If the honeysuckle bush on your site pleases with its yield and taste of berries, then it can be propagated by cuttings. This method allows you to get several seedlings from one plant, repeating all varietal qualities. DIY grafting is a fun activity that can save your budget. After all, seedlings are expensive today, besides, purchased ones do not always meet the expectations of the gardener.
- 2 Green cuttings of honeysuckle in summer
2.1 Video: propagation of honeysuckle by cuttings in summer
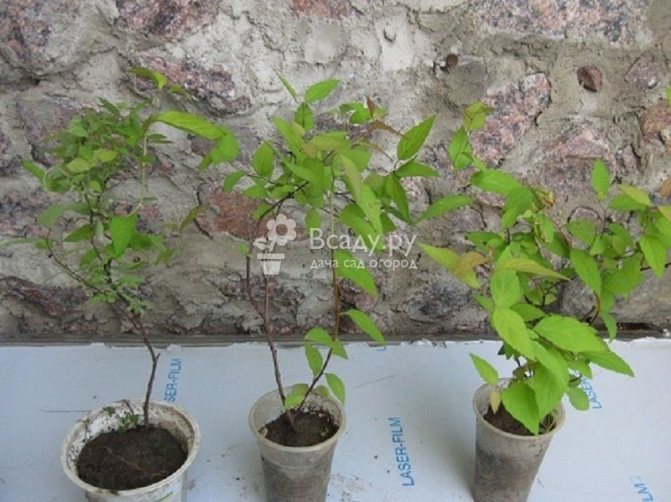
- 2.2 Photo gallery: the path of the cutting from the shoot on the bush to the seedling
- 2.3 Video: rooting a cuttings in a bottle
- 3.1 Video: propagation by cuttings and dividing the bush in the fall
- 4.1 Video: rooting in water and planting in cups
How to breed honeysuckle on the site
The success of honeysuckle breeding activities directly depends on the observance of several important conditions related to the biological characteristics of the berry culture:
- Plants should be planted in well-lit, open areas. Only by getting enough warmth and light will the honeysuckle bear fruit well.
- Suitable for reproduction are young and vigorous bushes that do not have signs of damage by pests and diseases.
- Cross-pollination is the most important factor for obtaining a good harvest, as well as a high taste of the berries. In close proximity to each other (curtain), it is necessary to place several (at least 4) different varieties of honeysuckle, which have different ripening times and different tastes (sour, piquant, dessert, etc.).
- At first, the seedlings need to create favorable conditions for the growth of the root system (shading from the scorching sun, constant and comfortable humidity of both air and soil, favorable temperature conditions). This is only possible in a greenhouse.
- Young specimens are relocated to their permanent place in the open field after 2-3 years. Before that, they are carefully nurtured so that they can adapt and harden.

To get a bountiful harvest of delicious berries, it is necessary to observe several important conditions for the reproduction and care of honeysuckle.
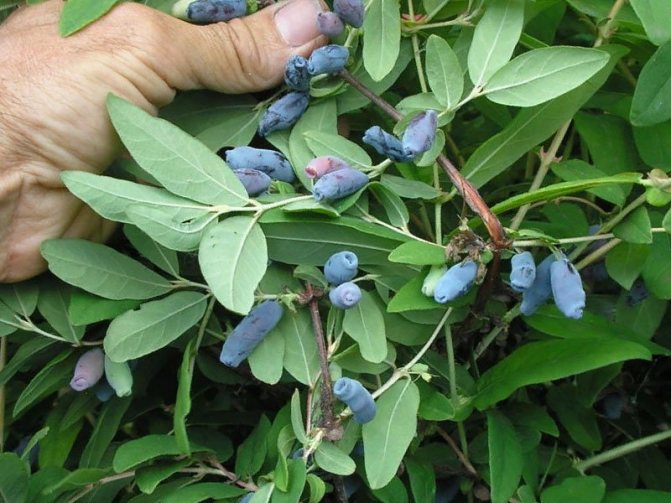
Two honeysuckle bushes of different varieties have been growing on our site for several years. But there were few fruits, because they were pollinated unimportantly. For some reason, bees and other pollinators rarely flew into this part of the garden. I had to remove already mature plants, separating several seedlings from them, and replanting them to another more suitable place.
