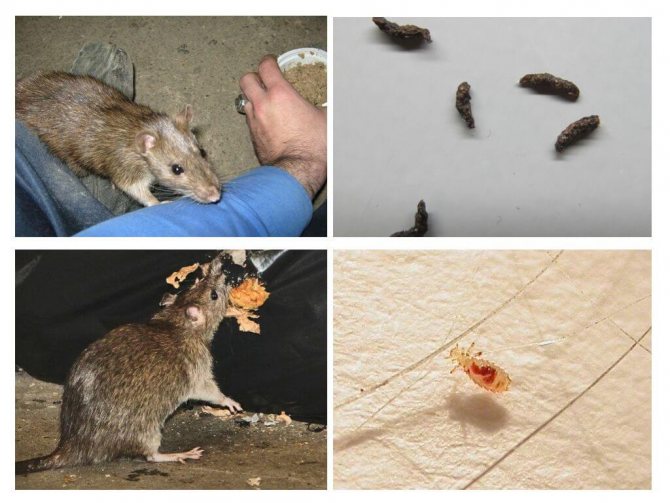
One of the pests that prefers to live next to humans is a mouse. These animals choose summer cottages and rooms for arranging nests, where unsanitary conditions prevail and there is a sufficient food base. These can be utility rooms, garbage chutes, basements, granaries, dumps, attics. Entering homes and food warehouses, they spoil food, leaving their droppings in them. But destroyed food supplies are not the biggest problem. A much greater danger is posed by mice that carry pathogens of serious diseases. Infection can occur through direct contact, through skin remnants, spoiled food, excrement and saliva. In the article, we will consider what diseases mice carry, and how to protect yourself and your family from the sad consequences.
Salmonellosis
Salmonellosis is a bacterial infection caused by Salmonella spp., Often referred to as food poisoning. People with infection experience:
- Pain, cramps in the abdomen, stomach;
- diarrhea;
- chills, fever;
- nausea, vomiting;
- headache;
- blood in the stool.
Severe cases lead to hospitalization due to dehydration. Humans become infected with salmonella bacteria by eating food contaminated with rodent feces.
Mice spread salmonella by contaminating food and water with feces containing Salmonella bacteria. Direct contact with infected rodents also causes disease.
Musophobia
This term refers to the fear of rats, or unconscious and uncontrollable fear of rats and mice. It should not be confused with an aversion to rats, which develop out of habit or a desire to follow generally accepted patterns of behavior. With musophobia, a person begins to panic at the sight of a rat, not being able to explain the reason for his fear and control himself.
It is simple to identify this symptom: it is enough for a person to show a neat decorative rat or mouse. If the patient begins to shake at the sight of her, it means that he really has a phobia. If it turns out that he is afraid only of basement rats or only stories about mutant rats, then we are not talking about the disease here, and the fear turns out to be far-fetched.
Musophobia is treated with the technique of rapprochement, which in simple terms can be called "knock out a wedge by a wedge". Simply put, the patient is shown rats, but at first - cute decorative, better - rats, perhaps - in videos, and then from afar and for a short time, and then gradually reduce the distance and increase the duration of contact.
With a competent medical approach, musophobia can be completely eliminated.
