Description and characteristics of the variety
The Amphora variety was created on the basis of the cultivated honeysuckle Roxanne and the wild-growing variety from Kamchatka; it has been included in the State Register since 1998. This unassuming berry bush is a real find for gardeners in colder regions. Amphora honeysuckle buds can withstand temperatures down to -45-47 oC. The plant also tolerates recurrent frosts: the flowers can withstand a prolonged drop in temperature to -4, -6 oC, and a short-term drop to 7 oC without damage. The variety is also valuable because it is resistant to repeated flowering.

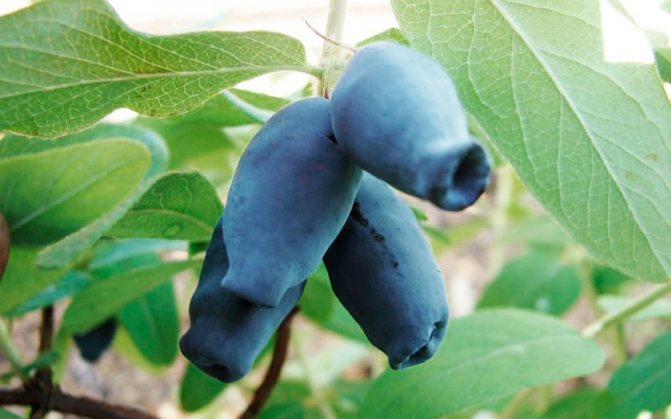
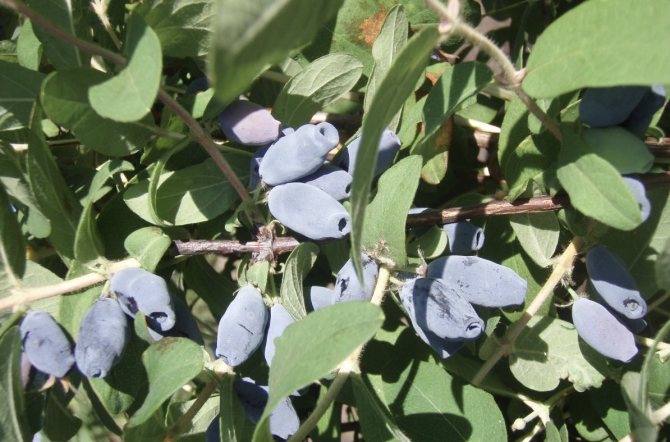
