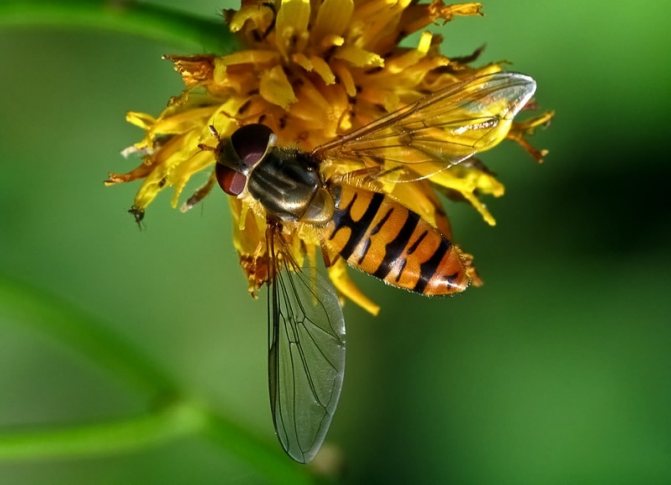
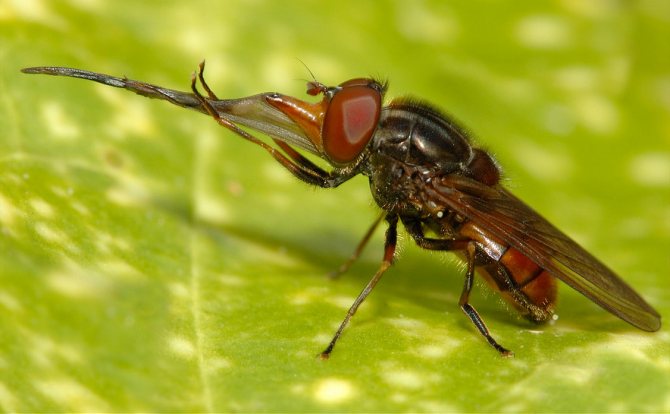
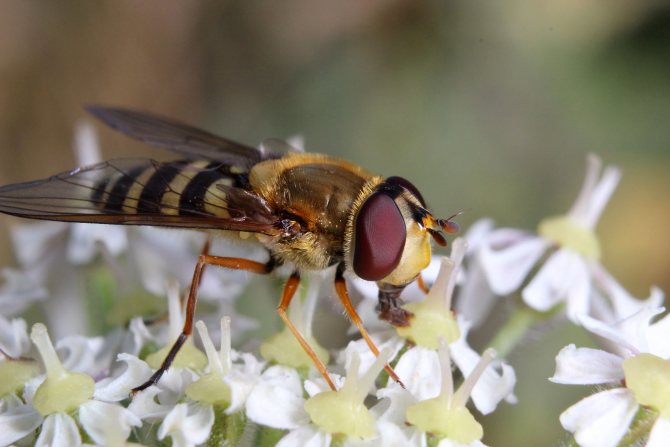
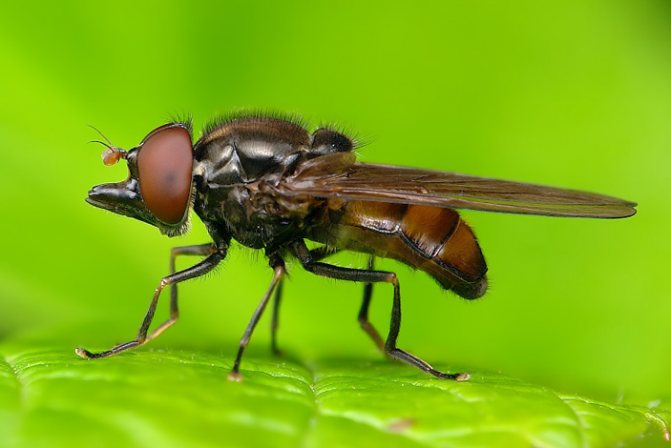
But are all types of babbling flies equally useful, let's try to figure it out.
Description
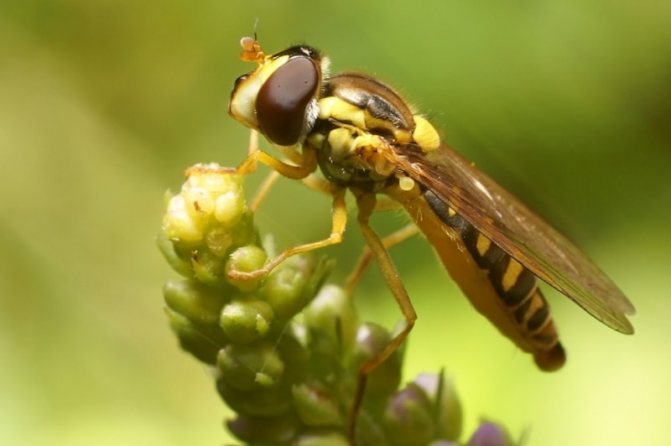
The soaring fly got its many names due to the fact that adults soar over flowers like a hummingbird or a hawk moth. Larvae can be voracious predators of small insects, especially aphids, and all aphid-eating species belong to the subfamily Syrphinae.

