Common raspberry
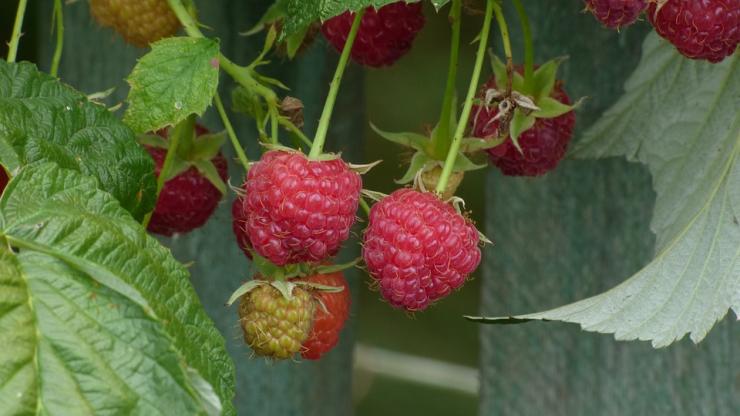
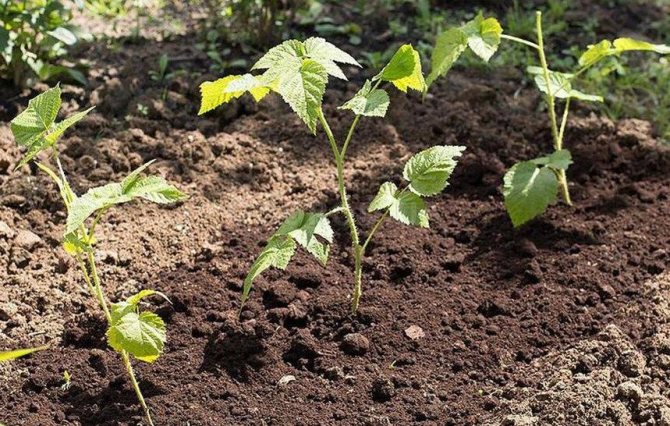
Common raspberry (Rubus idaeus l.) - The medicinal properties of the fragrant fruits of raspberries were known back in the Stone and Bronze Ages. In ancient Greece and Rome, they were used in the treatment of many diseases. Nowadays, the most famous common raspberry belongs to the Rosaceae family. Sakhalin raspberries (R. Sachal Linensis Levl.) And Komarov raspberries (R. Komarovii Nakai) are also used for medicinal purposes. This genus is represented by 250 species, of which 60 can be found in the territory of the former USSR. Raspberries grow wild in the European part of Russia, in the Caucasus, in Central Asia, in Western Siberia (up to Lake Baikal). Common raspberry is a small deciduous shrub up to 2 m high with a perennial rhizome. In the first year, raspberries develop sterile herbaceous shoots with thorns. From the second year, fruiting shoots are formed, slightly woody to the base. After fruiting, they dry out and lose their thorns. Raspberry leaves are odd-pinnate with three to seven leaves, covered with a white tomentose bloom below. The flowers are whitish, up to 10 mm in diameter, on long pedicels. They sit in the axillary racemes and are collected in a corymbose-paniculate inflorescence. Juicy, ripe, fragrant fruits - spherical, red, sometimes yellow polysperms (up to 18 mm long and 14 mm wide). They are easily detached from the conical receptacle. Juicy drupes are covered with hairs. Seeds are small, hard, round. Raspberries are planted in light areas protected from cold northerly winds. The best location of the trenches is considered to be from north to south or from north-east to south-west. The root collar of seedlings should not be allowed to deepen, as this leads to slow development and death of plants. The soil around the plantings of raspberries is mulched with manure, peat, sawdust, etc.


The lifespan of a raspberry shoot is one and a half years, a remontant raspberry is one year, so pruning the shoots during planting has a beneficial effect on the survival rate of raspberries. Planting raspberries too late in the fall in open ground is not recommended. Late purchased seedlings can be stored in a plastic bag with slightly damp fresh sawdust; it is advisable to store them in a cold room at a temperature not higher than + 4 ° C. If raspberry seedlings are planted in fertile soil, then in the first year of planting, you can not feed them. In early spring, you can fertilize with a complex fertilizer "Sotka" Universal in a dose of 80 - 100 g per m2.