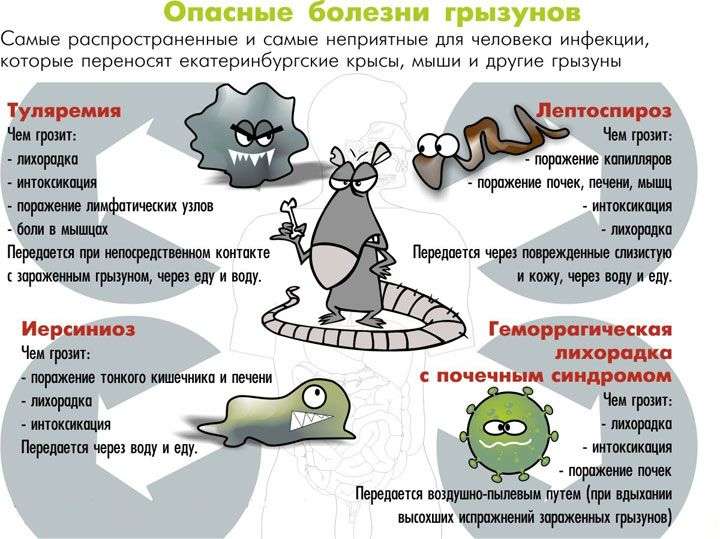
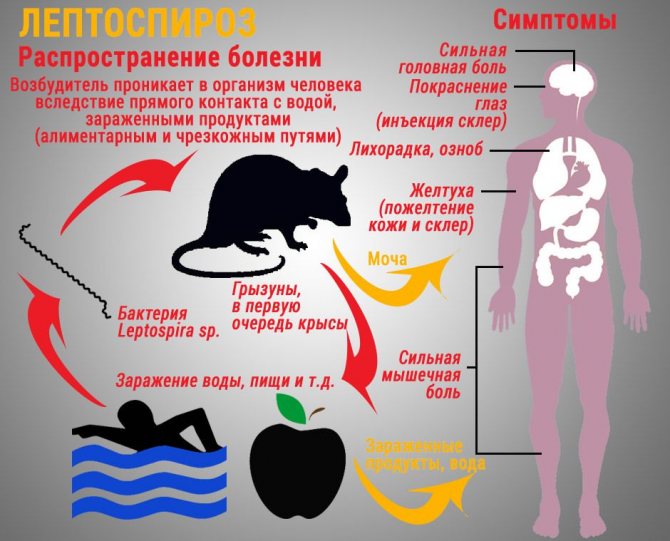
Leptospirosis (Weil's disease)
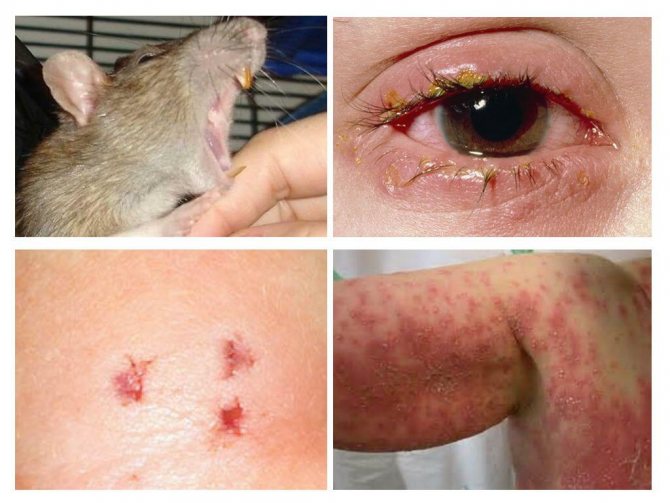
Bacteria (Leptospira spp.), Similar to Salmonella, which are transmitted to humans by mice, wild animals, domestic animals, including dogs, rats, pigs, cattle. It is transmitted through direct contact with the urine of an infected animal.
Contagious as long as the urine remains wet. The urine of infected host animals contaminates the food or water that humans consume. A variety of symptoms are associated with this disease, such as:
- redness of the eyes;
- jaundice;
- vomiting;
- chills.
In mild cases, the symptoms resemble a severe case of flu with headache, fever, vomiting, and diarrhea. Progresses to meningitis, hepatic, renal failure.
Antibiotic treatment is successful when the disease is diagnosed early.Without treatment, people usually recover, although the healing process takes months.
There is a risk of death if the disease progresses to meningitis (inflammation of the brain, spinal cord), kidney or liver failure. Distributed in regions with high temperatures.
Learn more Mice: what they eat, how long they live, how to deal with them
Dangers of man-made accidents caused by rats
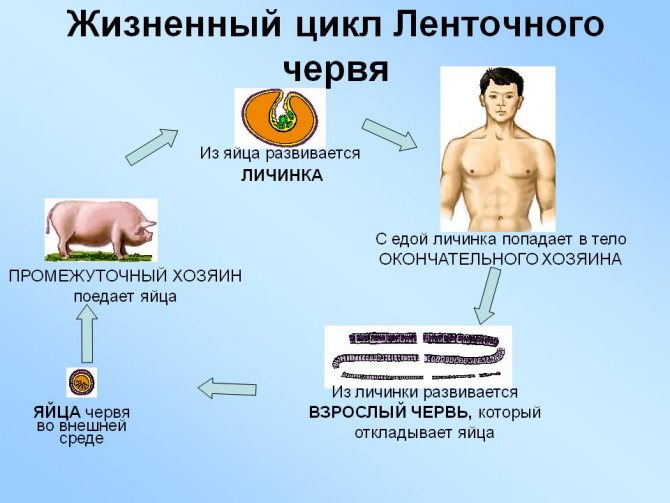
There are few common types of helminths in humans and rats. There are two types of tapeworms that parasitize rats and can be dangerous to humans, as well as one species of Trichinella, the larvae of which, according to some studies, can also develop in the human body.
