- The appearance of a mole
- Differences from other mammals
- Mole lifestyle
- When and how often moles molt
- Places where moles settle
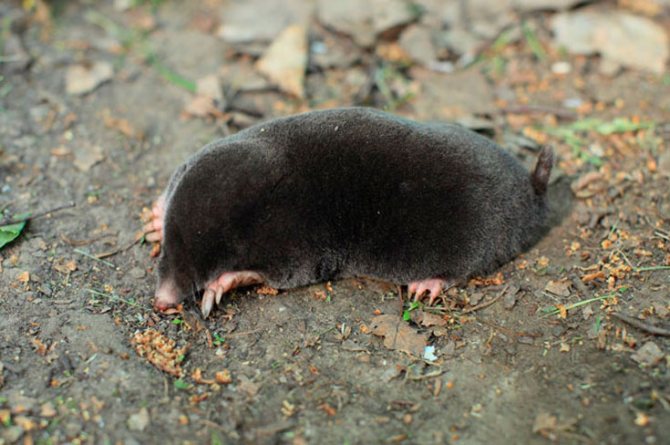
- Families and species of moles Common mole
- Blind mole
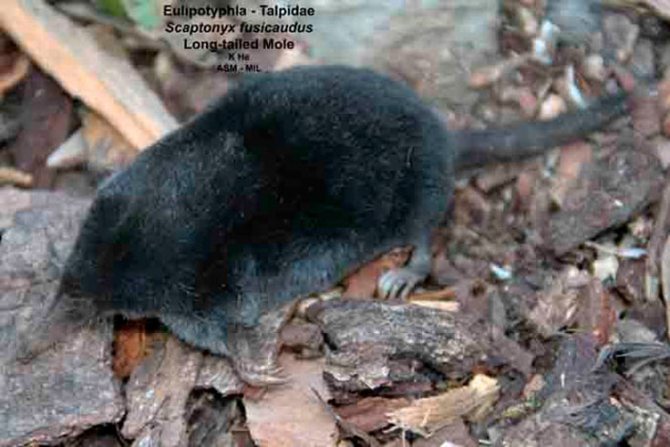
- Long tailed mole
- Caucasian mole
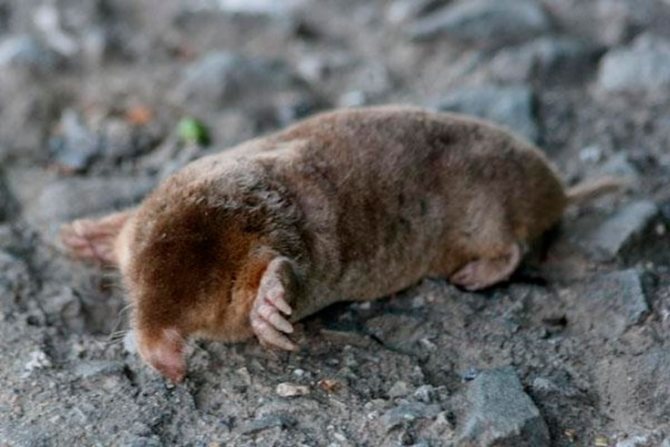
- Siberian mole
- Japanese shrew mole
- Japanese moguer
- Star-nosed
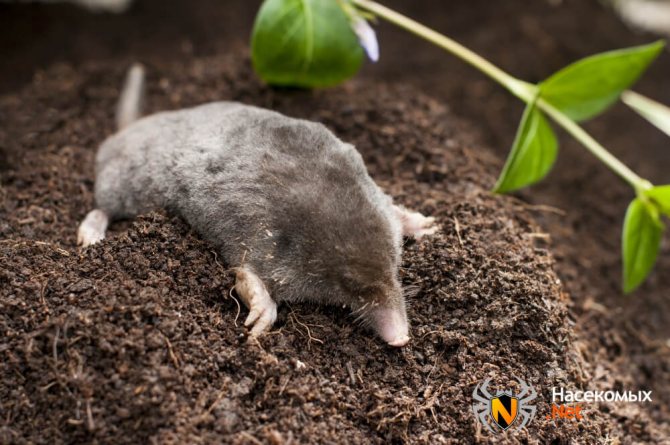
Moles are small animals that are included in the mammalian class. They eat insects, worms and larvae of various insects. It is well known that the life of a mole is limited to 4-6 years, they have 44 teeth in their mouth. Its front limbs are similar to a shovel, thanks to them the animal is able to burrow rapidly into the soil in a short time.
The name "mole" in translation means "digger". This name can be translated from German as "digging mouse". What is the appearance of a mole, how long does its life last, where are its habitats, how does reproduction take place? These and other questions will be devoted to this article.
