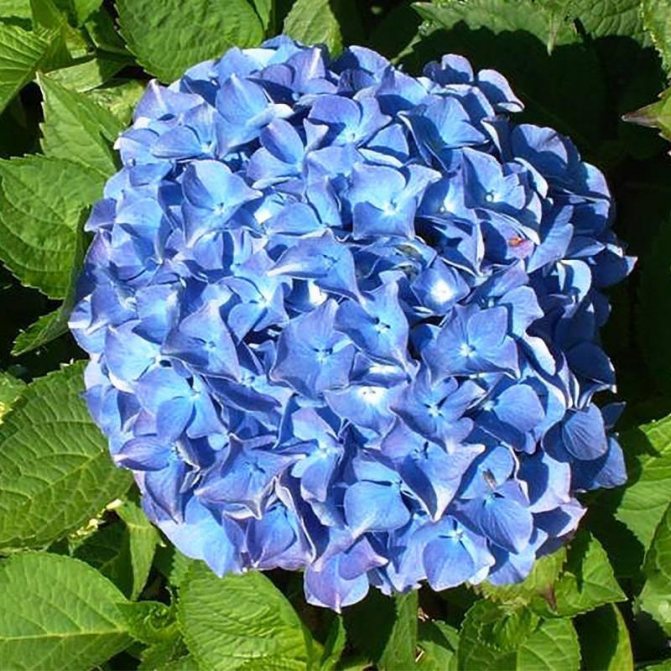
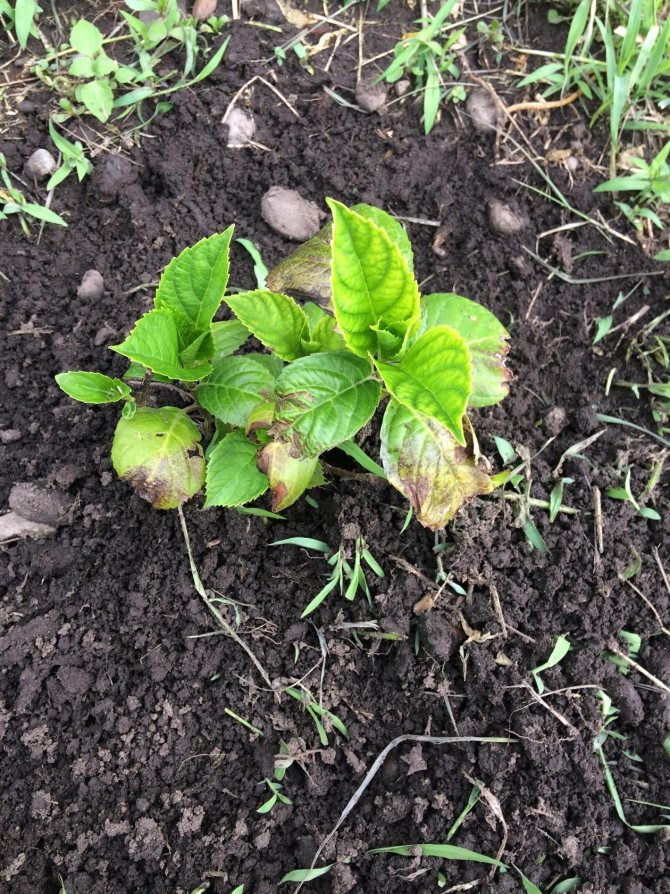
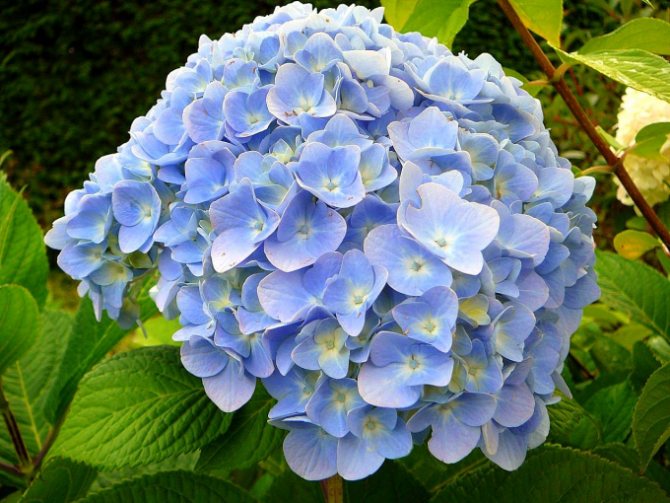
Hydrangea is an amazing flowering plant that can decorate a room, terrace, balcony, flower garden or garden.
Lush bushes with bright green foliage are strewn with caps of flowers of various delicate shades: white, pink, red, lilac, blue. I always want to see such a plant healthy and blooming, however, some problems may arise during the cultivation process.
Hydrangea is quite resistant to diseases and pests., but still requires constant care and attention. The vagaries of nature and improper care can provoke the appearance of various diseases. In this case, it is important to identify the problem in time and know how to solve it correctly and quickly.
In the article you will see everything about hydrangea diseases and pests and plant treatment, as well as photos of problems.
External stimuli
In addition to pest infestation and pronounced diseases, there are external factors that negatively affect the beauty and health of hydrangeas. For example, yellowing of leaves can be caused by such irritants:
- Bright scorching sun. The plant prefers to be in partial shade, so too much light can be harmful.
- Waterlogging of the soil. Although hydrangea loves moisture, excessive accumulation of water can cause yellow foliage.
- Lack of fertilizer. For growth and lush flowering, hydrangea needs regular feeding.
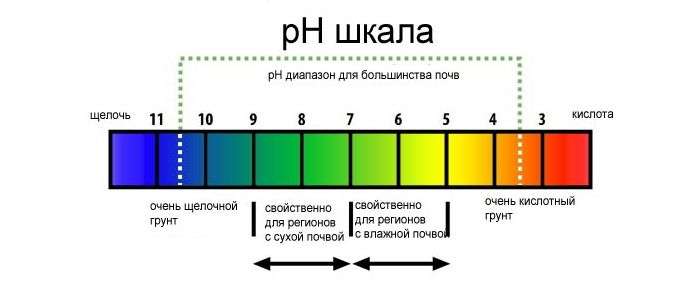
- Reduced soil acidity. The flower needs an acidic soil (pH 3-6). Even the color of the flowers depends on the level of acidity: the more acidic the soil, the more purple and blue colors appear, closer to neutral - white and pink shades prevail. To increase the acidity, periodically during watering, add 2-4 drops of lemon juice to 1 liter of water.
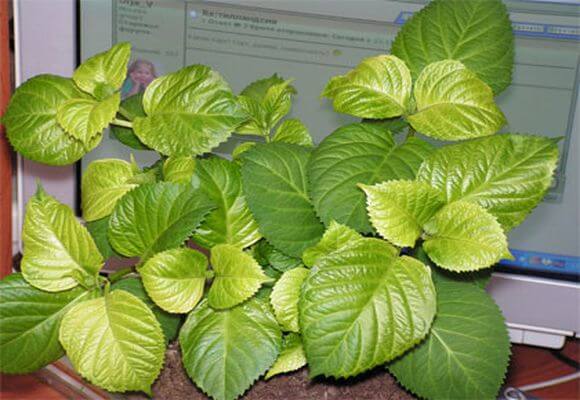