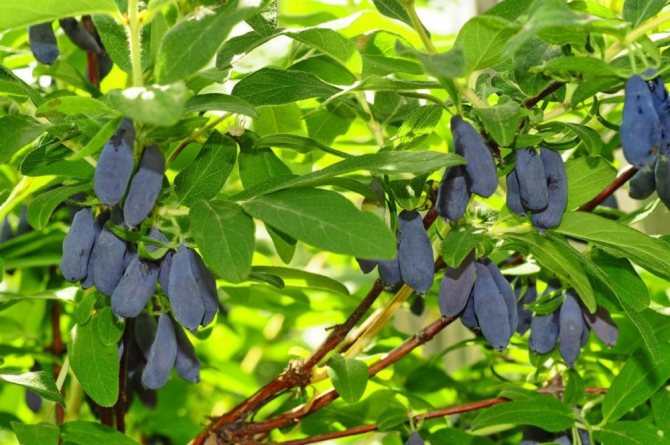
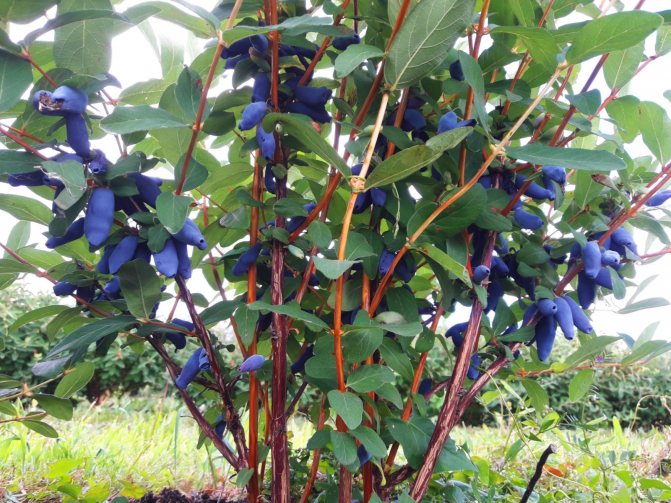
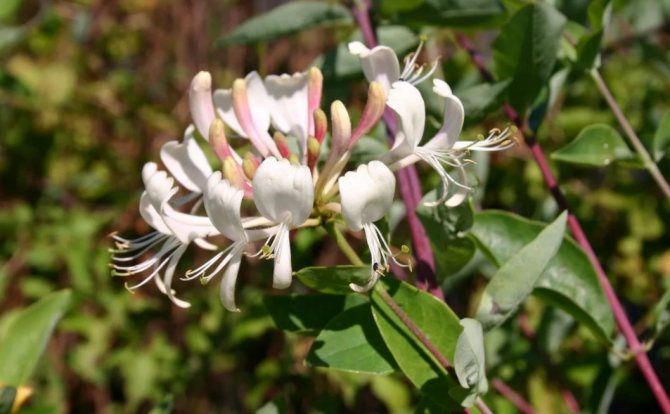
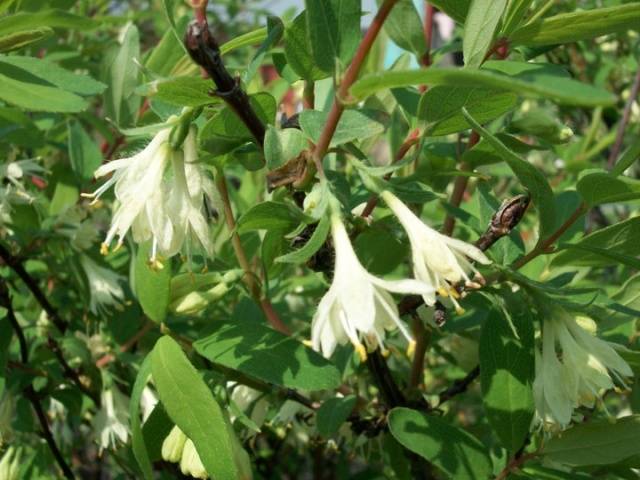
Amphora bush with a rounded dense crown grows up to 1.5 m. The trunks are straight, strong, extending obliquely from the root. The bark of the honeysuckle is brownish-red, the pubescent shoots are crimson. Leaves are oblong-oval, dense, fleecy. The flowers are pubescent, tubular-bell-shaped, yellow-green.
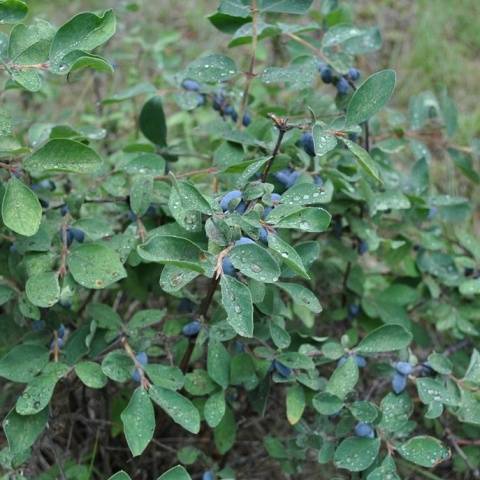


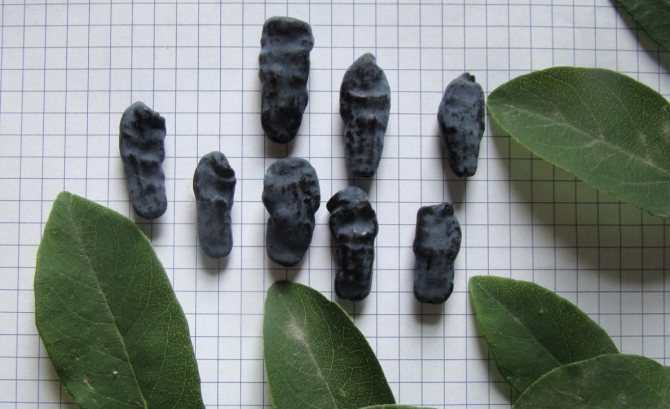
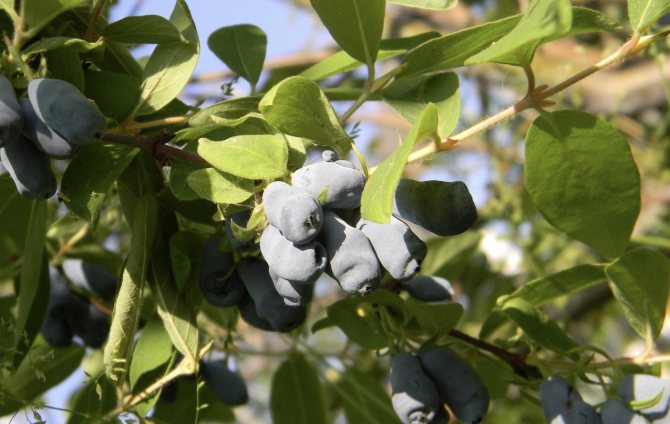
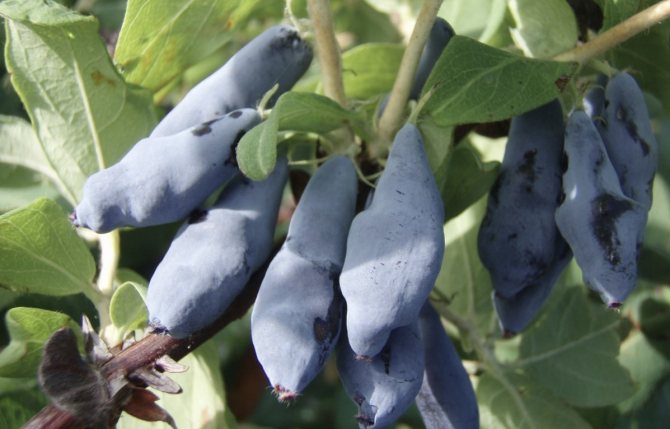
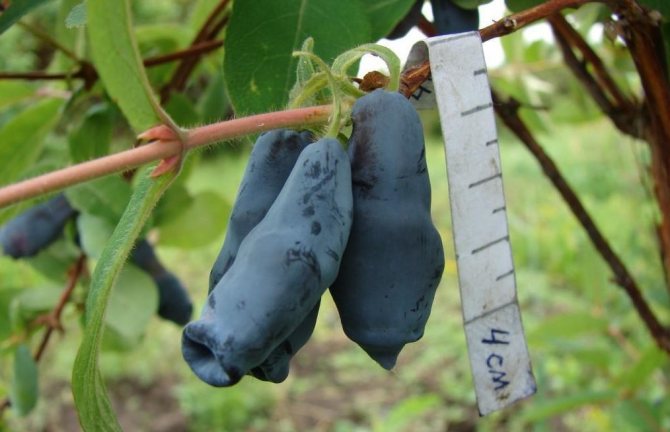
