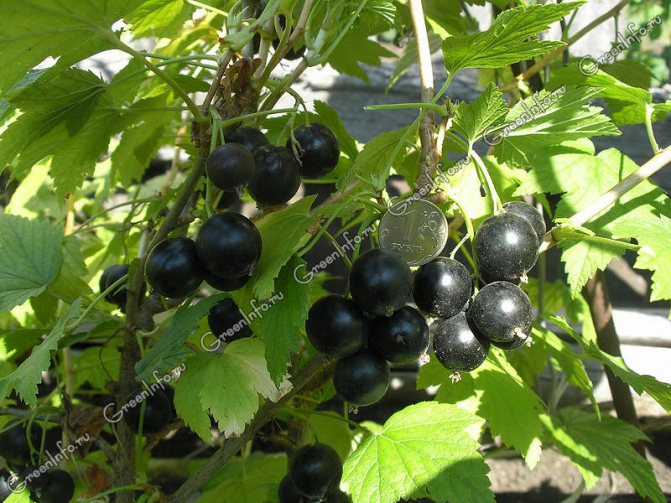
Many gardeners still grow old small-fruited currant varieties. For example, sometimes I am asked if I grow Dovek currants. Yes, it was once, fifteen years ago, considered large-fruited: it has berries of 1.5-1.8 g. And today it is an outdated variety, considered small-fruited.
New varieties, created by scientists in recent years, have berries of 4-5.5 g. They are more productive, more resistant to diseases and pests. There are sweet-fruited, with dessert berries, there are early-ripening ones, there are late-ripening ones, in general, for every taste.
The gardener is always worried about the eternal question: what varieties to choose? I would like to share some of the results of my annual horticultural tests in recent years. I try dozens of varieties, then select the best of the best and multiply.
|
Currant is one of the most plastic crops. Therefore, here we can afford to choose varieties according to our taste - they will grow well and bear fruit in our gardens. After testing the varieties of the Chelyabinsk, Altai, Bryansk, Oryol selection, I decided to stop at the varieties of the Orlov VNIISPK selection. These varieties attracted me with an early entry into fruiting (literally in the second year), large-fruited, pleasant berry taste and high resistance to major diseases and pests of currants. Some varieties, with high agricultural technology, literally overload themselves with the harvest, while others are capable of bearing fruit annually and well with a minimum of maintenance.
Separately about the size of the berries. For comparison: the berries of the previously widespread variety Pamyat Michurin have a mass of 0.7-0.9 g, and the mass of the berries of the Orlov and Altai varieties I tested is from 2.5 g to 5.5 g. One of our gardeners, having looked at them in my garden, exclaimed: "The varieties are praised, large as cherries, but here they are like grapes!" Therefore, I decided to dwell on their characteristics in more detail.
- Lucia - a variety of medium ripening, fast-growing, very high-yielding. The bushes are low, medium spreading. The berries are large and very large (3.6-5.5 g), one-dimensional, large both at the beginning and at the end of the cluster. The variety is resistant to many common diseases. Due to the annual high yields, it consumes a lot of nutrients and is picky about agricultural technology. With insufficient agricultural technology, the bushes can age quickly.
- Hercules - a variety of late ripening. The bush is powerful, with thick shoots, erect, consistently high-yielding. Berries are large (3-3.6 g), one-dimensional, dessert taste, with a thin skin. It attracts gardeners by its high winter hardiness, and also by the fact that it is not very picky about growing conditions.
- Treasure - early ripening variety. The berries are large, 2-4 g, sweet and sour taste. The bush is undersized, semi-spreading, the yield is high. Resistant to diseases and pests.
- Lazy person - despite its name, it turned out to be an excellent high-yielding, medium-late variety: the berries are large, up to 3-3.5 g, the taste is pleasant, sweet (4.8 points), the yield is high. The bushes are quite powerful, somewhat spreading. After harvesting early-ripening varieties for a long time "treats" with its sweet berries directly from the bush.
- Openwork - in many characteristics it is similar to the previous variety, but differs from it in earlier ripening - the ripening period is average. The berries are sweet.This is the highest yielding variety in my garden.
- Grace - a fast-growing, large-fruited and high-yielding variety with a medium early ripening period. The berries are large, with a dessert taste. The bush is powerful, upright. The yield is high. This variety of gardeners pleases with the fact that it is not at all affected by powdery mildew and is resistant to kidney mites.
|
- Exotic - a high-yielding and large-fruited variety. Berries weighing 3.5-5 g, uniform along the entire length of the brush, very pleasant to the taste. This is perhaps the largest-fruited variety of early ripening black currants for the conditions of central Russia. Bushes are powerful, vigorous, erect. The branches, even under the weight of a bountiful harvest, are weakly inclined to the ground. The variety is early-growing, in my propagation beds even some cuttings of the autumn planting period for another year bloom and try to bear fruit, but I, naturally, remove such flowers. The shoots of the first year are thick, powerful. The variety is resistant to powdery mildew. I believe that this variety has the right to take a place in every garden.
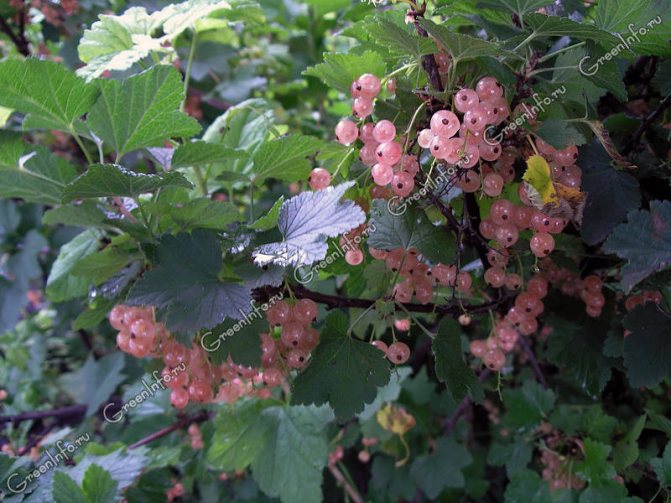
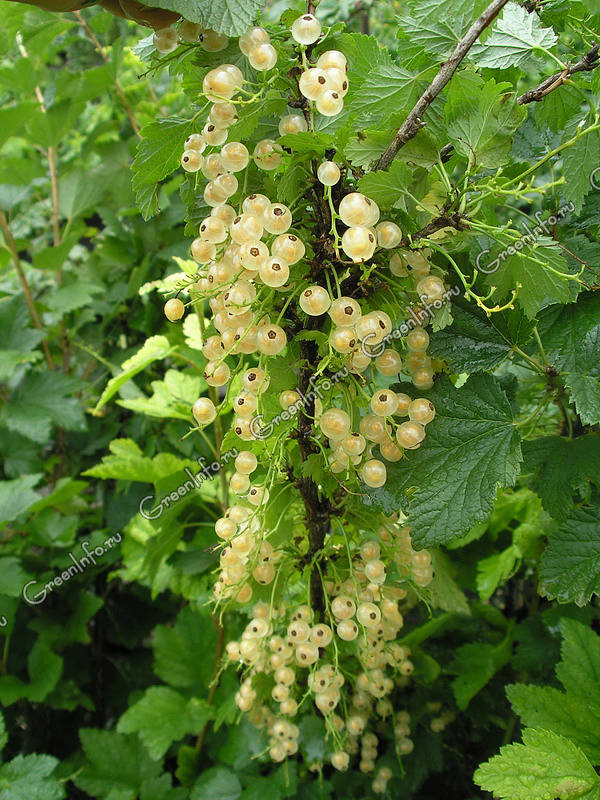
Of the varieties of red and white currants, large-fruited were: Jonker Van Tets (red), Dutch Pink and Versailles White. These varieties have another positive quality - the berries hang until winter without crumbling, and we feast on currants right from the bush when there are no other berries in the garden.