Most popular varieties
Reproduction of honeysuckle by green cuttings, in the same way as lignified, must be carried out in compliance with a certain technology. But even if the summer resident follows the method exactly, he may still fail. Rather, the seedlings (or at least part of them), of course, will grow. However, it often happens that mature plants do not bear fruit. The reasons for this trouble are simple - without cross-pollination, this culture always remains sterile.


Therefore, an operation such as propagation of honeysuckle by cuttings in spring should be performed using planting material of at least two or three varieties.The most popular varieties of honeysuckle, often bred by summer residents, at the moment include:
- Blue bird. Bushes of this variety can reach a height of one and a half meters. Its elongated sweet and sour fruits weigh about 0.8 g.
- Blue spindle. This is a fairly high honeysuckle (up to 1.8 m), giving elongated sweet fruits.
- Titmouse. Honeysuckle bushes of this variety can reach a height of 2 m.The fruits are also quite large - up to 0.9 g.
As you can see, propagation of honeysuckle by cuttings, as well as in any other way, is a rather simple operation. The most important thing is to adhere to its technology exactly. And, of course, young plants need to be well looked after. In this case, the honeysuckle will certainly please the owners of the site with good development, and in the future with good yields.
How to propagate honeysuckle from a bush
The most accessible and simple way of breeding honeysuckle is considered to be the division of the mother bush. It should be a sturdy, vigorous plant between 3 and 6 years old with several skeletal branches extending from the rhizome and buried at the base. Work can be carried out in early spring, as soon as the soil thaws or in early autumn.
It is recommended to huddle the bush (20–25 cm) beforehand (in spring) to stimulate the formation of lateral roots.
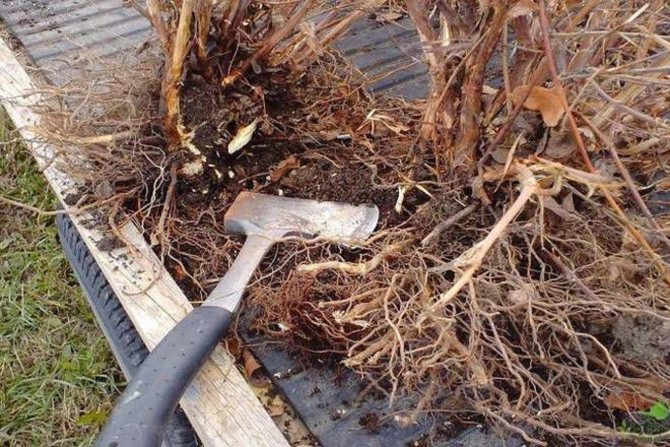


By dividing the bush, only young plants are propagated.
The technology is as follows:
- The plant is dug in, removed from the ground.
- Shake off the remnants of the soil from the roots.
- With a sharp knife, garden shears or a shovel, after disinfecting the cutting edges, the bush is divided into several parts, each of which should have a decent piece of rhizome and at least 3-4 shoots.
- Places of cuts are treated with a solution of potassium permanganate or sprinkled with crushed coal.
- Shoots are shortened to 30-40 cm.
- Then the resulting divisions are determined in the right place.
How to propagate honeysuckle by cuttings
Breeding of honeysuckle by cuttings is widely used.... To do this, use both the already lignified young branches of the current one, and a completely still green growth.
Green cuttings
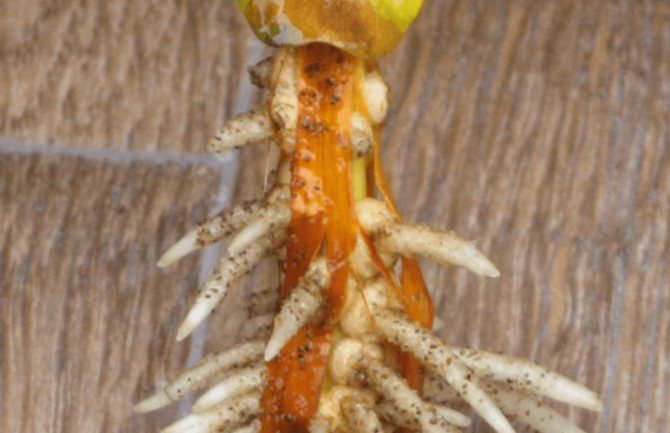
Planting material is harvested in the spring, during the period after foliage bloom and before the formation of the first berries. It is better to do this in gloomy cloudy weather, or in the morning or evening hours. When bent, the shoots ready for grafting should already break with a crunch, but at the same time remain green.
