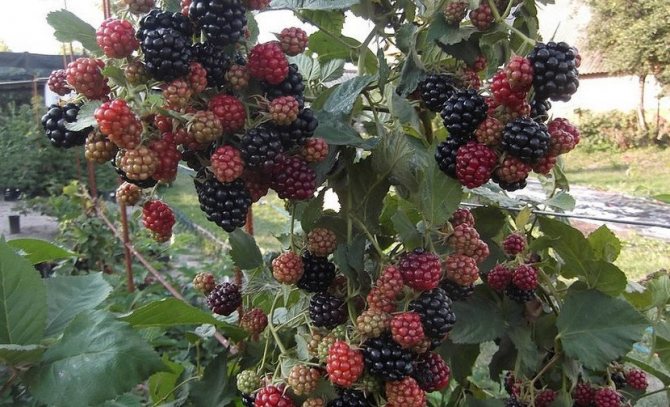
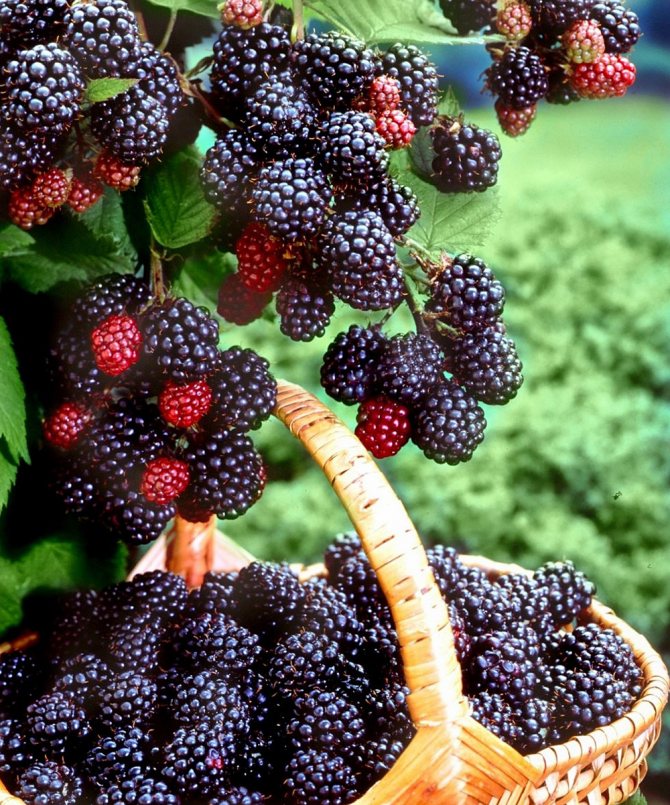
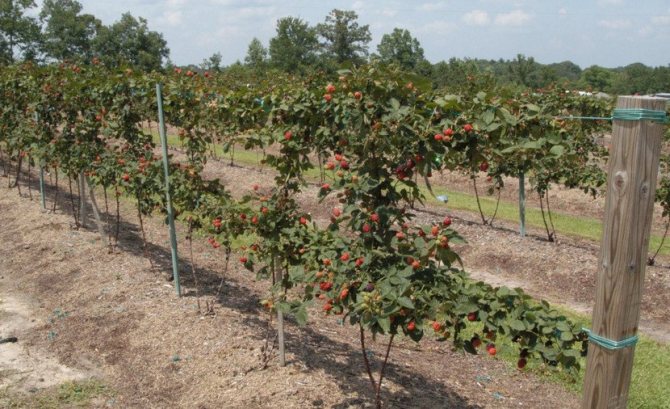
Hybrid plant varieties are especially popular with amateur and professional gardeners. The late blackberry variety Chester Thornless, known for its high yield, quality and taste of fruits, and frost resistance, gained great popularity.
There are no thorns on the bush, which simplifies the process of picking berries and regular maintenance. It is self-pollinated and resistant to most common crop diseases. This American hybrid is great for both commercial cultivation and garden planting.
Description of the variety
Photo:
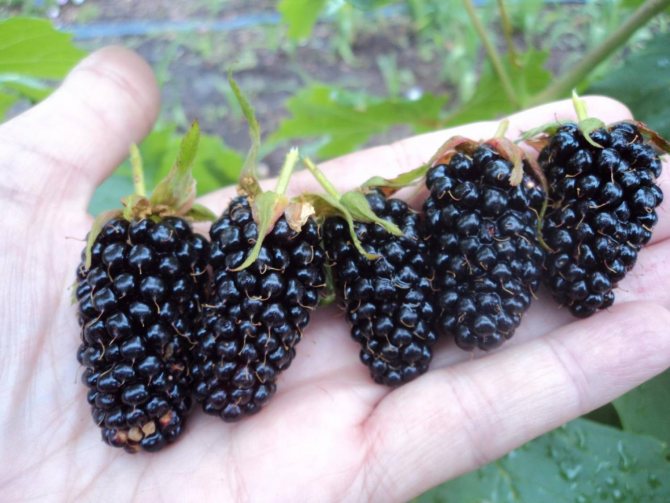