White currant Versailles WhiteJonker Van Tets (Jonker van Tets) - a variety of early ripening. The bush is vigorous, erect (more spreading with age), dense, forms quickly. Enters fruiting early. Differs in early flowering, resistance to powdery mildew. Weakly affected by anthracnose, medium - kidney mites and gall aphids. Berries of medium size 0.7-1.4 g, bright red, with a dense, transparent skin of a pleasant delicate taste.
- Versailles White - a variety of medium ripening. Grows well even in poor soils. The bush is medium-sized, spreading, wide, irregular in shape. The brush is long. Berries of medium size with a long petiole, light cream, round or slightly compressed from the poles, transparent (veins and seeds are visible), sour taste, juicy. Maturation is amicable. Average winter hardiness, not resistant to anthracnose.
- Dutch Pink - a variety of medium ripening. The bush is vigorous, slightly spreading. The brush is long. The berries are quite large (0.9-1.1 g), bright pink, transparent, sweet, dessert taste. Self-fertile and fruitful - up to 9 kg per bush). Responds well to care. Medium resistant to anthracnose, rather resistant to other fungal diseases. Average winter hardiness.
I continue to test other new ones. In the spring I am going to plant a completely new, very large-fruited variety - Arcadia... According to the characteristics of the authors - GA Plenkina, TP Ogoltsova, - it combines large-fruited with high resistance to powdery mildew and kidney mites.
Description of black currant variety Incomparable
Incomparable is considered one of the best varieties for both amateur cultivation and industrial production. This fast-growing, high-yielding crop adapts well to various climatic conditions, is unpretentious in maintenance and has an excellent berry taste.
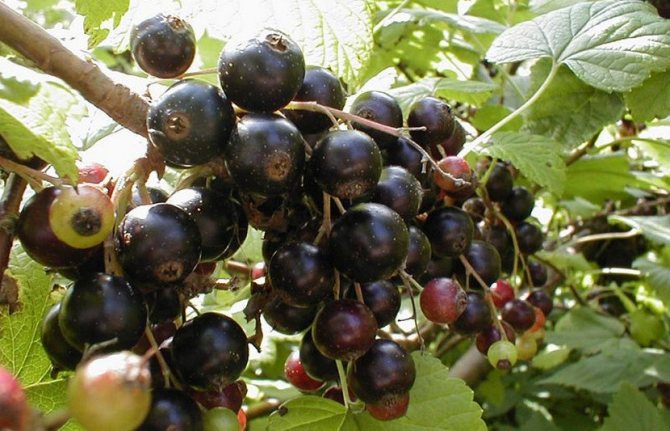


On a dense, compact bush of medium height, there are straight, shiny shoots with an anthocyanin bloom and yellow-green, dense and slightly wrinkled leaves. On long, up to 14 cm, brushes, there are on average 8-14 sweet-sour berries. A medium-early ripening variety with medium self-fertility.
Breeding history
The black currant variety Incomparable was bred by specialists from the All-Russian Research Institute of Genetics and Breeding of Fruit Plants in the Tambov Region. Obtained by hybridization of closely related varieties Zelenoplodnaya and 94/3 (produced by crossing Sanders and Primorsky Champion). The authorship belongs to a group of scientists led by I. Tolmachev. Since 1986, work has been carried out on state variety testing, and in 1995.the variety was included in the State Register for the Central Black Earth Economic Region.
Did you know? If we compare the aromas of black and red currants, then the former wins thanks to the large amount of essential oils it contains. Therefore, fragrant currant leaves are used as flavoring additives for dishes and are used for homemade preparations.
Appearance, characteristics of berries, ripening time, yield
The variety Incomparable in terms of ripening time belongs to the mid-early varieties, the berries ripen at the beginning of summer almost simultaneously. The fruits are large, weighing from 1.2 g, and the maximum weight recorded by breeders is 7.5 g. Rounded berries are covered with a thin but dense black skin with a matte surface. The calyx is also rounded, open, disappears when ripe.
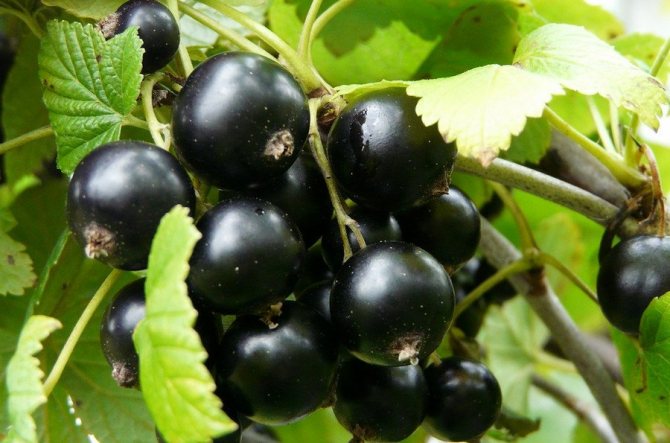


The average yield is 3.7 kg per bush or on an industrial scale 12.5 tons per hectare. Yields peak between 4 and 6 years after planting. The taste qualities of the berries were highly appreciated by the tasters: 4.8 points on a five-point scale. The taste is sweet with sourness, characterized as refreshing.
Berries are consumed both freshly harvested and processed in the form of compotes, preserves, and jams. Black currants are favored by housewives as an ingredient for a variety of confectionery products.