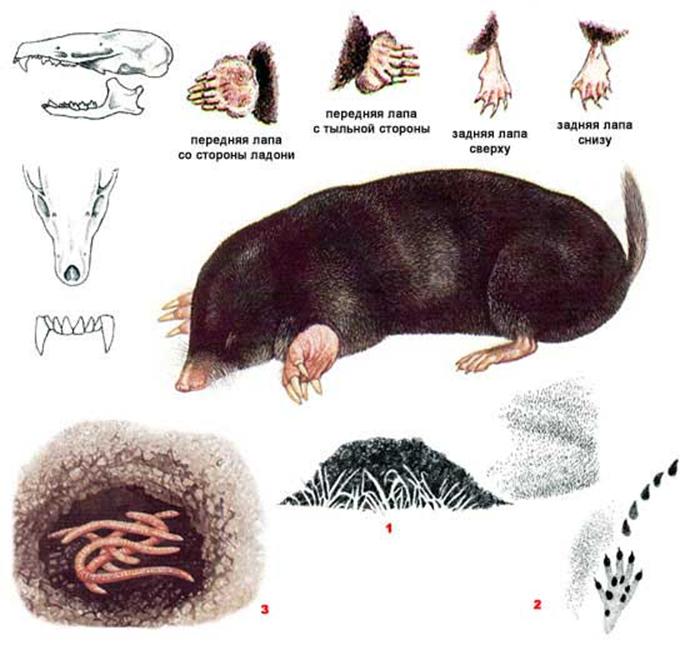
The appearance of a mole
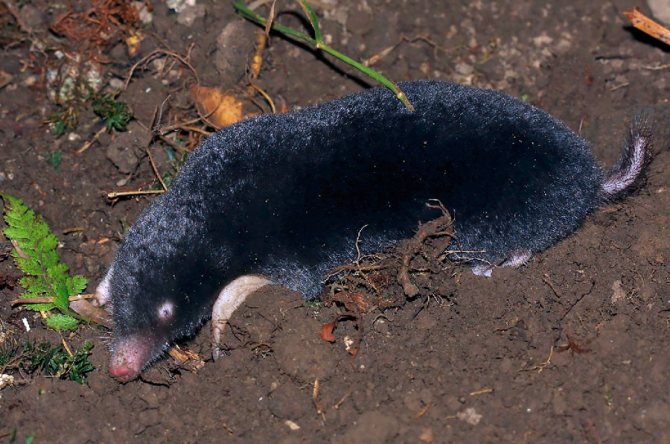
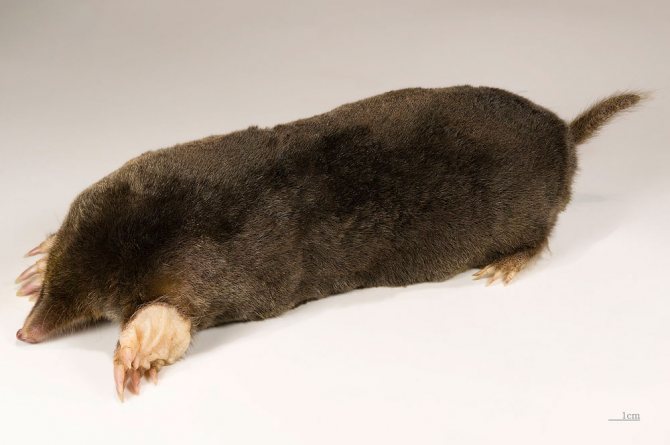
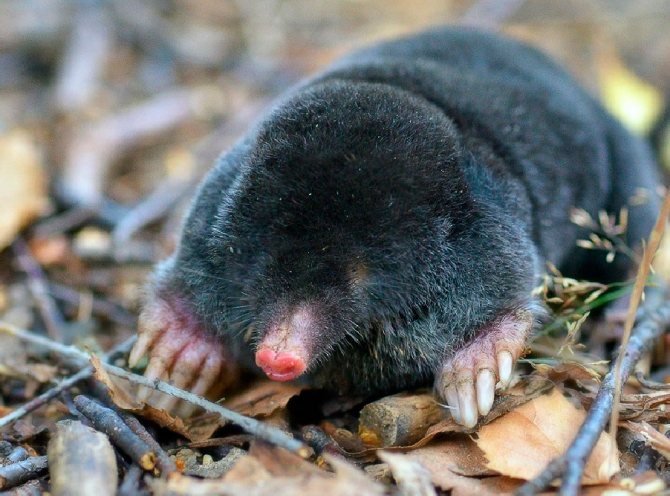
The mole is a small mammal that belongs to the order of shrews and the mole family. The size of the body of this animal can reach 20 cm. There is a shortened tail behind the body.