Sometimes hydrangea foliage begins to dry out and fall off. The reason also lies in external stimuli:
- Insufficient watering, especially in hot weather.
- Low environmental humidity. This often happens in closed rooms, greenhouses. Regular ventilation and humidification of the air is important.
- Lack of nutrients. Top dressing of hydrangeas is carried out 1 time in 7-10 days. This is especially important during bud formation and flowering.
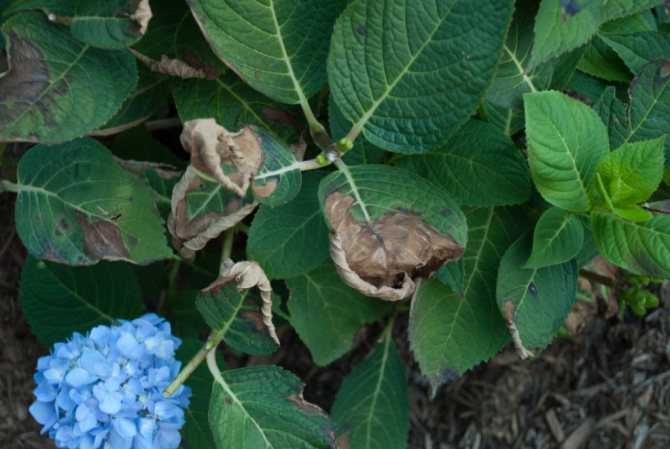
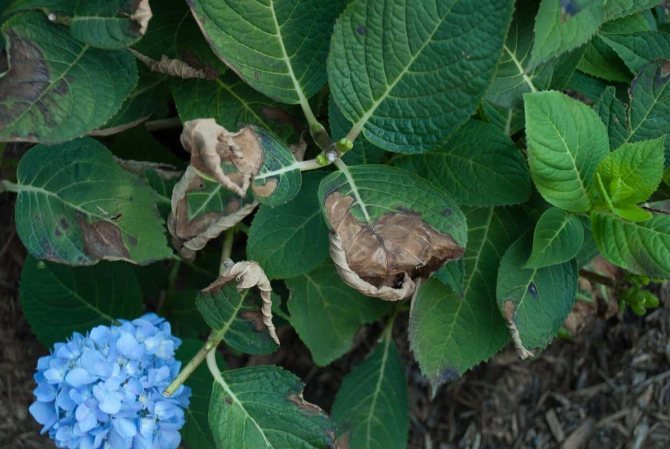
Sometimes a grower may be faced with the blackening of hydrangea leaves. It can be dry or wet and is also caused by external factors.
Dry blackening manifests itself in the formation of brown spots on the edges of the leaves, which subsequently lead to wilting of the foliage. The reason may be:
- Hard water. Before watering, it is recommended to settle the water for at least 24 hours;
- Sunburn. It is important to protect the plant from direct sunlight.
Wet blackening determined by limp, darkened leaves. It may appear due to:
- Sudden temperature changes, drafts;
- Excessive watering;
- Heavy soil that traps moisture and prevents breathing.
Features of the content of the flower
Subtropical plants have a hard time adapting to northern latitudes, while maintaining their inimitable decorative effect. Therefore, the owner should provide exotic pets with the most acceptable living conditions. In the case of hydrangea, grooming is not that difficult.
Lighting
The diffused intense light guarantees the bush succulent foliage and abundant flowering.If it is not possible to place a pot of hydrangea on a windowsill facing the south or west side, you can artificially extend the daylight hours for it with additional lighting. It should be borne in mind that the scorching sun causes irreparable burns on the leaves, and the prolonged absence of sunlight makes the bush look lifeless.
Watering
Hydrangea is moisture-loving. It is necessary to moisten the soil at the first signs of drying out of the top layer. However, the water should not linger in the pot. The death of the root system, and after it the entire aerial part, will cause flooding, in which the flower will “float” in the pot for several days. In hot dry weather, the bush will be "grateful" for spraying from a spray bottle. In this case, water droplets should not remain on the sheet plates in order to avoid burns and the release of salts from the water.
Temperature regimes
The requirement for constant warmth is perhaps paramount to hydrangea care. Moreover, it can be destroyed by a cold wind from windows or drafts in the apartment. The optimal temperature regime for maintaining vital activity and the formation of buds ranges from +25 to +300 C. In winter, when the bush "falls asleep", the temperature should not fall below +160 C.
The soil
Hydrangea prefers acidic soil. If the bush is "forced" to grow in an alkaline environment, the leaves begin to turn yellow and crumble on it. Planting soil can be purchased at specialized stores or made by yourself. This will require turf, leafy soil, peat chips and coarse sand in a ratio of 2: 1: 1: 0.5.


