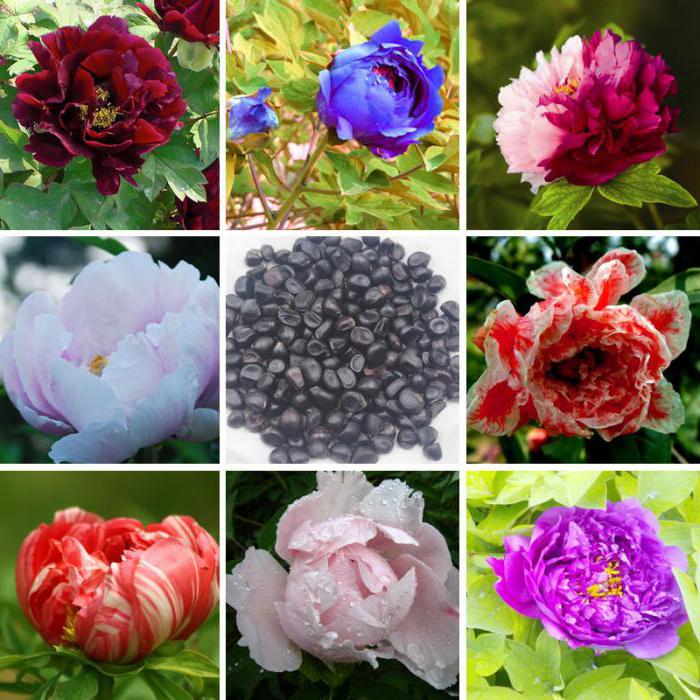
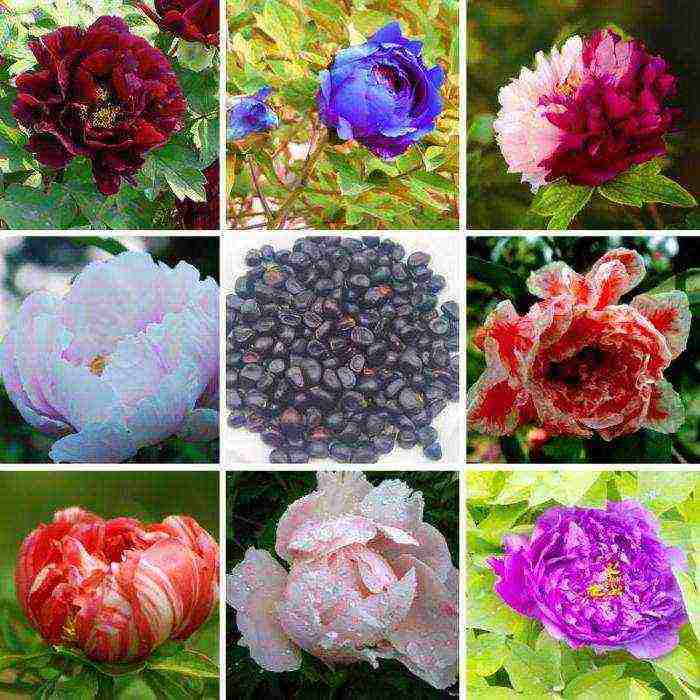
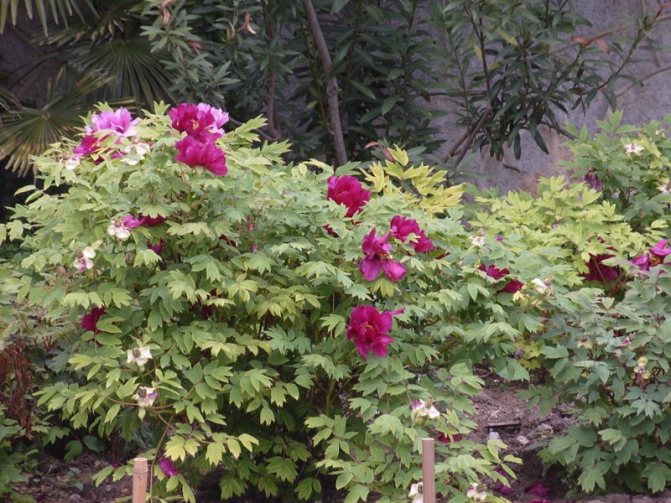
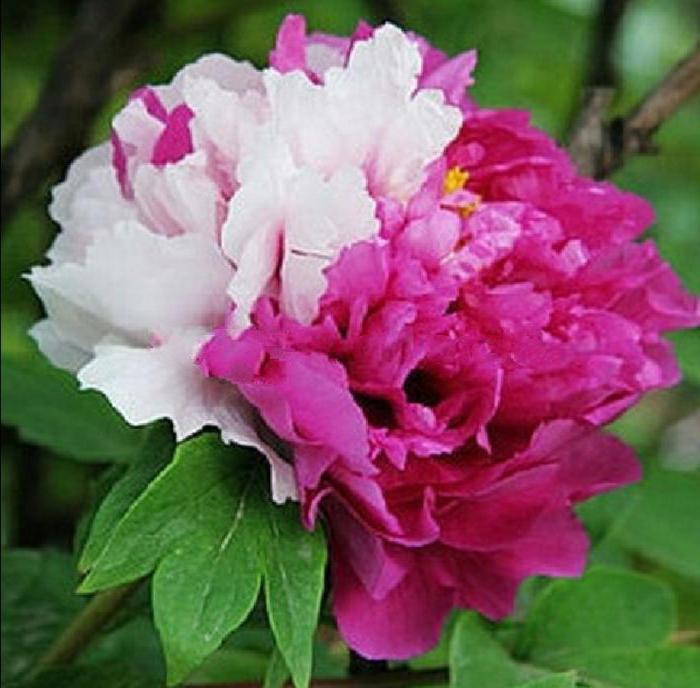
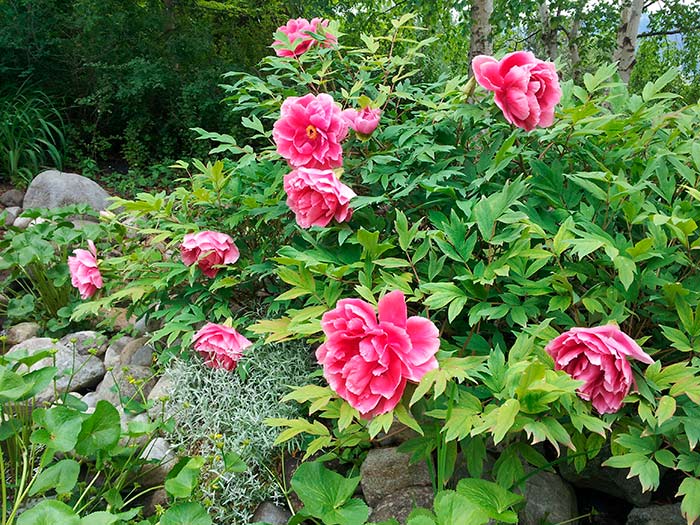
Few flowers can compete with the beauty of the spring peony. Its large scarlet blossoms rise majestically over carnations and ornamental onions. The sweet heady scent of luxurious peonies is most durable in a vase. Therefore, it is not surprising that this self-sufficient flower is most in demand for weddings and special events. In addition to being extremely popular, peonies are easy to grow. Usually the plant is divided into two groups: herbaceous and tree-like. Most often, the first group of flowers is grown in gardens. The peony is unpretentious and can delight the owner with abundant flowering for decades. Its foliage appears in late spring along with large buds. Transplanting and dividing the roots of a cupped flower is best done in the fall.
When can you plant peonies
There is an opinion that the less you touch the bushes, the better they grow. It is advisable to rejuvenate luxurious flowers after five to seven years of bush growth in one place. Gradual overgrowth of roots, aging of the root collar and lack of nutrients lead to the formation of small buds or their complete absence. Such plants are most susceptible to various diseases and pests: ants, worms and slugs. The most optimal time for peony rejuvenation is considered to be early autumn - late August, early September. The flower does not tolerate heat and heat, and its delicate roots can suffer from the scorching sun, so peonies do not disturb in summer. During the autumn procedure, the plant will be able to fully root itself before frost and in the spring to please the owner with its flowering. Sometimes the peony is planted in the spring, before flowering, but it takes a long time to adapt. In such cases, it can bloom after a year or two.

