What to do with blueberries in the fall: basic winter preparations
So, here's what you should do with your blueberries in the fall to get them ready for winter properly:
- Feed immediately after the end of fruiting and harvesting.
- Conduct sanitary pruning.
- Can be transplanted (if necessary, it is best to do this
Advice! It is better to replant blueberries in autumn when the leaves have already begun to crumble or at least turn red.
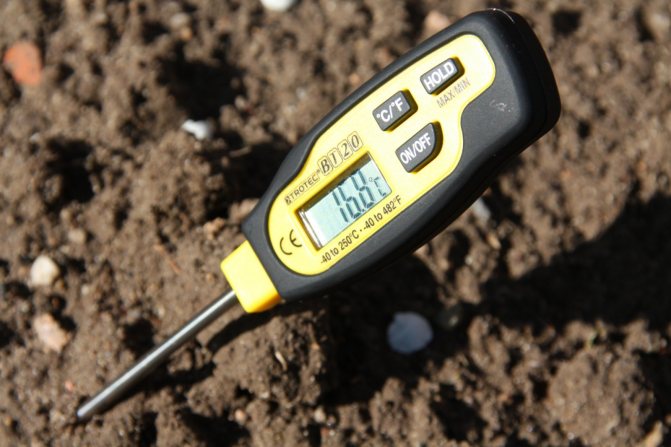
- Monitor humidity, i.e. continue to water (remember that blueberries belong to heather crops, which are very demanding on watering) and carry out moisture-charging watering (if the autumn is rainy enough, then it is not necessary, if it is dry, then it is very desirable - the earthen lump must be soaked to a depth of 15-30 cm) ...
- Shelter for the winter (mulch).
Video: how to care for blueberries in autumn and properly prepare for winter
Watering
Typically, the peak of watering for blueberries occurs in July - August. With the onset of autumn, it is recommended to significantly reduce the amount of water that is consumed to moisten the soil under the bush. If, for example, it rains regularly enough, then you can skip the blueberry watering can.
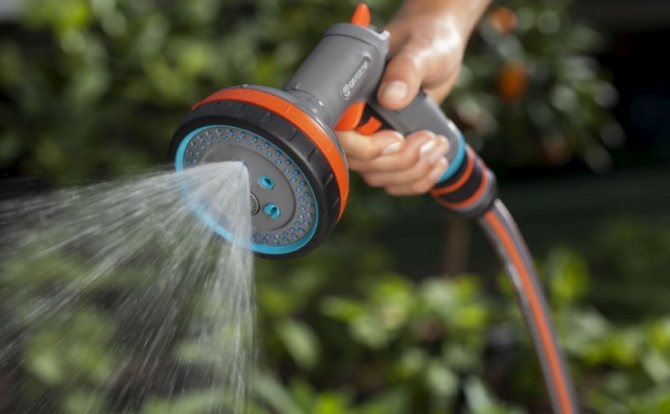

Use a spreader to water the blueberries in the fall to avoid scouring the soil.
But still, if the weather is dry and you are worried about the bushes, then 5 liters of water per bush every 3-4 days is enough for the blueberries to feel comfortable and not suffer from an excess or lack of moisture.
When and how to feed blueberries in autumn
The purpose of the autumn feeding is to help the shrub to lay new flower buds for the next year, as well as prepare the plant for winter (strengthen its immunity and improve winter hardiness).
When to fertilize
The last (autumn) feeding of blueberries is done after fruiting and picking berries, i.e. in the fall.


What to feed
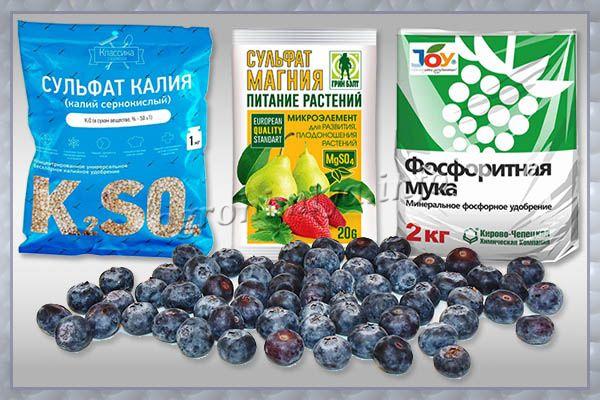
Remember that the end of fruiting and the onset of autumn (i.e. August-September) is the period when phosphorus-potassium fertilizers must be applied under all perennial plants (including blueberries).
So, phosphorus is necessary in order for the plant to strengthen the root system, and potassium for better ripening of the shoots, so that the branches do not freeze in winter, as well as for better laying of fruit buds for the next year. In short, the autumn feeding of blueberries is required for a good wintering and a rich future harvest.
It is especially desirable to feed if at the end of summer the growth of young shoots becomes noticeable.
What fertilizers are suitable (apply according to the instructions on the package):
Naturally, it is much more effective to use quickly and easily dissolving fertilizers, while the same superphosphate dissolves very poorly and does not act immediately.
- potassium sulfate (potassium sulfate) + superphosphate (slow);
- diammofoska (slow);
- potassium monophosphate (fast);
- plantafol or plantafid (fast).
Note! Blueberries are a "acid-loving" plant, which means that in alkaline soil it will very poorly assimilate any food.
So by no means do not feed blueberries with wood ash (use as potash fertilizer).
How to apply top dressing:
- Better at the root (root top dressing), but you can also on the leaf (foliar top dressing).
Advice! Top dressing in any case should be liquid: pour dry fertilizer and wait for the weather from the sea, i.e. rain is not the best idea.
Video: how to fertilize blueberries in the fall
Do I need to acidify the soil in the fall
As a rule, acidification of the soil under blueberries is done in spring and summer, but not in autumn.
By the way! The site has a separate material about how and what can acidify the soil under blueberries.
Blueberry disease tracheomycotic wilting and its treatment
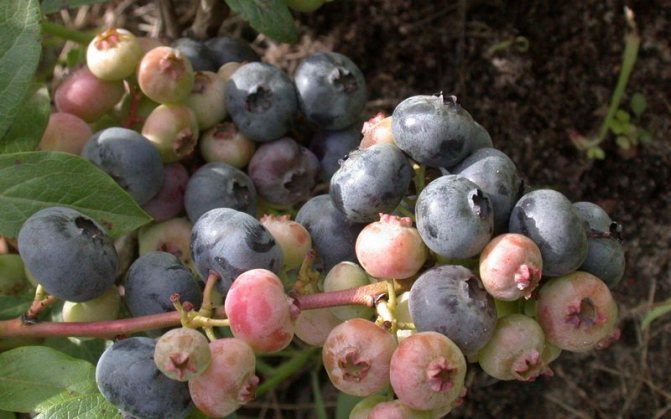


See how the diseases of garden blueberry manifest themselves - only some clinical cases are shown in the photo, they are described further on the page:
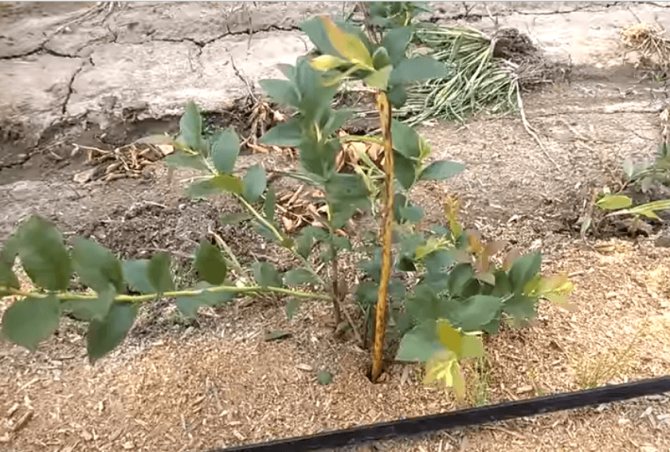
This blueberry disease and its treatment will be considered under the first number for a reason. It is the most common one. The causative agents of tracheomycotic wilting are fungi Fusarium oxysporum Schl. and Verticillium albo-atrum Rein, et Bert. These soil pathogens persist for many years on plant debris. The root system is affected, the roots turn brown and rot, the mycelium penetrates into the vessels of the root collar and stems and fills them with its mass. The influx of nutrients stops, and the affected plants, starting from the upper young shoots, wither, turn yellow, gradually turn brown and dry out.
When the roots decay in the autumn-winter period, blackening of the buds and drying out of the stems are observed on many bushes in the spring. On the affected parts of plants, especially on the cuts of shoots and roots, mycelium plaque develops. With Fusarium, the mycelium is pinkish-white, dense; in the spring, blackening of the buds and drying out of the stems are observed. On the affected parts of plants, especially on cuttings of shoots and roots, mycelium plaque develops.
With fusarium, the mycelium is pinkish-white, dense, with verticillium it is grayish, more airy. The infection spreads through contaminated soil, plant debris and contaminated planting material, in which the disease is often latent. Tracheomycotic wilting occurs precisely on young blueberry plants, which we acquire both in containers and with an open root system. Young plants with weak, fragile roots, affected by tracheomycotic wilting, die very quickly. The development of the disease is facilitated by low areas with stagnant water, heavy, clayey soils and a lack of sunlight.
Look at the manifestations of this blueberry disease in the photo, which demonstrates the most characteristic symptoms of the presence of a fungal infection:
Control measures. Use of healthy planting material without visible root necrosis and stem browning. Timely culling of dried plants along with roots, collection and removal of plant residues. Compliance with all agrotechnical requirements for the cultivation of this crop. At the first symptoms of wilting and root rot, the soil is shed under the plants with a solution of one of the drugs: phytosporin-M, alirin-B, gamair. In industrial cultivation, preventive spraying and root spills with a 0.2% solution of foundationol are carried out.
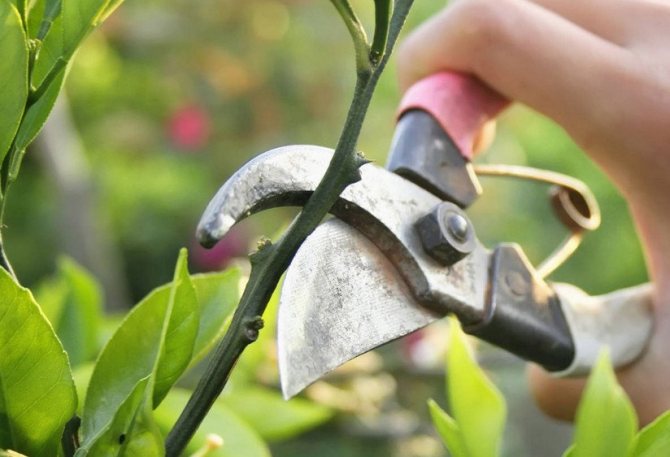
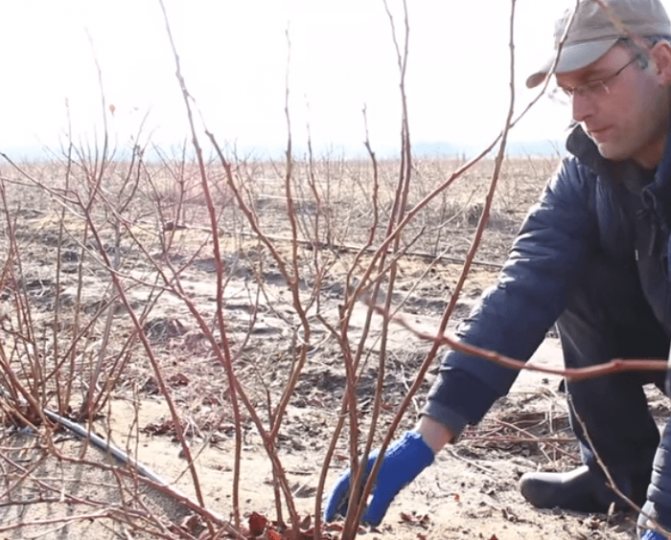
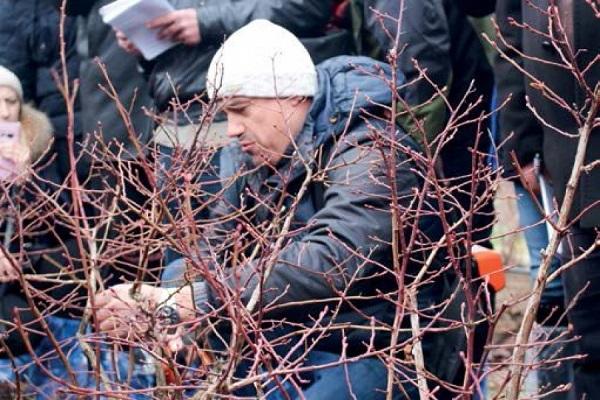
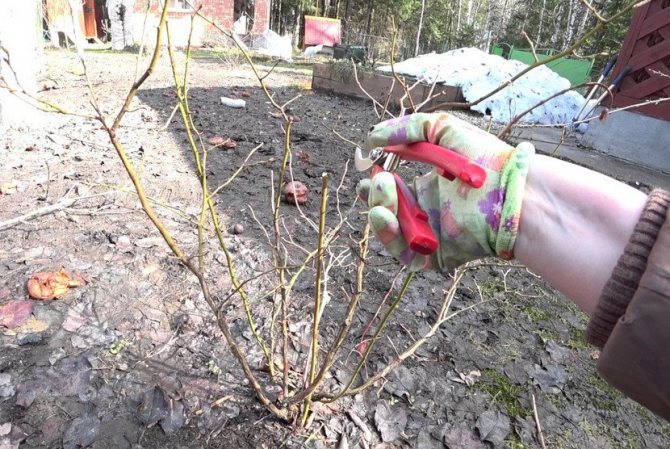
Pruning blueberries in autumn
Let's say right away that main trim blueberry it is better spend in the spring... The fact is that you never know what winter will be like and how your berry bush will survive it.
Another thing - autumn sanitary pruning of blueberries (with the beginning or after the fall of leaves), when necessary to get rid of broken, dry and painful twigs... Also subject to removal unripe young shoots.
Worth knowing! In general, blueberries require rejuvenating and regulating pruning.
If you do not prune in the future, then the bush will thicken over time, and the blueberries will simply be crushed and become sour.
The best time to prune blueberries is early spring, before the buds swell.
Types of trimming
Blueberry pruning is divided into three types: sanitary, shaping, and anti-aging.
See also
Why blueberries do not bear fruit and what to do, reasons and solutionsRead