Fertilizers
As the buds form, the plant needs feeding. These are mainly complex organic and mineral fertilizers, which must be applied in the form of aqueous solutions, stopping with the arrival of the winter dormant period.
Transfer
Hydrangeas are transplanted annually with the onset of spring, while pruning stiff shoots. For transplanting, they buy a new, slightly larger pot and fill it with fresh soil, and the one in which the flower has lived all the previous year is thrown away.
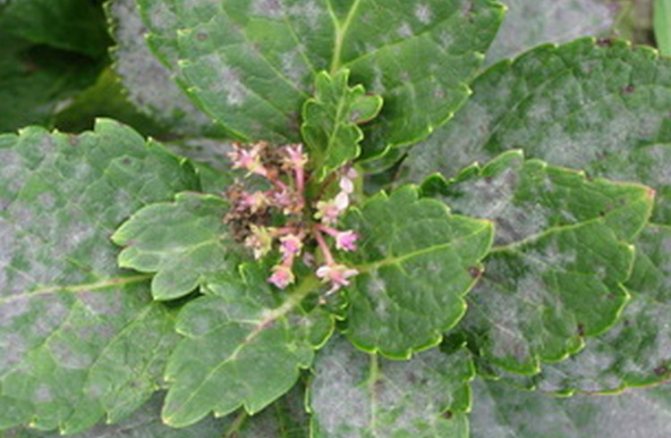
Hydrangea chlorosis
Chlorosis occurs due to a lack of iron in the soil or as a result of metabolic disorders in the plant itself, due to which it cannot absorb iron.
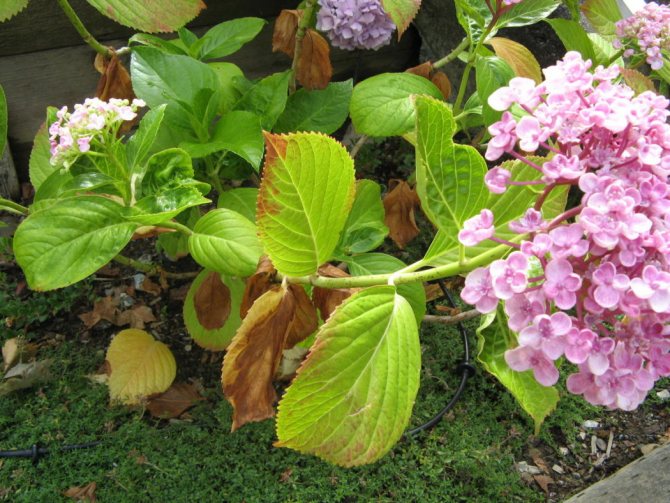
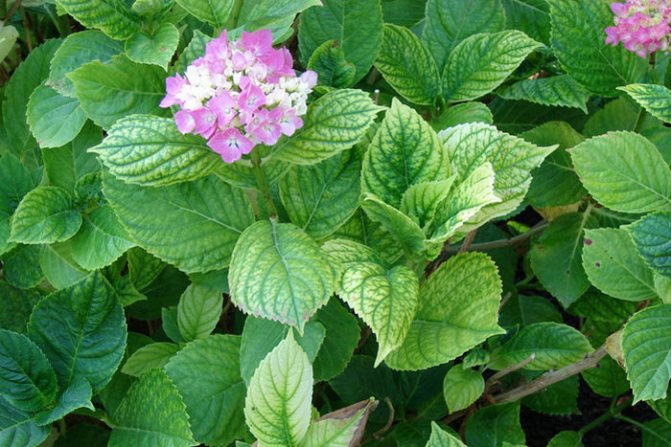
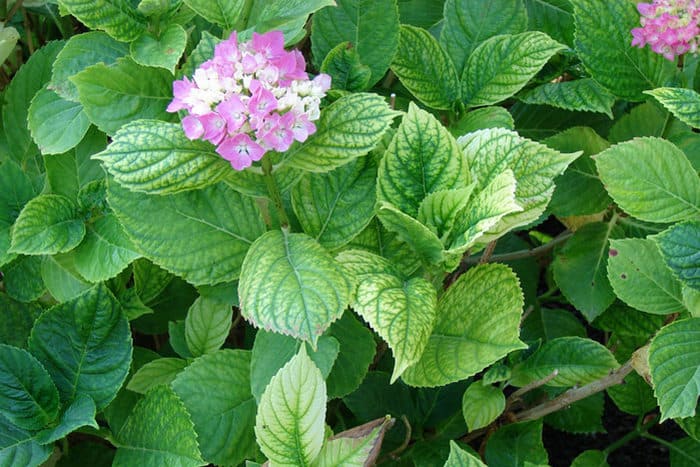
The main symptom of chlorosis is lightening and yellowing of foliage.... In this case, the veins on the leaves remain dark.
In addition, there may be a decrease in leaf size, deformation of buds, twisting of leaf plates, drying of shoots.
When a disease is detected, it is important to feed the plant with preparations containing iron in a chelated form, for example, Antichlorosis and Ferovit.
Also, the medicinal composition can be prepared independently. To do this, dissolve 2 grams of ferrous sulfate and 4 grams of citric acid in a liter of water. This solution should be sprayed with hydrangea leaves, and with an advanced form of the disease - and watered at the root.
Another way to treat hydrangea chlorosis is to use a solution of potassium nitrate and iron sulfate... To do this, 40 grams of potassium nitrate is diluted in a bucket of water. The hydrangea is watered with this solution 2-3 times. After 3 days, irrigate with iron sulfate in the same concentration.
How to cover a hydrangea for the winter
In the fall, after performing sanitary pruning, removing all faded inflorescences, the hydrangea should be prepared for wintering. In the near-stem circle, remove all the fallen leaves and remove the remaining on the branches. The older the plant, the less shelter it needs.
Important! Depending on the region of residence, permanent shelter may be required for all varieties of hydrangeas.
The plant needs to protect the buds. To do this, bend the shoots to the ground and close (you can even cover with a film), leave holes for airing.In the Urals and Siberia, the growing season will begin later and end earlier, the shelter will need warmer. Only with proper care will the shrub annually decorate the garden with its abundant multi-colored flowering.
Fungal diseases of hydrangea
White rot begins with the defeat of the root system, since the pathogenic fungus is in the soil. As a result, the plant cannot receive the necessary nutrients, turns brown and eventually dies.
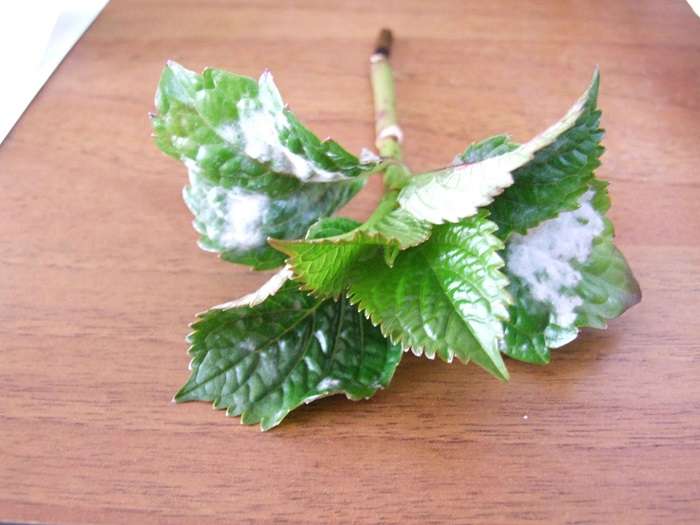
A sign of the disease on young hydrangeas is the darkening of the shoots and the appearance on them of a white bloom, similar to cotton wool. If the flower is not treated, black blotches appear on the cotton wool - sclerotia.
To combat white rot, fungicides are effective, such as Fitosporin, Fundazol, Copper oxychloride.
Gray rot manifests itself in the softness and wateriness of hydrangea tissues. In a humid environment, a gray "fluff" appears on the plant. In dry weather, the affected parts dry out and die off, leaving holes in the leaves and stems.
How to save a garden hydrangea
There may be several reasons for the disease; the methods of salvation are not much different. If the shrub is burnt by the sun, then it should be removed from the light or transplanted into the shade, the same should be done when drafts are detected. Maintain a constant temperature and is easiest to handle when the plant is indoors. A bright shaded spot in the garden will also help achieve the desired result.
Hydrangea soil - how to acidify hydrangea soil
In case of excessive watering, urgently free the root system from waterlogged soil and replace it with fresh one. The same should be done if the soil in which the hydrangea is planted is heavy and does not allow air to pass through well.
Attention! If the water in the tap is too hard, then you must first collect it in a large container so that heavy particles and metals settle. After that, the bush can be watered.
The main diseases of hydrangeas and their treatment
Chlorosis
Most often, hydrangeas develop chlorosis. With this disease, the leaves of the hydrangea turn yellow and fall off, dryness and fragility of the branches appear, and there is also a gradual crushing of the inflorescences. The disease is caused by a metabolic disorder that usually occurs with a lack of iron. Plants planted on soils with a significant amount of lime are more susceptible to chlorosis. An excess of humus in the soil also leads to chlorosis. The development of chlorosis can also be caused by watering the plant with cold and not settled water, excessive use of organic fertilizers.
Chlorosis should not be ignored, since this disease can lead to the complete loss of the attractive appearance of the plant. Moreover, the hydrangea may stop blooming altogether.
Control measures: At the first signs of the disease, the plant must be treated with a solution of nitric acid potassium for 3 weeks: 40 g is diluted in 10 liters of water.
After this course of treatment, the plant should be treated with a solution of ferrous sulfate in the same concentration for several days. To prevent the development of chlorosis, hydrangeas should be periodically fed with fertilizers containing iron.
Gray rot
Gray rot is a fungal disease that can kill hydrangeas. Rot affects the entire plant - leaves, stems, buds and even flower stalks. When tissues are damaged by this fungus, their structure becomes soft and watery. A symptom of the disease is the appearance of wet spots with a gray coating, which grow to a fairly large size. In dry weather, the stems of the affected specimens dry out and fall off.
With the development of gray rot, rainy and damp weather is especially dangerous, since with high humidity, the fungus spreads at a rapid rate, infecting new areas of the soil.
When these spots appear, you must immediately take measures to combat the disease. Destruction of diseased leaves is an important condition for preventing disease.
Control measures: If the rot has not spread to the entire plant, only the affected parts of the hydrangea are removed, and healthy stems and leaves are treated with Bordeaux liquid or foundation. If the spots have spread to the stem, the plant must be dug up and destroyed.
White rot
White rot is a fungal disease that primarily affects the root system of a plant. With the development of white rot, the roots of hydrangea begin to rot, as a result of which the plant does not receive the necessary nutrients. Soon the leaves and stems of the hydrangea turn brown and die off. The causative agent of white rot is a pathogenic fungus that enters the soil with plant remains.
In the case when white rot affects young specimens, a white bloom forms on the leaves and shoots, resembling cotton wool in its appearance. After a while, black dots - sclerotia can be found in this plaque. Fungicidal preparations, for example "Fitosporin", are effective against white rot.
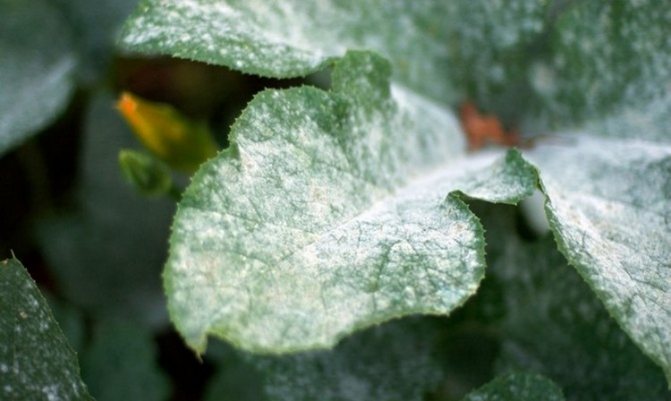
Powdery mildew
There are two types of this fungal disease that affects hydrangea:
- downy mildew, or Peronosporosis;
- real.
Less commonly, hydrangea is sick with downy mildew. It attacks the leaves and stems of hydrangeas. Its first signs are the appearance on the leaves of oily, later yellowing spots, gradually darkening and increasing in size. A yellowish bloom appears on the bottom of the leaves, the same bloom can be found on young stems. The development of the disease is facilitated by high air humidity and a temperature of 18-20 ° C.
If hydrangea doesn't wake up in spring
If the hydrangea does not wake up in spring, what to do, simple tips and a small instruction will prompt. At the end of March - beginning of April, it should already be opened, it is enough to leave the mulched trunk circle. It is quite simple to check if the shrub is frozen, just cut off a few branches and see if they are alive or not. You can save the hydrangea by planting surviving roots.