Flies are common in many crops affected by aphids and other small soft-bodied insects.
Are the larvae harmful?
The larvae of harmful hoverflies destroy all available crops. The insect prefers:
- garlic;
- daffodils;
- tulips;
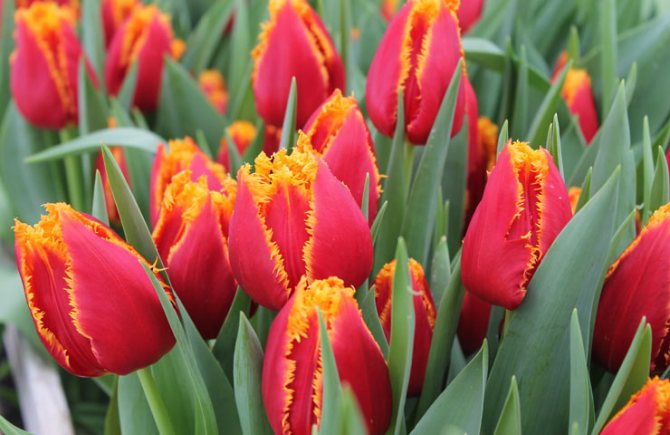


Fly larvae often destroy flowers such as tulips
- onion;
- hyacinths;
- gladioli.
After contact with a harmful larva, the plant stops growing and developing. Withering occurs gradually. The sheets dry up.
Appearance
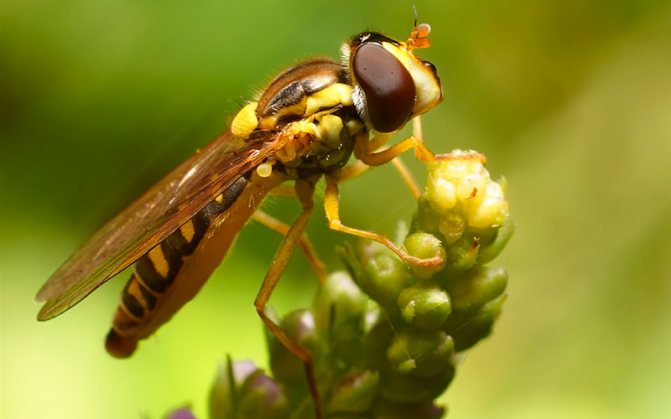
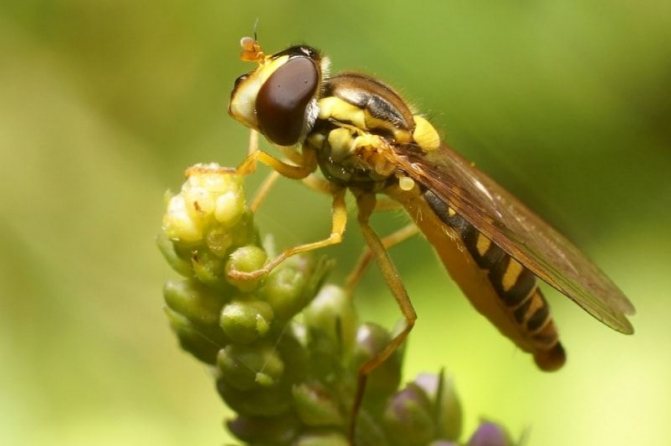
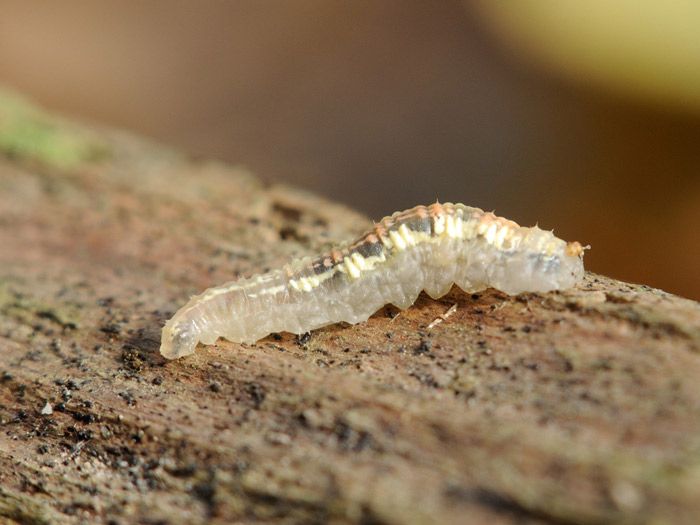
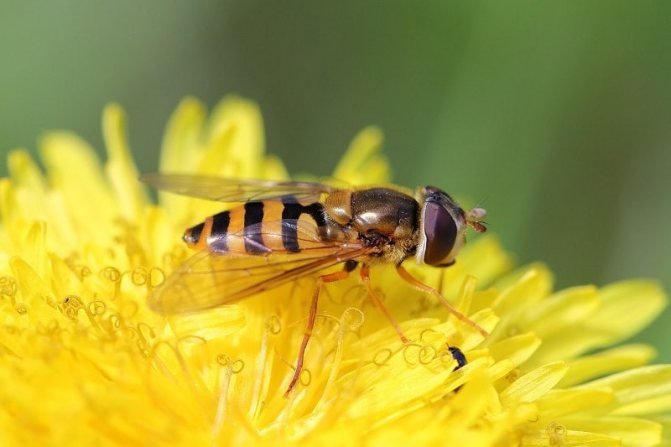
Adult flies reach a length of 3 to 13 mm, depending on the species. The body of the fly is black or brown with stripes (or dots) of white or yellow covering the belly and / or chest. Adult hover flies resemble small wasps. Their yellow- or white-black striped abdomens serve to scare away predators. However, they can be distinguished from OS by a single pair of wings, with rudimentary hindwings as balancing organs. Syrphid fly larvae are slimy caterpillars that are shriveled and narrowed in front. Their color can be pink, yellow, green or brown, ranging in size from 4 to 18 mm in length.
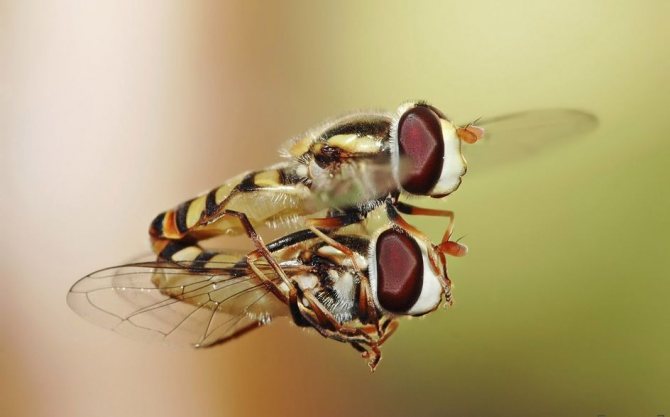
Male and female flies
Like many other flies, males and females often look the same, have the same color, size, etc. However, it is always easy to tell males from females. Like all other flies, males have large eyes that converge at the top of their heads. In females, eyes are much smaller and farther apart. The tiny eyes, or sockets, are made up of individual cells and are located at the top of the head in a triangle between the large faceted eyes.
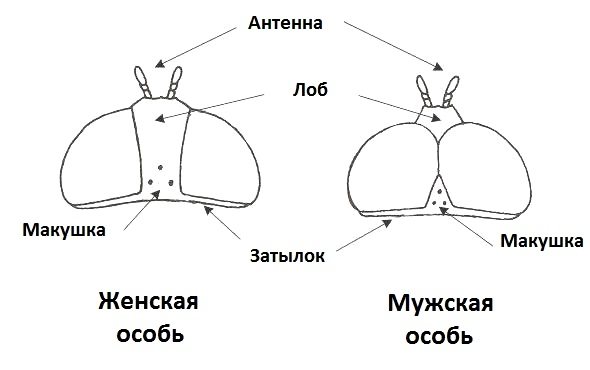