The sequence of actions is as follows:
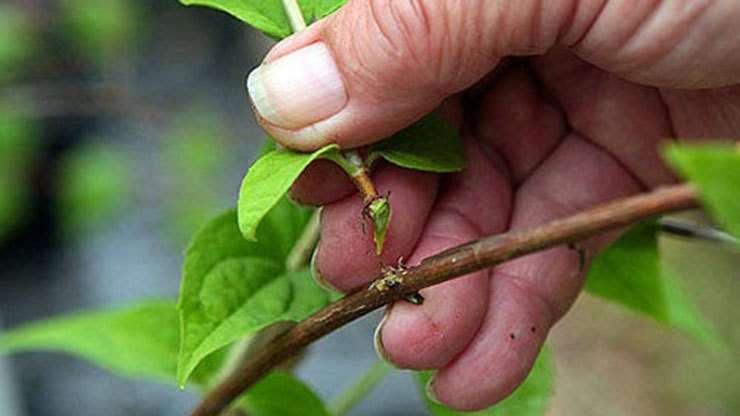
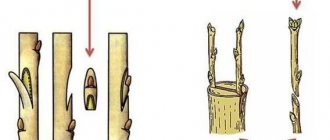
- The strongest powerful shoots are chosen, cuttings 8-12 cm long and having 3-4 internodes are cut from their middle part.
- Leaves are cut off from the bottom, the upper ones are shortened by half.
- The lower cut is treated with any growth stimulant (Heteroauxin, Epin, etc.).
- Cuttings are stuck into a loose soil mixture of sand and peat (1: 1).
- Cover with foil, cans, cut bottles to create greenhouse conditions.
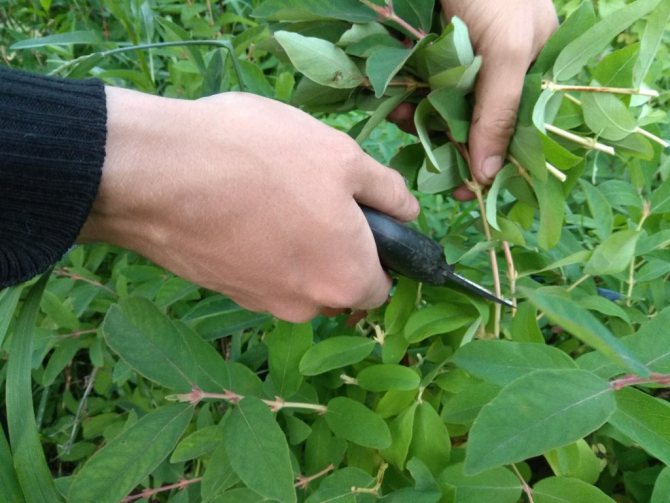


Green cuttings are cut in spring
You can root green cuttings in water, where they are lowered to the bottom node.
Lignified cuttings
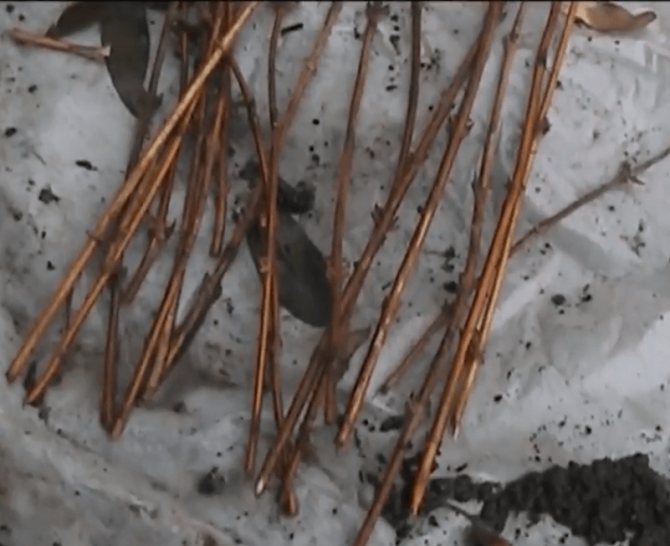
Work on the harvesting of lignified cuttings is carried out in the fall after leaf fall. They choose thick (from 7-8 mm) shoots of this season, cut them off, wrap them in a damp natural cloth and store them in a cellar or basement until spring (you can dig in the sand). With the onset of heat, the mother material is removed, cut into pieces and rooted in the same way as green cuttings.