Reproduction of raspberries
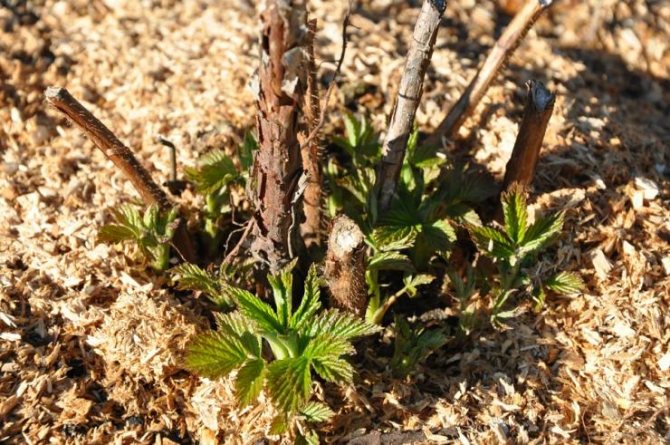
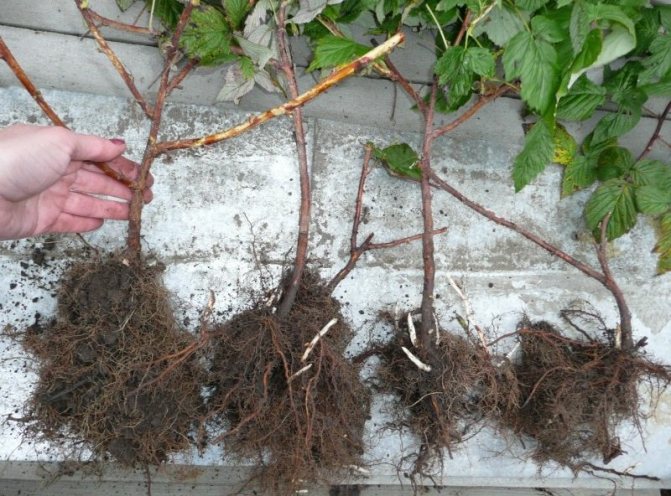
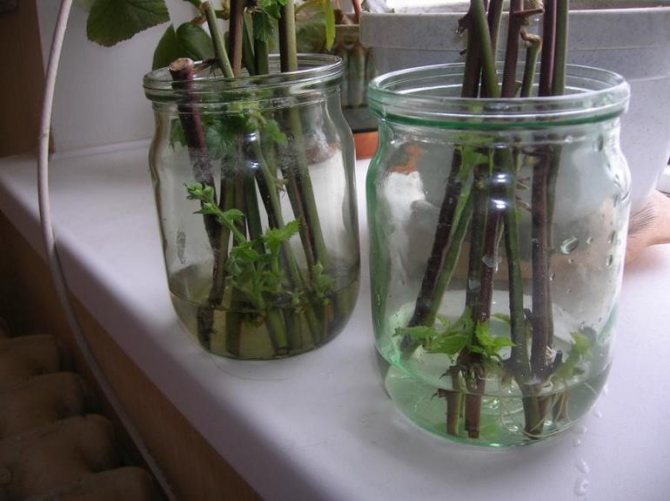
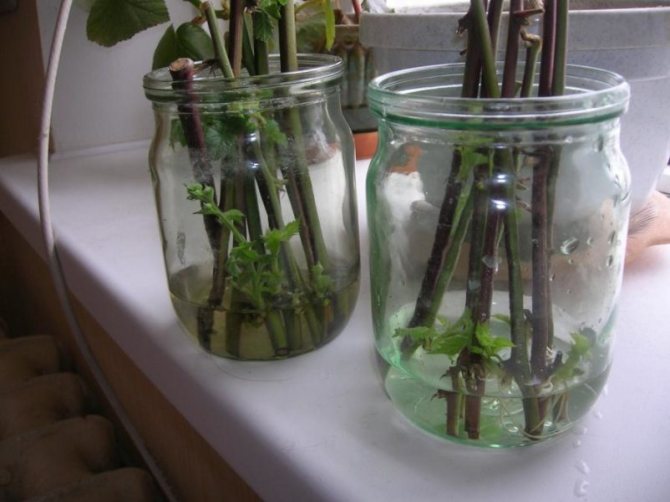
The main breeding method for raspberries is by root suckers. In autumn, root suckers with a thickness of at least 1 cm and with 1-2 large buds are cut to a height of 30-40 cm and dug up. Raspberry varieties that form a small number of offspring are propagated by root cuttings. Cuttings are dug up in the fall and stored until spring in wet sand in the basement. Cuttings can be planted in the fall. Also, the reproduction of raspberries can be carried out by green cuttings, which are formed in early summer. When the root suckers reach 2-3 cm in height, the formation of 2-3 leaves, they are cut off and planted in a substrate of peat, soil and sand in a ratio of 1: 1: 2
Repair raspberry
There are many varieties of remontant raspberries.I will cite only some of them that are suitable for cultivation on the territory of our republic. These are: polana, brilliant, hercules, golden domes, Bryansk miracle, firebird, golden autumn, penguin, ruby necklace, Indian summer.
Conditions for rapid breeding
In the process of breeding raspberries, certain rules must be taken into account. This will help to grow high-quality planting material and get a bountiful harvest in the future.
It is advisable to pay attention to the following points:
- It is better to take sprouts only from strong bushes. Strong shoots and clean foliage are signs of a healthy plant.
- It is better to place the garden in the southwest. Raspberries love the scattered rays of the sun.
- During rooting, young shoots are watered more often. But at the same time, an excess of moisture should not be allowed.
- The soil should be slightly acidic and loose enough. When planting shoots, it is undesirable to strongly compact the ground.
- When growing seedlings in a greenhouse, the humidity level should be about 90%.
It can be maintained using a special pump that is placed in a water tank. Or sprinklers are installed - devices for creating a fog effect.


Hercules
The Hercules variety is medium-sized (1.6 - 1.8 m), the shoots are strong, erect, do not require support, the autumn fruiting zone is more than 1/2 of their length. The first harvest is carried out in early - mid-August, before frost has time to ripen 60 - 80 percent of the crop. Berries weighing 5 - 6 g of intense ruby color. Productivity 1.5 kg per bush. Shoot-forming ability is low, forms only 3 - 4 shoots. The variety is resistant to major diseases and pests, its disadvantage is excessive spine of the shoots.
Healing properties
Few people do not know about the healing properties of raspberries. It is actively used for the prevention and treatment of respiratory diseases, eliminating the signs of fever. Also, raspberry root helps to stop bleeding., which is important for people who have a low platelet count.
If you regularly take infusions and teas from raspberry root, you can cleanse the body of toxins and toxins. Based on the reviews, this product helped in the fight against sciatica, atherosclerosis and anemia.
