Causative agents: Pythium debaryanum Hesse, P. ultimum, P. aphanidermatum
species of the genus
Fusarium (F. culmorum (W. G. Sm.) Sacc., F. solani App. Et Wr., F. gibbosum App. Et Wr., F. oxysporum Schlecht),
and also
Rhizoctonia solani Kuhn, Ascochyta cucumis Fautr. et Roum., S. sclerotiorum (d By).
Harmfulness.
A common disease in cucumber that causes the death of young and fruiting plants grown in all types of greenhouses. A very important factor in determining the level of losses from root rot is the time of plant infection. The earlier the infection occurs, the more damage will be done to the plantings. In many cases, there are no symptoms of the disease at the seedling stage. The first symptoms appear after planting plants in a permanent place. Losses from root rot of cucumber increase under the influence of extreme values of soil temperature (below 16 ° C and above 28 ° C), the disease manifests itself especially quickly in the winter-spring period (at low air and soil temperatures), as well as in the summer-autumn crop rotation ( at high soil temperatures).
Features of the
Root rot belongs to the category of fungal and bacterial diseases that are resistant to the action of medicinal preparations. On the affected plant, the cutting begins to turn black, after which the infection penetrates the root system of the culture. Most often this leads to its complete decay and, as a result, death.
Plants can become infected with root rot in any growing season. A fungal infection can spread to other plants that are near the diseased specimen in a short time. It is necessary to take seriously the prevention of this disease and its localization.
Root rot can be spread with planting material, soil or tools. Weak, defective plants are most susceptible to it, and excessive soil or air moisture often becomes a provocateur.
The soil, infected with a fungal infection, contains fungal spores for a long time. Leaving plant residues in greenhouses and greenhouses, gardeners thereby provoke the subsequent occurrence of root rot of cucumbers.
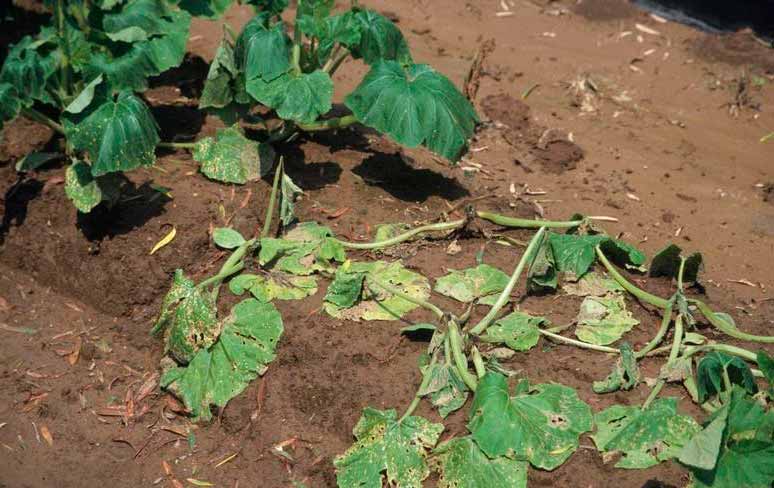
Cucumber infestation symptoms
The first symptoms that your cucumbers are starting to rot appear after transplanting the crop into the ground or greenhouse.
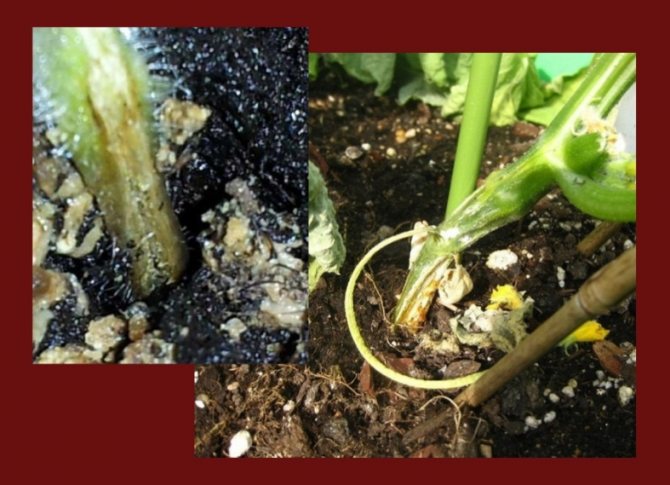
- Turns brown and the leg of the cucumber begins to rot.
