourself and your loved ones a calm, and most importantly healthy life.
What happens if you do not remove lice?
In the absence of timely treatment, head lice will gradually turn into a chronic form.... The colony of parasites will begin to grow, the number of bites will increase. The skin will begin to thicken, and bruises will appear in the lice habitats. The bites will cease to be painful, and the rash will become bearable.


Along with the growth of the colony, the risk of contracting an infectious disease increases... Perhaps the development of pyoderma - a purulent-inflammatory skin lesion.
Human head louse
There are 3 types of lice in nature:
The latter is found most often, lives on the head, annoys a person with bites and severe itching.
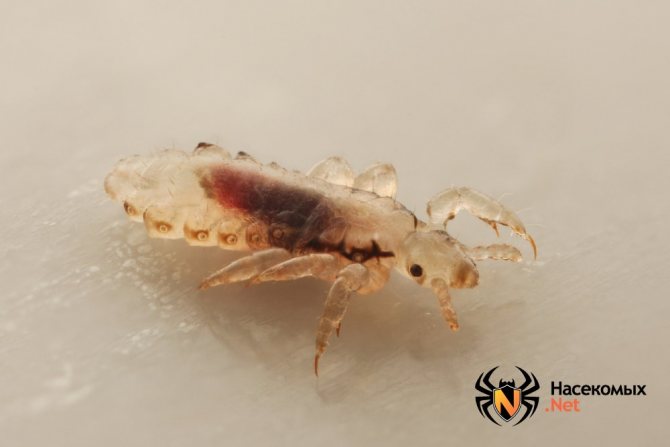
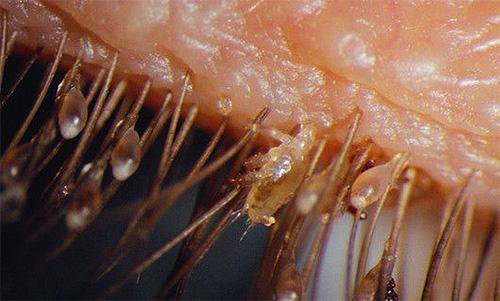
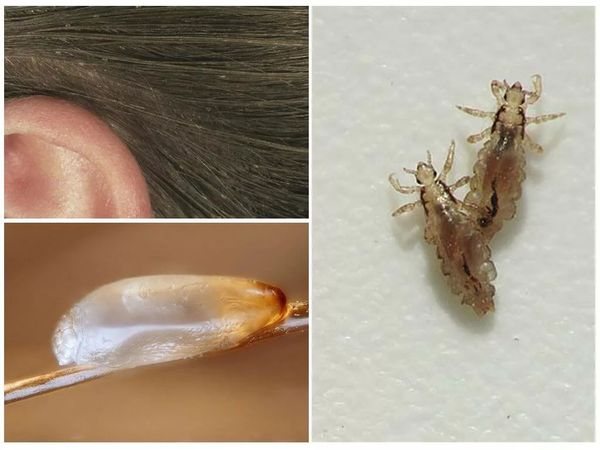
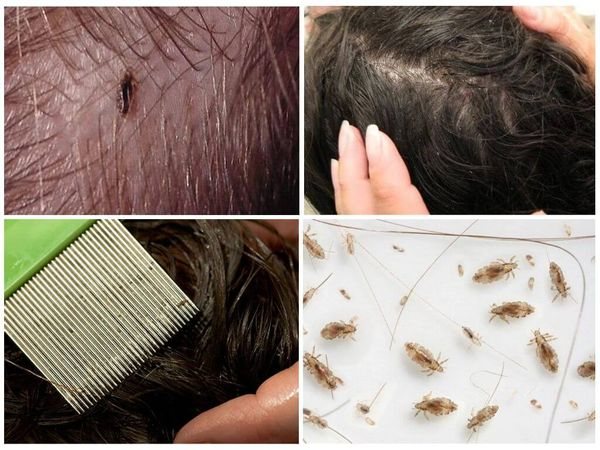
The incubation period of the disease lasts 10-14 days. Getting on the head of a person, the louse begins to lay eggs-nits. 4 or more eggs daily. Attaches them with an adhesive to the hairs at a distance of 1 cm from the roots. What lice and nits look like is shown in the photo.
The larvae develop from 10 to 14 days. Immediately after birth, they begin to parasitize. During the week, 3 molts pass, gradually increasing in size. Symptoms of head lice appear.
At the last stage of development, the genitals are formed in nymphs. Within a week of its existence, the new generation starts mating. The female lays eggs 2 hours after fertilization. The semen from the first contact is enough to reproduce the offspring all her life - 45 days.
Lice feed exclusively on human blood. The procedure takes about 40 minutes, every 2 hours. When bitten, the insect releases a special substance that thinns the blood and causes an allergic reaction. The person feels severe itching, which does not go away after light scratching. We have to "tear" the skin to blood.
Pediculosis is developing at a rapid pace. For a month, a whole population of parasites appears on a person's head. However, even with a strong infection on the head of adults, there are no more than 200 pieces. There is a constant struggle for survival. The weakest give up their positions, leave the person's head.
The consequences of head lice relate to the physiological, psychological aspects of life. In order to avoid trouble, it is necessary to carry out treatment in a timely manner.
The reason for the appearance of lice is the ingress of insects or their eggs (nits) on the hairy areas of a healthy person from a patient with head lice (from the Latin "pediculosis" - lice). Blood-sucking insects cause discomfort, allergic reactions, skin lesions. Lice are carriers of dangerous diseases. Pediculosis is a satellite of wars and disasters.
Why are lice on the head dangerous for humans and the harm of nits?
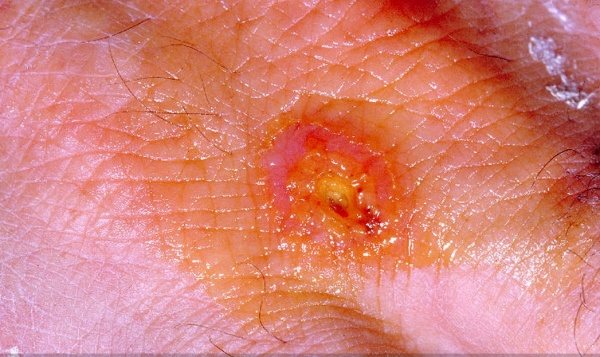
The head louse becomes dangerous when the colony grows large... In addition to discomfort, there is pain and itching at the site of the bite. The louse makes a puncture with needles in the mouth apparatus and throws enzymes into the wound that cause an allergic reaction. Parasitic invasion is accompanied by the development of skin inflammation on the scalp. When an infection enters the site of the bite, an abscess appears.