Indoor hydrangea
Planting tree hydrangeas in open ground in spring is very effective. It is important to consider at what distance to plant hydrangeas from each other. Spring is a good time for plant propagation. In the Moscow region, preparation can begin in April. A healthy twig should be divided into cuttings of 5 buds and planted in wet soil by 2/3 of the size. Division will help the plant survive in uncomfortable conditions. This method can be used on a dying flower.
If it is determined that the hydrangea is alive, then you should help her wake up. Some drugs will help with this.:
- Epin should be applied to the root collar, if it is inaccessible, then you need to dig a little ground near the trunk;
- Zircon or Kornevin can be used as pathogens of root growth, for this it is enough to water one of them under the root (after spilling the soil with water);
- Regular watering with ordinary settled water will also help the plant wake up and revive the buds.
When all else fails, you can try pruning the branches, leaving a little more than 5 cm. This will help stimulate the plant to sprout from living roots.
Inappropriate conditions and care
Before studying the types of possible diseases, it is necessary to pay attention to the compliance with the required conditions of detention. often a violation of care provokes the appearance of fungal diseases and other troubles.
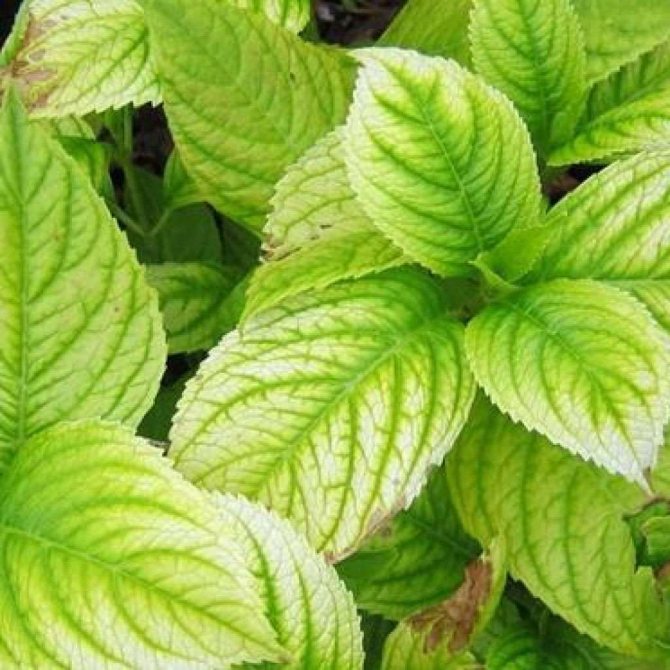


Yellowness on the leaves can manifest itself for one of the following reasons:
- Long-term exposure of the flower in the direct rays of the summer sun. Hydrangea grows well in semi-shaded areas, so it is best to remove it from a windowsill that faces south.
- The plant loves moisture, but over-watering can cause root rot. As a result, enough moisture does not enter the upper part, the leaves turn yellow, wither, dry and crumble. It is important that there is a drainage layer at the bottom of the pot, as well as holes for draining excess water.
- Lack of nutrients. You should regularly fertilize the soil using a self-prepared solution or by purchasing a ready-made mixture in a store.
- Low soil acidity. The normal indicator is in the range of 3-6 pH. If it is lower than required, then the color of the petals changes. To increase the acidity level, use a few drops of lemon juice diluted in a liter of water.
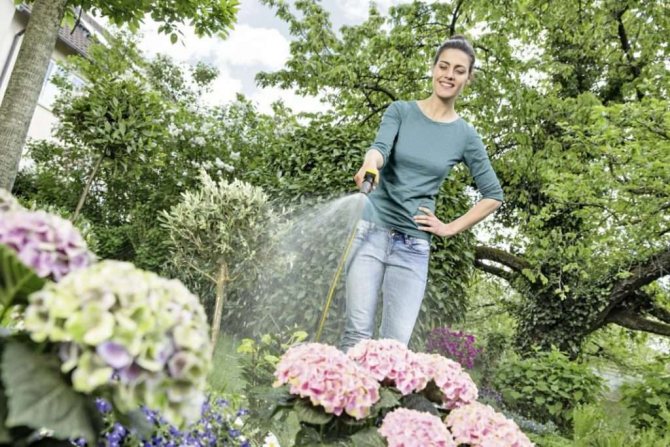


It is recommended that before starting the treatment of diseases of the garden hydrangea, diagnose and make sure that the following conditions are not violated:
- In the summer months, the plant does not suffer from a lack of moisture. Inconsistency between this and the following factors can lead to drying of the leaves.
- The humidity in the room is at a sufficient level. Especially important in hot weather and after the central heating has been switched on. In the summer, the plant should be sprayed with water, and in the winter, move it away from the batteries or install a container of water nearby. A more effective solution would be to purchase an air humidifier.
- The soil lacks useful trace elements. Ideally, the flower should be nourished once a week, but in fact, this schedule should be adhered to at least during the period of bud formation and further flowering.
Treatment methods
Ring spot virus
Cherry pests and control
It is useless to treat the redness and drying out of the shrub from annular spotting. Even a transplant won't help. Experienced gardeners advise to dig up the crop and burn it. The soil in which the shrub grew is disinfected.
White spot (septoria)
Septoria hydrangea treatment implies a comprehensive treatment. First, all diseased parts of the culture are removed and burned. Further, the soil under the bush is disinfected. To do this, you can apply:
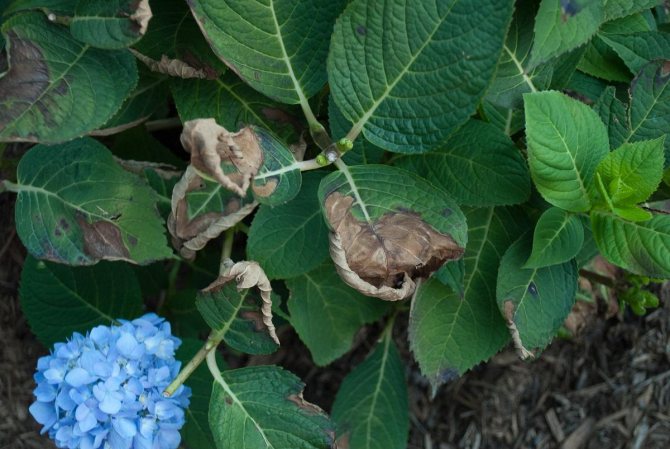