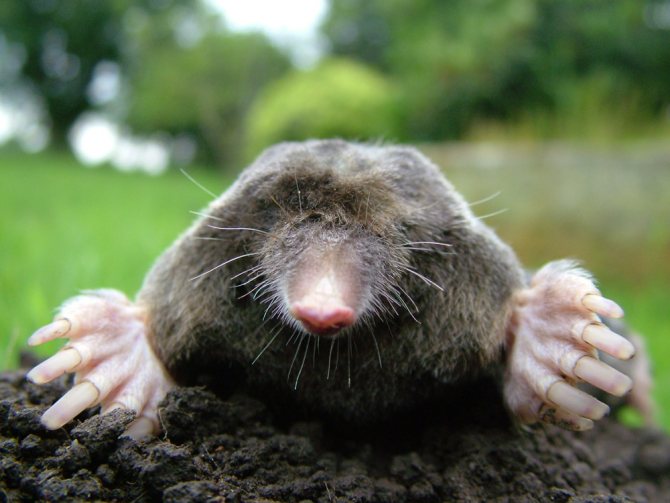
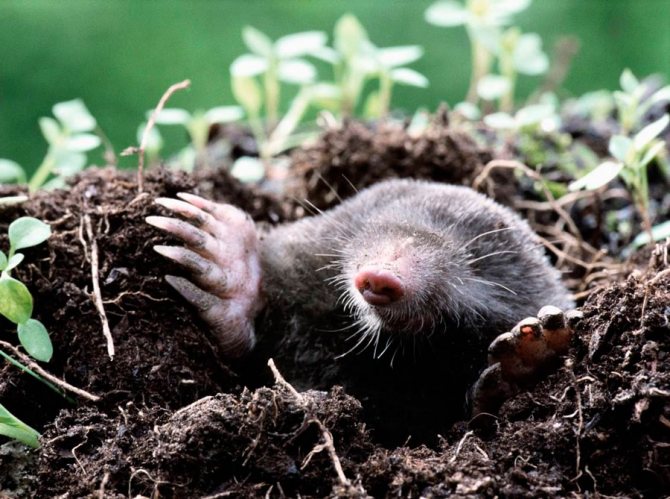
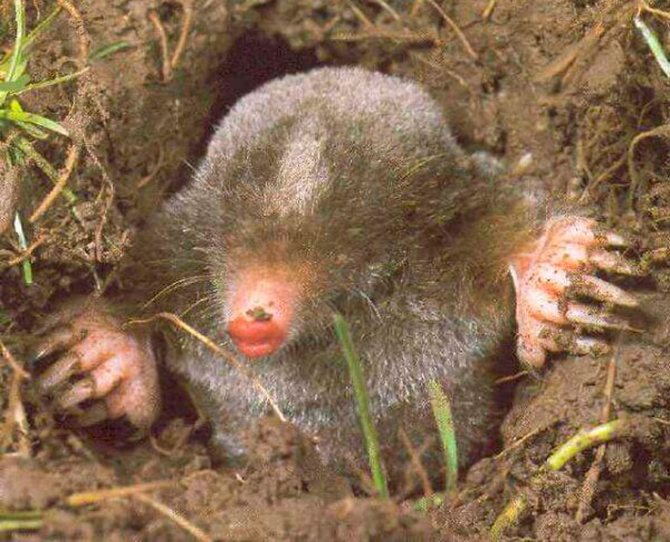
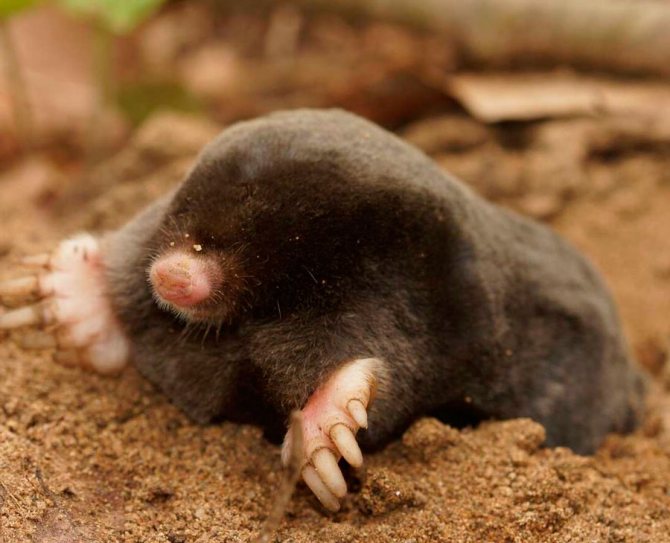
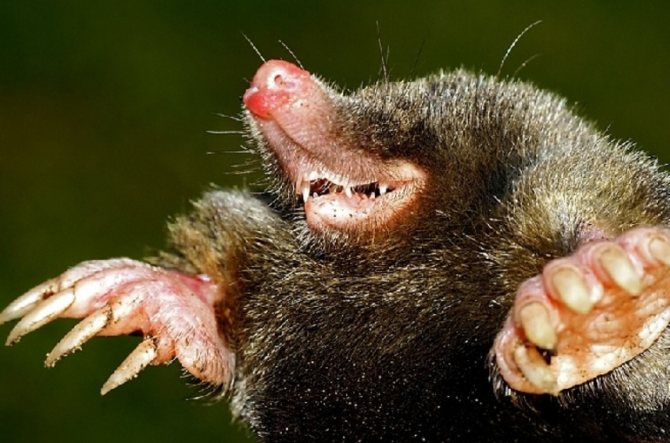
The mole is equipped with four limbs. Its front legs are very different from the hind legs, they are more powerful and look like shoulder blades turned to the sides.