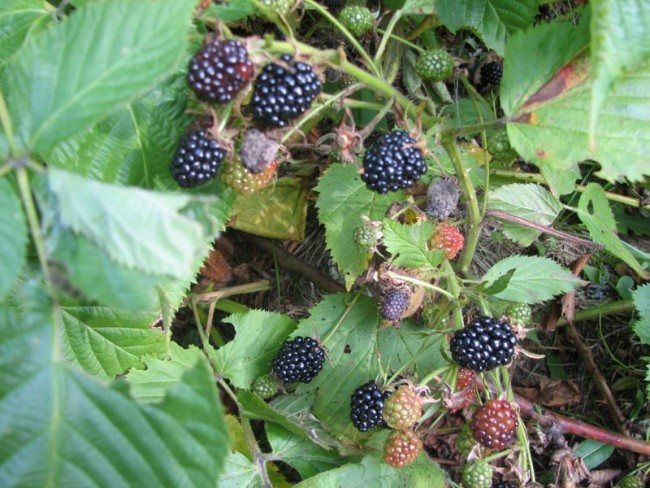
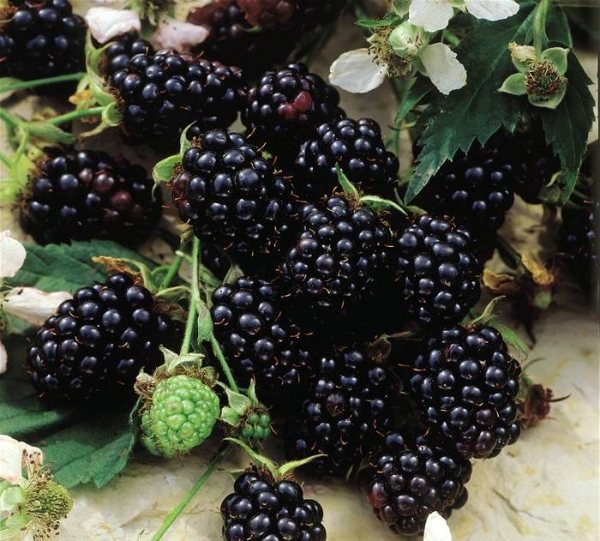
The berries are medium or large, weighing up to 8 g. The average size is 2.5-3 cm. The skin is dark blue with a characteristic shine. The fruit tastes sweet, there is a slight sourness. The pulp is juicy and aromatic. Unlike other hybrid varieties, Chester Thornless has a high density of berries on one bush, but this can affect their shape.
The bush is powerful and strong, has a semi-creeping shape, and the length of each light brown shoot can reach 2-3 meters. Strong branching is noted, which begins from the lower buds. After fruiting, the stems dry out, every two years the aerial part is completely renewed.
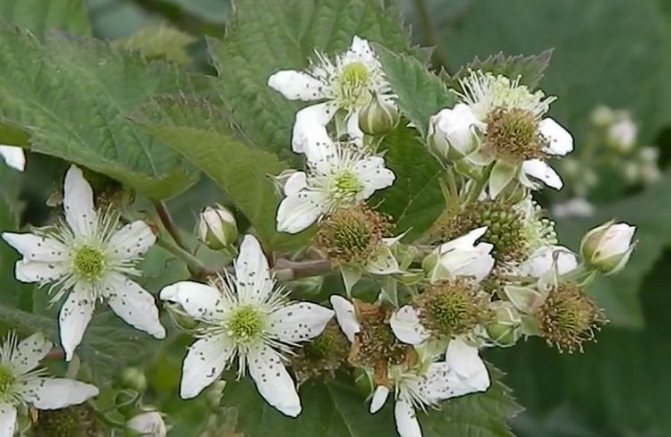
On flexible shoots, dark green trifoliate leaves are formed, arranged in sequential order. At the base there are fruiting ovaries, from which buds will form later.
Flowering begins in June, in some regions 7-10 days later. The flowers are painted in a white or pink shade, from which fruits begin to form from the beginning of August. The variety is self-pollinating, no other plants are required.
Agrotechnics
The Chester variety is unpretentious, if you follow the simple rules of agricultural technology, you can feast on a fragrant berry every year.
Watering and loosening
Blackberry is a drought-resistant crop, a strong root system allows you to protect yourself from drought... But for good growth and productivity, it must receive the required amount of moisture. With a lack of water in early spring, shoots grow slowly; during the flowering period, drought leads to weak pollination. And if enough water has not been accumulated in the autumn, the cold resistance of the shrub is greatly reduced.


The blackberry is well moistened after planting, then it is watered once a week.
The blackberry is watered once a week, adding 6 liters of water under the bush. During rainy periods, additional watering is not carried out: excess moisture contributes to the occurrence of root rot. Before the onset of frost, if the autumn is dry, it is necessary to carry out water-charging watering (8 l / plant).
Water under the shrub is brought into the irrigation furrows, by sprinkling or by means of a drip irrigation system. When sprinkling, water under pressure is sprayed over the crown and soil, while the humidity of the air rises. For less moisture evaporation, such watering is carried out in the morning or evening hours.
Recent Entries
5 of my favorite tomato varieties that are great for pickling 7 super early and delicious potatoes to plant in 2020 6 rare 2020 tomato varieties that will bring you a decent harvest
During flowering, sprinkling is not carried out: a strong jet of water can wash off the pollen, as a result of which the yield will decrease.
More often, summer residents use watering along grooves made at a distance of 40 cm from the bush. Water is introduced into the watering grooves 15 cm deep from a watering can or a hose. After absorbing moisture, the grooves are closed.
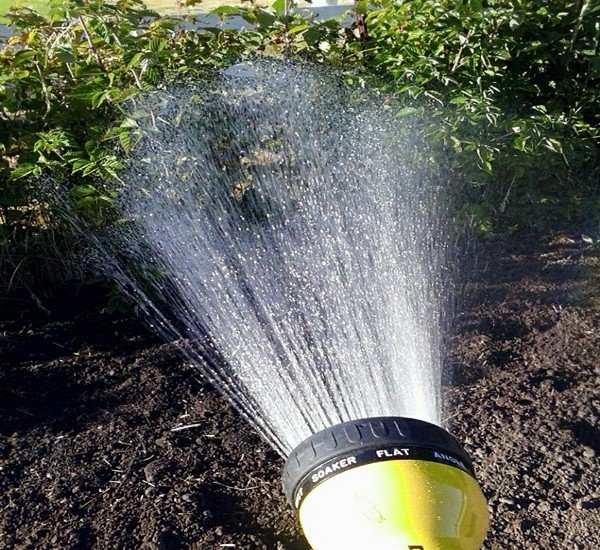