The nutritional value of black currant berries is 44 kcal per 100 g of product. The berry contains 1 g of protein, 0.4 g of fat, 7.3 g of carbohydrates. The table shows the chemical composition of berries and the percentage of the recommended daily requirement of an adult. Pay attention to the content of vitamin C - only 100 g of fruit contains 2 times the daily value.


| Nutrient name | Serving Size 100 g | % of the recommended daily allowance |
| Vitamin A | 8 mcg | 1 |
| Vitamin E | 0.7 mg | 5 |
| Vitamin C | 200 mg | 222 |
| B vitamins | 5.6 mg | 20 |
| Vitamin H, biotin | 2.4 mcg | 5 |
| Potassium | 350 mg | 14 |
| Calcium | 36 mg | 4 |
| Magnesium | 31 mg | 8 |
| Phosphorus | 33 mg | 4 |
Features of culture
Black currant is a shrub with a height of 0.5 to 1.5-2.0 m, consisting of 5-10 erect or slightly spreading shoots, covered with large single 3-5 lobed leaves, pale green on top and rich green and covered villi from below. Small flowers are collected in drooping brushes. Currant blooms from late April to late June. The fruit is a juicy berry, up to 10 mm in diameter. In a mature state, it has an inky black color, sour, sweet and sour, sweetish or sweet taste.
In addition to the bush forms of this culture, there is also such a variety as the columnar currant. It is an erect, powerful and very tall shoots that grow in the form of a cylindrical column.
Advantages and disadvantages of the variety
- Among the advantages of the incomparable currant variety are:
- frost resistance and resistance to humid air;
- high early maturity - the bush yields a crop already 2-3 years after planting;
- good productivity;
- resistance to fungal diseases and the effects of kidney mites;
- valuable biochemical composition of berries;
- taste and juiciness of berries and, as a result, a high degree of demand in enterprises;
- unpretentious care.
- Unfortunately, even the best varieties have their weak points:
- sometimes in early spring, flower buds are damaged due to temperature changes, which leads to a sharp decrease in plant productivity;
- diseases are often transferred from neighboring infected gardens to currants with wind and pests;
- instability to drought - currants can shed berries and leaves due to the heat, therefore, during such periods, the shrub requires frequent and abundant watering.
conclusions
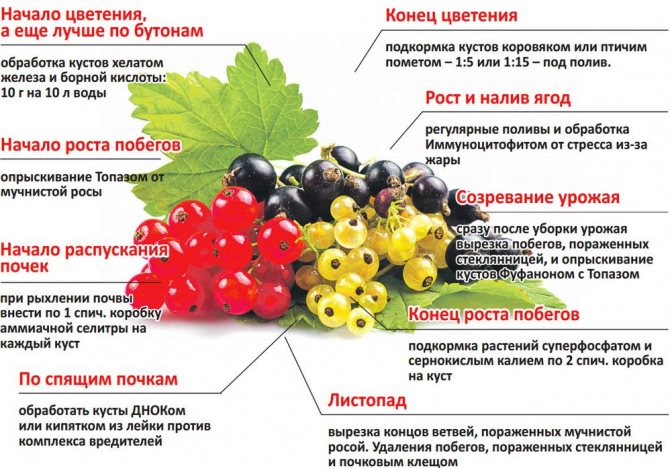
Altai red is the result of the work of Russian breeders. The berry of this variety is sweet and sour, medium in weight. The bushes are self-pollinated, winter-hardy, tolerate spring frosts well.Basic agrotechnical care techniques:
- Watering. Red currants of the varieties Roland, Rovada, like others, grow and bear fruit better, growing on moist soil.
- Pruning. Annual pruning is mandatory, in which a bush is formed and dry and damaged branches are removed.
- Top dressing. During the fruiting period, the plants must be fed with organic matter or mineral fertilizers.
- Disease prevention and treatment. Altai red has immunity against many diseases. But in order to protect themselves from their manifestations, the bushes are treated with Bordeaux liquid in early spring.
Agrotechnics
Next, you should consider the features of planting and caring for the incomparable currant variety. The root system of the plant consists of branched fibrous roots, which are shallow - 15–35 cm deep. The branches of the bush of different ages are located at different levels, so that it can bear fruit for up to 15 years. The Incomparable variety is self-fertile, which means that it does not need pollinators for fruiting.
You will be interested to know how and when currants bloom.
Seat selection and landing
The currant grows well and bears fruit in sufficient light. The high demand for light suggests that it is worth choosing a place for planting on the site that is accessible to the sun's rays. It is advisable that trees do not grow in the neighborhood, as they provide shade. The place must be protected from the wind.


Black currant is a very moisture-loving plant, this is due to the shallow location of its root system underground. Therefore, wild currant bushes can often be found on the banks of water bodies and in swampy forests.
Important! Despite its moisture-loving nature, this culture does not like stagnant water in the garden: it begins to grow poorly, becomes covered with lichens and ages quickly.
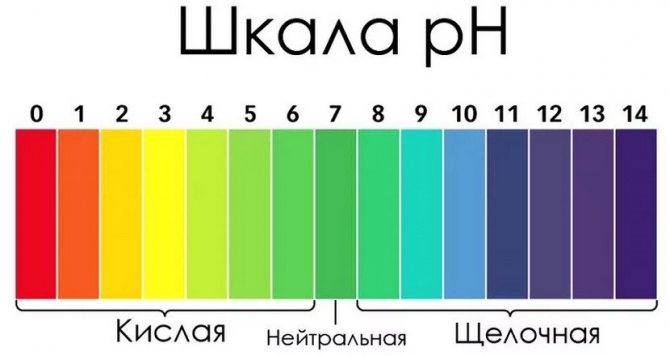
Currants do not like podzolic, saline and acidic soils. It is best to use clay, but not dense soils for planting. Others are possible, provided that they are well fertilized with organic matter and moisturized. The optimum acidity for the cultivation of this crop is in the range of 6–6.5 pH.