In fact, in developed countries, there is no danger of transmission of helminths from rats to humans. This is due to the fact that both tapeworms and trichinella enter the human body with the meat of the first host. Simply put, in order to become infected with worms from a rat, it must be eaten, and before that its meat should not undergo significant heat treatment, that is, it should be practically raw. For cultural reasons, this can only happen in very remote areas (for example, in tribes leading a semi-wild lifestyle).
We suggest that you familiarize yourself with: Tick bite - detailed instructions on what to do.
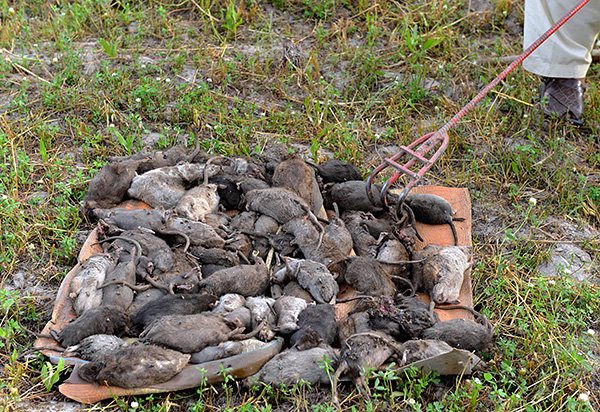

Finally, the consequences of accidents caused by rats can be dangerous to humans. So, there are known cases of dams breaking due to the fact that rats literally riddled them with their holes. After that, houses located nearby were flooded.
And in 1989, half of New York sat without light for several hours, when a rat closed the contacts at a distribution station and, having burnt out, started a fire. The power of several lines was automatically turned off.
In the annals of the Renaissance, cases are reported of rats on ships spoiling food and the crew starving while on the high seas. And relatively recently, in one of the Chinese cities at the airport, the plane did not start the engine due to the fact that a rat gnawed one of the hoses in the fuel supply system. It is not known how many victims this rodent could lead, if he gnawed the same hose already during the flight ...
In any case, rats are very dangerous simply because there are too many of them living next to us. Even if one in several hundred of them will be infected with an infection, among the millions of animals in a big city, there will be thousands of infected. Even if one in a thousand will discover the way to a residential building or apartment, and already hundreds of people will eat spoiled food, and then try to catch rodents. And a few home-grown hunters - "lucky ones" will surely be bitten ...
And it should always be remembered that the most dangerous rats are not at all mythical dog-sized mutants, which in reality no one has ever seen. The fearful small inhabitants of basements and entrances, often literally stuffed with pathogens of infections dangerous to humans, are a real threat to humans. You need to stay as far away from them as possible, and if you find them close to housing, you should diligently fight them.
Lymphocytic choriomeningitis (LCM, LCMV)
A neurological disorder that causes cerebral edema, neurological problems including aseptic meningitis (inflammation of the meninges surrounding the brain and spinal cord), encephalitis (inflammation of the brain).
People become infected with LCM by exposure to droppings, urine, and inhalation of dust contaminated with the waste of an infected animal. Signs of infection in humans, mild, are not diagnosed. The most common first symptoms are:
- nausea;
- temperature increase;
- lack of appetite;
- muscle, headaches.
At the second stage, the disease turns into meningitis, encephalitis, causing confusion, and other symptoms.
Only 1% of reported deaths. There have been cases where people have contracted lymphocytic choriomeningitis from domestic mice or a hamster.
In pregnant women, lymphocytic choriomeningitis can cause birth defects such as poor vision and mental retardation.
Mouse bites, although rare, can transmit disease to humans.
Treatment requires hospitalization, the appointment of large doses of anti-inflammatory drugs. Prevention - careful avoidance of contact with rodents or places of presence where rodents have been present.