When sprinkling, the soil is well watered and foliage is moistened
With linear planting of blackberries, it is more convenient to use a drip irrigation system. Pipes or belts with droppers are laid along the rows of bushes and water is supplied under pressure, which flows evenly through the dispensers to the roots of the plants. At the same time, water consumption is significantly saved and the soil is not washed out.
The soil around the bushes should be loose and free of weeds. Weeds, especially wheatgrass, extract nutrients from the soil and inhibit the growth of blackberries. After watering or rain, the soil is loosened to a shallow depth (8 cm), taking care not to damage the suction roots located in the surface layer. Loosening is carried out between rows of bushes to a depth of 12 cm.Then straw and humus are laid - a layer of mulch not only keeps the soil moist, but also activates its beneficial microflora, suppresses the development of pathogenic organisms, protects the root system from overheating in the summer heat, and in winter - from freezing ...
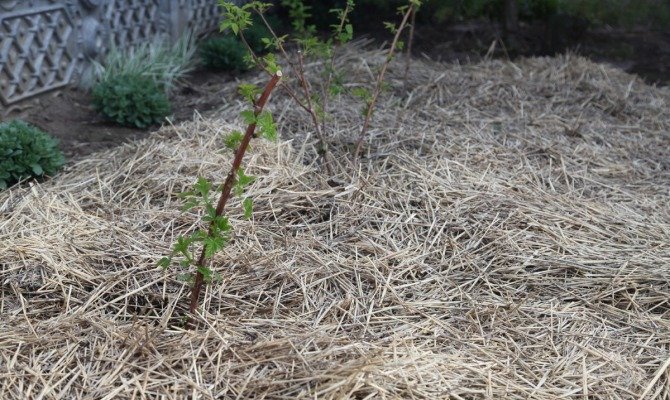


To retain moisture, the soil around the bush is mulched with hay.
Good nutrition
Top dressing saturates the plants with the necessary microelements that increase their productivity and strengthen the immune system. When planting bushes on fertilized soil in the first season, they do not need additional nutrition. Only next spring, blackberries are fed with a nitrogen composition: urea (10 g) or saltpeter (20 g / 5 l). During the fruiting period, the bushes are fertilized with nitrophos (70 g / 10 l), after harvesting with superphosphate (100 g) and potassium salt (30 g).


Agricola is a highly effective water-soluble compound fertilizer designed for root irrigation and spraying
With foliar dressing, the plants are quickly saturated with nutrients. Spraying on a leaf during fruit setting and in autumn with a solution of Kemir Universal (15 g / 10 l) increases productivity and resistance to changing environmental factors.
Instead of the mineral composition, organic matter (300 g / m2) can be used: chicken manure (solution 1:20) or liquid manure (1:10) is applied before flowering and after harvesting. During flowering, the berry is fed with an infusion of ash (100 g / 10 l).
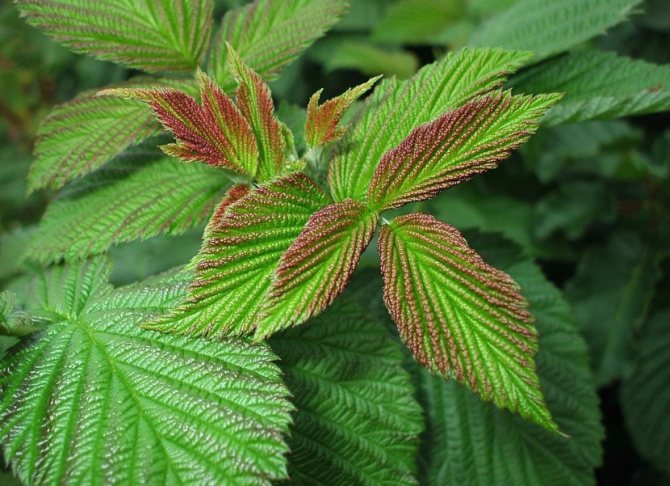


The deficiency of trace elements immediately affects the appearance of the blackberry: with a lack of magnesium, the leaves become reddish.
Bush formation
When forming a blackberry, its two-year development cycle should be taken into account. In the first season, shoots grow and buds are laid, the next year the branches bear fruit and die off. In the fall, two-year-old shoots on which the berries were formed are cut off. Dry and damaged branches are also removed, leaving 8-10 strong shoots. In the spring, overwintered branches are shortened by 15 cm and tied up.


When grown on a trellis, the bushes are evenly warmed up by the sun and well ventilated
Growing blackberries on a support provides good ventilation and uniform illumination of the bushes. In addition, the separate placement of fruiting and growing stems on the trellis makes it easier to care for the shrub. Wire is pulled on the supports in several rows and the whips are fixed on them. With the fan-shaped formation of a bush, they are placed on a support in this way: overwintered shoots are raised in the center, new shoots are sprouted on the sides. In autumn, the central branches are cut at the root, annual shoots are pressed tightly to the ground for the winter, and raised vertically in the spring.
Video: pruning thornless blackberries in summer and autumn
Preparing for winter
The Chester variety is frost-resistant, withstanding cold up to -30 ºС. And thanks to late flowering, it is not afraid of returnable spring frosts. However, so that annual shoots do not suffer in a too harsh winter or with sudden temperature changes, they are insulated. After pruning, pre-winter watering and mulching with humus, the branches are removed from the support, bent and laid on the ground, covered with agrofibre on top. In winter they throw snow on the bushes. To protect the plants from rodents, poison is placed under the whip or spruce legs are thrown over the insulating material.
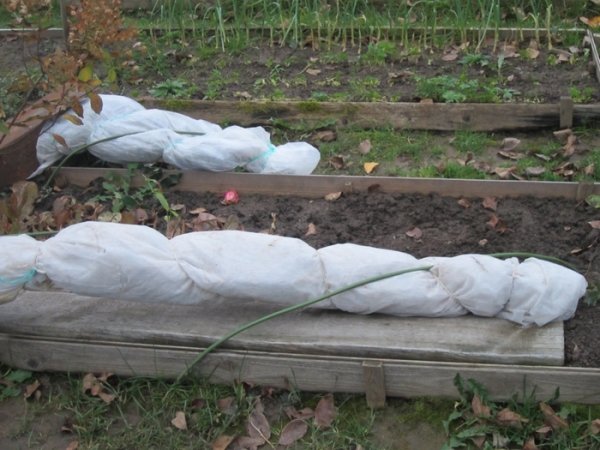


