"Gardening" Apple tree "Bacterial burn on an apple tree - prevention and treatment
0
159
Article rating
Bacterial burn of an apple tree is a dangerous disease of infectious etiology. It is caused by pathogenic microorganisms that enter plant cells and have a toxic effect by poisoning the body with substances secreted during their life. It is often found in plants of the Rosaceae family.
Bacterial burn on an apple tree - prevention and treatment
Symptoms of the disease
A bacterial burn is caused by the flagellar rod bacteria Erwinia amylovora, which infect almost all plants of the Rosaceae family, but pear and apple trees are especially affected by it. In one season, the disease can destroy the entire garden, so it is extremely important to recognize the symptoms of its appearance at an early stage.
| Stage | Manifestation on an apple tree | Manifestation on a pear |
| Latent - from one week to 12 months in dry years | Single inconspicuous lesions in the form of reddish necrotic spots and veins on leaves and fruits. | Dark brown spots along leaf veins, thickened veins. May be asymptomatic. |
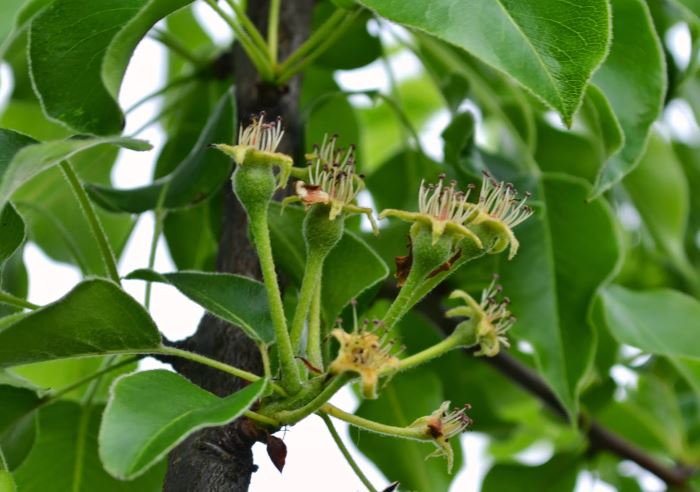
| Active - bacteria multiply exponentially | Pollinating insects actively spread bacteria around the blooming garden. Affected flowers become watery, turn brown, and then turn black. Young shoots take on the appearance of a "shepherd's staff". | Young ovaries acquire a dark green color, later blacken and mummify. Affected later, brown fruits emit cloudy white, later yellow, drops of gum. |
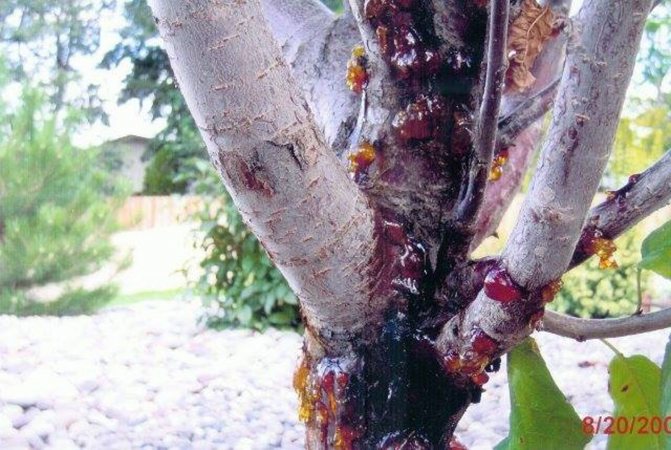
| Bacterial leakage or secondary infection phase | Bacteria are washed off the affected, dried branches by the rain, get on the trunk, in the roots, in the cracks in the bark and infect the tissues of the tree. The pathogen is spread by wind and insects. | Hanging of young shoots with the release of drops of white sticky exudate turning brown in the air. Subsequently, the shoots turn black, the leaves do not fall off. The bacteria enter the bark and attack the wood. |
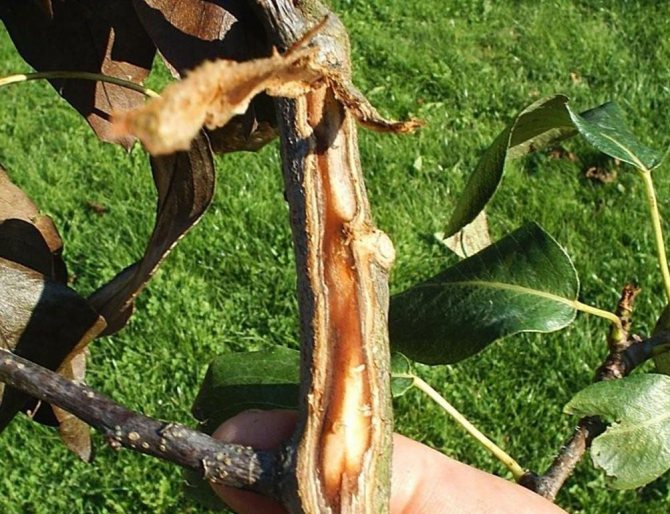
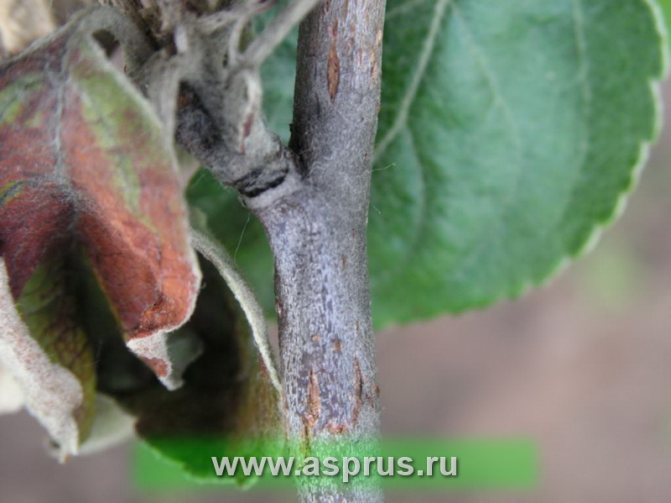
| Terminal stage | Deep damage to wood. The bark thickens, cracks, discharge appears. On the cut it has a marbled red-brown color. | On the cut, the affected wood has a loose texture, milky white, turns brown at the edges. |

Etiology and symptoms
The causative agent of fire blight is a gram-negative, motile bacterium, Ervinia, originally from America.