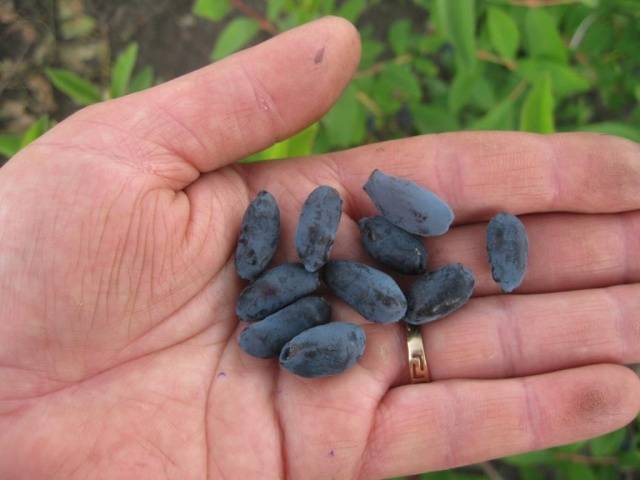
Amphora honeysuckle berries are elongated-pitcher-shaped, 2 cm long, weighing 1.2-1.5 g, in good conditions on fertile soils - 3 g. On dense blue skin there is a strong waxy bloom. The dense, gristly, sweet pulp of the Amphora honeysuckle berries has no aroma, the sourness is poorly expressed, there is a lingonberry flavor and a slight bitterness. Small seeds are invisible when eaten. Berries are rich in ascorbic acid: 58 mg per 100 g, respectively, the percentage ratio of acid, sugar and dry matter looks like this: 2.6: 7.6: 13.8. After the test, the tasters rated the Amphora honeysuckle berries 4.5 points.