Hello dear readers!


Peonies are noble and lucky flowers, some of the most attractive in the garden.
No wonder the ancient Greeks were actively engaged in the reproduction of peonies, considering these beautiful centenarians (flowers bloom profusely and magnificently for many decades) as powerful amulets from evil spells, protectors from adversity and misfortune.
The kings of the garden area begin to savor in the last spring month and delight us with their lush flowering until mid-summer.
There is never too much beauty! How to properly propagate exquisite flowers?
Saplings of these wonderful flowers are quite expensive.
Therefore, if we want to plant more bushes of this plant in our garden, let's master the reproduction of peonies ourselves.
The topic of our article today will be the reproduction of peonies in several main ways.
It's time to deal with this interesting and important question.
Transplanting peonies in autumn
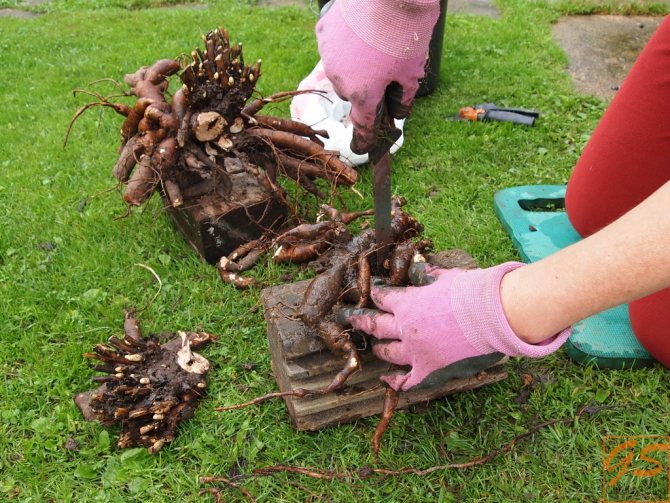
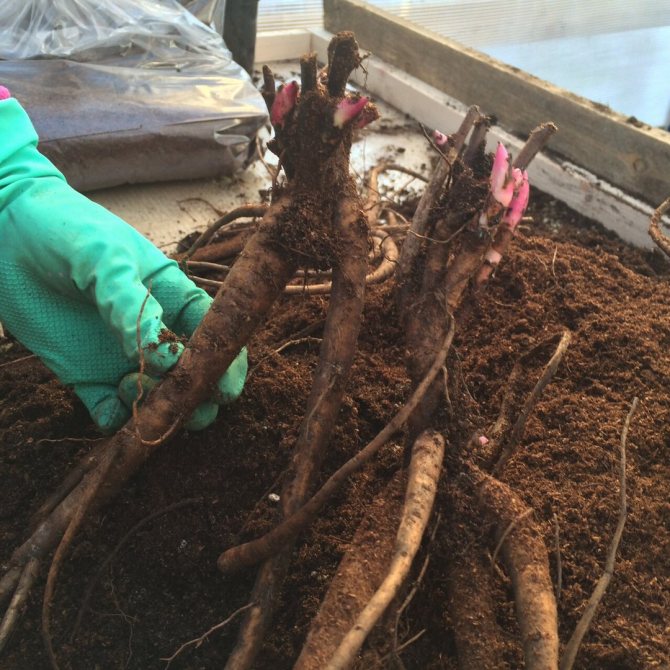
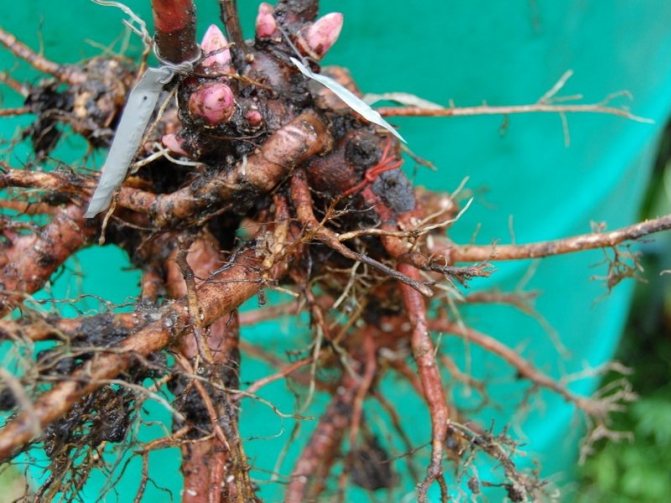
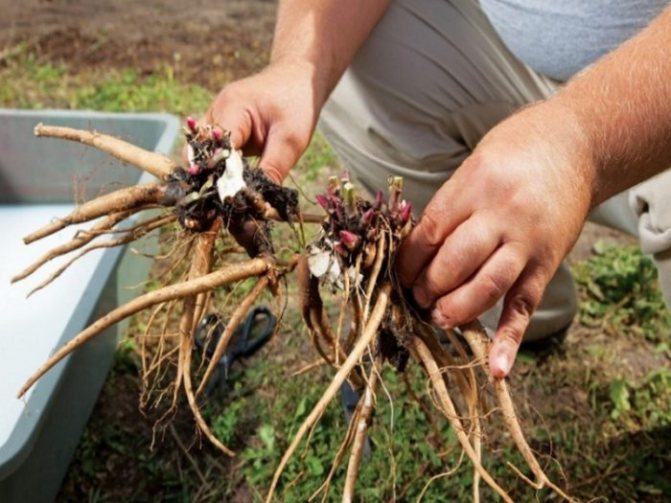
The rejuvenation of the bushes begins at a time when the buds for the next year have already been formed, but the roots are still missing. It is advisable to carry out the procedure in September. Before dividing the bush, the old stems are cut, leaving 5-7 cm of the shoot from the rhizome. Autumn foliage pruning is carried out even without transplanting to prepare peonies for the cold weather. Due to the large volume of the root system, the plant is rarely dug out without damage.To minimize harm for transplanting, choose a dry day when the soil is crumbly and falls off the roots by itself. To begin with, the bush is poured with water, dug in a circle at a distance of half a meter from the rhizome and up to 40 cm deep. They try to gently, without unnecessary jerking, pull the plant out of the ground. To preserve all the peony buds, two shovels or a crowbar are used for work. The earth is shaken off, and the roots are washed. The plant is left in the shade for a couple of hours so that the fragile roots wilt slightly and only then begin to divide.


