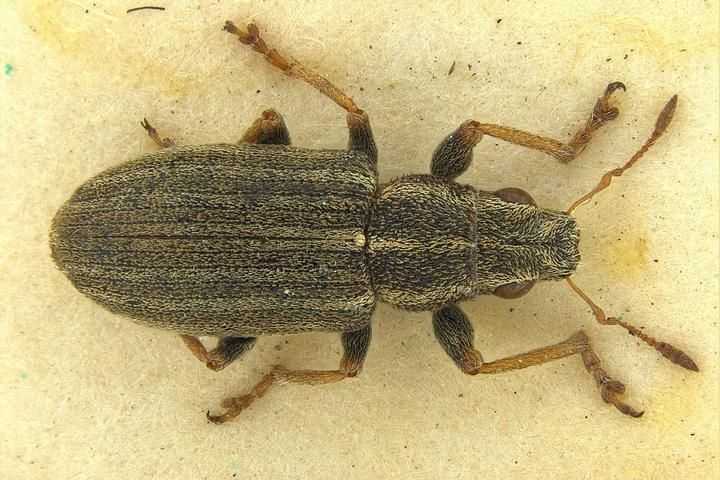
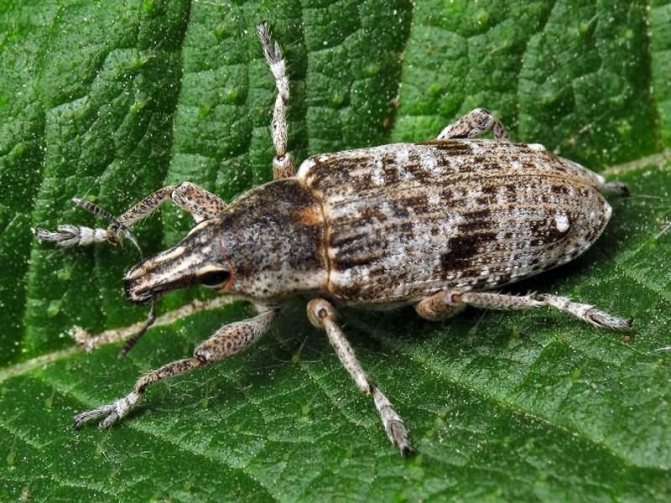
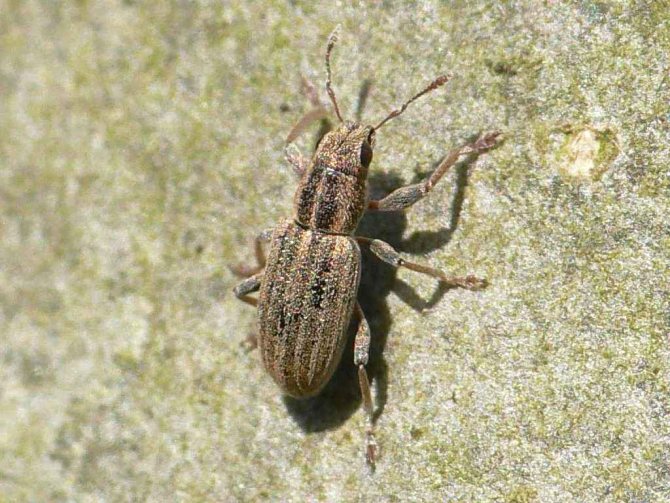
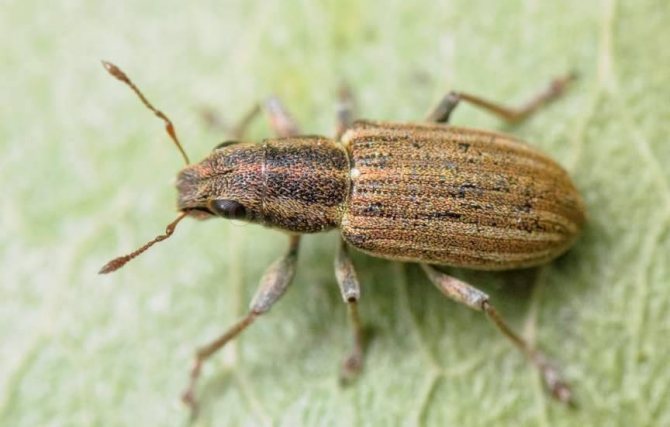
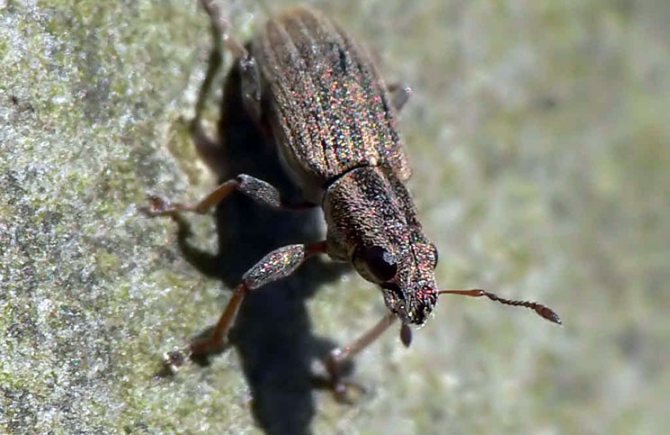
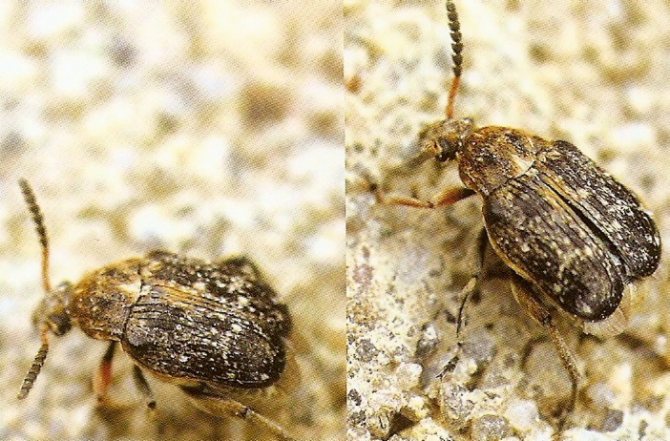
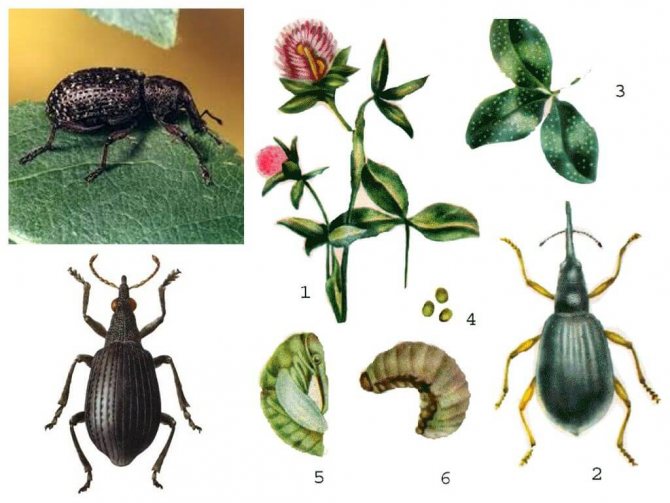
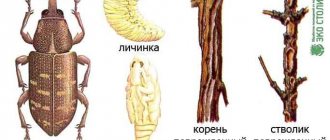
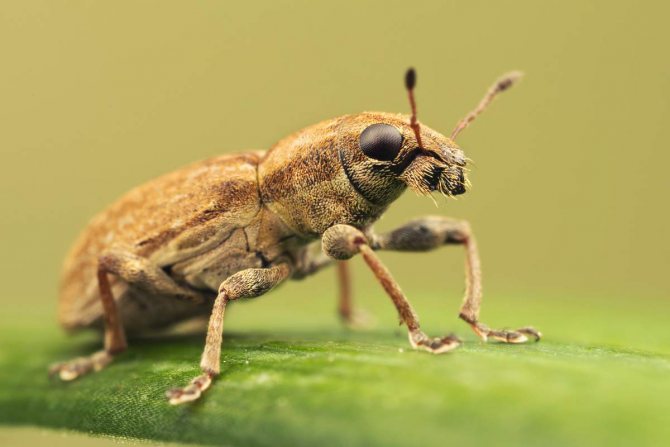
Representatives of the family of weevils are mainly found in tropical zones, but in Russia there are about 5 thousand species. A distinctive feature of beetles is an elongated rostrum, into which the front of the head has turned. The nodule striped weevil is the most common species of its kind. Adults 3-5 mm long are dangerous pests of legumes, the larva feeds on nodules.