As the itching increases, the person begins to itch, damaging the thin skin. As a result, the skin peels off, overgrows with scabs. The nutrition of the hair follicles is impaired, and the hair becomes brittle. In addition, the constant itching and migration of parasites lead to the development of neuropsychiatric disorders. The patient's sleep is disturbed, a feeling of anxiety arises, efficiency decreases and concentration of attention worsens.
Than phthiriasis or pubic lice threatens
Pubic lice never live on the head.Their habitat is a triangular-shaped hairline and pubic hair, the same structure in the armpits and on the chest.
Severe itching caused by them is not the last problem. Pubic louse is a dangerous species that can survive in extreme conditions: in water for almost 2 days, in sand at a depth of 30 cm for 4 days.
These sexually transmitted insects are carriers of genital diseases. It is known what diseases are transmitted through open wounds formed by lice bites. It:
- chlamydia;
- syphilis;
- gonorrhea.
Pubic lice are now found in much smaller numbers, as the sexual hygiene of modern people has improved.
The consequences of the vital activity of pubic lice are very severe itching. In addition, they can act as carriers of genital diseases. The penetration of infections into the body occurs during sexual intercourse, through dirty bedding and personal hygiene items.
The human pubic louse, like the head louse, can make up to one hundred bites a day, which are accompanied by severe itching. A person begins to itch badly, scratches appear, into which pathogens penetrate. With complications, pustular diseases of the skin are formed. Further, the infection spreads through the lymph nodes and fatty tissue, boils and abscesses are formed. In this case, it is necessary to treat the disease with the help of operations.
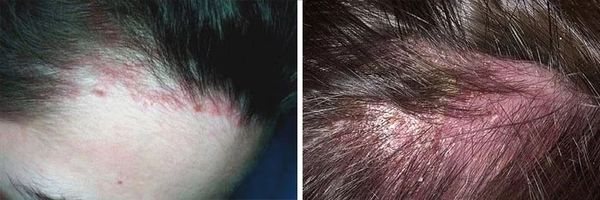
Phthiriasis and head lice are prerequisites for the development of serious diseases, and pubic and head lice do not directly transmit infections, but provoke its penetration into the human body.

Phthiriasis creates conditions for the occurrence of serious diseases
What diseases do lice carry?
Small insects carry a number of infectious diseases:
- brucellosis;
- typhoid;
- tuberculosis;
- listeriosis;
- salmonellosis;
- plague;
- tularemia;
- influenza viruses.
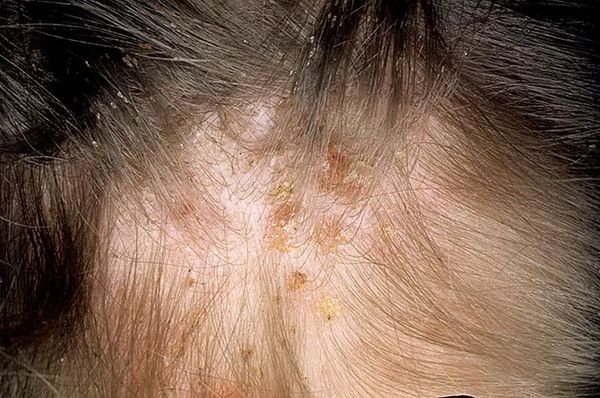

If symptoms of an infectious and inflammatory disease appear against the background of head lice, you should immediately seek medical help. It is possible to determine the type of pathology only after passing instrumental studies and passing laboratory tests.
Could there be typhus from lice?
Lice carry 2 types of typhus: relapsing and typhus.
Relapsing fever
Relapsing fever is carried by head lice and body lice. The pathological process is characterized by severe fever, which alternates with periods of remission. An infectious disease is caused by spirochetes or borrelia, which penetrate into the blood of a person when scratching wounds or lice bites.
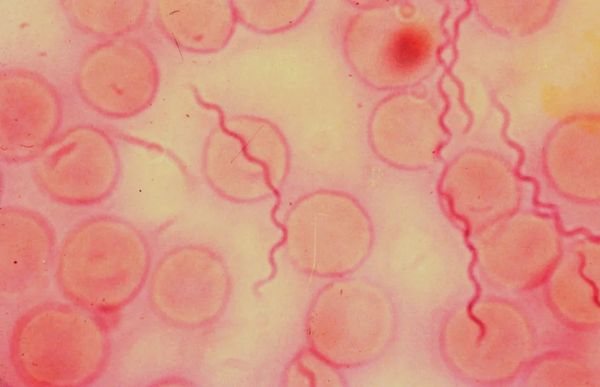

Microorganisms enter the lymph, where they begin to multiply actively. After the growth of the bacterial colony, the spirochetes return to the bloodstream. As a result, borrelia cause disorders of the nervous and cardiovascular systems. The following symptoms are observed:
- fever, accompanied by high fever, vomiting, headaches;
- microinfarctions with the development of bleeding;
- disruption of the spleen and liverwhich manifests itself as jaundice and skin rash;
- heart and respiratory failure.
After recovery, persistent immunity does not form against the re-development of the disease.
Typhus
Typhus develops when rickettsiae enter the bloodstream, which are carried by blood-sucking parasites... Usually, a person becomes infected from body lice, in rare cases the head louse acts as a temporary host of pathogenic bacteria. The infection enters the bloodstream during an insect bite. Rickettsiae cause warty endocarditis, which is characterized by thrombus formation and subsequent blockage of the affected vessel.
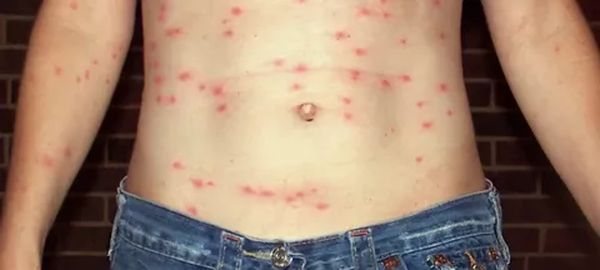

Usually, bacteria actively multiply in the capillaries localized in the subcutaneous fat. Because of this, skin rashes occur.
REFERENCE. In rare cases, pathogenic microorganisms affect the arteries of the brain, provoking the development of meningoencephalitis. After recovery, a strong immunity is developed in the human body.
The incubation period lasts about 2 weeks. Symptoms appear unexpectedly:
- fever;
- blurred consciousness, fainting;
- chills;
- severe headaches.