Propagation of a tree peony by seeds, cuttings, dividing and layering
In the Moscow region, the reproduction of a tree-like peony can be carried out by seeds, as well as by vegetative methods: dividing the bush, layering and cuttings.
Seed reproduction. For reproduction of a tree peony, freshly harvested seeds are sown in the ground in September-October. Seeds of tree peonies germinate only in the second or third year. However, germination can be accelerated. Carry out warm stratification for 6-7 hours at +18 ° С, then at +30 ° С until the root appears. Then - cold stratification at temperatures from +2 to +6 ° C until the first leaf appears.
By the end of the first year, 1-2 leaves are formed in the tree-like item, the shoot dies off by winter. By the end of the second year, a lignified shoot 20-30 cm tall is formed. In the third year, another 2-3 shoots develop. The plant blooms in the fourth or fifth year.
Vegetative propagation by dividing the bush. In September, dig a 5-6-year-old bush, wash off the soil from the roots and divide the bush (split - 2-3 shoots). Treat the wounds with potassium permanganate or sprinkle with crushed charcoal.
Vegetative propagation by layering. Before propagating tree peonies by layering, in May, before the flowers bloom, make a shallow incision on the shoot from below, and treat with growth substance. Pin the shoot to the ground, cover with soil with a layer of 12-15 cm. Moisten the soil constantly. In September, cut the rooted shoot from the mother bush and plant it in a permanent place.
Vegetative propagation by cuttings. For propagation of a tree-like peony by cuttings in mid-June, cut the semi-lignified shoots with air buds obliquely under the bud, treat the cut with growth substance. Trim the blade off the cutting by two thirds. Pour a mixture of peat with river sand into the boxes, on top - clean river sand with a layer of at least 2 cm. Plant the cuttings at an angle of 45 °, deepening the bud. Cover the boxes with glass or foil. Moisten the soil constantly.
How to divide a peony root
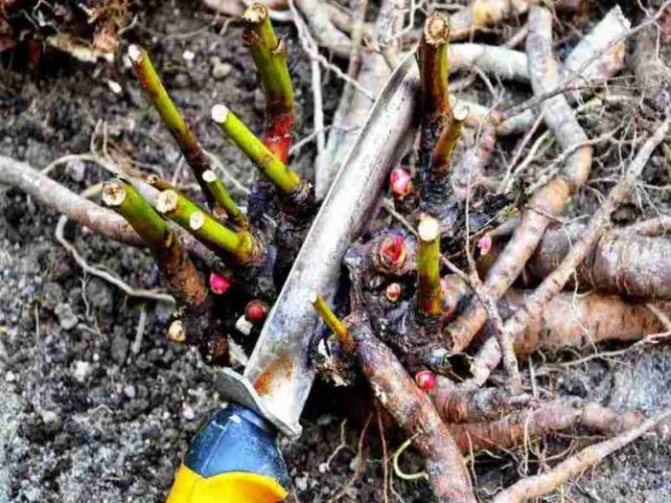
A garden knife, chisel, hammer and other tools are used to divide the fallen roots.
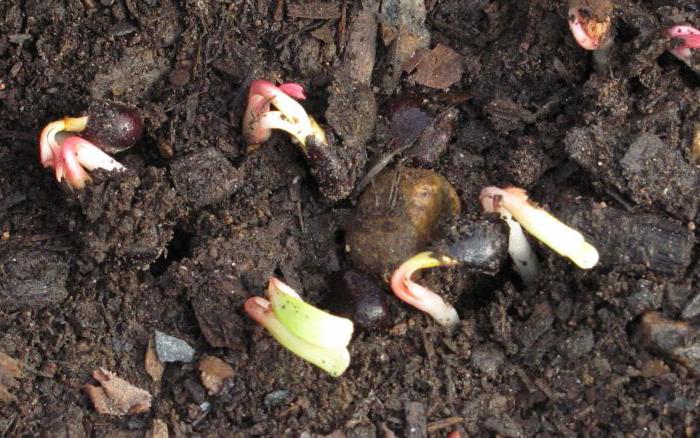
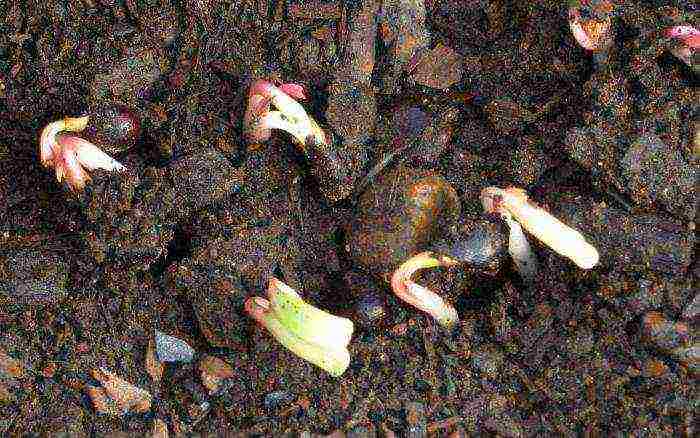
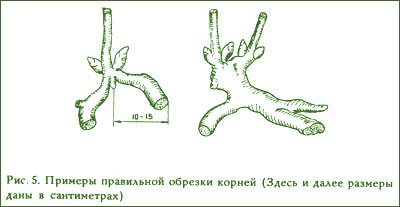
It must be remembered that one planting unit of a plant should have a piece of rhizome with 1-3 roots and 2-5 renewing buds. The development of too small divisions is slow, and of large ones - fast (due to the resource of old roots), but not durable.
The excavated root is first examined from all sides and determined with a division scheme. Old or rotten roots are removed. The rhizome can be cut in bridges between thick roots or in half. When dividing, they try not to hurt the newly formed kidneys. The roots on each section are left up to 20 cm, and the excess is cut with a knife or chopped with an ax. It is advisable to lower the prepared layers before planting for half an hour in a solution of potassium permanganate, dry and rub the sections with ash. Another option for disinfecting the roots is to apply a clay talker to the rhizome (0.5 buckets of clay are diluted with water to a mushy state and sprinkled with ash). In some cases, ash-treated cuttings are stored for up to 10 days in boxes with moss and only then are planted. During this time, the sections harden.
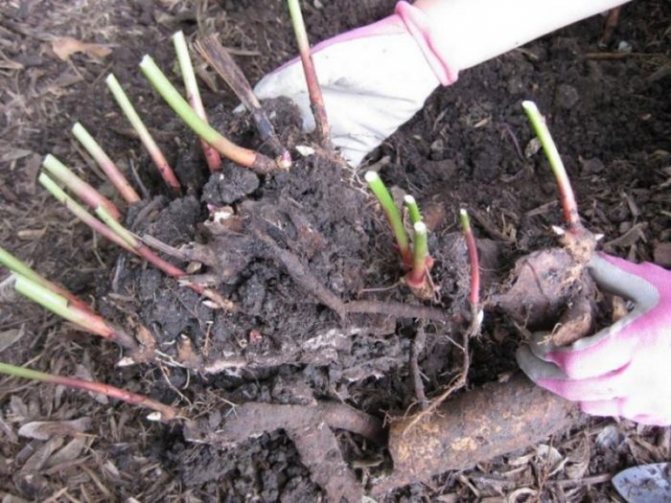