Common signs
Egg
In different species of nodule weevils, the appearance of the eggs can vary from small oval to large, more ball-like. Egg sizes range from 0.25 mm to 0.3 mm.
Larva
White curved larva, without legs and eyes, covered with stiff, recessed hairs. Protected by chitin, the yellow head is equipped with dark mandibles, the shape of which differs in representatives of different species of weevils.
Chrysalis
The pupa, like in most species of beetles, is similar in appearance to an adult. The weevil pupa is not covered with hard chitin, since it has an earthen cradle for protection.
The soft body changes color as it grows up: if initially the pupa does not differ in color from the larva, then by the time it leaves the shelter it acquires the color of an adult beetle.
Adult
Sizes can vary from 2.5 to 9 mm.


Distinctive features of the beetle are a short rostrum with antennae attached at the base and a wide forehead with noticeable round eyes decorated with cilia, the color of which varies from species to species.
Elytra of beetles are covered with protruding bristles and dull rounded scales, mostly white or gray. On the back and elytra, specks and stripes of dark colors are scattered in disarray. The color of the legs and legs varies from deep red to dark gray.
Beetles are incredibly shy and at the slightest danger fall to the ground, freezing for several minutes.
The most dangerous species
The beetle of the weevil family is capable of harming any plant. The most dangerous of all are the beetroot, barn, nut weevil and stone fruit beetle.
Beetroot
dangerous insect for sugar beet. In the spring, before the emergence of product shoots, the beetle eats weeds, after which it gradually moves on to crops. After their "work", the beets are thinned out and lose their sugar content.
Barn view
Barn weevil - lives in grain. It is the most common in the world. Females are able to lay about 200 eggs in holes gnawed in crops. Further, the deposits are covered with secretions. After such processes, the grain is already unusable.
Walnut
Inhabits the bushes. The female eats the green fruit of the nut. The larva spoils the nut from the inside, completely eating away the flesh. If the fight is not started in time, the insect can damage the entire tree.
Stone fruit beetle
The adult eats buds and leaves. The laid-off larva is located inside the fruit (bird cherry, plum, sweet cherry and cherry). When new fruits appear, the female makes a hole in the still soft bone and lays an egg.
Breeding stages
Adult insects hibernate in the fields, waking up when the air temperature reaches a stable three to four degrees Celsius.When the air warms up to + 13 ... + 17 ° C, the beetles get up on the wing and migrate in search of leguminous plants, which lasts about ten or fifteen days.


After feeding after winter, females begin to lay eggs in May and continue this activity until July, after which they die of exhaustion. One female per season can lay from 90 to 900 eggs (the amount depends on weather conditions and food).
Eggs are laid randomly, without any preparation in the form of burying them in the ground. A sticky egg that turns out to be on a stem or leaf, after drying, simply rolls onto the ground, with which it mixes after the rain. If the air temperature is above thirty and there is no rain, the embryo dies.
The development of the embryo, which has fallen into favorable conditions at a temperature of 25 ° C, lasts about a week, after which the released larvae settle in nodules, which they subsequently feed on. After a couple of eaten tubers, the larva grows, feeds on the outside, also eating the roots of plants. Growth continues for a month, after which the larvae, which have gained the necessary mass, dig a cradle for themselves in the ground, the walls of which are cemented with saliva and earth. The cradle is easily destroyed during excavation, but if it is intact, it allows the soft pupa to develop into a young beetle in a few days.
Reproduction and development of weevils
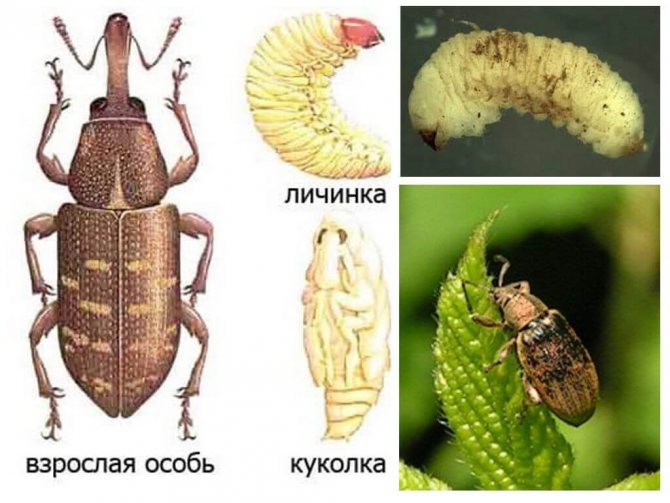


Nodule weevil larvae
Nodule weevils are famous not only for gluttony, but also for fertility. Oviposition begins in late spring. One female lays up to 30 eggs per day, during her short life she is able to produce up to 30 eggs. The female does not choose special places and scatters eggs randomly. Initially, the embryos are light in color and covered with a sticky membrane that holds the eggs on the leaves and stems. Gradually, they roll to the ground, become almost black in color, and during the rains they mix with the soil.