- The yellowing of the leaves begins.
- Cracks are formed at the bottom of the central shoot.
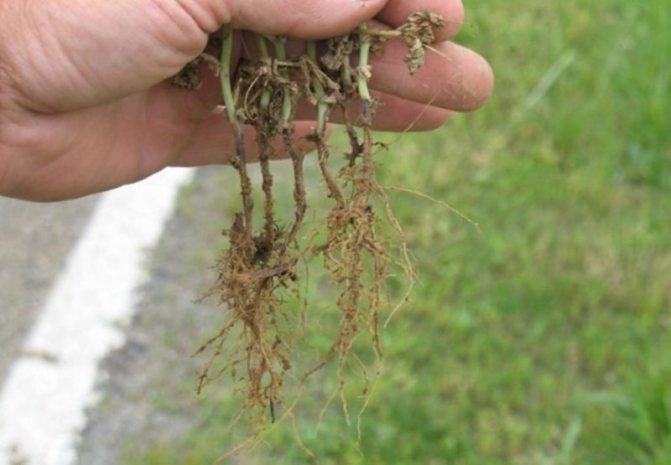
- The roots become brown and soft.
- In the advanced stage of the disease, the ovaries begin to fade.
Rot is especially active at low (below 16 ° C) and high (from 27 ° C) temperatures. If you find these signs in plants, it is necessary to urgently start treatment, otherwise the cucumbers will die.
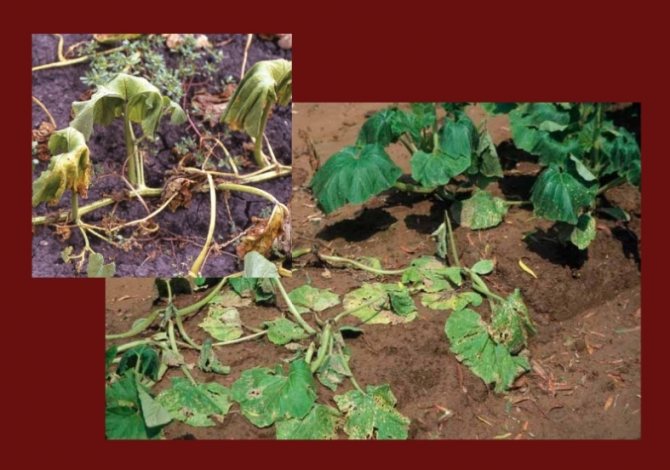
Signs of the disease
The sooner the disease is detected, the more chances are to localize and eliminate it in time. On young seedlings of cucumbers, root rot rarely occurs. The infection affects young plants after the seedlings are moved to a permanent place (in a greenhouse, open ground, greenhouse).
The main sign that a culture is sick is lethargic and lifeless leaves. Inexperienced gardeners begin to water the crop, which is extremely imprudent. Before watering, the root system of the plant should be checked for root rot.
The main signs of root rot damage to cucumbers are:
- at the base, the stem of the plant becomes thinner, its color changes to yellow or gray-brown;
- the bottom of the central shoot of the culture cracks;
- the root system is exposed, loses its elasticity, becomes soft;
- leaves on the lower part of the stems begin to turn yellow and fall off;
- with advanced disease, young ovaries wither and become lifeless.
If you notice at least one of the listed signs in cucumbers, you should start treating them immediately. This will make it possible to save nearby plants from spreading infection. Depending on the variety of cucumbers, this culture may be more or less susceptible to fungal diseases.
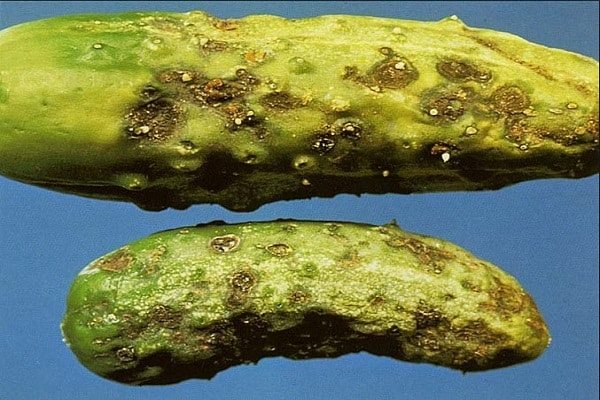
Cladosporium disease of cucumbers
For gardeners, this disease is more often known as cucumber olive spot. It is caused by a fungus that is very resistant to harsh environmental conditions, although it is more common in southern and humid regions. In heated glass greenhouses with dry air, it is less common.