Golden autumn
Golden Autumn is a large-fruited remontant variety with bright golden yellow fruits. Suitable for low-cost and environmentally friendly cultivation technology with annual removal of the aboveground part after fruiting. The berries are large (weighing 4.5-5.0 g, maximum - 7.0 g), beautiful elongated-conical "chiseled" shape, dense, transportable, drupes are small, homogeneous, tightly adhered to each other. Dessert berries with a delicate "raspberry" aroma. The fruits are suitable for fresh consumption and all types of processing. The yield is high - up to 15 t / ha and more. Autumn harvest in the Bryansk region is 2-2.5 kg per bush. The beginning of ripening of berries is in the second half of August, fruiting is long. Potential yield is realized by 90-100% before autumn frosts. The variety "Golden Autumn" was obtained from free pollination of interspecific elite selection 13-39-11. In 2001, it was allocated to the elite under the number 24-139-2, since 2004 it has been multiplied as a variety. Authors - I.V. Kazakov, S.N. Evdokimenko. This variety received recognition for its high productivity, large-fruited, unusual for yellow-fruited varieties, and attractive color.


What is it good for and what is it that heals?
It is good to take raspberry root if you have a weak immune system. This part of the plant is considered healthier than leaves and berries. Many people take this part of the bush to heal from bronchial asthma and diseases of the lymphatic system.


If a man or woman develops hemorrhoids, this product will help relieve the symptoms by stopping the bleeding. There is information that malaria can be cured with the help of raspberry root.
- Other diseases that this product treats include:
- Pharyngitis and laryngitis.
- ARVI.
- Diseases of the skin.
- Diarrhea and heartburn.
- Pain in the abdomen and inflammation of the digestive organs.
- Open ulcers.
Due to the presence of salicylic acid, it has an analgesic effect. It also increases sweating, which helps reduce fever and strengthen the immune system. If a woman has painful periods, then a decoction of raspberry root will help ease the pain.
Did you know? The minimum amount of useful components is contained in yellow raspberries. The most useful is the black variety, which is rarely found in European countries.
Penguin
Penguin is an early ripening variety with a standard type of bush, prickly. The crop fully ripens in the first half of September, on average 1.7 - 2 kg are removed from the bush. Berries weighing 4 - 5 g have a dark raspberry color, good taste, can survive on the bush for up to five days without crumbling. "Penguin" is a short 1.1 - 1.3 m, compact bush of 5 - 8 shoots.
It is recommended to plant remontant raspberry plantations in late September - early October or early spring. Early autumn planting before the second half of September leads to poor plant survival and overwintering. This is due to the fact that the biorhythm of development of remontant raspberries differs from the usual one. In remontant raspberry varieties, the outflow of nutrients into the roots, the growth of the root system and the accumulation of reserve nutrients occur later, so you should not rush to planting the plants. When planting, care should be taken that the root collar is at the level of the soil surface, and only on light soils it is allowed to deepen by 3 - 5 cm. With deeper planting, seedlings develop slowly, offspring appear out of time, often plants die. If the root collar is placed too high, the roots may dry out in the spring-summer period and freeze them in winter.
After planting, watering and mulching with rotted manure or peat is required. The choice of a planting scheme is largely determined by the biological characteristics of varieties, soil fertility and the level of agricultural technology. For most varieties, a distance between rows of 1.5 - 2 m is recommended, and between plants in a row of 0.5 - 0.7 m. If raspberries cannot be planted in autumn, then they are planted in early spring. In this case, the seedlings are dropped in an inclined position and must be watered.
To obtain high yields, it is necessary to have strong and well leafy shoots.
Repairing raspberry of all nutrients removes nitrogen from the soil the most. Phosphorus and potassium with good filling of the soil during planting can be enough for many years. In the first half of summer, preference is given to nitrogen fertilizers; in the second half of summer, complex fertilizers are used. Specific doses and rates of their introduction are selected in accordance with the level of fertility and the quality of the pre-planting soil preparation of the site. For better plant development and obtaining a sufficient number of root suckers in the strip, raspberries should not bear fruit in the first year after planting. As buds form on fruit twigs and when replacement shoots appear, the entire old aerial part of the seedling is cut off with a secateurs and burned. This causes the active awakening of root buds and the formation of new offspring. It is enough to have 4 - 6 fruiting shoots on one square meter.
Most varieties of remontant raspberries have erect bushes and can be grown without support. In case of strong winds and high crop load, it is still recommended to tie them to a trellis. The first garter is carried out when a height of 30-50 cm is reached, the second is 1.2-1.5 m. After harvesting, the above-ground system is completely mowed.
Reproduction of remontant raspberries
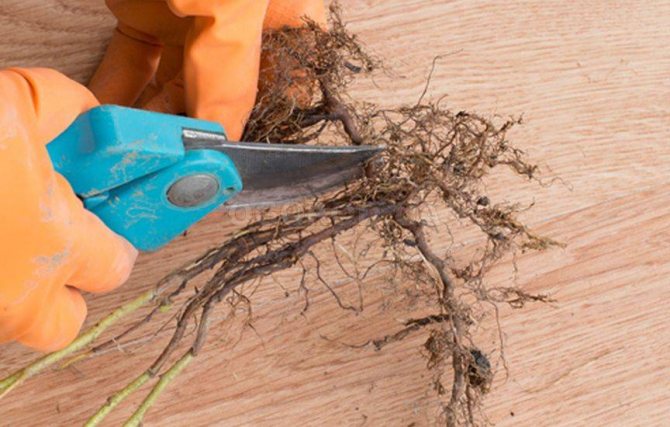
A feature of the remontant raspberry is the relative difficulty of its reproduction by traditional methods.On the one hand, a moderate number of replacement shoots and root suckers greatly simplifies planting care, on the other hand, it creates a shortage of planting material. However, there are several agrotechnical techniques with which you can accelerate the reproduction of remontant varieties. So, if in the fall or early spring, 2 - 3 years after planting, carefully remove the central part of the bush (10 - 15 cm in diameter), then up to 2 dozen high-quality offspring-seedlings will develop from the roots remaining in the soil.