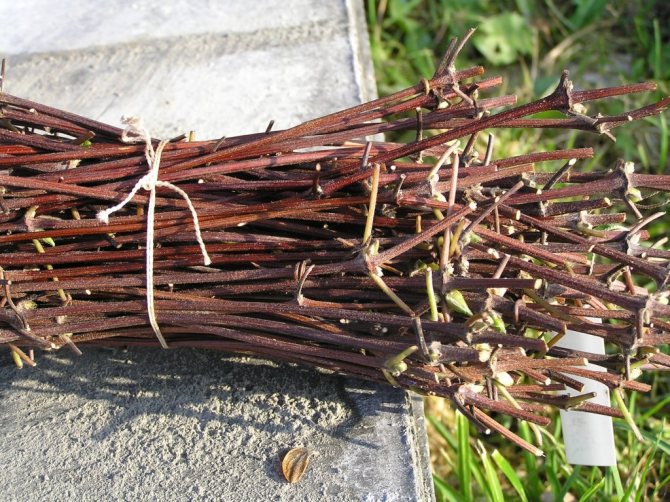


Lignified cuttings are harvested in autumn
Some gardeners manage to successfully root planting material, cut very early in the spring from last year's well-wintered branches with swollen buds and even after flowering with green shoots that have begun to grow.
Video: propagation by cuttings
Vegetative propagation methods
At home, vegetative methods of reproduction of honeysuckle are most often used.They allow reproduction of offspring with the preservation of all the genetic characteristics of the mother plant. To do this, use its various parts:
- shoots (stems) - green and lignified;
- layering from shoots in contact with the soil;
- root suckers developed from adventitious buds on the roots;
- root by mechanical division into several parts.
Let's take a closer look at each option.
Green cuttings
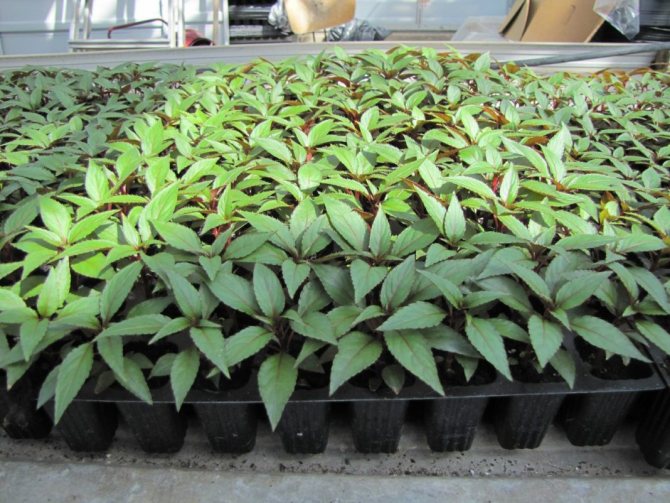
The method of propagation of honeysuckle by green cuttings is used in the summer.
First of all, you need to correctly determine the time for harvesting the cuttings. In the literature, there are different recommendations - simultaneously with the appearance of green fruits, when the first berries ripen, immediately after harvesting. The optimal date is mid-June. By this time, the shoot of the current year completes its growth, it is no longer so juicy, not prone to decay in a humid environment. In addition, there is plenty of time ahead to form a viable root system and prepare for winter.
Advice! Check young shoots for flexibility before harvesting. If the stems bend, let them grow even more, if they have not lost their green color, but are already breaking - they are suitable for grafting.
The most powerful young growths are chosen for grafting. Slices 8–12 cm long are cut from the middle part of the branch so that each part has one internode and 2 pairs of leaves. The cut under the lower knot is oblique, at an angle of 45⁰, the leaves are removed. The upper cut is straight, 1–2 cm above the node, the leaves are shortened by half.
There are 2 ways of rooting green honeysuckle cuttings:
- in the substrate;
- in water, with transplantation into the soil after the appearance of roots.