| Photo | |
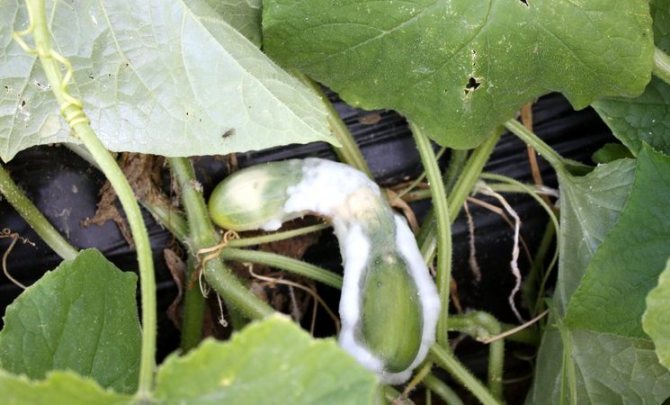
| Signs | Most often, the disease affects young fruits. They bend and small brown and dark brown spots appear on them. Less often, leaves and stems get sick, which are covered with a network of small brown spots. Over time, these spots dry out and form sores and scabs. |
| Activity period | June to late August. |
| How is it formed | It gets on healthy shoots by any means: with insects, tools infected with weeds, shoes and clothes, wind, etc. |
| What cucumbers amazes | Mainly greenhouses (growing in film greenhouses, less often in glass ones). |
| Result | Leaves and stems die off, fruits cannot be eaten, they quickly rot and are not stored for a long time. |
| Control measures | 1. Disinfection of the greenhouse and tools at the end of the season, destruction of old plants. 2. Maintaining an even temperature. 3. Airing the greenhouse (humidity level in it should not exceed 80%). 4. Spraying the bushes with Bordeaux liquid (1% solution). 5. Treatment with a 0.3-0.4% solution of copper oxychloride. 3-4 times per season with an interval of 10-12 days. |
We suggest that you familiarize yourself with Vitamin E liquid: instructions for use, effect on the body
Cladosporium-resistant cucumber varieties: Adam F1, Amazon F1, Cupid 1801 F1, Cornflower F1, Aquarius, Hector F1, Danila F1, Makar F1, Marta F1.
Causes of occurrence
In order to prevent the occurrence of this dangerous disease in cucumbers in the future, you need to know about the reasons that provoke it. Root rot of cucumbers in the greenhouse occurs more often than in the open field. Among the factors that can cause the appearance of a fungal infection are:
- non-compliance with the rules of crop rotation;
- insufficient or poor-quality processing of the soil or tools that are used to care for the plant;
- purchase of infected planting material;
- excess moisture in the soil;
- prolonged damp weather;
- use for irrigation of cold water;
- irregular ventilation of the greenhouse or frequent temperature fluctuations;
- lack of dressing.
When in soil, root rot spores can parasitize for years. Seedlings of cucumbers, which are placed in contaminated soil, are not yet matured and vulnerable, therefore they become easy prey for infection.
You should regularly conduct thorough examinations of plants, periodically take preventive measures to prevent the occurrence of the disease.
Protection methods
There are many ways to protect yourself from a painful condition. Gardeners should use these methods, which can significantly reduce the risk of spreading infection:
- Disinfect and warm up the seeds when planting.
- For peat pots, it is recommended to use equal parts of turf, humus and peat. Compost mixes that have been biologically sterilized for 2 years are also suitable. They can also be steamed before use.
- To carry out the obligatory disinfection of the soil and utensils for seedlings.
- Use cassettes with mineral wool corks and cubes.
- Purchase new sterile mats.
- Water the seedlings with warm water.
- Try not to overmoisten the soil.
- Avoid soil salinization.
- Remove the remnants of diseased plants in a timely manner.
- Use chlorine-free fertilizers.
- Compost organic matter before spreading (at least 6 months).
- Grow seedlings on rootstocks that are resistant to painful conditions.