Differences between female and male Soaring Fly.
A more intrusive method of sexing a babbling fly is to look at the lower abdomen; males have reined, asymmetrical genitals. The abdomen of the female is pointed with inconspicuous genitals.
General information
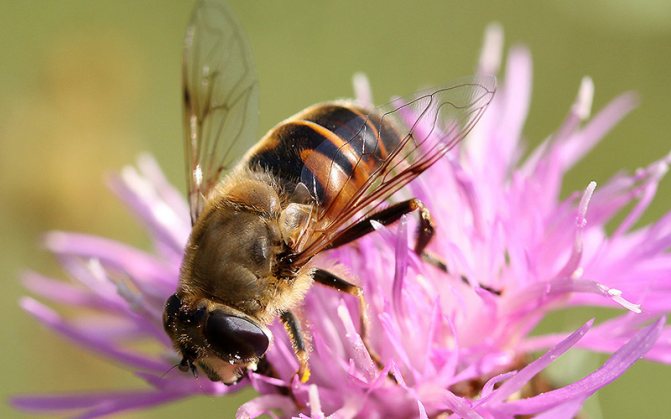


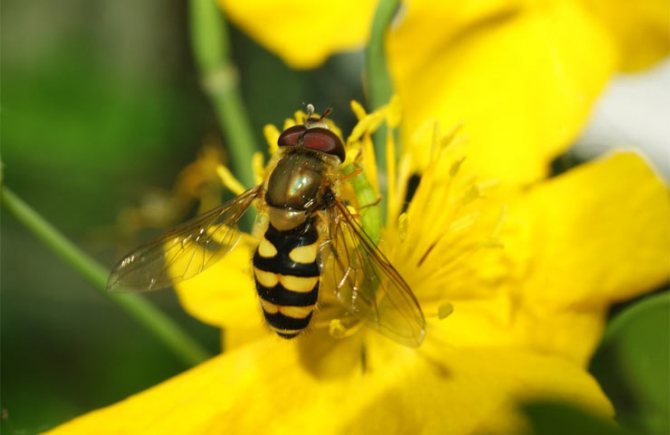
What an insect called a hoverfly looks like is shown in the photo. According to the description, all types of hoverflies have the same black and yellow color. Only a specialist can distinguish one species from another.
Have questions? Ask and get useful advice from professional gardeners and experienced summer residents. Ask a question >>
Thanks to the variegated colors, it is easier for flies to disguise themselves from their enemies, and these are mainly birds. Mimicry (a biological concept denoting the ability to be similar, to imitate) saves the same onion hoverfly from destruction by a gardener. Due to inexperience, people mistake the pest for a beneficial insect - looking at the photo, it becomes clear why.At the same time, a beautiful silky hoverfly relieves the garden of pests.
Hoverflies appear in mid-May, and their years lasts until August. Mating of these insects occurs in the second decade of July.
Females can lay eggs both directly on plants and on the soil surface. The eggs are in the shape of an elongated ellipse. Their color can be white, yellow or green.
One individual lays up to 200 eggs per season. So the flies spread quickly. After 10 days, larvae emerge from the eggs.
Life cycle and habitat
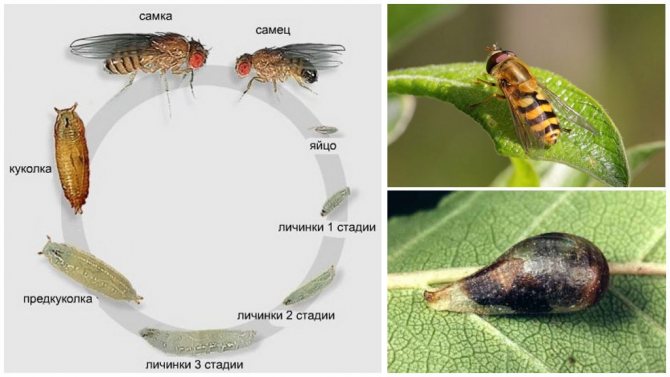
Like other flies, Hoverls go through all stages of insect life: egg, larva, pupa, imago (adult).