Raspberry cuttings
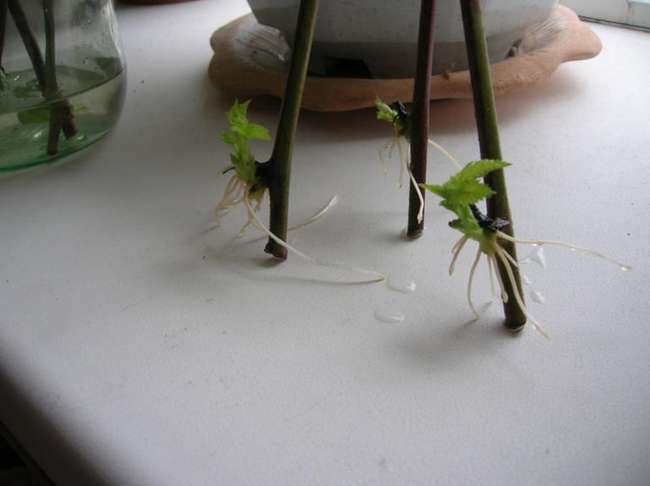
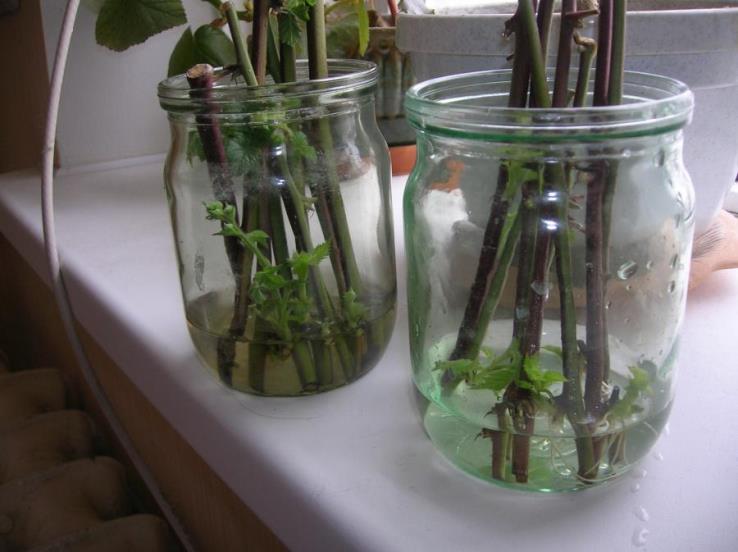
Good results are obtained by propagating raspberries with green cuttings. Unlike other berry crops, in which green cuttings are harvested only from the aerial part of annual, not yet lignified shoots, raspberries on a green cuttings must have a part of the shoot that grew underground. This is the so-called bleached or etiolated area. Usually, green raspberry cuttings are harvested in late spring or early summer. Due to the fact that the formation of buds on the roots and their awakening do not occur simultaneously, the offspring also appear at different times. For this reason, the operation of harvesting and rooting green cuttings should be carried out several times. At the same time, the best results can be obtained with spring cuttings. This is due to the fact that the first green cuttings develop from larger buds on the roots of the plant and they are better supplied with nutrients and growth substances. In addition, the development of plants in the initial period during spring cuttings occurs in more favorable weather conditions. For harvesting green cuttings, shoots are considered the best, in which the aerial part is not more than 3 - 5 cm. Usually, such shoots have not yet begun to grow the shoot, but only a rosette of leaves has formed. (In fact, a very young root offspring is considered a green cuttings in raspberries). These shoots are sometimes called nettles. It is quite possible that the leaves of this "nettle" will not yet be fully formed and have not yet green, but a dark crimson or bronze color. Shoots with a larger aerial part, in which the stem growth has already begun, take root worse, therefore, overgrown green cuttings (offspring) are not very suitable for rooting in a greenhouse. It is better to leave them in place and then use them to obtain a seedling from a well-developed green offspring, or leave them next to the mother plant until autumn to obtain a lignified root offspring from it. Some varieties of remontant raspberries, at a young age and with good care, form an excessive number of replacement shoots. If some of them are not removed in time, the bush will thicken and, as a result, the yield will sharply decrease. In this case, with early spring removal of excess shoots, they can also be used for green cuttings. Cuttings suitable for rooting are not dug out. As a rule, it is cut with a sharp knife at a depth of 3 - 5 cm and carefully removed from the soil. Excess shoots of replacement from the base of the perennial rhizome can not be cut off, but carefully broken off. Usually, cuttings for green cuttings are harvested in the morning, when they have the maximum amount of moisture. It is advisable to carry out the work in cloudy, rainy weather in order to protect the leaves from rapid evaporation of water. When harvesting green cuttings in dry and hot weather, they are immediately slightly moistened and stored in the shade, wrapped in a damp cloth and polyethylene, until planting. Do not store cuttings in water before planting. Such cuttings will root poorly, because water will wash out a significant part of the nutrients and growth substances from their delicate tissues. For high-quality rooting of green raspberry cuttings, the preparation of a greenhouse or greenhouse is of decisive importance. Rooting should take place in a well-moisture and air-permeable soil, which is prepared by mixing equal parts of coarse washed river sand and peat.(Good results on rooting green cuttings were obtained on other substrates - on pure perlite, a mixture of sand and vermaculite.) The layer of such soil for rooting should be about 10 cm. A large amount of nutrients during rooting of green cuttings is not required, therefore, during preparation no mineral fertilizers are added to the soil. The lower cuts of cuttings, in order to avoid rotting, can be powdered with charcoal before planting. The scheme of planting green raspberry cuttings for rooting is 5 x 10 cm. They are planted at the same depth at which they grew in the open field or 1 - 1.5 cm deeper. The planted cuttings are watered. On top of the landings, you can throw a non-woven covering material, and cover the arcs with plastic wrap over the arcs. In sunny, hot weather, gauze, old tulle or 1 layer of newsprint can be thrown over the polyethylene, which will prevent overheating, which is undesirable for the cuttings. In conditions of high soil and air humidity in the greenhouse, as well as at optimal temperatures of 18 - 250 C, rooting of green raspberry cuttings will occur in 15 - 20 days. As soon as the cuttings begin to grow, they can be fed with a solution of complete mineral fertilizer and gradually begin to accustom them to direct sunlight and low air humidity. In 3 - 4 weeks after planting, green plants begin to be transplanted either into containers with a volume of 0.5 - 1 l, filled with loose nutrient soil, or to the growing area (according to the scheme 10 x 30 cm). Green cuttings can be successfully carried out on a windowsill in an ordinary flower pot under an ordinary glass jar, just like houseplants are propagated. With this method, an amateur gardener can easily control soil and air humidity, as well as light and temperature conditions, which allows up to 90 - 95% of cuttings to root. As noted, remontant raspberries can be propagated by green root suckers. Unlike green cuttings, they have a more developed aerial part, a stem 5 - 20 cm high and leaves with a sufficiently large supply of nutrients are formed. In addition, many green suckers already have small roots on the bleached (etiolated) subterranean part. * Green suckers are not so tender compared to green cuttings and do not require special attention when growing them further. The most developed offspring from the mother bushes can be immediately transplanted to a permanent place. At the same time, in order to reduce moisture loss, they remove 1 \ 3 - 1 \ 2 of the leaf apparatus and shade for the first 10 days. If the green offspring are weak, or a new place for planting remontant raspberries is not prepared, they are planted in a small greenhouse or in open ground, while providing shading and a small shelter for the first 2 weeks. Planting scheme 10 x 30 cm.