Typhus is dangerous by the development of complications arising from the cardiovascular system.
Quintan
Body lice carry the Volyn fever... A person becomes infected when saliva or insect feces enter the bloodstream. The course of the disease passes with alternating periods of remission and exacerbation. The incubation period lasts from 7 to 20 days. During this time, there is severe chills and fever. A person suffers from pain in the eyes, aching joint pain and muscle weakness... Papules appear on the skin, the liver and spleen increase in size, and problems with blood vessels begin.
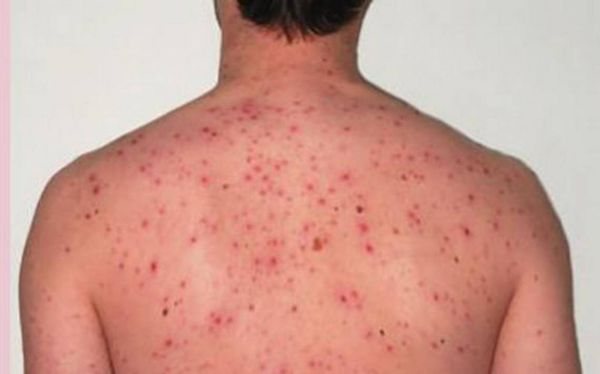

IMPORTANT. Volyn fever is not fatal. Recovery happens suddenly.
Tularemia
Tularemia is carried not only by small rodents, but also by blood-sucking insects. With the development of an infectious disease against the background of head lice, lymph nodes increase, a rash, fever appear. There are signs of acute intoxication, characterized by vomiting and dizziness. Outwardly, tularemia is similar to the plague.
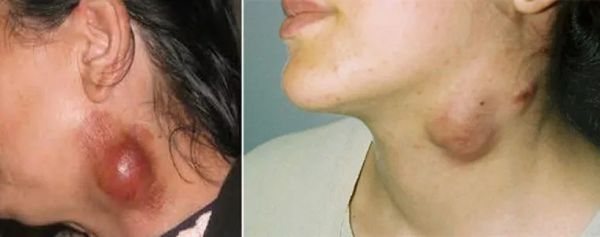

Chronic head lice
The danger arises when an acute form of head lice flows into a chronic... In this case, you can notice a change in the structure of the epithelial tissue. The skin coarsens, loses its elasticity. The stratum corneum of dead cells thickens, scab appears. Numerous insect bite wounds cause reddening of the skin. The body stops responding to itching.

Chronic head lice implies colony growth. This disease is typical for people living in an unfavorable environment. In the absence of the necessary treatment and non-compliance with the rules of hygiene, there is a risk of developing dangerous diseases.
Do lice carry HIV and hepatitis?
The hepatitis virus and HIV infection, when they enter the external environment, begin to break down. Even when the blood of an infected person is transferred to a new host, the parasite is not able to transmit dangerous diseases, because the viral RNA begins to be instantly cleaved outside the body. In addition, lice do not inject sick blood into other people. therefore pathogens of dangerous pathologies, such as HIV or hepatitis, cannot be transmitted along with head lice.


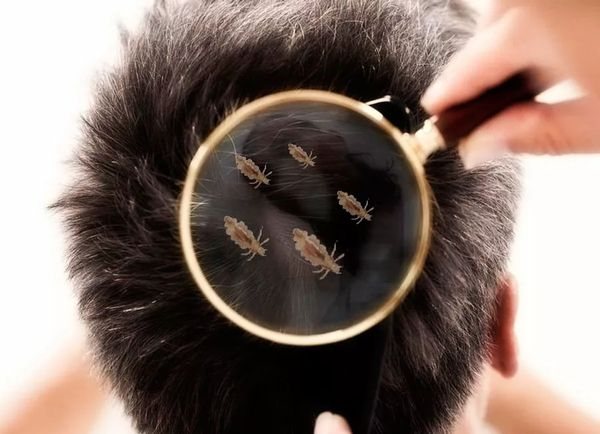
Why are lice dangerous for children?
The child's body is more susceptible to insect poisons. Despite their small size, lice can inject a toxic substance into the bloodstream. The immune system of an adult easily copes with the pathogen and instantly eliminates it with the help of leukocytes. But the child's immunity is weak - he is not able to produce the required amount of antibodies and adequately respond to the ingress of a strong allergen into the body.
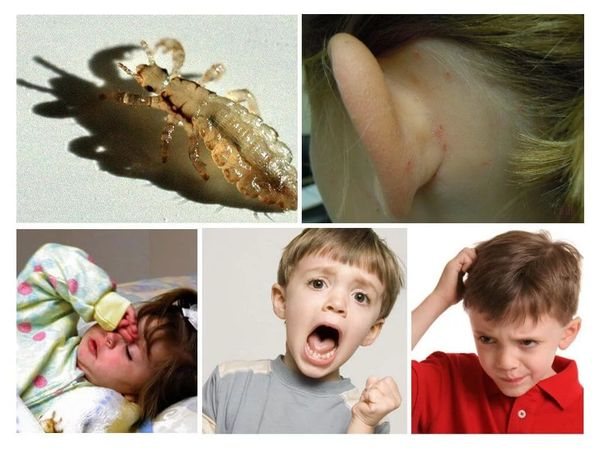