The life cycle varies from species to species and depends on environmental conditions and the availability of food. Under optimal conditions, single white eggs are laid on leaves infested with pests or other suitable food sources. After hatching, after about 3 days, the larvae develop in 3 growth stages to the pupa. If the pupa does not remain for the winter, adults appear in 1-2 weeks. Up to seven generations can be born during the year.
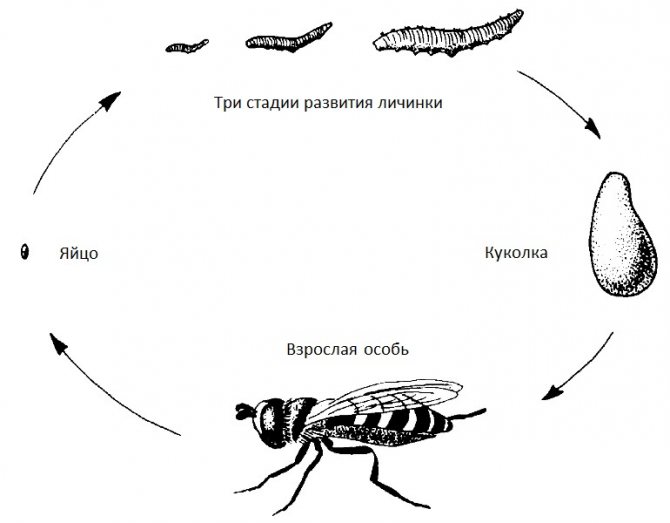

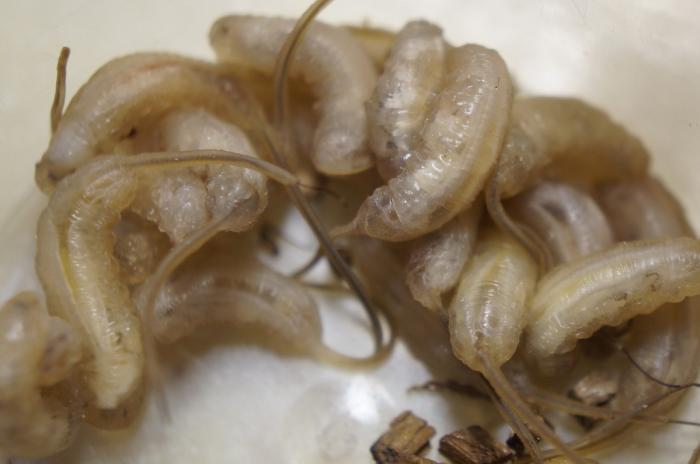
Stages of development of a syrphid fly.
The hover fly larvae are surprisingly diverse.
The aquatic life cycle of the larva
Some have adapted to aquatic life in dirty water (including stagnant water) by eating all kinds of decaying materials. In order to breathe, they expose a long tube at the back of their body to the surface of the water. Examples are rat-tailed larvae (about 40 species).
Predatory grubs of the babbling fly
Other larvae prey on plant lice or aphids. More than a third of the goverlin have aphid-eating larvae (more than 110 species).
Scavenger larvae
Some hover fly larvae live in rotting wood, or places where sap spontaneously flows out of living trees (33 species).
Larvae pests of garden plants
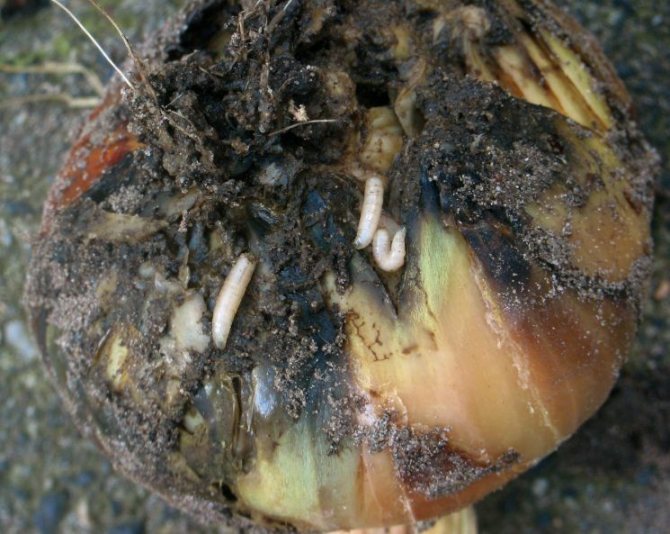
Some larvae are pests in agriculture, eating roots, stems, and flower bulbs from the inside (about 30 species).
A unique and secretive type of larvae living with ants
The larva of the soaring fly Doros profuges, lives in the nests of the ant Lasius fuliginosus (Woodworm). There is no reliable information, but one assumption is that the larvae either feed on the root aphid that was driven away by ants, or receive some other benefit from life in their nest.