Outwardly, it represents single sticks or sticks assembled in chains, 0.7-0.1 * 0.9-1.5 microns in size, driven by flagella. It affects cultivated and wild plants.
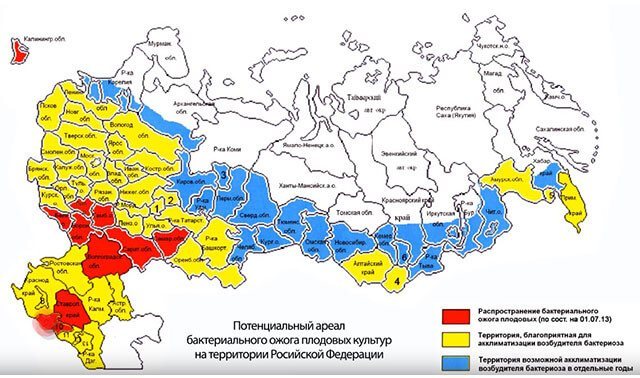
Ervinia came to European countries by the middle of the 20th century. In Russian gardening, they first encountered it in Kaliningrad, Karachay-Cherkessia, Samara, Saratov, Tambov, Belgorod and Voronezh.
Hawthorn, apple, mountain ash, quince are susceptible to the disease, pear and dogwood show the least antibacterial resistance.
An infectious disease has characteristic signs that appear on damaged vegetative parts.
Foliage
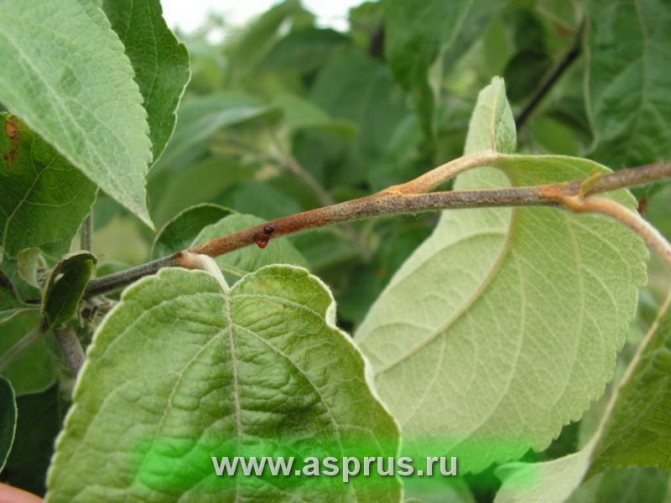
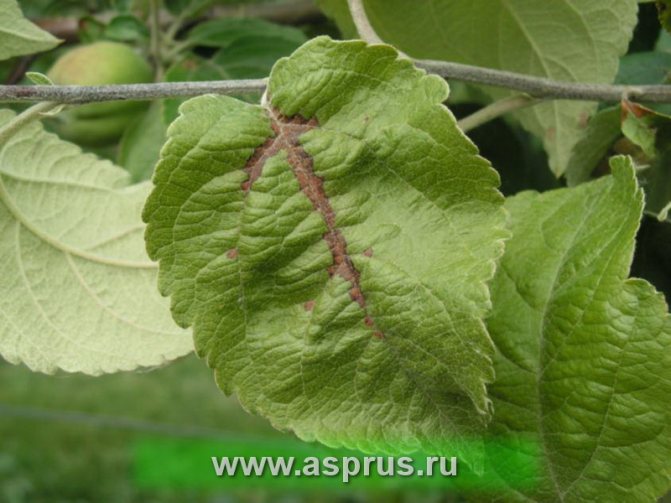
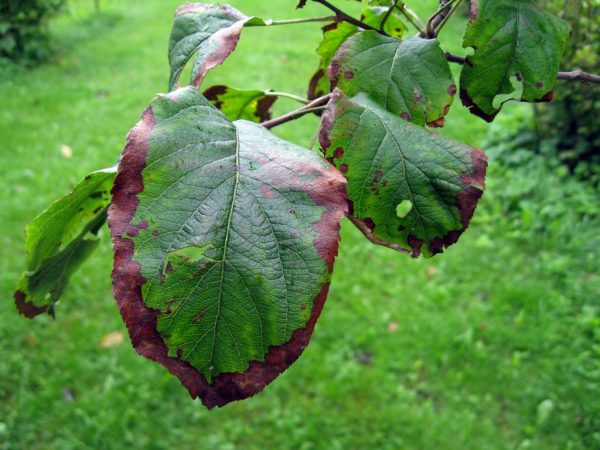
Under the influence of infection, the foliage between the veins is covered with necrotic foci of a reddish color, gradually spreading to the peripheral region.