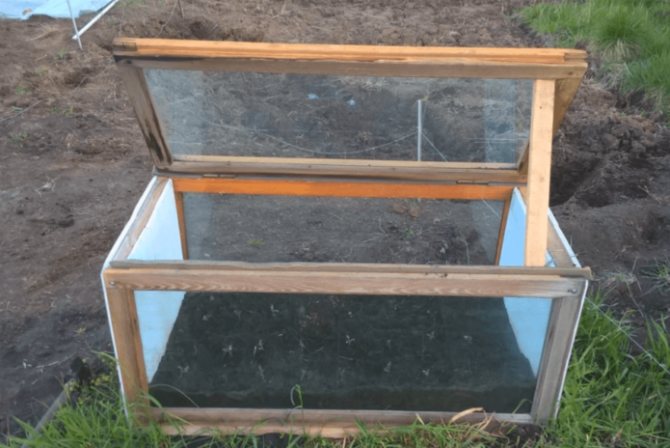
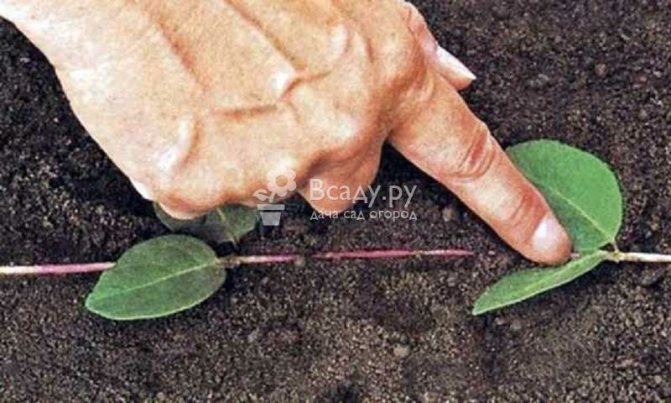
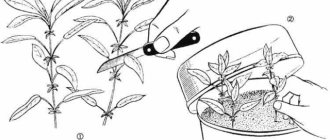
In the first case, the cutting is immediately planted in a light, loose, moist substrate consisting of peat and sand (1: 3), immersing the lower cut to the middle of the internode. Cover with a transparent cap on top to create a greenhouse effect. If this is a garden bed, put arcs and cover with a film (to retain moisture) and spunbond (to protect from direct sunlight).
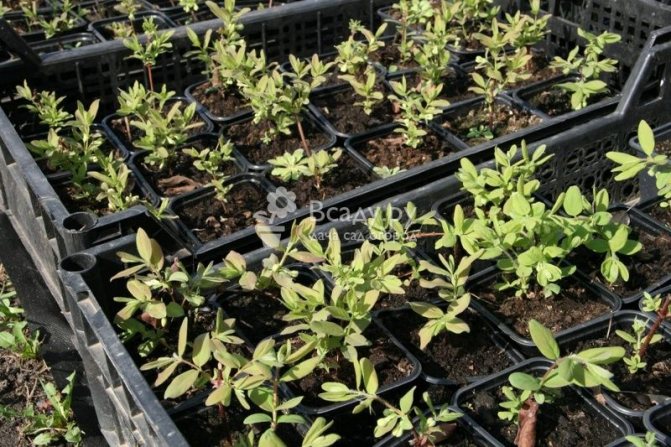
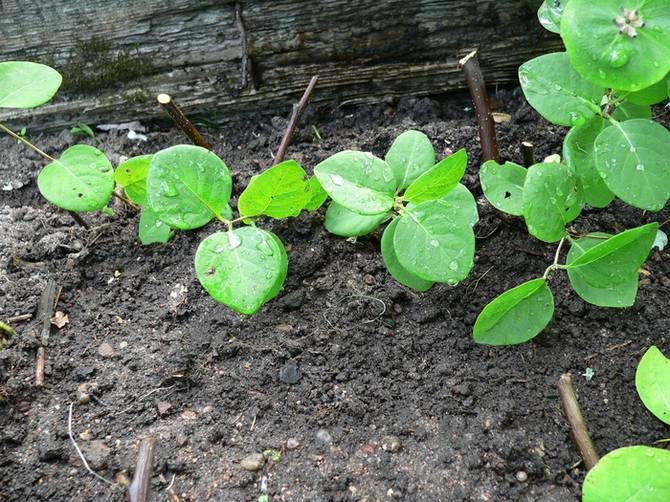
The soil and air are kept moist for 2-3 weeks - this can be easily checked by evaporation on the inside of the film. After the appearance of the roots, watering is reduced, the cuttings are aired, but the shelter is kept for some time, accustoming the young plant to the street gradually.
In autumn, young plants rooted in the garden are covered with spruce branches and leaves. In early spring, they will start growing and will be growing for at least one growing season, after which they can be transplanted to a permanent place.
