Beetles are the largest order of insects in terms of numbers. Among these, seemingly safe insects beetle diving beetle - the most merciless and original.


Lifestyle
Swimming beetle swims fast, being on the surface of the water, and it will not be possible to carefully examine it immediately, since it stops for a short time, after which it flaps its fins and moves on. The principle of his life is based on hunting... As a predator, he seeks destroy all inhabitants of the reservoir, even those who are several times larger than it. If the prey is small, then it holds it with its front paws and bites off piece by piece, and the larger individual can come to the aid of fellows.


What eats


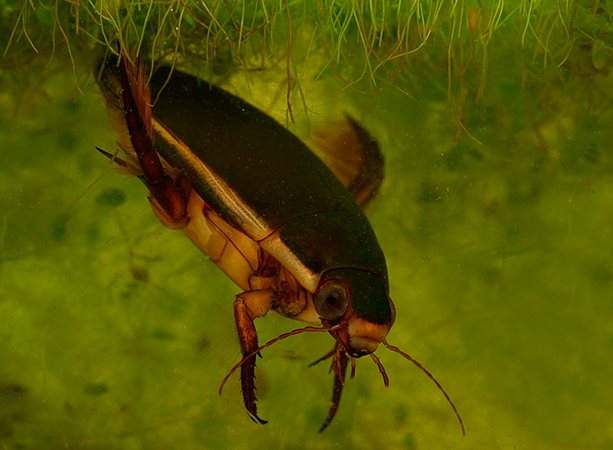
The beetle is a predator, therefore its diet consists exclusively of animal food, such as small fish, all kinds of insects, tadpoles, mosquito larvae, as well as dead fragments of underwater inhabitants.
The beetle is capable of attacking a living object that is larger than the beetle itself. It is enough for him to injure his victim so that his relatives join the attack. Since droplets of blood begin to stand out from the wound, this begins to attract other predators.
Interesting to know! If you keep a diving beetle in the aquarium, then you should offer him pieces of fish or pieces of meat as food. You should not put this predator in an aquarium with ornamental fish, as it will begin to hunt them.
External features
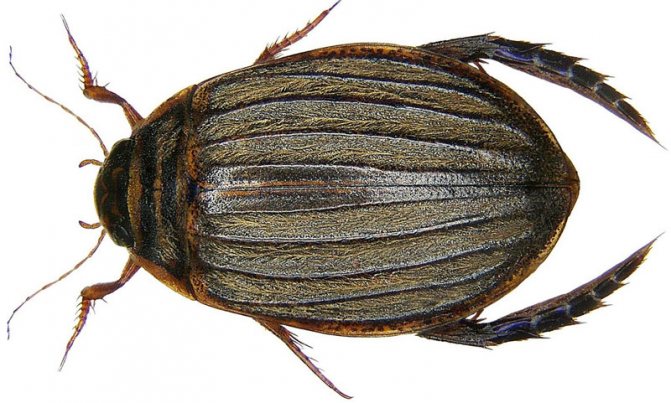
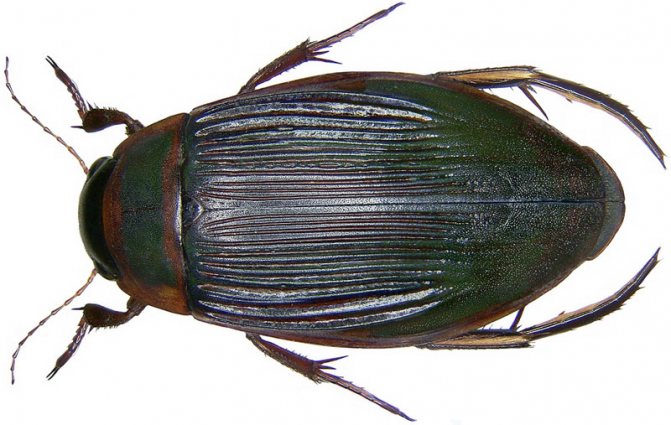
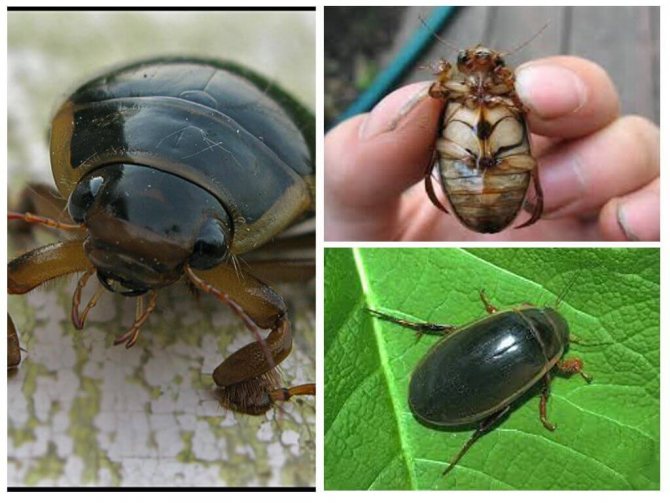
The beetle has a dark green back, and the length reaches 3-5 centimeters... There are a lot of their types in the world, about 4 thousand... The habitat is reservoirs with stagnant water, and they are more preferable to areas overgrown with local vegetation, since such conditions are teeming with various insects that are food for the swimming beetle.