Reproduction of raspberries by green cuttings
Reproduction of remontant varieties of raspberries by green cuttings and green offspring is constrained by their insufficient number formed on mother plants. In part, this problem can be solved by regular (1 - 2 times a month) mulching of row spacings on plantings with humus, as well as by covering the row spacings with plastic wrap in spring. At the same time, mulch stimulates the development of a powerful root system and the laying of a large number of buds on it, and the spring shelter increases the temperature in the root layer and thereby accelerates the awakening of these buds. A large number of high-quality green cuttings can be obtained if individual bushes of remontant raspberries are grown in large and strong plastic bags in the year preceding cuttings (according to the technology described in the "New Opportunities" chapter). The next year, if these bags are brought into the greenhouse, then in conditions of high temperature and humidity, green shoots will begin to grow rapidly in them.The experiment carried out in Chelyabinsk has shown that up to 30 high-quality green cuttings can be cut from one such package, with a volume of 10 liters of nutrient soil, in one season. This method of obtaining a large number of cuttings has another advantage. The plastic bag itself, although there should be drainage holes in it, prevents the spread of the root system and the intertwining of the roots of different varieties of raspberries. This excludes re-grading and makes it possible to reproduce several varieties of it at once in one greenhouse, which is especially important for small backyard plots. For the propagation of scarce raspberry plants and especially new varieties, the so-called Scottish method of obtaining seedlings is used by rooting green seedlings from root cuttings. This method was successfully tested at VSTISP by Professor V.V. Kichina and other scientists. The essence of the method is that in late autumn, before the onset of frost, the roots are harvested from the desired varieties of raspberries. Root cuttings are harvested in late autumn before the onset of frost. The dug roots are cut into cuttings 10 - 15 cm long, while their thickness should be at least 1.5 - 2 mm. The moistened cuttings are placed in boxes, layered with fresh moss and stored until March in an ordinary basement at a temperature of 2-40 C, avoiding drying. In early March, root cuttings are horizontally placed in boxes up to 5 cm filled with a mixture of 25% sand and 75% peat and sprinkled on top with the same mixture, with a layer of 1 - 1.5 cm.Then the boxes are well moistened and transferred to the greenhouse, where the air temperature is maintained about 22 - 250 C. After 10 - 12 days, the first offspring appear, and after another three to five days they can already be separated from the root cuttings. At this time, the height of green offspring is at least 3 cm and they have 1 - 2 leaves. The offspring are cut from the root with a sharp knife or safety razor blade. Green offspring harvested in this way must necessarily have an etiolated lower part with a length of at least 1 cm and end with a heel (part) consisting of root bark. Further, rooting and growing are carried out according to the same scheme as described above for growing seedlings of remontant raspberries from green cuttings. From one root cutting, you can get 10 or more green offspring, which are cut as they grow every 3 to 5 days during the month. Using this method, you can get up to 200 seedlings from one raspberry bush in a year. Less effective from the point of view of the multiplication factor, but a simpler (not requiring the use of greenhouses and storage facilities) method of propagation of raspberries by root cuttings planted directly into the ground. With this method, the roots and rhizomes harvested in late autumn with a diameter of more than 1.5 mm are cut into cuttings 7-10 cm long.Then they are planted on a well-prepared area filled with organic and mineral fertilizers, in furrows cut through 25-30 cm to a depth 2 - 3 cm. The plot is watered, mulched and covered with tops or coniferous spruce branches for the winter in order to freeze the soil more slowly. In the spring, as early as possible, the shelter is removed and the ridge is covered for two weeks with plastic wrap. As soon as green offspring begin to appear, the film is removed and the usual planting care continues. By the fall, seedlings grown from root cuttings grow to standard sizes. The lower yield of seedlings with this method of reproduction, compared with the previous one, is due to the fact that the first seedling from the most developed bud on the root cuttings begins to dominate, substances are synthesized in its tissues that prevent the germination of other buds. If it is not removed in order to obtain a green cutting for further rooting in the greenhouse, then this shoot may be the only one that will develop from a root cutting into a standard seedling. "
Raspberry application
In medicine, fresh raspberries are used, containing substances valuable for the human body: carbohydrates - fructose (up to 8.1%), glucose (up to 4.2%), sucrose (up to 6.5%); organic acids (up to 3.0%) - malic, citric, formic, tartaric, nylon, folic, salicylic; tannins (up to 0.3%); vitamin C (up to 45 mg%), carotene (0.3 mg%), B vitamins (traces), PP; anthocyanins, coumarins, pectin substances. The seeds contain fatty oil (up to 15%) and phytosterol (up to 0.7%), P-sitosterol, fatty acids. Infusion of fruits or raspberry tea is used as a diaphoretic and antipyretic agent for colds. Dry raspberries brewed in the form of tea are considered a good remedy for colds and flu. The method of application is simple: 2 tablespoons of dry raspberries are brewed with a glass of boiling water, infused for 15-20 minutes and filtered. Drink as hot tea 2-3 times a day. Vitamin tea is also widely used: rose hips, raspberry, currant and lingonberry leaves, taken in equal proportions. Two tablespoons of the mixture are brewed with a glass of boiling water, left in a tightly sealed container until cooled, then filtered and sugar or honey is added to taste. Drink 1/2 cup 2 times a day.