* if you have any thoughts, write your guess in the comment.
What are the features of reproduction
An adult female is capable of laying 150-200 eggs. The eggs are small and white in color. The number of clutches directly depends on external conditions. The fly lays eggs in the stems of plants, as well as on the buds of trees. After a week, the larvae hatch. According to external data, they resemble maggots. During the month, the representative will actively eat for full development.
Pupation occurs over time. Adult flies begin years in July-September. The larvae hibernate at the first cold snap.
Hoverfly larvae pose a danger to spider mites and small insects. Also, a fly can eat a hundred aphids.
You will learn more about hoverflies from this video:
The undeniable benefits of the hoverfly fly
Most syrphid fly larvae feed on aphids, thrips, grasshoppers, and other soft-bodied predators such as small caterpillars. They move along the surface of plants, raise their heads to grope for prey, grab and suck it dry, and then discard the exoskeleton.


The Murmur Fly larva eats aphids on the plant.
Each larva can consume up to 400 aphids during development. When sirphid larvae are abundant, they can reduce the aphid population by 70-100%.
External signs of a buzzing fly
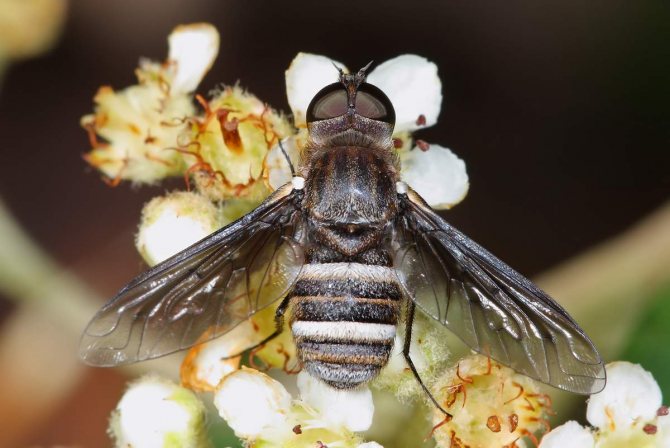
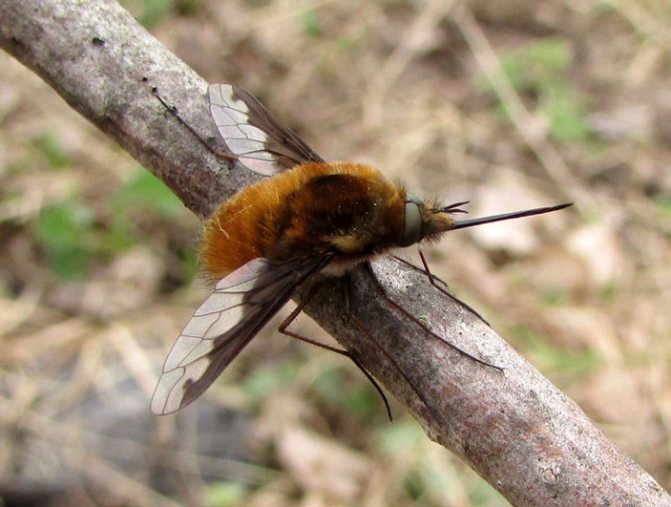
It was buzzing - an insect with transparent smoky wings, sharply pushed back, like in a jet plane. The entire surface of the body is covered with short, dense hairs directed backward. The fly's head fits snugly to the body and has a long proboscis.
The body of a buzzing fly is short, rounded, almost spherical, 1–1.2 cm in size, including the proboscis; the wingspan is 2.0-2.5 cm.
In flight, the fly often emits intermittent buzzing sounds. This feature served as the name for the entire family - buzzed. Not all flies in this group look beautiful. Bombyliidae has more than 3,000 related species, and among them there are completely nondescript flies: curved, covered with scales or sparse hairs, or even completely devoid of any outgrowths on the body. The buzzer is mistaken for a bee, but the insect has a dark brown pattern on the wings and a long proboscis.
How to attract a flying fly to your site
Because adult hover flies feed on pollen and nectar, planting flowering plants in or between crops will attract them and increase the likelihood that they will lay their eggs on infested plants.
We recommend planting plants such as: alisum, aster, coreopsis, daisies, dill, fennel, lavender, marigolds, mint, statice, sunflower, wild mustard and zinnia.
Try to keep plants rich in nectar and pollen from blooming in your area from spring to fall.


The use of insecticides and other chemicals, especially those with a broad spectrum of activity, should be avoided whenever possible.
What are the folk remedies
Folk remedies are safer than chemicals. Do not harm plants. Experienced gardeners recommend:
- process the soil with copper sulfate;
- destroy overly damaged plants by burning;
- sprinkle the beds with tobacco powder or wood ash;
- plant carrots near onions and garlic, as well as bulbous flowers, since the fly does not tolerate the aroma of the vegetable.
It is better if the gardener uses several methods at the same time.
Natural enemies of the hoverfly
Soaring flies, as a rule, have no serious enemies, except for spiders and birds. However, no species is complete without an enemy somewhere in the food chain. Sand wasp species specialize in catching hover flies, common wasps will also catch hover flies in summer when numbers are high. Wasps can attack the babbling fly larvae and kill up to half of the juveniles.