Clutch of eggs
Immediately after mating has taken place, the female begins to lay eggs. Their length is about 7 millimeters, and their diameter is 1.2 mm. One female lays about 1000 eggs per season, especially fertile - up to 1500. Perhaps this is only with successive maturation, so the whole process drags on until the end of June. Eggs are laid in For protection, the female cuts them with the ovipositor, however, this does not always save future offspring from parasites. One of the most dangerous enemies for swimmers is the predominance rider. These parasites lay several dozen of their own in each beetle egg. The wasp larva feeds on the diving beetle's egg, pupating inside it. Young parasites that emerged from the dolls mate and then leave the shell. Presticia and carafractus are the only enemies of the swimmers.
Fit for life
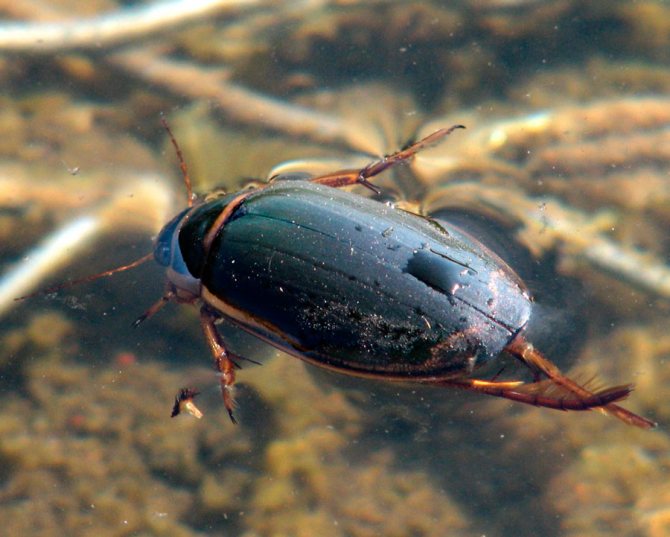
In the aquatic environment, they feel great due to lots of food and fast travel... Their hind legs act as oars, which are widened at the ends and covered with dense hairs. The principle of their movement can be compared to the movement of a submarine. They are able to stay on the surface of the water due to the fact that their body is lighter than it. When diving, beetles require a lot of energy. Plunging to the bottom, in order to stay on it, they cling to an object with the help of two front legs equipped with special hooks for this.
Diving beetle bite
The swimming beetle is a common inhabitant of fresh water bodies with a lot of vegetation and other living creatures. Therefore, anyone who is close to such water sources can meet him. Of the features of the swimming beetle, one can distinguish its rather large size (about 3-5 cm), a convex surface and an oval shape, the presence of solid wings. It spends its main life cycle in water. Sometimes it can be seen on land near the reservoir. Swimming beetle bites are more common in water.
Even the memory of a swimming beetle bite causes fear in people who have been attacked by it. The moment of the bite is felt as a sharp, sudden pain. It persists even after the termination of direct contact with the beetle. The bite resembles a puncture of the skin with a sharp object with the localization of pain in only one place. After a while, skin appears with infiltration of the surrounding tissues. If a parallel infection occurs, reddening of the skin occurs. Very often, the bite of a swimming beetle results in the formation of painful bumps that dissolve after 2-3 weeks. In case of neglect of the elementary rules for treating wounds, suppuration of the bitten site may occur. Danger to life, allergic and toxic reactions does not occur.