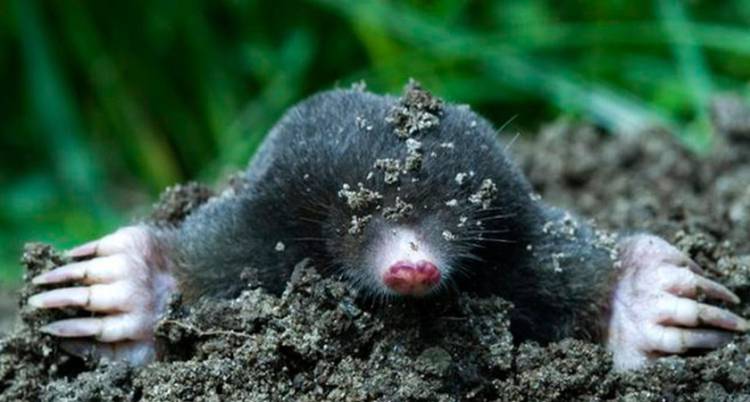
The paws have 5 toes, ending in sharp claws. At the end of the phalanx of the claws are bifurcated. It is with them that the mole digs its underground passages. Because of such bizarre front paws, the animal looks unusual, which can be seen in the photo.

The clavicles of a mole are made like a crest, they are quite well developed. The hind legs are elongated and resemble those of rats. A mole's tail is not long; its size can vary from 2 to 8 cm.
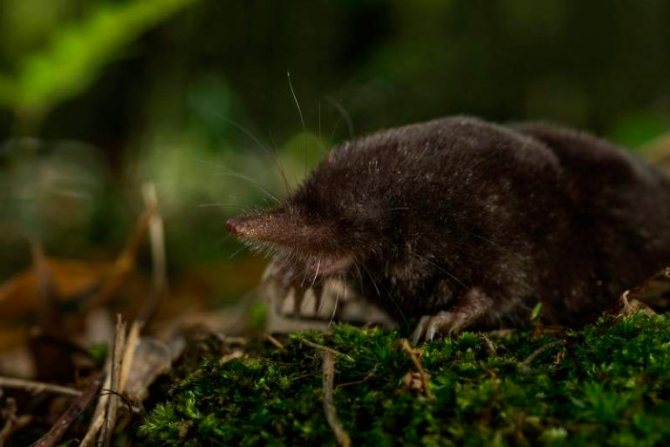
The head part of the body of the animal is of medium size, has a conical shape. The nose is slightly elongated, and the auricles are not visible at all. The sockets for the eyes are very small, and the eyes themselves are devoid of a lens. The eyelids are very flexible. In some species, a thin skin covers the eyes. Vision is so poorly developed that it can be called blind. But moles have an excellent sense of smell, hearing and touch.
The coat of a mole is usually black and evenly colored. However, there are species with brown or dark gray coat color. The hair villi grow in a strictly perpendicular direction from the skin. This allows the animal to move quickly underground in the usual way and backwards. Molting occurs in warm weather, three times within one year.
Differences from other mammals
Some people believe that moles and rodents are one and the same. However, this judgment is far from the truth. Moles have many differences from other rodents:
- Moles are not endowed with such powerful jaws, which are characteristic of rodents, so they live where the soil is very loose. It is easy to make long passes in it with paws.
- Rare rodents can swim, and the mole is an excellent swimmer. It will not be difficult for him to swim across a river of medium width.
- These diggers are completely unsuitable for life on earth.When they accidentally hit the surface, their behavior seems awkward, since they hardly see and are unable to perceive the environment adequately. On the ground, they can only move by crawling.
- Moles are endowed with weak eyesight, designed to be able to distinguish light from darkness. Therefore, with such characteristics, a mole ideally lives only underground.


Moles are distinguished from small rodents by the following characteristic features:
- shortened black fur that shines;
- an elongated proboscis in the head part, there are nostrils at the bottom;
- rather large and widely spaced forelimbs of a shovel-like type, the back of which is turned upward;
- hind legs are not large, they are poorly developed;
- small, visually impaired eyes;
- the length of the mole varies from 11 to 21 cm, and the body weight can be about 60-150 grams;
- shortened tail.