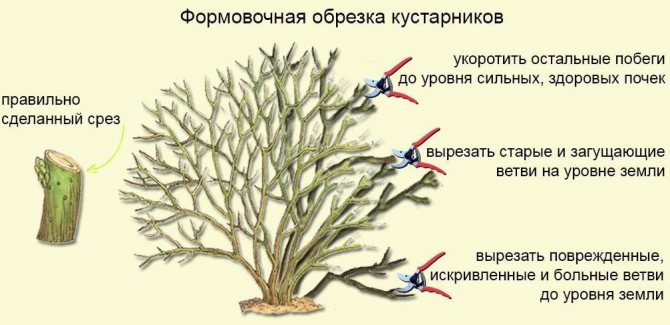
Sanitary
This type of pruning is carried out when the need arises, as a rule, this is done immediately after wintering. It is needed to get rid of broken or infected shoots. Cut off dry, diseased branches to normalize the movement of juices in the stems. Get rid of recumbent branches and bushy growth. The frozen tops are cut off.
Forming
From late autumn to early spring, shaping pruning of blueberries is carried out. Cut off the buds on seedlings to avoid premature fruiting, since early harvests are scarce and take a large amount of energy from the plant.
The plant is shortened if there is a disproportionate crown in relation to the roots, in order to provide the roots with energy so that they can grow. Formative pruning is carried out, as a rule, for plants from three years old. First of all, they get rid of small growth. In large farms, the growth begins to be removed already in the first year.


Rejuvenating
It is carried out in order to restore the ability of blueberry bushes to bring a large and high-quality harvest. In well-tended gardens, blueberry bushes can bear fruit for more than three decades, however, from the age of five, the plant's yield drops noticeably.
Old blueberry branches are overgrown on top with a large number of short branches. As a result, very small berries grow on them. However, vertical shoots often extend from the middle of the old branches. It is necessary at the right time to make a cut above the shoot in order to transfer the branch to it. If there are no such shoots on the old branch, then it should be cut off at the very base.


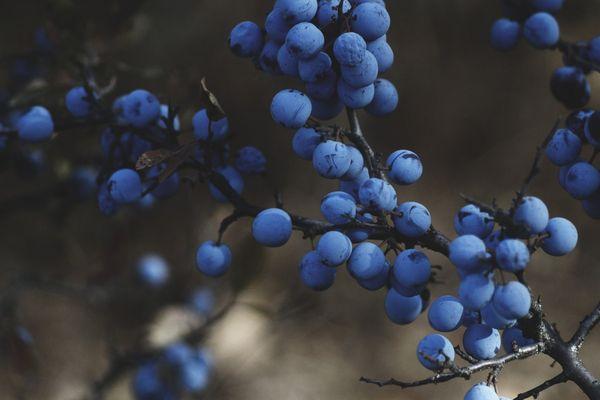
Shelter blueberries for the winter
Blueberries are quite frost-resistant and can easily withstand frosts down to -34 degrees (but there are some thermophilic varieties that can withstand a maximum of -24 degrees), especially if the winter is snowy (Remember that snow is the best insulation!).
But, if your winters are usually frosty, but snowless, then the blueberries should definitely be insulated.
It is especially important to do this with young seedlings planted this year.
In general, the direct preparation of blueberries for winter consists in its shelter, or rather, in warming by mulching the trunk circle.
Video: the last preparation of blueberries for winter - mulching
Important! It is not necessary to wrap with agrofibre (spunbond, lutrasil), it is better to just mulch well and tie up the shoots so that they do not break off due to snow and winds.
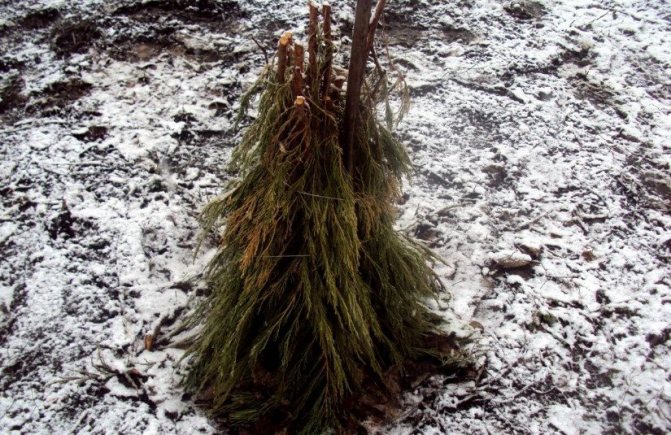
As a maximum, young blueberry bushes (up to 2 years old) can be covered with spruce branches, putting it in a hut and tying it up. Thus, the snow will linger better on the bush, and it will be warmer in winter.
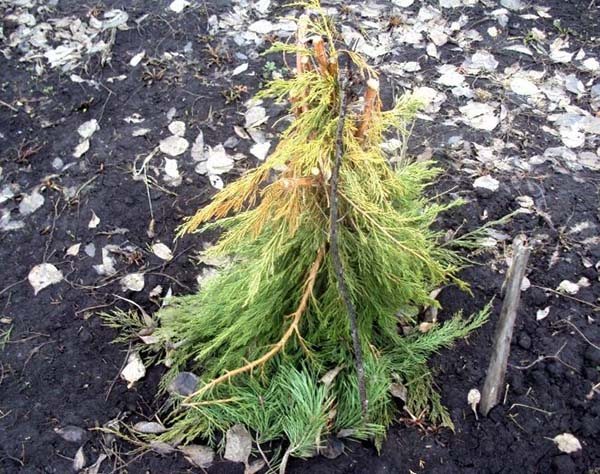


How can you mulch blueberries for the winter?
- dry sawdust:
- spruce or pine litter from the forest (preferably rotted);
- straw.
At what height to mulch:
- 5-10 centimeters (young, 1-2 years old, 8-10 s higher, older, 4-5 years old, - 5 cm).


Many people ask quite a logical question: “What to do with mulch in spring, namely sawdust?»
As a rule, it is better to lightly rake the sawdust on the sides and add some coniferous litter or sour peat in them, which do not harden and pass moisture well, in other words, loosen.
Thus, now you know what to do with blueberries in the fall, so that next season it will please you again (or for the first time) with a generous harvest. Good luck!
Video: preparing blueberries for winter
Adding an article to a new collection
To keep the blueberry berry in order, you need timely feeding, watering, pruning and other procedures. We will tell you how to organize the care of your crop from spring to autumn.
Blueberry care is strictly tied to the annual cycle of cultural development. Agricultural technology includes fertilizing, organizing irrigation, pruning, organizing pollination of the berry, controlling the activity of pests and weeds, and harvesting.
In the period from November to mid-March, blueberries are in vegetative dormancy. At this time, caring for it involves only the introduction of autumn herbicides that inhibit the growth of perennial weeds. But with the arrival of spring, culture gradually revives and requires a whole range of measures for full development. The most important steps in caring for the berry are presented in the memo.
How and what to fertilize
You need to start with the most important thing - in the fall, in no case apply organic fertilizers under the bush, whether it be compost, humus, or fallen leaves. Otherwise, instead of blueberries "falling asleep" with the arrival of winter, on the contrary, they will begin to awaken to life again, to dissolve leaves and flowers.
Also, because of this effect, one should refrain from introducing nitrogen into the soil in the fall. Usually soil fertilization occurs after sanitary pruning, when all dried, diseased and old branches have been removed from the bush.
This is done so that the already unnecessary parts of the blueberry do not take away nutrients for themselves, which in the end may not be enough for the younger growth.
First, each bush needs to be well watered using 4-5 buckets of water.
After moistening the soil, 40 g of double superphosphate and 40 g of potassium sulfate should be added under each plant.


Usually, for better assimilation of fertilizers, they are applied directly to the ground, but since the root system of blueberries is located very close to the surface, it is highly discouraged to do this. Better sprinkle superphosphate and potassium at the base of the bush and sprinkle the minerals with earth.
Spring blueberry care work
Already from mid-March, you can remove covering material from the berry, check how the bushes survived the winter, and prepare them for the upcoming season. Major spring jobs include pruning, mulching and fertilizing.
Spring Blueberry Pruning
Duration: mid-end of March
Without spring pruning, the growth of the berry plant slows down, the number of flower buds decreases, and the berries themselves become smaller. The procedure is carried out from the third year after planting: young blueberries only require sanitary thinning. But already from the age of 4-5 years, there is a need to rejuvenate the bush, as well as to prevent its excessive thickening.
Blueberry viral diseases
This large group of diseases is dangerous because there is no effective treatment. The fight against infection is reduced to adherence to agricultural cultivation techniques, rules of care. The virus is resistant to external influences, can be in the soil for a long time, fallen leaves. Shows activity at high humidity, prolonged heat.
Red ring spot
It is rare, most often infection is observed in regions with dry and warm climates. The pathogen is in the ground or enters an area with poor-quality planting material. When infected, old leaves and shoots begin to die off. Then, on all parts of the bush, reddish, ring-shaped spots appear. It is almost impossible to save the plant; in order to prevent infection, a high-quality pre-sowing treatment should be carried out, and the planting density and crop rotation should be monitored.
Dwarf bush
It is caused by mycoplasmas, an intermediate life form between bacteria and viruses. The development of the disease takes several years; it is almost impossible to detect infection in the early stages. The plant gradually weakens and stops growing. The leaves turn red and then deform and crumble. A typical sign of dwarfism is the presence of a strip on the shoots from the second year of life. There is no cure for this disease, so it is important to follow simple preventive measures.
Mosaic
A viral disease characterized by rapid development.It can lead to the death of the bush within several months, is actively spreading throughout the area and does not respond to treatment. Signs:
- slowdown in the growth and development of shoots;
- ovaries are not formed, the berries stop ripening;
- characteristic light spots appear on the leaves in the form of a mosaic pattern;
- the shoots and stem are deformed and then wither.
The main carrier of the causative agent of this disease is spider and kidney mites. To avoid the development of infection, it is important to carry out prophylactic treatment with a broad-spectrum insecticide. It is necessary to spray not only the shrubs, but also the soil nearby, the recommended working time is early spring and autumn.