Important!
Temperatures above 32 ° C and lack of rain lead to mass death of eggs. Temperature and humidity levels also affect the development of embryos.
The development of the egg lasts from 6 to 30 days, then a mobile, legless larva with a small head and no eyes appears from it. A young insect crawls under the soil, where it finds plant nodules. You can determine the place of entry of the larva by a dark speck. Having penetrated into the nodule, it begins to absorb all the contents. After one shell remains from the tuber, the larva moves to the next. In the larval phase, one insect destroys 5-6 nodules.
After eating several nodules, the larva grows in size and does not fit in the tubers, so it begins to eat the outer root tissues. One pea plant can simultaneously have up to 20 young individuals. The development of the larva lasts from 25 to 40 days, depending on the climate of the habitat and weather conditions. The matured larva is buried in the soil to a depth of 10-15 cm and equips itself with a cradle for pupation. After 9-14 days, a young beetle emerges from the pupa. The newborn nodule weevil begins to feed intensively and eats the juicy leaves of peas, alfalfa vetch. After harvesting annual crops, insects fly to perennial legumes, where they remain for the winter.
Nodule weevil - pest
Already from the first days of spring, the beetles begin to feed, trying to make up for the hungry winter months. The appearance of beetles in the field can be traced by first a weak, and then an avalanche-like appearance on young leaves of legumes gnawed out areas.
In good warm weather, beetles can completely destroy the leaves of seedlings over a fairly large area, since after migration, weevils do not leave their feeding places and do not stop it even at night.
In one day, one beetle can eat up to 2 square meters. see foliage, with females eating three times as many males.
Subsequently, the larvae will join the beetles, devouring the plants from below, and adding to the mechanical damage the possibility of contracting infections.
All this leads to massive weakness and even death of plants, greatly affecting the yield. So, the yield of peas after an attack on it by beetles is reduced by 70%.
If you want to get a rich and healthy harvest, then you need to spray with urea in the fall. Pest control of the garden should include not only chemical treatment, but also mechanical methods of control. What insects can destroy our crops, read here.
Not all insect bite ointments are suitable for children. Find out which products are safe for your child by following the link.
How to deal with weevils in the garden?
Weevil Fight: Essential Tools for Effective Help.
- Top dressing with living organisms that prevent adult parasites and larvae from attacking the soil.
- Spraying chemicals. Remember to handle such substances with care. Spray the berry bushes for the first time five days before flowering. In mid-July, process the bushes a second time - this way you will destroy the new generation of beetles.
- Folk recipes for the destruction of weevils, which were successfully used by our great-grandmothers.
We suggest that you familiarize yourself with How and why the garden is processed with copper sulfate


Spraying with chemicals is a reliable protection against hostile insects. Popular drugs include Karbofos, Metaphos, Atellix.
There are so-called biological insect control drugs - Antonem-F and Nemabakt. Another way to resist is fumigation with not too aggressive drugs.
Weevil methods of struggle with the help of folk recipes have many variations. A popular recipe is to dilute one hundred grams of mustard powder in three liters of water and carefully spray the bushes with this liquid. Wormwood, tansy and hot pepper in pods are effective pest fighters. Berry bushes are sprayed with infusion from these plants.
Mix three kilograms of ash and forty grams of laundry soap. Spray the affected plants. By the way, dry ash is an effective savior of berry bushes and beetroot shoots. Sprinkle generously around the plants in early spring.
For reference! Folk remedies have a gentle effect, but remember - such safe procedures should be carried out often. Otherwise, do not expect the effect.
Good Tips: Fighting Weevil on Strawberries
The beetle eats strawberries quite often. To get a good berry harvest, arm yourself with anti-harmful insect remedies in advance. Treat plant seeds with special insecticides if desired.