REPRODUCTION BY DIVISION OF BRUSHES
You can divide the bushes from the age of three to four (at an earlier age, the medicinal peony and interspecific hybrids are propagated). However, the best results and a significantly larger amount of planting material are obtained when dividing five to seven-year-old bushes. By this age, a large amount of nutrients accumulates in the rhizome of the bush, which ensures the development of young seedlings. For mother material, it is impractical to grow bushes older than eight years, since, despite good growth and flowering, due to a strong rotting of the underground part, the yield of high-quality planting material decreases.
Peony bushes intended for division are usually dug out after the formation of renewal buds on the rhizome, before active growth and development of small suction roots resembling white hairs begin. For the climatic conditions of the middle zone, the optimal dates for digging are from August 10-15 to September 10-20. You can dig up and divide peonies later (until October 5-10), depending on the weather conditions of summer and autumn, however, the survival rate of seedlings decreases, and the likelihood of their death increases accordingly.
After digging, the bushes are washed with a stream of water and placed in the shade for 5-6 hours for drying, after which the roots become less fragile and do not break when dividing. The stems are cut at a height of 10-15 cm from the rhizome and immediately, to avoid confusion, tags with the name of the variety are tied to them. For dividing, a set of tools is prepared in advance: knives, chisels, pruning shears, chisels, and other cutting tools and they are carefully sharpened.
The standard planting unit of peonies is a delenka with three to five renewal buds on the rhizome and several adventitious roots. Dividing inevitably leads to the formation of divisions with one or two buds. Such delenki are considered non-standard - they require special care when growing, since the likelihood of their death is higher. The cultivation of such divisions in special "schools" will be discussed below.
Dividing bushes, especially those over four to five years old, requires a certain amount of experience and skill. By this time, the peonies have formed a massive and tangled root system, therefore, before dividing, you should carefully examine the bush and try to understand all its intricacies. The main thing is to determine with what roots after dissection this or that part of the rhizome will depart. In the cut, it is desirable to observe the proportion between the number of buds and the volume and the number of adventitious roots: the more buds, the larger both the volume and the number of adventitious roots should be. If you choose the wrong line for cutting the rhizome, it may turn out that a large number of buds will correspond to an insufficient number of roots and vice versa. As a result, it will not be possible to obtain a significant number of standard divisions.
Therefore, when examining the bush and determining the place of its dissection, you can try to shake it with your hands. If, as a result, inflection points are formed, then the rhizome should be dissected along them. It is better to dissect the rhizome with a chisel or a wide chisel, knocking them out with a wooden hammer. After dissection, parts of the rhizome are continued to loosen with their hands and try to separate the intertwined roots. Even when dividing very large bushes after one or two dissections of the rhizome, further division into delenki is not difficult.
The resulting cuttings are washed and inspected again.Excess roots, mostly diseased, intertwined, directed upward, are cut out. The rhizome is carefully cleaned of rot with a garden knife, being careful not to damage the renewal buds. The remaining roots are shortened to 10-15 cm with a sharp knife, trying to keep the cuts smooth.