In regions with cold climates for the winter, the blackberry should be removed from the support and covered with non-woven material.
Reproduction methods
Blackberries are propagated vegetatively, since varietal characteristics are lost with the seed method.
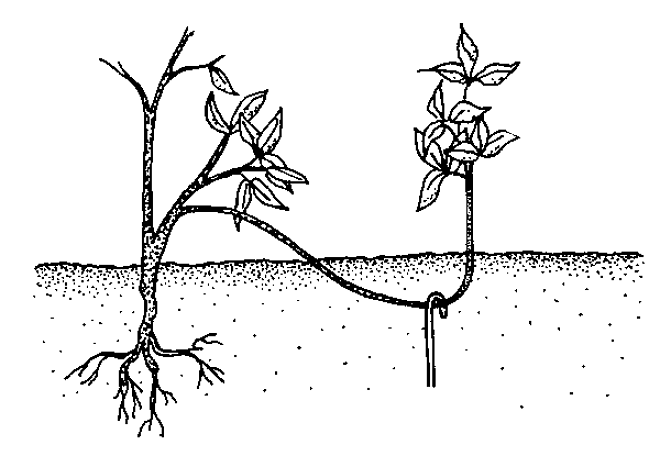

Reproduction using layering - an easy way to breed blackberries
It is not difficult to propagate the shrub with the help of layering: the top of the shoot is added dropwise near the bush, watered and fixed with staples. After 3 weeks, a sprout 45 cm long with formed roots is separated from the bush and planted separately.
Video: how to root a blackberry
When grafting, proceed as follows:
- Young shoots at the end of June are cut into 10 cm pieces and planted in pots.
- Watered and covered with foil.
- Within a month, the soil is moistened, airing is carried out.
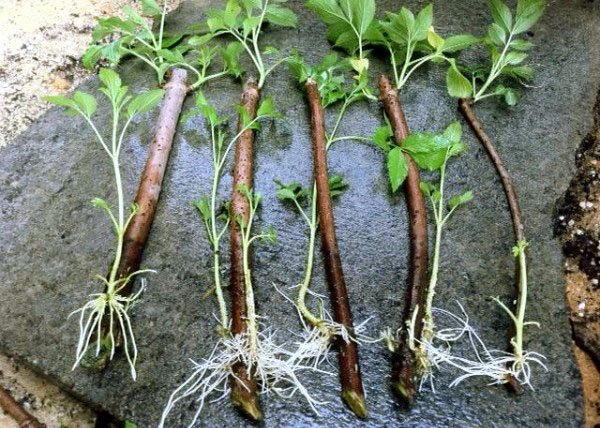


After a month, the cuttings have roots.
- Rooted green cuttings are planted in the garden.
Disease prevention
The variety has good immunity, resistant to gray rot, which destroys many berry crops. However, in bad weather, the bushes can be affected by diseases. Prevention can help reduce the risk of infection.
Table: prevention and control measures for blackberry diseases
| Disease | How does it manifest | Prophylaxis | Control measures |
| Purple spot | Leaves, covered with dark spots, fall off. Buds and young shoots dry up. The disease leads to poor flowering and shedding of the ovaries. The spread of the fungus especially progresses with increased moisture and thickening of the plantings. |
|
|
| Anthracnose | Excess moisture often leads to the spread of fungal spores. The foliage and shoots are covered with gray spots with a purple border, and gray ulcers form on the berries. |
| Spray with a 5% solution of copper sulfate, Fundazol (10 g / 10 l) before flowering, after the buds have fallen and after harvest. |
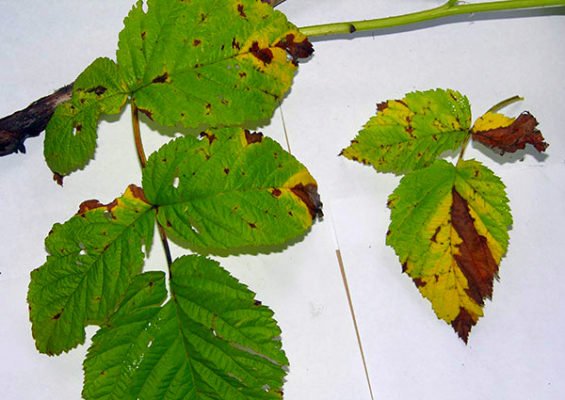
| Septoria | Infection occurs in warm, humid weather. Light spots with dark edging develop on the leaves. The foliage dries up, the shoots turn brown. Bushes are maximally affected at the stage of fruit ripening. |
|
|
Photo gallery: diseases affecting the blackberry Chester


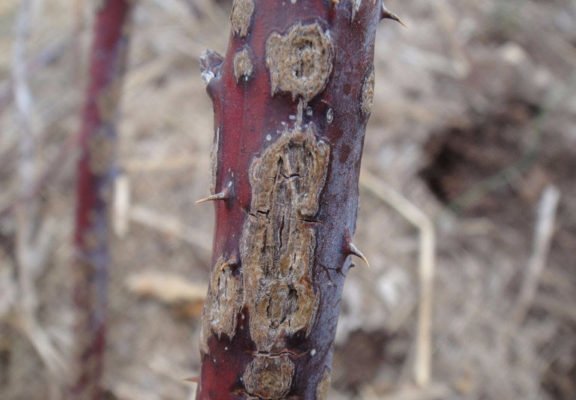
Purple spot affects thickened plantings


Long rainy periods contribute to anthracnose.
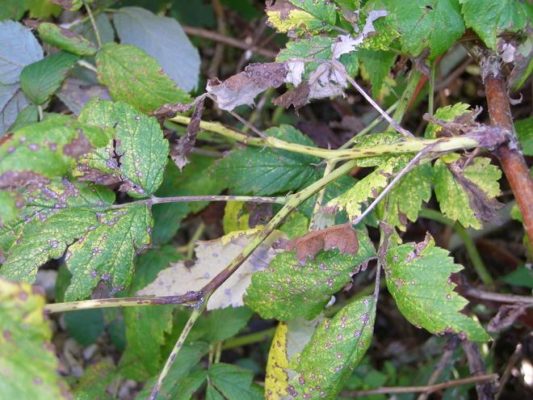