As a result, head lice can provoke the development of a strong allergic reaction.... The pathological process is accompanied by the appearance of a skin rash, swelling, itching. In rare cases, it is possible to develop migraines, enlargement of the lymph nodes and the occurrence of anaphylactic shock.
IMPORTANT. Lice are most dangerous for children who have not received timely vaccination. In the absence of vaccinations, the child quickly becomes infected with serious infections: tuberculosis, brucellosis, typhoid and other diseases.
TOP 15 most common myths about head lice
- Myth # 1: "Lice are a disease of the poor." No one is protected from head lice, since even money will not help to completely isolate from the outside world.
- Myth # 2: "Lice do not affect people with dyed hair."Lice are absolutely not tasty hair, they need skin and blood, so dyed hair is not an obstacle for them. On the other hand, with already existing head lice, hair dyeing due to ammonia can partially kill parasites.
- Myth # 3: "Lice carry HIV." Fortunately, neither lice nor other insects can transmit HIV, since the virus is very quickly destroyed by the enzyme system of lice or mosquitoes.
- Myth # 4: "Lice love a special blood type." The blood type is absolutely not important for lice, they prefer and digest absolutely any "menu from human blood".
- Myth # 5: "You can get lice from animals." Animals can also have lice, but of a different species, and the causative agent of head lice - human and pubic lice, lives only on the human body, and, conversely, animal lice do not pass on to us. Interesting! For many animals, a special type of lice is characteristic, for example, camel, elephant, deer, seal, hare, pig lice, and so on.
- Myth # 6: "A louse jumps or flies from one person to another." The anatomy of lice does not allow movement in any other way, except to slowly crawl at a speed of 23 cm per minute. Therefore, lice are transmitted directly through direct contact with a sick person or care items.
- Myth # 7: "Pubic lice are transmitted only through sexual contact." Although sexual contact is the main route of transmission of pubic lice, this type of parasite can also be picked up in public places (baths, swimming pools), as well as through contact with personal hygiene items.
- Myth # 8: "Lice only love long hair." Lice need hair in order to cling to it and have free access to the skin, for this a hair length of 3-4 mm is sufficient.
- Myth # 9: "Lice only love dirty hair." But in fact, lice prefer a clean scalp, as it is easier for them to penetrate through the skin without a layer of thick sebum.
- Myth # 10: "Lice get inside the human skin." This is also not the case, lice cannot penetrate the skin, their anatomy allows them to cling to hair or tissue fibers, live, sleep and reproduce there, and human skin is only a "feeding trough".
- Myth # 11: "It is believed that lice from the head can be completely combed out with a thick comb." Mechanical removal of parasites and nits gives efficiency only up to 40%, while chemical methods (application of insecticides) give 98%.
- Myth number 12: "Lice do not survive without a person." Lice can live without blood in the environment for up to one week, during which time it is very easy to find a new victim. So very often people become infected on the beach, where parasites can wait in the sand or when using "public pillows" (in children's groups, hospitals, and so on).
- Myth No. 13: "Lice is only an unpleasant disease that violates the aesthetics of the body, and after treatment with special drugs, you can forget about them." Unfortunately, this is not the case either. In young children, pregnant women, allergy sufferers, people with reduced immunity, lice can leave complications in the form of chronic skin diseases, as well as provoke a pronounced allergic reaction. And also these parasites carry especially dangerous infections - typhus and relapsing fever.
- Myth No. 14: "Alcohol in the blood is the best prevention against various parasites." Special studies on this topic have not been carried out, but statistics indicate that people who are addicted to alcohol and drugs get sick even more often with head lice than people without bad habits.
- Myth number 15: "Lice love dandruff, as they feed on the scales of the epidermis." Lice are a blood-sucking parasite, they do not feed on any other secretions and parts of the human body.
Interesting Facts!
- People of the Negroid race suffer from head lice less often than people of the "white" race, perhaps this is due to the fact that dark skin is thicker, adapted to harsh weather conditions, and it is more difficult for lice to bite through it.
- Body lice are more common in poor countries with low levels of sanitation (for example, India, Pakistan, Bangladesh, African countries, and others).
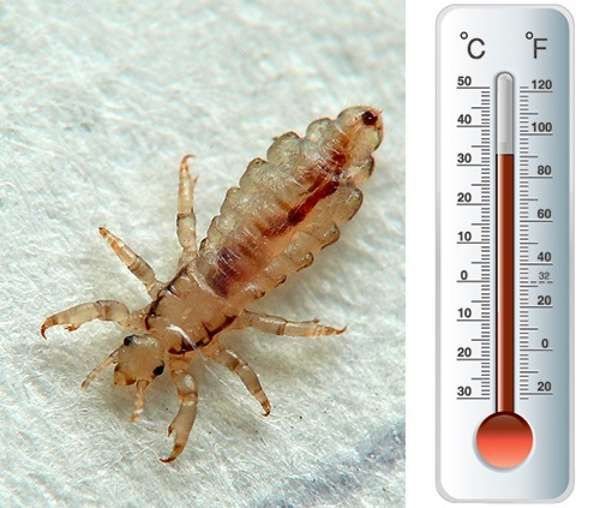
- Lice leave their host on their own when the body temperature drops sharply (in case of his death) or vice versa rises (fever of various origins), since for lice the most comfortable temperature is from 33 to 36 ° C.
- According to the classification, lice belong to the subclass of Diptera insects, but they do not have wings, but they have a similar structure of the respiratory tube. Flying insects may have been the forerunners of lice.
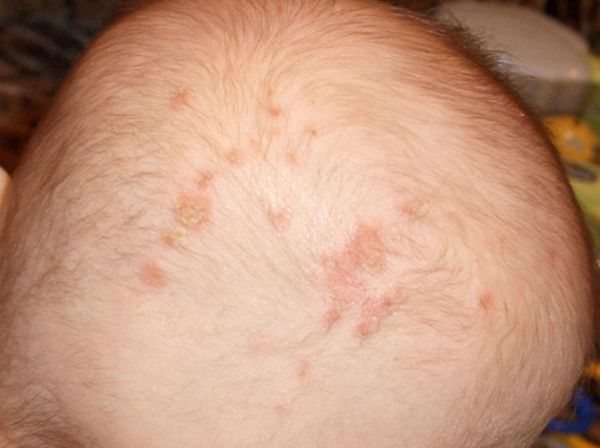
Lice - consequences and complications, is it possible to die from head lice
Pediculosis causes not only discomfort, but can also lead to the development of complications. The oral apparatus of parasites is a long tube with a sharp tip, thanks to which the louse easily pierces the epithelial layer of the skin and gets to the capillary vessels. At the time of the bite, the insect injects special toxins into the wound.