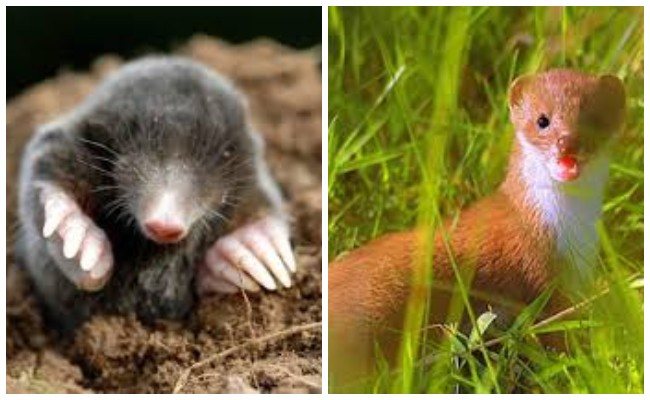
Natural enemies
As such, moles have relatively few enemies. The powerful scent protects them from foxes. They are only good for badgers. Sometimes dogs and cats hunt animals, but not to kill them, but out of "sports interest."
Pets can control the number of moles in the garden. In those households where dogs and cats live, there are almost no moles.


Mole lifestyle
Moles are considered quarrelsome animals, therefore, for a significant part of their entire life, they stay under the thickness of the earth in complete solitude. The only exception is the mating period of animals.
These diggers rarely change their habitats; most of their lives pass in the same system of tunnels, which they once dug.
Moles are endowed with two glands that produce a secretion that smells like musk. With this smell, they attract individuals of the opposite sex for mating, as well as worms, which form the basis of their food supply.
To survive, a mole needs to eat such an amount of worms and insects per day, which is equal in weight to half its weight. For this purpose, these diggers make such an extensive network of tunnels so that there are more worms and insects in them that lead an underground lifestyle.
If the network of passages does not fully provide the mole with food, it begins to expand it to the required size.


The total length of the underground passages can be several hundred meters. Moles constantly move along them in search of insects and worms, which turned out to be their easy prey. All underground communications formed by a mole can be conditionally divided into 2 types:
- Labyrinths of passages located at the surface of the earth. They act as traps for insects and worms, providing food for the mole. It is curious that a mole cannot live more than 15 hours without food.
- Moves of another type are located much deeper. There, the animals arrange sleeping quarters for themselves, take refuge in the cold periods of the year. Since the animals need moisture, they break through passages from sleeping quarters leading to water sources.
Important! Moles never hibernate in winter. They are awake at all seasons of the year and need food sources.
Habitat
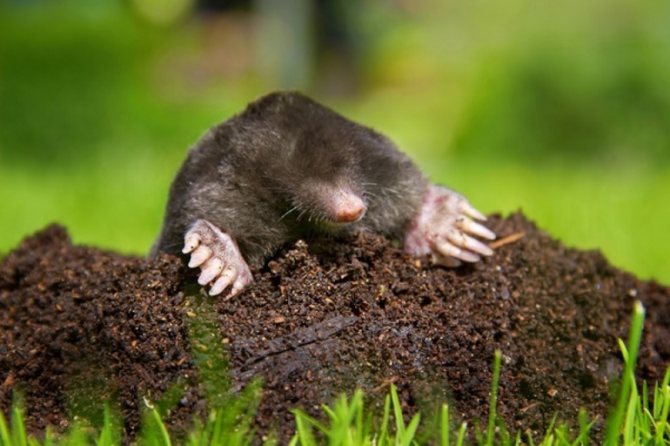
The mole spends almost its entire life in underground burrows, but not any soil is suitable for it. The animal carefully chooses its place. It prefers moist and loose soil. Another habitat for the mole is simply not suitable: it cannot break hard lumps of earth.


But sometimes soil mounds are found in fields and meadows. Excess soil is usually thrown up by the mammal. Mole rats can be active both at night and during the day. They do not care what time of day it is outside, since their eyes do not distinguish between darkness and light.
The biological rhythms of a mole are different from other animals. In a mammal, periods of activity and rest alternate. It prefers to work four hours and then sleep three hours.It is not easy for a mole to move underground, so it does not make long movements. Only on hot summer days does the animal break through the passages to the reservoirs.
Mammals do not like to be in the company of their own kind. They are loners, so they are ready to defend selected areas. Moles have a difficult character, they often show aggression. If they had to share land with neighbors, then the passages are dug so that they do not intersect with the paths of another individual. But if one animal dies, the second tries to quickly occupy its site. As a mark, moles secrete a special substance - a secret with a pungent odor.