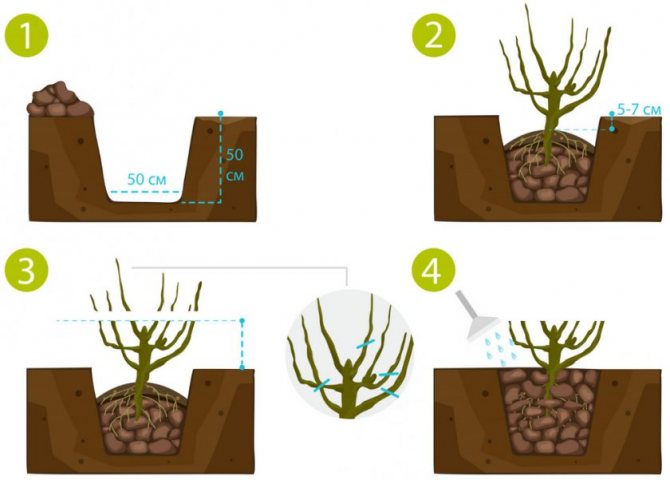
The best time of the year for planting currants is autumn, until mid-October... In the spring, gardeners try to avoid planting, as the plant buds too early and it can be stressed.
The scheme for planting must be drawn up immediately, so as not to transplant the shrubs later. The optimal distance between bushes is 1.5 m, and between rows - 2 m... Stay a meter away from the fence. With such a sparse planting scheme, currants bear fruit well and are less sick.
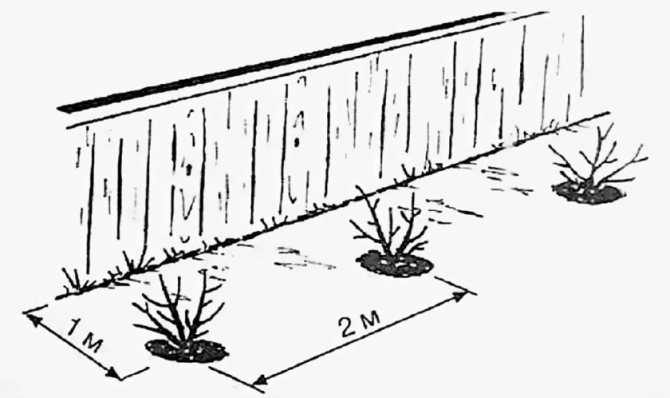

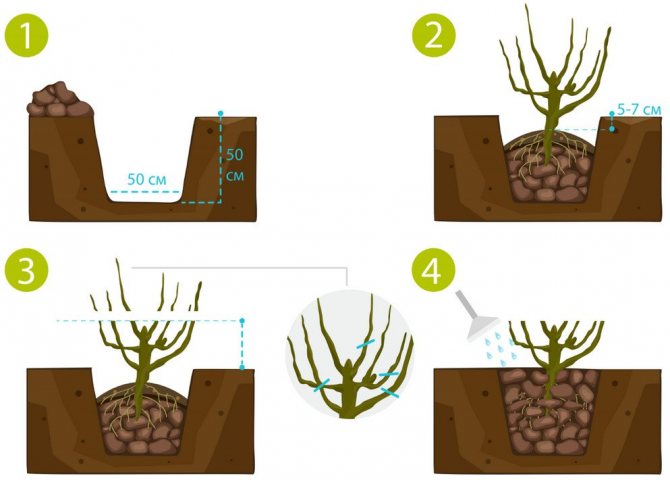
When landing, it is recommended to follow these instructions:
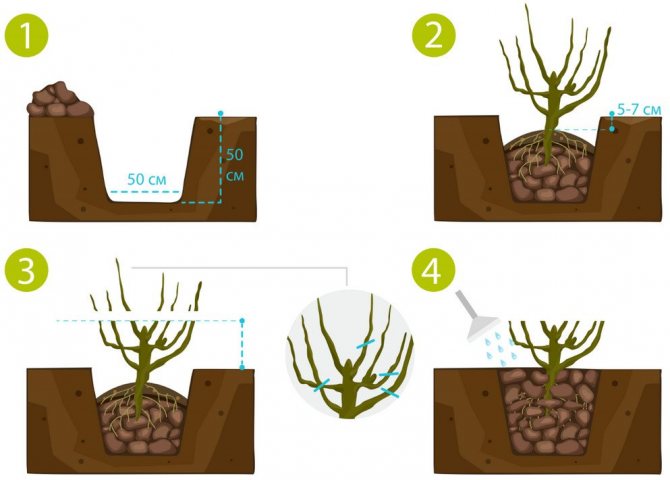
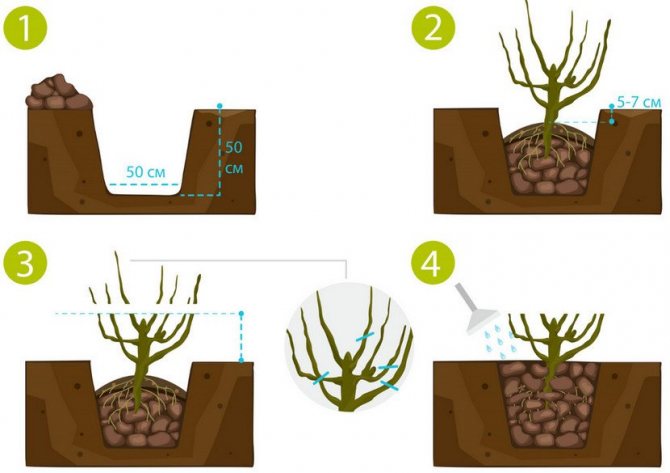
- Dig a planting hole measuring 60 × 60 × 60 cm, taking into account the future root system.
- Pour organic and mineral fertilizers into the pit: mix 2 buckets of compost, peat or humus, 0.5 kg of ash and add about 0.5 kg of superphosphate.
- It is necessary to deepen the root collar by 7–10 cm so that there are many basal buds in the soil. If this is not done, then only short-lived and unproductive standard bushes will form.
- Water the seedling immediately, regardless of the moisture content of the soil.
- Prune 20–25 cm above the ground, leaving 4–5 buds. This stimulates the growth of strong zero shoots at the bottom of the bush, which will be carriers of future fruits.
- Mulch the soil around the currants with organic matter - peat, sawdust or humus.

Care (features of watering and feeding)
Currants must be watered 4-5 times per season. And in dry and hot summer weather - once a week. Due to the lack of moisture, the berries will be small, and the growth of the shoots will slow down. Water the plant under the root with settled water in the amount of 8-10 liters per one bush, best of all in the evening after sunset.


According to the reviews of amateurs and professionals, the culture gives good large berries only on living, organic-rich soil. Therefore, do not forget to loosen and mulch the soil around the bushes with humus, rotted manure, peat. Cutting weeds are also suitable for this purpose, plus it will attract earthworms, which loosen the soil, contribute to its moisture and air saturation, and make the land fertile. The mulch layer should be at least 5-7 cm.