Chemical compounds are digestive enzymes that suppress blood coagulation. The liquid cannot coagulate, so the insect calmly drinks blood for a long time. At the same time, these enzymes begin to irritate the skin, which triggers an immediate immune response. A focus of inflammation arises, into which the infection enters. Gradually, a purulent exudate formed inside the puncture, itchy ulcers appear on the skin.
Pediculosis can lead to the following unpleasant consequences:
- peeling of the scalp, the formation of dandruff;
- the development of dermatitis, ulcers and hematomas in places where the colony of parasites is growing;
- if an infection enters the wound possible infection with infectious diseases;
- the appearance of boils, abscess, pyoderma;
- Pnervousness rises, sleep is disturbed, a person becomes irritable;
- weakened immune system, decreased appetite;
- hair condition worsens.
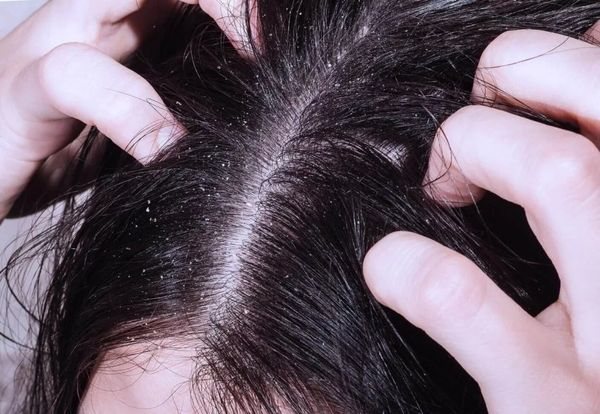


The unpleasant consequences of head lice appear gradually. They appear in the absence of treatment. Pediculosis does not lead to death. But parasitic invasion can cause the development of infectious diseases that pose a threat to life in the absence of timely treatment.
Lice can cause hair loss?
Lice belong to a group of blood-sucking insects that pierce the scalp without affecting the hair follicles. Sores and skin irritation at puncture sites can bleed and stop hair growth. At the same time, alopecia is not observed. Hair can grow dull, become brittle due to insufficient nutrition of the bulbs, but does not fall out.


Lice allergy
During the bite, blood-sucking parasites inject digestive enzymes into the wound to prevent blood from clotting. These toxic compounds cause local irritation, which causes the immune system to produce antibodies. People who are prone to allergies develop itching all over the body, rashes and red spots appear on the skin. In some cases, an anaphylactic reaction may occur.

Head lice temperature
A high temperature with head lice means that an infection has entered the wound and a generalized inflammatory process has begun... The immune system begins to produce antibodies that attack pathogenic microorganisms. The thermoregulatory center in the brain raises the body temperature to inhibit the growth and further multiplication of bacteria. If you have a temperature above + 38 ° C, you should immediately consult a doctor.


How to get rid of lice
These parasites are often confused with fleas or bed bugs. The type of bites and other symptoms are similar, moreover, they all do not live on a person.
If there is suspicion of infection, it is necessary to inspect the bed, often worn clothing, paying attention to folds and folds. This is where parasites can hide
Traces of vital activity - excrement, dead insects, empty nits - are also found in textiles.
If even small traces are found, it is necessary to begin an integrated fight. First, all linen and clothing must be washed. Before washing, you can soak things in a pediculicide solution. Insects die at temperatures above 40 degrees, therefore, for reliability, it is advisable to wash clothes at 60 or more degrees for at least 30 minutes
You also need to iron things with an iron, paying attention to the seams and folds so that there are no nits left in them. When unfavorable conditions occur, they can go into a kind of hibernation, and then continue their life cycle
In summer, in hot weather, you can take out linens, pillows, blankets in the sun. Lice are afraid of direct sunlight and high temperatures.
Heat treatment works in the opposite direction, that is, the lice can be frozen. In winter, you can dry your clothes after washing in the cold.
A steamer can be used to treat mattresses, pillows, blankets, sofas and other upholstered furniture that may also contain pests. You can have your clothes dry cleaned. It is especially effective on carpets, bedspreads and other heavy textiles.
Cabinet furniture, such as closets for storing clothes and bed linen, must be treated with insecticides. A vinegar solution is suitable for these purposes. You can also use professional remedies - pediculicides, for example, Medilis-Super or Medilis-Malathion. They are suitable for processing any surfaces, that is, they can handle cabinets, other furniture, wash floors, window sills and other places where pests may be with them. The treatment should be complex, since during selective etching, the lice can simply move to another place. Without shelter in underwear and without food, a louse can live up to a day, and then it will continue to parasitize and multiply. To prevent this, you need to process all possible places where the pest can hide.


Body treatment for body lice infection is the use of pediculicide preparations. They come in the form of a spray, lotion, or soap. Diluted in the right proportion or with a ready-made product, you need to wash the entire body, including the head. Since lice do not live in the hair, one such treatment will be enough to wash away all pests. Skin lesions, scratching, abscesses in their place are treated with conventional antiseptics and wound-healing preparations.
When dealing with lice, appropriate safety measures must be taken. For example, chemicals should not be used in the presence of pregnant or lactating women, children under 5 years of age.
When using special drugs, you need to be careful and strictly follow the instructions. It is impossible that funds fall on the mucous membrane
Do not inhale them, as they are toxic in high concentrations.
In general, dealing with body lice is easier and faster than dealing with head lice. The main thing is not to leave unprocessed clothes, linen or storage places. If one family member has body lice, then the things of all household members need to be processed.
Other types of lice and diseases they carry
Parasitic infestation in humans with lice is of three types:
- head licethat form colonies on the scalp;
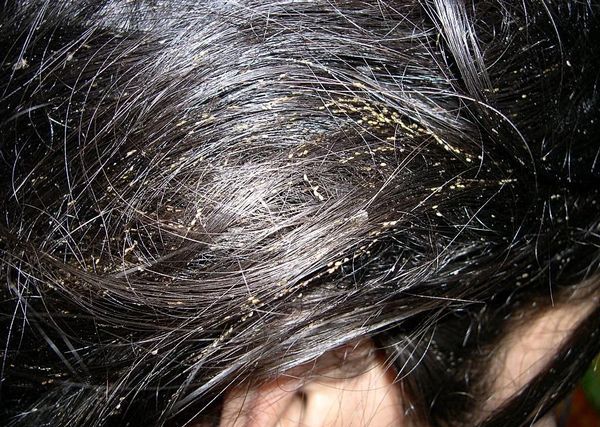