The spider has caught and is eating a hovering fly on a leaf.
How to deal with an onion hoverfly
It is the onion hoverfly that is the most dangerous pest. The insect destroys both vegetables and plants. Damaged bushes rot and die completely.


To fight, you can use the drug Decis
To combat the onion hoverfly, it is recommended:
- remove damaged plants and burn;
- treat the beds with drugs - Decis, Agita;
- change the place of planting of bulbous plants annually;
- process the beds with ammonia;
- loosen the soil.
It is necessary to get rid of the pest as early as possible, until the number has reached a critical level.
Harm from a babbling fly
Narcissus fly or gurgling, causes great harm to the bulbs of daffodils, tulips, hyacinths, gladioli, iris rhizomes.
Before winter, the larvae, which have not passed three stages of development, are buried in the ground near the bulbous plants and hibernate in the bulbs. They eat up the inside of the bulb, and if the plant does not die, then in the spring it grows extremely slowly and does not bloom.
The pest does not like peat, therefore, one of the methods of plant protection is mulching the planting with peat.
Infected plants can be watered with a solution of coniferous flour powder, and during the washing and drying process, it is recommended to subject the planting material to heat treatment.
The harm and benefits of the beekeeper
Feeding on pests like aphids, the hoverfly larvae protect fruit trees or shrubs from such parasites. And if they live in a mountainous area where the number of bees is reduced, then the sirfids render a great service to people.They actively pollinate flowering crops, significantly increasing their productivity.
On the other hand, some species of wasp flies cause serious harm to bulbous crops. Gardeners and flower growers suffer from the larvae of such insects when they damage onions, garlic or tulip bulbs, daffodils, hyacinths. Damaged plants slow down their growth and also wither quite often. And the harvested onion or garlic, which has been attacked by the sirfid, is stored very little and quickly decays.
The small
The fly is 0.7-1.1 cm long. The body is covered with thick gray-yellow hairs, the legs are yellow. The proboscis is more than half the length of the body. Wings transparent, devoid of dark spots; pronotum lacking light longitudinal stripes.
It is found in the center of the European part of Russia, in Western Europe, in the Caucasus, North Africa, Asia Minor. Rare view.
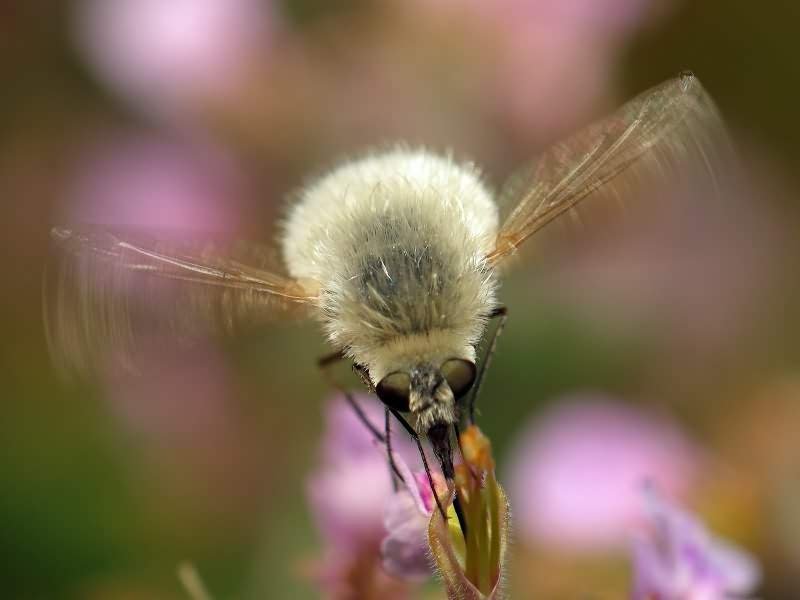


Small buzzed (Bombylius minor).
Prophylaxis
During the elimination of insects, crops may suffer, especially if chemicals are used. In order to prevent the appearance of a pest, it is recommended to take a number of preventive measures:
- the harvested crop is dried in the sun for 3-4 days;
- landing sites need to be changed every year;
- the soil must be loosened, eliminating the appearance of compaction;
- the onion set is soaked in a solution of potassium permanganate before planting;
- seeds of seedlings are sprinkled with chalk - 20 g per 1 kg.
Simple preventive measures can help reduce the likelihood of hover flies and their larvae.
Some of these insects sting painfully. Do not grab them with your hands.
This article is about biters and buzzers, and if scientifically, then about the order of Hymenoptera (Latin Hymenoptera) and the order of Diptera (Latin Diptera). Due to the lack of time, because one cannot grasp the immensity, only the most noticeable representatives will get here, because they are invisible to us and come across less often, and we often know nothing about them ... I will add belonging to families - genera - species as I understand them, there the devil will break their leg, besides, in 2008 the classification changed. Understanding - from my point of view, I can be wrong and understand nothing at all.
The mosquito is drinking nectar!
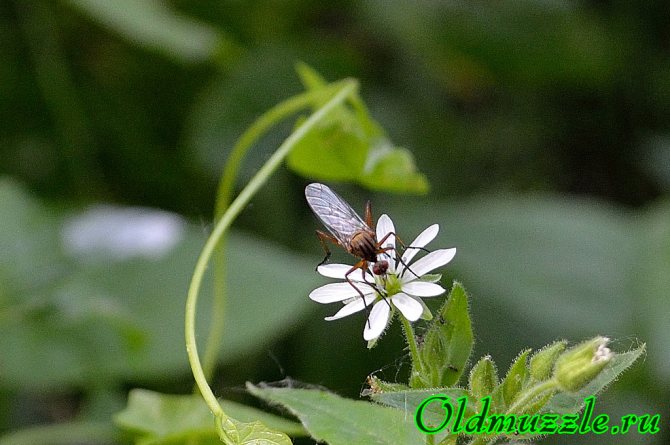