Prevention methods
Following simple preventive measures is the easiest way to avoid garden blueberry diseases. Effective prevention methods:
- regular sanitary pruning of bushes;
- checking the planting material before planting;
- use of resistant varieties with immunity to infections;
- planned chemical treatment of the entire planting and soil in autumn and winter;
- cleaning of fallen leaves, flowers and fruits.
In addition, it is important to observe the regime of watering, top dressing and regularly carry out deep loosening of the soil. When using mulch, the material should be changed at least once every two months.
Summer blueberry care jobs
Summer is the period when blueberries develop and ripen. At this time, caring for the shrub consists of controlling weeds, fertilizing, watering and scaring away birds.
Weed control
Duration: throughout the season
Even if you mulched the soil in the spring, in the summer you still have to cultivate row spacings to reduce the pressure of weeds on the berry crop. The herb competes with blueberries for access to moisture and nutrients. In addition, thickets of weeds change the microclimate in the lower part of the bush, increasing the temperature. This leads to the risk of bacterial and fungal diseases.
For extensive planting, the simplest weed control solution is herbicide (Roundup, Starane). However, if you have only a few rows of a berry, you can easily cut off the grass with your hands and mow it in the aisles.
Watering
Duration: regularly throughout the season
Blueberry is a moisture-loving plant, but at the same time it is afraid of excess water no less than drought. The peculiarity of the culture is that up to 70-90% of its root system lies at a depth of only 30-40 cm. This layer of soil dries up quickly. Therefore, watering should be not so much abundant as frequent. As a rule, 5-10 liters of water is enough for an adult bush twice a week.
In the hottest months, when the soil surface dries out much faster, the berry needs more frequent watering. In this case, automatic drip irrigation systems help. In addition, blueberries are very responsive to leaf watering. Spraying is a must during the driest months, as the leaf blade of the culture is not adapted to self-regulation of the level of evaporation. Spraying is best done in the afternoon (after 16.00). This reduces stress from overheating and speeds up photosynthesis.
Maximum attention should be paid to watering during the period of fruiting and laying of flower buds for the next season (in July-August). At this time, a lack of moisture will lead to the loss of part of the crop not only this, but also next year.
Blueberries prefer acidic soils, so during the whole season, water the bush with acidified water a couple of times a month (the watering rate remains - 5-10 liters for one adult plant). The water is acidified with table vinegar, citric acid or special compounds. It is quite difficult to indicate the rate of acidifier for a 10-liter bucket, since the initial hardness of the water is different for everyone. We recommend focusing on the pH balance of the irrigation liquid, which after acidification should be 4-4.5 units.
If you do not have a pH meter, you can use the average acidifier rates. For 10 liters of water, add either 100 ml of table vinegar or 3 tsp. citric acid (no slide).
Fertilization
Duration: early-mid July
Additional application of fertilizers in the form of spraying or root dressing is necessary if a deficiency of individual nutrients can be diagnosed by the appearance of the plant.
Here are some examples.
| Lack of micro- and macronutrients | Symptoms | Fertilization rate |
| Nitrogen | Shoots grow slowly, the leaves turn yellowish-green according to the norms of applying complex mineral fertilizers in accordance with the age of the bush | According to the norms of applying complex mineral fertilizers in accordance with the age of the bush |
| Phosphorus | The tops of the leaves take on a purple hue and nestle tightly against the stem | |
| Potassium | The tops of the leaves die off | |
| Calcium | Leaves curl and turn yellow at the edges; a yellow-green spot appears in the apical part of the leaf plate | Dolomite limestone introduction (100 g per 1 sq. M) |
| Magnesium | The edge of the leaf turns red | Spraying with magnesium sulfate (100 g / l of water) |
| Sulfur | Chlorotic spots appear |
Sulfur is applied not in pure form, but in the composition of sulfate forms of nitrogen or phosphorus fertilizers. |
A planned three-stage application of complex fertilizers allows avoiding mineral starvation. With the proper organization of feeding, the need for additional application of minerals is extremely rare.
Installation of bird scarers
Duration: June July
During the period of berry development, it's time to take care of bird scaring devices. After all, when the blueberries begin to ripen, only these devices will help you save the crop from birds.
Harvesting
Duration: July-September
The early blueberry varieties begin to ripen in July, while the later ones delight with fresh berries until September. At this time, it is important to organize the harvest.
If the berries are intended for sale, it is rather difficult to determine the timing of their collection. Early removal of blueberries from the bush will guarantee their good transportability, but such berries will have a sour taste. On the contrary, fully ripe, blueberries gain sweetness, but at the same time they will be easy to crinkle.
Blueberry leaf diseases
The most common blueberry leaf diseases are blotches of various kinds, which develop in high humidity conditions. The causative agents are various kinds of fungi and viruses.
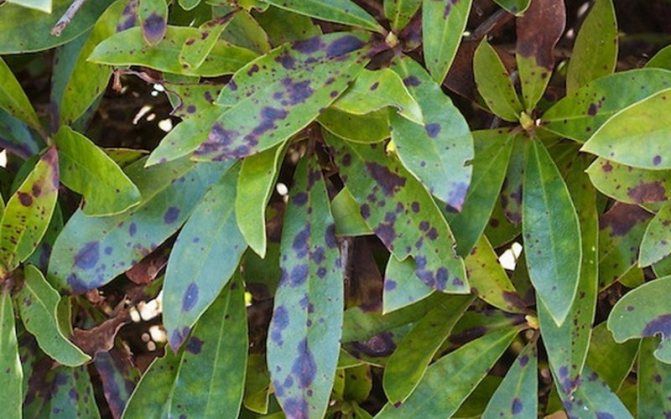


Phylostic blight of blueberry leaves.
The causative agent is the mushroom Phyllosticta leptidae Fr. The spots on the leaves are round, large, dark brown with a wide purple-brown border. Over time, the center of the necrotic tissue becomes grayish, but a wide purple border always remains. In the necrotic tissue, small dotted fruit bodies of the wintering stage are formed - pycnidia. Very often, necrotic tissue cracks and falls out. Affected leaves turn yellow and fall off prematurely. The infection persists in the affected fallen leaves.
Control measures. Use of healthy planting material, compliance with all requirements of cultivation agrotechnology, collection and disposal of plant residues. Preventive spraying of bushes when opening leaves with 1% Bordeaux mixture or its substitutes (HOM, Abiga-Peak). With a massive manifestation of the disease, spraying is repeated after picking berries with the same preparations.
Read also How to start renovating an apartment in a new building
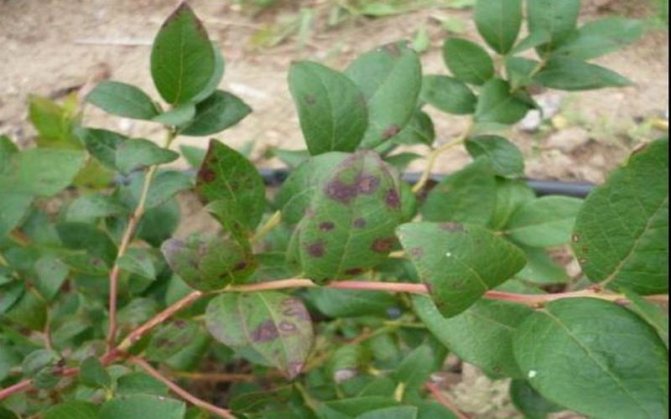


Blueberry septoroid spot.
The causative agent is the mushroom Septoria allopunctata Demaree and Wilox... Numerous small, rounded, reddish-brown spots appear on the leaves in mid-summer.Gradually, the center of the spots brightens and becomes gray-brown, but a red rim remains. Over time, small dotted black fruiting bodies of the hibernating stage are formed in the necrotic tissue. Affected leaves turn brown and dry out. With a strong spread of the disease, necrotic spots appear on the petioles and young shoots. On the branches, the spots are small, rounded, light in the center and surrounded by a thin red rim. As the bark dies off and fruiting bodies form in it, the affected stems gradually dry out. The infection persists in the fallen diseased leaves and in the bark of the affected shoots.
Control measures. Same as against blueberry phyllostic spot.


Red spot of blueberry leaves.
The causative agent is the Tobacco ringspot virus (TRSV). Chlorotic translucent spots appear on the leaves along the veins. Gradually, they turn red and dry out. Affected leaves turn yellow prematurely, become smaller, the shoots lag behind in development, the bushes overwinter badly and often freeze out. The virus is transmitted by a nematode.
Control measures. Use of healthy planting material, timely culling and burning of affected plants.
Autumn blueberry care work
The main task of the autumn period is to prepare the berry for wintering.
Watering
Duration: September - mid-October
Watering in the fall is carried out taking into account the weather conditions, because rain becomes a faithful assistant in this work. Remember that you cannot fill the berry, otherwise the root system can rot. Also, do not forget to periodically water the bushes with acidified water.
Weed control
Duration: September - mid-October
In the fall, the last few weeding should be carried out and the aisles should be cultivated so that the weed does not drown out the berry.
Dismantling bird scarers
Duration: September - mid-October
When the berries have already been harvested, you can dismantle the devices for scaring away birds. After all, now the birds do not threaten the harvest.
Pruning
Duration: after falling leaves
Formative pruning of blueberries starts from the 4th year of cultivation, before that only sanitary pruning of bushes is carried out, removing dry, accidentally broken and diseased shoots.
Traditionally, formative pruning is done in the spring. However, the event is allowed to be postponed until autumn (after leaf fall) in areas with mild winters and significant snow cover. Remove cut shoots from the site and burn to prevent diseases and pests from overwintering in your garden, and act as a source of infection in the spring.
Shelter for the winter
Duration: end of October - November
Garden blueberry is a cold-resistant crop. Various varieties can withstand temperatures as low as –25-28 ° C. However, one should beware of winters, when frosty weather often gives way to thaws. The lack of snow also causes damage to the berry. In other words, it will not hurt to play it safe and protect the above-ground part of the bushes from freezing. To do this, use nonwovens and spruce branches.
In the spring, remove the covering material. And do not be afraid of late frosts. Blooming blueberries easily tolerate frosts down to –7 ° C without any significant losses.
By understanding what kind of care blueberries need during the season, you will not be aware of problems with this culture. And in your garden every summer you will have a personal storehouse of berry vitamins.