Escapes
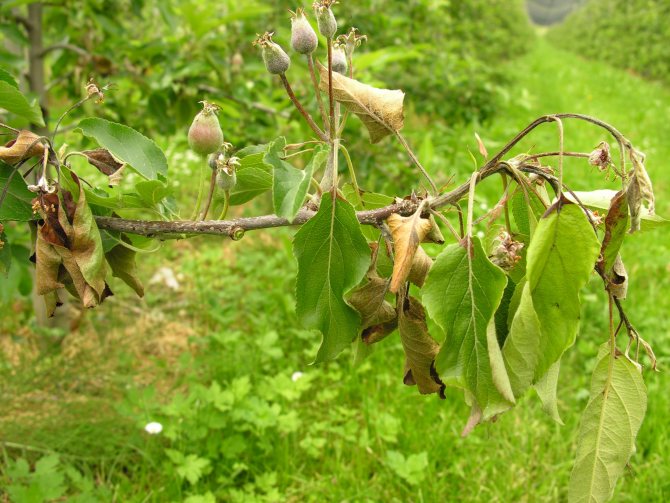
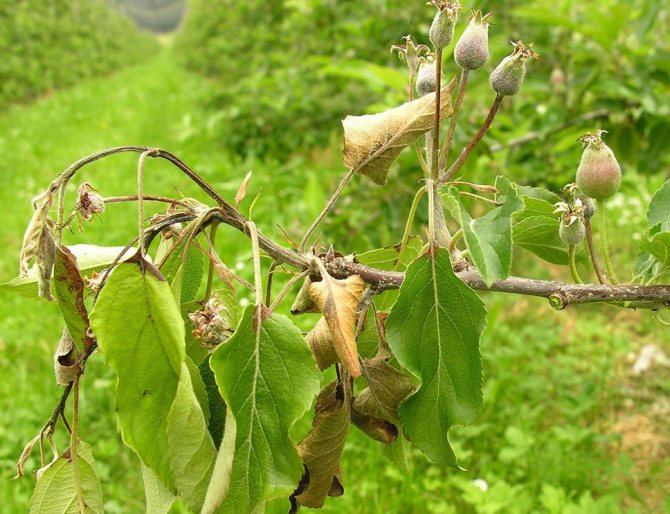
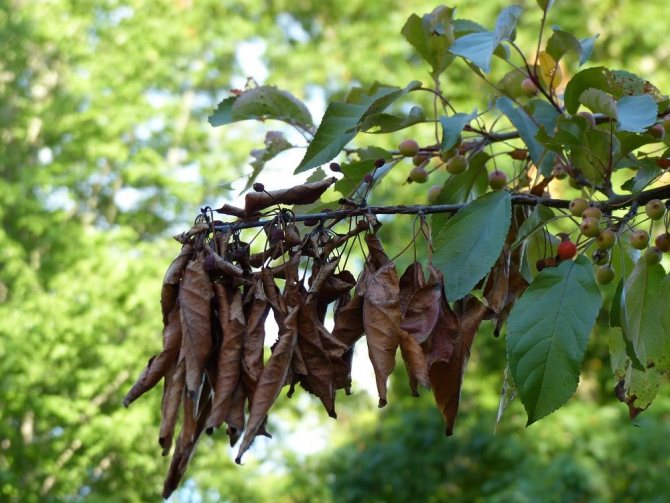
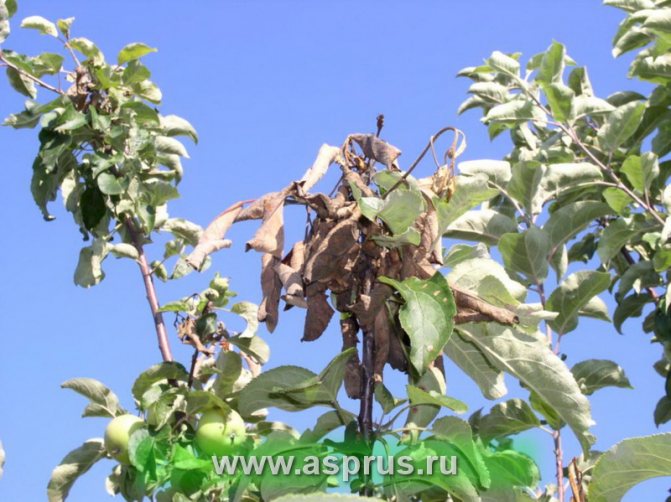
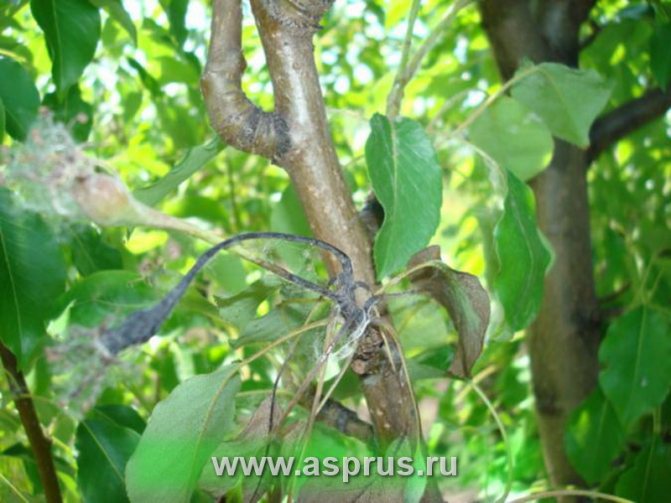
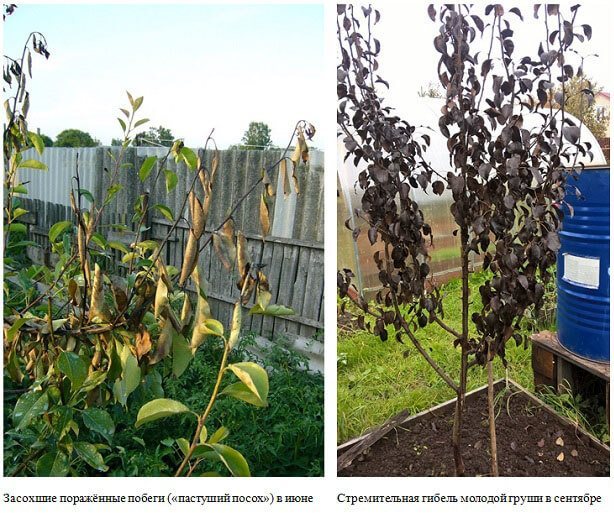
Dry top is observed in young processes. When the infection is activated, they wither, bending in the form of a hook. Sunburned apple shoots die off, remaining straight in shape.