Some gardeners prefer to start breeding honeysuckle by germinating green cuttings in water. Only the part with the lower unit is immersed in the container, water is periodically added, but not changed. To enhance root formation, during the first day, the cuttings are kept in a growth stimulant solution. As soon as the roots are nailed, the cuttings are transplanted into the substrate.
Lignified cuttings
Lignified cuttings can be used for reproduction of honeysuckle, only they are harvested not in summer, but after leaf fall. Cut strong healthy branches with a diameter of at least 7-8 mm. Store the mother material in the basement, after wrapping it with a damp cloth and digging it into the sand.
In the spring, as soon as the honeysuckle starts growing in the garden, the prepared material is cut into cuttings and planted using the same technology as the green ones. Rooted and established seedlings will form an independent root system by autumn, they will overwinter without problems. In another year they will be ready for planting.
Root and horizontal layers
For those who do not dare to cuttings or consider this method too troublesome, a simpler version of the reproduction of honeysuckle is possible - by obtaining layering and then transplanting daughter shoots to a permanent place.
A horizontal layering is obtained if in early spring one or more branches of the lower tier are pinned to the ground. To stimulate root formation at the point of contact of the shoot with the soil, shallow cuts are made in the bark (furrowing). This method gives 100% survival rate, since the child branch maintains contact with the parent bush before rooting. By the fall, the cuttings form their own roots, but they are separated from the main bush only next spring, when they are transplanted to a permanent place.
Note! Honeysuckle infrequently, but still produces root layers (suckers). This happens when an adventitious bud wakes up on an overgrown root system and grows into an aerial shoot. Such an offspring is grown on site for 2 years, then separated from the mother bush and transplanted.
Air layering
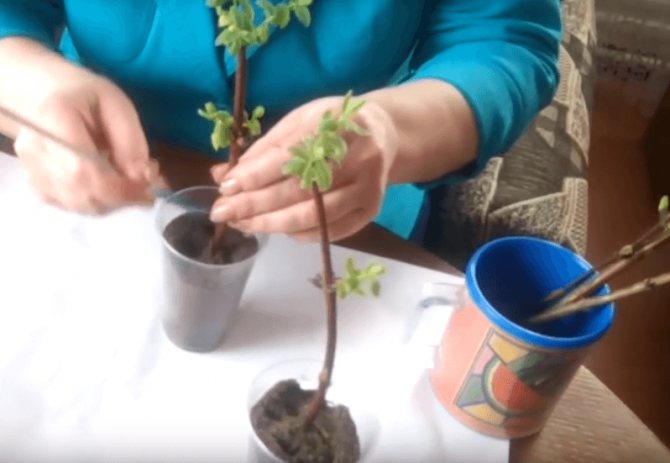
Another way to reproduce honeysuckle is by air layers. It is used for vertical growth of branches and the impossibility of bending them to the ground. The branch chosen for the layering is furrowed in the lower part under one of the buds. A plastic cup for seedlings or a bottle is cut lengthwise, the halves are filled with a loose, moist bud and "put" on a branch in the place of furrow. The halves are connected, fastened with tape, as shown in the photo below. During the summer, the air layer is watered, and after the formation of the roots, it is cut off below the planting container, sent to the garden bed for growing.
Bush division and transplant
By the appearance of the honeysuckle, you can determine whether it is suitable for reproduction by dividing the bush or not. It should be an adult, but young plant, no older than 5–6 years old, with 6–8 skeletal branches buried in the soil at the base. If there is no confidence in the presence of a root system suitable for division, the bush from spring can be piled up to a height of up to 20 cm, thereby stimulating the formation of lateral roots.
In the fall, the plant is dug up, divided into parts with the help of a secateurs. Each fragment should contain at least 2-3 shoots and a decent piece of rhizome. The technology of planting the cuttings is the same as for ordinary seedlings.
Advice! Spring hilling of the bush is carried out if they want to get vertical layering. In this case, not the whole bush is dug in the fall, but several lateral branches with independent roots that have grown over the summer are separated.
Honeysuckle propagation by layering
A very simple way, which also gives one hundred percent effectiveness, is to breed the honeysuckle by layering. The process looks like this:
- In the spring, 3-4 strong lower shoots of last year are carefully bent down, trying not to break or damage.
- They are pinned to the ground (with a hairpin, staple, slingshot, etc.) at several points, and the crown is raised.
- In places where the branches come into contact with the soil, soil is poured with a layer of about 3-5 cm.
- Then, throughout the summer, they are regularly moisturized and slightly poked.