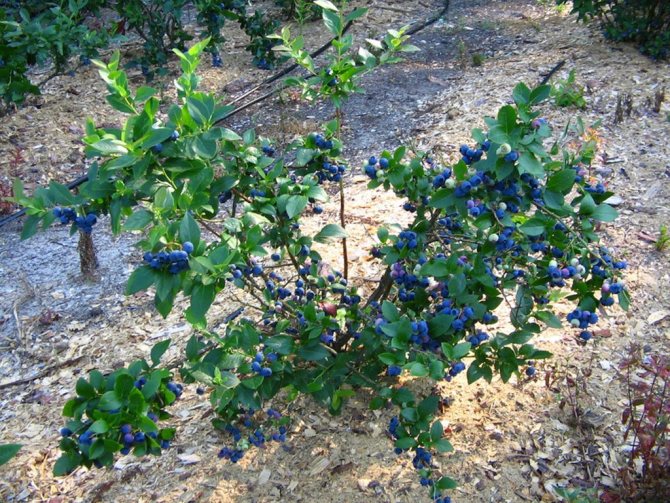
Garden blueberry is a tall, deciduous shrub native to North America. Unlike cold-tolerant species, American-bred blueberries are suitable for temperate and warm climates. The bush reaches a height of two meters and produces up to 10 kg of berries, which makes it profitable to grow blueberries even in the country or in the garden.
Planting and caring for garden blueberries is not very difficult. The plant is demanding on the composition of the soil, warmth and light.All these needs must be taken into account immediately, when choosing a site, because blueberries are a long-liver, and can grow and bear fruit in one place for several decades.
Mulching
The mulch needs to be changed annually, in the fall, after you've fertilized the soil and oxidized it. The most important thing is to be in time before the frost. The bark of trees, sawdust, needles, straw or dry earth are suitable as a basis.


The layer of the mulch itself can range from 4 to 15 cm. Such a precaution will help reduce the number of weeds on the site and protect the bush from the negative effects of spring frosts.
Read also What paint to paint a chipboard floor
Delicious and healthy berry
Blueberries are a shrub that grows up to 1 meter in height. In high-altitude places it grows as a low shrub. Shoots are oblong, pubescent in the initial period of growth. Leaves are elliptical, slightly folded at the edges, bluish-green, matte on top.
Green or whitish flowers appear on the tops of the lateral branches. Blooms in May. The berries are spherical, purple-black, with a blue waxy coating.


The shrub grows in swamps, in swampy forests, on infertile soils containing little humus. In the mountains it grows at high altitudes. The berry has excellent taste and nutritional value and is rich in vitamins. It is important to know how to plant blueberries correctly, prepare the soil for planting, how to care for blueberries.
Fertilizer for blueberries when planting
Check out these articles as well
- Aphids on the drain
- Insecticide Imidor from pests
- Insecticide Bazudin from insects
- Acaricide Sunmight


In order for the culture to quickly start and grow, it is recommended to purchase a special “Four Seasons” soil for blueberries and wild berries.
Garden blueberries do not have any special requirements for growing. Yet good land is needed for its normal growth. In order for the culture to quickly begin and grow, it is recommended to purchase a special “Four Seasons” soil for blueberries and wild berries. In this case, when planting, it will not be necessary to use fertilizers, since this land already contains all the necessary nutrients for the normal development of the culture.
Important!
When planting blueberries, it is not so much fertilization that is important as the acidity of the soil. Experts recommend adding sour peat to the planting soil so that the bush takes root faster.
Landing rules
When choosing plants, you need to take into account the compliance of the variety with the agro-climatic conditions of the region. Selecting a site and preparing the soil is straightforward, but with just one blueberry variety, it is difficult to create the conditions for good quality cross-pollination. At least 2-3 plants of various varieties should be planted side by side. Bushes located nearby will lead to better fruiting and early ripening of the crop. It should be borne in mind that without insect pollination, blueberry fruits are smaller and have a thick skin. It is advisable to cultivate honey plants near the berry, which attract insects well.


Landing time
Varietal seedlings of fruit shrubs are always sold in plastic boxes or pots. This is the most comfortable planting material. Plants can be grown at home until the planting site is prepared. When planting blueberries is important to achieve good results. You can transplant a seedling to a permanent place throughout the growing season. Planting a closed-rooted garden blueberry is similar to transferring a potted plant from a smaller container to a larger container. A lump of substrate protects the roots from damage, which allows a 2-3 year old seedling to quickly adapt to new conditions.
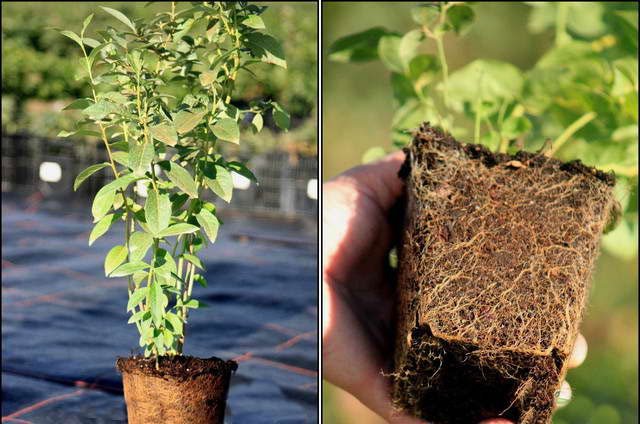


It is better to transplant adult bushes in the fall, after leaf fall. A planting pit or trench is prepared in advance, filled with a prepared substrate so that the soil has time to settle.
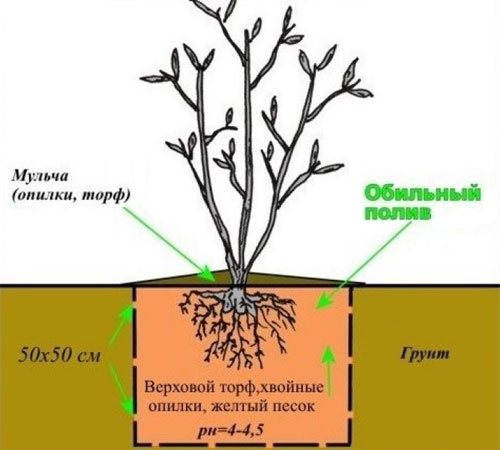
Soil preparation
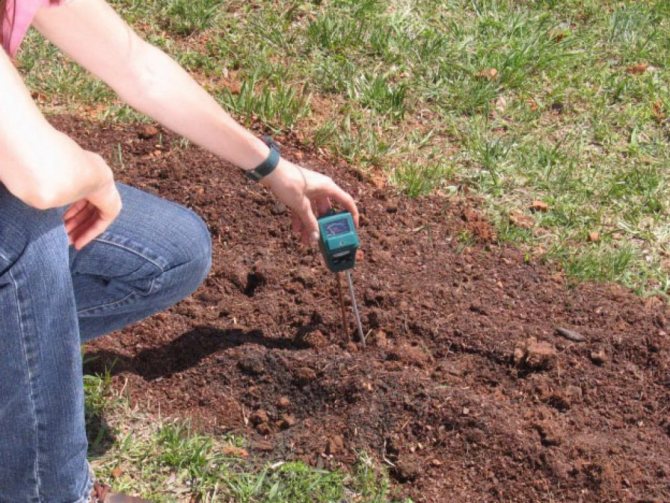
Well-drained, light, peaty-sandy, loamy soils are favorable for the berry. The acidity of the substrate is from 3.5 to 4.8 units.All heather crops grow well only on acidic soils, neutral, and even more so alkaline environment is unfavorable for plants. This feature is due to the fact that the fibrous root of the plant functions in symbiosis with the fungal mycelium.
Important! Mycorrhiza is a form of symbiosis of plants with fungi, in which there is an interchange of nutrients. Fungal mycelium actively develops only in an acidic environment.
The soil mixture is prepared from:
- peat;
- sand;
- sawdust;
- fallen leaves, needles;
- tree bark.
The components are mixed by adding 40-60 g of sulfur.
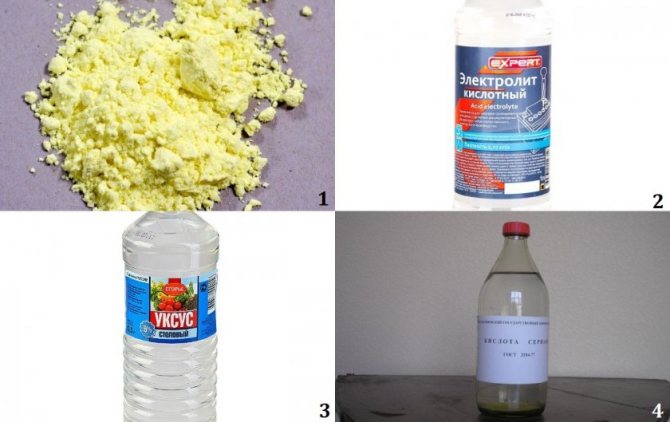
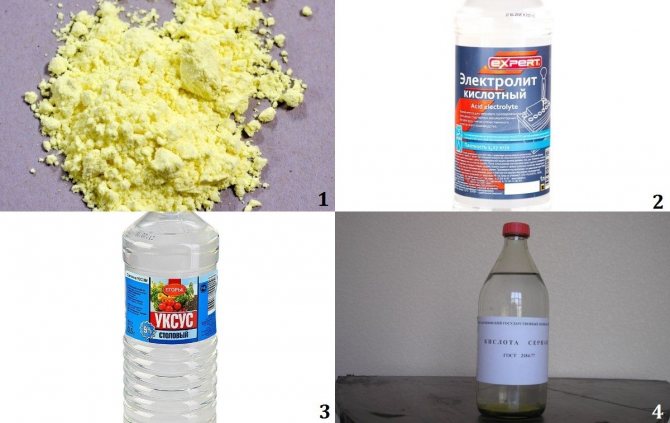
Also, a solution of citric, acetic, malic acid helps to bring the acidity of the soil to 3.5-4.5 units. A cheaper option is battery electrolyte, 5 ml of which is diluted in 1 liter of water. The preparation of the pit will require 1.5-2 buckets of solution.

Planting in spring
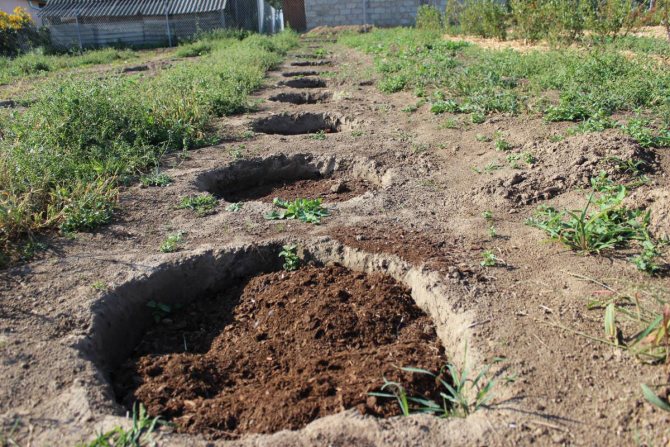
A place for blueberries is chosen sunny, on a hill, it is desirable that the land in this place be fallow for several years. In addition to lighting, the level of groundwater should be taken into account. In areas where flooding and stagnation of water are possible, drainage is mandatory. The feeding area for tall varieties should be 1.5-2 sq. m. When planting several plants, planting holes are dug at a distance of 1.2-1.5 m from each other, with a diameter of 60 cm and a depth of 40-50 cm. The bottom is lined with a thick layer of rotted leaves, prepared soil is laid on top.
The seedlings are transplanted to a permanent place after a couple of weeks, when the soil settles. Previously, containers with seedlings are placed in a container with water for 15 minutes. A well-moistened lump is easier to reach without damaging the small and thin blueberry roots. It is advisable to gently straighten the pressed roots in order to change the direction of their growth in the horizontal direction. The seedling is placed in a dug hole and sprinkled with the removed soil. The earth is slightly compacted, watered and mulched with sawdust with a layer of 5-8 cm.