In winter, mammals do not hibernate. The inhabitants of the underworld prefer to spend their time differently in cold weather. They dig deep holes and fill them with supplies. Only underground can moles hibernate and remain safe. If they get to the surface, they will become prey for owls, foxes and martens.
When and how often moles molt
Moles, in comparison with other animals, molt not twice a year, but three or even four times. This need arises due to the fact that with the continuous movement of a mole along underground passages, its fur quickly wears out.
As a result, it turns out that the mole molts throughout the warm period of the year. In places where molting has already occurred, the animal's skin becomes darker and thicker 3 times. However, hair on such areas of the skin does not adhere well and quickly wear out.
Moles molt for the first time from April to June. In females, molt begins a little earlier than in males. Instead of worn-out winter fur, moles receive a less warm spring skin.
In the zenith of July, adults molt again. In the same month, young animals molt for the first time.
As soon as the summer molt is completed, only a week passes and the autumn molt of animals begins. When it is completed, the mole appears in its most attractive form. Autumn fur of moles is the warmest and most elegant. It is thick, tall, velvety, black with a silvery sheen.


Places where moles settle
Moles love to inhabit the following places:
- meadows;
- forest clearings;
- birch forests and copses;
- areas near roads;
- city parks;
- garden and vegetable allotments.
Moles are often found where the soil is enriched with humus, inhabited by worms, arthropod larvae and warmed by the sun. Soil moisture is also of great importance, it should be of average values.
Mole tracks are unlikely to be found in the following places:
- dense forest;
- Pinery;
- swampy places;
- places where plants with strong roots grow.
The mole's choice of a place to live also depends on the annual precipitation and soil temperature. If the climate on the site is not stable, moles move closer to the forest, where the depth of freezing of the soil is less in winter, and moisture in the soil keeps better in summer.
The mole will constantly change its places of deployment until it finds conditions for a comfortable stay.
Families and species of moles
The Krotov family includes 4 subfamilies:
- Chinese moles;
- desman;
- mole of the New World;
- Moles of the Old World.
More than 40 species are included in these subfamilies. Six species inhabit the CIS space:
- Small Moguera;
- Deaf;
- Great Moguera;
- Common mole;
- Siberian mole;
- Small mole.
Next, we will dwell in detail on the characteristics and descriptions of each common type and see how they differ from each other.
Common mole
It is also called the European mole. Its size is 12-16 cm, and body weight varies from 55 to 90 g. The tail of an animal can have a size of 2 to 4 cm. The eyes are small, barely visible through narrow slits, they are devoid of eyelids and eyelashes.
The coat is painted in black-gray, black-brown or black tones, and the back is slightly darker than the belly. Females give birth to cubs once a year.Similar moles can be found in the meadows and forests of European countries, on the European territory of Russia, in the Urals and the territory of Western Siberia.
Blind mole
It is also called a small mole. Animals of this species are considered one of the smallest. In length, they barely reach 12 cm, and the length of their tail is only 2-3 cm. With a slipper, the mole weighs only 30 g, its eyes are covered with a skin.
Its diet includes various arthropods and their larvae. As a last resort, he eats worms. Females give offspring once a year - in early spring. This species lives in the mountains of the Caucasus, in the Turkish and Iranian territories.


Long tailed mole
This animal is 8 to 9 cm long, its weight does not exceed 12 g. The tail of the animal is 4.5 cm. The fur is sparse and tough. The system of their moves is underground at a shallow depth. Moles belonging to this species live on the Indochina Peninsula, as well as in the southern regions of China.
Caucasian mole
Animals of this species are endowed with medium size - their body length ranges from 10 to 14 cm, weight is 40-95 g, and the tail size is 3 cm. Males are larger than females. The color of the coat, after molting, is intensely black, but then gradually turns brown. The eyes are hidden under the skin.
Moles are usually located at a depth of 7 to 18 cm, and sleeping quarters are located at a depth of 85 cm. The basis of its food consists of earthworms, in addition, it does not refuse to eat arthropods, along with their larvae. Once a year, females give birth. The habitats of the Caucasian mole are the territories of the Caucasian region.
Siberian mole
It is also called Altai. Outwardly, it is identical to the European species, but surpasses it in size. The body size of males can reach 19 cm, and the mass of individual individuals is 225 g.
The size of females does not exceed 17 cm, and their body weight can be equal to 70-140 g. The length of the tail of both sexes is not more than 3.5 cm. The eyes of the animal are covered with movable eyelids. The color of moles differs depending on the area in which they live. It can be dark brown, black, smoky.
Siberian moles eat worms and larvae of various insects. They differ from other species in that the gestation period lasts 9 months. After summer mating, females are inhibited in the development of embryos until spring.