Raspberries
Fresh frozen and dried raspberries are used as an anti-sclerotic agent due to the presence of fatty acids and beta-sitosterol in them. However, raspberries are contraindicated in kidney disease (nephritis) and gout, since the fruits contain many purine bases. People with medicinal purposes, along with the use of raspberries as a diaphoretic and antipyretic agent, also use leaves that have a good astringent effect. Raspberry juice is very tasty. The washed berries are passed through a juicer, followed by filtration through a canvas cloth. After that, the juice in an enamel pan is heated to a temperature of 85 ° C, kept for 5 minutes and poured into jars preheated in a water bath. Pasteurized in the same way as blackcurrant juice. Raspberry juice can be used to make a healthy drink. To do this, mix a glass of juice with 1/2 cup of orange juice, add 2 tablespoons of lemon juice and sugar syrup to taste. All this is mixed with a bottle of mineral water and immediately served on the table. Raspberry is an excellent honey plant, the honey productivity of which is up to 100 kg / ha.
Raspberry leaves
In Tibetan medicine, the leaves and stems are used for neurasthenia and nephritis. Infusions and decoctions of flowers in folk medicine are used externally for erysipelas of the skin, acne of the face. For acne, an ointment prepared from one part of fresh juice of raspberry leaves and four parts of petroleum jelly or butter is also used. Water infusions (10 g per 200 ml of boiling water) of the leaves gargle with sore throat and inflammation of the larynx. They are used internally for inflammatory bowel diseases, respiratory and skin diseases (eczema, atopic dermatitis, acne, etc.). In home cosmetics, they previously used a decoction of raspberry leaves with potash to dye hair black.
How to propagate, depending on the season?
When planting raspberries, you need to focus on certain dates. Then young plants will take root well. Each season has its own characteristics:
- In the spring, planting begins after the snow melts. In this case, the soil should warm up, but not dry completely.
- In the summer, you need to be in time before the full budding. In the heat, raspberries will not be comfortable. Therefore, it is better to plant it no later than mid-June.
- In the fall, the transplant is carried out before the first frost. Plants need time for rooting - at least a month. Otherwise, there is a risk of freezing and death of seedlings.
Important! For the winter, young shoots are sheltered. For this purpose, hay, sawdust or needles are suitable. In the spring, the protective layer is removed. In extreme heat, the buds will not bloom.
How to breed in the summer?
In the warm season, it is better to propagate raspberries by dividing the bush. In this case, the height of the shoots should be at least 15 cm. If the stems are higher, they must be shortened. Then the dormant buds will begin to develop.
Breeding technology:
- the bush is dug out together with an earthen lump;
- divided into several parts;
- place the seedlings in the prepared holes;
- fertilized with humus and potassium salt;
- watered abundantly.
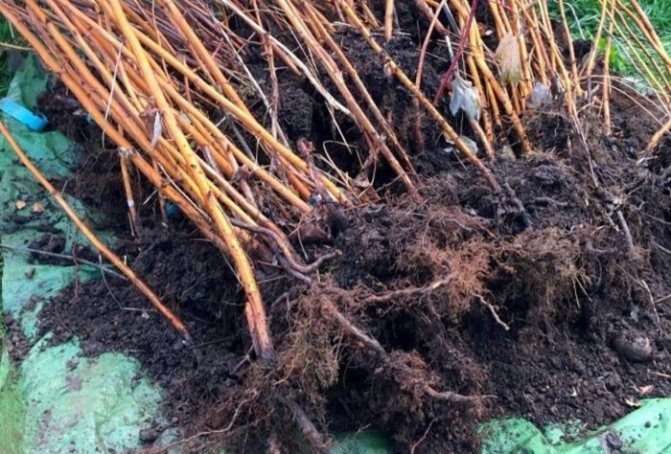


Attention! The strongest shoots are located closer to the center of the bush. This must be taken into account when selecting material.
How to dilute in the fall?
It is necessary to plant raspberries before mid-September. Then the seedlings will take root before the arrival of cold weather. For this, the method of propagation by root suckers is used.
The order of work will be as follows:
- Garden bed preparation. First, a trench 20-25 cm deep is dug. Thin branches and mown grass are laid at the bottom. A layer of plant compost is poured on top. The remaining space is filled with soil.
- Application of mineral fertilizers. You will need phosphorus and potassium - 30 g for each sq. m beds.
- Selection of planting material. Root offspring are cut to 20 cm. For small shoots, you can simply pinch off the top. Then all the food will go to the stem.
With the arrival of spring, young shoots will grow in place of the old shoots. But for this, raspberries must have time to take root.