Currant bushes require feeding with nitrogen, potassium and phosphorus. Nitrogen is most needed for budding in early spring. A sufficient amount will increase the size of the berries and the yield. Dry nitrogen fertilizers are suitable, such as urea (50 g per bush), ammonium nitrate (60 g per bush). They are evenly distributed around the bush and sprinkled with mulch.
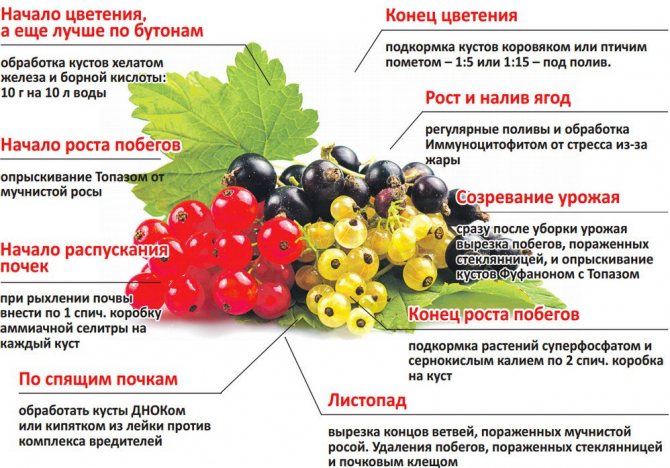

Potassium directly affects the sugar content of berries and yield. Starting from the third year of life, in the fall, currant bushes are fed with potassium sulfate (50 g per bush). Phosphorus is no less important, it is brought in in the fall, before digging, in the amount of 30-40 g per bush in the form of double superphosphate. In combination with organic mineral fertilizers, they give a good yield result.
Did you know? To increase the yield of black currant, experienced gardeners know one secret: during the flowering period, it is fed with infusion of potato peel. One liter jar of dried peel is poured into 10 liters of boiling water, after cooling it is poured at the rate of 3 liters of infusion per 1 bush.
Disease and pest control
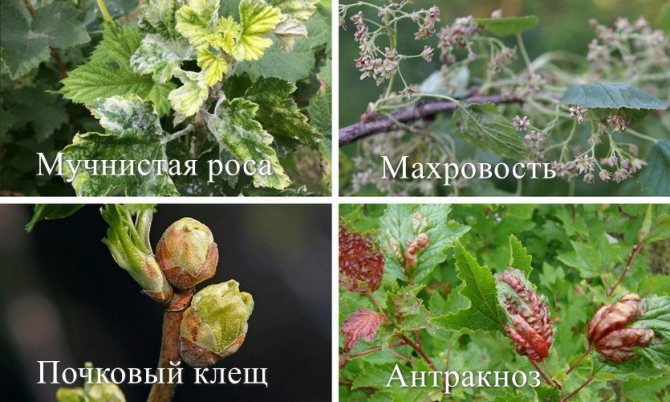
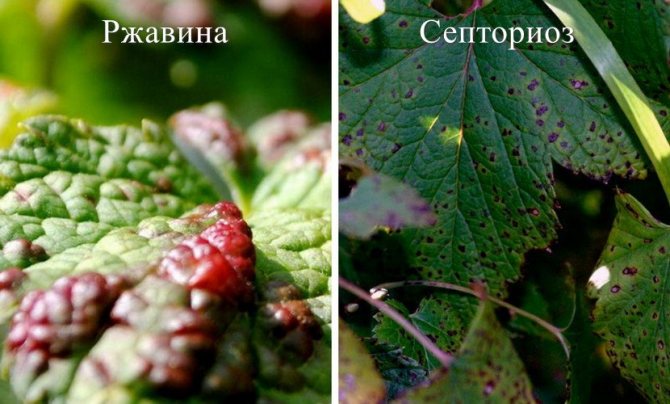
Despite the resistance of the variety to fungal diseases, there is still a risk of infection. Powdery mildew, septoria, anthracnose, gray rot, rust are the most common black currant diseases.
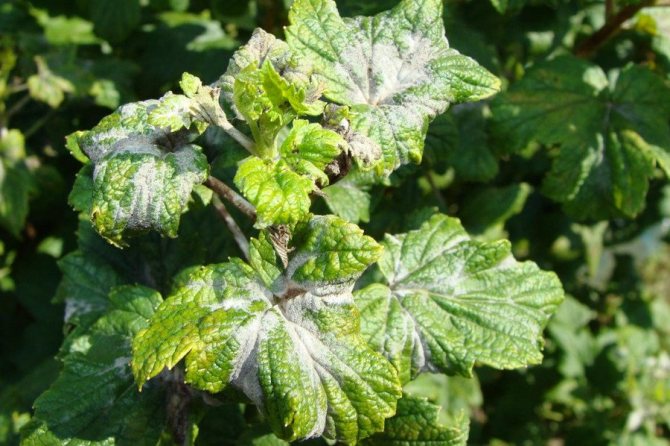
White loose bloom on young leaves, which gradually spreads to berries - this is a symptom of American powdery mildew. Copper sulfate is used against this disease in a proportion of 250-300 g per 10 liters of water. The plant is sprayed in early spring before the buds begin to bloom. During the growing season, before and after flowering, the currants are treated 4 times with a solution of soda ash and soap (50 g of soda and 50 g of soap per 10 liters of water).


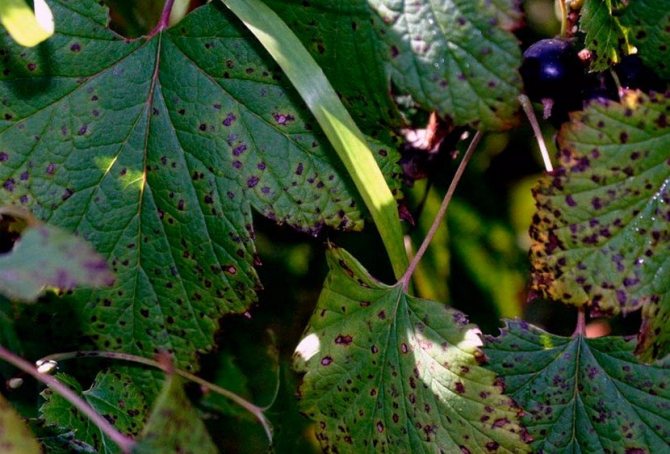
Septoria blight on currants can be seen as whitened leaves, on which small dark spots appear.... This disease is also called white spot. In this case, copper sulfate will help at the rate of 40 g per 10 liters of water.