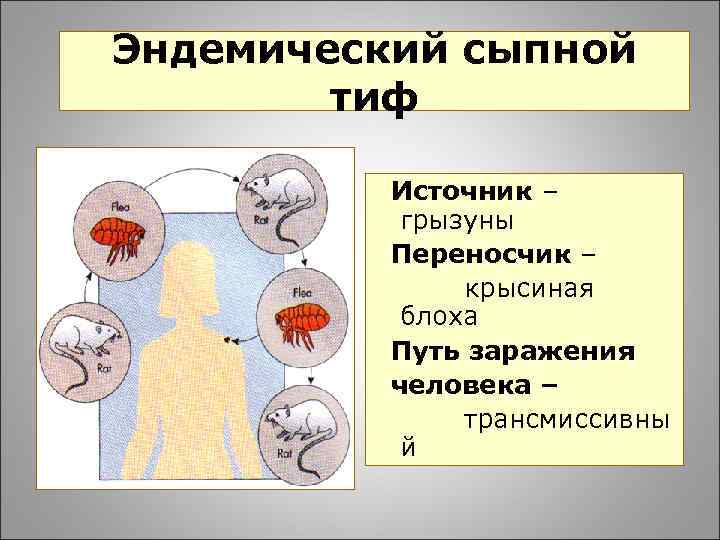
Rat endemic typhus
Other names for this disease are endemic typhus and flea endemic typhus. Its symptoms are fever, headache, persistent temperature within 39-40 ° C, severe malaise and characteristic skin rashes.


In severe cases, the meninges are involved in the pathological process with typhoid, which leads to certain nervous disorders. In addition, the disease is dangerous due to complications in the blood vessels, due to which myocarditis, thrombophlebitis and cerebral hemorrhages can develop.
Nevertheless, today, rat endemic typhus is successfully treated with affordable and inexpensive antibiotics, and its complications are prevented with the help of blood anticoagulants. Fatalities are rare and occur mainly in developing countries.
It is important that fleas are the carriers of rat typhus. Neither ticks nor lice can tolerate this disease.
The mechanism of transmission of its pathogen is not the same as in the plague: rickettsiae do not penetrate into the blood of a person with the saliva of a flea, but are simply in its excrement. A person infects himself by combing the bite, while simultaneously crushing the remaining flea secretions on the skin. The bacteria themselves penetrate into micro-scratches on the skin, and from them - into the blood, with which they spread throughout the body.
Hantavirus Pulmonary Syndrome (HPS)
Potentially fatal, severe respiratory illness. The syndrome is caused by a number of different viruses, most often affecting the lungs, heart, and kidneys.


Transmitted by mice, Peromyscus maniculatus, cotton rats (Sigmodon Hispidus), rice rats (Oryzomys palustris), white-footed mice (Peromyscus leucopus). Infection with HPS viruses occurs through:
- Inhalation of dust contaminated with urine, rodent feces;
- Touching infected animals or their urine, feces;
- Bite of an infected mouse, rat.
Airborne transmission of the virus is the most common way of spreading the disease. Hantavirus cases are more common in rural areas.
Diagnosis is difficult because the disease resembles the flu. The disease has two distinct stages. In the first phase, infected people experience flu symptoms such as fever, chills, and vomiting.
The state of health worsens in the second stage, shortness of breath, accumulation of fluid in the lungs, decreased heart function, kidney failure, which lead to death. HPS has no vaccine or cure.
Treatment for HPS requires hospitalization with supplemental oxygen, and severe forms are fatal.
How can you get infected from a rodent?
If you acquire a healthy decorative animal from the order of rodents or lagomorphs (decorative rabbits) and properly maintain it, the risk of infection from a pet is not great. But since it exists, we will consider the most common diseases that a person runs the risk of "catching" from animals with sharp front teeth.
Rabbits and rodents get sick with almost all types of infectious ailments:
- bacterial;
- viral;
- parasitic;
- fungal.
Each of the subgroups contains one or more pathologies that can be transmitted to humans and other warm-blooded creatures.
Hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome
Hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome (HFRS) is a group of related diseases caused by hantavirus.Early symptoms include headaches, chills, and body aches. Later symptoms progress to low blood pressure, acute shock, and kidney failure.