When the first symptoms of the disease are detected, “rejuvenate” the culture: lower the stem to the ground to form new and healthy roots. The soil is poured onto the stem as the roots are formed. The soil is treated with fungicide solutions.
Types of treatment
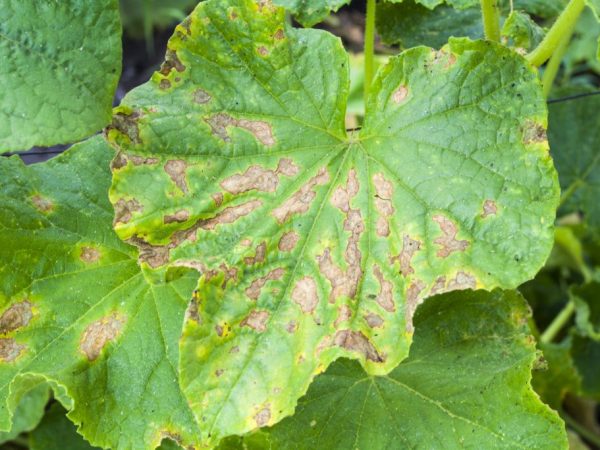

Diseased plants must be destroyed
Cucumbers diseased with root rot are practically not amenable to treatment. It is recommended that such specimens be immediately removed from the site and destroyed away from it. You can try to start the struggle for the preservation of culture, resorting to the help of special means.
With the help of chemicals
At the initial stage, root rot can be neutralized with chemicals. An approximate scheme for processing cucumbers from the disease is as follows:
- at the beginning of the culture wilting, moisten the soil with a solution of such a pesticide as "Previkur", you need to dilute it in the amount of 20 ml in 10 liters of cold water;
- after 5 days, repeat watering with "Fitolavin", the solution of which is made in the same way as the first;
- after that, treat the soil on the site with one of the preparations - "Gamair" or "Alirin B" - this will allow the soil microflora to recover after applying chemicals to it.
Among other popular chemicals in the fight against root rot, "Tiram", "Narcissus", "Oberig" are successful.
Use of biologics
Biological agents also help to protect cucumbers from fungal diseases: "Baktofit", "Integral", "Glyocladin", "Trichodermin", etc. To reduce the risk of disease, it is recommended to process cucumber seeds with them before sowing.
Also, solutions of biological substances are used to treat the soil surface and directly the base of the seedling stems. The concentration of the product must correspond to the instructions that are attached to it, and depends on the stage of the plant disease.
The use of biological products allows not only to prevent the appearance of root rot in cucumbers or to cure the plant, but also to significantly increase the yield of the crop. Means that are available in tablets are recommended to be preliminarily diluted with water, and the treatment should be carried out by irrigation.
This will enable the drug to spread evenly over the ground and begin its therapeutic effect in the most problematic areas.
Traditional methods
Treatment of cucumbers from root rot by folk methods must necessarily be combined with other means - chemical or bacterial preparations. This disease is highly resistant, so the use of improvised folk remedies may not give the expected result.
At any summer cottage, you can find coal, ash or lime. These crushed substances are used to treat the root collar of the plant and the base of its stem. These funds slow down the development and spread of infection on the site, as well as the process of rotting of the rhizome and stem of the culture.
Boric acid is widely used, the treatment of which increases the immunity of plants, accelerates their growth and strengthens them.
To combat root rot in cucumbers, the following mixture is often used:
- 6 tbsp. l. chalk;
- 2 tsp copper sulfate;
- 1 liter of water.
The solution must be shaken well, treated with the upper part of the root system and the lower part of the plant stem.
Powdery mildew on cucumbers
This disease is also called the cucumber mosaic virus, and it combines several diseases that are similar in symptoms (white cucumber mosaic, green speckled (English) mosaic and ordinary). Affects most plants and garden crops (over 700). A sharp activation of the virus occurs when the ambient temperature rises to 28-30 ° C.