- As a rule, by the fall, the branches give their own roots, but they are separated and planted only next spring.
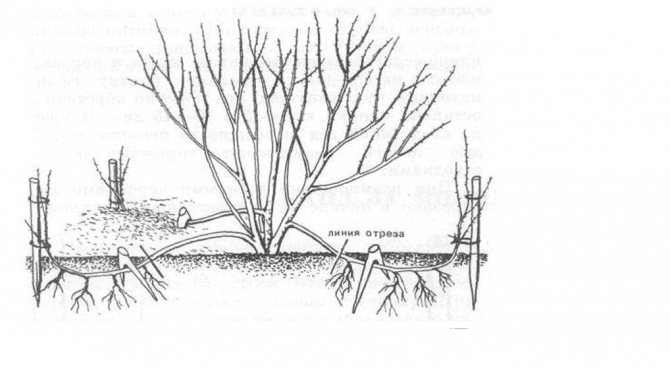

The easiest way to propagate honeysuckle is by layering.
Shallow grooves made in the right place on the bark and processing them with a rooting stimulator will accelerate the rooting process.
Some varieties of honeysuckle do not have lower branches that can be bent painlessly. In this case, air layers are obtained. An incision is made on a horizontally growing stem, then this place is placed in a container with a nutrient substrate (a bag, a cut plastic cup, etc.). After the roots appear, the seedling is cut off and transplanted for growing.
Video: reproduction by layering
How to propagate honeysuckle by seed
The generative (seed) method is considered the most time consuming... Only slightly more than half of the plants grown from seeds retain varietal characteristics (size of berries, their taste, etc.). Fruiting begins at 4-5 years, and not after the season, as with cuttings.
Sowing is carried out in June, selecting for this the most ripe, even overripe berries. You need to act like this:
- Prepare the bed in advance by adding humus or compost when digging. Level the surface well and water.
- A few days later, when the ground subsides a little, rows of small (up to 2 cm deep) dimples are made in the garden bed at a distance of about 8–10 cm from each other.
- One berry is squeezed into each hole (or simply put crushed).
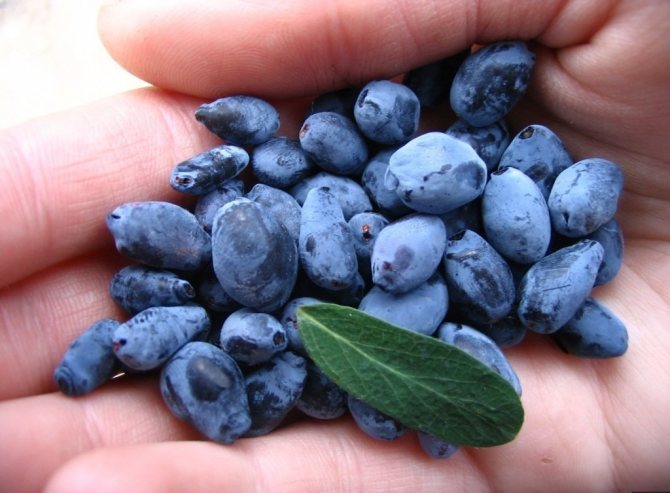


The largest and ripe berries are chosen for sowing.
- Sprinkle with a layer of loose soil mixture no thicker than 1 cm.
- Cover with plastic wrap or any covering material.
- Regularly ventilate and moisten from a spray bottle. The weeds are pulled out.
- Sprouts will appear in 2-3 weeks.
- Seedlings are left in the winter, warmed with dry leaves with straw or spruce branches.
- In the spring of next year they dive.
You can sow dry seeds before winter (at the end of October, at the beginning of November) directly into the ground or in containers. Planting material that has undergone long-term stratification will give friendly shoots in the spring. In February or March, seed boxes are brought into a warm room to accelerate seed germination. As soon as the seedlings have about 3-4 pairs of leaves, they are split into seed beds (in the school).