Honeysuckle bushes are interesting for their decorative effect, are often used for hedges, and bear fruit well when cross-pollinated.
Important! Honeysuckle fruits help gardeners even in years unfavorable for other, less frost-resistant fruit crops.


A bit of history
Initially, honeysuckle was considered exclusively a wild plant. But gradually man learned to grow this shrub in his gardens. Breeders at the Pavlovsk Experimental Station of the VIR named after V.I. N.I. Vavilov. The progenitor was a wild variety of Kamchatka honeysuckle, which was subject to free pollination by a variety of the Roxana plant. The plant was entered into the State Register of Breeding Achievements in 1998, the authors are M.N. Plekhanov, K.F. Efimova and A.V. Kondrikov.
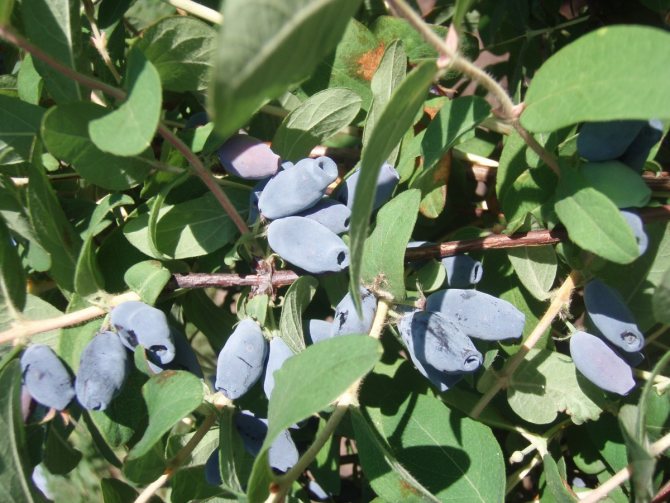


Honeysuckle Amphora is a popular variety in our country.
Features of fruiting
On average, 1.3-1.5 kg of useful and medicinal berries are harvested from one plant. Agrophone corrects the yield of Amphora honeysuckle bushes within 0.8-2 kg. Signal fruits often appear in the first year of planting. The variety shows its full potential from the third year of growth. Honeysuckle fruits are firmly attached to the branches, do not crumble for a long time, and tolerate transportation well. In the Moscow region, honeysuckle bears fruit since the beginning of June. In cold regions, the mid-late Amphora variety ripens from mid-June, slightly earlier than strawberries and raspberries. The productivity of honeysuckle is long-lasting - more than 30 years, the yield is stable. Honeysuckle bushes have been documented, bearing fruit for 80 years or more.