Inflorescences and fruits
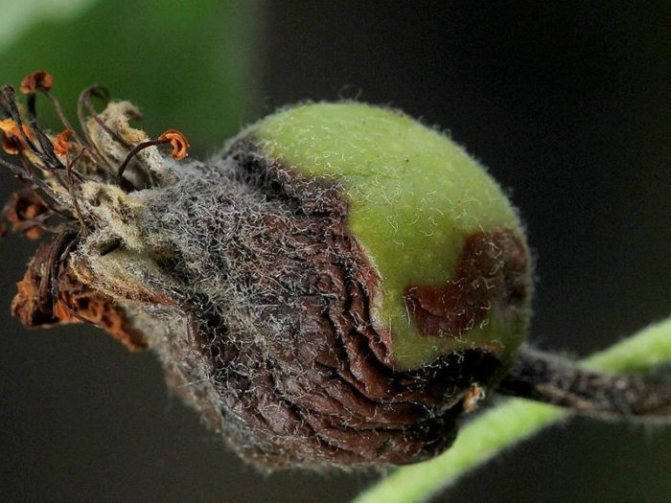
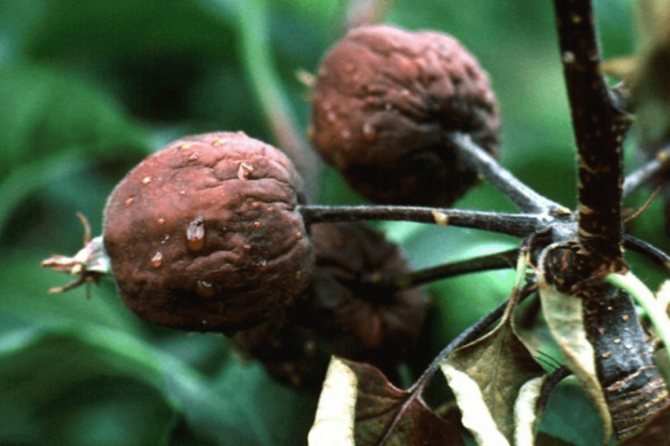
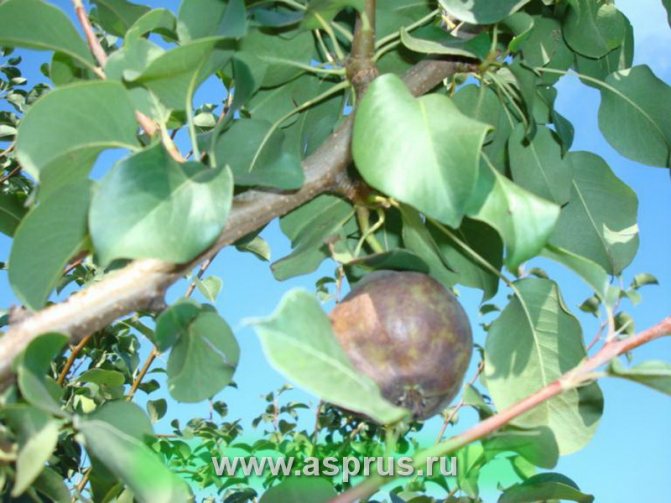
The burn covers the inflorescences, which acquire a dark color and subsequently die. Darkened ovaries stop developing. Apples become covered with cloudy secretions - milky-white exudate that turns brown in the air, subsequently mummified.
With a sunburn, the buds and inflorescences do not change their color, and when infected with Erwinia, apples and inflorescences do not fall off for a year or more.
General characteristics of the disease
Young trees are more often exposed to infection, but old ones are not immune from it either. The insidiousness of the infection is that it is not always possible to make the correct diagnosis, determine with precision what to treat, and start therapy on time - sometimes the symptoms are similar to those of other diseases.
Causative agent
The causative agent of the infection is the bacterium Ervinium amilovor, a member of the enterobacteriaceae family. It penetrates into the vessels of the plant and feeds on its juices. It coexists well with some pathogens of fungal diseases. Under favorable conditions for it, it causes the death of a fruit tree in 1-2 seasons.
Reasons for the appearance and favorable environment for development
The source of infection is usually a diseased plant (tree, shrub). A liquid infected with bacteria is released from it, small particles of which, under the influence of wind, are able to move through the air over long distances. The rate of infection depends in part on:
- on the age and general condition of the tree;
- pear varieties;
- growing conditions (soil, climate).
Bacteria begin to multiply more actively in high humidity and accompanying warm weather. Erwinia reproduces rapidly even in water droplets. Obvious signs of the disease can appear in both spring and summer.
Symptoms
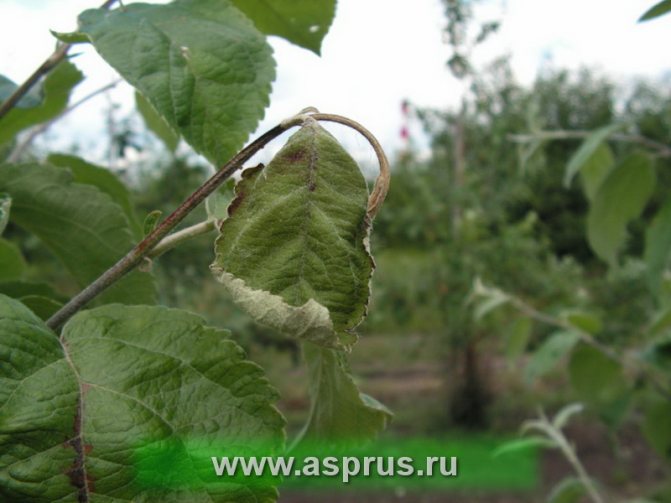
The first symptoms of the disease with a bacterial burn are darkening and drying of the buds, wilting and blackening of flowers during spring flowering. Having dried up, the flowers do not fall, but remain on the tree, after which the infection moves to young branches and leaves. Burns on leaves and branches, as well as flowers, are dark in color. Shoots and leaf plates are deformed, curled up and dry.