Important! With insufficient light, the berries become smaller, fewer flower buds are laid, which affects the next year's harvest.
Planting in autumn
In the fall, when part of the site is completely vacated, you can transplant blueberries to a new place or plant a new variety on old bushes. It is advisable to prepare the soil in advance and fill the landing pits with it. The work must be done on time - this is the main feature of planting blueberries in the fall. Plants must settle in a new place before the onset of a stable cold snap, and for this they will need 30-45 days. For adult plants, leaf fall is a signal of readiness for transplanting. For the winter, plantings are mulched and covered with spruce branches.


Fungal diseases
They are found everywhere, especially often, infection occurs against the background of hot and humid weather. The pathogen can be in the ground for a long time, it tolerates severe frosts. Leads to massive damage to the bush, against which the yield is significantly reduced. Fungal infections respond well to early treatment.
Anthracnose
The causative agent of the disease is a fungus of the genus Botrytis cinerea. Infection usually occurs against the background of excessive planting density, stagnation of water in the ground and prolonged drought. Young bushes and plants are especially susceptible to disease during flowering and fruiting. Infestation can be determined by the appearance of dark spots on the leaf blades. They gradually increase in size and dry out. Blueberries are lagging behind in growth, flowers are not tied, and the fruits fall off.
Read also Moulinex home bread baguette recipes
For the treatment of anthracnose on varietal garden blueberries, treatment with copper-containing fungicides is used as a Bordeaux liquid. In the early stages of lesion, complex drugs are effective, for example, Topsin M, Skor, Euparen and others.
Gray rot
A common fungal disease that occurs in almost all climates.The pathogen is activated at high air and soil moisture, stable warm temperature. Leaves and stems are affected first. Yellowish spots appear on them, which gradually darken and affect a large area of the plant. The berries rot, and the bush itself withers and looks weakened. Even if there is no gray coating on the fruits, they cannot be used for food, as the taste and aroma change. All infected shoots die off within one season. Gray rot quickly spreads over the site, can overwinter on fallen leaves and in the soil.
The main method of treatment is spraying the planting with fungicides with a high copper content. For prevention, work is carried out in the fall and spring. In addition, it is important to remove all fallen leaves, the remains of other plants.
Phomopsis wilt
The disease is caused by a fungus of the genus Phomopsis vaccinii. Most often found on tall varieties of dove. Infection develops through the upper parts of the bush, then the entire stem, flowers and fruits are gradually affected. Symptoms:
- brown spots appear on the shoots, which merge and form brown-gray ulcers with a distinct border along the edge;
- after 2-3 months, active drying of the branches begins;
- the tops of the shoots are wrapped.
Outwardly, Phomopsis wilting resembles a sunburn, but the disease is extremely contagious for neighboring bushes. Treatment should begin with mass pruning of the affected parts of the bush. After that, the plant must be treated with a solution of Fundazol or Topsin.
Moniliosis, or fruit rot
A fungal disease that usually develops after a cold and snowy winter. The pathogen can tolerate low temperatures, it can stay in the ground for several years, retaining its potential activity. The first sign of moniliosis is a yellowing of the top of the stem. Flowers do not form or wither. If fruits have already formed on the plant, they darken and become wrinkled.
The infected plant should be pruned, leaving a few young and healthy shoots from the first year of growth. Then carry out a two-stage treatment of the planting with any copper-containing fungicide.
Stem cancer
The fungus enters the plant through the root system or the bottom of the bush. The peak of infection occurs in the first half of summer; young and weakened plants are at risk. Infection symptoms:
- the formation of red spots on the leaves in the form of dots, which gradually grow;
- deep ulcers develop on shoots and leaf blades, leading to death;
- the flowers become smaller, the fruits dry up and crumble;
- the plant gradually reduces the growth rate, stops developing due to metabolic disorders.
Stem cancer in garden blueberries is difficult to treat. The problem can be completely eliminated only in the early stages of infection. To combat the fungus, the bush and soil are treated with a 1% solution of Bordeaux liquid or Fundazole.
Growing garden blueberries
Blueberries are quite unpretentious, at the initial stage, after planting, caring for blueberries is reduced to timely watering and weeding. In subsequent periods, when the plant takes root and starts growing, additional care will be required, which will include annual pruning, protection from pests and diseases.


Watering
The upper, root layer of soil under fruit bushes should always be kept moist.
- Water the blueberries abundantly - 1-2 buckets of water per bush, twice a week.
- In hot weather, it is advisable to spray blueberries to reduce the stress of the leaves from overheating.
- Adequate watering of mature shrubs is especially important during the period of fruiting and bud formation.
In case of drought and lack of watering, blueberry fruits become shallower, the yield of this and next season decreases.


Top dressing
The plant is not demanding on fertility, however, the use of mineral fertilizers for blueberries replenishes the nutrients washed out of the soil during irrigation.
On soils with acidity from 3.5 to 4.8, it is recommended to use:
- ammonium sulfate - 90 g;
- superphosphate - 110 g;
- potassium sulfate - 40 g.
The rate is calculated for 1 fruiting bush. Top dressing is carried out twice during the growing season, every 6-7 weeks.
When growing in a garden, it is advisable to use a simpler feeding method using complex mineral fertilizers.
Important! When feeding blueberries, it is completely forbidden to use any organic fertilizers.
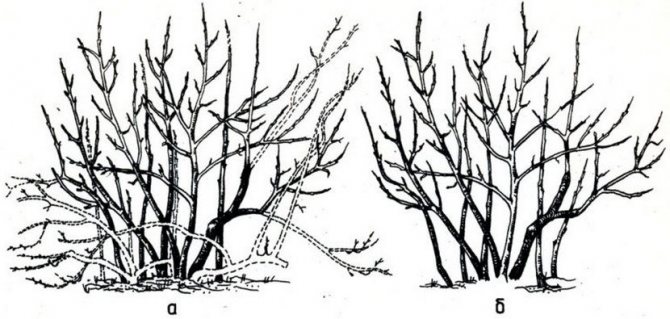
Pruning
A technique such as pruning seriously affects the growth and development of the bush. It can be used to change the quality of blueberries and the amount of harvest.

Annual pruning is done after 4 years of age.
- Thinning of shoots is carried out, cutting the middle, removing dry branches.
- Remove spreading, low-lying branches around the entire perimeter. Leave only erect, strong growths.
- Cut thin, small branches to provide adequate lighting and nutrition for strong, skeletal shoots.
Pruning fruiting bushes has a specific purpose. To obtain large berries, remove all branches older than five years of age. If yield is important, then it is permissible to keep the shoots up to the age of 6-7 years. Of the annual increments, no more than 5 of the strongest are left.

It is recommended to prune blueberries in the spring, as early as possible, before the buds have blossomed. Autumn pruning is practiced only in areas with a mild climate and a high level of snow cover.
Important! After flowering, large doses of nitrogen are not applied under the bushes, which provoke excessive growth of shoots in autumn. The growths that did not have time to ripen do not tolerate wintering well.
Blueberries in autumn
After harvesting and falling leaves, you should prepare the blueberries for winter.
- It is necessary to remove broken eyelids, fallen leaves. At the slightest sign of fungal diseases, diseased shoots and foliage are burned.
- If autumn is dry, then intensified watering is carried out in order to saturate the root layer with moisture. To do this, up to 6 buckets of water are poured under each bush.
- The land under the bushes is mulched. Plants will need an extra dose of nitrogen when using fresh sawdust. Top dressing of blueberries in the fall should restore its deficiency. Microorganisms that decompose sawdust intensively absorb nitrogen from the soil.
- In the conditions of a region with low winter temperatures for blueberry bushes, they create additional protection from any available materials, except for plastic wrap. It can be spruce branches, burlap, spunbond, pieces of foam rubber.
Caring for blueberries in the fall includes protection from rodent infestations. Hibernating under a layer of mulch, mice gnaw the bark, dig in the roots. It is necessary to set up traps in the fall and spread the poison in places of their possible habitat.
Features of the berry
The blueberry is a bush with oval green leaves, reaching a height of one to two and a half meters. The berries are blue, 1-2 centimeters in diameter.
The blueberry bush contains shoots of different ages. The branches on the sides over two years old are distinguished by the highest yield. Old branches that are more than four to five years old bear much less fruit than two to three years old.
Young stems have a smooth bark of bright color, there are no branches on them. Older stems are characterized by strong branching and yield the richest yields. In order to achieve a rich harvest in plantation conditions, it is customary to leave ten fruiting branches on the bushes.
In summer cottages, gardeners, as a rule, leave the blueberries thicker, getting more harvest from the bush, but the berries grow smaller.
Blueberry propagation
Blueberries are propagated vegetatively or by seed.
- Seeds are collected from ripe berries and immediately planted for germination, or dried and stored in paper bags. Seeds do not lose their germination for about 12 years, but before planting they must be awakened by keeping them at a temperature of 3-5 degrees in wet sand for about three months.Seeds are sown in pots with well-moistened peat and placed in a warm, bright place. With the appearance of 5 true leaves, the seedlings are transplanted into a greenhouse. In the summer, the seedlings are fed with mineral fertilizers, keeping the soil moist. In October, plantings are mulched with peat and covered with two layers of spunbond for wintering. In the spring, plants are transplanted to a training bed or containers.
- Vegetatively, blueberries are propagated by cuttings or layering. Lignified cuttings are harvested from December to March, semi-lignified - in summer, from late June to mid-July. The cuttings are rooted in the greenhouse, processing them before this means for better root formation. In small greenhouses, the soil is constantly kept moist. By the end of August, the film is removed from the greenhouses. In October, plantings are mulched with peat and from the first days of November they are covered with spunbond. In the spring, seedlings are transplanted into pots, boxes for further cultivation.


- In the garden, blueberry bushes are also propagated by layering. To do this, the side shoot is pressed to the ground and sprinkled with sawdust and soil. After a couple of seasons, roots form at the base. The branch is separated from the bush and grown in a nursery or container. Since blueberries do not take root well, the process takes a long time and produces a small amount of planting material.
Obtaining seedlings from seeds is a lengthy process, while the signs of the garden blueberry variety are not preserved. It will be possible to identify the advantages and disadvantages of the plant only after the first harvest is obtained, which may take 5-6 years. This method is suitable for amateurs of breeding work. It is much more convenient for the gardener to propagate the plant he likes by cuttings, while the varietal characteristics are fully preserved.
Bush care after pruning
After the autumn pruning, blueberry bushes are treated with garden varnish so that harmful bacteria and pathogens do not penetrate into open wounds. Garden varnish processing is done for thick stems, from one centimeter and thicker.
In addition, it is necessary to feed the plant so that it regains its vitality before wintering. For these purposes, mineral fertilizers rich in potassium and phosphorus are used. In this case, it is impossible to use nitrogen fertilizers, in order to avoid freezing of the bush.


Pests
Insects that eat leaves and buds and feed on plant sap can cause minor harm to tall blueberries.
- pine silkworm caterpillars;
- leaf rollers;
- scabbards;
- aphid.
Chemicals are used against insects; it is enough to collect the caterpillars by hand.
More damage can be caused by birds that attack berry growers during the ripening period of the crop. For protection, the blueberries are covered with a fine mesh, shiny objects are attached to the branches, and sound cannons are installed.