It is important to reduce the number of waterings
- Copper sulfate;
- Fitosporin;
- Bordeaux liquid;
- Baikal;
- Bleach (only in autumn).
Note! It is also important to reduce the number of waterings.
In order to fight the pathogen and its vital activity, drugs are used:
- Captan;
- Profit;
- HOM;
- Abiga Peak;
- Oxyhom;
- Phthalan.
Note! According to reviews, in advanced cases it is better to pay attention to Ftalan and Oxyhom. Fungicide Phthalan is not washed off by rain and quickly kills the fungus. Oxyhom is good because it contains copper, which the causative agent of septoria hates.
Rust
Why do hydrangea leaves turn red what to do? An effective measure in the fight against rust at the initial stage is the use of Ferovit nutrient solution. It will help the plant cope with excess nitrogen and normalize metabolic processes. Spraying with a stimulant will not help in advanced cases. Here agronomists advise using the means:
- Raek;
- Speed;
- Falcon;
- Topaz.
Gray and white rot
In the early stages of the development of diseases, drugs show the effect:
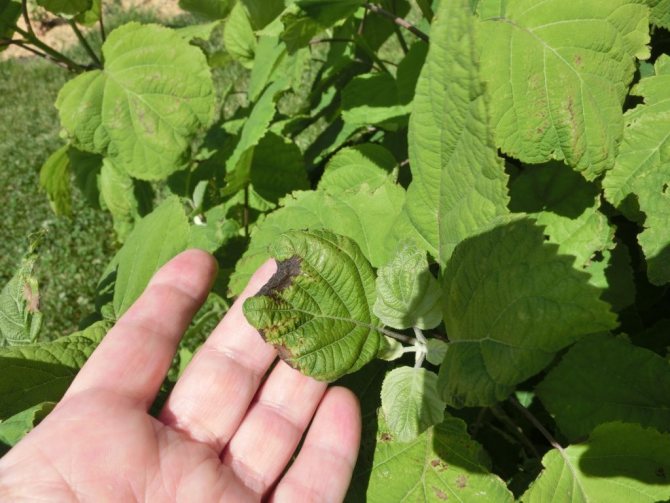


All damaged parts are removed before spraying.
- Fundazol;
- Topsin M;
- Pure color;
- Bayleton.
Important! Before spraying the plant, all damaged parts are removed. For the best effect, it is recommended to carry out a spray cycle. The procedures are carried out 3-4 times every 7-10 days.
A folk remedy for fungi that causes rot is water with horsetail. Horsetail can be used both dry and fresh. For 5 liters of water, you need 500 g of fresh grass (or 100 g dry). Then the mixture is infused for 20-28 hours and filtered. The infusion is diluted with 20 liters of settled water.The product is used for spraying and watering.
Iron chlorosis
Note! Treatment of iron chlorosis consists in immediate high-quality feeding. For this, modern micronutrient fertilizers with iron are ideal, for example, Ferovit solution or other stimulants of photosynthesis with iron chelate.
Processing is carried out in the form of spraying a shrub or watering the root zone.
For those who do not want to purchase a ready-made product, agronomists advise to prepare the nutrient solution on their own. To do this, you need a bowl of soft boiled water. There is placed 3 g of food citric acid and 1-2 g of iron sulfate (ferrous sulfate). Everything is thoroughly mixed. The cocktail is suitable for spraying a bush. However, self-prepared medicine is used in the early stages of the disease. For more effective treatment, it is better to use industrial products.
It is important for the gardener to be able to recognize the diseases that attack the Endless Summer. Diseases of hydrangea paniculata and the fight against them involve the use of fungicides. You can resist ailments and folk methods, but they are more often suitable for the initial stages of diseases.
Dry and wet blackening
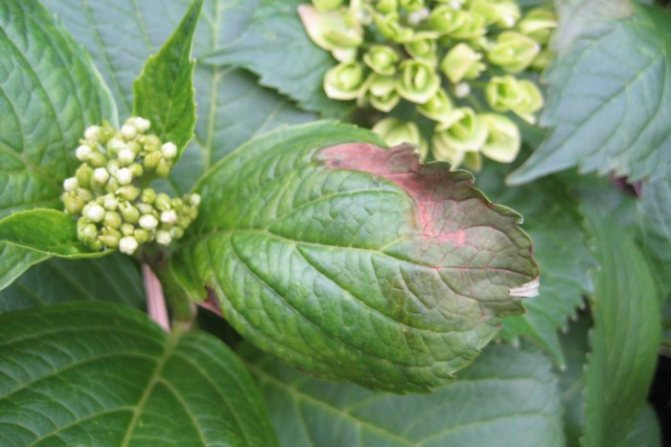
Brown spots on the hydrangea indicate dry blackening. Marks appear along the edges of the leaf blade and lead to its wilting.
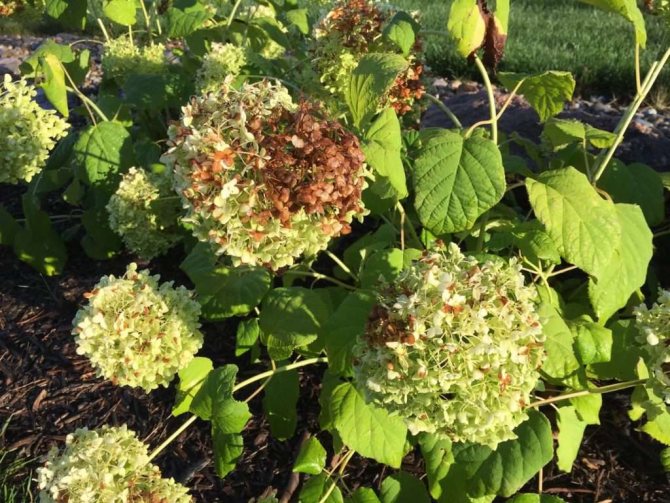


Among the reasons are:
- Excessive water hardness. Using tap water requires daily settling before watering.
- Getting sunburn. The pot should be moved to a shaded area.


If the foliage on the plant is limp and darkened, then this is a wet darkening. The reasons for its appearance are as follows:
- a sharp change in temperature;
- the appearance of drafts;
- excessive soil moisture;
- too dense soil - loosening is required to improve the access of moisture and oxygen to the roots.
Do I need to prune hydrangea for the winter
Many gardeners cut shrubs in the spring, but this is quite dangerous for the plant and can destroy it. If sap flow has begun in the bush, then pruning will be too painful, its absence can lead to the formation of small inflorescences.
Important! When pruning large-leaved hydrangeas, the greatest care and attention should be taken.
Do not prune branches too late in the fall, as they can freeze and die. In the spring, after opening the bush, you should carefully examine it and remove all dead parts before the start of sap flow. Frost-resistant species will feel better, paniculata at this time can still freeze too much.
Chlorosis
The reason for the appearance is a lack of iron in the soil or a violation of the metabolism of the flower, which makes it impossible to assimilate this component. A sure sign of the disease - the leaves of the hydrangea turn white, after which they turn yellow. The veins themselves do not lose their dark green color. In addition, buds can be deformed, branches dry, the size of leaf plates can decrease, with their simultaneous twisting.