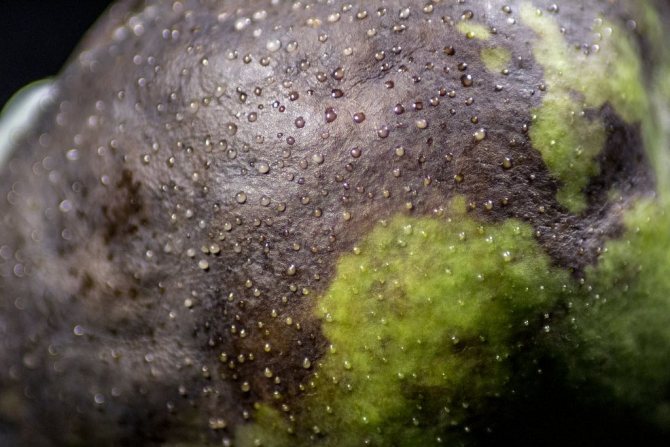
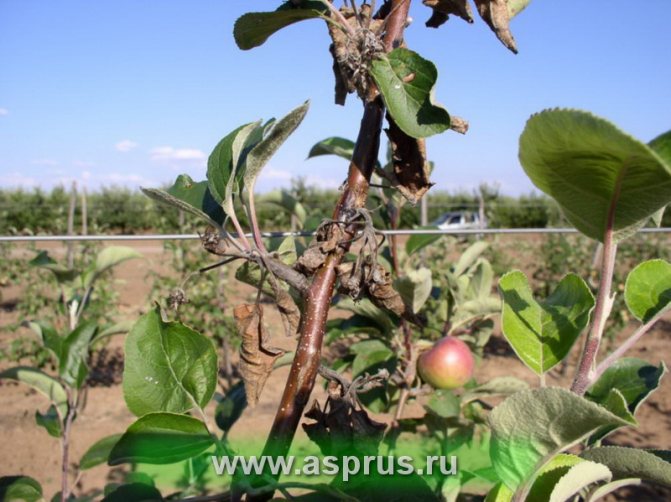
Fruits darken and dry out on the branches. When the disease spreads to the trunk and branches, the bark becomes soft, brown streaks appear on it. Cloudy droplets of a light liquid - exudate - appear on the pear, which indicates an active inflammatory process. Drops frozen in air acquire a dark color. A completely blackened trunk indicates the death of the tree.
What factors provoke the spread
Bacteria from a diseased tree can be carried in several ways:
- pollinating insects or pests, less often birds;
- with the help of the wind;
- rain - the risk of infection increases if there is damage to the bark of trees;
- through infected garden tools.
Literature
- Belyaev, S.V. American fire blight of pome fruit. / S.V. Belyaev // Gardening and viticulture. - 1998 - No. 4. - P. 14
- Smetnik, A.I. Bacterial fruit burn. / A.I. Smetnik // Plant protection and quarantine. - 2003. - No. 10. - S. 38-39
- Blachinsky, D. Effects of growth regulators and pruning on the susceptibility of pear trees to Erwinia amylovora. / D. Blachinsky, D Shitenberg, D. Weinthal, Sh. Manulis, E. Zamski // Phytoparasitica - 2005. - V.33, N 3.- P.294-295
- Braun, P.C. Epidemiology of fire blight of floricane fruiting red raspberry caused by Erwinia amylovora. / P.C. Braun, P.D. Hildebrand // Can. J. Plant Pathol. - 2006. - v.28, N1. - P. 95-99
- Buban, T. The nectary as primary site of infection by Erwinia amylovora (Burr.) Winslow et al: a mini reviem. / T. Burban, Zs. A. Orosz-Kovaes // Plant Syst. end Evol. - 2003. - 238.N1-4. - P. 183-194
- Klietman, F. Erwinia amylovora populations resistant to oxolinic acid in Israel: Prevalence, persistence and fitness. / F Klietman, D. Blachinsky, D Oppenheim, M Zilberataine, O. Drar, S. Manulis // Plant Pathol. - 2005. - 54.N2. - P.108-115
- Laux, P. Studies on the biological control of fire blight in Egypt (8 Symposium “New Aspects of Resistance Research on Cultivated Plants Bacteral Diseases.” Aschersleben, Nov. 15-16. - 2001). / P. Laux, W. Zeller // Bundesanst Z? Chtungsforsch Kulturpflanz. - 2002. - 8.N3. - C.46-48
- Norelli J.L. Factor affecting the development of fire blight blossom insections. / J.L. Norelli, S.V. Beer // Acta Horticultural. - 1984 .-- 151: 37-39
- Paulin, J.P. Comparison of the efficiency of some chemicals in preventing fire blight blossom infections. /J.P. Paulin, G. Lachaud // Acta Horti-cultural. - 1984 .-- 151: 209-214
Additional measures to combat bacteriosis of fruit trees
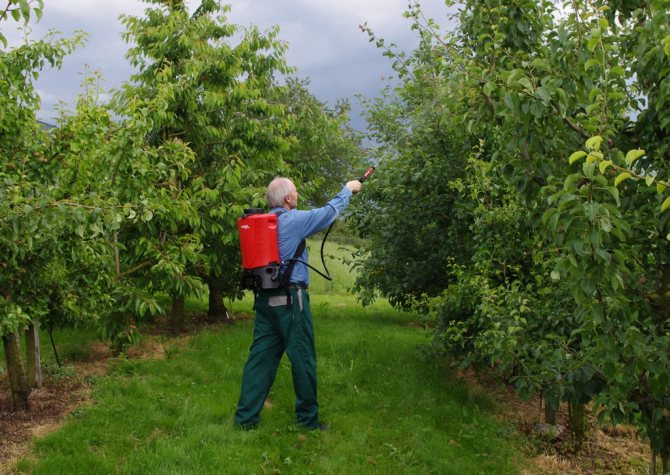
They consist in the timely removal and burning of the affected parts of the apple and pear trees, five-fold treatment of fruit with copper-containing preparations at intervals of five days, and mandatory disinfection of garden tools before each treatment.
Some plant protection specialists recommend regular treatments of the garden with Bordeaux mixture:
- in the phase of swelling of the kidneys;
- at the beginning of flowering;
- during the formation of ovaries;
- after harvesting fruits;
- at the beginning of leaf fall.
The copper in the solution inhibits the growth of bacteria, and the fungicide itself fights fungal infections, which maintains the health of the tree. How to cook it is shown in the following video:
Another scheme of five-fold processing with Bordeaux mixture is only during flowering. The first is in the budding phase, the second is in the phase of partial opening of the buds, the third is when the tree is in full bloom, the fourth is after the petals fall, the fifth is in the ovary phase. Timely whitewashing of trees is also recommended.