Another recipe is to loosen the soil near the bushes more often (to get rid of the larvae) and fight the weeds (they are an additional bait for weevils). Try to irrigate the land regularly - beetles love dry weather, and water will disturb them.
Weevils beetles are dangerous enemies of defenseless plants that peacefully live in their summer cottage. They love to attack flowers, vegetables and berry crops - strawberries, strawberries and raspberries. Pay close attention to pest control and get a high yield from every garden.
Control methods
The beetle population is best controlled by natural factors, such as late frosts or, conversely, dry and hot weather. In such weather conditions, the number of eggs laid by females decreases, and the eggs themselves, for the most part, die.
But, of course, it is stupid to rely only on the weather, so there are a number of measures aimed at destroying beetles on landings.
Options for the destruction of beetles:


- deep plowing of fields after harvesting the previous harvest, which will allow the destruction of late larvae and pupae;
- sowing crops early, so that by the time the beetles leave the ground, the plants have time to lose their tenderness and become unsuitable for beetles to eat;
- early spraying of fields with organophosphate compounds, pyrethroids and other insecticides, which will poison adult beetles and reduce the number of eggs laid;
- spraying the edge of crops with metaphos or hexachlorane dusts, which will allow the destruction of beetles at the beginning of their migration.
Countermeasures
But, of course, it would be extremely unreasonable to rely solely on natural factors in solving the problem of pest control. Therefore, over the centuries of domesticating legumes in general and peas in particular, various effective control measures have been developed to protect plantings from all varieties of this parasite.
They can be divided into the use of a whole set of agricultural techniques and a significant arsenal of insecticides and pesticides produced by the modern chemical industry.
Harm of weevils to agriculture
The common beet weevil is not liked because of damage to the plantings of mainly various types of beets, since adult beetles eat a young plant to the state of hemp. In general, adult weevils can destroy even young deciduous plantings of oaks and lindens.
Beetles are replaced by larvae, damaging already sufficiently developed root systems of plants. The result is not difficult to predict: the plants dry out and eventually die. Taking into account the fact that up to three or four beetles per square meter on contaminated soil, the scale of the disaster is not difficult to imagine.
As a species, the African bee arose as a result of a scientific experiment. There are various ear remedies in the home. Sprays are most effective, and adhesive tapes are safest. You can find a description of these and other tools here.
You can get rid of rat mites only by calling the pest control service.
Prevention measures
It is difficult to prevent the appearance of a beet weevil on the site. In order to prevent damage to vegetable crops, it is recommended to dig deeply in the beds where the plants grew in the fall, and to remove the germinated weeds in the spring. Lack of food after waking up from hibernation will force the pest to leave the site.
If infection of crops is detected, then the bed with the affected plants must be isolated. To do this, a deep furrow is dug around, and the ground with larvae and adult beetles is treated with insecticides.
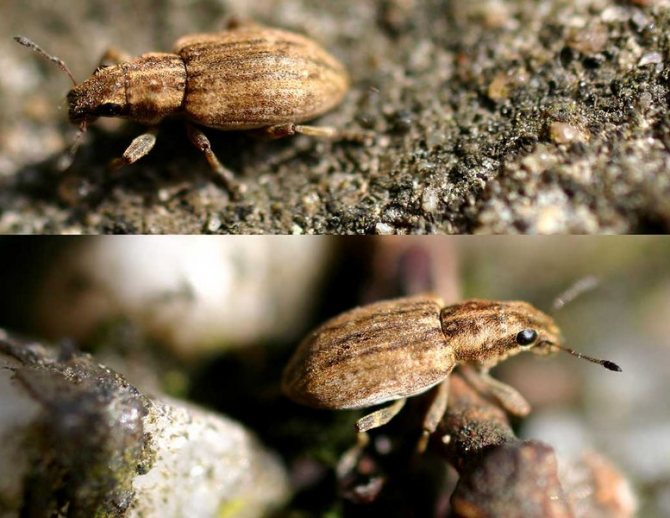
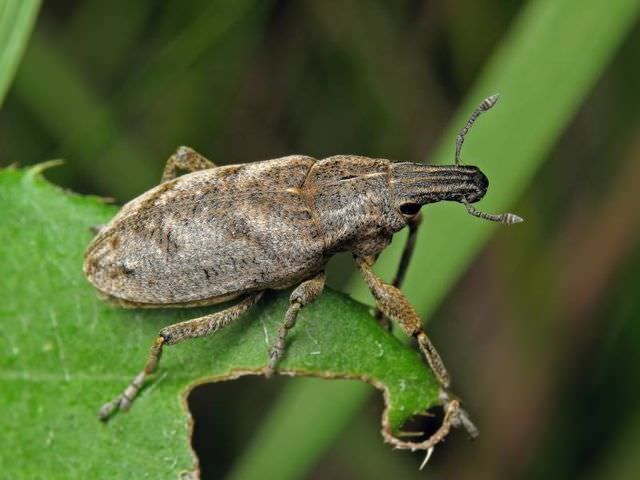
Features of the beet weevil beetle
Beet pests are up to 15 mm in size, dark in color, with thick short scales, called a sling. You can see the dogonos pattern in the photo.