Plant disease with anthracnose is expressed in the appearance of first yellowish-green, and then brown spots on the leaves, shoots and fruits. Spraying with copper sulfate (dissolve 100 g in 10 liters of water) with further watering with clean water also helps against anthracnose. Before bud break, nitrafen is used (250-300 g per 10 liters of water).
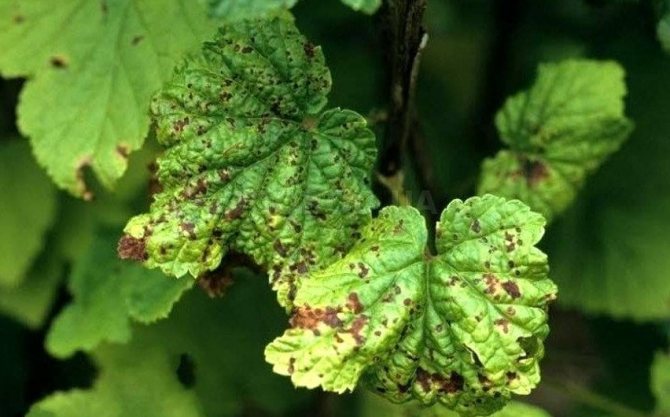


Infection with gray mold appears on the leaves, which are covered with brown spots along the edges, and in wet weather a gray coating forms on them. Treat the plant with ash infusion at the rate of 3 kg per 10 liters of water. This should be done before and after flowering and after harvest. A good remedy in the same periods is soda ash and soap (50 g of soda and soap per 10 liters of water).
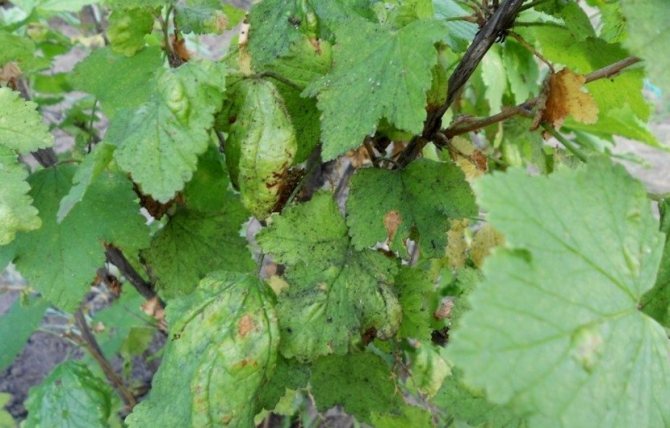


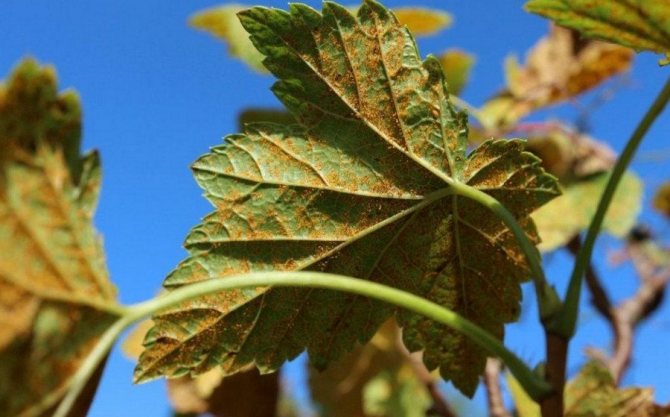
If you find orange dots or bumps covering the currant leaves, this is a sign of rust. You can fight the disease with Fitosporin, using it according to the instructions.


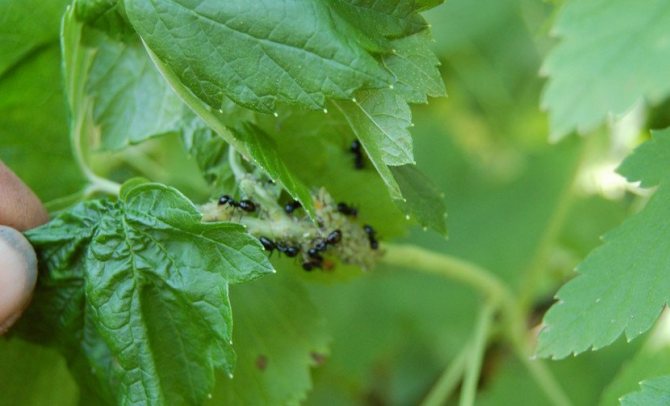
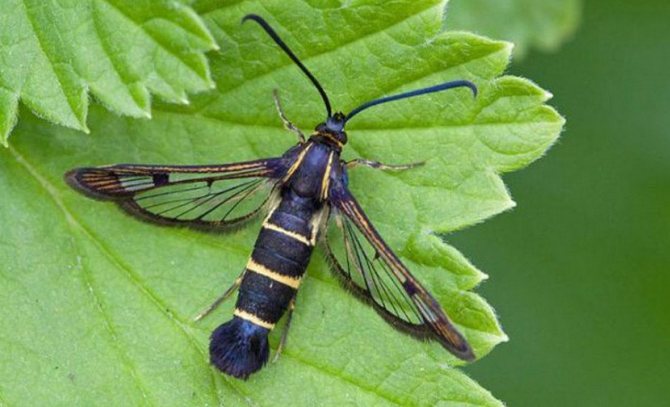
Unfortunately, the currant bush is a favorite spot for the kidney mite. It mainly spreads with planting material, as well as wind, rain, and other insects. Damages buds, which then do not form leaves and flowers.