| Photo | |
| Signs | The leaves become wrinkled and reduced. The stem is cracked along its entire length. The number of female flowers and fruits is decreasing. Zelentsy become covered with spots, grow worse and die quickly. |
| Activity period | From late May to late August. |
| How is it formed | The virus is transmitted with the sap of diseased plants during a dive. It penetrates through wounds and injuries, remains in plant debris and inventory. Carriers like aphids are actively spreading the mosaic. |
| What cucumbers amazes | Previously, mosaic was predominantly a disease in open ground, but recently it has also been found in greenhouses. |
| Result | The fruits grow with a yellow dense pulp, and are of little use for food and storage. |
| Control measures | 1. Thermal pre-sowing disinfection of seeds for 3 days. 2. Disinfection of containers and tools with a solution of potassium permanganate or bleach. 3. Elimination of pumpkin crops and weeds near the plantings of cucumbers. 4. Before sowing, you need to treat the seeds with a 15% solution of trisodium phosphate or a solution of pink potassium permanganate. 5. Avoid reproduction of aphids - one of the main vectors of the disease. |
Mosaic-resistant cucumber varieties: Adam F1, Amur 1801 F1, Anyuta F1, Vicenta F1, Hector F1, Danila F1, Makar F1, Marta F1.
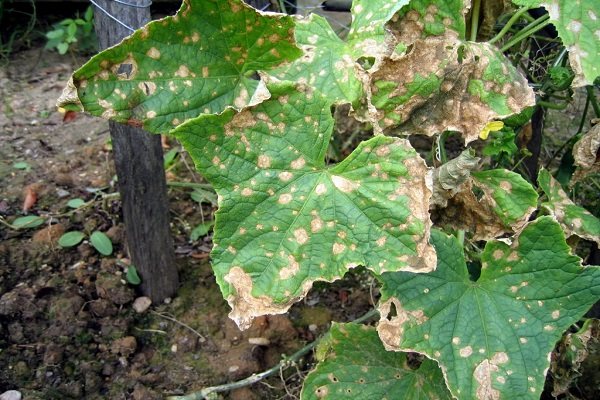
Powdery mildew is the result of rainy and cool summers. Sometimes it is mistakenly believed to be caused by acid rain or chemical exposure to leaves. But then it is not clear how the cucumbers are affected in the greenhouse and under the shelters. In fact, the culprit for the appearance of powdery mildew is a fungus that eventually infects flowers, stems and leaves of plantings. If pumpkin, zucchini, radish, squash and turnip grow next to cucumbers, then most likely they will also be in the “affected area”.
| Photo | |
| Signs | A subtle white bloom appears on the underside of the leaves. Gradually, rounded white spots appear on the upper part, which darken over time. The leaves become wavy and dry out. The fruits are bitter and also dehydrated. |
| Activity period | Mid to late summer. |
| How is it formed | The fungal disease spreads with dripping moisture. Hibernates on other (including affected) plants. |
| What cucumbers amazes | Any, most of all in film greenhouses. |
| Result | The area of leaf damage reaches 100%, the plant loses liquid, as a result of which few fruits are formed. |
| Control measures | 1. Disinfection of soil and seed and planting varieties resistant to powdery mildew. 2. Spraying plants with a solution of baking soda (0.4%) with the addition of soap. 3. Use of drugs Pseudobacterin-2 and Baktofit. 4. Among the chemicals, treatment with Novosil, Topaz, Privent, Cumulus, Karatan is recommended. |
Powdery mildew-resistant cucumber varieties: Adam F1, Amur 1801 F1, Anyuta F1, Athlete F1, Cornflower F1, Vicenta F1, Voyage F1, Vyaznikovsky 37, Hector F1, Danila F1, Delpina F1, Swallow F1, Navruz F1, Romance F1, Svyatoslav F1, Julian F1.
Prophylaxis
Among the methods that are used as prevention of the disease, the most effective are distinguished:
- thorough processing of the planting material, its disinfection with the help of special antibacterial agents (a weak solution of potassium permanganate, "Fitosporin"). The same means can be used to cultivate the soil on the site 7-14 days before planting the crop;
- regular maintenance of the greenhouse or plot - timely cleaning of plant residues or functional debris will prevent fungal infections from accumulating in the soil.To do this, use a solution of copper sulfate, which is used to process all plant care tools, as well as wooden elements of the greenhouse;
- an infected greenhouse in the fall, after harvest, can be treated with a sulfur stick. It should be borne in mind that with all the pathogenic microbes, useful ones will also die. In spring, the soil is enriched with modern biological products that will help its microflora to recover;
- when planting cucumbers, be sure to consider the crop rotation. It is not recommended to plant this crop in one place for several years in a row - this increases the risk of disease. There are also plants after which cucumbers should not be sown. Among them, there are zucchini, pumpkin, tomatoes, etc.;
- the distance between crops must be sufficient for their normal growth and development. This measure will facilitate the care of cucumbers, including weeding and loosening, inspection, will make it possible to get a bountiful and high-quality harvest.