Septoria is especially dangerous during the ripening period of blackberries.
Table: blackberry pests and control
| Pests | Manifestations | Prophylaxis | How to help |
| Blackberry mite | The mite hibernates in the buds of plants. With the onset of heat, it settles on shoots and berries. The fruits affected by the pest do not ripen partially or completely. Yield losses during the development of a blackberry mite can reach 50%. | Thin the bush. | Before bud break, spray with solutions of Envidor (4 ml / 10 l), Bi-58 (10 ml / 10 l), repeat after 10 days. |
| Aphid | Aphid colonies, covering the leaves and branches, suck the juices out of them, weaken the plant. |
|
|
| Khrushch | The larvae gnaw at the roots of plants, the beetle feeds on leaves. The mass flight of the beetle falls on the flowering period, the affected buds and ovaries fall off. |
| Treat at the beginning of the growing season with a solution of Antichrusch (10 ml / 5 l), Confidor Maxi (1 g / 10 l). |
Photo gallery: the most common blackberry pests


Yield losses during the development of a blackberry mite can reach 50%
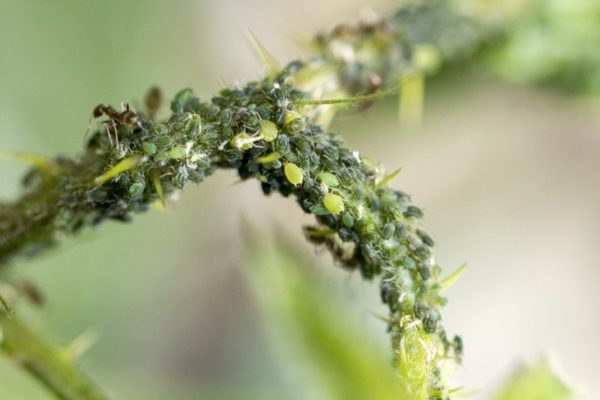


Aphids stick around leaves and shoots, sucking juices out of them


Khrushchev and its larvae infect berry bushes, which can cause violent fall of leaves, ovaries, flowers
Birds pose a serious threat to beetles and their larvae. One pair of starlings catches up to 8 thousand beetles and other insects per season. By hanging feeders and houses in the garden, you can increase the number of birds. And you can attract ladybirds - the worst enemies of aphids - by planting fragrant calendula in the garden.
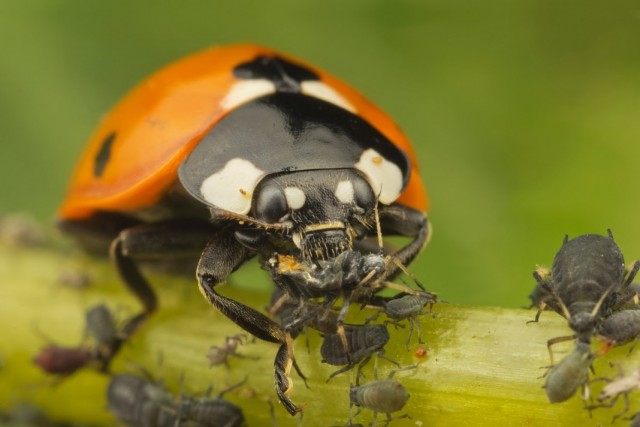


Ladybug is a natural enemy of aphids
Yield
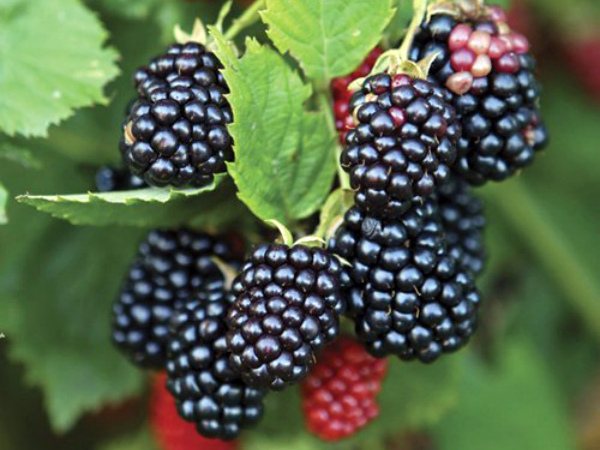