In addition, the tick is a carrier of an incurable viral disease - black currant terry. This disease leads, first of all, to a change in the leaves, which become three-lobed, asymmetric. Flowers dry up, fruits are absent.
Important! Purchase only healthy planting material from proven nurseries to avoid the introduction of kidney mites.
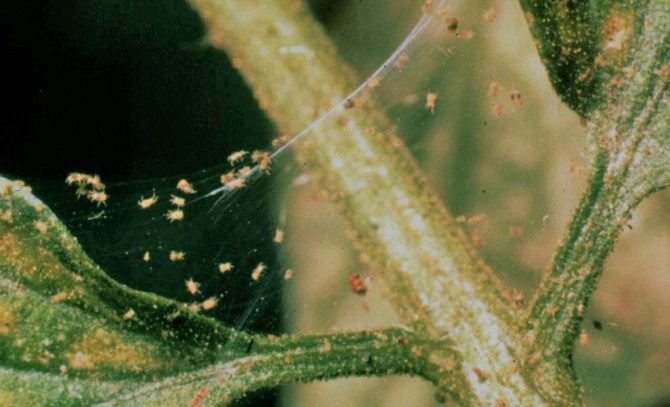
To combat this pest, the first thing to do is remove the branches and buds inhabited by it. Before flowering and immediately after it, the plant is treated with 50% karbofos (30 g per 10 l of water). The same method is also good when dealing with spider mites.
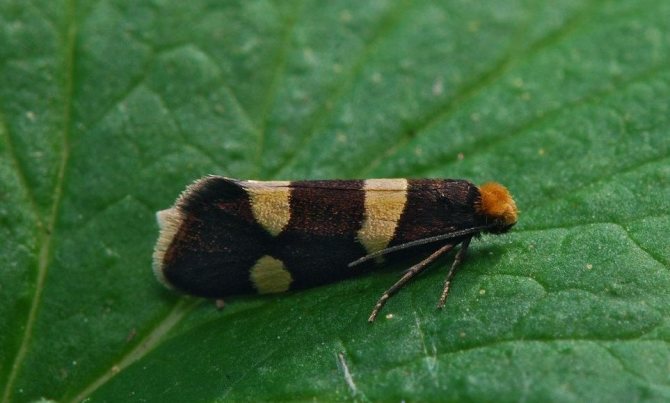


The currant kidney moth damages the kidneys and infests green berries with its larvae. It is necessary to loosen the soil before flowering to prevent the larvae from pupating. During the period of swelling of the kidneys, nitrafen is used (treatment with a solution of 300 g per 10 liters of water). The drug in the same proportions is also used to combat gooseberry shoot aphids, often affecting currant bushes.
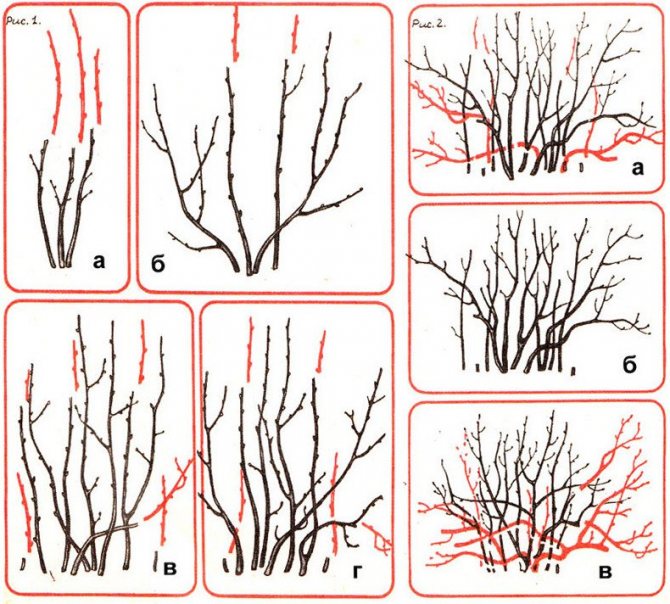
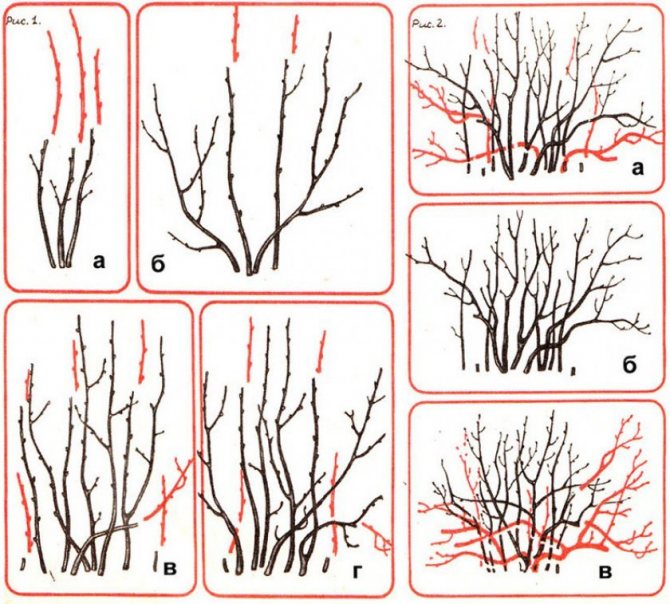
Pruning and shaping the bush
Each currant branch bears fruit well for 3-5 years on average. The bush should have 12-14 branches of different ages with strong growths from the previous year. Every year 3-4 root shoots are left, the healthiest and strongest. When forming a shrub, it is not recommended to thicken its middle, especially if it has a wide base. Therefore, a distance of 10-15 cm is left between the basal shoots.
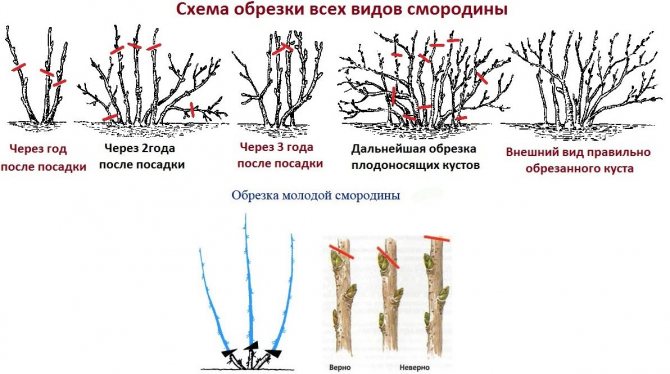