After cleaning and pruning the roots for dressing against root rot, the cuttings are dipped in a solution of potassium permanganate for several hours so that a burning lamp can be seen through a liter jar with it (Approximately 3-4 g per 10 liters of water). At a higher concentration of the solution, kidney renewal burns may occur. Every day for work, a fresh solution of potassium permanganate should be prepared. You can prepare a concentrated solution of potassium permanganate in a sealed dark glass container in advance, and then, if necessary, dilute it with water to the required concentration.
The method of disinfecting the planting material of peonies with a solution of copper sulfate (100 g per 10 liters of water) is quite common. In this case, it is especially important to observe the exact dosage of copper sulfate and the holding time of the material in the solution. The latter should not exceed 20-25 minutes, since otherwise the delenki can get burns, which will dramatically reduce root formation and can lead to the death of the planting material. It should be remembered that copper sulfate cannot be diluted in galvanized dishes; for its preparation, only enameled containers are taken.
Many amateurs use non-chemical methods of disinfection of planting material, in particular, an infusion of garlic, which is prepared as follows: 0.5 kg of peeled cloves are turned through a meat grinder, poured into a three-liter jar and poured with water. After three five days, the solution is filtered and poured into a tight-fitting container. To disinfect the roots, take 30 g of infusion per 1 liter of water and keep the planting material in it for 30-40 minutes. The infusion of garlic retains its properties for three months.
After disinfection, the cuts of the roots and places on the rhizome, which have been cleaned from rot, are sprinkled with crushed charcoal or a mixture of crushed charcoal and colloidal sulfur in equal parts. After such treatment, the delenki are placed in the shade for a day so that a cork layer forms on the root cuts, preventing the penetration of pathogenic microflora into the wounds.
5-6 hours before planting, the delenki should be dipped into a clay mash containing both disinfecting and growth substances: copper sulfate - 50 g and heteroauxin - two tablets (dissolved in 10 liters of water), mixed with clay, bringing to a pasty state. You can add 500 g of wood ash to the mixture and mix thoroughly as well.
Having dipped in a chatterbox, the delenki are folded into boxes for drying on the roots of a layer of clay. Delenki processed in this way can be stored without drying out for a long time, which is sometimes used when sending planting material for peonies by mail. After planting, the crust protects the seedling from rot, and the growth substance (heteroauxin) stimulates the formation of a young root system. Excellent results are also obtained by long-term storage and shipment of cuttings in moss.
If the planting is not carried out immediately, the planting material is placed in a shaded hole in the ridges with good garden soil, where it can be for one to one and a half months before planting. In dry weather, the dug-in seedlings are periodically watered.
Sometimes flower growers divide the bushes into large parts with six or more renewal buds. They leave a significant part of the root system without pruning, believing that such a plant will grow better and develop faster. Indeed, in the first year the plant develops rapidly and may even produce some nice flowers. However, the rapid development of such a plant is due to the nutrients accumulated by old roots.The formation of young suction roots practically does not occur, which negatively affects the development of the bushes in subsequent years. In addition, uncleaned roots rot, as a result, in the second year after planting, the plants begin to hurt and by the third year they may die.
REPRODUCTION BY VERTICAL BRANCHES
It is easy enough for amateurs to reproduce peonies with vertical layers. Of course, not all varieties are equally amenable to propagation in this way. However, if certain rules are followed, good results can be obtained. It is advisable to use shrubs at the age of five to eight years for vertical layering.
In early spring, in April, as soon as the ground thaws and warms up, and the buds of the peony's renewal start to grow, they are exposed as much as possible, carefully scraping the soil around the bush, and a box without a bottom measuring 50 × 50 cm, 34-40 cm high, is placed. If the bush is large , take a larger box. A 10 cm box is filled with good garden soil mixed with compost and sand in a 2: 1: 1 ratio. Then a soil mixture is prepared, consisting of compost, garden soil and preferably rotted manure in a 1: 1: 1 ratio. Add 300-400 g of bone meal or 150 g of crushed superphosphate per box to the mixture.
The finished mixture is poured in layers into the box to a height of 25-30 cm as the shoots grow. From above, the soil is mulched with a layer of peat 3-4 cm in order to avoid the formation of a crust and watered with water as it dries. Outside, the boxes are covered with garden soil to reduce the drying out of the indoor soil, especially in hot weather. It is advisable to carry out three foliar dressings (see section "Agrotechnics"), as well as two or three root dressings with heteroauxin (2 tablets per 10 l) with an interval of 10-15 days. Flowers in the phase of a burst bud are removed, preserving the leaves as much as possible.
In the second half of September, the boxes are removed, the bushes are undone and all the shoots are cut off. Those of them, on which renewal buds have formed, are immediately planted in specially prepared ridge-schools with light nutritious soil. For the winter, it is advisable to cover the plantings with a layer of peat or compost 5-6 cm thick. In the spring, as soon as the soil thaws, the shelter is removed. Grooming in the first and second years, as for young seedlings (see section "Agrotechnics"). For the second time, the same bush should be propagated in this way no earlier than two years later.
REPRODUCTION BY ROOT CUTTINGS WITH A KID
A root cutting with a bud is a piece of horse with a small adventitious root and, as a rule, with one bud of renewal. Most often, propagation by root cuttings of a milky-flowered peony is used in cases where they do not seek to obtain rapid flowering, but a large amount of planting material, for example, when propagating new, especially valuable varieties. In this case, the yield of planting material is several times higher than in the case of ordinary division.
All prepared operations are performed as in the previous method. However, it is advisable to carry out operations for the preparation, processing and planting of seedlings as early as possible and finish by the end of August. The difference is that the rhizome is dissected into the maximum possible number of units, each with buds and a small root 1-3 cm long.Good results in rooting such units (80-85%) are explained precisely by the fact that the available piece of root and rhizome provides a kidney supply of nutrients.
The resulting material is planted for rooting and growing on pre-prepared ridges, schools, filled with good garden soil with compost.
The planting scheme is 15X15 or 20 × 20 cm. Usually, the seedlings are grown for one or two years, after which they are planted in a permanent place.
One of the varieties of this breeding method is pruning the rhizome without digging. For this, bushes are used at least five years of age. The older the bush, the more effective this method is.Around the bush, the soil is raked to a depth of about 10 cm and the upper part of the bush is cut off with a sharp shovel 5-7 cm thick below the buds of renewal. The entire upper part of the bush breaks up into pieces of rhizome with root and renewal buds. The rhizome remaining after pruning is covered with garden soil mixed with compost and left until next year. The next year, on the remaining rhizome from dormant buds, shoots develop, as a rule, non-flowering. Next year, these bushes are dug up. They very easily disintegrate into small pieces, which are planted in school ridges for growing. Thus, a double crop can be harvested from one bush. The success of reproduction in this way can be achieved only if all agrotechnical measures are observed.
REPRODUCTION BY STEM CUTTINGS
Peonies are rarely propagated by stem cuttings due to the laboriousness of the method and the low yield of planting material. The multiplication factor is highly dependent on the variety and can reach 60-70%. Many varieties (especially interspecific hybrids) do not lend themselves to grafting at all, on average they take root and produce a renewal bud of 15-25% of the total number of cuttings. The advantage of this method of propagation is to obtain seedlings with a completely rejuvenated root system, while there is no need to dig out mother bushes for a number of years and you can use this method annually on the same bushes.
The best results are obtained by stem cuttings of bushes at the age of four to ten years. Three to five days before the blooming of the buds, 30-40% of the strongest flowering shoots are cut from the mother bush and cuttings are cut from them. Usually, two or three cuttings with two internodes are obtained from the lower and middle part of one stem. Cuttings are cut with a very sharpened knife. The bottom sheet is cut off, and part of the leaf blade is removed from the top sheet to reduce moisture evaporation. The lower ends of the prepared cuttings are immersed in a fresh solution of heteroauxin (one tablet per 1 liter of water) for 8-10 hours and the cuttings are placed in the shade. Better to harvest them early in the morning. After treatment with heteroauxin, the cuttings are planted in a pre-prepared greenhouse, in the lower part of which a mixture of good garden soil, compost and rotted manure is filled in to a depth of 30-40 cm, and on top - a layer of washed river sand 5-6 cm thick.
The cuttings are planted obliquely to a depth of 3-4 cm so that the cut of the lower leaf is closed, but the leaves do not touch each other. The distance in the row is 8-10 cm, between the rows - 15-20 cm. Before planting, the soil in the greenhouse is thoroughly shed with plenty of water.
The optimal conditions for rooting at the first stage of life during the first month are maximum humidity and temperature 20-25 ° С. In industrial conditions, the maximum humidity is created by artificial fog installations. For this purpose, we used a room electric humidifier, which was turned on during the day as needed, on average for 8-10 minutes per hour. In the first two weeks, it is advisable not to raise the frame, and in hot weather, regulate the temperature inside the greenhouse by shading if it is located in a sunny place. After two weeks, you can start lifting the frames for airing for 15-20 minutes, gradually increasing the time over the course of a month to several hours a day. One to one and a half months after planting, the frames can be left open during the day and closed only overnight. For the prevention of fungal diseases, it is better to water with a weak solution of potassium permanganate once a week, and if signs of disease appear, spray it with copper oxychloride (50 g per 10 liters of water).
For the winter, the cuttings are left in a greenhouse. In early October, their aboveground part is cut off, the soil is mulched with peat and covered with a layer of leaves, straw or spruce branches. In the spring (usually at the end of April - beginning of May), the shelter is removed and the cuttings with the formed renewal buds with a lump of soil are transferred to the previously prepared ridges.At first, the seedlings are regularly watered and shaded, after the start of active growth, they are looked after as for ordinary plantings.
SEED REPRODUCTION
Peonies grown from seeds do not retain the varietal properties of the parent plant (except for the species obtained from self-pollination). Therefore, this method of reproduction is used mainly in breeding work when developing new varieties. The flowers from the bushes are not cut off after flowering, but left until the formation of seeds, which usually ripen in late August - early September. In inclement weather, the ovary with a piece of stem is placed in a warm, dry room for ripening. The mother plant is pollinated by bees and other insects, and self-pollination is possible, or the father plant remains unknown.
Experienced breeders, in order to obtain certain characteristics in future hybrid seedlings (color, flowering period, flower shape, smell, etc.), carry out directional crossing, that is, selection of a parental pair: pollen is collected from selected plants (paternal) and pollinated with it. mother plants. The latter are sterilized - all the stamens are removed and isolated by putting paper caps on the flowers. Directional crossing is quite laborious and requires skill and experience. Due to the fact that the period of development of the plant from the moment of sowing the seeds to flowering is long (five to eight years), amateur flower growers rarely use this method of propagation. In addition, when growing seedlings, significant planting areas are required, and highly decorative new seedlings, as a rule, turn out to be no more than 10% of their total number.
The main advantage of seedlings grown from seeds is their much better adaptability to the climatic conditions of the zone in which they are grown, in comparison with varieties of foreign selection. Therefore, many flower growers prefer to grow varieties of peonies of domestic selection in their garden.
The seeds are harvested when they are fully ripe, when they turn dark brown, and stored in the refrigerator until sowing.
In all cases, before planting, the seeds should be dipped in a dark pink solution of potassium permanganate for several hours to destroy the spores of various fungi. There are several ways to grow seedlings from seed. You can immediately sow seeds in prepared ridges or greenhouses with a 3-4 cm layer of river sand poured on top. Sow in rows every 10-15 cm, the distance in a row is 1-2 cm. The planting scheme is recorded in the journal. Pegs are placed in the rows with the names of the varieties from which the seeds were collected. Throughout the autumn, until the first frost, the soil of the ridge is kept moist. For the winter, the ridges are covered with a layer of peat, sawdust and other materials 5-7 cm thick. Some of the seeds can germinate next year, the rest - in a year.
In subsequent years, ridges with seedlings need regular loosening, cleaning of weeds and maintaining a certain soil moisture. A year after sowing (in August), seedlings with a well-developed aerial part, carefully, so as not to damage the roots, are removed and transplanted into ridges with prepared nutrient soil according to a 20 × 40 cm scheme.The rest of the seedlings are transplanted after a year.
In another method, the seeds are sown in October in pots or planting boxes filled with good fertile soil and, with a layer of river sand on top of a thickness of 2 -3 cm, into which the seeds are placed. Seeds can be sown quite thickly - at a distance of 0.5-1 cm from one another. Pots or boxes are placed in a room with a temperature of 20-25 ° C for two to three months. The soil must be moist at all times. After about two months, they begin to periodically check whether root formation has begun.
After the formation of the roots, the seedlings are transferred to a room with a temperature of 3-5 ° C (basement, refrigerator, cold greenhouse, etc.).Under these conditions, leaves are formed within two to three months, after which the seedlings are placed in a greenhouse with a temperature of 15-18 ° C, where they are left until planting in the ground. Seedlings are planted in prepared ridges in April-May according to a 20 × 40 cm scheme.
Stimulate root formation according to N.S. Red can be done by acting on the seeds for the first two to three months after sowing with variable temperatures during the day: during the day 30 and at night 15 ° C. The rest of the period the temperature is normal (similar to the one above).
After two to three years, the bushes with a lump are transplanted to a permanent place, where they develop before flowering. Usually, the flowering of the first, and sometimes the second years is defective. In seedlings of terry varieties during this period, the doubleness may be poorly expressed. Therefore, the assessment of the flowers of seedlings is usually done in the third year of flowering. However, monitoring the timing of flowering, the height of the bushes, the tendency of plants to fungal diseases is performed annually. When evaluating flowers, the color, doubleness, shape, structure and size of the flower, and the presence of odor are noted. All data is logged. After the third year of flowering and the first evaluation of the seedlings, the best plants are dug up and planted. They are being constantly monitored for four years.
How to split a peony root to bloom next year
In order for the bush to bloom immediately, several nuances must be taken into account:
- for disembarkation, choose a sunny place without an excess of moisture;
- do not place the peony close to other shrubs and trees, the optimal distance is 1 m;
- prepare a hole for planting in advance by creating a drainage of crushed brick and sand;
- the division should have 2-3 roots up to 20 cm and 3-5 buds;
- obligatory pickling of the cut in potassium permanganate or copper sulfate;
- the plant should be rejuvenated in the first half of September;
- when transferring a whole bush to another place, remove it along with the soil;
- immerse the buds in the ground at least 5 cm so that they do not freeze in winter;
- the distance between adjacent bushes must be at least 1 meter.
At first, it is advisable to monitor the moisture content of the soil. With proper planting, watering and feeding, you can avoid the annual interruption in flowering. Although experienced gardeners recommend picking off the first buds of a new peony to develop a strong root system.