Youngsters are born at the junction of April and May. This species is widespread in Western Siberia, partially inhabits Eastern Siberia, and is also found in the southern territories of Transbaikalia and in the northwestern regions of Mongolia.


Japanese shrew mole
He is also a mole-shaped urotrichus. The animal received this name because of its identity with a shrew and a mole. The species is represented by a small animal, which is no more than 10 cm. The length of the tail is only 3 cm, it is hairy, and ends with a brush.
Their fur is soft and thick, but not velvety. The color of the coat is black with a touch of metal or dark brown. Representatives of this species jump equally quickly on the ground and along the labyrinths of underground communications.
In addition, he climbs bushes and trees, sometimes climbing up to 4 meters in height. The animal hibernates in its underground premises, as well as in empty bird nests. Females give birth to cubs once a year. The species lives on the slopes of the mountains, from their foot to a height of 2 thousand meters. Large colonies of this animal have been found in the southern territories of Japan.
Japanese moguer
The length of animals of this species is 12-15 cm. The tail is not more than 2.5 cm, and the body weight varies within 96-208 g. On the back and on the sides, the fur is painted in black, dark brown or dark gray colors. The color of the abdominal part is lighter.
The diet of the Japanese moguera consists of insect larvae, and it eats earthworms when it cannot find the larvae. Animals of this species build their moves in two levels. The first level runs at a depth of 60 cm from the surface of the earth, and the second is located at a depth of more than 1 meter.
The habitats of the Japanese Mogers are the middle and northern islands of Japan, the lands of both Koreas, the eastern provinces of China, as well as the south of the Russian Primorsky Territory.
Star-nosed
The body is 20 cm long, it has a scaly tail not exceeding 8 cm, and rare villi are observed on it. In winter, the tail becomes thicker. This species is similar to common moles in the following characteristics:
- the same structure of the forelimbs,
- no ears,
- small eyes, not covered with skin,
- thick dark brown or black fur.
Star-nosed moles are distinguished from other moles by a star-shaped stigma, which consists of 22 processes. These tentacle outgrowths help him find food in the pitch darkness. All its tentacles are mobile, with the exception of two, which are located in the upper middle. They are directed forward and do not bend.


Moles of this species are excellent swimmers and divers, and they do this not only in the summer, but also in the winter cold - under the ice. Moles do not immerse themselves in the water for fun; there they look for and eat small crustaceans and fish.
Being on land, the mole is content with its usual food - shellfish and worms. These moles can lead terrestrial life and move quickly over the ground or snow cover. They can build their own nests under rotting stumps, or they can occupy an abandoned muskrat mink.
Zvezdnos prefers moist soils located in flooded meadows or forests. It can be found in Canada, the United States, and northern Mexico.
Lifestyle


Mole lifestyle
Moles are insectivorous animals that lead an active lifestyle throughout the year. The life of a mole in nature is completely underground. The female even brings the young in a burrow at a depth of 1.5-2 m. Because of the inaccessibility of wormholes, everything about moles is not known even to scientists who study these animals.
The environment where moles live presupposes the presence of loose, moist soil. The depth of the mole passages is only 5–20 cm. They are located in the upper loose layer of soil, as the mole digs the ground with its paws. Moles cannot gnaw through passages in the ground, this is how they differ from mole rats rodents. Animals push the excess soil to the surface, forming moleholes - holes, if hit into which you can break your leg.
The mole will climb to the depth in three cases:
- Dig a passage under a strip of trampled earth and for breeding. If the animal digs a passage under the footpath, it can go deep into the ground by 0.5-1 m.
- To protect the offspring, the female arranges the birthing chamber under the roots of trees at a depth of 1.5-2 m.
- The food went too deep into the drought.
In the absence of an urgent need to bury. moles at what depth they live, on that and make their tunnels. The usual shallow depth of the passages allows the animals to breathe calmly and ventilate their homes.
Interesting!
The Caucasian species is buried to a depth of 1 m in search of food.
In nature, moles are more beneficial and harm from them is minimal. Mole tunnels help to aerate the soil, which improves plant growth. But garden owners see them as their enemies and are constantly trying to fight the moles.
What does the diet of a mole consist of?
The main mole food is earthworms. The worms, drawn by the smell of a special secret secreted by the moles, themselves penetrate the labyrinths of the animal's forage passages. The mole is busy looking for food 24 hours a day throughout the year. The animal feeds from 3 to 5 times a day, eating from 25 to 45 g of food per day.
Once full, the animal retires to the dormitory and sleeps there for 3-5 hours, curled up in a ball. When the dream passes, the animal again rushes in search of food. If the mole finds more worms than it can eat, it deprives them of their heads and drags them into special pantries. He starts eating them when he wakes up again.