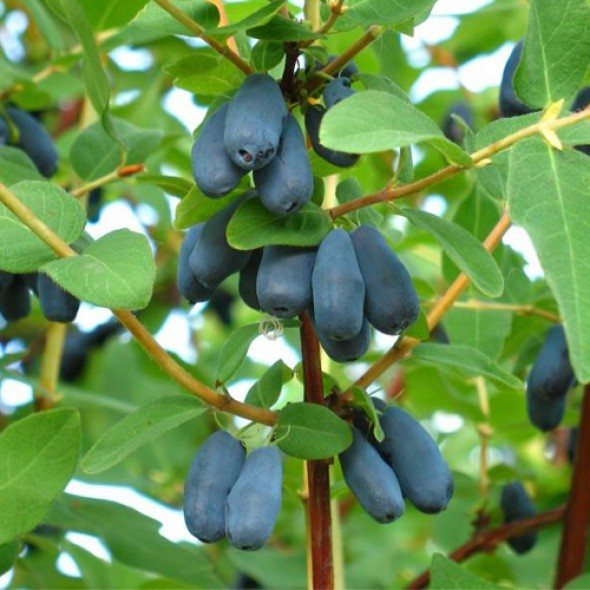
Honeysuckle Amphora - versatile, suitable for fresh and harvested consumption. Gardeners growing berry bushes of the Amphora variety assure that the jam is delicious to taste, there is no bitterness.The fruits are also frozen and vitamin raw jam is prepared.
The future of Amphora in private farmsteads


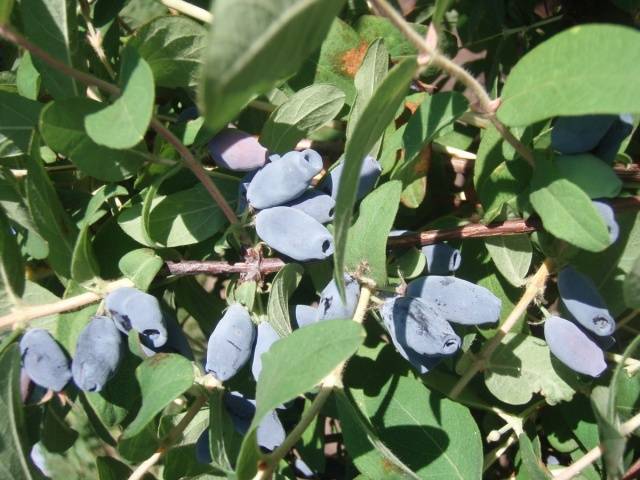
There are not so many enthusiasts today who are engaged in the cultivation of Amphora honeysuckle in private farmsteads, therefore there are not many reviews about it either. But their generalization suggests that this variety of honeysuckle can eventually take its rightful place in our gardens. There are several prerequisites for such a statement.
Honeysuckle is not too demanding on either soil or care. Spending a minimum of effort on it, you can not only diversify your menu, but also take care of your health. Honeysuckle has long been used in folk medicine as a diuretic, anti-scaling and antimalarial agent, is a good antiseptic and improves digestion.
On summer cottages and private farmsteads, it can bring not even double, but triple benefits: firstly, to serve as a fence for the site, secondly, to decorate the site, and thirdly, to delight their owners with tasty fruits rich in vitamins, and do this much earlier than traditional currants or raspberries.
Amphora honeysuckle fruits are better than other varieties for processing and long-term storage. All this taken together suggests that Amphora is worth it to highlight at least a small area in your courtyard.