Structural features
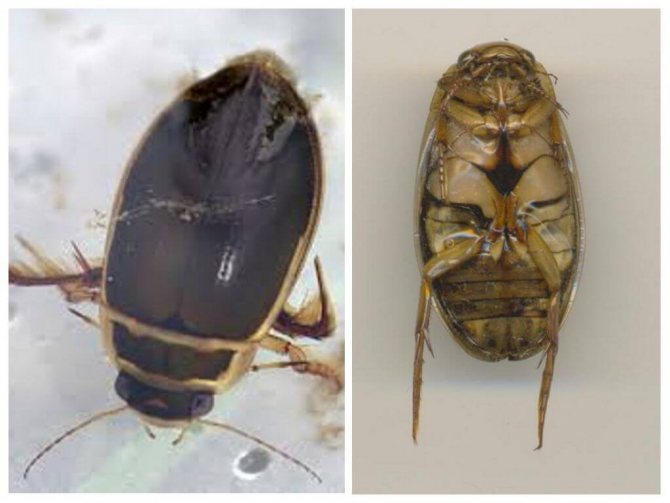
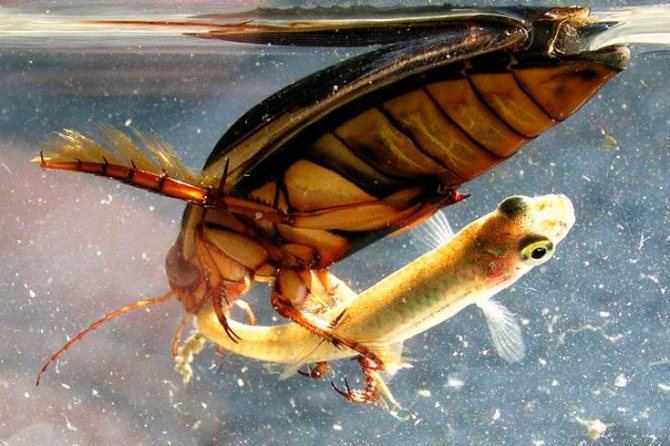
The body of these beetles consists of three parts: head, chest and abdomen... Despite the dark green color, some representatives have orange or gray edging on the body. The belly of the beetle consists of 8 segmentscovered with rigid elytra.
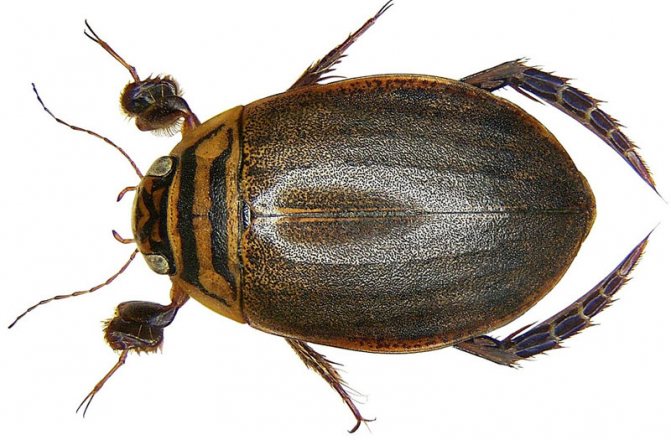
The head of the swimming beetle is flat and wide, with large eyes on the sides, each of which consists of whole 9 thousand simple eyes... They allow them to orient themselves in space, to distinguish between static objects and those in motion. The transverse plate of the upper lip conceals strong jaws, which are intended to capture, and after chewing, caught live prey. The articulated antennae located on the sides of the forehead act as an organ of smell.