- body licesettling on clothes;
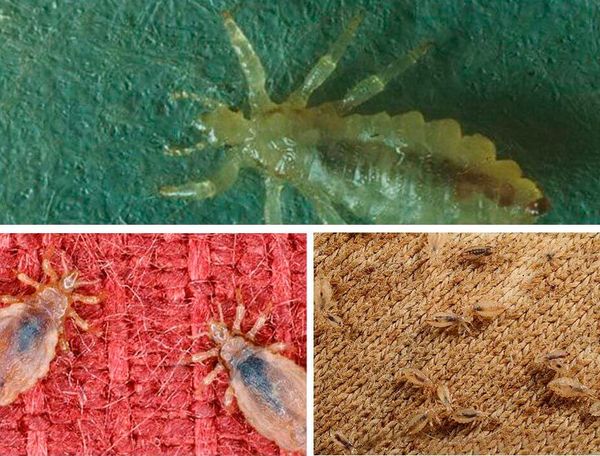


- pubic lice - living in the genital area.

Lice lay eggs only in their habitats. For reproduction, they need a temperature of at least + 15 ° C. The larvae hatch within a week and replenish the existing parasite colony. The lifespan of adults is about 40 days.
What disease is carried by the body louse?
The body louse is the largest parasite in comparison with the head and pubic insects of its kind.She hides in the seams and folds of clothing, where she lays her eggs. These are dangerous parasites that carry dangerous diseases: typhus and relapsing fever, Volyn fever, tuberculosis. With a bite, the probability of transmission is more than 80%.
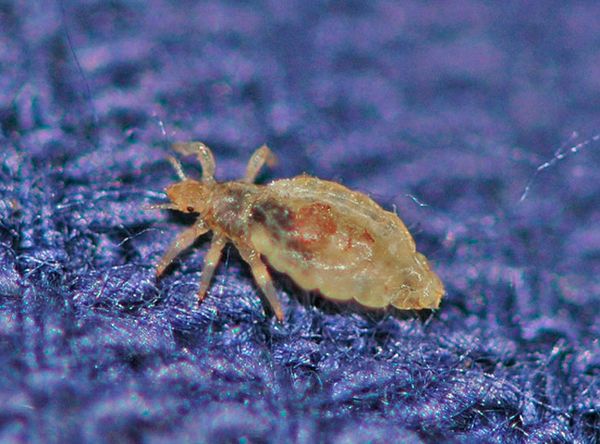


Clothes head lice is accompanied by the development of unbearable itching that spreads throughout the body... Rashes occur over the entire surface of the skin. At the sites of healing of ulcers, age spots appear, which, if untreated, acquire a bluish tint.
With parasitic invasion, an increase in temperature is observed, the appearance of signs of intoxication:
- headache;
- weakness;
- increased fatigue, loss of performance;
- nausea.


With suppuration of a large area of the skin, the psychoemotional state of the patient worsens.
Phthiriasis or pubic lice
Pubic head lice affects the groin area where pubic hair grows... Rashes are localized near the genitals, on the mucous membranes of the anus. With a long course of the disease, the hairline of the armpits is affected, lice fall on the eyelashes and eyebrows. The phthiriasis area is very itchy, there is a burning sensation on the genitals. When the eyelashes are damaged, the eyes begin to itch.
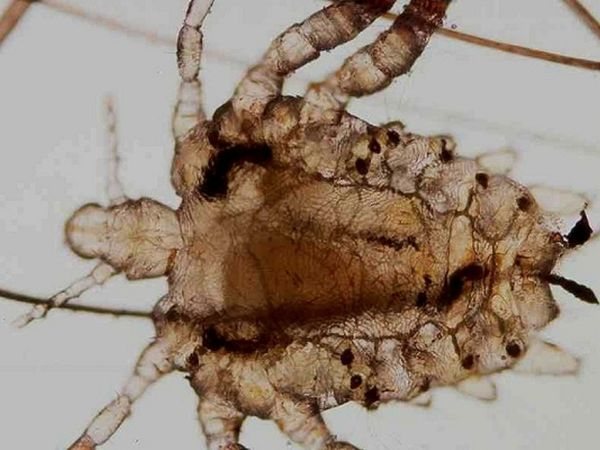


What are lice, their varieties and where do they come from
So, a small, wingless, blood-sucking insect is called a human louse. Scientists distinguish between the main three types:
- Head.
- Wardrobe.
- Pubic.
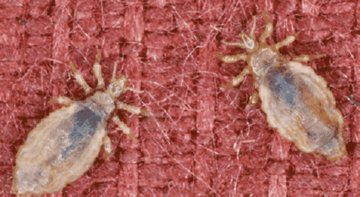
According to the description, the head louse is pale in color, is 3 to 4 mm long and exists in the scalp (less often in the eyebrows and eyelashes). The parasites move quickly enough by crawling, overcoming skin fragments at a speed of 20-23 cm per minute and clinging to hairs. They are not able to jump.


Head louse
The most frequent cases of mass destruction of this type are in children's institutions, places of greatest human congestion. Close contacts, the exchange of hats, hairbrushes and other things allow the insects to spread quickly. A trusting relationship between loved ones will allow you to notice and repulse the annoying inconvenience in time.
You should also be careful when traveling to countries that are not hygienic, for example, India, Vietnam and others.
Insects feed on the host's blood from 3 to 5 times a day and multiply in a favorable environment constantly. The result of their reproductive activity are numerous milky larvae - nits, no more than 1.5 mm in size, firmly attached to the hair with a special adhesive. Mostly the bloodsucker exists in the scalp, but sometimes the infection also covers the eyebrows and eyelashes. The life cycle in an adult lasts 3 weeks under normal conditions for it.