After an outbreak of the disease, the next year it is recommended to cut off all flower buds or unblown buds from young trees. This will help the weakened trees regain their strength.
Research is being actively carried out on the use of bacteriophages in the fight against Erwinia amylovora. There are also colloidal silver preparations such as Zerox, but they have no proven effectiveness against disease.
Preventive measures against bacteriosis
Be sure to treat the wood regularly
The best measure to combat bacterial burns of apple trees is preventive therapy and agricultural technology:
- active use of fertilizing complexes, among the components of which are present in an increased proportion of phosphorus and potassium, these components improve the resistance of fruit trees to phytopathogenic microorganisms;
- use for planting healthy seedlings;
- selection of varieties resistant to bacteriosis;
- prevention of thickening, thinning of tree crowns;
- disinfection of technical equipment used for pruning and vaccinations;
- timely removal of infected leaves and apples;
- pruning infected shoots to a length with the capture of a healthy area of at least 0.2 m;
- regular treatment of horticultural crops from pests.
Among the physical phytosanitary measures is the uprooting of wild crops that are most often exposed to contamination.
Distribution mechanism
The bacterial bacillus hibernates in the affected wood, and with the beginning of sap flow, in the spring, begins active reproduction, appearing on the surface of the bark along with exudate.
The penetration of ervinia into tissue cells occurs through damage to the tree bark - frost holes, mechanical wounds due to pruning, violation of the integrity of foliage and apples.
During the flowering stage, pollinating insects, birds and pests carry infectious exudate to the inflorescences of healthy apple trees. Thus, the disease continues to spread with flower nectar and through the peduncle, penetrating into the conducting vessels.
Distribution through the tissues of organs occurs through the vascular system and leads to systemic damage to the tree.


Bactria spread very quickly
Contributing factors and allies of bacteria
The spread of infection is facilitated by prolonged rains at moderate temperatures, including a rise to 20 ° and above and an excess of 70% humidity. With the onset of hot summer weather, the development of Erwinia slows down and re-enters the active stage in the fall.
Frequent mistakes in the treatment of bacteriosis
In the fight against a bacterial burn, gardeners often make a number of typical mistakes that lead to complications in the treatment of apple trees.
The most common:
- Incorrect diagnosis. Often, signs of bacteriosis are perceived as symptoms of tree drying out due to insufficient watering. Starting with abundant watering in the absence of a correct diagnosis of a bacterial burn, they provoke the intensive development of the bacillus.
- In the treatment of bacteriosis, some begin to use fungicidal preparations, the action of which is aimed at destroying infections of fungal etiology. But ervinia belongs to bacteria - and the effect of antifungal fungicides for it is not destructive.
- Improper care.In the process of caring for the affected tree, especially in gardens with tall varieties, the maintenance of which is difficult due to their height, bacteria affected by the fruits are left on the tops of the crowns. However, infested apples are reservoirs for the conservation of Erwinia throughout the winter. After that, the stick penetrates into the tissues and organs of the tree through the stalk.
Prevention measures
Treatment of a bacterial burn can often be ineffective, since bacteria tend to mutate, adapting to the action of antibiotics and bacteriostatics. There are cases when it was necessary to destroy hectares of gardens, despite the efforts made. It is much more correct to take measures to prevent the penetration and spread of infection in your garden.
Prevent contaminated planting material from entering the garden
- Carefully inspect the planting material upon purchase.
- Do not buy seedlings "off hand".
- Do not buy seedlings from areas where fire blight has been reported.
- Require a quarantine certificate from sellers.
Prevent the spread of infection
- Sterilize tools with 70% alcohol when pruning after each tree, even if there are no symptoms of disease.
- Treat cuts and cuts with copper-containing preparations and garden pitch.
- Minimize green operations in the garden during the most active reproduction of Erwinia - by infecting an instrument from one tree, you can spread the disease throughout the garden.
- In the event of a disease outbreak, it is necessary to uproot all wild fruit and hawthorns within a radius of half a kilometer around the garden. They can serve as a hotbed of infection for years.
Strengthen the immunity of trees
- To carry out the prevention of fungal, viral diseases and parasite lesions. A weakened tree is more quickly affected by infection.
- Do not use mineral nitrogen fertilizers in late summer and autumn. They lead to overgrowth of shoots that suffer from frost, and frost holes are the gateway for infection.
- Add rotted compost, manure, ash to the soil, lime acidic soils. A starving tree that is malnourished will not be able to withstand disease.
- Moderate watering. Waterlogging, like a lack of moisture, has a bad effect on the immunity of trees. Erwinia amylovora reproduces only in a humid environment, so it is better to wait with watering in case of an outbreak of infection in the region.
- Water and spray trees with preparations containing effective plant-friendly microorganisms. The beneficial microflora will destroy the pathogenic one. Suitable preparations are Baikal, Silk, Zircon, Fitosporin, Gamair.
- Use biological immunostimulants such as Epin or Moldstim.
Biological agents in the treatment of bacteriosis
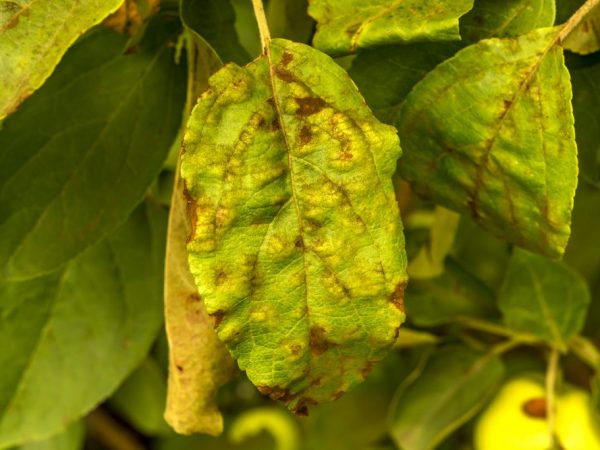


Treatment should be started immediately
An additional measure in the fight against bacteriosis is the use of compositions of a biological spectrum of action in combination with antibiotics and folk remedies. They saturate the soil and apple trees with useful flora, strengthening and revitalizing the land and garden culture.