Conscientious gardeners regularly inspect the plants grown on the site. Having noticed the appearance of root rot in a timely manner, you will have a better chance of stopping its further spread in the shortest possible time and saving the future harvest.
Who is the causative agent of rot
The root rot of cucumbers is caused by the work of many harmful microorganisms. The most common and dangerous among them are:
- Pythium debaryanum - this microorganism infects the roots during germination, as a result of which the cucumbers begin to rot at the root, the leaves and cotyledons turn yellow.
- P. ultimum is a fungal pathogen that affects 150 different plant species in addition to cucumbers. It is spread by nematodes.
- P. aphanidermatum - affects more than 80 plant species, but the greatest harm is done to cucumbers, as well as soybeans and tomatoes. It multiplies in the affected tissues during root molt.
Autumn activities
After the end of the season, all plant residues, along with the roots, are removed from the greenhouse and burned. It is in them that the main part of the fungi hibernates.
Greenhouse growing conditions complicate crop rotation. Usually the structure is built to grow one crop. Therefore, the fertile soil layer should be completely replaced every year. The soil quickly accumulates fungal diseases and pests.


Some vegetable growers practice soil treatment with fungicides, insecticides. Even with this method, it is necessary to remove the top layer of soil 5-6 cm, in which the main amount of pests and fungi accumulates. Heat treatment of soil with steam has proven itself well.
All parts of the structure and tools must be treated with an antiseptic, for example, bleach (400 g per 10 liters of water).


Terms and technology of plant processing


The medicinal solution is made in advance. Before processing, the soil is removed from the stem to the very root. The product is applied to the plant with a small brush. The approximate height of the stem of an adult crop for processing is 12 cm. Ash or chalk is applied to the place of rot.
Biologicals are diluted in water according to the instructions. The resulting solution is poured over the root cucumbers. This method allows the active substances of the agent to penetrate deeply into the soil, acting on the vegetable in the most inaccessible places.
A diseased plant is watered strictly at the root, avoiding splashing liquid. The optimum solution temperature is 23-26 degrees. The dead bushes are removed, and copper sulfate is added to the place where they grew.
In order for the treatment to give positive results, the treatment of the affected cucumbers must be done 2 times. The break between the use of funds is a week. If everything is done correctly, then after 14 days the signs of the disease will disappear.
Output
Thus, the timely detection of the defeat of cucumber crops by a PEST fungus and the use of simple agrotechnical techniques (harvesting and destruction of plant residues, compliance with crop rotation and regime, the introduction of resistant varieties) together with the use of biological products (seed dressing, soil disinfection) will help you easily overcome this " disease "and save the plants. And by keeping the planting, you will not be left without a good harvest.
* Changes and additions were made on 11.07.2019.
Diseases of cucumbers and their treatment is not particularly difficult, therefore, it is quite possible to get rid of infectious diseases with the help of simple folk remedies. The question to answer: "how to treat cucumbers from diseases with folk remedies" you now know. However, it should be noted that the effectiveness of the drugs depends on the degree of infection of the plant, and often the solution can only be prophylactic, not curative. With significant infections of cucumbers, it is worth using chemical preparations.
Gray rot
Are the leaves, stems or even flowers of cucumbers covered with brown, vague, watery, quickly merging spots with a smoky gray bloom? This is manifested by gray rot - a bacterial disease that affects all parts of the plant.
Gray rot. Photo from the site apsnet.org
Possible causes of occurrence
The main reasons for the development of gray rot are waterlogging and low temperatures.
How to warn
For the prevention of gray rot:
- do not thicken the crops of cucumbers and observe the crop rotation;
- remove plant debris from the beds in a timely manner, on which the infection persists;
- take protective measures in a timely manner.
Ambulance
If the disease has just begun to spread, treat the affected areas with a fungicide, for example, Rovral paste, which includes contact preparations against gray rot, or Bayleton. Remove affected fruits, leaves and stems of the plant immediately.