Growing secrets
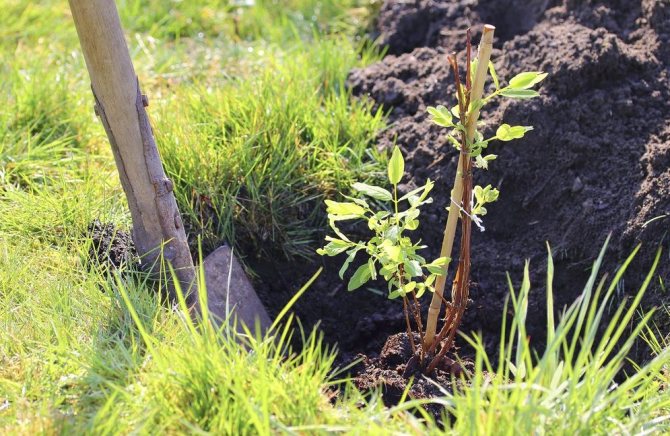
The bush begins spring awakening very early, so an autumn planting, in September, is the best option. Only in the south, the culture can be transplanted until mid-March. It is necessary to seriously approach the selection of a place for a seedling. Honeysuckle Amphora grows in any conditions, including in the shade. At the same time, the shrub is photophilous, it bears fruit better in warm and moderately rainy weather. In the sun, the berries of the Amphora variety are tastier and sweeter. Honeysuckle bushes are planted at intervals of 1.5-2 m.
Advice! A seedling with a closed root system is planted in the spring.
Site and soil selection
For Amphora honeysuckle, choose a sunny place or with light partial shade if the bush is grown as a fruitful one. In the shade, the plant will develop, but it is unlikely to bloom. Can be planted in an open place, honeysuckle is not afraid of the cold wind. Although this will also negatively affect the quality of fruiting. The plant is hygrophilous, but develops poorly on swampy soil and in areas where spring or rain water accumulates. Honeysuckle should not be placed in the lowlands.
Light soils, slightly acidic and neutral, are suitable for shrubs. On heavy soils, a substrate is prepared in the hole from equal parts of the local fertile soil, humus and sand. Experienced gardeners advise placing the bush in the light midday shade of an apple tree, which is considered a favorable neighbor for honeysuckle.


Planting a bush
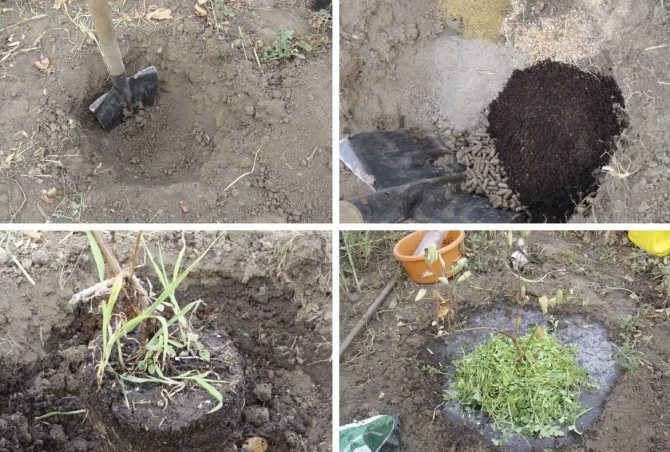
For a fruitful bush, choose 2-3-year-old seedlings of the Amphora variety with a root system diameter of up to 20 cm.A hole is prepared at the chosen place a week before planting.
- The size of the landing pit is 0.3 mx 0.3 mx 0.3 m;
- The drainage layer of ceramics, pebbles is at least 10 cm;
- The soil is mixed with humus, 1 liter of wood ash, 60 g of potassium sulfate and 150 g of superphosphate;
- Before planting, the hole is watered, a mound of fertile soil is poured and the roots of the seedling are carefully laid on it;
- Falling asleep the hole, the root collar is deepened by 3 cm;
- The soil around the trunk is compacted, a circular groove is made along the edges of the hole for irrigation and filled with water;
- Then the soil is mulched with grass, old sawdust, compost, peat.
A warning! Post-plant pruning of Amphora honeysuckle is not recommended in order not to weaken the plant.
Edible Honeysuckle
To date, more than 100 types of honeysuckle are known. The fruits of almost all of them are inedible, and some are poisonous. So, eating the berries of the common honeysuckle (Lonicera xylosteum), which is widespread in the forests of our country, can be fatal.
In Russia and the CIS countries, only one species of this plant with edible berries is cultivated - blue honeysuckle, or blue (Lonícera caeruléa). It is a deciduous shrub 1 to 2 m high with bluish-black oblong berries that taste like blueberries. In the wild, this species of honeysuckle is most commonly found in East Asia.