Stimic
A drug with a biological spectrum of action that enhances metabolic processes, neutralizes the harmful effects of toxic substances and acts as an immunomodulator.
Applied in different forms:
- concentrate - 100 ml per 10 liters of water, intended for irrigation of garden crops at the end of the harvest;
- standard - 50 ml per 10 liters of water, applicable for spraying on apple leaves up to 7 times during the growing season with intervals between treatments of 14 days;
- phytostim - 50 ml per 10 liters of water, intended for watering once every 30 days.
Baikal-EM1
Biological preparation Baikal-EM1 is an immunostimulant and antidote. Used for spraying.
Recipe: 10 ml per 10 liters of water. The frequency of application is 3 times per weight during the growing season.
Shining-1
Shining-1 refers to the means for restoring the microflora of soil. Designed for spring watering.
Recipe: 1 bag for 0.5 l of water, the dissolved active substance (10 ml) is diluted in 10 l of water.
Experienced gardeners recommendations
Without some experience, it can be difficult to recognize the onset of a fire blight, especially since it spreads from top to bottom. Many people notice him only when it becomes impossible to save the fruit tree. Therefore, you should regularly inspect all the plants in the garden.


Plants should be inspected regularly
Plus a few more tips:
- Garden tools need to be decontaminated. For this, formalin is well suited. If this is not done, then when using them, you can transfer bacteria from a diseased tree to a healthy one.
- Plants such as hawthorn (however, like all wild stone fruits) provoke the appearance of the bacteria ervinium, so they must be removed from the site.
- Care should be taken when choosing drugs. Beginners have repeatedly tried to treat fruit trees with fungicides, in the hope that this will help the situation. However, fungicides have a therapeutic effect only on fungal diseases, and no matter how advertised, almost all of them are powerless against bacteria.
It is extremely unpleasant to find a bacterial burn on your site, since the disease is quite complex. As has been noted more than once, it is important to notice the first symptoms as early as possible, and then antibiotic treatment will give the maximum effect, will show the result. Gardeners who constantly monitor and care for their plantings have nothing to fear.
Fire-blight-resistant apple and pear varieties
Fruit bacteriosis is increasingly spreading across Russia, moving to the north of the country. Unfortunately, there are no resistant varieties to this disease. However, it has been observed that some varieties are more susceptible to bacteria than others.

The rootstock plays an important role in how resistant the trees are to fire blight - grafted onto local rootstocks are highly immune to disease.
Varieties of pears that are extremely susceptible to bacteriosis - General Leclerc, Duranda, Triumph Pakgama, Winter Deccan, Santa Maria, Williams pear. More resistant are the pear varieties Noyabrskaya, Maria, Conference, Carmen, Exhibition, Jubilee.
Apple varieties susceptible to tank. burn - John Red, Crimean Winter, Stark, Ranger, Winter Plesetsky. In terms of the degree of damage, these varieties scored from 3 to 4 points. Apple trees are little and medium susceptible to bacteriosis - Jonagold, King David, Osennee, Ampir, Bosco, Golden Delicious, Red Delicious, Cortland, Paulared, Pinova, Krasnopolyanskoe, Zhigulevskoe, Krasivoe, Vishnevoe, Dream, Melba.
The susceptibility of a particular variety can vary greatly. This can be influenced by weather conditions throughout the year, soil composition, growing conditions. In wet years and with poor care, a variety considered to be less susceptible can completely die from a fire blight. At the same time, adherence to preventive measures and proper care helps susceptible varieties to be minimally affected by the disease.
The first signs of the disease
When infected with Erwinia in spring, the buds on the pear do not open for a long time and gradually turn black, but they do not crumble from the branches. On an infected tree:
- Flowers wither and dry up.
- Leaves curl.
- The bark is covered with stains.


As the fire blight progresses, a viscous white liquid begins to flow from the cracks and wounds. When the wood peels off, the pear cannot be saved. She looks like she's been on fire.
Folk remedies
It is impossible to get rid of the disease with the help of folk remedies. They are used as a supplement and prevention. With home remedies, you can create a destructive environment for Erwinia, feed the apple trees to increase resistance.
| Boric acid Stages:
|
| Yeast Stages:
|
Chemicals in the treatment of bacteriosis
Infections with bacterial etiology are treated with medications from the antibiotic group:
- ampicillin - 1 ampoule per 10 liters of water, applicable for spraying throughout the entire growing season;
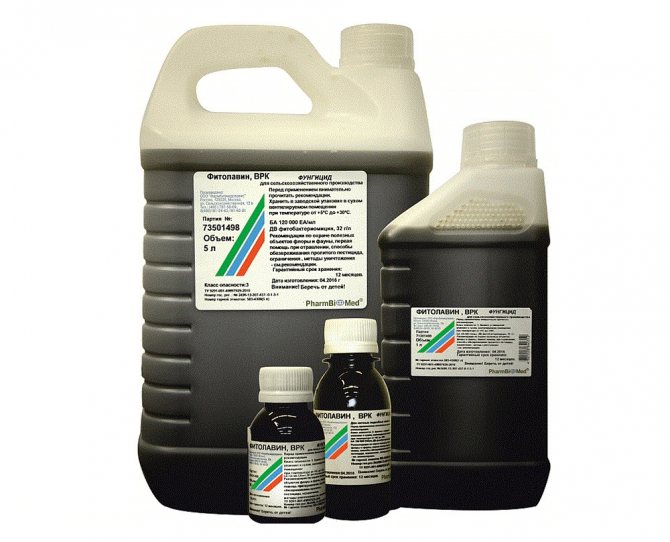
- phytolavin - 20 ml per 10 liters of water, applicable for wood processing and watering in the area of the trunk circle;
- tetracycline (3 tablets) with streptomycin (1 ampoule of 500 thousand units) for 5 liters of water, are applicable for spraying before, during and at the end of the flowering stage until the apples ripen;
- gentamicin - 1 ampoule per 1 liter of water, applicable for soaking a garden bandage, which is used to tie previously cleaned places of damage to the tree bark that have exudate secretions;
- ofloxacin - 2 tab. 10 water, suitable for spraying before and after the flowering stage.