How many times have I met with statements that male mosquitoes feed on nectar, but only recently I had a chance to see it myself (I hope that there is a male in the picture). Now, yes - I do.
Subfamily Xylocopinae
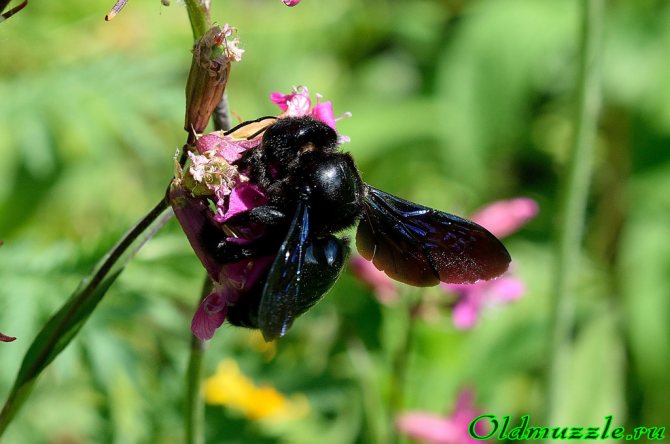
Common carpenter bee (Xylocopa valga)
Upd. 2020.03
Bees, like wasps, bumblebees belong to the order of Hymenoptera. They have two pairs of wings, unlike flies. I hope that in the photographs I really have a carpenter bee. True, the closest related species - the purple carpenter bee - differs, it seems, only in the color of the reflection of the wings: purple, in contrast to the blue in the common carpenter bee. In general, we don't care about this difference, the main thing is that it is a carpenter bee.
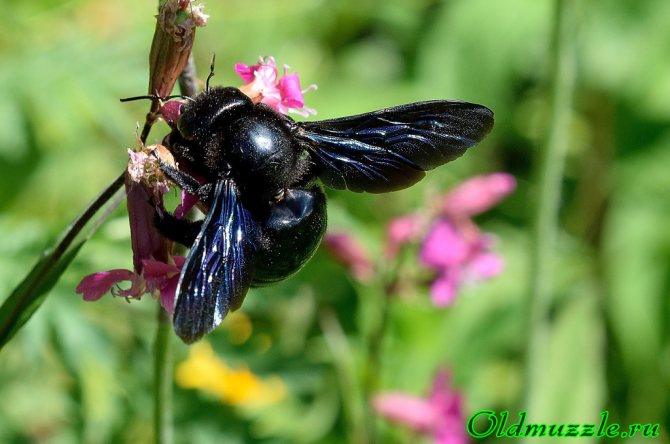


Upd. 2020.03
In these two shots, the lighting changes only slightly, and the reflection is either blue or purple. Apparently, there are some other distinguishing features, but there is very little information about this, practically nothing. Even large entomological portals contain only scant information about the Russian and Latin names. Downright problem ... By the way, I came across an interesting thought in one reference book: "To date, more than 130,000 species of Hymenoptera have been described in the world, but, apparently, the number not yet described is at least three times more." That is, there is simply not enough hands to describe everything, but at least find it.
Upd. 2020.03
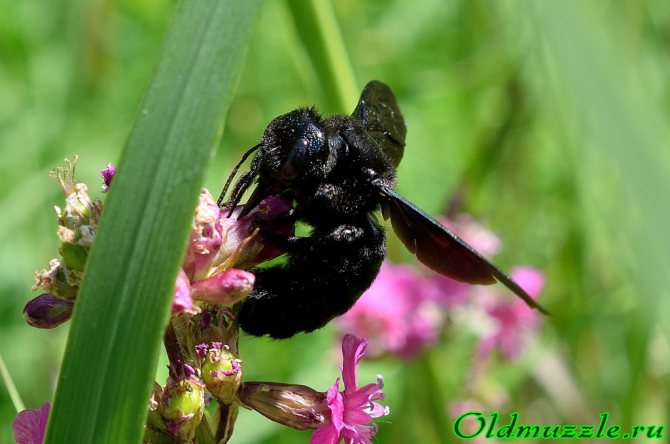
The pictures show that the bee's abdomen is attached to the chest on a very thin bridge, therefore they are classified as a suborder of stalk-bellied hymenoptera, which also have a sting. The effect of the poison of a carpenter bee will not seem weak, it is not weaker than that of a wasp, moreover, in size, a carpenter bee is 3 times (up to 3 cm) larger than, for example, an ordinary domestic bee.Fortunately, the carpenter bee is not aggressive and does not attack a person just like that. And she also takes a photo session calmly, but it's hard to shoot it, because she is constantly moving.