Blueberry pests
The following are the most common blueberry pests and control measures using plant protection chemicals.
Acleris schalleriana F... - a small butterfly with a wingspan of 18-20 mm. Caterpillars damage blueberry leaves by pulling them together with cobwebs. Caterpillars are light green with two dark green lateral stripes and a thin line on the back. The head is light brown, the occipital plate with two black spots on the sides. On the body
Control measures. Destruction of single leafworm caterpillars in rolled leaves. Preventive spraying of bushes when opening leaves with one of the drugs: fufanon, kemifos, actellik, kinmix, spark, Inta-Vir.
Blue moth Arichanna melanaria L... - a butterfly whose caterpillar has two pairs of abdominal legs. The body of the caterpillar is yellow with many black longitudinal lines. Caterpillar feeding and development is observed in May.
In addition to the moth, blueberry leaves damage caterpillars of other butterflies with 5 pairs of abdominal legs - yellow peat jaundice and heather lancet.
Yellow peat jaundice Coliaspalaeno L... - a butterfly, the caterpillars of which are green with bright yellow, bordered below by black lateral stripes and covered with thin short hairs. They feed in May.
Sagittarius Apatele abscondita I Tr... - a butterfly whose caterpillars are covered with short hairs, black-brown with black and white specks. They feed and develop in June - September, eating blueberry leaves.
Control measures. Preventive spraying of bushes when opening leaves with one of the drugs: fufanon, kemifos, actellik, kinmix, spark, Inta-Vir. With a large number of caterpillars, spraying is repeated in the summer, taking into account the waiting times for the preparations. Single caterpillars are collected and destroyed.
When autumn comes, gardeners begin to put their site in proper order in order to meet and survive winter without loss. Each owner tries to do the best preparation so that his plants bloom next spring and give a rich harvest. And one cannot do without the experience of many lovers of summer cottage business.
If you are a blueberry owner and meet winter with this bush for the first time, then without clear recommendations to preserve the yield or even the life of the plant can be problematic. And if you are an experienced summer resident, then refresh your memory will not be superfluous. But, on the other hand, blueberries are not very demanding on care, so a lot of investment is not required.
Diseases
The most common and similar in appearance is stem cancer and drying out of branches. Also, blueberries are affected by such a common disease as gray rot. To combat fungal diseases, three times spraying of plants is used before and after flowering with a 0.2% solution of topsin or euparen. All damaged branches must be cut and burned in a timely manner.
Diseases of a mycoplasma or viral nature pose a great danger to varietal blueberries. These include red and necrotic spotting, dwarfism, mosaic. Such diseases are extremely rare, but when they are diagnosed, the plants must be destroyed.
Preventive means of combating pathogens that cause blueberry disease are elementary agricultural techniques. Thanks to regular weeding, soil mulching, timely watering and feeding, the plant will fully develop and be able to resist diseases.
Blueberry stem diseases and how to treat them
Before examining the diseases of garden blueberry stems and the fight against them, it is worth mentioning that the most common pathogen is the Godronia cassandrae Pesk mushroom. Brown blurred spots appear on the shoots and stems. Gradually, the bark dries up, cracks, the wood dies off and a shallow, elongated drying ulcer with raised edges forms. Ulcers are most often located at the base of the stems and in the forks of branches. First, the side branches dry out, and gradually the entire stem. When starting to consider these blueberry diseases and how to treat them, it is worth understanding that the infection persists in the affected stems and in plant debris.
Control measures. Use of healthy planting material, timely pruning and burning of dying branches. Disinfection of sections with a 1% solution of copper sulfate and smearing with oil paint on natural drying oil. Annual preventive spraying of bushes before leafing out with 1% Bordeaux mixture or its substitutes (HOM, Abiga-Peak)
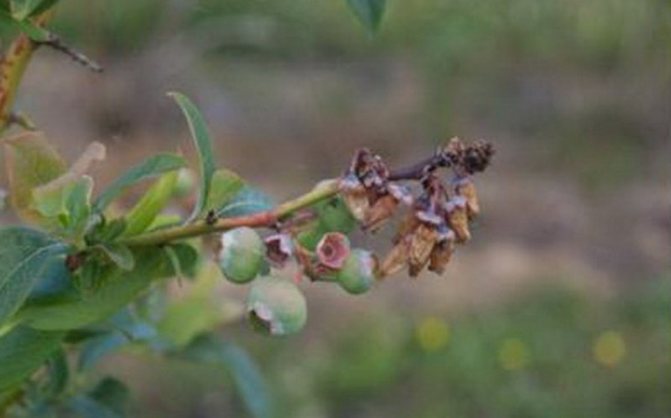


Cytosporosis of blueberries.
The causative agent is the mushroom Sytospora delicatula Shear... The disease is manifested by browning and death of the bark. On the affected cortex, numerous convex stromas are formed in the form of gray-brown tubercles. At first they are submerged, then erupting, slightly obtuse-conical. The affected bark dries up, but does not flake off, but pee.The fungus enters the plant through mechanical damage and spreads from the bark into the cambium and wood, causing premature drying of the branches. The infection persists in the affected branches.
Control measures. Same as against blueberry stem cancer.
Features of pruning blueberries, depending on the variety, including tall ones
Tall blueberry varieties are very popular among modern gardeners. They develop a tall bush (up to 2 m), consisting of powerful shoots. The thickness of some reaches 3-4 cm. This means that you will need a reliable tool for trimming, and sections with a diameter of more than 1 cm will have to be covered with pitch. If the bush seems too high to you, it is inconvenient to harvest, then in the summer, pinch the tops, at the right height.


To trim tall blueberries, you will have to make more effort, but the yield of such varieties is higher.
The rest of the pruning principles are the same. More important than the height of the bush is the blueberry variety. Some tend to build up vertical shoots. In this case, you need to thin out the center of the bush well. Others, on the contrary, produce many horizontal branches. Then your task will be to transfer their growth to vertical shoots.
Do I need to fertilize blueberries
Garden blueberry is one of those berry bushes whose need for additional nutritional support is especially high. Most often, the natural composition of the soil on the site does not contain in sufficient quantities all the macro- and microelements required by blueberries - therefore, they must certainly be introduced artificially. At the same time, violation of the rules and proportions during the introduction of fertilizers results in a slowdown in growth and a weakening of the plant, a drop in yield, the appearance of pests and diseases.


Attention! Tall varieties of garden blueberries need more feeding than undersized ones. The first are fed with fertilizers without fail in accordance with the schedule; the latter, in the event of a shortage of certain substances in the soil.
Description
Blueberry is a small shrub with foliage falling off for the winter, belongs to the Heather family. People often call it a waterhouse, dove or blue grape. The plant prefers the cold and temperate climate of the northern hemisphere. It is usually found in swampy soils, hills or coniferous forests.
The highest height of blueberry bushes is 1m. Its branches are straight with brown or dark gray bark, covered with small rigid leaves planted on short petioles. The upper side of the leaves is covered with a waxy bloom and has a bluish-green color, the lower one is lighter. At the time of flowering, the shrub is covered with small drooping five-toothed flowers of a white or pinkish hue. Then, in their place, blue small oblong berries are formed, covered with a bluish bloom.
Under the conditions of the Russian climate, common blueberries or some varieties of garden varieties with an early ripening period are successfully grown. In southern regions with favorable climates, American blueberries can be grown. It is distinguished by large berries weighing 10-20 g. The yield is up to 7 kg when properly grown.


When are blueberries cut to the root?
The reasons why the bush is cut to ground level:
- In winter, the shrub was very cold, which is why the leaves and flower buds did not bloom in the spring. It is recommended to cut such a plant completely. The root shoots that have made their way in the new season must be left. A few years later, a new bush will form from these shoots.
- Old, wild blueberries, with small berries and almost fruitless branches, can no longer be saved. It is advisable to cut such a bush to zero.
- The shrub barely bears fruit, spends a lot of nutrients to maintain a lush crown. The old bush can be cut at the root.
Application procedure
Plant feeding begins only from the second year after planting.In the first year, the berry does not need additional nutrition. For active growth, the following additives are most often used:
- If the acidity of the soil is more than pH-5.0, ammonium sulfate is necessarily used. The optimal amount is 100 g per 10 m² of soil.
- At normal pH values, the soil is also enriched with ammonium sulfate in the amount of 85 - 90 g. Each fruiting plant is additionally fed with potassium sulfate (40 g) and superphosphate (100 g).
- Many gardeners use balanced mineral mixtures, for example, Florovit, Kemira Universal. Such fertilizers effectively acidify the soil, ensure the active growth of each bush, even at low pH values.
- In autumn, colloidal sulfur is additionally introduced to areas with low acidity, which compensates for this deficiency.
Any fertilizer is always applied only in dry weather, in the morning or evening, when the sun's rays do not hit the plants. It is not recommended to feed blueberries in the rain or immediately after it. Bushes are fertilized from the second year on the basis of:
- Biennial plant - 1 tbsp. l .;
- Three-year plant - 2 tbsp. l .;
- Four-year-old plant - 4 tbsp. l .;
- Five-year-old plant - 8 tbsp. l .;
- From 6 years old and more - 16 tbsp. l.
The harvest
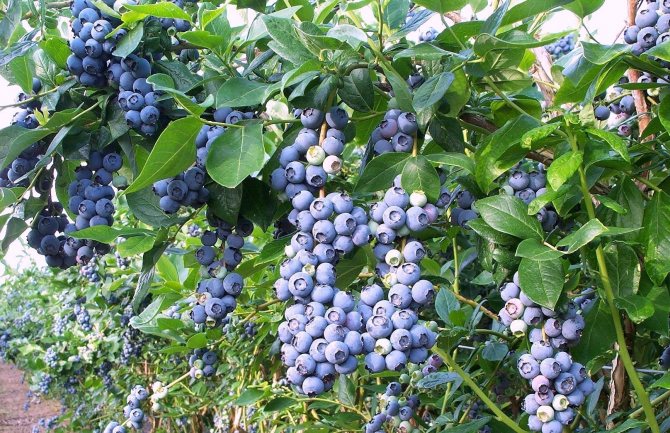
The harvest of this berry can be extended from late June to early September. Choose the right varieties - and a healthy product will be on your table all summer long. One bush of any variety bears fruit for about a month. The top berries ripen immediately, and then the subsequent ones in turn.
It is worth picking those that move well from the stalk. Depending on the variety, ripe berries can hang for a very long time. And on some varieties, they crumble some time after ripening. Therefore, the harvest that is not harvested at the time may be lost.
After harvesting, it's time to start feeding plants in autumn, preparing for wintering. For good care, the culture will thank you for an excellent harvest next summer.
Blueberries: growing and care
Blueberries are a very healthy berry. It contains a lot of potassium, calcium, magnesium, sodium, iron and phosphorus. It is rich in vitamins C, B1, B2, K and PP. When growing blueberries, grooming is especially important when the bushes are young, and weeds and drought are its worst enemies. We have described how to care for blueberries and some of the subtleties of growing in this article.