Nits
The appearance of clothes is usually detected in people without a fixed place of residence, who do not observe hygiene standards and do not change their clothes. As a living environment, he prefers exclusively linen, more often made of cotton or wool. In appearance, this type is very similar to the inhabitants of the head. The larvae can also be attached to the inner side of the fabric with an adhesive base.
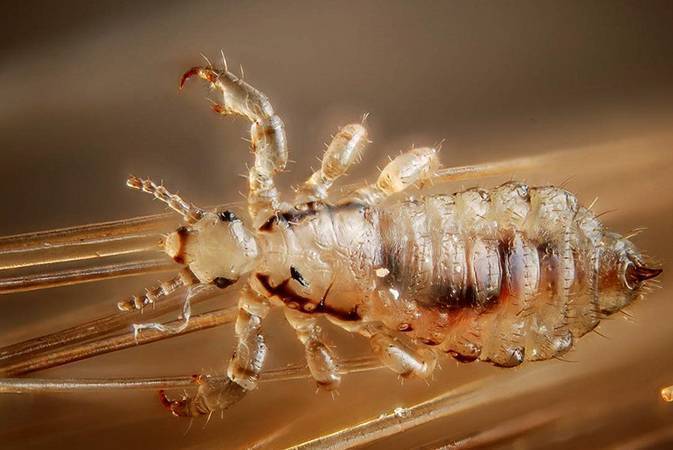


Cootie
This subspecies is easily transmitted when exchanging wardrobe items, and can live for several days on clothes removed and left without food.
The pubic or ploshchitsa was called a louse exclusively according to its habitat. In rare cases, it can also be found in the armpits, beard. The shape of this bloodsucker is slightly different from the two previous ones with a shorter and wider body, which allows it to parasitize precisely in the intimate zone. The length of the plate is no more than 1.5 mm, and in color, it looks darker than its "brothers".


Pubic louse
The main way of introducing such natural representatives is, of course, sexual.
How to deal with the parasite and possible treatments?
When confirming the diagnosis, wash all clothing, bed linen and towels at + 90 ° C. In such conditions, not only lice die, but also pathogenic microorganisms carried by parasites. If head lice was discovered in winter, it is recommended to carry the washed bedding to frost. Nits also die at temperatures below -5 ° C. It is necessary to disinfect with alcohol or rinse combs, rubber bands and hairpins with boiling water.
To combat parasites, 2 methods of treatment are used:
- Mechanical. Washing the head with hot water with tar soap or shampoo, rinsing long hair at a temperature of + 55 ° C. Drying with a hairdryer for half an hour, combing with a metal brush.


- Chemical. Treatment of the scalp with an insecticide, followed by combing out the parasites.
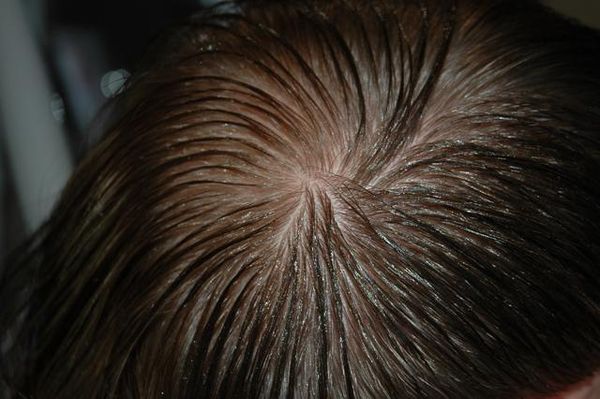

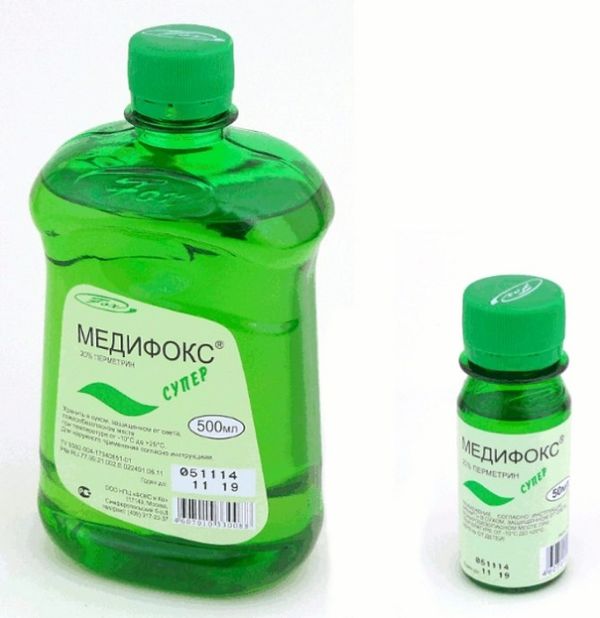
The pest control drug should be prescribed by the attending physician. The specialist will help you establish the dosage and duration of the drug. It is not recommended to purchase medicines on your own due to the high risk of side effects if the drug is taken incorrectly. Doctors usually prescribe permethrin-based drugs: Medifox, Nittifor. These are the least toxic drugs for humans. In some cases, the Para-Plus aerosol agent is additionally used. But it contains the organophosphate substance malathion, which has a negative effect on the liver.


IMPORTANT. Together with drug therapy, you must rinse your head with a special shampoo. The drugs are not taken during pregnancy and lactation, in children under 3 years of age. In such situations, use a shampoo to cleanse the hair or resort to a mechanical method of getting rid of lice.
HDo not use the same medication or shampoo for head lice treatment more than 3 times. Gloves should be worn when washing your hair with insecticide. After applying the product, it is necessary to comb out dead parasites and their eggs at least 2 times a day. After using the shampoo, do not wash your hair for 48 hours.
Complications
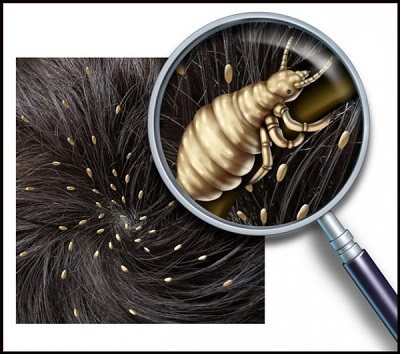