Antibiotics are used in the treatment of bacterial burns in combination with fungicidal agents. often the infection is accompanied by concomitant fungal diseases. Skor, Ridomil-gold, Acroba and the like are recommended as fungicides for complex treatment.
Competent choice of a seedling
A tree for growing in a suburban area or dacha must be purchased in a nursery. It is advisable to find out from which region it was brought, and find out if there are cases of infection with a bacterial burn. You shouldn't risk buying seedlings from Belarus, Tambov and Saratov regions. A healthy young tree has no scratches on the stem, the roots are not damaged, and the pear itself has an even light brown color.
When choosing seedlings, it is worth giving preference to varieties that are resistant to infection with a bacterial burn:
- Maria;
- Potomac;
- Williams;
- Carmen.
We must not forget that when treating trees with the same compounds, pathogenic microorganisms can get used to them, and even worse, mutate. Fungicides should be changed more often.
In early spring, pears are sprayed with Bordeaux liquid, dried and diseased shoots are removed, lubricating the cuts with garden pitch. In the summer, in order to stimulate the defenses of the plant, biological products such as "Zircon" are used. In regions where fire blight occurs, pears are sprayed with antibiotics for prophylaxis. Pear Bacterial Burn
Preventive measures
It is impossible to fully insure yourself against the appearance of a bacterial infection on the site, but mandatory prevention will reduce the risk of infection. Preventive measures begin with the correct selection of pear seedlings. Regular inspection of trees will detect the first signs of the disease, and treatment will be carried out in a timely manner. Full care is no less important - thanks to it, the immunity of a young tree increases.
It is impossible to excessively moisten the soil and overfeed the trees with mineral fertilizers, especially nitrogen.
In addition, it is recommended to regularly disinfect garden tools.
What you need to know when choosing seedlings
Often, seedlings are initially infected with an insidious infection. Hazardous planting material is easy to purchase from hands in untested places. Therefore, the purchase should be sent only to specialized nurseries and retail outlets.
The seedlings should have a healthy appearance: no external damage, an even and natural color. In addition, there are pear varieties that are resistant to bacterial burns - they are less likely to be infected. These include:
- "Williams"
- "November",
- "Maria",
- "Carmen".
The resistant variety is suitable for gardeners who have no experience in growing fruit trees.
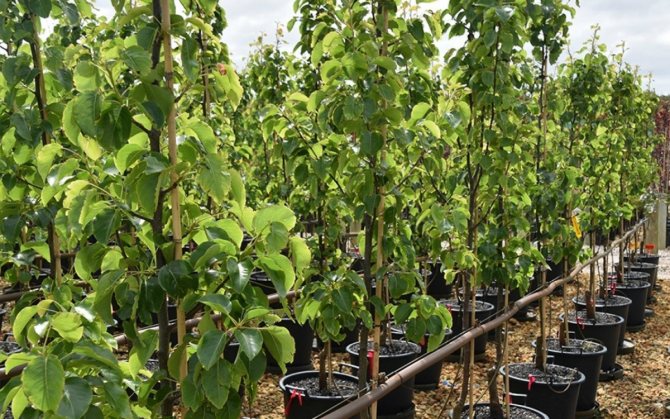


Gardener activities in spring, summer and fall
In March, pears are sprayed with a solution containing copper, such as Bordeaux liquid, and sanitary pruning is carried out. All damages and cuts are treated with garden varnish. Trees are carefully examined so as not to miss one of the signs of infection - white drops protruding from the trunk and shoots.
In June-July, you can carry out a single prophylactic spraying with a solution of ofloxacin (or another antibiotic). And apply a special agent that activates the immunity of the plant organism ("Zircon", "Silk"). In October, trees should again be treated with a copper fungicide. These actions are taken to destroy the fungus, the destructive activity of which makes the pear vulnerable to the bacteria Erwinia.
Contributing factors and allies of bacteria
In gardens, the typical fire blight has allies. Two more types of bacteria are often found on crops, one rather weak, and the second very pathogenic.
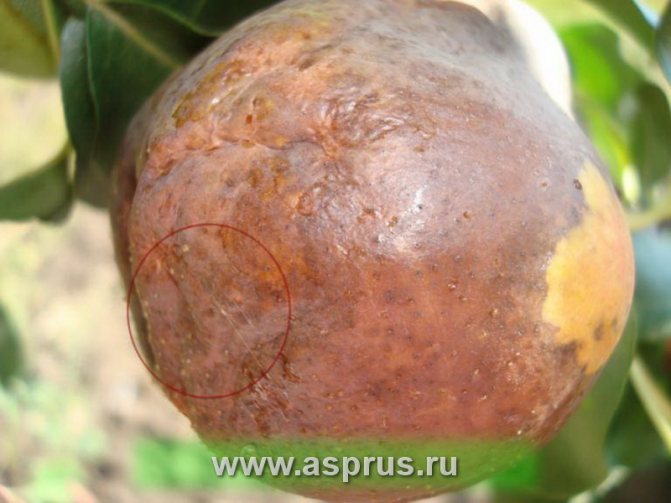
And also fruit rot often appears along with a bacterial burn. It can be easily identified by the rather distinct concentric rings on the fruit.
Another ally can be scab. It manifests itself in spots of a brown-olive color and often appears on all parts of the plant. However, very often the manifestations of diseases are confused, so you need to pay attention to other symptoms.
The manifestation of infection in neighboring gardens and plots will also be a contributing factor. If the appearance of dry tips of young shoots and flowers is observed, then foreign bacteria can be expected on their own site.
There is a possibility of infection with the Erwinia bacteria if affected by other diseases. There is no room for disease-causing infections in a clean and healthy garden. But when some parasites have already settled, the causative agent of a bacterial burn will quickly settle on a plant with a weakened immune system. He also easily enters into a symbiotic relationship with other infections.