5 / 5 ( 1 vote)
When to harvest planting material
The methods of harvesting planting material can be used for almost the entire calendar year. For example, breeding with horizontal layers - in summer, on spring days - harvesting green cuttings, breeding by the "nettles" method, reproduction by dividing the bush. In autumn, they take care of root and stem cuttings, as well as offspring of the rhizome. Seeds from ripe berries are picked in the middle of the autumn season.


We will tell you about everything in detail, including the optimal timing of the reproduction procedures, later in each of the methods. You will be able to decide when to start propagating remontant varieties and which method is acceptable for you both in terms of time and labor costs.
Care after landing
Regardless of which of the propagation methods was chosen, the seedlings after transplantation always need care and attention. At first, you need to carefully monitor them, water them so that the soil is moist. Moreover, it should not be too waterlogged, in such a ground the roots can rot. It is also impossible to overdry it, in which case the plants will not develop normally. For watering, it is better to use a watering can, rather than a hose, so as not to wash away the soil near the plants with a stream. A good option would be to use a drip irrigation system.
Do not forget about loosening, they must be carried out carefully, not going too deep, so as not to hurt the growing roots. It is necessary to remove weeds in a timely manner so that they do not stun low raspberry plants. It is possible to reduce the labor intensity of growing seedlings in a garden plot by covering the soil surface around them with mulch. Thus, the number of watering will be reduced, there will be no need for loosening and weeding.
It is necessary to feed the cuttings and offspring immediately after planting. Nitroammophoska is suitable - for 1 sq. m. requires 1 tbsp. l. fertilizers. Before watering with a solution of chemical fertilizers, the soil must first be watered with plain water. In addition to mineral fertilizers, for feeding raspberries, you can use an infusion of manure (1 to 10) or herbal infusions from a mixture of weeds, freshly cut grass, tops of root crops.
For the winter, the plants planted this year must be covered: the soil must be mulched with hay, fallen leaves, sawdust, straw, needles. In the northern regions, it is necessary to use a more reliable shelter - spruce branches, roofing felt or special dense agrofibre.In the spring, we must not forget to take it off with the onset of heat, so that the buds that begin to bloom do not die under it.
Adding an article to a new collection
To plant raspberries in the garden, just one seedling is enough. Everything else is a matter of technology. We figure out what methods of breeding raspberries are the most effective.
Raspberries are a good plant for gardening experiments. It multiplies easily and takes root well in a new place. There are several effective ways to propagate raspberries.
Preparing a site for planting seedlings
Seedlings are planted in prepared beds, 10-15 cm of the top layer of which should consist of a mixture of fertile soil, sand for drainage and peat. If prepared cuttings are planted, then deepening is done by 5 cm in protected ground conditions. In a greenhouse or greenhouse, cuttings are planted for rooting according to the scheme of 5 cm between the plants and 10 cm between the rows of seedlings.
If you are planting strong and healthy seedlings with leaves in a permanent place, then choose a sunny and wind-free place for permanent beds. The planting pattern is standard: 50 cm between seedlings, and about 1 meter between rows. Add superphosphate and ash containing almost a full range of mineral fertilizers to the planting holes. For the development of the green part, nitrogen fertilizers must be added additionally. Previously, we posted step-by-step instructions on how to properly plant a raspberry seedling.
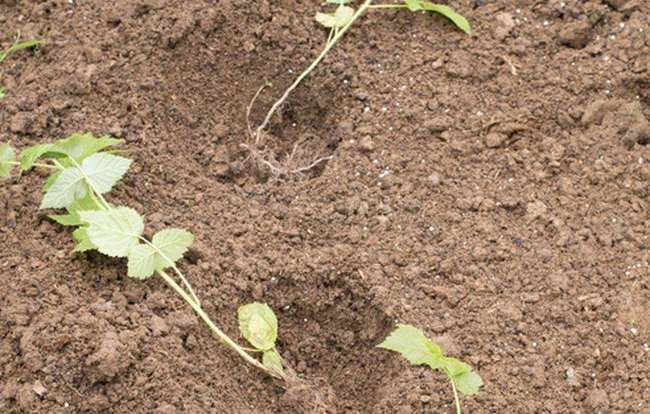


Spill the holes well and wait for the water to soak. Install supports for the bushes immediately, after planting, mulch the root zone of the seedlings.
Micropropagation
This method is used in specialized laboratories with special equipment. The value of the method lies in the complete recovery of seedlings from diseases. Micropropagation of raspberries allows you to get a huge number of seedlings by breeding in nutrient media.
In the future, the difficulty lies in the complex procedure of transplanting and growing seedlings with a height of only 1.5 cm. For this, greenhouses with fogging installations are used.
Microclonal cultivation is constrained by the high cost of seedlings and the limited number of such laboratories. Such seedlings are used for planting nurseries.
Seed reproduction
For each variety, 10,000 seedlings are used from seeds that have been pollinated with selected parental forms.
The propagation of raspberries by seeds is not used on personal and farms. This method is suitable for selection work with the subsequent selection of promising seedlings.
Seed collection takes place at the end of summer. They are obtained from ripe fruits. The required amount of berries is picked and placed in nylon bags. Washed from the pulp. The resulting seeds are dried and stored at a temperature of + 1-3 ° C.
Seeds are sown after stratification and scarification, after which the germination rate is 100%.
The seeds are sown in sand to a depth of 0.3 cm, sprinkled with sand or peat, covered with glass and placed in a warm and bright place. Make sure that the soil does not dry out. Seedlings appear at a temperature of + 20-22 ° С.
When the seedlings grow up, they are seated in individual cups. The seedlings are ready in 2 years.
This method has several advantages:
- obtaining a very large amount of planting material;
- very tight fit;
- obtaining seedlings with different ripening periods.
General information
Seeds and vegetative parts are suitable for propagation of common raspberries. In home cultivation, vegetative propagation is used in most cases, it is less laborious and more practical.