Among the ready-made mixtures, you can use Antichlorosis or Ferovit. Self-preparation requires mixing 2 g of ferrous sulfate and 4 g of citric acid with a liter of water. With a mild form, spraying is carried out, in more severe cases - watering at the root. An alternative option for your own treatment:
- Dilute 40 g of potassium nitrate in 10 liters of water.
- Perform 2-3 watering of plants.
- After 3 days, prepare a solution in similar proportions, only with iron sulfate.
- Repeat watering.
Ways to solve problems
The first step in restoring lustrous green foliage is to restore the right conditions for the development of the shrub:
- watering normalization;
- restoration of neutral soil acidity;
- organization of high-quality drainage from the roots;
- adding nitrogen in the form of organic fertilizers (you need 10–20 kg of compost per 10 m² of soil).
Did you know? It is believed that the first hydrangeas were grown in ancient Japan. But archaeologists have discovered ancient fossils of this plant in North America. Their age
—
40
–
65 million years.
Viral diseases
Among viral diseases, hydrangea is most often affected by ring spot. It manifests itself in the form of brown round spots of small diameter. Their middle is lighter, the edge is almost black. Over time, a through hole forms in the center of the spot, and the sheet itself changes its shape and dies off.
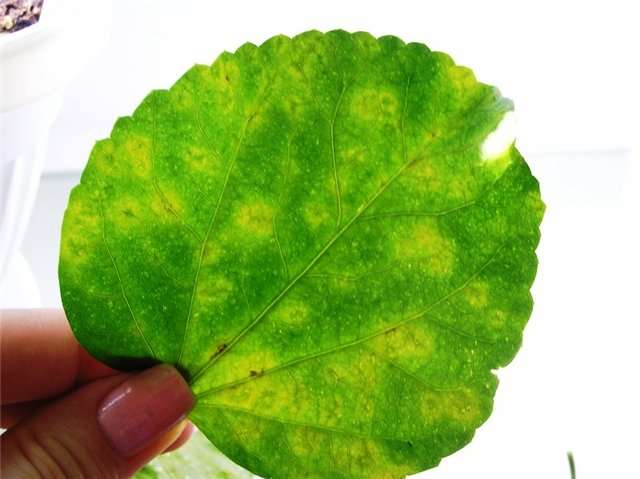


Currently, no methods have been found to eliminate this disease. It is necessary to check the seedling carefully before purchasing. When dividing by cuttings, the adult plant should be completely healthy.
Ring spot
The most common viral disease of hydrangea is ring spot. In the beginning, it manifests itself in the form of vague spots in the form of rings, with a diameter of about 2 cm.
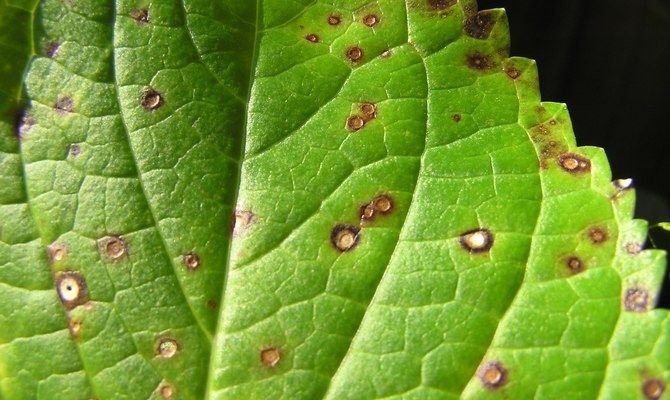


Because of them, the leaves of the plant are deformed, wrinkled and eventually die off. The disease affects the ability to plant buds: either the hydrangea loses it altogether, or the flowers turn out to be weak and small.
Unfortunately, there is no cure for ring spot yet.
When planting, it is important to choose healthy seedlings.as this disease is transmitted through seedlings. And when propagating by cuttings, it is important to make sure that the mother plant is completely healthy.
Preventive measures
To protect the hydrangea from pests and diseases, proper care will allow, which consists in the following:
- The pot or garden bush of hydrangea should be located in partial shade. Prolonged exposure to direct sunlight leads to wilting of foliage.
- Moistening the flower should be done in a timely manner, because it loves water. At the same time, an excess of moisture and root decay should not be allowed.
- The plant does not develop well in heavy alkaline soils. Preference should be given to light and moderately acidic soil, which will pass liquid and oxygen without problems.
- At the end of spring, the plant is fertilized with substances containing nitrogen. In the summer period, phosphorus-potassium fertilizers are applied, and in the fall, phosphorus fertilizers.
- Hydrangea bushes should be periodically treated with copper sulfate (100 g per bucket) as a preventive measure.


The hydrangea diseases presented in the article and their treatment with visual photos will help keep the plant healthy and beautiful. The flower will surely thank the caring owner with lush flowering and will become a visual decoration of the room or garden area.
Prevention of diseases and pests
Prevention is the best cure. If the hydrangea is healthy, it is unlikely to get sick, and if it does happen, it will endure the disease. If the plant is weakened, then viruses, fungi or pests can severely damage it.
What will become the prevention of diseases and pests and help grow a strong, healthy and beautiful flower:
- Correct location. In the scorching sun, the leaves and flowers begin to fade quickly. Therefore, it is optimal for hydrangeas to grow in partial shade;
- Sufficient watering. The plant loves moisture, so the soil should not be allowed to dry out. On hot summer days, it is necessary to water the bush every other day;
- Choosing the right soil - hydrangea will not survive on heavy alkaline soils. She needs an acidic light soil that is good for air and moisture;
- Correct feeding: in late spring, emphasis should be placed on nitrogenous fertilizers, in summer - on phosphorus-potassium fertilizers, and in autumn - mainly phosphorus;
- Preventive treatment of hydrangea wood. In the spring, before the start of the growing season, it is recommended to process the hydrangea bush with copper sulfate at the rate of 100 grams per bucket of water.Another option is to use more modern drugs for preventive treatment - Topaz, Iskra, Fitosporin.
With proper care and constant care, hydrangeas will grow lush and beautiful. It will become a bright decoration for your home or garden!
Now you know everything about diseases of leaves and flowers of room and garden hydrangea and their treatment, and you have also seen a photo.
Methods of dealing with leaf beetle
Leaf beetles are pests that damage all parts of the plant. This insect got its name because of its peculiarity - to gnaw whole holes in the leaves of hydrangea. The larvae of the leaf beetle eat the leaves of the plant entirely, leaving only streaks of them. The stems can also suffer from this pest, which gnaws at them right from the inside. Some leaf beetle larvae live in the soil, where they damage the roots of the hydrangea.
How to deal with hydrangea pests? To combat the leaf beetle, you should resort to complex methods, including:
- Manual collection of both adults and their larvae;
- Pruning of damaged parts of the plant and their subsequent burning;
- Digging the soil around the hydrangea at the first frost in order to destroy the hibernating larvae;
Read also: Buckwheat porridge: benefits and harms to human health
Damage to bushes by pests
| Leaf aphid Microscopic insect parasite 0.3 mm in size. The integument of the body is translucent, greenish tone. Harm:
Control measures:
| |
| Spider mite Microscopic arthropod (up to 0.15 mm in size). It sucks out hydrangea juices, spreads in dry, hot years. Sign of appearance - the thinnest cobweb on leaf blades. When the colony grows, it is visible as tiny red dots on foliage and peduncles. Harm:
Pest control:
|
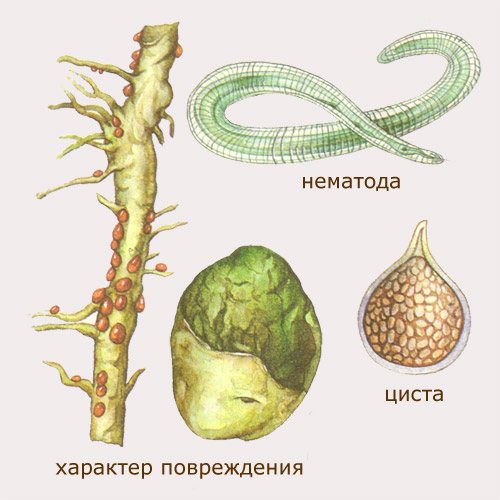
| Gall nematode It is a round small parasitic worm 1–2 mm long. His body is white or pearl. Symptom of infection - reddish galls (swellings) on the root system and at the bottom of the peduncles. These "blisters" rot and dry out. Harm:
There are no effective treatments for nematodes, so preventive measures are important.
|
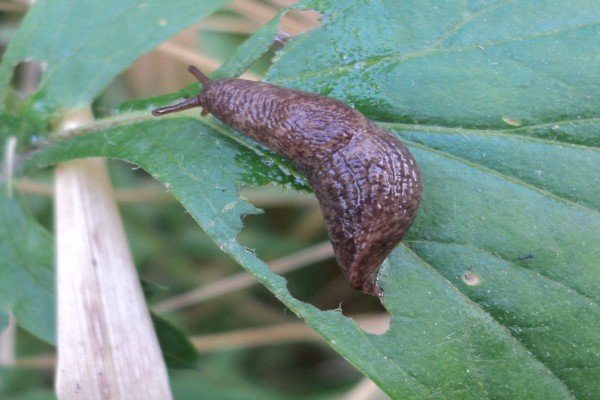
| Garden slugs and snails These are small terrestrial gastropods. They make refuge in dense thickets, under stones, in the axils of foliage, in shaded and damp areas of the garden. Harm:
Pest control:
|
Useful video
Learn about one of the diseases of hydrangea - chlorosis:
A lushly blooming hydrangea can be a decoration for any garden. Growing this culture is a lot of work, but diseases and parasites that carry them can cause the death of the plant.In the material, we will consider the most common hydrangea diseases and their treatment, as well as methods of preventive protection against infection.
Hydrangea, or hydrangea (Latin Hydrangea) is a plant of the flowering genus, the Hortensia family. This culture adored by many gardeners has more than 80 species; the most common ones:
- hydrangea;
- garden;
- large-leaved;
- paniculate.
All of them differ in the shape of the bush and inflorescence, in size, but common hydrangea diseases and pests are characteristic of all species.