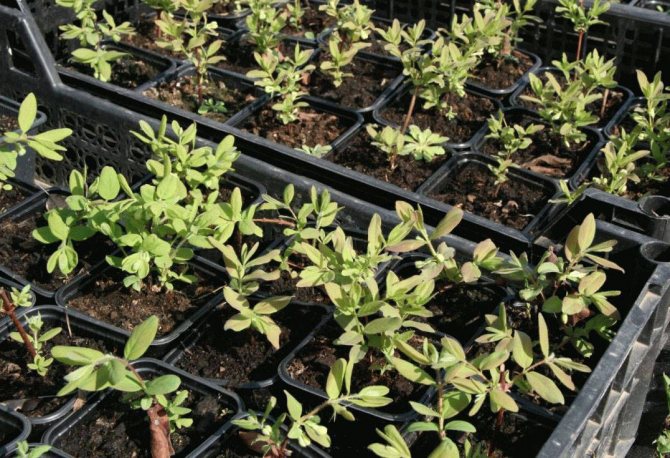


Honeysuckle can be propagated by seedlings in containers
You can sow in spring, bypassing stratification, but only fresh seeds (after 4 years of storage, germination is lost by half).
Honeysuckle cuttings honeysuckle
Honeysuckle cuttings honeysuckle is the most commonly used and effective way to propagate it.
One bush can produce planting material in the amount of about two hundred cuttings. In order to know how to grow honeysuckle from cuttings, you need to take into account that both green young cuttings and already lignified ones are used - both species are suitable for reproduction.
When to harvest cuttings
To carry out cuttings of honeysuckle in spring, you need to use lignified cuttings,
at the same time, you need to prepare the material before bud break. If you want to use green cuttings, then they are selected before the green berries appear. If you did not have time to cut the honeysuckle cuttings of honeysuckle for its propagation in the spring, then in the fall you can also prepare them in a lignified form.
How to prepare honeysuckle cuttings
Before propagating honeysuckle by cuttings, you need to properly prepare them. To harvest the lignified species, you need to choose those shoots that are about a year old and at least 1 cm thick. The length of the cutting should be about 20 cm, four buds should be left on each.
Shoots for green cuttings, on the other hand, should bend and break easily. Better to choose the central part of the shoot. Each stalk should contain two or three buds, its length is from 7 to 12 cm.
Cutting cuttings is carried out at an angle of 45 degrees from the bottom, but from above the cut remains straight, it should be 1.5 cm higher than the remaining buds. If leaves remain on the cuttings, then they must be removed from below and shortened from above.
Rooting cuttings


Rooting of lignified cuttings takes place within a month, so that it is more effective, it is better to cover them. If the harvesting was carried out in the fall, then they are stored in a cool place until spring, and then they are planted in the ground.
The green species is planted in the ground immediately after cutting, but you can hold them for one day in a container of water. The soil mixture is prepared as follows: mix 1 part of peat and 3 parts of sand.
The success of rooting depends on the observance of the following conditions:
- Maintaining high soil and air humidity
- Keeping the temperature at the level of 20-25 ° С.
Roots of green cuttings appear within 7-10 days.
Planting a seedling


Before you breed honeysuckle in your garden, you need to choose a place for planting cuttings. The plant loves sun and fertilized soil.
The lignified species is planted in greenhouses in spring, while leaving at least one bud above ground level.Planting in the ground is carried out in the fall. The most important thing in further care is
it is regular watering and maintaining the optimum temperature.
The green species is planted in the ground or greenhouse immediately after harvesting, and transplanted to the place chosen for them in the second year, and starting from the third spring, flowering and the appearance of the first fruits can be expected.
How to care for a plant after breeding
Young plants need systematic and careful care:
- The seedlings are watered regularly. The substrate must always be moist.
- The weeds are pulled out, the soil is loosened. Lay mulch from cut grass, straw, etc.
- The greenhouse (it is very desirable that the entire rooting period of the plants be under the film) is ventilated daily, maintaining high humidity.
Up to the age of four, honeysuckle seedlings do not need additional fertilizing (if the bed was well seasoned when planting) and do not need pruning.
How to plant
Honeysuckle propagation by edible cuttings is carried out using a soil mixture of a special composition. To prepare it, you need peat and sand. They are mixed in a 1x3 ratio. It is best to grow green planting material in a special cuticle - a box with high sides. The prepared soil mixture is poured into this container, moistened and cuttings are stuck in an inclined position (45 g).
The planting material should be placed in the box in such a way that the distance between the individual plants is at least 5 cm, and between the rows - 10 cm. At the final stage, the box is tightened with film or glass. Cuttings will be well accepted only if the air in the immediate vicinity is sufficiently humid and warm.
In the future, the planting material should be periodically watered and sprayed. Cuttings take root about a month after planting. The next year, in April-May, they are grown. Seedlings obtained in this way begin to bear fruit already in the third year.