Learn More The Best Mouse Poison And What You Need To Know About It
Similar to hantavirus pulmonary syndrome, the virus that causes hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome is transmitted through particles containing droppings or urine. People get sick if rodent waste gets into the eyes, nose, mouth.
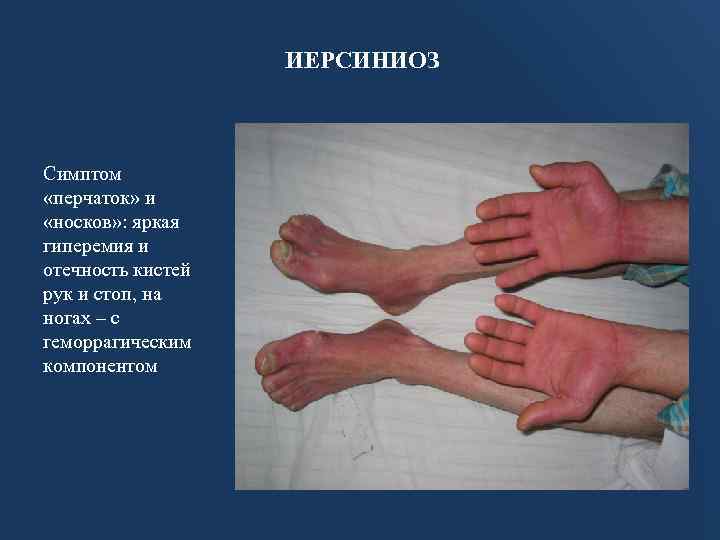
Rat Fever (RBF)
Rat fever (Streptobacillus moniliformis) is an infectious disease transmitted through the bite of rats and mice. Most often found in North America, Europe. Soon after the onset of the disease, a rash appears on the hands and feet. Symptoms:
- fever;
- rash;
- vomiting;
- pain in joints, muscles;
- headaches.
Sometimes swollen lymph nodes, bite wounds develop into ulcers. If untreated, the disease progresses to an infection of the lungs, liver, kidneys, brain, heart.
You can get rat fever if:
- will be bitten or scratched by an infected rodent;
- touched a dead sick animal;
- consumed food, water, which is contaminated with rat excrement.
RBF treatment consists of heavy antibiotics that are effective. If left untreated, the disease is fatal.
Allergy to wool, urine and excrement of rats
Allergy to rats occurs with about the same frequency as allergies to other animals, and proceeds with similar symptoms: sneezing, increased tearfulness, conjunctivitis and allergic rhinitis. It can be caused by both rat hair and dry excrement, in rare cases - urine, and an allergy with the same probability can develop to both a house and a street rat.
You can temporarily stop allergy symptoms with the help of antihistamines or local hormonal agents - ointments, nasal sprays, tablets. A complete cure is possible only after a course of specific immunotherapy.
If you are allergic to a street rat that regularly climbs into the room, you just need to get rid of it and thus eliminate the allergen itself.
Diseases indirectly transmitted by mice
Lyme disease, babesiosis
It is transmitted by ticks, which mice often receive. This is a very serious, health hazardous disease that is easily transmitted by ticks and has long-term consequences.
Babesiosis may be asymptomatic for some people and life-threatening for others.
Symptoms:
- fever;
- chills;
- sweat;
- nausea;
- fatigue.
Sometimes people experience failure of vital organs, death. Dogs and cats are also infected with the parasite and show symptoms such as lack of energy, decreased appetite, enlarged abdomen, discolored stools. The severity of the disease depends on the type of animal.


Plague
Bubonic plague (Yersinia pestis bacteria) was thought to be caused by mice and rats, but it turned out to be the fleas they carried. Fleas feed on blood and transmit this potentially fatal disease.
Domestic mice usually do not carry the human plague (bubonic) because they have fewer flea infestations than rats.
It is now easily treated with antibiotics if diagnosed early, but it is still a serious illness. Plague is relatively rare, affecting 1,000 to 2,000 people worldwide every year. Transmitted through:
- Touching an infected animal;
- Infected flea bite.
The most common symptoms of plague are:
- abdominal pain;
- diarrhea;
- nausea, vomiting;
- fever, chills;
- headaches;
- muscle weakness.
An accurate diagnosis is made based on blood tests. Treatment includes the use of powerful antibiotics. There are vaccinations for people who are at constant risk of contracting the plague.