It is curious that moles do not eat food of plant origin.The fibers of plants can sometimes get into the stomach of the animal quite by accident, for example, when eating worms, which had fibers in the stomach. The body of moles is not able to digest plant fibers, they are not digested out of the body.


When there is not enough food, the mole begins to dig new passages, expanding its hunting grounds. If the usual food becomes insufficient, moles begin to eat frogs, small vertebrates and even rats.
The animal spends a lot of energy on digging passages. To restore the balance of energy, the mole needs to eat a lot. On some days, the mole can eat such a mass of food that exceeds its weight.
This animal has a very good metabolism, it can digest 50 g of food within 35 minutes, moreover, only 20 grams can fit in its stomach. After 4 hours, after eating, the mole again feels hungry.
Important! In winter, moles usually do not make new moves. They spend less energy during this period and they also eat less.
Moles also need water for drinking all the time. Therefore, they equip their system of moves not far from water sources.
What do they eat
Most of the menu consists of invertebrates. They get about 90% of their food in the feed passages (tunnels). Moles are omnivorous and can eat any food available to them on the site, but most of all they prefer the larvae of beetles, earthworms and slugs.
In the first half of autumn, the mole makes food supplies near its home. They usually consist of worms, which the animal immobilizes with a bite. The volume of such "conservation" in some cases reaches 2 kg.


Reproduction and life expectancy
Moles are, in a sense, solitary hermits. They are mated in pairs only during the rutting season, when they mate for a short period of time.
Mating of males and females occurs once a year - in early spring. However, there are exceptions, for example, in Belarus, females have time to give offspring twice a year.
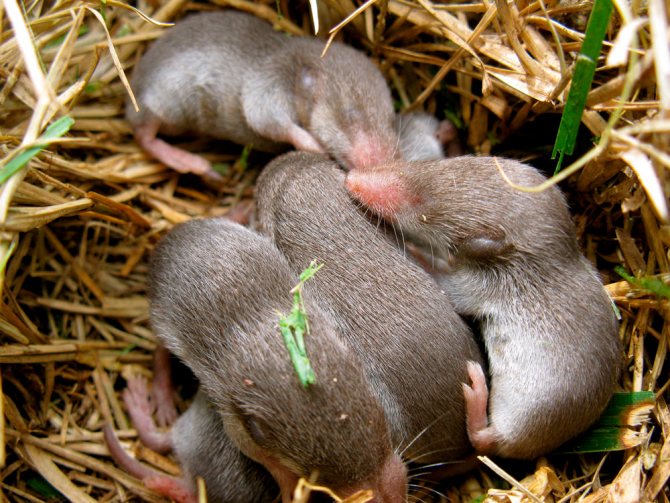
Fertilized females carry offspring for 35-42 days. The average litter consists of 6 cubs, but sometimes up to 9 of them can be born. Only the female builds the brood nest. Babies are born completely naked and blind.
Intensive feeding of young stock continues for 5-8 weeks. Only the female provides food for the cubs; the male does not take any part in feeding and raising the offspring.
By about two months of age, young animals begin to show increased aggression towards their relatives. During this period, the cubs leave the parental nest, and each of them digs its own system of moves, moving on to an independent way of life.
Mass resettlement of young moles occurs in July-August. This process takes place very quickly, in a day a young mole can be at a distance of 700 meters from the birth nest. Young animals reach sexual maturity in 6-12 months. Next spring the young are ready to mate and reproduce.
Attention! Moles in the natural environment, under normal living conditions, live from 4 to 6 years.
Economic value of moles
During the Soviet era, people greatly appreciated mole fur. The beautiful velvety skins of the animal are very durable, they were used for sewing fur coats. These fur coats were not the warmest, but they were in fashion and cost a lot of money.
In the middle of the last century, mole fishing in the USSR was in full swing. The skins of the animal were harvested in significant quantities on the territory of the country, especially in the Urals and in central Russia.
In our time, the fashion for fur coats made of mole fur has gone, and with it, such a craft has lost its significance. In some regions of Russia, moles continue to be caught and their skins are used for sewing clothes. But the volumes of such trapping are quite insignificant.
Beneficial features
The European mole has useful traits. They are expressed in the fact that earlier the animal was the object of the fur trade.The mammal has beautiful and durable fur. At the beginning of the last century, moles were hunted for their valuable skin. But the massive catch led to the fact that the animal began to need protection. In 1928 alone, about 20 million skins were procured.


In the Soviet Union, mole fur clothing became popular in the 1980s. But today in Russia mammals are not hunted, thanks to which their population has grown. Their numbers are also increased by mild winters, the construction of greenhouses, care of lawns and flower beds.
Moles improve the condition of the soil. They make it loose, saturate it with oxygen, which can save the earth from the formation of swamps. Animals exterminate pests, because they feed on them. Moles eat May beetles, beetles, insect larvae.