Raspberry propagation by seeds is carried out mainly in special institutions when new varieties are developed.For summer cottages and vegetable gardens, it is also possible to propagate raspberries by seeds, but it must be borne in mind that such plants do not always inherit all the properties characteristic of the variety, therefore it is better for gardeners to opt for vegetative propagation. In this case, the culture is propagated by offshoots from the roots - green and lignified, or by cuttings from shoots and root sites.
Optimal terms for work
Transplanting raspberry plants is permissible in spring and autumn. In spring, the most optimal time is after the snow melts, when the soil warms up a little, but you need to be in time before it dries. In dry ground and in the heat, raspberries will take root badly. The second condition for the successful engraftment of seedlings is that the buds on the shoots should not have time to bloom.
In autumn, plants are transplanted before the onset of constant cold weather. This is necessary so that the seedlings have time to take root, then they will not freeze in winter frosts. The transplantation date must be chosen so that the raspberry has a month left for rooting.
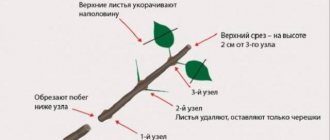
Methods for harvesting green cuttings
Cutting of green cuttings is carried out in May - early June. Experienced gardeners use several techniques.
1 way
Work with this year's shoots:
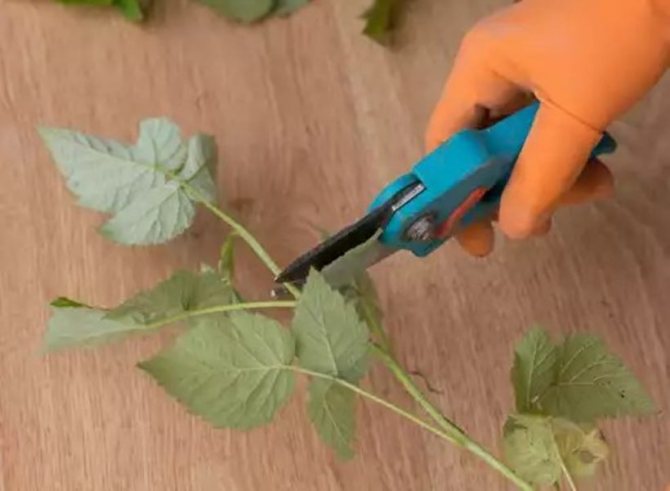
- Cut 15-20 cm from the crown at an angle of 45 degrees.
- The leaves are removed from the bottom, leaving only the "factory" - 2 upper leaves.
- The upper part of the cutting is removed with pruning shears.
- In the lower part, using a knife, make longitudinal notches up to 5 cm in length.
The workpieces are placed in a root-forming solution, fermented nettle tincture, honey solution or aloe juice combined with water. The lower sections are treated with heteroauxin or another acid. It is first dissolved in alcohol, then water is added.


You can use 200 grams of heteroauxin per liter of hot water. Cuttings are soaked in the solution for 15-18 hours, planted in the ground and watered with this liquid.
The green stalk should be immersed in the solution at a spacing of the notches.
2 way
The strongest and healthiest shoots of this year are taken. Divide them into pieces 7-10 cm long with buds. Before planting in a greenhouse, soil or greenhouse, the material is treated with growth accelerators.


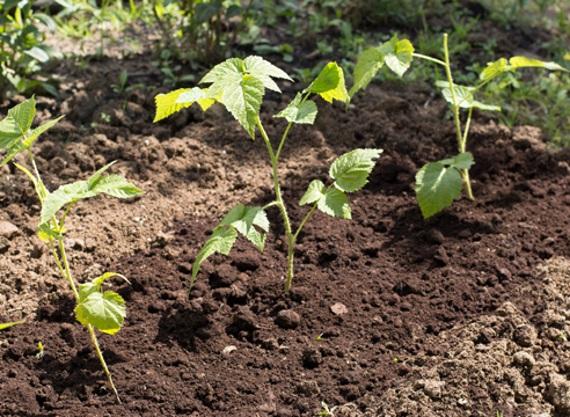
3 way
Designed exclusively for raspberries and provides for cutting green "nettles", which have high growth activity:
- Shoots with a barely formed leaf rosette are chosen.
- With the help of a pruner or a knife, the offspring is cut off, rising 4-5 cm from the ground, together with the etiolated (light) part.
- The material is immediately planted in the soil.
- The bottom cut is sprinkled with charcoal so that it does not rot.
Gardeners recommend making harvesting on a cloudy day or in the early morning - the sheets contain a lot of moisture.


Contraindications
There are several contraindications to eating raspberry root. If you ignore these recommendations, you can harm the body.
- You should refrain from using this product if you have symptoms of the following diseases:
- Nephritis.
- Kidney stone disease.
- Stomach ulcer or gastritis.
- Inflammation in the area of the spleen, liver or kidneys.
- Gout or osteochondrosis.
Some people suffer from individual intolerance to raspberries, so if you notice the appearance of skin rashes, itching or headaches, stop using it.
In many countries, raspberry root is considered a panacea for diseases. It is used for the preparation of ointments, tinctures and tea. Before using such funds, take a test for individual tolerance so as not to harm your body.
Monitor the dosage so as not to provoke side effects (diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, weakness and dizziness). If you experience these symptoms, see your doctor right away.
Features of use for children
If adults are advised to consume 300-500 ml of infusions per day, then the dosage in children should be lower. This is due to the fact that the child's body may not accept traditional medicine.
During the day, the child needs to drink no more than 100 ml of tea or tinctures. It is advisable to do this 1 hour after a meal, so that nutrients are absorbed into cells along with vitamins from food.
Learn more about how to use raspberries in a child's temperature.