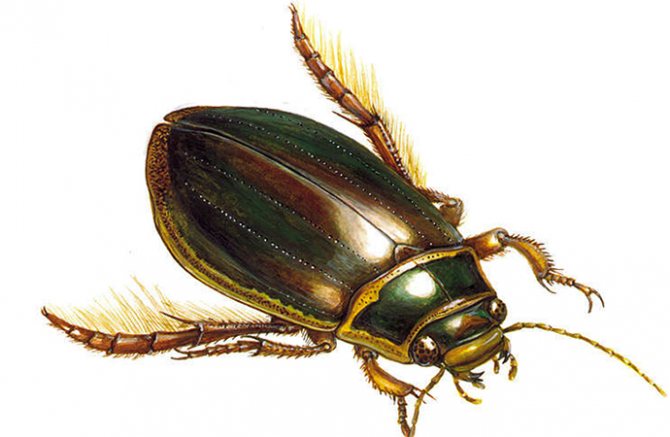


Insect lifestyle
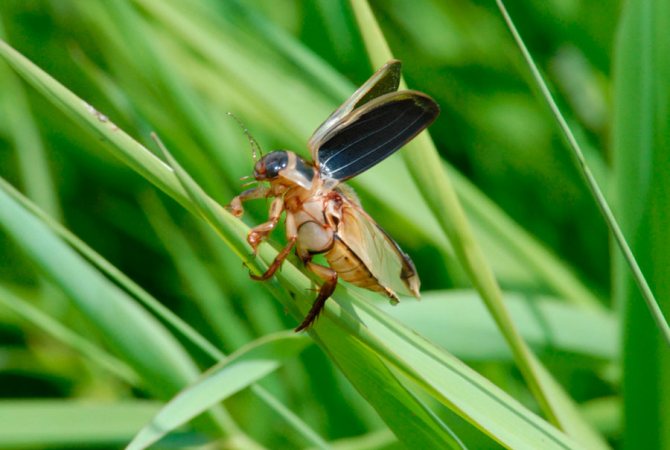


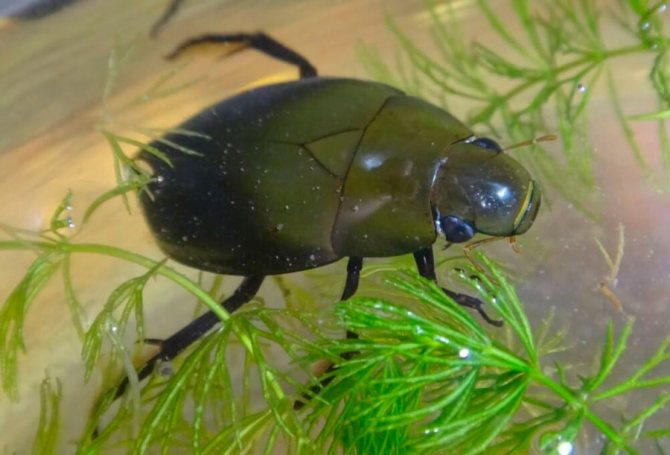
Despite the fact that the beetle can fly, it practically does not leave the reservoir if there is enough food for it. At the same time, it quite often rises to the surface of the water in order to stock up on oxygen. To do this, the beetle has a special place that is filled with air, it is enough for it to expose the back of its body out of the water.
In winter, especially in severe cold conditions. The swimming beetle does not show any activity, being in a state of suspended animation. To do this, insects dig special holes in the ground, where they wait out the cold.
Natural enemies
It would seem that small dimensions and remarkable appearance make prey for larger representatives of a small predator. However, the swimming beetle has absolute fearlessness and armed as a last resort chemical weapons... There are glands in the chest that secrete a toxic fluid, and if another predator takes it in its mouth, it will hurry to spit out such prey.