Beetle eggs have an oval shape of light yellow color up to 1.5 mm. The larvae of the beetroot beetle have a light yellow color, and an arched curved shape.


The pupa of the beetle is distinguished by an oblong ovoid shape, up to 15 mm long with a characteristic yellowish coloration and a pronounced proboscis. Features of the structure dismantle photographic materials.
What damage do insects do
The beet weevil damages all types of beets, including fodder, table and sugar beets. The harm caused is noticeable even during the germination of crops, when the beetles, starving after winter, begin to gnaw the leaf mass, gnaw through the stems. The larvae damage the root system, which leads to the drying out of the testes and the death of the plants. The combination of the actions of beetles and offspring leads to a decrease in the yield of beets.


Beet weevil
Beet weevils also infect flowering plants from the family of purslane, amaranth, young shoots of oaks, maples.
What a pest of beet fields looks like
Common beet weevil - a beetle from the numerous family of weevils. In some regions, it is called the beetroot. Widely distributed throughout Europe and Central Asia. The size of the adults reaches 1.5 cm. A distinctive feature is an elongated thick rostrum. The elytra and sides are densely covered with scales. The color of the color is variable and depends on where the weevil lives. The overwhelming majority of insects are gray with dark, almost black strokes.
The beet weevil hibernates in the soil at a depth of 20-25 cm at the beet planting sites, in regions with more severe conditions it can burrow to a depth of 45 cm.With the onset of heat, when the ambient temperature reaches 8-10 ° C, the beetles come to the surface.
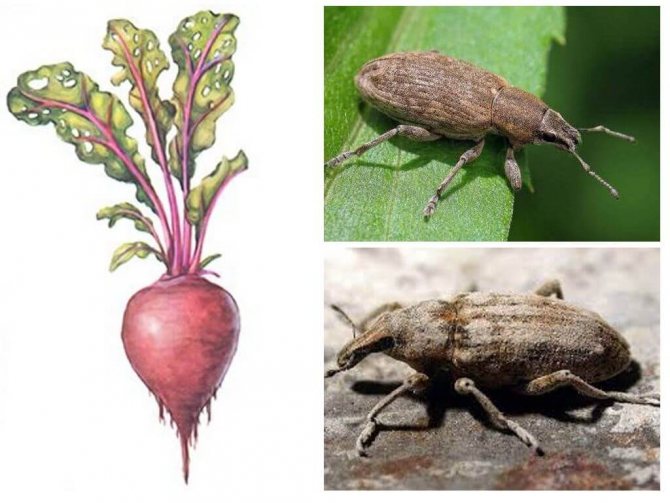

Beet weevil
Interesting!
In 5-10% of the population, the wintering stage of development passes into diapause. Insects do not leave the lower layers of the soil and remain in them until the next year.
After wintering, beetles are very mobile. Thanks to the developed legs, the gray beet weevil is able to overcome up to 300 m per day. Under favorable weather conditions, the years of weevils begin. They fly only on a hot day, when the soil temperature exceeds 30 ° C. According to the observations of biologists, the peak of flight activity occurs at lunchtime. Beetles do not rise above 4 m above the surface, in one take-off they overcome up to 500 m, and several kilometers in a day. Biology of body structure and natural data help beet weevils migrate to beet fields and populate them in a short time.
The diet of beetles after wintering consists mainly of weeds. After the emergence of beetroot seedlings, insects begin to feed on young leaves. It is possible to determine that the culprit of the defeat is the beet weevil by the specific notches on the edges of the leaves.
Interesting!
One adult beetle eats up to 15 g of green leaf mass, which is 100 times its own weight.