Where and when to plant tree peonies in open ground


Planting a tree peony in the photo
Material for planting tree peonies is sold in several varieties:
- adult bushes (age 8-10 years);
- plants in a container (in a pot);
- plants in sealed packaging (in a plastic bag).
As a rule, this is grafted material (cuttings of tree-like peonies, grafted on the roots of herbaceous ones), very rarely - delenki (divided small plants).
Before planting a tree peony, keep in mind that when buying a plant in polyethylene or in a pot, it is difficult to assess the state of the root system.
If you bought a flowering specimen, it is grafted material. Such plants are most susceptible to various diseases. A much more reliable material is one that is obtained as a result of dividing a bush.
Do not plant tree peonies near the house, large trees and shrubs - in the shade, the plants stretch out strongly and lose their varietal characteristics. However, peonies should be protected from direct sunlight. The ideal option where it is recommended to plant a tree-like peony is a semi-shady area: here the flowers last longer and their color does not change. Plant peonies out of the wind. In open, heavily blown places, plants, as a rule, die. In Japan and China, the flowers of tree peonies are often sheltered from the sun, wind and rain with special canopies.
It is very important to know when to plant tree peonies outdoors. Do not forget that the timing of planting significantly affects the survival rate of peonies.Planting too late has a negative effect on root development, and, accordingly, on the further flowering of plants.
In peonies, the timing of all physiological processes is clearly defined: in April-May they bloom, in July-August they bear fruit, and by the end of September they go into hibernation. The best time to plant tree peonies in the middle zone of the European part of Russia and in particular in the Moscow region is from mid-August to the end of September. With a late transplant, the root wound sites do not heal for a long time, and the bush is sick.
The following describes how to properly plant a tree peony in open ground.
How to choose the right place for planting a peony
For peonies, you need to choose a sunny place on the site that is well ventilated. It is desirable that the plant receives sunlight in the morning. The flower tolerates the shadow, but it will not bloom. It is not recommended to place the peony too close to housing construction, because the heat radiated from the walls will contribute to overheating. Plant growth slows down in flooded areas or areas with high groundwater levels. An excess of moisture leads to decay of the roots, so they try to plant flowers in raised beds. Loamy or neutral soils are most suitable for planting peonies. The clay area can be corrected by the application of peat, sand and organic fertilizers.


Storage of spring planting material
If you plan to purchase new varieties of peonies in the next season, then you need to consider the following. Planting material begins to go on sale in the spring, in March - April, and, perhaps, the variety you need will have to buy at this time. It is too early to plant a peony in the garden and you need to somehow save it until the season.
- Rhizomes, on which the eyes have not yet begun to grow, are sent for storage in a refrigerator, loggia or basement.
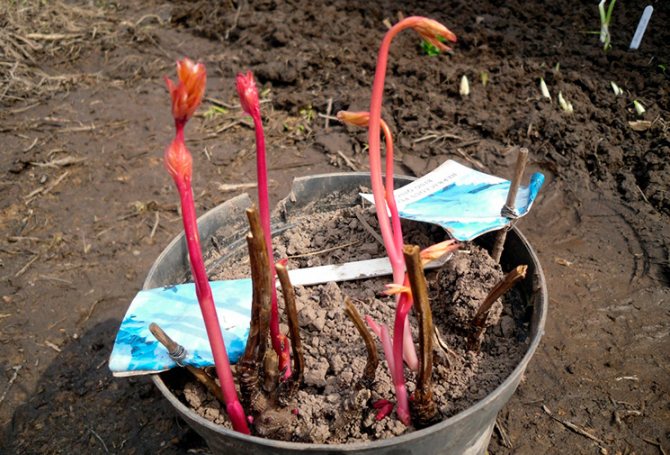
- Delenki, on which the kidneys have woken up, are planted in containers, which are placed in a bright place for growing. These plants are planted in the garden in May - June, when the danger of frost passes. The first time of planting must be protected from the bright sun.
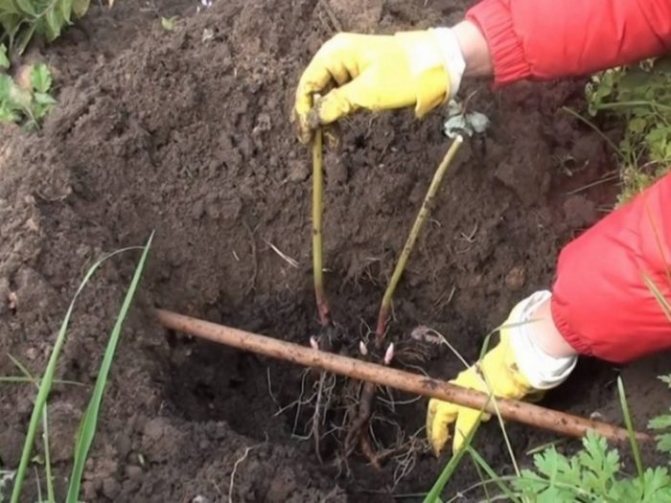
How deep to plant peonies
Planting holes for a peony must be made 70x70x70 cm in size, otherwise the powerful root system of the bush may be damaged. The cut itself is placed in a prepared hole no deeper than 7-9 cm from the surface of the earth. Overburdened roots are one of the reasons for the lack of flowering. The bottom of the pit is lined with small stones, bricks or branches for drainage. Then they place a cut in the hole and sprinkle with a mixture of earth with compost or humus.
It is important to ensure that the roots are freely positioned in each hole.