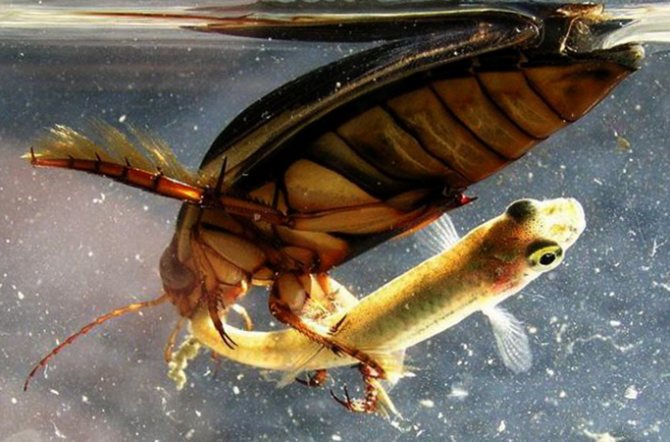


Water beetle description
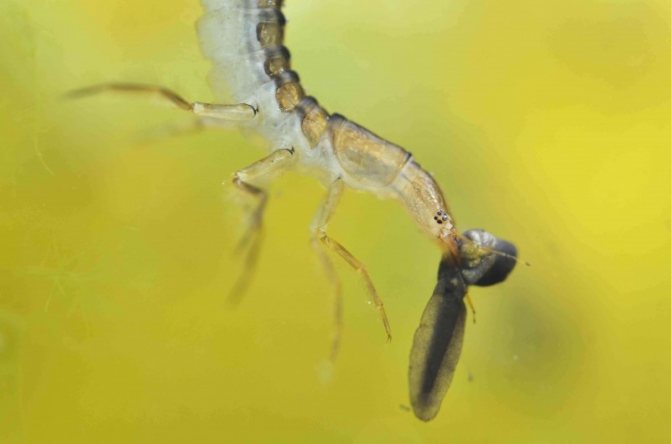
One of the most widespread representatives of the family of diving beetles of the order Coleoptera, the suborder of carnivores, is the bordered diving beetle. It is found in all the way to Asia. The family name translated from Greek means "diving". All species have a similar life cycle. Female beetles lay eggs in plant stems (only under water). The larvae that hatch from them grow rapidly and, as a result, turn into terrible hunters for the inhabitants of the reservoir. They are even called water tigers. As a rule, the size of the larva is much larger than that of an adult beetle. In just a couple of weeks, the aquatic “tiger” will become the top predator in the reservoir. The length of the swimming beetle can reach 37 millimeters.
Mating season
At the onset of winter, the swimmers hibernate, and after waking up they immediately begin look for a female for mating... To this end, they leave their habitats, and, rising into the air, are taken in search of a more suitable reservoir. When they find him, they begin to hunt females.
Mating games are not accepted by these representatives, and when the beetle sees another individual, then without unnecessary steps starts the process... The male is on top of the female and puts his abdomen on the surface for breathing, but the female has to limit herself to oxygen reserves under the elytra. It can be attacked by several representatives, which leads to death.
If the female survives, she is engaged in laying fertilized eggs in the vegetation. They are large - 7 millimeters long... The larva hatches after 40 days, and has the sole purpose of eating as much food as possible.
What to do with a beetle bite
Beetle bites are not common. They are accompanied by local changes in the skin and soft tissues in the area of the bite. Toxic reactions are extremely rare. These data suggest that you can cope with such a problem yourself.
The main thing is to know some of the features of the treatment of such bitten wounds. These include:
- Washing the bite site with plain water and laundry soap;
- Treatment of the wound with antiseptic solutions (peroxide, alcohol, brilliant green, iodine);
- Applying cold;
- Pressing down on the bitten site;
- Applying a dry bandage;
- If wound suppuration occurs, it is subject to surgical treatment of the purulent focus. It is better for a specialist to do it. After removal of purulent-necrotic tissues, daily dressings are performed with washing the wound with hydrogen peroxide and applying ointment dressings;
- The need for antihistamines and antibiotics is rare.
Education: in 2008 received a diploma in the specialty "General Medicine (General Medicine)" at the Russian Research Medical University named after NI Pirogov. Immediately passed an internship and received a diploma of a therapist.
Other doctors
‹
How to lose weight at home without dieting?
More facts
- The small size black beetle is one of the best swimmers among the order of insects, but he will not be able to rise into the air, being in the aquatic environment. To fly, you first need to climb onto a dry surface.
- If the population of the swimming beetle is too large, it will cause severe damage to fish reservoirs, since beetles and their larvae consume large amounts of fry.
- Beetles spend most of their lives on the water.
- Their habitats are not only reservoirs with stagnant water, but also ponds, ditches and even deep puddles.
- The larvae flounder in the water about 5 weeks, after getting out of it and buried in soft soil on the shore. Several days pass and adults are already emerging from there.
- To take in air, the swimming beetle needs pop up every 8 minutes.
- The paddle legs allow the beetle to reach high speeds while moving, and it does not even inferior in this to some fish... The flat and rounded body allows it to move freely in the water column.
- A representative of this species can be found near a body of water on land, which is explained by the ability to fly thanks to the wings.
- The beetle is able to attach not only to bumps, roots and debris, but also to a smooth surface... To do this, he has plate-shaped extensions located on the front pair of paws.