Care
The early ripening berry shrub of the Amphora variety is undemanding, but still the yield will be much better if the plants are paid more attention. The ground is slightly loosened, up to 5-6 cm, so as not to damage the superficial root system, weeds are removed on which pests settle. They work especially carefully under bushes over 5 years old, in which the root system rises to the soil surface.
Watering
In the southern regions, honeysuckle must be watered every other day. In the middle lane, in dry weather, the shrub also requires regular watering, especially in the phase of ovary formation and before fruiting. To saturate the bush with moisture, it is watered after harvest, in July and August.
- A groove 10-15 cm deep is dug along the crown line, and it is filled with water;
- When watering, the soil does not need to be soaked very much, it must remain crumbly;
- In a drought, the bush of the Amphora variety is watered in the morning and in the evening by sprinkling through a fine nozzle to keep the delicate leaves from drying out.


Top dressing
In the third year, the Amphora honeysuckle bush begins to bear fruit and requires nutrient support.
- In early spring, the bush is mulched with humus and compost;
- Before flowering and in the ovary phase, they are fed with mullein infusion in a ratio of 1:10;
- At the end of summer, a natural potash fertilizer is applied under the Amphora bush: 0.5 liters of wood ash is dissolved in 10 liters of water;
- If they are fed with minerals, a carbamide solution is introduced in the spring: 20 g per 10 liters of water;
- After collecting the berries, pour a solution of 10 g of carbamide, 20 g of ammonium nitrate, 60 g of superphosphate in a bucket of water;
- In August, 60 g of superphosphate and 40 g of potassium sulfate are diluted in 20 liters of water for one bush;
- Foliar dressing with a ready-made mineral complex is given to young plants of the Amphora variety.
Comment! On acidic soils, honeysuckle is regularly watered with water with diluted ash, in a volume of 0.5 liters.
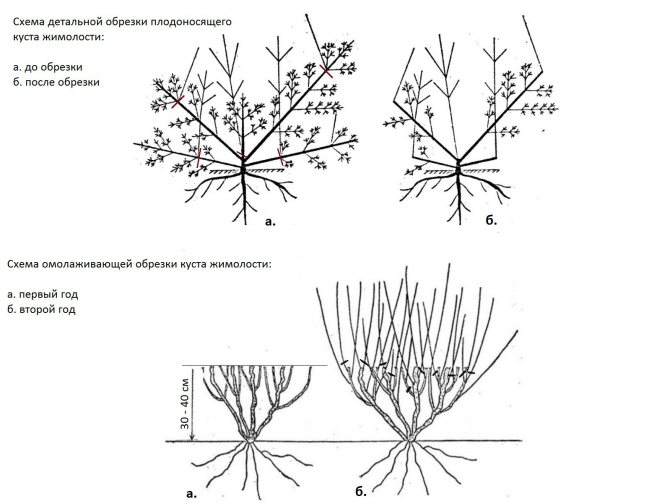
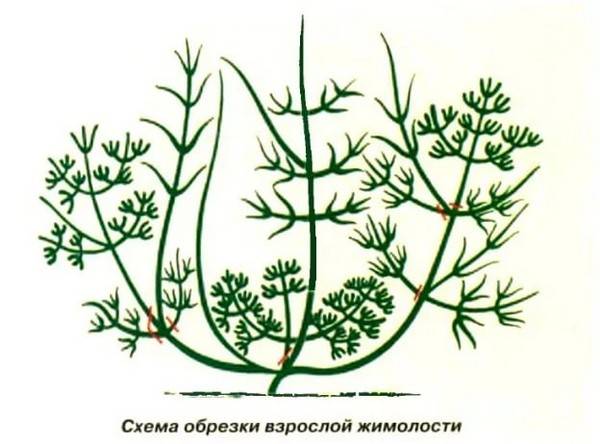
Pruning
Young plants of Amphora honeysuckle are pruned only from dry, very low-lying or damaged branches.