Garden hydrangea grown during the flowering period
They share such ailments of this culture:
- caused by metabolic disorders;
- fungal;
- viral.
Why is it growing poorly?
Every year a healthy bush grows new shoots and grows vigorously. If this does not happen, and the hydrangea dies, there may be a number of reasons for this.
Unsuccessful wintering
Not all varieties of hydrangea are distinguished by good winter hardiness, so this fact must be taken into account. This becomes especially evident after a cold winter, when the plant spends it unprotected. When choosing seedlings, you should prefer those species that can grow in the climatic realities of a particular area. But they also need additional care during severely frosty winter periods, especially with minimal snow cover.
Without a cover with a "humus" pillow, the roots freeze slightly, and there is a risk that the aerial part of the plant will suffer.
The shrub will be helped by sanitary pruning and the regular introduction of feed from complex dressings.


Incorrect cropping
This process is necessary for absolutely all hydrangeas, because pruning contributes to the branching of the bush. But some species need only minimal intervention, such as the serrated hydrangea varieties, as well as the prickly, coarse and oakleaf varieties. It is undesirable to radically cut the listed varieties.


Depleted soil
Insufficient growth on "starving" shrubs is especially pronounced. Without regular nutrition, hydrangeas are only trying to survive, that is, they are not at all up to growth. An obvious impetus will be given by the introduction of nitrogen supplements early in the spring. They will help revive the plant and grow it. Before laying the buds, you need to fertilize with mineral complexes.
Large-leaved and paniculate hydrangea species prefer to grow in acidic soils. It is important to know about this, periodically acidifying the soil with oxalic acid (2 tablespoons per 10 liters of water).
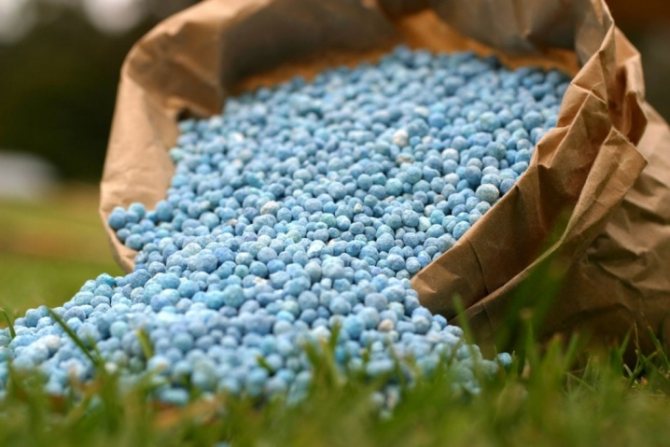


Hydrangea disease due to metabolic disorders
When a panicle hydrangea bush grows in one place for a long time and it is not regularly fed with special fertilizers, then in the end, the soil becomes poorer and the plant begins to feel an acute lack of nutrients. Then the leaves of the hydrangea begin to turn yellow en masse. This disease is called chlorosis. It affects the bushes when their metabolism is disturbed and they feel a lack of iron. Chlorosis can be distinguished from other garden sores by the typical yellowing of the leaves. When the plate becomes bright yellow, and the veins retain their natural dark color. This disease cannot be ignored, since a lack of iron can lead to the fact that the shrub will become completely weakened, its leaves will lose their decorative effect and it will not bloom at all. In addition, weak plants are much more susceptible to fungal and viral diseases, which are practically not amenable to treatment.
Therefore, in order for panicle hydrangeas to fully develop and have no metabolic disorders, the bushes should be periodically fed with fertilizers with iron preparations.
Also, the development of chlorosis (metabolic disorders) is facilitated by watering flowers with cold and not settled water, excessive enthusiasm for fertilizing with organic fertilizers and frequent liming of the soil.
But if chlorosis still struck the hydrangea, then you need to immediately start restorative measures and heal the bush. For this, spraying with drugs is carried out:
If the degree of damage is large, then in addition to spraying, fertilizer must be applied under the hydrangea root.
Also, fertilizing with a solution of potassium nitrate (dissolve forty grams of a substance in ten liters of water) and iron vitriol will also help restore metabolism. The treatment regimen is as follows: the plant is watered three times with potassium nitrate, at least five to seven days should pass between waterings, after which the bush is fed with iron vitriol.
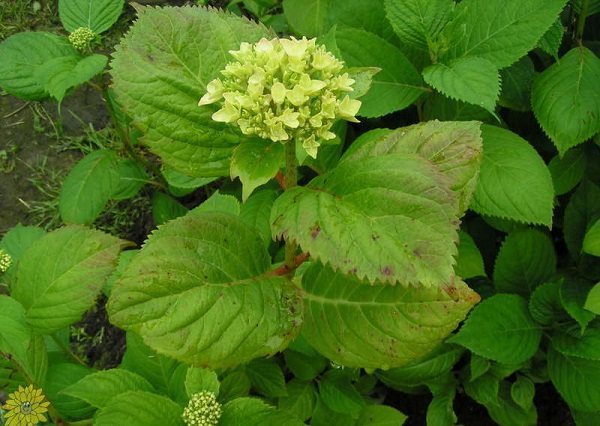