Why are lice dangerous for a person on the head? Lice feed on human blood up to four times a day, while several dozen insects can live on the head.
For more information about the types of lice, how they reproduce, as well as the incubation period, read on our website.
Based on these data, it is easy to calculate that the head is exposed to tens and hundreds of bites per day, each of which, although microscopic, together they have a significant effect on the skin and irritate it.
During a lice bite, an enzyme that prevents blood clotting is injected into the wound, subsequently it causes such a symptom of the disease as severe itching, which cannot but be quenched by constant scratching of the head.
If you scratch it frequently, it is likely to introduce dirt and harmful bacteria from your hands and nails into the wounds, after which it will penetrate the skin and cause suppuration. A large number of such abscesses can cause negative systemic reactions of the body, such as fever and inflammation of the lymph nodes.
On a note: in allergy sufferers, the enzyme secreted by lice causes even more itching, therefore, the likelihood of suppuration also increases. To avoid this, with head lice, they should use antihistamines.
Why is head lice dangerous? If you do not treat isolated suppurations, sooner or later they will develop into pyoderma - general purulent skin lesions. Pyoderma eventually flows into impetigo, which is characterized by the appearance of a bubbly purulent rash, indicating that the skin is affected by streptococcus.
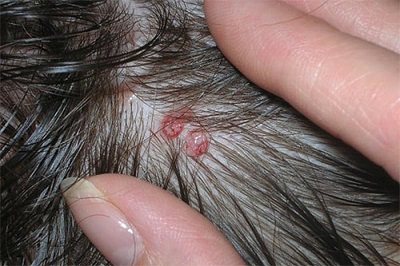

These are extremely unpleasant diseases, their treatment requires serious medical intervention and the use of strong medications.To avoid the occurrence of such pathologies, you need to remove lice quickly and decisively: only in this case, the itching will not bother you, which means that the likelihood of infection will be minimal.
Superficial treatment of head lice will not give the desired result. If nits remain on the head, they will later develop into lice and the parasites will continue to irritate the skin. Relapses of head lice are harmful because the scalp, which has not yet recovered after the first infection, again faces this scourge and is even more damaged.
If between relapses of the disease the fleeces do not have time to heal, then the chance of their suppuration increases.
In order to avoid complications of head lice, it is necessary to start treatment immediately after the diagnosis of the disease. On our site you will find information about some medicines for lice - sprays for lice and nits: Nyuda, Paranit, Para plus, Pedikulen Ultra; anti-lice ointments: benzyl benzoate, sulfuric, anti-lice shampoos; and about folk remedies: essential oils (for example, tea tree oil), kerosene, vinegar, hellebore water, hairspray, dichlorvos, hair dye, dust, hydrogen peroxide.
Prevention of head lice
To prevent parasitic infestation, preventive measures should be taken:
- keep the apartment clean: carry out wet cleaning of premises 2 times a week, wash pets regularly;
- prohibit children from putting on other people's things, 1-2 times a month to examine the scalp of the child's head for the presence of parasites;
- wash and iron clothes, hats;
- take care of hair: wash your hair, cut the regrown tips;
- change bedding and underwear weekly.


Strict adherence to preventive measures can be timely to prevent the appearance of lice, the development of head lice and reduce the risk of dangerous infectious pathologies.
- about the author
- VK profile
Video
Lice are blood-sucking skin parasites on the human body, giving it a lot of unpleasant sensations and problems. The excruciating itching and irritation begins to haunt, the hair becomes faded and loses its attractiveness. Since they are small in size and multiply quickly, it can be difficult to breed them.
Infection with head lice is dangerous because parasitic insects are carriers of many dangerous diseases. Lice feed on blood through the mouth organs, piercing the upper layers of the skin, which means they can infect and transmit various diseases to a person.
The louse and its way of life
The louse is an insect that feeds exclusively on human blood. The need for food is quite frequent, in one day the parasite makes four to five bites. Its jaws are shaped like long, sharp stilettos.
If the density of infection is low, then single bites do not cause significant concern. However, over time, after the release of the first offspring, itching appears, intensifying every day, noticeable blue-gray spots appear on the scalp.
When punctured, along with saliva, not only blood-thinning substances enter the wound, from which pinpoint bruises of a characteristic shade appear. Saliva itself is an irritating factor, itching occurs almost immediately after the puncture. The bites are comparable in strength to mosquitoes, and with multiple infections they cause severe irritation.
Moving insects over the scalp also contributes to itching and deep discomfort.
Every day, the female lays 4-5 eggs, which she attaches with a special composition to the hair. The nit remains on it even after the larva leaves it.
It can be estimated that in 30 days, only one female louse will lay approximately 140 eggs.

The presence of lice as such should not be considered a serious illness.If you find them in time, then you can avoid not only the manifestation of signs of severe infection, but also protect the whole family (although in any case, all household members will have to be processed).
Lice are dangerous, first of all, because they cause a negative reaction of the body to bites - scratching, irritation, itching. In addition, in unsanitary conditions, insects act as carriers of especially dangerous infections.
What to do if head lice is detected
When lice are detected, do not despair and treat your hairline with everything that comes to hand. Traditional methods can only aggravate the situation. Do not use solvents, kerosene, vinegar or pesticide on your body.
This can cause severe burns or an allergic reaction. Today, there are special medications that successfully rid a person of parasites within a few days. Also, don't cut your hair.
In order to get rid of parasites completely, it is necessary to wash all outer clothing, bedding and underwear. After that, you need to treat all parts of the body, where there is hair, with a special product purchased at the pharmacy.
You must first consult a dermatologist. Treatment should be carried out throughout the week in order to ensure that all nits and young individuals that appear from them will be removed.
You do not need to treat yourself. There are, of course, a large number of folk remedies: children are sprinkled with cologne, dichlorvos, rubbed with gasoline. But it will hurt more. It is necessary to visit a dermatologist at your place of residence or at the Republican Center for Dermatovenereology.
The doctor will prescribe the treatment. After going to the doctor, parents will need to wash, dry and iron all things well. If the lice are on the head, eyebrows and eyelashes, then their eggs must be mechanically combed out.
Medicines do not quite work on nits: some of them die, some remain half asleep. With the right treatment, parasites can be quickly eliminated. Well, of course, we need to find the source of infection. If this happened in an educational organization, then doctors notify the Sanitary and Epidemiological Service.