Fresh blueberries are tasty and healthy, contain vitamins and minerals. 100 grams of berries contain 0.81 g of potassium, 0.14 g of vitamin C, 0.01 g of iron. Blueberries are used medicinally. Blueberries have a healing effect on the kidneys, stimulate cardiac activity, improve vision, increase the secretion of gastric juice, are useful in diabetes and in dietary nutrition. The berries are suitable for freezing and, with this method of conservation, retain their dietary and medicinal properties. Jam, jelly, jams, juices are also made from them.
The blueberry bush looks quite decorative throughout the season - in spring (mid-May) during flowering, in summer during fruiting, and especially in autumn, when the foliage turns red. Therefore, you can plant blueberries as an ornamental plant and harvest delicious berries at the same time. Blueberries are quite long-term; in good conditions they bear fruit for up to 30 years.
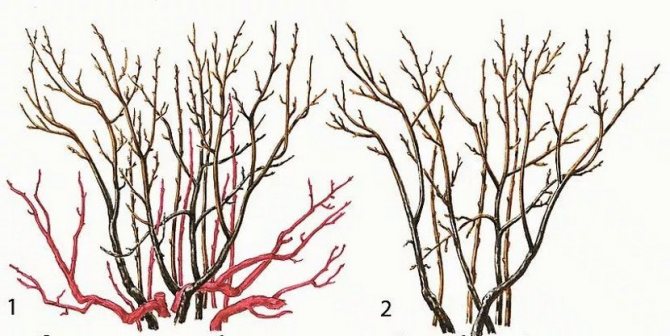
Autumn pruning of bushes
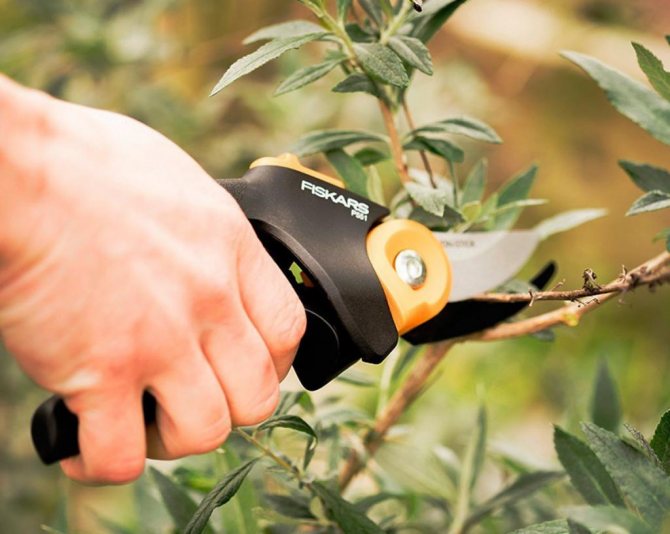


The formation of a strong plant skeleton is the main condition for caring for fruit shrubs. Garden blueberries are no exception. In the absence of this procedure, the annual growth of young animals will not be able to fully develop and bear fruit. As a result, the bush will begin to degenerate into wild growth, and the fruits will become smaller and lose their taste.
In addition, the thickened crown of the bush is a favorable place for the development of fungal diseases, since it is poorly blown by the wind.Therefore, the formative and sanitary pruning of blueberries in the fall is an integral part of the care of the berry. It is during this period that the sap flow in the shoots slows down, so the plant tolerates this procedure painlessly.
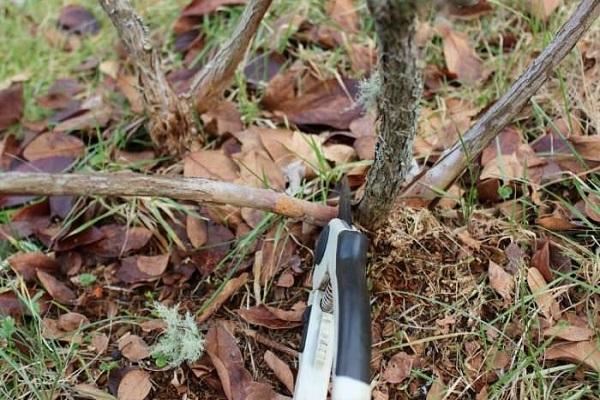
Prepare a secateurs to trim blueberries. The instrument must be pre-disinfected to exclude the possibility of pathogens entering the open sections.
Basic feeding rules
In the first year of planting shrubs, soil saturation occurs due to soil mulching. Needles, bark, sawdust are used as mulch. Mulching the soil is also necessary to maintain the optimum level of soil acidity, since blueberries prefer acidic soil.
Nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium are of paramount importance for the berry. The deficiency of these macronutrients negatively affects the yield and quality of the fruit.
The next most important group of elements, consisting of calcium, sulfur and magnesium, is introduced into the soil as needed.
Despite the fact that the consumption of other trace elements in blueberries is minimal, their lack negatively affects the development of the plant.
Mineral formulations are used to feed the bushes.
Organic fertilizers
The organics used to feed most crops are not suitable for blueberries. Organic matter makes the soil alkaline, and this berry grows on acidic soil. Therefore, for feeding the berry, it is not recommended to use such agents as manure, mullein, compost, humus.
From organic fertilizers, it is allowed to use only high-moor peat. For the manufacture of mulch, they resort to coniferous materials: bark, pine chips, sawdust, needles. This coating traps moisture and helps maintain an optimal level of soil acidity.
What do blueberries need?
You need to look closely at your favorite. She will tell you what she is missing.
Lack of nitrogen. Then the shoots practically stop growing, and the foliage will turn yellowish.
If the leaves are pressed against the branch and turn purple, then phosphorus must be added. The dying tips of leaves and shoots will tell about the lack of potassium. Leaf deformation and yellow rim - take calcium. Magnesium is needed if the rim turns red and the middle turns green. Blueness on the tops of the leaves will indicate a lack of boron. Yellowing between the veins - about a lack of iron. Sulfur is needed when the leaf has turned yellowish-white.
What can not be fed blueberries
It is categorically not to be used as a fertilizer for blueberries:
- organic feeding;
- products containing chlorine or nitrates.
You should also not feed this culture with compositions based on folk recipes suitable for other berry plants (wood ash, eggshells, lime, dolomite flour, various herbal infusions). The listed fertilizers are not suitable for blueberries, as they cause strong alkalization of the soil.
The same goes for the yeast-based feed mentioned in some sources. The benefits of it are very doubtful, since yeast in large quantities absorbs the oxygen necessary for the plant, and also competes with other useful soil flora.
Harvesting
Blueberry care also includes harvesting. The ripening time of the berries depends on which varieties you have planted.
So if the blueberry variety:
- early ripe, then we begin to pick the berries from the first decade of July;
- mid-season - from the second or third decade of July;
- late-ripening - from the second or third decade of August.
Blueberry fruits do not ripen at the same time, so harvesting on the bush lasts more than a month.
The first sign of the onset of ripening of blueberries is a change from the green color of the berries to bluish purple. This means that in a week, in good weather, the berries will ripen.
You need to pick from the bush only those berries that easily come off.The largest and most delicious berries are the first and second harvest, so they are best consumed fresh.
Shelter blueberries for the winter
An important thing in caring for blueberries is the shelter of the plant for the winter; the future harvest depends on the shelter. In most cases, the limit of frost resistance of blueberry bushes is a temperature of 23 - 25 degrees, and there is also a high probability of freezing of the plant in a snowless winter.
If you decide to grow late-ripening varieties, then do not forget that they often suffer from early-autumn frosts and, therefore, these varieties should be covered first. Preparation of bushes for winter should be started well in advance.


How to insulate blueberries
Blueberry branches are bent to the ground, for this you can use twine or wire arcs, placing them crosswise.
Then, with the onset of stable frosts, we cover the bushes with burlap or agro-cloth. It is better not to use plastic wrap. In winter, the bushes can be sprinkled with loose snow so that the tops of the stems are constantly under a white blanket.
With the onset of spring, we remove the shelter, cut off the tips of the frozen branches. Blueberry flowers usually do not need additional protection from a sharp spring cold snap, as they can tolerate frosts down to -7 degrees.
Blueberry propagation
Blueberries propagate by cuttings, cuttings, and shoots.
Diseases and pests
Diseases: gray rot, anthracnose. Pests: birds, May beetles.
Autumn feeding
Correct, timely fertilization is considered an important factor in successful blueberry cultivation. The use of additives can achieve the following results:
- increased productivity;
- activation of the growth of bushes;
- improved taste.
In the fall, it is necessary to carry out measures to prepare for the cold weather. Plants are able to tolerate frosts down to -25 ° C in the presence of a thick layer of snow. In snowless winters, the permissible temperature indicators decrease, and the probability of freezing of branches increases. Late blueberry varieties are especially susceptible to cold.
To protect the plant, the branches are bent to the ground, wire arcs are installed around the bush. Burlap or other non-woven materials are fixed on them. Spruce legs are pounced on top and snow is poured. Warming is removed with the arrival of spring, the tips of all frozen branches are cut off.
Useful Tips
Novice gardeners who plant blueberries on their site often make serious mistakes. Several important recommendations will help them avoid many of the problems associated with growing this healthy and tasty berry:
- you should not place seedlings in partial shade, since their growth will slow down, and the fruits will ripen longer;
- bushes 2 - 3 years old are considered ideal for planting in the ground;
- it is not recommended to loosen the soil too often, this can dry out the blueberries;
- mulching is a mandatory procedure that protects against freezing, moisture loss, overheating;
- moderate regular watering is the key to successful berry growing;
- compost, chicken droppings, manure are not suitable for plant nutrition;
- after applying mineral fertilizers, the bushes should be watered;
- to maintain optimal soil acidity, it is enough to water blueberries with a citric acid solution twice a month (based on 2 tsp of acid per 3 liters of water);
- in extreme cold (from -25 °), the bushes are covered with spruce branches, a wire frame is first created for this;
- a significant decrease in the number of berries is observed from 10 years or more, therefore it is necessary to cut off old branches.
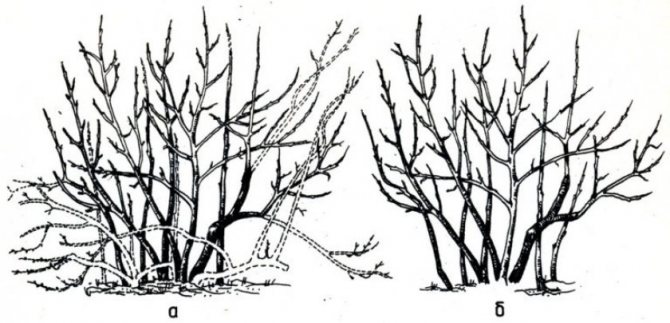
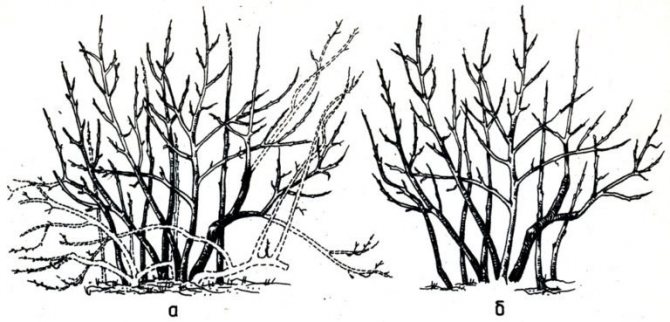
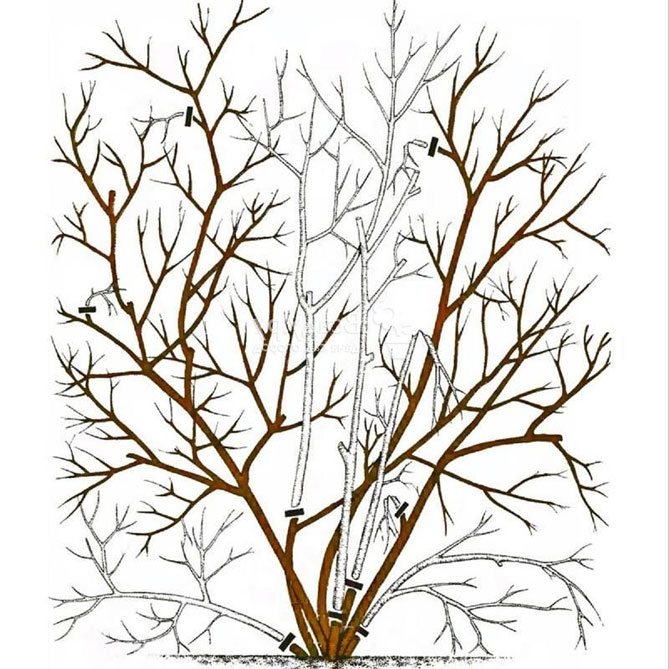
Pruning an adult bush
Mature shrubs require a different approach to shaping and pruning. The procedure begins 3-4 years after blueberry planting. This removes:
- all horizontal branches up to the main strong shoot;
- improperly growing branches and shoots;
- damaged tops of shrubs;
- all low-growing branches;
- lignified branches, the bark of which is already cracked.