- After 7 years of development, thinning pruning is carried out in the fall: old shoots and thickening ones are removed, leaving no more than 10 developed branches;
- Anti-aging pruning is applied to honeysuckle bushes 15 years of age, removing most of the branches. This procedure is repeated after 10 years.

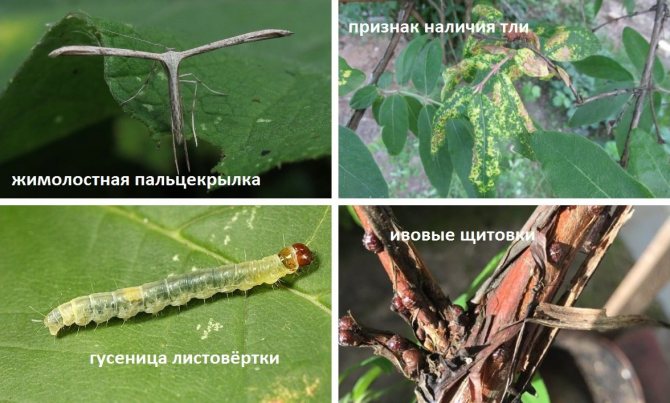
Protection against diseases and pests
Honeysuckle Amphora is susceptible to fungal diseases - peronosporosis and rust only in years with rainy summers. In early spring, for prevention, the bushes at the choice of the gardener are treated with:
- 5% urea solution;
- 0.2% solution of Actellik or Rogor preparations;
- In summer, after picking berries, fungicides "Skor", "Strobi", "Flint", "Topaz" are used to combat pathogens;
- Increase immunity by spraying with the preparations "Epin" or "Zircon", according to the instructions.


Aphids can settle on young shoots of the Amphora variety, sometimes a whitefly, a scale insect attacks the bushes.
- Aphid colonies are sprayed with hot pepper tincture;
- Other pests are fought with insecticides "Iskra", "Inta-Vir", "Fitoverm", "Aktellik";
- If you have to protect honeysuckle with growing fruits, use biological agents: "Glyokladin", "Fitosporin", "Alirin" -B, "Gamair".
Reproduction
The Amphora variety is propagated by layering, bending the lower branch in the spring into the dug groove. The top is left on the surface. The shoot is constantly watered. The sprouts that appear are transplanted the next spring or autumn.Amphora bushes can also be split with a sharp shovel or cut into cuttings in spring.
Gardening tips
To get as many berries as possible, the variety must be pollinated. This will help not only pollinating varieties, but also insects. The best among them are bumblebees, which are more willing to fly to large landings. Therefore, it is better to plant shrubs not in a row, but in groups - in clumps. Spraying the bushes with a sugar solution will be no less effective. This requires 2 tbsp. l. sweet crystals must be dissolved in a bucket of water and sprayed abundantly at the beginning of flowering.
Annual thinning of the bush also helps to increase productivity. Honeysuckle has a very dense crown, so insects cannot get inside it to pollinate all the flowers. From the fourth year of the life of the bush, it is imperative to do thinning pruning.
Honeysuckle berries are very fond of birds. In order not to be left without a crop, it is necessary to protect the bushes with a net or put a scarecrow.
A real find for the northern garden is the Amphora honeysuckle variety, which tolerates frost perfectly and is very unpretentious. The culture begins to bear fruit early, and even a novice gardener without much experience can cope with the growing process. In addition, honeysuckle bushes look very decorative and will become a real decoration of the garden.
Other uses for amorphous
Once upon a time, American settlers gave the amorph their name - Shrub Indigo or False Indigo. This is due to the fact that the plant was used to prepare blue dye, which served as a substitute for indigo made from Indigofera tinctoria. However, there is still little coloring pigment in amorphous, and industrial use of this property is impossible.


The substance gilcosin amorphin is isolated from the seeds, which serves as the basis for the creation of a drug called "Fruticin", which is distinguished by calming and cardiotonic properties.