Learn more All about the water rat: what it eats, where it lives, what it looks like
Colorado tick fever
Another serious and life-threatening disease spread by ticks carried by mice.
Rickettsial pox
Rickettsial pox, murine typhus (endemic) caused by the bacterium Rickettsia akari, is similar to chickenpox. Transmitted by rat, cat, mouse fleas. It is spread by mice, but very rarely. The disease is usually mild and resolves in 2–3 weeks if left untreated.
No fatalities were registered. Endemic typhus responds well to antibiotic treatment.
Anaplasmosis
Anaplasmosis-transmitting ticks are often carried by deer mice. Not a fatal disease that affects both humans and pets.
Symptoms:
- chills;
- headaches;
- muscle pain.
Pets exhibit loss of appetite, lethargy, and delayed movement.
Tularemia (rabbit fever)
Tularemia is a disease caused by a bacterium (Francisella tularensis) carried and spread by wild rodents (including muskrat, gophers, beavers) around the world. With an illness caused by an insect bite, it causes an ulcer at the site of injury.
When infected while eating, drinking, the disease causes swelling of the glands, cough, and lung infection. Symptoms range from very mild to life threatening. The final diagnosis is difficult and requires a blood test.
Transmission to humans occurs through:
- Handling the carcasses of infected animals;
- Bites from infected insects such as ticks, flies;
- Eating contaminated food, water;
- Inhalation of air with bacteria.
Once diagnosed, tularemia is treated with large doses of antibiotics. Symptoms can last for many weeks. The person recovers completely after treatment.
Prevention - preventing insect bites with repellents, avoiding direct contact with rodents, using respiratory protection to avoid inhaling landscape dust while gardening or agricultural work.
Rat bites and their danger
Rats are also dangerous because they often bite people. Recall that with such bites there is a risk of infection with sodoku and tetanus, but even without that, the rodent bite itself is very painful, often accompanied by bleeding. This is not surprising: with its jaws, a rat can develop a pressure of up to 500 kg / cm2, which allows it to gnaw on copper and lead.
Biting a human finger to the bone is not a problem for an adult rat. The bites themselves can fester when infected with a third-party bacterial infection, and without therapy, ulcers often develop in the place of abscesses.
However, rats bite to blood, mainly for self-defense, when they are caught or driven into a dead end. It is very rare, but documented cases when these animals bite through the skin of sleeping people.


Often rats bite when they are very hungry. In this case, they tend to gnaw off the strong skin on the heels of humans, they also bite large animals on the feet, and in elephants they can gnaw off the heels so that they cannot walk.
At the famous animal dealer Karl Hagenbeck, three elephants died in one night from the fact that rats gnawed their feet. Small animals - rodents, lizards and frogs, birds in their nests - are easily killed and devoured by rats. If this happens in a chicken coop or rabbit house, the harm from rats can be very serious.
Are mice dangerous?
The short answer is yes. They spread numerous diseases around the world. Diseases are transmitted to humans directly: through contact with excrement, saliva, urine, through mouse bites, simple contact.
However, they can spread indirectly: through ticks, fleas that feed on infected animals, then transmit the infection to people.
Getting rid of mice in an apartment is more than just protecting furniture from damage, it is dangerous to leave them free. If you have come into contact with mice, be sure to take appropriate measures such as cool traps and seek medical attention if necessary.
How the infection is transmitted
Food, soil, water, dust - all this can cause human infection with various infections that mice carry. Some of their diseases are treated quickly and easily, others are deadly. But you can prevent its occurrence if you know how the infection is transmitted:
- The use of grain, flour, other food and liquids, into which the droppings of a sick mouse have got, is an alimentary route of infection.
- Inhalation of dust with particles of mouse excrement and hair. Workers in fields, construction sites and house cleaners are most at risk.
- Contact with the corpse of an animal.
- Accidental ingress of water from an open reservoir while swimming.
- There is a high probability of infection when a person is bitten by a mouse. In this case, infectious agents enter the body with the saliva of a sick individual.
- Through parasites that live in the coat of rodents.
- Through pets that have previously been infected with pathogenic bacteria from rodents.


Knowing the main routes of transmission of pathogens of serious diseases, you can prevent their occurrence. Residents of country houses and summer cottages, where large populations of rodents like to settle down, should be especially careful.