Chester Thornless is one of the highest yielding blackberry varieties. The average yield is 10-15 kg per bush. Ripening of berries is quite extended, the fruits begin to form from the beginning of August, the process can last up to a month.
The yield is influenced by the quality of care, climatic conditions and the age of the bush. Full fruiting occurs only in the third year.
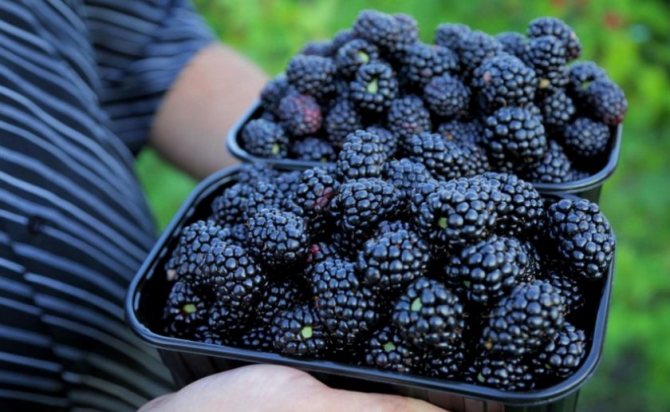
Berries tolerate transportation and storage well. The score for this parameter is 4.8 points out of 5. Due to the absence of thorns, the harvesting process is simplified. The fruits are used for fresh consumption and preparation of preparations and conservation.
The size of blackberries of this variety is optimal for storage and transportation in blisters, the berries practically do not crumple, keeping their presentation.
Pros and cons of the variety
Among the advantages are:
- resistance to winter cold;
- rich harvest for the season;
- attractive appearance;
- possibility of transportation over long distances;
- long keeping quality.
Disadvantages:
- the need for shelter;
- poor growth in dark areas.
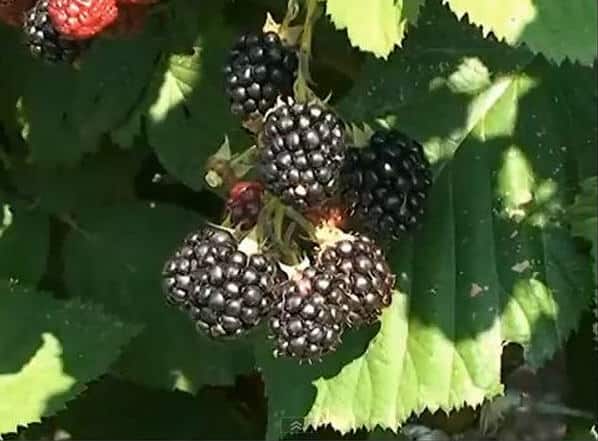


Despite the fact that blackberries tolerate cold well, it is recommended to cover for the winter. To do this, use any available means. Blackberries do not like to grow in lowlands and ravines.
How, where and by whom was it bred?
The variety was bred in the 70s of the last century by American breeders in a Maryland laboratory. During the selection, the varieties of blackberries known at that time, Darrow and Thornfrey, were used, which have completely different characteristics of the bush and the taste of berries.
The result is a unique variety, represented by a large, spreading shrub, on which dense clusters of berries are formed. A distinctive feature of the Chester Thornless blackberry is the absence of thorns on the branches, as well as high frost resistance and productivity. Today it is recognized as one of the best hybrids for industrial cultivation.
Blackberry Diseases Chester Thornless
Blackberry Chester Thornless is susceptible to diseases such as verticillosis, gray rot, anthracnose.
Verticillus (verticillus wilting) is a fungal disease that affects the conducting system of the plant. The first signs of the disease, which often appear already during the growing season, are yellow and curling lower leaves. The diseased plant should be destroyed, and the adjacent bushes should be fumigated with smoke.
Gray rot affects blackberry bushes during periods of prolonged rains or heavy dense fogs. The berries that are set and ripen are covered with a gray bloom. To prevent the disease, it is necessary to plant blackberry beds in open, well-ventilated places. When blackberry bushes are affected by gray rot, the soil around the bushes is covered with a 3-5 cm layer of ash or needles.In late autumn or early spring, blackberry beds are treated with potassium nitrate (100 g of substance per 1 bucket of water).
Anthracnose attacks blackberry bushes in late May - early June. The leaves of the plant are covered with purple spots, which gradually acquire a reddish border and spread to the stems. Light brown stems become covered with gray spots with a red border and die. Experienced gardeners are advised to add peat-manure compost to fertilizers and destroy weeds in the aisles of the blackberry beds in time. On warm days (+16 degrees), you can spray the bushes with colloidal sulfur. Dilute 20-30 g of the drug in 10 liters of water until a homogeneous suspension is obtained. Processing should be carried out in calm weather during the growing season of the plant (before the flowering period).
Photo Gallery: Blackberry Diseases Chester Thornless
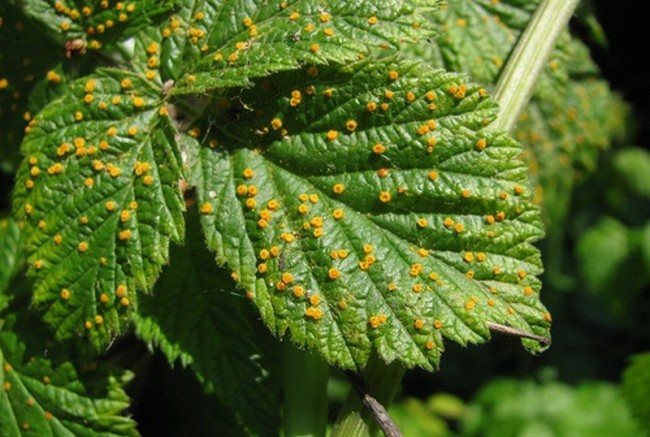


Verticillosis is a fungal disease that is manifested by loss of elasticity and wilting of shoots
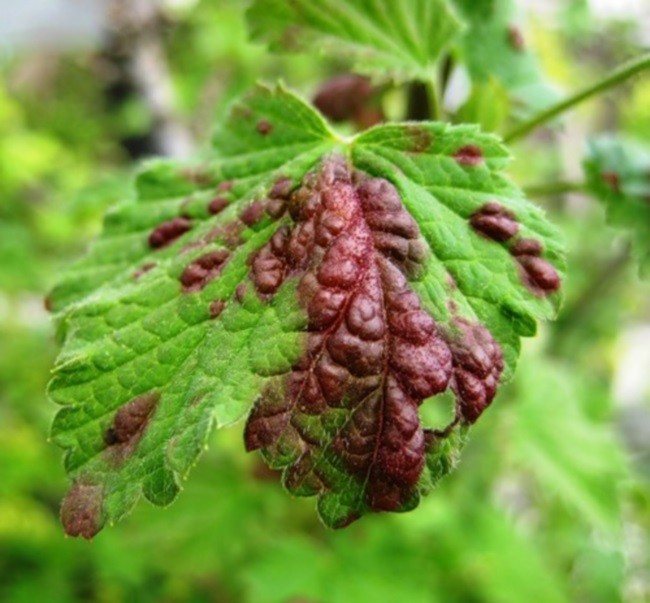