Tips for dividing a peony
If the peony is 8 years old, then it is high time to rejuvenate it. Divide the bush every 4-5 years. This is due to the roots. In old bushes, which have been growing for many years without dividing, they are strongly intertwined and connected at the top by a dense tissue formed by dead stems, various growths that make up the root collar, on which the renewal buds are located.
Such roots have to be dug out with great difficulty, since in a peony they themselves are fragile and brittle, and in older bushes they also go into the ground by at least 80 cm. It is necessary to rejuvenate the bush, otherwise there will be more foliage and diseases every year, and the flowers themselves are getting smaller, and the blossoming ones will become smaller, they will fade faster. It is necessary to start rejuvenating the peony bush from the second decade of August to mid-September, and in warm autumn - until the end of the month. Around the bush at a distance of 20-25 cm, you need to dig a deep trench for 2 bayonets of a shovel.
After that, start swinging the bush with the crowbar until it is completely out of the ground. Lightly clean the roots of the soil and remove the bush from the hole. Leave it on for 3-4 hours to let the roots wither and not be so brittle. Then cut the stems to a height of 10 cm, wash the roots from the ground with water and peel them off with a wooden peg.


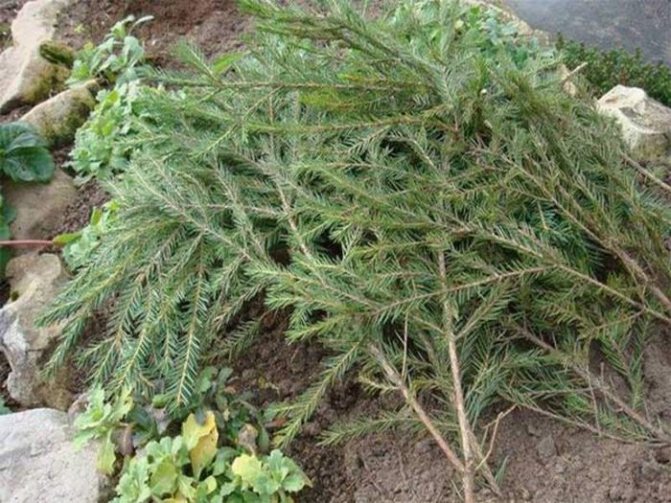
How to prepare peonies for wintering after transplanting
The peculiarity of the structure of the peony requires careful preparation for the winter from flower growers. The growth buds of the plant are located at a depth of 3-7 cm from the surface, so it is advisable to cover them at the end of autumn. For such purposes, use dry grass, sawdust or peat. The optimal mulch layer should be up to 20 cm. In a snowless winter, peonies are protected by small snowdrifts.


If you approach this procedure responsibly, planting peonies will not cause special difficulties for flower growers, and the time spent will more than pay off with the bright flowering of luxurious bushes.
THREE basic principles of dividing perennials
1. As a rule, spring-flowering crops are divided in autumn, autumn-flowering crops - in spring. But there are also exceptions to the rule.
- In autumn they divide: peonies, astilbe, phlox, primroses, hellebores, liverwort.
- Divide in spring: autumn asters, sedums, echinacea, autumn anemones, buzulniks, primroses.
- In any season can be divided: hosts, daylilies.
2. The division of perennials is carried out at temperatures above +5 °
3. Delenka is a piece of rhizome with a growth bud. In the meantime, there is no need to worry about it. ”


on the photo of the delenka: 1. lacto-flowered peony, 2. daylily hybrid, 3. paniculata phlox
Warm phase
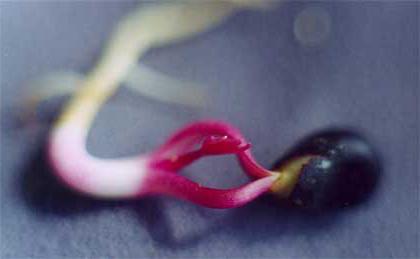
The seeds should be sown in a wide, shallow container in moist sand. It is placed on an electric heating pad (a heating battery is also suitable). The sand should be warmed up to 30 ° C, after which it is cooled and reheated, periodically moistening it.
The procedure takes about two months for the seeds to burst and roots to appear. Immediately after that, they are removed from the sand, the roots are pinched and placed in a container with soil mixture or in peat pots, lightly sprinkling them. This will significantly reduce the likelihood of injury to seedlings when planting in the soil.

Reproduction by grafting
The grafting technique, which is the most effective way to propagate tree peonies, and is performed at the end of August, is used to obtain large quantities of planting material for sale.
The grafting method is so complicated that even experienced flower growers do not always succeed. For the stock, the roots of herbaceous peonies are usually used, the length of which does not exceed 15 cm, and cuttings with two eyes, cut only from the shoots of the current year, are used as a scion. Stocking of rootstock roots is carried out three weeks before the scheduled procedure. The selected material is stored in a cool dark place.
We will describe in detail the different methods of vaccination. The most common technique for performing wedge-shaped cuts. One of the conditions for successful grafting is the coincidence of the thickness of the root taken for the stock and the grafted cuttings with at least two buds.
The lower cut of the cutting is made in the form of a wedge, and a wedge-shaped cut is made in the upper part of the spine, the parameters of which ideally coincide with its dimensions. Of great importance is not only the perfect coincidence of the shape and size of both sections, but also the absolute smoothness of their surface (this is necessary for the coincidence of the cambial layers).
After making the cuts, the scion (stalk) is inserted into the stock (root) and wrapped very tightly with a strip of plastic wrap. If insulating tape is used for this, its adhesive layer must face outward. The place where the scion and rootstock are fastened is tied with hemp twine or coated with garden pitch. To reduce moisture evaporation, the scion should be freed from the leaves. Techniques that improve the fusion of the scion with the stock
- For 4-5 weeks, necessary for the growth of the scion and rootstock, the grafted material, laid out in horizontal layers and sprinkled with moist sphagnum, sawdust or peat, is kept in a shaded and cool place.
- Some growers plant the grafted peony in the greenhouse immediately after the grafting, making sure that the scion is located above ground level.Watering should be regular, but moderate. Avoid direct sunlight into the greenhouse. The grafted plants are planted in the ground, placing them vertically or at an angle of 45 degrees.
A simpler option is the lateral grafting technique, in which a diagonal cut is made on the scion at a very small angle. After that, exactly the same cut should be made in the upper part of the spine. Having combined both parts, they are tightly tied, coated with garden var.
Four weeks later, the grafted tree peonies are planted in a greenhouse so that the lower bud is buried about six centimeters in the soil. The surface of the soil must be well milled. The grafted plants will be ready for transplantation to a permanent place in 1.5-2 years.
Where to buy peony seedlings
The Scientific and Production Association "Sady Rossii" has been introducing the latest achievements in the selection of vegetable, fruit, berry and ornamental crops into the wide practice of amateur gardening for 30 years. In the work of the association, the most modern technologies are used, a unique laboratory for microclonal reproduction of plants has been created. The main tasks of NPO Sady Rossii is to provide gardeners with high-quality planting material for popular varieties of various garden plants and novelties of world selection. Delivery of planting material (seeds, onions, seedlings) is carried out by Russian post. We are waiting for you for shopping: NPO "Sady Rossii"
Seedling care
When a bud appears on the seedlings, they must be transferred to a warm room (not lower than + 16 ... + 18 ° C). The acceleration procedure will require patience and hard work from the gardener, but it will save a whole year.
The seedlings are transferred to the garden in early May, they grow in partial shade at a distance of about five centimeters from each other. The soil around them is leveled and mulched with sawdust, which retains moisture and does not allow weeds to develop.
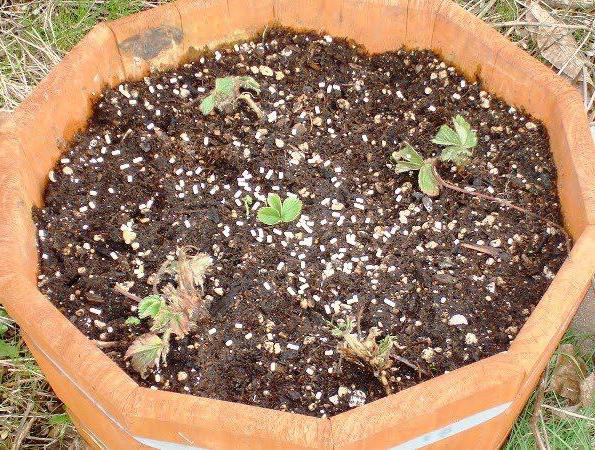