- The swimmer adapts well to any conditions where there is stagnant water and can feel quite comfortable even in a home aquarium.
- This representative does not have a good attitude to his fellows, and their meetings usually end in beatings, sometimes cases have even been noticed cannibalism.
Lifestyle and habitat
In nature, very rarely there are living creatures that can both fly and stay under water for a long time. Beetle diving beetle lives only in places where there is fresh water, and there is no strong current. These beetles fully confirm their name by their way of life. 90% of the time, the predator is underwater, tracking down prey or resting. Rest is most often combined with oxygen replenishment.
You can see how the beetle lies on the surface to the top with its belly, thus, it fills the organs with air so that you can then stay under water for some time and return to hunting.
Water beetle water beetle swims great, and you rarely see him in any pond. Thickets on the shores of forest lakes and small lakes in flooded meadows often collect a huge number of insects. The fast current apparently creates tangible hindrances when hunting small predators, and they also have problems when it is necessary to draw air, which is why the habitat is stagnant water.
Although the wings of an insect are adapted for flight, in order to take off, it needs to get out onto land. On land, the beetle moves rather awkwardly, goes to the wobbling, waddling from foot to foot. Swimmers leave their favorite pond only in case of drought and other natural causes of shallowing of the water space.


An interesting feature: diving beetles are also active at night. They continue to hunt even in the dark, at this time of day there are flights from one reservoir to another. Beetles do not see very well at night, which is why they often get trapped, mistaking surfaces with glare for the water surface. Diving on wet and shiny objects, diving beetles often break.
The small size and conspicuous appearance should have made the diving beetle an affordable prey for other predators, but it has a defensive weapon in its arsenal. When a danger arises, the glands of the beetle throw out a cloudy white liquid that has a disgusting pungent odor and a pungent unpleasant taste. This scares off even larger predators and is a guarantee of safety.
Relationships within the community are complex, if not violent. When two individuals meet, they fight for territory, biting and beating one one. The diving beetles experience the winter cold in cozy burrows, which they suit themselves with the approach of frost. They sleep at this time of the year.


Larva development
The larva of the swimming beetle, launching its powerful jaws into the body of the victim, releases gastric juice. This composition liquefies the insides of the victim, turning them into a liquid state. After that, the larva proceeds to the meal, sucking food in two holes located on the sides of the jaw.
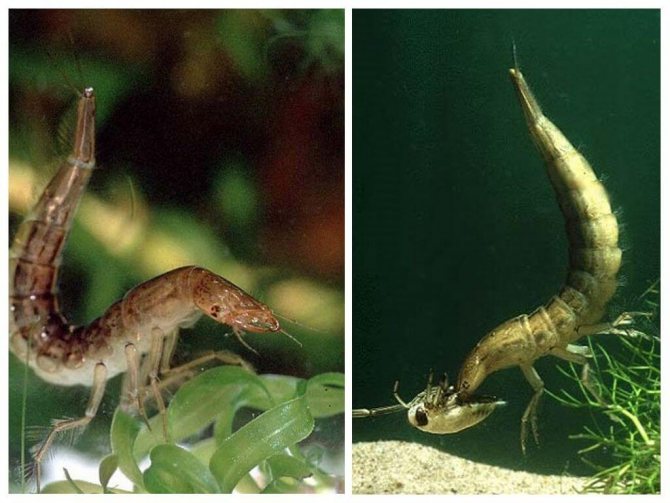


Diving beetle larvae
After two molts, young individuals strive to land, where they make shelter for themselves in moist ground. They pupate in it and stay there for 0.5-1 months (depending on weather conditions). After that, a swimming beetle appears from the pupa. He spends about 7 more days underground, until his covers become strong. As soon as the beetle acquires a strong shell, it leaves its shelters and goes into the water. The lifespan of a swimming beetle is about a year.
Unwanted neighborhood
Having settled in an ornamental pond, the predatory beetle attacks ornamental fish and other inhabitants. The owners of ponds are faced with a difficult problem, how to get rid of the swimming beetle in the pond? The least time-consuming way is to get carp, which actively destroy the larvae of the diving beetle. Another option is to temporarily install a pump or fountain that creates the movement of the water mass. The insect prefers stagnant bodies of water, so it will leave the shelter and go in search of a better habitat.