Upd. 2020.03
Looking at this bee I always think of either Darth Vader or some Black Knight. It's like a bee is wearing black armor. The feeling of the power of this insect is also present during flight. However, all bees are not particularly graceful. The carpenter bee is a loner; it does not form families, like those of domestic bees. It lives in old trees, gnawing through its passages and forming a shelter. For this feature, she was nicknamed the carpenter.


Upd. 2020.03
These two wonderful photographs show that there are cunning people in the insect world too. Either the bee's tongue is too short, or she is too lazy to get to the nectar in the right way - through the mouth of the corolla, but here we see how the bee bites a flower in the area of nectaries and effortlessly feeds on vusnyashka. Pay attention to the eyes: they are elongated, oval and located on the sides of the head and slightly shifted forward. The entire body of the bee is covered with a short black fluff.
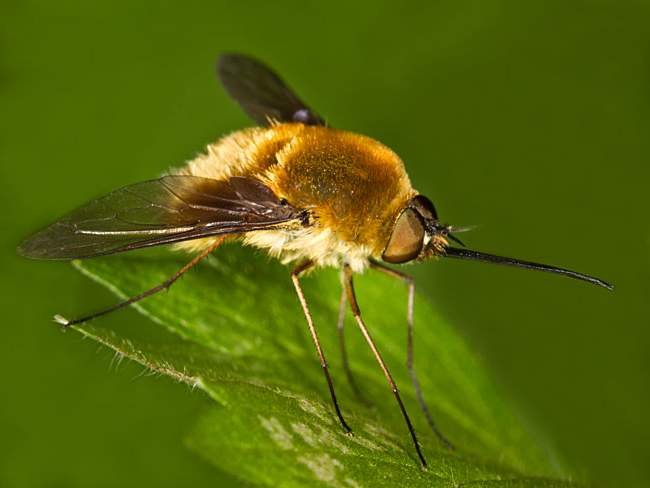
Buzzed stickticus
A large spherical insect, up to 1.6 cm in size. The head has a long proboscis. Antennae black, with 3 elongated segment. The chest is black with a thick fluffy pattern of black and white hairs.
Legs are black, covered with bristly hairs. Abdomen black, covered with black hairs with rows of dots of white hairs. The species lives in North Africa, Central and Southern Europe, in the south of the European part of the Russian Federation, in Central Asia, in the Middle East.


On the chest of the stiktikus characteristic fluffy pattern of black and white hairs.
Types of flies, names and photos.
The world population of flies numbers 3,650 species, some of which are especially common:
- room(house) fly
- a gray insect, originally from the Asian steppes. Distributed everywhere, most often near human habitation. Outwardly, many species are similar to the house fly, but it is distinguished by a special kink at the edge of the wings. Under favorable conditions, the insect can live up to 2 months;
- hover fly
(
sirfida
) - looks and habits similar to. The insect is distinguished by a black and yellow striped body and transparent wings. The hoverfly feeds on the nectar of flowering plants and is absolutely harmless. The fly got its name due to the bubbling sound made by the wings when hovering;
- green(carrion) fly
... An insect with a shiny emerald body, living near sewage and fell. In order not to be eaten after mating, the male fly first brings some food to the female;
- common ooze (tenacious) or bee ooze
considered a subspecies of hoverflies. A large insect, up to 1.5 cm long, with a dark body, covered with hairy pubescence. The larvae of the bee-shaped ooze trap, which have entered the human body, can cause serious intestinal disorders;
- ktyr -
a large predatory fly that poses a danger to midges, as well as flies of their own kind. Killing various dangerous insects with a sharp sting and poison, the ktyri flies bring significant benefits to mankind;
- Tsetse fly -
inhabitant of the African continent. The main food source of this dangerous predator is the blood of wild mammals, as well as livestock and humans. Tsetse flies are carriers of trypanosomes, which provoke an incurable disease that destroys the immune, nervous system and leads to death.
Tsetse fly. Alan R Walker, CC BY-SA 3.0
Buzzed multicolored
The fly is 1.0-1.6 cm long. The body is densely covered with yellow hairs, the proboscis is more than half the length of the body. The upper part of the abdomen is covered with dense black hairs. On the mesonotum there is a spot in the form of the Latin letter "V", pubescent with brown hairs. The wings are darkened and stained. Lives in Central and Southern Europe, North Africa, the Caucasus. Rare view.
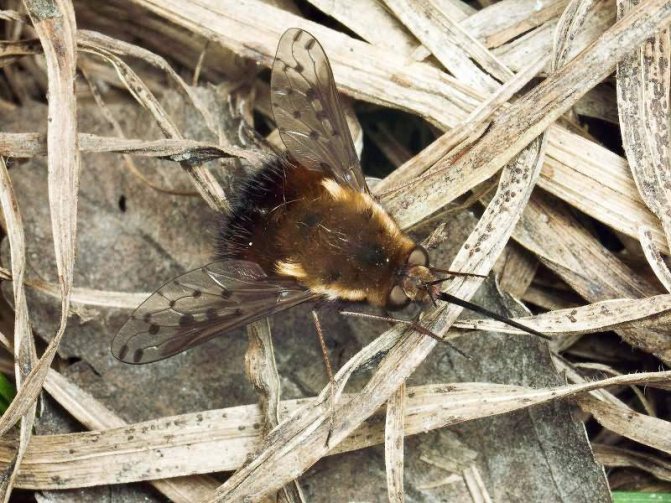


The multi-colored buzz is widespread, mainly in dry tropical and subtropical zones.