When the bush reaches the age of 7 years, it is necessary to cut out the main branches (4-5 years of age) and the branches of the lower layer.
After this procedure, the bush should have 9-10 perennial branches and 5-6 strong young shoots (perennial). Old bushes should have 8–10 strong perennial branches and 3–6 strongest annual shoots.
In order for the fruits to be larger, old shoots must be pinched with a change of five fruit buds. The described procedure contributes to a good yield of blueberries if carried out annually in the spring.
Features of growing blueberries: what fertilizing are required
The main distinguishing feature of growing blueberries in the garden is the need for an acidic environment (3.5-5 pH). Therefore, blueberries are planted in an acidic peat mixture (based on swamp red peat, 50%), mixed with coniferous litter (rotted pine needles, 40%) and sand (10%).
If you plant blueberries in ordinary garden soil of a neutral reaction, or even more so in alkaline, the same loamy or sandy loam, then you can not even dream of significant yields. The shrub will grow poorly and stunted.
However, simply planting blueberries in acidic soil and using conventional fertilizers is not enough, over time, in any case, you will need to maintain acidity at the required level (since it will decrease), namely, feed the blueberries with acidic fertilizers or use special acidifiers (not fertilizers! ).
Interesting! The fact is that a specific fungus lives on the roots of blueberries in close symbiosis (symbiotic relationship) - ericoid mycorrhiza, which helps the plant absorb nutrients from the soil, and it lives only at low acidity. In other words, the acidic environment is needed not by the blueberries themselves, but by the mycorrhiza, which is located on the roots of the blueberries.
However, often novice gardeners focus exclusively on creating an acidic environment, not paying due attention to feeding with basic macro- and microelements, and blueberries, like other cultivated plants, need nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, magnesium, sulfur and other nutrients.
Advice! Be sure to purchase special instruments for measuring the acidity of the soil.
Video: how to water and fertilize blueberries
How to fertilize blueberries in summer
We recommend reading our other articles
- How to plant peppers correctly
- Freesia - planting and care
- How to plant a plum
- Organomineral fertilizers
In summer, garden blueberry fertilizers do not need to be applied. But, if the culture is weakened, sick, damaged by pests, such a procedure will benefit it. Potash-phosphorus fertilizers are used at this time. There should be a minimum of nitrogen in them, since, starting from summer, blueberries do not consume large quantities of it.


Fertilizers in the summer are recommended to be applied by the foliar method, processing blueberries on a leaf
- Phosphorite flour will contain about 30% phosphorus, 30% calcium and 2% magnesium. It also contains iron, copper, sulfur. 200-300 g of fertilizer are used per square meter. It is simply buried in the ground to a depth of 5 cm.
- Potassium sulphate used for potassium deficiency. Dissolve 100 g of the substance in 10 l of water and use the resulting liquid to spray blueberries.
- Magnesium sulfate Is a very useful fertilizer for blueberries. It is brought in once a year, around the summer or late spring. Only 15 g of this product is enough for a bush.
Important!
If you apply a lot of nitrogen fertilizers under the blueberries in summer and autumn, it will increase the crown, start up many young branches, but the yield will greatly decrease. In addition, such a plant will not have time to prepare for winter and may freeze out already during the first frosts.
Fertilizers in summer are recommended to be applied by foliar method, processing blueberries on a leaf. This procedure is carried out only at sunset or during sunrise. If you spray blueberries during the day, sunburn will appear on the leaves by the evening.
How to plant blueberries
Before planting blueberries, you need to dig up the area where we are going to plant them. For acidification, peat can be added, which is ideal for blueberries. Mix sawdust, bark, fallen leaves, needles to it. To achieve the desired acidity, you can add sulfur (50-100 g / m2) or you can pour it with acidified water (for 1 square g of 10 liters of water). Oxalic or citric acid (3 teaspoons per 10 liters of water), malic acid (100 ml per 10 liters of water) are suitable for acidification. For digging, a complex mineral fertilizer is introduced 60-100 gr per 1 sq. M.
It is advisable to prepare holes for planting in advance, 2-3 weeks before planting blueberry seedlings, so that the soil settles during this time. The distance between low bushes is 0.3-0.5 m, bushes of medium size 0.7-1 m, for tall ones the required distance is 1.2-1.5 m.If you plant in rows, then the width between the rows depends on the height and width of the bush in adulthood (from 1 to 3 m).
The size of the planting holes depends on the soil and the size of the blueberry bush. It is better to plant tall blueberries in heavy loams - the width of the pit is 100 cm, the depth is 20 cm. This is due to the fact that after heavy precipitation in deep pits, the water will stagnate for a long time, and has a bad effect on the roots of blueberries.


Important! In no case, when planting, it is impossible to simply transfer the seedling from the container into the pit, because the tender roots of blueberries cannot develop to the sides in a dense clod of earth and the root system will not be able to develop normally, in this regard, the plant will most likely die in a few years. To prevent this from happening, it is necessary to lower the container with the seedling into water for only 10 minutes before planting, then remove the plant from the container and try very carefully to knead this earthen ball, and if the roots are tightly entwined with the ground, then you must carefully spread them with your hands.
The seedling must be planted 5-6 cm deeper than it grew in the container, water it and mulch with sawdust (or some other mulch). Mulch in the summer will be able to protect against weeds, retain moisture, and simply serve as an additional fertilizer; in winter, it will protect the roots from freezing.
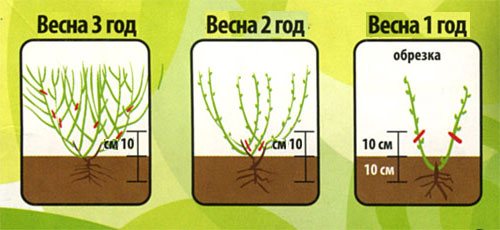
Pruning a young blueberry seedling
A common mistake gardeners make is neglecting blueberries in their first two years of life. If you do not take care of the seedlings at this time and do not prune, then the bush will give new short shoots, the fruits of which will be small, and their number is small.


In addition, these young shoots will take all the juices and strength from the main ones, which will cause the shrub to deplete faster. In this regard, it will be difficult for blueberries to resist various diseases and climate changes.
Thus, in order to get large and tasty fruits, experienced gardeners begin to form the shrub in the first year after planting. The procedure is carried out as follows:
- removal of zero shoots;
- trimming excess branches that are on the main shoots at a distance of more than 30–40 cm from ground level;
- removal of the tops of the main shoots with the removal of fruit buds.
All this will help the shrub to grow strong shoots that will give a regular and rich harvest. It is advisable to prune young bushes (weak sanitary pruning) in March - April. In this case, it is necessary to remove dry, damaged branches. For thinning, gardeners usually cut thinner shoots of the lower tiers. The intensity of pruning should be increased for 3-4 years of the life of the bush, which will give a good crop growth.
Preparing blueberries for winter


Hilling protection
Making a mound of bark, soil, or peat at the base of the bush is a simple and effective way to protect American blueberries for the winter. This simple measure protects the base of the shoots and roots of plants from frost. The embankment should be approximately 20 cm high.
The pine bark used for this purpose not only protects the bushes from freezing, but also maintains constant soil moisture and helps to maintain the acidic pH of the soil.Hilling is necessary for all young, newly planted berries. It is also recommended for older bushes.
Brushwood protection
If you want to protect your lovingly grown blueberries, you can line the shrub with brushwood made from branches of coniferous trees. Branches protect the base of the bush and roots well from low temperatures. A “fence” made of spruce or fir branches, as a rule, is used as additional protection of a previously prepared pile of bark, peat or earth.
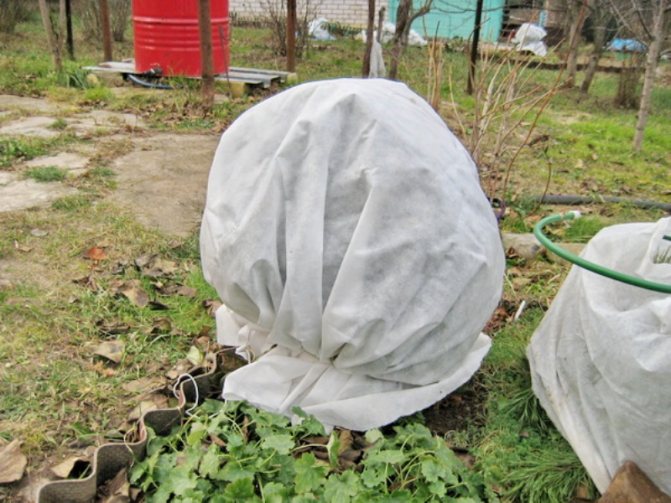
Shelter blueberries for the winter with agrofibre
To protect sensitive varieties for the winter, it is worth using agrofibers, which protect from the wind, while allowing air and water to pass through. It is a fabric that is easy to buy at gardening stores - either cut into pieces (eg 1.6x2m) or in rolls. It is best to wrap Canadian blueberries with this cloth 2-3 times and tie them with twine.
On a note. If you want to save time covering shrubs, or if you have a lot of them, it might be worth getting a spunbond winter plant hood with a ready-sewn rope at the base.
Such a simple preparation of blueberries for winter will help even the most delicate shrubs to survive the frosts safely.
Dates of the
When pruning, you need to take into account the climatic conditions of a particular area. In warm regions, pruning is done in early spring, in cold regions - closer to May. After wintering, young healthy branches easily rise, so it is not difficult to find old branches that need to be disposed of. Remove branches that remain on the ground.
Branches containing rot and damage should not only be cut off, but also burned. This is necessary to prevent the spread of the infection.
In summer, pruning of blueberry bushes is extremely rare. This procedure is carried out in the summer only when you need to get rid of broken branches. Before winter, it is customary to cut off rough branches that cannot be bent.
Useful properties of blueberries
Blueberries are extremely healthy berries. Blueberry increases concentration, has anti-inflammatory, anti-sclerotic, antipyretic, capillary-strengthening effect.
Recent studies have shown that blueberry leaves and berries can lower blood sugar levels. Mashed berries and blueberry juice are useful for enterocolitis, cystitis, gastritis with low acidity.
A decoction of the leaves is used as a mild laxative. It is also beneficial for diabetes, anemia, and heart disease. Sour blueberry drink is useful for colds, fever, inflammation of the kidneys and bladder. Blueberry juice in the amount of 0.5 liters daily prevents age-related weakening of memory.
American (Canadian, tall) blueberries are generally highly frost-resistant. But low temperatures can be very harmful to young seedlings and some sensitive varieties. How are blueberries prepared for winter?


Caring for blueberries in the fall means getting them ready for winter. There are several ways to save it, they can be combined or applied separately. Learn how to cover blueberries for the winter and which varieties require frost protection.
What kind of care is needed after the procedure
After trimming, the sections and wounds must be disinfected. For the treatment of wounds, a solution of copper or iron sulfate, potassium permanganate or Bordeaux liquid is used. When the cut dries up, you need to cover it up. For putty, garden var or Ran No paste is used, as well as Blago Sad, Robin Green preparations.
In the spring, the shrub can be whitewashed with lime and fertilized with urea; in the fall, in addition to whitewashing, it is recommended to add potash and phosphorus fertilizers to the soil. The bush can be watered with a solution that increases the plant's immunity, for example, Epin.
For the prevention of diseases, shrubs after pruning are sprayed with fungicidal solutions (Skor, Fitosporin, Gamair).
To prevent possible contamination, it is also recommended to disinfect garden tools before pruning. For example, using alcohol or a solution of potassium permanganate.