If the listed methods do not work, then it remains to drain the water, clean and disinfect the bottom. This will destroy the adults and beetle larvae.After processing, water is poured and new inhabitants are released.
You can come across a predatory beetle while swimming in the lake or in your own pool. The insect rarely shows aggression towards humans. The bite is painful, but does not pose a threat to health. The swimming beetle bites in the water if it feels threatened. The pain from the puncture of the skin remains for several minutes. After a while, the wound swells, a lump may form. Beetles are not poisonous, so there is no allergic reaction.
The victim needs to be given first aid:
- rinse the wound;
- treat with an antiseptic (iodine, hydrogen peroxide);
- apply a bandage;
- apply ice to relieve swelling.
Reproduction
Sexual dimorphism of swimmers is expressed in the difference in size (females are larger) and in the structure of the fore and middle limbs. In males, the first three segments of the tarsi are widened. They have suction plates - from ten to hundreds of pieces. They are used to hold the mate during mating. The breeding season for beetles is in the spring.
After fertilization, the females start laying. The water beetle has large eggs, reaching a length of 5-7 mm. Laying is carried out in the bottom substrate, plant tissue. The number of eggs laid per season is 1000 pieces. A sharp ovipositor makes incisions in the stems and leaves, into which an oval egg is placed. After 10-12 days, the larvae appear. In cold weather, embryo development takes up to a month.
Larva development
The color of the larva of the swimming beetle is yellow, gray, brown. Often the body is covered with a pattern of dark stripes and spots. Outwardly, the offspring looks like scorpions, not swimmers. From birth, the larvae are voracious predators. Their first food is caviar, larvae of caddis flies, dragonflies, and mosquitoes. The head is flattened, the chest consists of three segments, the abdomen of eight segments. There are 6 simple eyes on each side of the head. Antennae thin, 3-segmented at first instar, 6-segmented after two molts.
The oral appendages are located transversely. The upper lip is absent, and the lower lip is formed by a wide plate with palps along the edges. Strong mandibles curved in the shape of a sickle, the edges are pointed. They only move horizontally. The mandibles are connected by canals to the pharynx. The larvae have no mouth opening. Food enters through the jaws.
The insect digestive system is also unusual. The prey is not fermented in the stomachs, but externally. The larva plunges its mandibles into the victim's body and injects digestive juice. After a few minutes, tissues and organs soften. The content of the prey is absorbed directly into the throat. Having finished feeding, the insect cleans the mandibles with its front legs. The larva of the swimming beetle is a tireless and voracious predator, having finished with one prey, it goes in search of the next.
The elongated wide body tapers towards the posterior end, crowned with two cerci. It contains various formations: spines, bristles, scales. Three pairs of long limbs are attached to the thoracic segments. The legs have 5 segments. There are swimming hairs on the thighs and legs; the tarsus ends in two claws.
In its development, the larva changes 3 instars. The last third age is the longest. In early autumn, the larva leaves the reservoir. On the shore, she builds a cradle from the remains of plants and lumps of soil. Pupation occurs in the cradle. The phase lasts about a month. Pupa is white, soft, open type. Imago, after emerging from the pupa, is also soft and light. After a few hours, their cover darkens and hardens.
Diving beetle larvae
The breeding process of swimming beetles is activated with the arrival of spring. Having left their hiding places, the beetles go in search of a reservoir. In a new habitat, they begin to choose a partner. In the process of fertilization, males do not show signs of gallantry.Having found a female, they attack it and hold it with the help of suction cups located on the front legs.
But sometimes one female can mate with several males in a row. In such cases, the likelihood that she will survive is rather low. After all, swimmers are periodically forced to rise to the surface of the water in order to breathe. Being below at the moment of fertilization, the female is deprived of such an opportunity. But the male, being on top, can stay at the surface and get the required amount of oxygen.
We suggest that you familiarize yourself with: Cockroach dust - which powder is better and how to use
You should also take into account the fact that the mating process takes much longer than an insect can be without air under water. Therefore, if the female does not manage to climb up in time, she may simply suffocate from lack of oxygen.
After mating, the female proceeds to lay eggs. She can lay up to hundreds of eggs at a time, and up to a thousand in a season. She lays eggs on the stems of aquatic plants in the water. After a while, small larvae are born, which are so voracious that they begin their hunt almost from the moment of birth.

