Anthracnose affects mainly leaves, less often young shoots and berries of blackberries


Prerequisites for the development of gray rot are high air humidity and stagnation of air masses near the plant.
Growing features


Blackberries of this variety prefer loose and nutritious soil. It is best to choose a plot in a well-lit place - with a lack of light, the berries lose their taste and gain volume poorly. Groundwater should be at least 1 meter deep to avoid waterlogging.
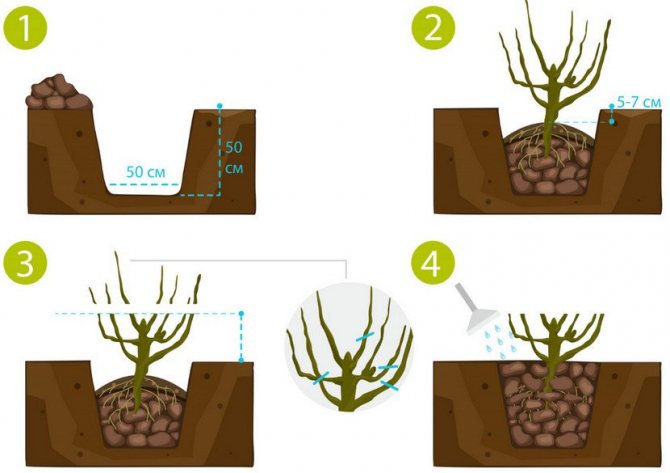
Planting is carried out with seedlings. It is recommended to purchase one-year-old bushes as planting material in order to speed up the process of berry formation. The root system must be at least 15 cm.
The seedlings are planted in early spring after the end of the spring frost. Before planting, the soil must be carefully dug to the depth of a shovel bayonet, and fertilizers must be applied - 50 g of potassium composition, 100 g of superphosphate and 10 kg of organic matter (compost or mullein solution) per 1 m2.
Blackberry bushes are planted in individual pits with a volume of up to 50 cm3 (0.5 liters) at a distance of 75-160 cm from each other. The seedlings must be placed in the holes in such a way that the varietal bud is deepened into the ground up to 3 cm. After that, the planting must be watered with water at the rate of 10 liters of water per bush.
Planting blackberries


Blackberry cuttings ready for planting
Berry bushes can be planted in two ways:
- Pinning the top sprout... The shoot is cut and planted separately from the mother bush in mid to late July.
- Growing green petioles... Also produced in July. The top of the shoot with a growth bud is cut off and placed in water. After the roots appear, the sprout is transplanted into a pot. When the root system grows, the seedling can be rooted in the soil.


Blackberries grow best in flat and sunny places. Loves loose and neutral soil
Stages of planting a blackberry:
- Dig holes at the site of the future plantation, 0.3 m deep. The step between the plants is 2-3 m, so that the bushes do not interfere with each other's growth.
- Mix the dug soil with a complex fertilizer (nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium).
- Pits are spilled with water (3-4 liters each).
- Immerse seedlings with straightened roots in holes and sprinkle with fertilized soil.
- Then water the seedlings again.
- Then the root space of the blackberry is covered with a layer of mulch. This can be straw, hay, sawdust or peat.


In the photo - organic mulch, it helps the plant to develop well, retains moisture in the soil and insulates the roots
In the video, it is clearly shown about the features of planting the Chester blackberry.
Care
Blackberry Chester Thornless is an extremely hardy and frost-resistant plant, but if planting care is not followed, yields decrease and there is a risk of infection with diseases and pests.
Specificity of caring for the variety:
- The support for the bushes must be built in the first year. For this variety, you can use single-strip trellises or T-shaped supports located at arm's length.It is important to place all fruiting shoots on one side.
- It is necessary to regularly prune the bush. The length of the pruning depends on the age of the plant as well as the planting density. It is recommended to leave 3-6 fruiting shoots, which is optimal for the formation of the full volume of the crop.
- Watering should be done throughout the season. Water should be applied most intensively in the first 45 days after planting, and then during the period of active growth and ripening of berries. To retain moisture, it is advisable to use mulching.
- As a top dressing, ammonium nitrate or urea is suitable at the rate of 20 g / m2 during the period of intensive growth, and during the growing season it is necessary to add organic matter (up to 4 kg / m2).
- Despite the high rates of frost resistance, it is advisable to cover the bushes for the winter. This should only be done after harvest. Straw or dense agrofibre is suitable as a covering material.
This cultivated blackberry variety can bear fruit in one place for up to 15 years. After this, a transplant to a new site or plant renewal is required.
Off-season work and care features


Blackberries will give higher yields if the shoots are tied to a trellis
Blackberry variety Chester Thornless, like all hybrid plant varieties, is quite unpretentious. The plant takes root well and bears fruit in almost any conditions; both sandy and loamy soils are suitable for it. However, the necessary minimum of agrotechnical work on the blackberry beds should still be done.
| Event | Necessary work |
| Watering | The plant tolerates drought well, abundant watering is not required. |
| Loosening the soil | The aisles are fluffed up or dug up once every 3-4 years. A few years after laying the beds in the aisles, you can plant vegetable crops, the roots of which will constantly loosen the ground. |
| Fertilization | Phosphorus-potassium fertilizers are applied once every 3-4 years. Nitrophoska, superphosphate, potassium nitrate (20-50 g per sq. M) in early spring or late autumn are mixed with loosened soil between rows. |
| Pruning | The first pruning is carried out no earlier than 2 years after the formation of the blackberry bed. Old, incapable of fruiting shoots are completely cut out, leaving 5-7 flexible shoots with light brown skin. In the future, pruning is carried out annually. |
| Formation | Chester Thornless Blackberries can be grown on a vertical trellis. Pillars 1.5–2 m high are driven into the ground every 7 meters, 2–4 rows of wire are pulled between the pillars at intervals of about 1.2–1.5 m. Flexible shoots are tied to the wire with twine. |
| Warming | The flexible stems of the Chester Thornless blackberry are bent to the ground and covered with plant or improvised material (spruce branches, fallen leaves, film, old mattresses) in the northern regions of the country and in areas with a sharply continental climate. |
Possible diseases and their treatment
The Chester Thornless variety has strong immunity and is rarely infested with diseases and pests. As a rule, problems arise with improper care or non-compliance with cultivation techniques. The most dangerous diseases are anthracnose, purple spot, mosaic and curl.
When the first signs of infection are detected, it is necessary to treat the planting with a complex fungicide (Topaz, Fundazol, Topsin M, Bordeaux liquid). In case of massive damage, it is necessary to completely clean the area with the subsequent destruction of diseased plants.
Advantages and disadvantages