Bush dividing method


Reproduction of peonies by dividing the bush is best done at the end of summer, when the soil stops overheating, but there is still enough time for the formation of the root system. The deadline is early October.
For breeding, you need to use bushes from 5 to 7 years old. They have strong and thick rhizomes with a lot of nutrients, so young plants will quickly take over.
Step-by-step instructions for breeding peonies by dividing a bush:
- Dig up the bush along with the roots.
- Clean it from soil with water.
- Leave the peonies in a cool place for 1-2 days to dry the rhizomes and gain strength.
- Cut off the aerial part of the plant at a height of 15 cm from the roots.
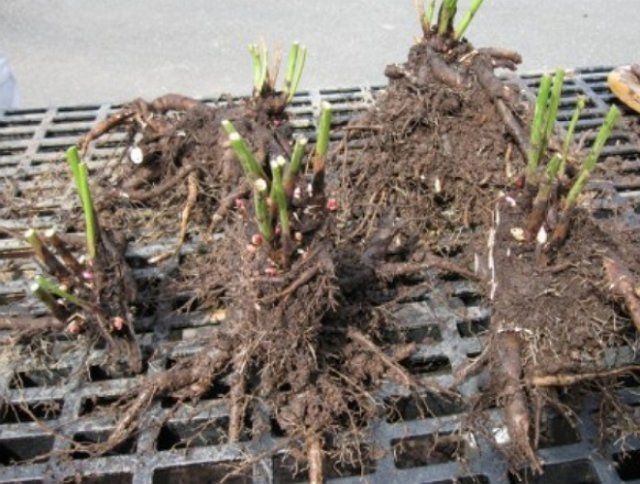
- Divide the roots into several parts so that each has 2-3 thick roots about 9-10 cm long, as well as 3 healthy buds.
- Rinse and inspect the separated parts again. Remove rotten and damaged parts of the roots.
- Dip the planting material for 2-3 hours in a dark solution of potassium permanganate.
- Remove the roots from the solution and treat them with a mixture prepared from wood ash, clay and 0.2% Fundazole solution.
Now the individual parts of the whole bush are ready for planting in a new location. Prepare planting holes, bury the roots in them so that the buds are on top, and water abundantly.
Cold phase
It's time to move on to the cold phase. It is necessary for the active development of the shoot growth point. During this period, the embryo is actively growing, and the seeds germinate. This phase lasts about three months. Florists have found a way to shorten this time too. To do this, it is necessary to treat the hypocotyl (a piece of the stem located under the cotyledons) with a growth regulator solution. Prepare a 0.01% growth stimulator solution. The seeds are opened, moistened with the resulting composition of gauze and applied to the hypocotyl. To maintain the necessary moisture, the seeds are covered with a light-permeable cloth.If the temperature is maintained from +5 to +10 ° C, then a bud of growth will form on the seedlings and leaves will appear. If after seven days the kidney does not appear, the treatment must be repeated.
Layers
Tree peonies are propagated by layering without waiting for flowering, usually in May. To do this, choose the most developed shoot, bend it to the ground and make a small incision on it, in the place where the stem touches the ground. For better rooting, the incision can be powdered with rooting stimulants and a small spacer inserted into it, after which the shoot must be pinned to the soil surface and covered with 8-15 cm. a layer of soil. It is very important to ensure that the ground does not dry out during the rooting process.
In the case of reproduction of a tree peony by layering, you can wrap the incised shoot without bending it to the ground, wrap it with wet moss, wrap it with polyethylene and tie or cover it with garden var, but this option is less effective than the first. But, in both cases, the roots, with a favorable outcome, should appear in late August - early September.


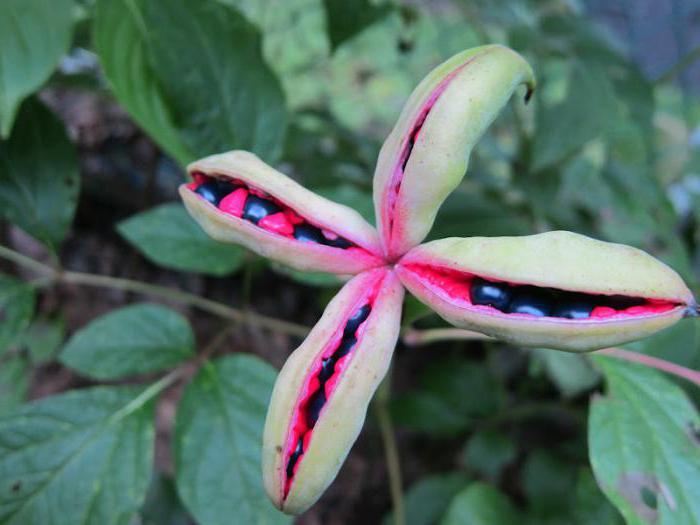
Why is growing from seed rarely used?
This method of growing popular flowers is rarely used. Even knowing how to grow peonies from seeds, most gardeners prefer to propagate plants by dividing the bush. Why? There is a simple explanation for this.
Usually gardeners, when purchasing peonies for their site, focus on the beauty of flowers. Therefore, they select hybrids bred by breeders. But the latter have one significant drawback - the preservation of the type of flowers is possible only when dividing the bush.
At the same time, it must be admitted that in amateur gardening, the purity of the variety is not so important in comparison with the beauty. The overwhelming majority of seedlings obtained from seeds pleases the owners with very interesting results. Knowing how to grow peonies from seeds, you can propagate wild-growing flowers. These include dodging and thin-leaved species.


Reproduction of peonies by seeds is not always possible for objective reasons - some varieties never bear fruit, they simply do not have seeds. These include Marchal MacMahon, Madame Forel, Celestial, Montblanc. In part, this applies to lactic-flowered and terry varieties, which have few seeds.
You should know that if you have collected seeds, then the plant you grow will resemble the parent bush very distantly. The main varietal characteristics, especially the brightness of the flower shade and the doubleness of the petals, will disappear. Nobody says that flowers will grow ugly, they just will be different. In addition, to see and evaluate the result of your work, you will have to wait at least five years.


Reproduction of peonies by seeds will require special skills from the grower. This is a laborious and rather complicated procedure with many features. But according to flower growers, all difficulties, long waiting for results, inconveniences are more than compensated for when you see flowers bred on your own.