Further pruning removes weakened branches 4–6 years old, as well as dry ones lying on the ground and damaged by insects and diseases. Every year, the root collar should be deepened so that the bush has a shape, since the buds sprinkled in spring will then give strong zero shoots.
Pruning bush formation
The biological characteristics of the growth and development of currants involve regular pruning and bush formation. Basically, it is formed in the first 3-4 years. A bush at the age of four years should consist of 16-20 branches, 4-5 pieces each year. For bushes over five years old, thinning and rejuvenating pruning is carried out. Part of the young branches is cut out, directed to the center of the bush and old branches over six years old. In currants, the most productive branches are from two to five years. The yield of black currants, the quality of the berries, the durability of the plantings largely depends on proper care and the choice of suitable varieties. I hope that my information will help the Kuban gardeners in growing this useful crop, in obtaining high yields.
Harvesting and transportation (shelf life), keeping berries
Before harvesting, determine the temperature at which the berries ripened: in hot and dry weather, they ripen much faster than in cloudy and rainy weather. Taste the berry and observe the uniformity of the fruit color in the cluster. The age of the shrubs should also be taken into account: young bushes are better and more evenly illuminated due to the small number of branches, therefore, the harvest ripens on them faster than on old ones.
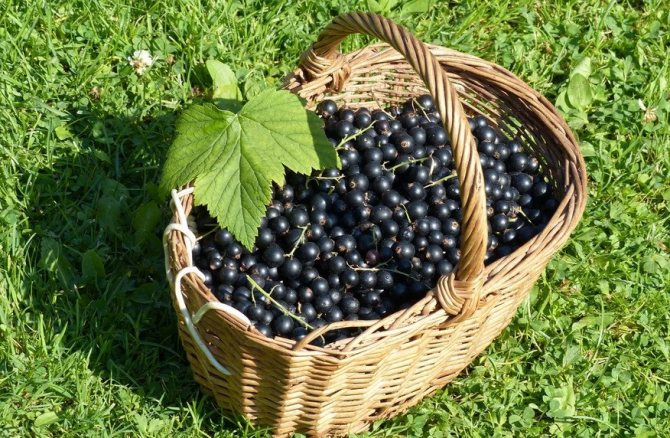


Do not delay the harvesting of crops, as overripe berries crumble, crack and lose their elasticity, which negatively affects further transportability and storage. Do not pick fruits in too hot weather, as this will degrade their quality. It is best to collect in the morning or late afternoon. You need to collect currants in a clean and dry container in which they will be stored, since it is not recommended to pour the fruits after harvesting - at the same time, they will be crumpled and cracked.
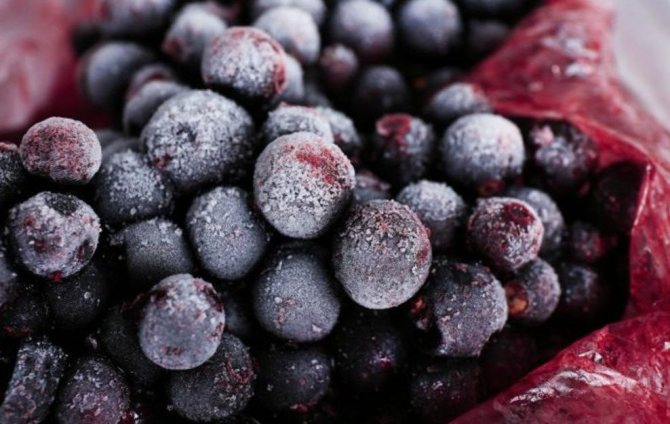
Fresh currants are stored in the refrigerator for up to 2 weeks, but remember that the berries should be washed only before use.... And if they are wet, then before putting them in the refrigerator, you need to dry them thoroughly. If you decide to freeze the fruits, then, on the contrary, you must first rinse them, then dry and place in the freezer, where they can be stored for a whole year.


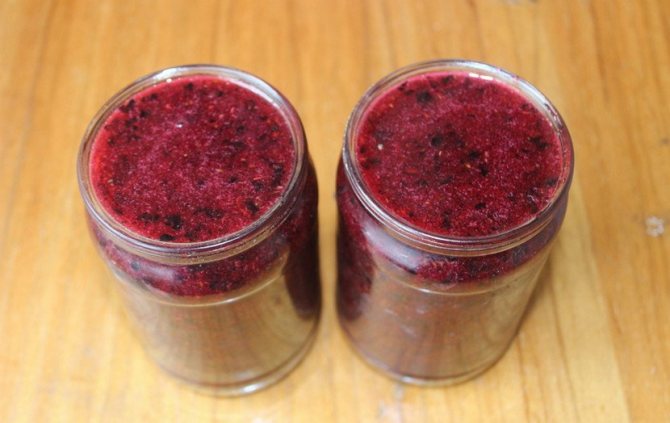
You can use the recipe for storing black currants, which will preserve most of the vitamins and nutrients - this is the so-called "raw jam":
- wash and dry 1 kg of currant berries;
- grind or grind through a meat grinder;
- add 1 kg of sugar to the resulting gruel;
- if there are more berries (or vice versa less), then the proportion is simple - 1 part berries to 1 part sugar;
- store in the refrigerator in jars with a sealed lid.


To maintain the Incomparable currant bush in a healthy, fruiting state, take care of it regularly, take measures against negative external factors, and then every year the plant will delight you with a generous harvest of berries of excellent taste.
Disease resistant
Various fungal diseases are a real scourge of modern gardening. For both prevention and treatment of diseased plants, it is necessary to spray the shrub with potent drugs. On the one hand, modern substances do not pose a threat to human health. On the other hand, the need for such events is tiresome. And the drugs are worth it.
Breeders are developing currant varieties that are resistant to most diseases.
Black sibilla
Sibylla is resistant to powdery mildew, and to other diseases, although in relation to septoria it has average immunity. In practice, Sibylla attracts not at all by its resistance to disease, but by its taste - 5 points on the tasting scale. This is a very tasty dessert variety with very large berries - from 3 to 5 g.
Fruits ripen by early July, ripen very amicably. Up to 3 kg are harvested from 1 bush. The skin is quite dense, which makes it possible to transport ripe currants.
Sibylla can withstand frosts down to -30 C, well tolerates heat and drought.
Gamma
Currants are immune to powdery mildew, columnar rust and other diseases. What's even more attractive: not afraid of kidney mites. Worse immunity to septoria and anthracnose.
The gamma produces medium berries - up to 2.5 g, with a dense, shiny skin and soft pulp. The taste is sweet and sour.


The yield is below average - 1.2 kg, but berries can be removed from the bush in a mechanized way.
The gamma needs good watering. This variety is sensitive to lack of moisture.
Sevchanka
Currants are resistant to powdery mildew, rust, scab, and anthracnose. Not afraid of kidney and spider mites, easily copes with aphids. In addition, the variety is not afraid of recurrent frosts and tolerates drought well.
The fruits of Sevchanka reach 3 g in weight, up to 2.2 kg are removed from the bush. However, the main advantage of the berries is different - an excellent dessert taste. Although the sugar content is low at 6.9%, the score on the taste scale is 4.6 points.
Grace
Currant has a very high resistance to the main enemies - powdery mildew and kidney mites. It is not so resistant to septoria. Grace tolerates both severe frosts and equally intense heat equally well, therefore it is grown in the southern regions and much further north. The variety belongs to dessert, the berries are very sweet with an almost imperceptible flavor. They reach a weight of 3.5 g. Up to 2.5 kg of berries are removed from the bush, and it can be removed by mechanical means, and not manually.