Blackberry bush Chester
With a large number of advantages, the Chester blackberry has few negative characteristics. But it's worth knowing about all aspects of the variety.
Advantages:
- The most important advantage of the Chester blackberry is its frost resistance. Firstly, the bushes tolerate frost well in spring. Secondly, in winter, the variety is able to survive even in 30-degree frosts.Thirdly, blackberries do an excellent job with sharp changes in weather conditions, which often become detrimental to such plants.
- The second advantage is high yields. One bush bears many fruits with good care.
- The bushes also endure another weather obstacle - drought. The root system of the Chester blackberry is deep enough, in addition, it is well developed. This helps to do without watering for a long time.
- The berries of this blackberry variety are very valuable from a dietary point of view. They are good for your health and also delicious.
- Excellent safety during transportation. This is very important when grown on an industrial scale.
- Decorativeness of plants. This is also an excellent quality that ensures the beauty of the site, and not just its benefits.
The disadvantages of the variety, as already mentioned, are much less. But it's worth knowing about them:
- The need to insulate the bushes. This is typical not for all regions, but only for places with possible severe cold in winter.
- The difficulty of the shelter. The bushes branch strongly at the very base. This creates some difficulties when covering plants for the winter.
- Blackberry Chester does not tolerate darkened places very well. She only wants to grow in sunny areas. The plant does not tolerate long rains.
- Some gardeners attributed varieties and heterogeneity of berries, which can be of different sizes, to the disadvantages. In addition, the ripening of blackberries is quite extended in time, not amicable.
Testimonials
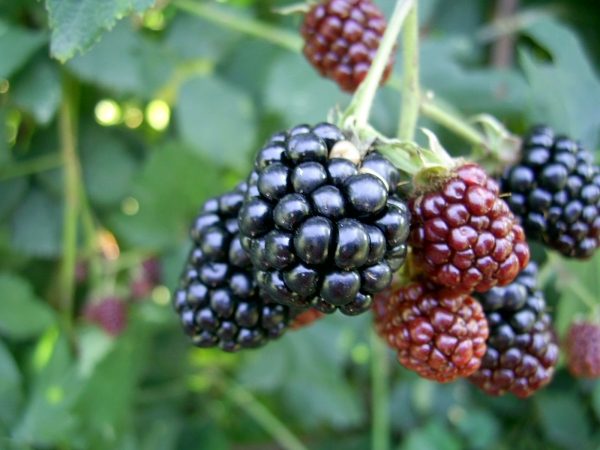


Gardeners who have chosen the Chester Thornless variety note the high yield and excellent quality of the berries. The absence of thorns simplifies the process of harvesting fruits in August. If pruning is carried out on time and the supports are correctly installed, then this variety is one of the best for growing in mid-latitude conditions. It has high frost resistance and endurance.
Users highlight the main drawback - a sprawling bush, as well as a tendency to deformation of the berries during growth, which occurs due to the crowding of clusters on fruiting shoots. Some people report uneven ripening, but this is a problem for most cultivated blackberry species.
Blackberry Chester Thornless is an unpretentious and fruitful plant. Suitable for growing even in unfavorable conditions, but proper care must be followed to achieve yields. The variety is frost-resistant, self-pollinated, suitable for beginners and industrial cultivation. Has the best characteristics among all hybrid varieties of blackberries.
Reproduction
The plant can be propagated by apical shoots or layering. To root the cuttings in the spring, you need to bend the lower branches to the ground, attach and sprinkle with earth. By the fall, roots are formed in these places. At this stage, the layers should be separated from the mother culture and planted in the school.
To breed a culture with apical shoots, you need to cut off processes 10-15 cm in size. This should be done with a sharp knife or pruner. In spring, shoots should be planted in boxes with a special substrate. To do this, you need to mix humus and sand in equal parts.
The shoots should be planted at an angle of 45 degrees. They must be covered with foil to maintain high humidity parameters.
Important! In order for the shoots to root well, they should be placed in partial shade. In autumn, with good rooting, plants should be planted in open ground.
Pest control
Blackberry bushes can damage insects such as raspberry beetle, weevil, shoot aphid.
The shoots on which the pests live become sensitive even to light frosts, freeze slightly and gradually dry out. For preventive purposes, during the growing season, it is recommended to spray blackberry bushes with Fitoverm (dilute 2 ml of the substance in 10 l of water) or Kinmix (dilute 2.5 ml of the drug in 10 l of water).
If raspberry beetles and weevils have already appeared on blackberry bushes, they can be shaken off onto a light-colored canvas spread under the bush. This procedure is carried out on a cool morning (8 degrees), when the beetles are weakly holding on to the stems. With the massive appearance of beetles, the bushes are sprayed with a solution of laundry soap (40 g of soap per 10 liters of water).
A good effect is given by treating the bush with a garlic solution. 20-30 g of garlic is infused in a bucket of water for 24 hours, and then filtered through cheesecloth and used for spraying.
When a shoot aphid appears, blackberry bushes are fumigated with tobacco smoke or sprayed with garlic solution. You can spray blackberry bushes with a solution of potash soap (300 g per bucket of water).