Insects attacking the plant
Diseases in hydrangeas often appear precisely because of pests that carry viruses from other plants or simply infect shrubs.
Leaf aphid
Leaf aphid
Aphids are a very tiny insect that moves with the help of 3 pairs of long legs. It is dangerous in that it sucks the juices from the culture, and sugary discharge also appears after it. A sooty fungus then develops on these secretions, and they also attract ants. As a result, the culture grows slowly. If there are a lot of aphids, then the foliage becomes yellow and deformed. If aphids are few, then you can wash them off the plant by watering them with a hose or rinse the culture with soap and water. Ladybugs also eat aphids. Therefore, if you plant marigolds near the hydrangea, it will attract ladybirds.
With a large number of aphids, only spraying with Fitoverm, Akarin will help.
Spider mite
These are the smallest pests ranging in size from 0.2 mm to 1 mm. They can be found by a small cobweb and yellowish spots on the foliage that grow and merge. Ticks like heat and low air humidity, and they actively reproduce. As a result, the foliage dries up. And the plant begins to shed its foliage.
Spider mite
If there are not very many mites, then you can wash the plants with a solution of soap. If there are many parasites, then it is worth treating the plants with such means as: Fitoverm, Lightning, Akarin. When using the drug Lightning (the third class of danger for humans), 3-4 ml of the product should first be diluted in 2 liters of water. Then add another 8 liters of water.
Akarin is safe for humans and warm-blooded animals. To process hydrangeas, take a sprayer that has a fine spray. Since the product does not penetrate the foliage, it is recommended to add soap for better adhesion. To kill ticks, it is enough to pour 3 ml in 1 liter of water, and to eliminate aphids - 6 ml in 1 liter of pure water. Parasites begin to die 3 days after treatment, and the maximum number of pests dies after 6 days.
From spider mites and aphids, you can spray the bushes with the biological product Bicol, which is safe, that is, it can only harm parasites. To create a working solution, dissolve 60-160 g in a bucket of water (10 l).
Gall nematode
These are tiny worms, they like high soil moisture. Their activity can be seen by the appearance of growths - galls on the stems, roots. These nematodes make their way through the roots to the stems and foliage, leaving a poisonous discharge. In this case, the plants stop growing, they may die.
Gall nematode
Professional gardeners advise to pluck and burn a plant that has been attacked by nematodes. True, you can still spray the bushes with Karbofos. But the remedy for direct sunlight quickly disintegrates and loses its effect. It is advised to spray with the agent in early spring, even before the flowering of the plants, as it destroys the bees. Make a working solution by adding 75 g to a bucket of water (10 L). Seedlings are sprayed on a warm sunny day, when there is no wind, and the air temperature has reached +15 degrees Celsius.
Slug
Slug
If the plantings are too thick, then slugs can multiply in them. They actively eat foliage. Slugs can be harvested by hand. You can also scatter the granules of the Molyuscid preparation on the ground.
Photo
For more photos on the topic of diseases of the garden hydrangea, see below:
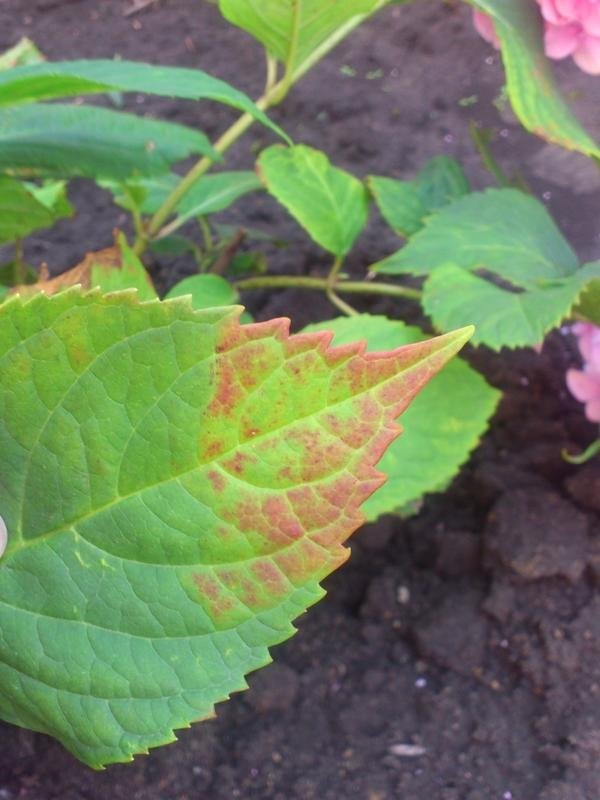


The pompous beauty of the lush inflorescences and the power of the flowering bush make the garden hydrangea an indispensable element of mixing beds, "bouquet" hedges and solo plantings. Read our articles on breeding, planting and caring for this plant.
Illness from poor conditions
These types of disorders are usually well visible and are caused by 3 reasons:
- Sunburn.
- Lack or excess of water.
- Poor soil mineral balance.
Chlorosis
It arises from a lack of iron or an excess of lime in the soil.
Symptoms: yellowness and drying of the leaves, while the veins remain green. The disease can take over the whole leaf or appear in the form of large spots.
Treatment: if it is not known exactly what caused the disease, you can start with measures to mitigate the Ph soil.
- Soften, acidify the soil with peat or aluminum sulfate. The dosage depends on the degree of alkalization of the soil and ranges from 2 to 5 kg / m3.
- As a preventive measure, flowers are watered with rainwater or softened for irrigation (the water becomes softer after standing for several days. You can also soften the water with ash or peat).
- Reduce fertilizing with mineral fertilizers.
If it's a lack of iron:
- Homemade preparation for feeding with iron. 2 g of ferrous sulfate per 1 liter of water. The solution is softened with 4 g of citric acid.
- When the hydrangea is in poor condition, it is wiser to use a store-bought preparation with iron sulfate - it will be absorbed by the plant faster.
Indirectly, you can judge the Ph of the soil by its colors. Bright flowers indicate normal soil acidity, dull or neutral tones may indicate alkalization.
Leaf burns
In the strong sun in summer, hydrangea can get burns. They look like translucent spots, usually white. The affected areas become thinner and may dry out.
Treatment: shade the plant. When transferring a flower from a shaded area to a strong sun, it is imperative to shade and gradually reduce the shadow.
Attack of garden pests
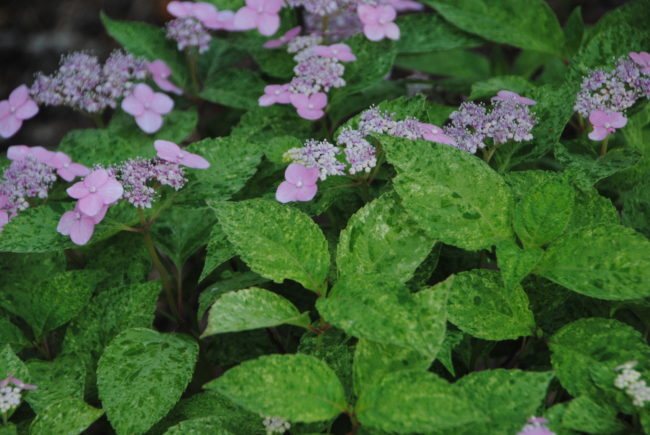


Insects such as spider mites, aphids, meadow bugs, slugs also threaten hydrangeas with a change in leaf color due to the absorption of plant sap by the pests. It is important to inspect the flower bed as often as possible and at the first signs of the appearance of insects to use drugs to destroy them. The presence of small yellow spots indicates the defeat of leaves by a spider mite. Fungicides sold in specialized retail outlets will help to cope with this problem. With the timely detection of pests, more gentle methods are used - processing the leaves with a solution of mineral oil or soap.
When hydrangea is affected by aphids, a slight yellowness of the upper leaves of the bush most often appears. It is also important not to miss the initial stage of infection and thoroughly treat the leaves with a soap solution on both sides. In case of mass leaf disease, such solutions as "Akarin", "Tobacco dust" or "Fitoverm" are used.